26b64e7fb55de0d38ecc9ce66ae30295.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57
 Richard Jones Service Director Cloud Computing: Transforming IT Cloud Computing / Data Center All Contents © 2009 Burton Group. All rights
Richard Jones Service Director Cloud Computing: Transforming IT Cloud Computing / Data Center All Contents © 2009 Burton Group. All rights
 Business Value: Key to Any Technology “The rise of the cloud is more than just another platform shift that gets geeks excited. It will undoubtedly transform the IT industry, but it will also profoundly change the way people work and companies operate. ”—The Economist, “Let it Rise, ” 10/23/08 2
Business Value: Key to Any Technology “The rise of the cloud is more than just another platform shift that gets geeks excited. It will undoubtedly transform the IT industry, but it will also profoundly change the way people work and companies operate. ”—The Economist, “Let it Rise, ” 10/23/08 2
 What is Cloud Computing? The set of disciplines, technologies, and business models used to deliver IT capabilities (software, platforms, hardware) as an on-demand, scalable, elastic service How can I make this. . . Look more like this? 3
What is Cloud Computing? The set of disciplines, technologies, and business models used to deliver IT capabilities (software, platforms, hardware) as an on-demand, scalable, elastic service How can I make this. . . Look more like this? 3
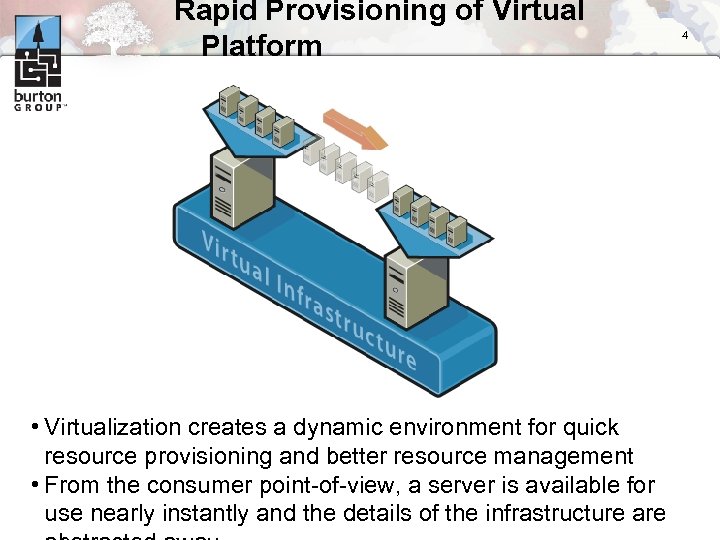 Rapid Provisioning of Virtual Platform • Virtualization creates a dynamic environment for quick resource provisioning and better resource management • From the consumer point-of-view, a server is available for use nearly instantly and the details of the infrastructure are 4
Rapid Provisioning of Virtual Platform • Virtualization creates a dynamic environment for quick resource provisioning and better resource management • From the consumer point-of-view, a server is available for use nearly instantly and the details of the infrastructure are 4
 On-Demand, Self Service • Consumer have the ability to consume cloud services as the need arises • Self-service increases IT agility to match the pace of business 5
On-Demand, Self Service • Consumer have the ability to consume cloud services as the need arises • Self-service increases IT agility to match the pace of business 5
 Consumption-based pricing model • Vendors charge customers based on amount of the service consumed. • Customers pay for only the IT services they use, thereby increasing IT ROI 6
Consumption-based pricing model • Vendors charge customers based on amount of the service consumed. • Customers pay for only the IT services they use, thereby increasing IT ROI 6
 Elastic and Scalable • Consumers can quickly provision and de-provision IT services • Cloud service appears infinitely scalable to the consumer 7
Elastic and Scalable • Consumers can quickly provision and de-provision IT services • Cloud service appears infinitely scalable to the consumer 7
 Shared Infrastructure • Vendors leverage the infrastructure to service multiple consumers • Multi-tenancy is vital to driving down infrastructure costs 8
