decee8777458ca1d6a2f8e731c846699.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Rice Sequence and Map Analysis Leonid Teytelman
Rice Sequence and Map Analysis Leonid Teytelman
 Rice Genome Annotation • Sequence Alignments • Automation Comparative Maps • Genetic Marker Correspondences • FPC Map • FPC I-Map Ens. EMBL Pipeline • Automated Annotation • Compute Farms
Rice Genome Annotation • Sequence Alignments • Automation Comparative Maps • Genetic Marker Correspondences • FPC Map • FPC I-Map Ens. EMBL Pipeline • Automated Annotation • Compute Farms
 Rice Genome Annotation
Rice Genome Annotation
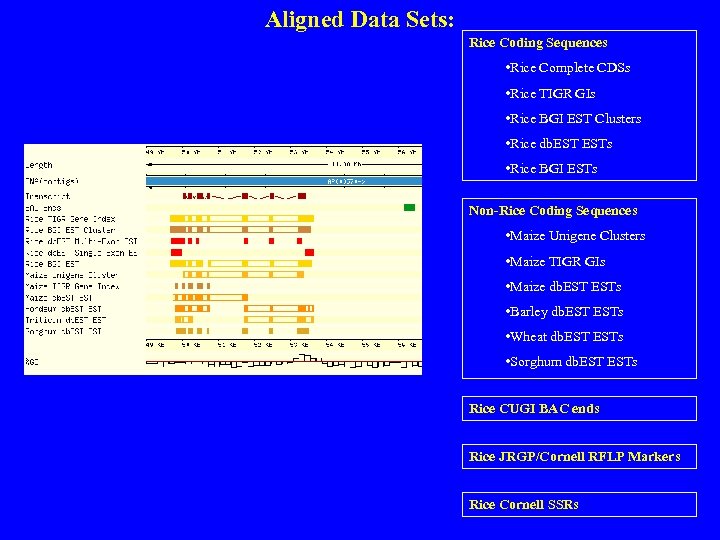 Aligned Data Sets: Rice Coding Sequences • Rice Complete CDSs • Rice TIGR GIs • Rice BGI EST Clusters • Rice db. ESTs • Rice BGI ESTs Non-Rice Coding Sequences • Maize Unigene Clusters • Maize TIGR GIs • Maize db. ESTs • Barley db. ESTs • Wheat db. ESTs • Sorghum db. ESTs Rice CUGI BAC ends Rice JRGP/Cornell RFLP Markers Rice Cornell SSRs
Aligned Data Sets: Rice Coding Sequences • Rice Complete CDSs • Rice TIGR GIs • Rice BGI EST Clusters • Rice db. ESTs • Rice BGI ESTs Non-Rice Coding Sequences • Maize Unigene Clusters • Maize TIGR GIs • Maize db. ESTs • Barley db. ESTs • Wheat db. ESTs • Sorghum db. ESTs Rice CUGI BAC ends Rice JRGP/Cornell RFLP Markers Rice Cornell SSRs
 Alignment Tools: BLAT: search & alignment psl. Reps: filtering of low-quality matches e-PCR: matches based on near-identity to the PCR primers, and correct order Target Queries
Alignment Tools: BLAT: search & alignment psl. Reps: filtering of low-quality matches e-PCR: matches based on near-identity to the PCR primers, and correct order Target Queries
 Alignment Tools: BLAT: search & alignment psl. Reps: filtering of low-quality matches e-PCR: matches based on near-identity to the PCR primers, and correct order Target Queries
Alignment Tools: BLAT: search & alignment psl. Reps: filtering of low-quality matches e-PCR: matches based on near-identity to the PCR primers, and correct order Target Queries
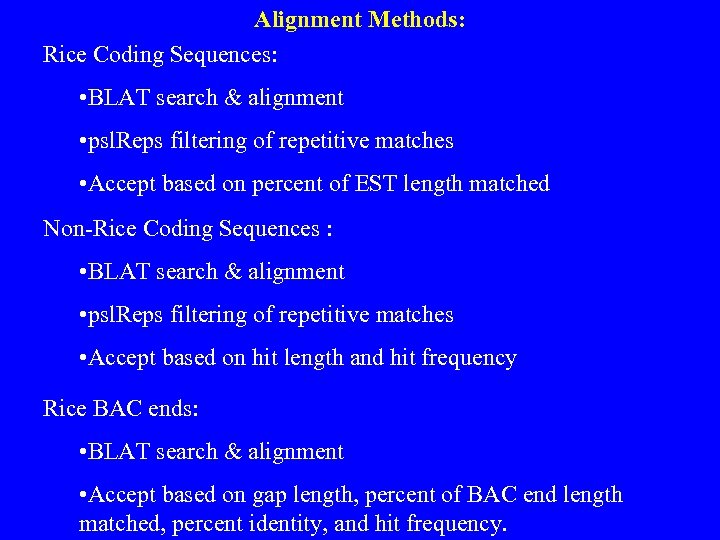 Alignment Methods: Rice Coding Sequences: • BLAT search & alignment • psl. Reps filtering of repetitive matches • Accept based on percent of EST length matched Non-Rice Coding Sequences : • BLAT search & alignment • psl. Reps filtering of repetitive matches • Accept based on hit length and hit frequency Rice BAC ends: • BLAT search & alignment • Accept based on gap length, percent of BAC end length matched, percent identity, and hit frequency.
