cbc41db797bc151a6b228d42e9543ff4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg COST-720 Integrated Ground-Based Remote Sensing Stations for Atmospheric Profiling Dirk Engelbart (DWD), Wim Monna (KNMI), and John Nash (UKMO) Concept · COST-720 Ø Objectives + Structure Ø Campaigns Ø Major Results Remote-sensing field site at Lindenberg Observatory Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006

Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg Goalsof COST-720 Ø development of integrated ground-based remote-sensing stations for atmospheric profiling Ø Assessment of their use for meteorological analysis, forecast, climate research and monitoring Ø Set-up of networks of integrated profiling stations during dedicated campaigns Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006

Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg Organisation - I WG 1, Basic Techniquesand Algorithms • Assessment of the state of the art of individual techniques in view of potential for integration • Improvements where necessary and possible • Considered measurement systems: Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de - Microwave and IR Radiometer - water-vapour and Doppler wind Lidar - Wind profiling radar/RASS - Cloud radar - SPC ceilometer - C-Band weather radar. WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006

Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg Organisation - II WG 2, Integration • Development / assessment of methods to derive - Temperature profiles - Humidityprofiles - Cloud characteristics - boundary-layer characteristics Ø from integrated remote sensing Ø for different kinds of users Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006

Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg Field experiments: TUC • Payerne, Switzerland • 15 November, 2003 – 15 February, 2004 • In-situ & ground-based remote-sensing systems Instruments Goals wind profiler • 1290 MHz • • 78 Test of basic ground-based GHz cloud radar T and U profiling systems • radiometers (ASMUWARA, • Study ability to detect Radiometrics, IR) PBL phenomena • radiosondes (3 types) • Assess automatic cloud • ceilometer systems detection • • GPS humidity system study Provide dataset to • total sky imager system integration • BSRN instruments Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006

Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg Field experiments: TUC Results: 10 reviewed papers published in a Special Issue «COST-720 TUC» of Met. Z. : Vol. 15, No. 1, 2006, 97 pp. • Intercomparisons found biasesin both …. Ø microwave radiometers Ø all radiosondeshumidity ’ • FMCW cloud radar can monitor fog base/top • Radiometer and wind profiler able to monitor: Ø T and humidity inversions near surface • First integration of Wind Profiler and Microwave Radiometer for humidity profiling Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006

Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg Field experiments: CSIP = “Convective Storm Initiation Project” Central-Southern England, June – August 2005 COST-720 and UK Universities • • Systemintegration studiesfor summertime PBL High-resolution NWP modelling Instruments : • • • Microwave radiometer Laser ceilometer 1290 MHzwindprofiler Chilbolton radar Radiosondes Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006

Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg Field experiments: CSIP Results • UHF radar can see of convective inhibition and resolve structure lids of convective plumes • Radiometer IWV in good agreement with most GPS sensors at high temporal resolution • Radar refractivity measurements can make humidity changes • Cold Pools behindmesoscaleconvective systems • Analysis is ongoing. . . See: • http: //www. env. leeds. ac. uk/csip/ Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006

Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg Field experiments: Helsinki. Testbed (see: Poutiainen paper) Ø Southern Finland, Finnish Met. Office August 2005 ( , start) Ø = permanent integrated profiling station Providesdata & experience for • • Mesoscaleweatherresearch Forecast-and dispersion-model development Instruments • • Finnishweatherobservation network Vaisala. WXT 510 weathertransmitter network(60) 1. 3 GHz windprofiler /RASS Dual-polarization weatherradar Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006

Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg Field experiments: LAUNCH-2005(see special poster) (29 th Aug. – 31 st Oct, 2005) (1) Assessment of new or improved humidity, temperature, and wind profiling systems: Ø Ø Ø Water vapour Lidar systems (Raman Lidar and DIAL) Doppler wind Lidar vs WPR (ZIE) inter-comparison of different types of MWP systems FTIR spectrometer High-range SPC ceilometer (2) Assessment of various algorithms, combining different techniques for profiling of cloud parameters (integrated profiling), in particular Ø Ø LWC profiling Improved rain rate profiling by radar (3) Provision of a data set, designed for validation and comparisons between measurements (4) and NWP output, (4) Provision of a data set for OSEs using 3 D-/4 D-VAR data assimilation for high-resolution WV-profiling systems in regional NWP modelling Ø Ø Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de 3 D-VAR / 4 D-VAR MM 5/ECMWF system of Hohenheim + of L‘Aquila (3 D-VAR) NWP output validation using the FZK-IFU MM 5 with a modified integration and advection scheme WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006
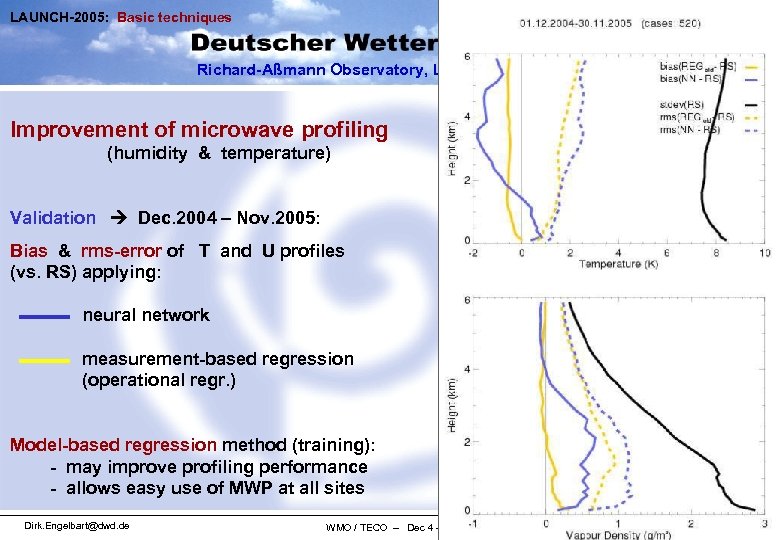
LAUNCH-2005: Basic techniques Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg Improvement of microwave profiling (humidity & temperature) Validation Dec. 2004 – Nov. 2005: Bias & rms-error of T and U profiles (vs. RS) applying: neural network measurement-based regression (operational regr. ) Model-based regression method (training): - may improve profiling performance - allows easy use of MWP at all sites Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006

