
 Rise in Price It is a rise in the general price level caused by an imbalance between the quantity of money and trade needs.
Rise in Price It is a rise in the general price level caused by an imbalance between the quantity of money and trade needs.
 The word "inflation" originally applied solely to the quantity of money. It meant that the volume of money was inflated, blown up, overextended.
The word "inflation" originally applied solely to the quantity of money. It meant that the volume of money was inflated, blown up, overextended.
 According to Pigou “ Inflation arises when money income is expanding more than proportionate to income earning activity”. Arthur Cecil Pigou (18 Nov 1877 – 7 March 1959)
According to Pigou “ Inflation arises when money income is expanding more than proportionate to income earning activity”. Arthur Cecil Pigou (18 Nov 1877 – 7 March 1959)
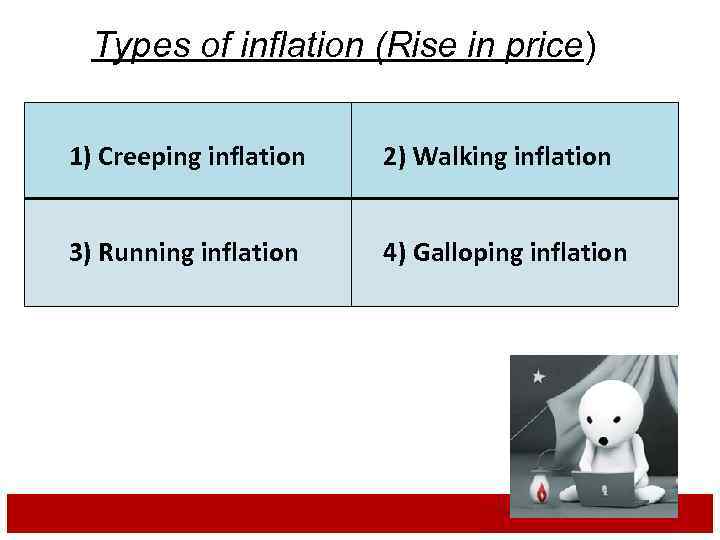 Types of inflation (Rise in price) , 1) Creeping inflation 3) Running inflation 2) Walking inflation 4) Galloping inflation
Types of inflation (Rise in price) , 1) Creeping inflation 3) Running inflation 2) Walking inflation 4) Galloping inflation
 Creeping inflation: The inflation of a nation increases gradually, but continually, over time. Walking inflation: When the price rise is moderate. It is a warning signal for the government to control it before it turns into running inflation.
Creeping inflation: The inflation of a nation increases gradually, but continually, over time. Walking inflation: When the price rise is moderate. It is a warning signal for the government to control it before it turns into running inflation.
 Running inflation: A rapid acceleration in the rate of rising prices more than 10% per annum is referred as Running Inflation Galloping inflation: Prices rise by double or triple digit inflation rates like 400% or 999% per annum.
Running inflation: A rapid acceleration in the rate of rising prices more than 10% per annum is referred as Running Inflation Galloping inflation: Prices rise by double or triple digit inflation rates like 400% or 999% per annum.
 CAUSES OF INFLATION: 1)Demand pull inflation(ex: petrol) 2)Cost push inflation(ex: cement) 3)Over- Expansion of Money Supply 4)Increase in Population 5)Expansion of Bank Credit 6)Black Money 7)Poor Performance of Farm Sector
CAUSES OF INFLATION: 1)Demand pull inflation(ex: petrol) 2)Cost push inflation(ex: cement) 3)Over- Expansion of Money Supply 4)Increase in Population 5)Expansion of Bank Credit 6)Black Money 7)Poor Performance of Farm Sector
 EFFECTS OF INFLATION BENEFITS • DEBTORS • ENTREPRENEURS • FARMERS • UPPER INCOME GROUPS LOSES • CREDITORS • FIXED INCOME GROUPS • CONSUMERS • MIDDLE AND LOWER INCOME GROUPS
EFFECTS OF INFLATION BENEFITS • DEBTORS • ENTREPRENEURS • FARMERS • UPPER INCOME GROUPS LOSES • CREDITORS • FIXED INCOME GROUPS • CONSUMERS • MIDDLE AND LOWER INCOME GROUPS
 Calculation of inflation: = New price – Old price * 100 For instance: Inflation for today’s petrol price. Old price = 70 New price = 75 -70 70 * 100 = 7. 14%
Calculation of inflation: = New price – Old price * 100 For instance: Inflation for today’s petrol price. Old price = 70 New price = 75 -70 70 * 100 = 7. 14%
 The Consumer Price Index and the Cost of Living Real-Nominal PRINCIPLE What matters to people is the real value of money or income—its purchasing power—not the “face” value of money or income. • Economists have developed a number of different measures to track the cost of living over time. • The best known of these measures is the Consumer Price Index (CPI). The CPI measures changes in prices facing consumers. 11 of 28