Shared Infrastructure • Vendors leverage the infrastructure to service multiple consumers • Multi-tenancy is vital to driving down infrastructure costs 8
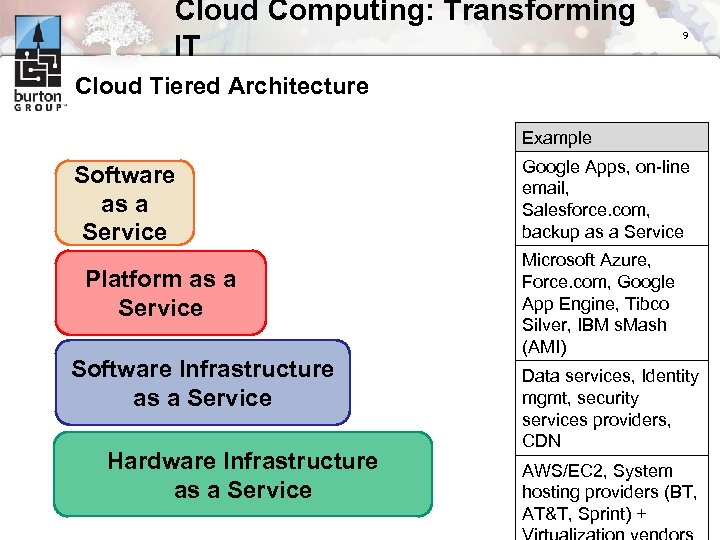 Cloud Computing: Transforming IT 9 Cloud Tiered Architecture Example Software as a Service Platform as a Service Software Infrastructure as a Service Hardware Infrastructure as a Service Google Apps, on-line email, Salesforce. com, backup as a Service Microsoft Azure, Force. com, Google App Engine, Tibco Silver, IBM s. Mash (AMI) Data services, Identity mgmt, security services providers, CDN AWS/EC 2, System hosting providers (BT, AT&T, Sprint) +
Cloud Computing: Transforming IT 9 Cloud Tiered Architecture Example Software as a Service Platform as a Service Software Infrastructure as a Service Hardware Infrastructure as a Service Google Apps, on-line email, Salesforce. com, backup as a Service Microsoft Azure, Force. com, Google App Engine, Tibco Silver, IBM s. Mash (AMI) Data services, Identity mgmt, security services providers, CDN AWS/EC 2, System hosting providers (BT, AT&T, Sprint) +
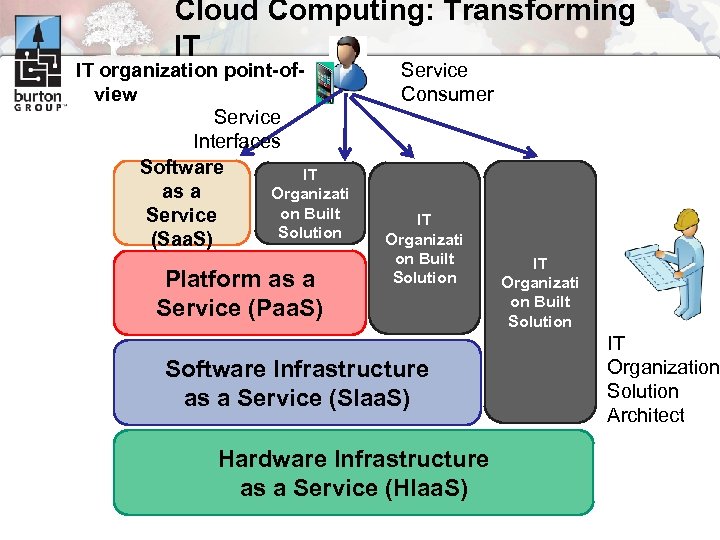 Cloud Computing: Transforming IT IT organization point-ofview Service Interfaces Software IT as a Organizati on Built Service Solution (Saa. S) Platform as a Service (Paa. S) Service Consumer IT Organizati on Built Solution Software Infrastructure as a Service (SIaa. S) Hardware Infrastructure as a Service (HIaa. S) IT Organizati on Built Solution IT Organization Solution Architect
Cloud Computing: Transforming IT IT organization point-ofview Service Interfaces Software IT as a Organizati on Built Service Solution (Saa. S) Platform as a Service (Paa. S) Service Consumer IT Organizati on Built Solution Software Infrastructure as a Service (SIaa. S) Hardware Infrastructure as a Service (HIaa. S) IT Organizati on Built Solution IT Organization Solution Architect
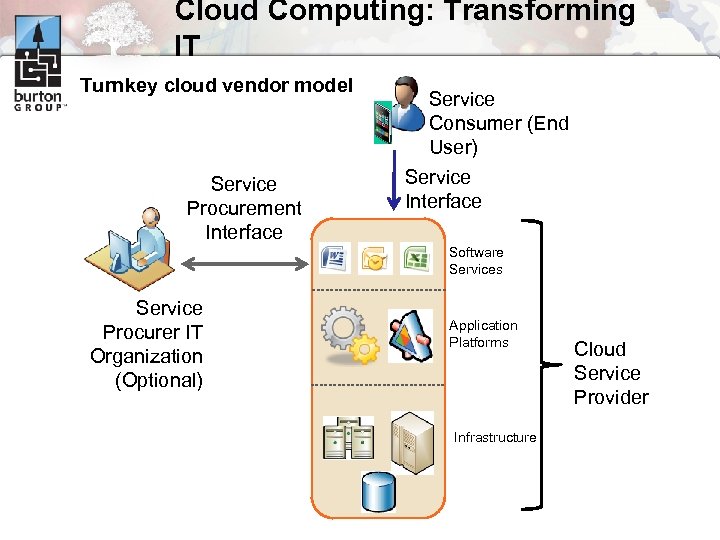 Cloud Computing: Transforming IT Turnkey cloud vendor model Service Procurement Interface Service Consumer (End User) Service Interface Software Services Service Procurer IT Organization (Optional) Application Platforms Infrastructure Cloud Service Provider
Cloud Computing: Transforming IT Turnkey cloud vendor model Service Procurement Interface Service Consumer (End User) Service Interface Software Services Service Procurer IT Organization (Optional) Application Platforms Infrastructure Cloud Service Provider
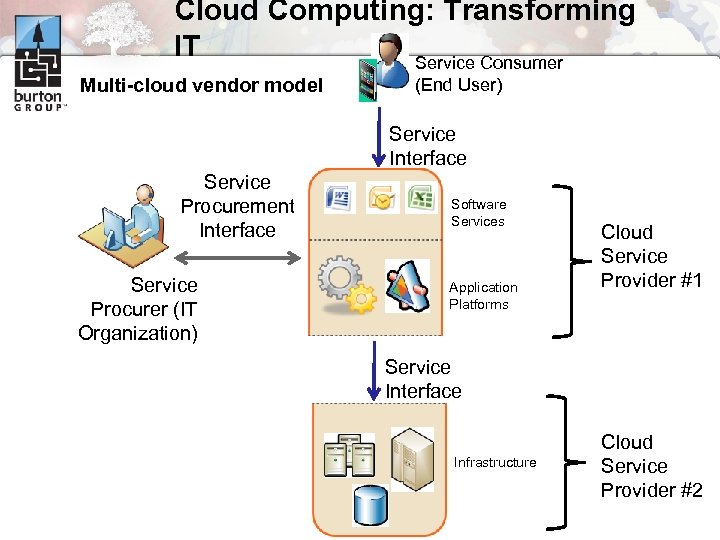 Cloud Computing: Transforming IT Service Consumer Multi-cloud vendor model (End User) Service Interface Service Procurement Interface Service Procurer (IT Organization) Software Services Application Platforms Cloud Service Provider #1 Service Interface Infrastructure Cloud Service Provider #2
Cloud Computing: Transforming IT Service Consumer Multi-cloud vendor model (End User) Service Interface Service Procurement Interface Service Procurer (IT Organization) Software Services Application Platforms Cloud Service Provider #1 Service Interface Infrastructure Cloud Service Provider #2