LAUNCH-2005: Basic techniques Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg Lidar: RAMSES data example: Sep 25/26, 2005 DWD - RAMSES ● automated operation, data acquisition, & evaluation ● at MOL-RAO now 15 months of test operation ● similar fully-autonomous systems are in test mode at Payerne and Cabauw ● commercial network systems below 150 k€ now available (COST-720 final workshop) DWD RAMSES (Raman Lidar for Atmospheric Moisture SEn. Sing) Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006
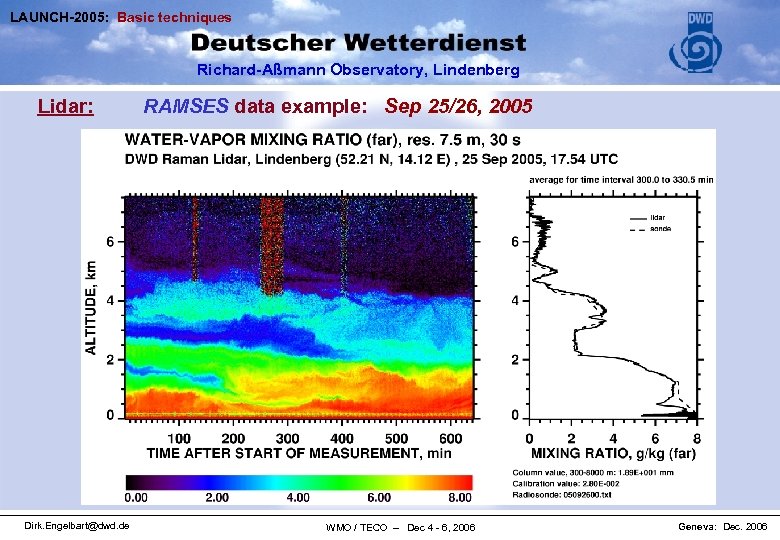
LAUNCH-2005: Basic techniques Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg Lidar: Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de RAMSES data example: Sep 25/26, 2005 WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006
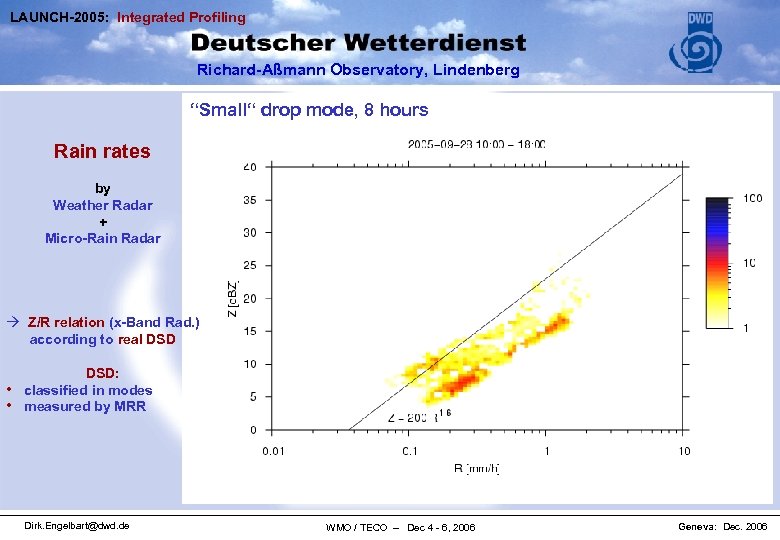
LAUNCH-2005: Integrated Profiling Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg Mean Z-R-relation over 30 hours “Small“ 8 “Large“ drop mode, 6 hours Rain rates by Weather Radar + Micro-Rain Radar à Z/R relation (x-Band Rad. ) according to real DSD • • DSD: classified in modes measured by MRR Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006
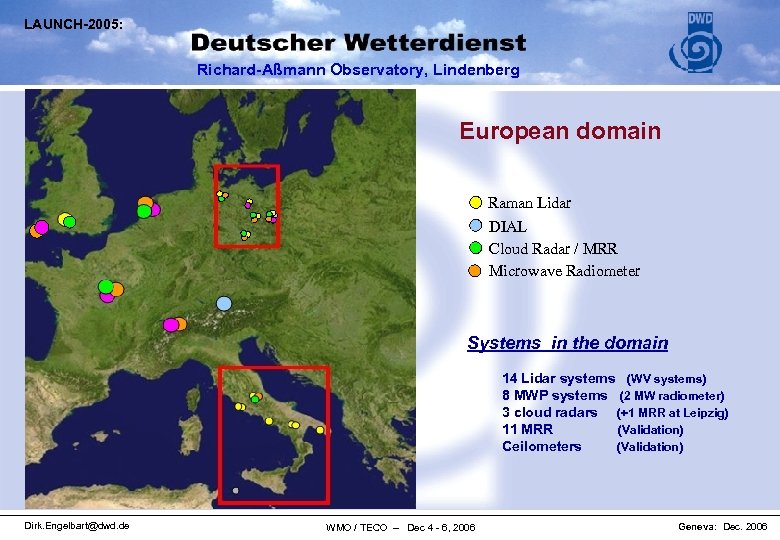
LAUNCH-2005: Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg European domain Raman Lidar DIAL Cloud Radar / MRR Microwave Radiometer Systems in the domain 14 Lidar systems (WV systems) 8 MWP systems (2 MW radiometer) 3 cloud radars (+1 MRR at Leipzig) 11 MRR (Validation) Ceilometers (Validation) Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006