The Consumer Price Index and the Cost of Living Real-Nominal PRINCIPLE What matters to people is the real value of money or income—its purchasing power—not the “face” value of money or income. • Economists have developed a number of different measures to track the cost of living over time. • The best known of these measures is the Consumer Price Index (CPI). The CPI measures changes in prices facing consumers. 11 of 28
 The Consumer Price Index and the Cost of Living • The CPI measures changes in a fixed basket of goods—a collection of items chosen to represent the purchasing pattern of a typical consumer. • The CPI index for a given year, say year K, is defined as: 12 of 28
The Consumer Price Index and the Cost of Living • The CPI measures changes in a fixed basket of goods—a collection of items chosen to represent the purchasing pattern of a typical consumer. • The CPI index for a given year, say year K, is defined as: 12 of 28
 Consumer basket Ukrainian diet bakery products cereals vegetables meat dairy products fishery products eggs sugar oil 125 of 296 items are food products, which is over 58% of household expenditures. Nonfood products amount 129 and the others are 42 services
Consumer basket Ukrainian diet bakery products cereals vegetables meat dairy products fishery products eggs sugar oil 125 of 296 items are food products, which is over 58% of household expenditures. Nonfood products amount 129 and the others are 42 services
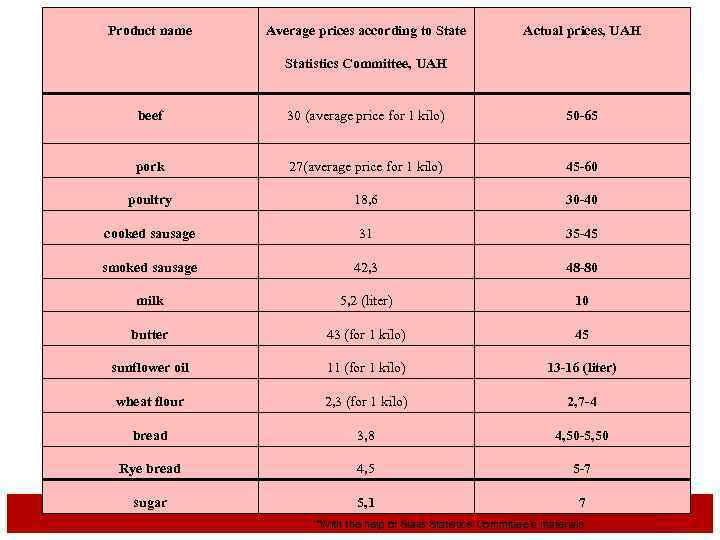 Product name Average prices according to State Actual prices, UAH Statistics Committee, UAH beef 30 (average price for 1 kilo) 50 -65 pork 27(average price for 1 kilo) 45 -60 poultry 18, 6 30 -40 cooked sausage 31 35 -45 smoked sausage 42, 3 48 -80 milk 5, 2 (liter) 10 butter 43 (for 1 kilo) 45 sunflower oil 11 (for 1 kilo) 13 -16 (liter) wheat flour 2, 3 (for 1 kilo) 2, 7 -4 bread 3, 8 4, 50 -5, 50 Rye bread 4, 5 5 -7 sugar 5, 1 7 *With the help of State Statistics Committee’s materials
Product name Average prices according to State Actual prices, UAH Statistics Committee, UAH beef 30 (average price for 1 kilo) 50 -65 pork 27(average price for 1 kilo) 45 -60 poultry 18, 6 30 -40 cooked sausage 31 35 -45 smoked sausage 42, 3 48 -80 milk 5, 2 (liter) 10 butter 43 (for 1 kilo) 45 sunflower oil 11 (for 1 kilo) 13 -16 (liter) wheat flour 2, 3 (for 1 kilo) 2, 7 -4 bread 3, 8 4, 50 -5, 50 Rye bread 4, 5 5 -7 sugar 5, 1 7 *With the help of State Statistics Committee’s materials
 Key point • In each group there are goods (services) with increased demand, which occupy a large proportion. It is on the bottom need to focus, trying to improve the method of calculation in general.
Key point • In each group there are goods (services) with increased demand, which occupy a large proportion. It is on the bottom need to focus, trying to improve the method of calculation in general.
 Conclusion • the object of inflation targeting should be controlled and based on the CPI, ie a level of inflation that is regulated or expected by state. • Application of IT regime in Ukraine will allow to maintain inflation at a low and stable level, which is a prerequisite for high economic growth.
Conclusion • the object of inflation targeting should be controlled and based on the CPI, ie a level of inflation that is regulated or expected by state. • Application of IT regime in Ukraine will allow to maintain inflation at a low and stable level, which is a prerequisite for high economic growth.
 ANY QUESTIONS…?
ANY QUESTIONS…?