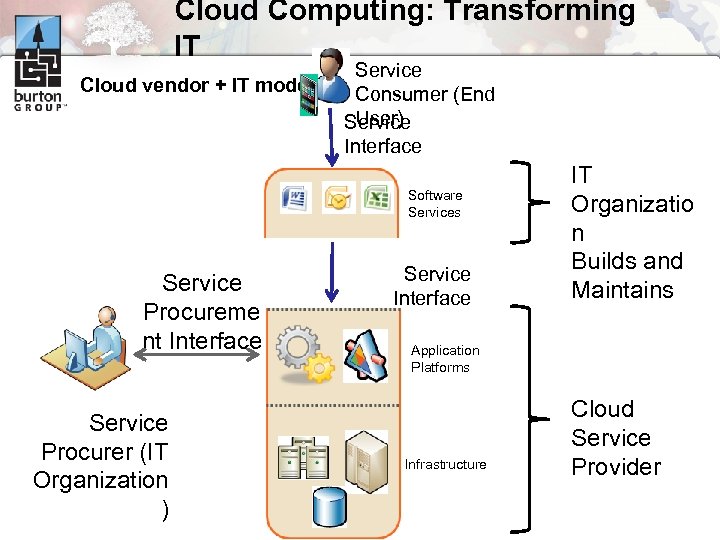 Cloud Computing: Transforming IT Cloud vendor + IT model Service Consumer (End User) Service Interface Software Services Service Procureme nt Interface Service Procurer (IT Organization ) Service Interface IT Organizatio n Builds and Maintains Application Platforms Infrastructure Cloud Service Provider
Cloud Computing: Transforming IT Cloud vendor + IT model Service Consumer (End User) Service Interface Software Services Service Procureme nt Interface Service Procurer (IT Organization ) Service Interface IT Organizatio n Builds and Maintains Application Platforms Infrastructure Cloud Service Provider
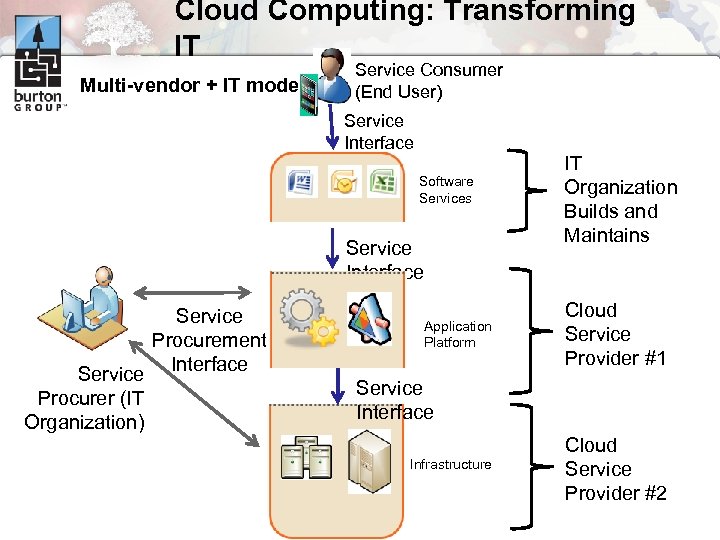 Cloud Computing: Transforming IT Multi-vendor + IT model Service Consumer (End User) Service Interface Software Services Service Interface Service Procurement Service Interface Procurer (IT Organization) Application Platform IT Organization Builds and Maintains Cloud Service Provider #1 Service Interface Infrastructure Cloud Service Provider #2
Cloud Computing: Transforming IT Multi-vendor + IT model Service Consumer (End User) Service Interface Software Services Service Interface Service Procurement Service Interface Procurer (IT Organization) Application Platform IT Organization Builds and Maintains Cloud Service Provider #1 Service Interface Infrastructure Cloud Service Provider #2
 On the Flip Side… 15
On the Flip Side… 15
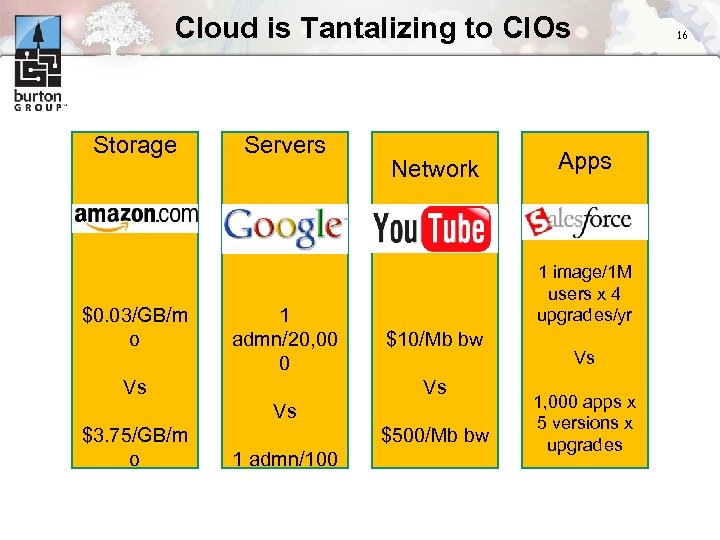 Cloud is Tantalizing to CIOs Storage $0. 03/GB/m o Servers 1 admn/20, 00 0 Vs Network $10/Mb bw Vs $500/Mb bw 1 admn/100 Apps 1 image/1 M users x 4 upgrades/yr Vs $3. 75/GB/m o 16 Vs 1, 000 apps x 5 versions x upgrades
Cloud is Tantalizing to CIOs Storage $0. 03/GB/m o Servers 1 admn/20, 00 0 Vs Network $10/Mb bw Vs $500/Mb bw 1 admn/100 Apps 1 image/1 M users x 4 upgrades/yr Vs $3. 75/GB/m o 16 Vs 1, 000 apps x 5 versions x upgrades
 Elastic and scalable 17 • What infrastructure is my applications running on? • How much of the service can I consume at one
Elastic and scalable 17 • What infrastructure is my applications running on? • How much of the service can I consume at one
 On-demand, Self-Service • Will the cloud enable/increase shadow IT? • Will we service brokers emerge? 18
On-demand, Self-Service • Will the cloud enable/increase shadow IT? • Will we service brokers emerge? 18
 Consumption-based Pricing 19 • What happens if you don’t pay your bill? Do you lose your data? • How do I control and monitor consumption? (Wireless phone bill)
Consumption-based Pricing 19 • What happens if you don’t pay your bill? Do you lose your data? • How do I control and monitor consumption? (Wireless phone bill)
 Shared Infrastructure • Who are you sharing that server with? As we open up systems, customers expect the same security, reliability, and availability. 20
Shared Infrastructure • Who are you sharing that server with? As we open up systems, customers expect the same security, reliability, and availability. 20