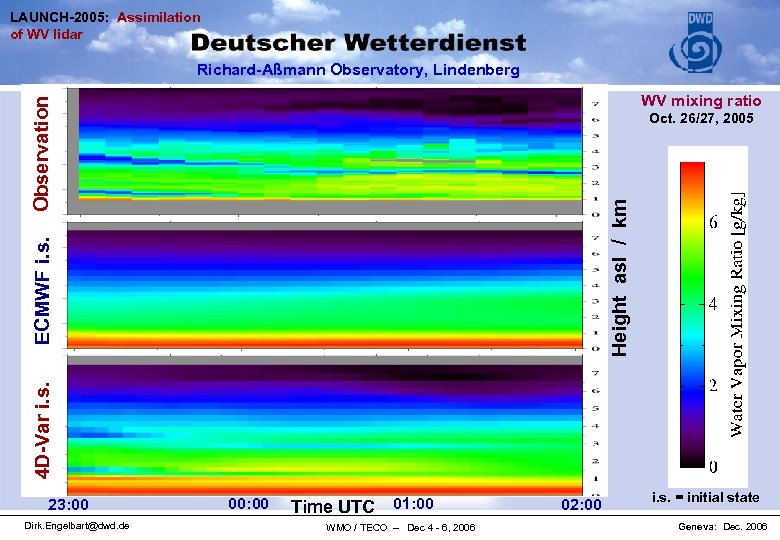
LAUNCH-2005: Assimilation of WV lidar Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg Observation WV mixing ratio 4 D-Var i. s. ECMWF i. s. Height asl / km Oct. 26/27, 2005 23: 00 Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de 00: 00 Time UTC 01: 00 WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 02: 00 i. s. = initial state Geneva: Dec. 2006
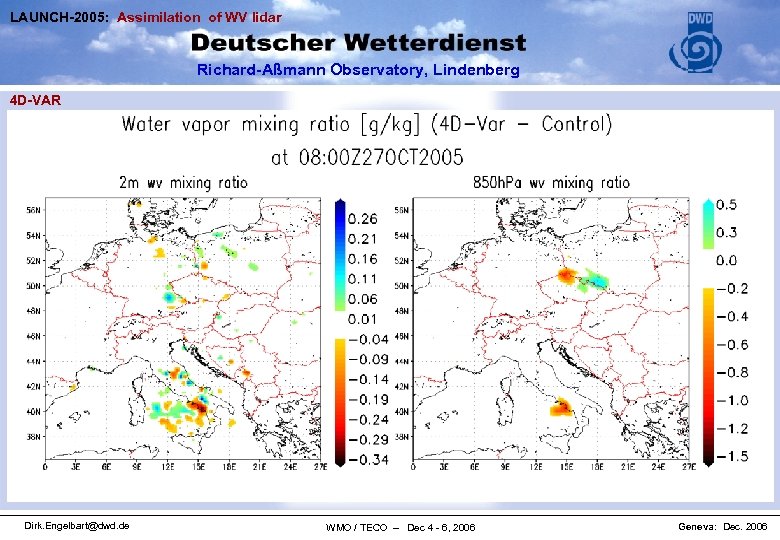
LAUNCH-2005: Assimilation of WV lidar Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg 4 D-VAR Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006
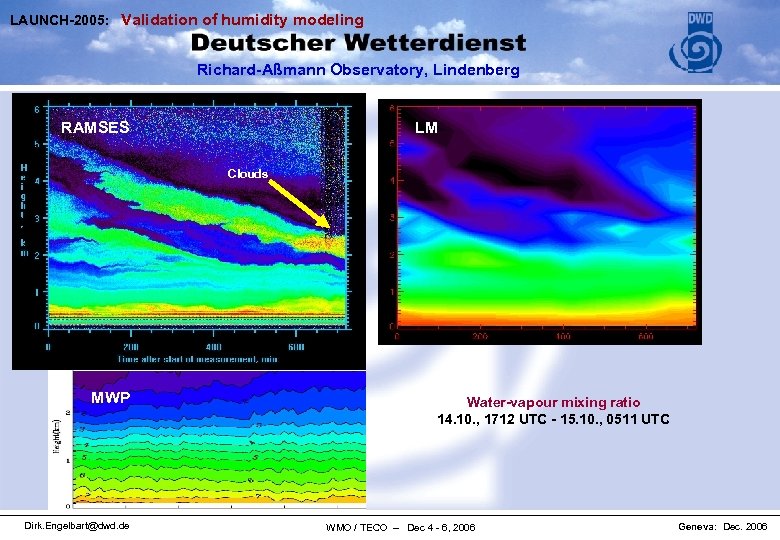
LAUNCH-2005: Validation of humidity modeling Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg RAMSES LM Clouds MWP Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de Water-vapour mixing ratio 14. 10. , 1712 UTC - 15. 10. , 0511 UTC WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006
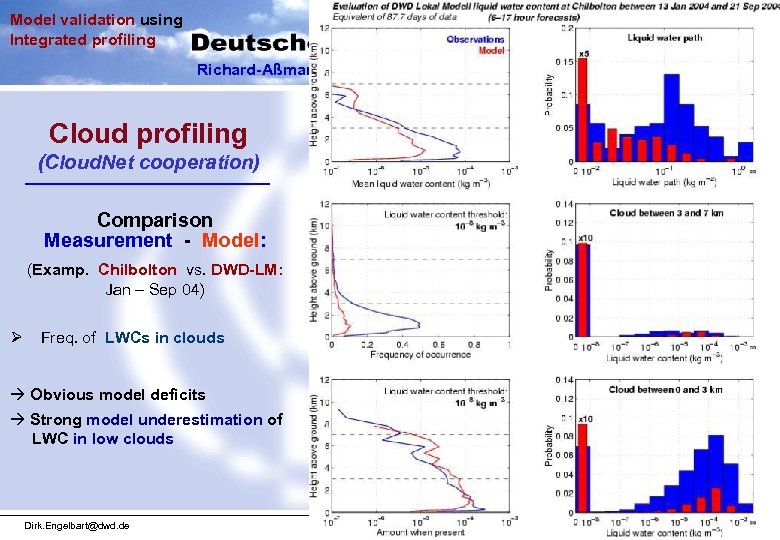
Model validation using Integrated profiling Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg Cloud profiling (Cloud. Net cooperation) Comparison Measurement - Model: (Examp. Chilbolton vs. DWD-LM: Jan – Sep 04) Ø Freq. of LWCs in clouds à Obvious model deficits à Strong model underestimation of LWC in low clouds Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006

Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg Major Results COST-720 / I of (related to operational users) (1) Basic techniques & algorithms (2) (3) - major improvements in microwave profiling (operationally applicable all-weather technique) (2) Algorithms for system Integration - combination of MWP and WPR for improved humidity sounding MWP, cloud radar, lidar, rain-gauge (Cloud. Net) weather radar and MRR for improved rain rates from weather radar MWP, cloud radar + lidar for profiling of cloud characteristics (3) Proposals for system integration a) b) c) d) Wind: Temperature: Humidity: Clouds: (see Results-III) compos. profiling using Sodar + WPR RASS + MWP + WPR (WV Lidar for validation & reference) MWP, cloud radar, lidar (+ rain gauge) (IPT, radar-lidar method or Cloud. Net retrieval) …. . still ongoing evaluations ( LAUNCH, CSIPHelsinki- estbed , T )…… Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006

Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg Major Results COST-720 / II of (related to operational users) (1) Results for NWP - definition and test of Net. CDFdata formats for MWP and Lidar humidity profiling - OSEs using WV-Lidar in data assimilation to NWP models clear impact high data qualities for - validation potential of NWP output (supply of reference quality for wind, temperature, humidity profiles and cloud characteristics) (1) New system developments related to COST-720: (2) (3) (4) (5) - hardware improvements of MWP systems enhanced all-weather capabilities - autonomous WV Raman-lidar systems in Lindenberg / in near future also Cabauw(in 2007) and Payerne(early 2007) - commmercial Doppler-wind (100 k€) and aerosol/humidity lidar (<150 k€) (6) Network stations for integrated profiling in Europe (7) (8) (9) Lindenberg (GER), Payerne + Bern (CH), Palaiseau (Paris, F), L’Aquila + Rome + Potenza (I), Cabauw (NL), Camborne + Chilbolton (GB), Helsinki (FIN) Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006

Richard-Aßmann Observatory, Lindenberg Major Results COST-720 / III of (related to operational users) Integrated station for NWP validation / cloud profiling: Instruments – Doppler cloud radar (Pulsed or FMCW / 94 or 35 GHz [less attenuation]) – SPC Ceilometer or (real) Lidar – Dual-frequency microwave radiometer (23. 8, 36. 5 GHz / use ceilometer to help calibrate) – Rain gauge (drop counting rather than tipping bucket) CLOUDNET has realized integration meanwhile: www. cloudnet. org • 4 remote-sensing sites (currently), 7 models (currently) • already provides yearly/monthly statistics for cloud fraction and IWC / LWC including comparisons betw. observations & models Algorithms (developed and/or assessed during COST-720) – Integrated profiling technique (IPT) – Radar-Lidar approach – Cloud. Net retrieval (classification) Dirk. Engelbart@dwd. de WMO / TECO – Dec 4 - 6, 2006 Geneva: Dec. 2006
cbc41db797bc151a6b228d42e9543ff4.ppt