13e09db771738f065c6d1abc5f084bac.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Richardson Lecture, April 25, 2007 Hemoglobin: O 2 binding equilibria and the T-R, Deoxy-Oxy Transition • Powerpoint introduction • High resolution crystal structures with electron density shown in Ki. NG • Good-parts version of Pro. Tour 8. kin shown in Mage Files available for downloading and on-line viewing at web-site: http: //Kinemage. biochem. duke. edu Look down in kinemage home page for: “Teaching: Course materials” … “CHEM 22 L” click on CHEM 22 L link --> …
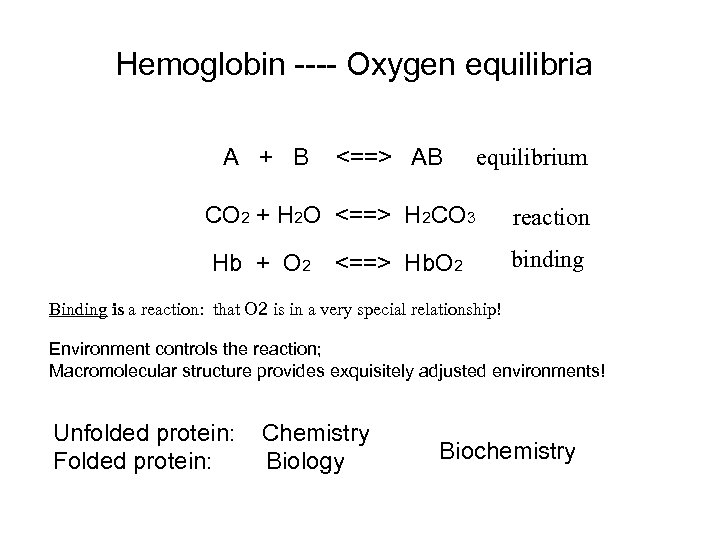
Hemoglobin ---- Oxygen equilibria A + B <==> AB equilibrium CO 2 + H 2 O <==> H 2 CO 3 reaction Hb + O 2 binding <==> Hb. O 2 Binding is a reaction: that O 2 is in a very special relationship! Environment controls the reaction; Macromolecular structure provides exquisitely adjusted environments! Unfolded protein: Folded protein: Chemistry Biology Biochemistry

Role of the globins in oxygen transport and storage The transport rate of a diffusing substance varies inversely with the square of the distance it must diffuse. O 2 diffusion through tissues thicker than 1 mm is too slow to support life: Myoglobin is the oxygen storage protein - High affinity for O 2 - Major physiological role is to facilitate oxygen transport in rapidly respiring muscle. Hemoglobin is used for transport of oxygen from the lungs, gills, or skin of an animal to its capillaries. - Lower affinity for O 2 than myoglobin - Also for removing CO 2 from tissues - CO 2 is a major product of metabolite oxidation Illustrates regulation of protein function and evolution. Figure 7 -1 Mathews, van Holde, Ahern, 2001
Summary: Role of the globins in oxygen transport and storage • Lungs: – • Oxygenation favors the oxy Hb form, which stimulates the release of CO 2. Arteries and tissues – The lower p. H and high CO 2 favor deoxy Hb • Promote O 2 release and binding of CO 2 – – CO 2 -- both in forming bicarbonate and in reacting with Hb -- causes the release of more protons, further stimulating O 2 release and CO 2 binding. Hyperventilation: dizziness from breathing too rapidly and purging CO 2 from the tissues, which impairs the release of O 2 into the tissues. (Correct by breathing into a paper bag to bring CO 2 back into the blood. Figure 7 -1 Mathews, van Holde, Ahern, 2001