 Virtualized and Dynamic • Can the vendor move my data or application? • Will that cause a data compliance issue? 21
Virtualized and Dynamic • Can the vendor move my data or application? • Will that cause a data compliance issue? 21
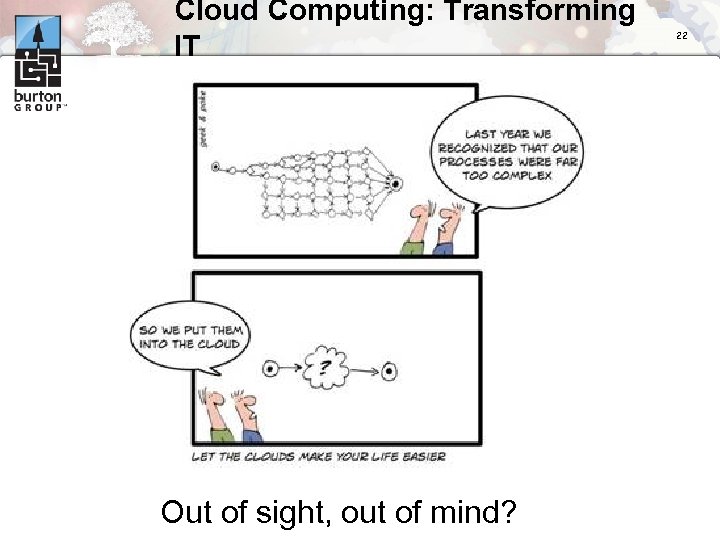 Cloud Computing: Transforming IT Out of sight, out of mind? 22
Cloud Computing: Transforming IT Out of sight, out of mind? 22
 Inflexible/Non-Existent SLAs 23 • Inflexible, boilerplate service-level agreements are norm
Inflexible/Non-Existent SLAs 23 • Inflexible, boilerplate service-level agreements are norm
 Inability to Manage Risks • Lack of vendor transparency and inability to audit service security measures obscures risk assessment • Vendors – Get used to being under the spotlight. When you’re hosting multiple 24
Inability to Manage Risks • Lack of vendor transparency and inability to audit service security measures obscures risk assessment • Vendors – Get used to being under the spotlight. When you’re hosting multiple 24
 Unclear Long-Term Return On Investment Return On Sorry there friend, your ROI is under the Investment other shell • Poor internal cost insight creates an inability to determine cloud service ROI 25
Unclear Long-Term Return On Investment Return On Sorry there friend, your ROI is under the Investment other shell • Poor internal cost insight creates an inability to determine cloud service ROI 25
 Market Immaturity • Vendor flux and poor service implementations creates consumer uncertainty 26
Market Immaturity • Vendor flux and poor service implementations creates consumer uncertainty 26
 Inability to Monitor/Manage 27 • Inability to manage and monitor service for events and issues • Lack of management APIs to monitor/verify service levels
Inability to Monitor/Manage 27 • Inability to manage and monitor service for events and issues • Lack of management APIs to monitor/verify service levels
 Vendor Lock-in Vendor Lock-In At the point you realize you’re locked in, it’s far too late to escape • Lack of cloud interoperability, proprietary data models, and poor application portability make cloud migration difficult 28
Vendor Lock-in Vendor Lock-In At the point you realize you’re locked in, it’s far too late to escape • Lack of cloud interoperability, proprietary data models, and poor application portability make cloud migration difficult 28
 Cloud market segmentation • Public Clouds: • Vendor Entry Point, Market Position 29
Cloud market segmentation • Public Clouds: • Vendor Entry Point, Market Position 29
 Cloud market segmentation Cloud Vendor Entry Point: • Internet Pure Play Vendors • • • Amazon, Google, Sales. Force, Bungee Labs, etc. No background in “traditional” enterprise data center Online play – opening up more of their infrastructure below their Saa. S entry • Traditional Internet Vendors (Hosting, etc. ) • • • Rackspace, Savvis, Op. Source, Microsoft (Hosted Exchange) etc. Building Cloud services on their hosting/infrastructure/business model – Saa. S through HIaa. S Understand enterprise data center customers 30
Cloud market segmentation Cloud Vendor Entry Point: • Internet Pure Play Vendors • • • Amazon, Google, Sales. Force, Bungee Labs, etc. No background in “traditional” enterprise data center Online play – opening up more of their infrastructure below their Saa. S entry • Traditional Internet Vendors (Hosting, etc. ) • • • Rackspace, Savvis, Op. Source, Microsoft (Hosted Exchange) etc. Building Cloud services on their hosting/infrastructure/business model – Saa. S through HIaa. S Understand enterprise data center customers 30
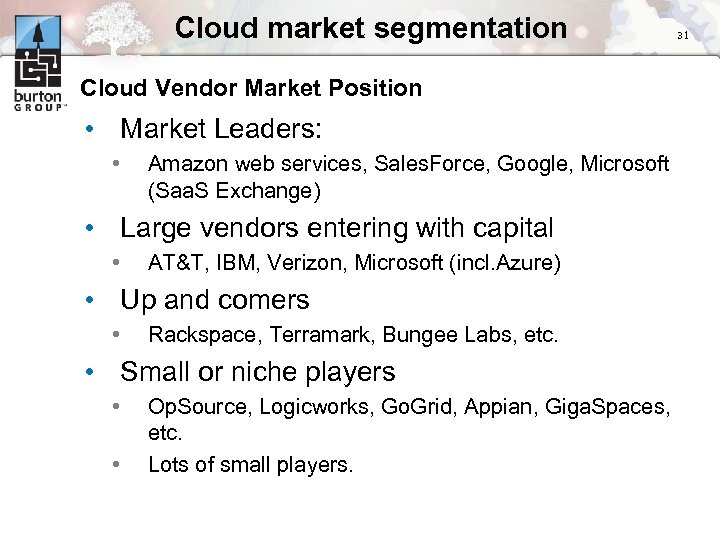 Cloud market segmentation Cloud Vendor Market Position • Market Leaders: • Amazon web services, Sales. Force, Google, Microsoft (Saa. S Exchange) • Large vendors entering with capital • AT&T, IBM, Verizon, Microsoft (incl. Azure) • Up and comers • Rackspace, Terramark, Bungee Labs, etc. • Small or niche players • • Op. Source, Logicworks, Go. Grid, Appian, Giga. Spaces, etc. Lots of small players. 31
Cloud market segmentation Cloud Vendor Market Position • Market Leaders: • Amazon web services, Sales. Force, Google, Microsoft (Saa. S Exchange) • Large vendors entering with capital • AT&T, IBM, Verizon, Microsoft (incl. Azure) • Up and comers • Rackspace, Terramark, Bungee Labs, etc. • Small or niche players • • Op. Source, Logicworks, Go. Grid, Appian, Giga. Spaces, etc. Lots of small players. 31
 Cloud market suppliers • The “Arms Dealers” • Open Source • • Xen/Linux from Red Hat and Citrix Amazon = RHEL 5 + Customized RHEL Xen Citrix Cloud Center (C 3) = Xen. Server+WANscaler+Netscaler Red Hat JBoss, Spring. Source, etc. • Closed Source – much more vendor marketing • VMware: v. Cloud Express • • • Purpose built offering for Cloud providers Microsoft. NET, SQL service (Azure) Oracle (Paa. S packaged as an Amazon AMI) 32
Cloud market suppliers • The “Arms Dealers” • Open Source • • Xen/Linux from Red Hat and Citrix Amazon = RHEL 5 + Customized RHEL Xen Citrix Cloud Center (C 3) = Xen. Server+WANscaler+Netscaler Red Hat JBoss, Spring. Source, etc. • Closed Source – much more vendor marketing • VMware: v. Cloud Express • • • Purpose built offering for Cloud providers Microsoft. NET, SQL service (Azure) Oracle (Paa. S packaged as an Amazon AMI) 32
 Cloud market deployment models 33 • A public cloud offers IT capability as a service to any consumer over the public Internet. • A private cloud offers IT capability as a service to a select group of consumers. • An internal cloud is a subset of a private cloud in which an IT organization offers an IT capability as a service to its own business. • An external cloud is an IT capability offered by a service provider to a third-party business.
Cloud market deployment models 33 • A public cloud offers IT capability as a service to any consumer over the public Internet. • A private cloud offers IT capability as a service to a select group of consumers. • An internal cloud is a subset of a private cloud in which an IT organization offers an IT capability as a service to its own business. • An external cloud is an IT capability offered by a service provider to a third-party business.