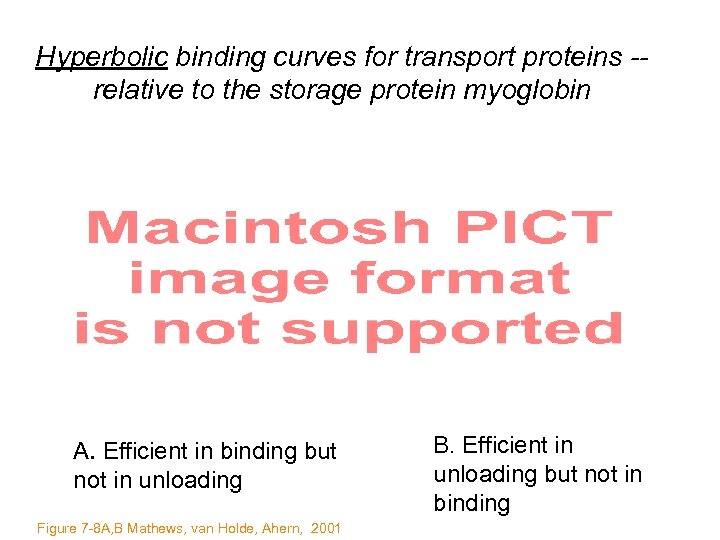
Hyperbolic binding curves for transport proteins -relative to the storage protein myoglobin A. Efficient in binding but not in unloading Figure 7 -8 A, B Mathews, van Holde, Ahern, 2001 B. Efficient in unloading but not in binding
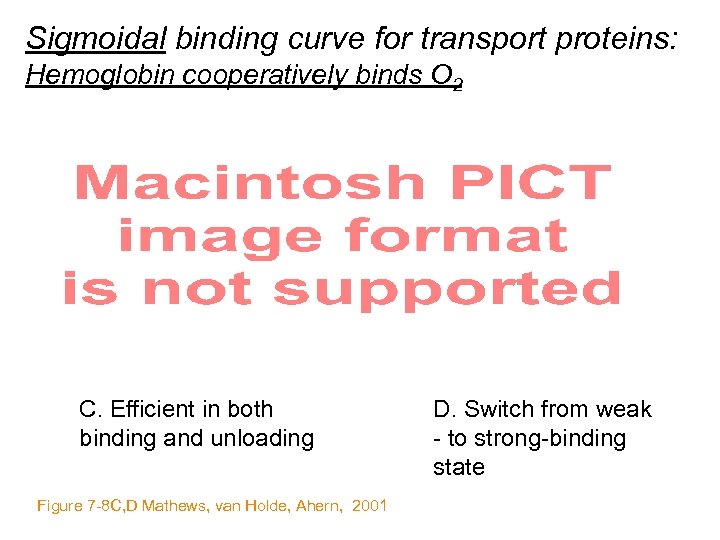
Sigmoidal binding curve for transport proteins: Hemoglobin cooperatively binds O 2 C. Efficient in both binding and unloading Figure 7 -8 C, D Mathews, van Holde, Ahern, 2001 D. Switch from weak - to strong-binding state
Comparison of myoglobin and hemoglobin Myoglobin (153 a. a. ) (Mb) (Monomer) Hemoglobin 4 x (146 a. a. ) (Hb) (Tetramer) Sequences of Mb and Hb are overall very similar Letters A-H indicate a-helical regions of polypeptide chains Hemoglobin contains two a- and two ß -chains (tetramer) Figure 7 -3 Mathews, van Holde, Ahern, 2001