 Cloud Uses • Understand the business need and understand the cloud offering! • Match application requirements to provider or supplier offerings • Know how and when to use the Cloud 34
Cloud Uses • Understand the business need and understand the cloud offering! • Match application requirements to provider or supplier offerings • Know how and when to use the Cloud 34
 Cloud Customer Use Cases Eli Lilly – Pharmaceuticals: IT Business Challenges • Fixed costs • At the same time, enhance capabilities: • collaboration space • data sharing • software code/development • computing resources • network access to data from anywhere at any time • seamless security • Dependence on robust, reliable, scalable, flexible, secure infrastructure • Sense of urgency to change 35
Cloud Customer Use Cases Eli Lilly – Pharmaceuticals: IT Business Challenges • Fixed costs • At the same time, enhance capabilities: • collaboration space • data sharing • software code/development • computing resources • network access to data from anywhere at any time • seamless security • Dependence on robust, reliable, scalable, flexible, secure infrastructure • Sense of urgency to change 35
 Cloud Customer Use Cases • Eli Lilly – Pharmaceuticals • Public Cloud: • Amazon Web Services • Private/Internal Cloud: • VMware for production • Eucalyptus/Xen for public cloud development and emerging cloud services • Research already heavily leverages compute grids 36
Cloud Customer Use Cases • Eli Lilly – Pharmaceuticals • Public Cloud: • Amazon Web Services • Private/Internal Cloud: • VMware for production • Eucalyptus/Xen for public cloud development and emerging cloud services • Research already heavily leverages compute grids 36
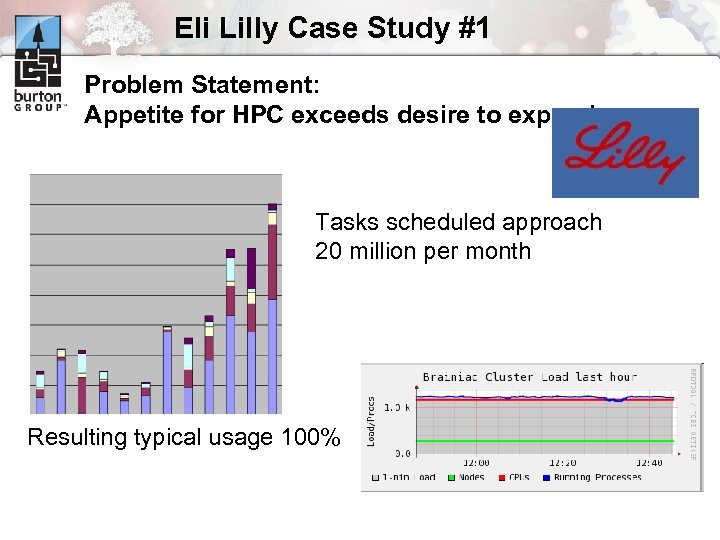 Eli Lilly Case Study #1 Problem Statement: Appetite for HPC exceeds desire to expand Tasks scheduled approach 20 million per month Resulting typical usage 100%
Eli Lilly Case Study #1 Problem Statement: Appetite for HPC exceeds desire to expand Tasks scheduled approach 20 million per month Resulting typical usage 100%
 Eli Lilly Case Study #1 Clinical Trial Optimization Before: §CPU bound processing § Predictable amount of workload § Extremely time critical deadlines § Turnaround depends entirely on the current utilization of our internal grid
Eli Lilly Case Study #1 Clinical Trial Optimization Before: §CPU bound processing § Predictable amount of workload § Extremely time critical deadlines § Turnaround depends entirely on the current utilization of our internal grid
 Eli Lilly Case Study #1 Clinical Trial Optimization After: §Workflow ported to Cycle Computing’s Cycle. Cloud service § Scheduling environment spun up on demand § The runtime is extremely consistent because there is no contention within the dedicated environment
Eli Lilly Case Study #1 Clinical Trial Optimization After: §Workflow ported to Cycle Computing’s Cycle. Cloud service § Scheduling environment spun up on demand § The runtime is extremely consistent because there is no contention within the dedicated environment
 Eli Lilly Case Study #2 Problem Statement: Strategy requires quick start/stop of collaborations weeks minutes
Eli Lilly Case Study #2 Problem Statement: Strategy requires quick start/stop of collaborations weeks minutes
 Eli Lilly Case Study #2 Collaboration Data Before: §Data passed via email § Files often lost due to email filtering § Sensitive data often transferred via physical media
Eli Lilly Case Study #2 Collaboration Data Before: §Data passed via email § Files often lost due to email filtering § Sensitive data often transferred via physical media
 Eli Lilly Case Study #2 Collaboration Data After: § Data sharing service runs in Amazon EC 2/S 3/EBS § Movement and storage is heavily encrypted § Cost scales linearly with usage
Eli Lilly Case Study #2 Collaboration Data After: § Data sharing service runs in Amazon EC 2/S 3/EBS § Movement and storage is heavily encrypted § Cost scales linearly with usage
 Cloud Customer Use Cases • Inter. Continental Hotels • IT challenges: • • Elasticity – demand is volatile Op. Ex Model – franchises and asset light Latency – compute resources near users Rapid Provisioning – respond to market changes 43
Cloud Customer Use Cases • Inter. Continental Hotels • IT challenges: • • Elasticity – demand is volatile Op. Ex Model – franchises and asset light Latency – compute resources near users Rapid Provisioning – respond to market changes 43
 Inter. Continental Hotel Case Study • Cloud Strategy: Internal Cloud • Prepare Organization Over 4 Years • People, Finances, Processes, Software • Restrict Cloud to Infrastructure as a Service • OS and up is IHG’s concern • Non-Production Environments to Public Cloud First • Development, QA, and Integration Environments lead the way 44
Inter. Continental Hotel Case Study • Cloud Strategy: Internal Cloud • Prepare Organization Over 4 Years • People, Finances, Processes, Software • Restrict Cloud to Infrastructure as a Service • OS and up is IHG’s concern • Non-Production Environments to Public Cloud First • Development, QA, and Integration Environments lead the way 44
 Inter. Continental Hotel Case Study • Why Internal Cloud? It Isn’t A Technical Issue • SLA’s not sufficient in Public Cloud • Perceived Data Risks • PCI Compliance Ambiguity • Maturity of Organization • Funding Model Differences • Applications not ready for the conformity 45
Inter. Continental Hotel Case Study • Why Internal Cloud? It Isn’t A Technical Issue • SLA’s not sufficient in Public Cloud • Perceived Data Risks • PCI Compliance Ambiguity • Maturity of Organization • Funding Model Differences • Applications not ready for the conformity 45
 Inter. Continental Hotel Case Study 46 • Solution: • Virtualization Platform • HP Blade Hardware • VMware ESX 3. 5 • Guest OS: RHEL 5. 3, Windows 2003 R 2, Solaris 10 • Base SW stack • Monitoring with Net. IQ v 3. 5 • Backup with Veritas Net. Backup v 6. 5 • Network Monitor - Op. Net 7. 0 • Configuration Management - Ops. Ware v 7. 5
Inter. Continental Hotel Case Study 46 • Solution: • Virtualization Platform • HP Blade Hardware • VMware ESX 3. 5 • Guest OS: RHEL 5. 3, Windows 2003 R 2, Solaris 10 • Base SW stack • Monitoring with Net. IQ v 3. 5 • Backup with Veritas Net. Backup v 6. 5 • Network Monitor - Op. Net 7. 0 • Configuration Management - Ops. Ware v 7. 5
 Inter. Continental Hotel Case Study • Solution: • Service Abstraction • Service. Mix ESB • Messaging Service • Active. MQ 47
Inter. Continental Hotel Case Study • Solution: • Service Abstraction • Service. Mix ESB • Messaging Service • Active. MQ 47
 Cloud Customer Use Cases 48 • CNS Response • IT challenges: Speed up processing • Patented Referenced-EEG process • • Couples electroencephalography (EEG) with a normalized database for dramatically improved psychiatric diagnostics for psychiatrists. Utilize Paa. S (Force. com) to automate process.
Cloud Customer Use Cases 48 • CNS Response • IT challenges: Speed up processing • Patented Referenced-EEG process • • Couples electroencephalography (EEG) with a normalized database for dramatically improved psychiatric diagnostics for psychiatrists. Utilize Paa. S (Force. com) to automate process.
 CNS Response Case Study CNS Response r. EEG Solution Stack Force. com (Force. com API) Managed / Hosted Server(s) Microsoft. NET, IIS, FTP COTS Microsoft. NET Adobe Acrobat Microsoft SQL Server, Force. com Storage User Authentication / Access, Security, Information presentation, Information orchestration / Integration, data management, business rule processing, reporting, user communication. Managed hosted environment (not Force. com) managing all custom code, IIS, FTP, , . NET, Acrobat and SQL Serer EEG Tech Portal, File Management, Application Integration EEG File Translation, EEG Artifacting, Normative Database processing, Correlation processing, r. EEG Report Generation r. EEG data storage, r. EEG outcomes, Robust Analytics 49
CNS Response Case Study CNS Response r. EEG Solution Stack Force. com (Force. com API) Managed / Hosted Server(s) Microsoft. NET, IIS, FTP COTS Microsoft. NET Adobe Acrobat Microsoft SQL Server, Force. com Storage User Authentication / Access, Security, Information presentation, Information orchestration / Integration, data management, business rule processing, reporting, user communication. Managed hosted environment (not Force. com) managing all custom code, IIS, FTP, , . NET, Acrobat and SQL Serer EEG Tech Portal, File Management, Application Integration EEG File Translation, EEG Artifacting, Normative Database processing, Correlation processing, r. EEG Report Generation r. EEG data storage, r. EEG outcomes, Robust Analytics 49