Sigmoidal Curve? Low affinity and High affinity interconverting forms: Multiple subunits interact with and control each other… Deoxy-oxy states board drawing
Bohr effect in hemoglobin is response to p. H changes • Allosteric effectors – CO 2 – protons – lactic acid • Consequences: – In the capillaries, hydrogen ions promote the release of O 2 by driving the reaction to the right. – As venous blood enters the lungs, re-oxygenation reverses the effect, releasing the H+ from Hb • n. H+ by shifting the equilibrium the left. – This in turn releases the CO 2 from the bicarbonate dissolved in the blood. Figure 7 -16 Mathews, van Holde, Ahern, 2001
Bohr Effect and CO 2 transport (a) f O 2 – lower O 2 affinity of Hb – Hb. O 2 + H+ Hb. H+ + O 2 (b) O 2 f O 2 (c) PG f O 2 A decrease in p. H of only 0. 8 units shifts the P 50 from 20 mm Hg to over 40 mm Hg, greatly increasing the amount of oxygen unloaded to myoglobin. The O 2 affinity of Hb increases with increasing p. H.
Bohr Effect - Mechanism (a) f O 2 – lower O 2 affinity – Hb. O 2 + H+ Hb. H+ + O 2 Mechanism: The O 2 affinity of Hb increases with increasing p. H. Certain proton binding sites in deoxy Hb are of higher affinity than in oxy Hb. (Example of details to be looked at…: ) • In the deoxy form, His 146 at the C-terminus of a -chain can make a salt bridge with Asp 94, if the His is protonated. • The salt bridge stabilizes the proton against dissociation. • In the oxy form, the p. Ka of His 146 falls to about 6. 5. The salt bridge cannot be formed. At blood p. H (7. 4) His 146 is largely unprotonated in oxyhemoglobin. Other amino acid residues are involved too, like those at the N-terminal of -chains.
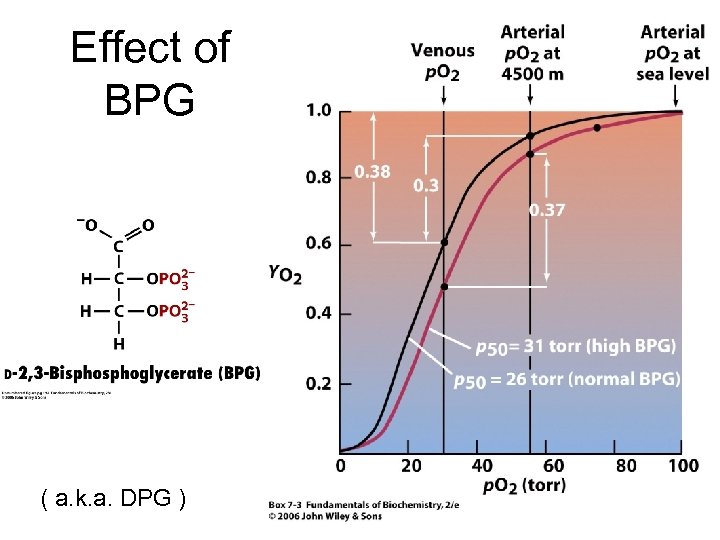
Effect of BPG ( a. k. a. DPG )
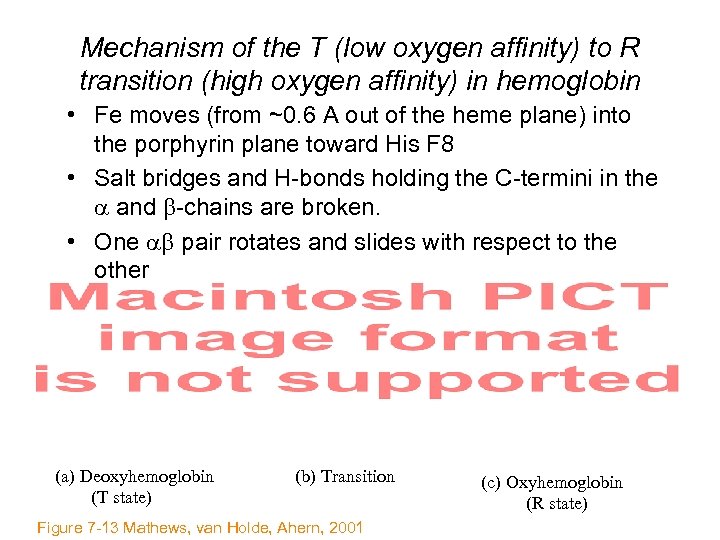
Mechanism of the T (low oxygen affinity) to R transition (high oxygen affinity) in hemoglobin • Fe moves (from ~0. 6 A out of the heme plane) into the porphyrin plane toward His F 8 • Salt bridges and H-bonds holding the C-termini in the and -chains are broken. • One pair rotates and slides with respect to the other (a) Deoxyhemoglobin (T state) (b) Transition Figure 7 -13 Mathews, van Holde, Ahern, 2001 (c) Oxyhemoglobin (R state)

Hemoglobin, the evidence… 1. 25 Å Resolution Crystal Structures of Human Haemoglobin in the Oxy, Deoxy and Carbonmonoxy Forms Sam-Yong Park 1 Takeshi Yokoyama 1, Naoya Shibayama 2, , Yoshitsugu Shiro 3 and Jeremy R. H. Tame 1 J. Mol. Biol. (2006) 360, 690– 701 Coordinates from Protein Data Bank: http: //www. rcsb. org 2 DN 1. pdb Oxy. Hb. A 2 DN 2. pdb Deoxy. Hb. A 2 DN 3. pdb CO-Hb. A Hydrogens added in Mol. Probity: http: //molprobity. biochem. duke. edu Electron density maps from the Electron Density Server: http: //eds. bmc. uu. se …and now into the crystals…

Hemoglobin, the story… "THE PROTEIN TOURIST #8 THE T-R, DEOXY-OXY TRANSITION IN HUMAN HEMOGLOBIN" David Richardson, Celia Bonaventura, and Jane Richardson Protein Science vol. 3, #10 electronic supplement, Oct. 1994. view on the web in Ki. NG: http: //kinemage. biochem. duke. edu/teaching/chem 22 l/index. php Pro. Tour 8. kin: Kin. 1 - Hb tetramer: deoxy vs oxy transition animated Kin. 2 - Hb T-R transition: alpha chain and heme closeup Kin. 3 - The alpha 1 -beta 2 allosteric interface Kin. 4 - Alpha 1 -alpha 2 salt bridges Kin. 5 - Beta 2 salt bridges Good parts version: Hb. Allo. kin
13e09db771738f065c6d1abc5f084bac.ppt