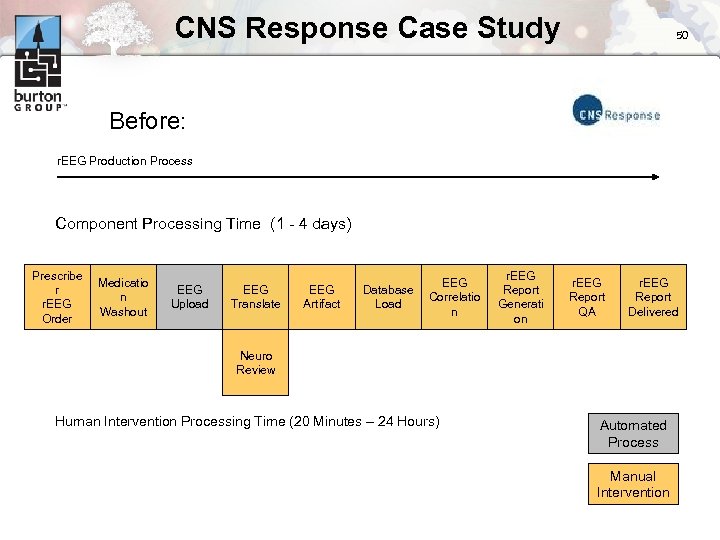 CNS Response Case Study 50 Before: r. EEG Production Process Component Processing Time (1 - 4 days) Prescribe r r. EEG Order Medicatio n Washout EEG Upload EEG Translate EEG Artifact Database Load EEG Correlatio n r. EEG Report Generati on r. EEG Report QA r. EEG Report Delivered Neuro Review Human Intervention Processing Time (20 Minutes – 24 Hours) Automated Process Manual Intervention
CNS Response Case Study 50 Before: r. EEG Production Process Component Processing Time (1 - 4 days) Prescribe r r. EEG Order Medicatio n Washout EEG Upload EEG Translate EEG Artifact Database Load EEG Correlatio n r. EEG Report Generati on r. EEG Report QA r. EEG Report Delivered Neuro Review Human Intervention Processing Time (20 Minutes – 24 Hours) Automated Process Manual Intervention
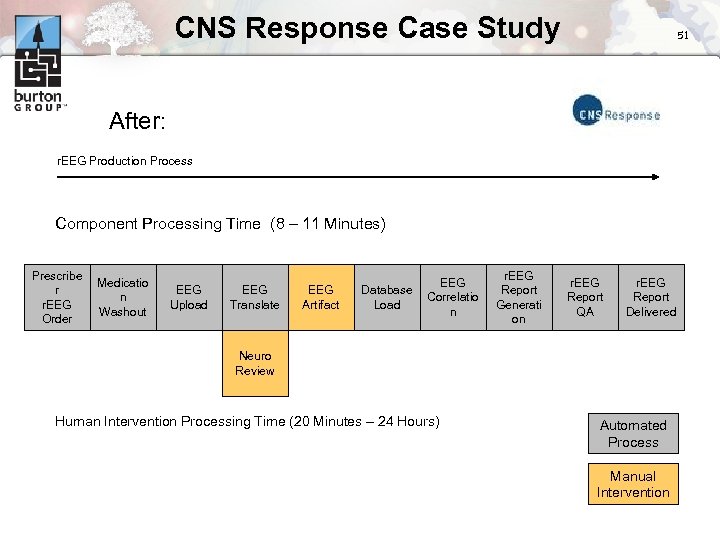 CNS Response Case Study 51 After: r. EEG Production Process Component Processing Time (8 – 11 Minutes) Prescribe r r. EEG Order Medicatio n Washout EEG Upload EEG Translate EEG Artifact Database Load EEG Correlatio n r. EEG Report Generati on r. EEG Report QA r. EEG Report Delivered Neuro Review Human Intervention Processing Time (20 Minutes – 24 Hours) Automated Process Manual Intervention
CNS Response Case Study 51 After: r. EEG Production Process Component Processing Time (8 – 11 Minutes) Prescribe r r. EEG Order Medicatio n Washout EEG Upload EEG Translate EEG Artifact Database Load EEG Correlatio n r. EEG Report Generati on r. EEG Report QA r. EEG Report Delivered Neuro Review Human Intervention Processing Time (20 Minutes – 24 Hours) Automated Process Manual Intervention
 CNS Response Case Study Benefits Realized: • Proven Solution Architecture • Easily leverage existing application engineering skill set • Inherent functional capability • Functional upgrades • Minimal solution downtime / maintenance risk • Industry standard security, reliability • Flexible on-demand data storage capability • User interface standards and flexibility • Unlimited scale • Flexible business process / application integration – remove information silos 52
CNS Response Case Study Benefits Realized: • Proven Solution Architecture • Easily leverage existing application engineering skill set • Inherent functional capability • Functional upgrades • Minimal solution downtime / maintenance risk • Industry standard security, reliability • Flexible on-demand data storage capability • User interface standards and flexibility • Unlimited scale • Flexible business process / application integration – remove information silos 52
 CNS Response Case Study Hurdles encountered: • Perceived loss of control • Business continuity • Service level agreements • Return on investment / total cost of ownership • Executive approval 53
CNS Response Case Study Hurdles encountered: • Perceived loss of control • Business continuity • Service level agreements • Return on investment / total cost of ownership • Executive approval 53
 Recommendations 54 • Understand your business: Don’t jump into Cloud just because it is “the thing to do” • Identify those business processes that could benefit from cloud automation: Internal or External • Decide on what would make sense internal vs. external • SLA requirements will clearly answer this question today • Cost Analysis • Know your internal costs. Without that, you are shooting in the dark • Expect a hybrid IT approach (at least initially) • Executive buy-in and support
Recommendations 54 • Understand your business: Don’t jump into Cloud just because it is “the thing to do” • Identify those business processes that could benefit from cloud automation: Internal or External • Decide on what would make sense internal vs. external • SLA requirements will clearly answer this question today • Cost Analysis • Know your internal costs. Without that, you are shooting in the dark • Expect a hybrid IT approach (at least initially) • Executive buy-in and support
 Questions 55
Questions 55
 Cloud Computing: Transforming IT Additional Materials 56
Cloud Computing: Transforming IT Additional Materials 56
 Cloud Computing Vendor Examples 57 Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization • Capacity Spill-over example using Messaging, Realtime, and Grid (MRG) • http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=o. Sm 7 Ff 8 k. Kj k
Cloud Computing Vendor Examples 57 Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization • Capacity Spill-over example using Messaging, Realtime, and Grid (MRG) • http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=o. Sm 7 Ff 8 k. Kj k