Alignment Methods: Rice Coding Sequences: • BLAT search & alignment • psl. Reps filtering of repetitive matches • Accept based on percent of EST length matched Non-Rice Coding Sequences : • BLAT search & alignment • psl. Reps filtering of repetitive matches • Accept based on hit length and hit frequency Rice BAC ends: • BLAT search & alignment • Accept based on gap length, percent of BAC end length matched, percent identity, and hit frequency.
 Alignment Methods: Rice Markers: • BLAT search & alignment • Accept based on percent of marker length matched and the gap length in case of genomic markers. • Utilize genetic map information; accept those whose genetic & physical chromosome assignment is concordant. Rice SSRs: • e-PCR with default parameters, allowing 0 mismatches in the primers
Alignment Methods: Rice Markers: • BLAT search & alignment • Accept based on percent of marker length matched and the gap length in case of genomic markers. • Utilize genetic map information; accept those whose genetic & physical chromosome assignment is concordant. Rice SSRs: • e-PCR with default parameters, allowing 0 mismatches in the primers
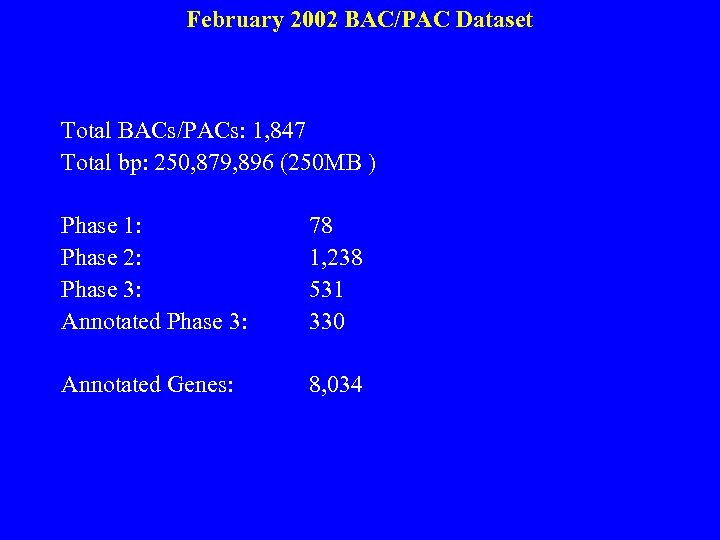 February 2002 BAC/PAC Dataset Total BACs/PACs: 1, 847 Total bp: 250, 879, 896 (250 MB ) Phase 1: 78 Phase 2: 1, 238 Phase 3: 531 Annotated Phase 3: 330 Annotated Genes: 8, 034
February 2002 BAC/PAC Dataset Total BACs/PACs: 1, 847 Total bp: 250, 879, 896 (250 MB ) Phase 1: 78 Phase 2: 1, 238 Phase 3: 531 Annotated Phase 3: 330 Annotated Genes: 8, 034
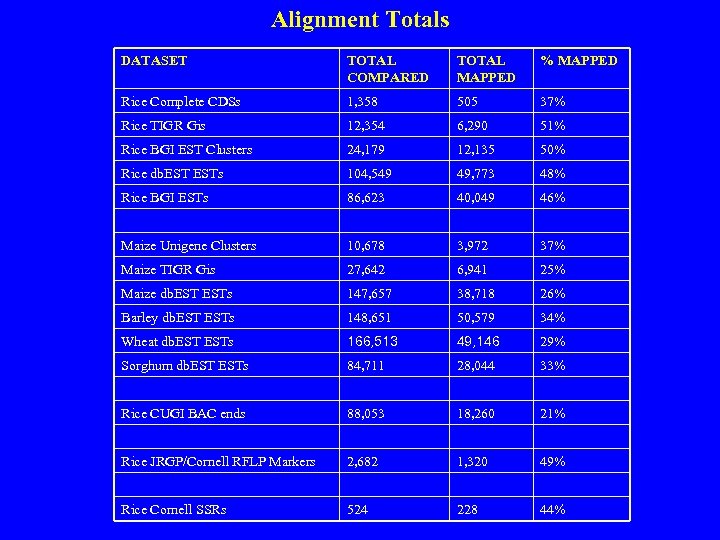 Alignment Totals DATASET TOTAL COMPARED TOTAL MAPPED % MAPPED Rice Complete CDSs 1, 358 505 37% Rice TIGR Gis 12, 354 6, 290 51% Rice BGI EST Clusters 24, 179 12, 135 50% Rice db. ESTs 104, 549 49, 773 48% Rice BGI ESTs 86, 623 40, 049 46% Maize Unigene Clusters 10, 678 3, 972 37% Maize TIGR Gis 27, 642 6, 941 25% Maize db. ESTs 147, 657 38, 718 26% Barley db. ESTs 148, 651 50, 579 34% Wheat db. ESTs 166, 513 49, 146 29% Sorghum db. ESTs 84, 711 28, 044 33% Rice CUGI BAC ends 88, 053 18, 260 21% Rice JRGP/Cornell RFLP Markers 2, 682 1, 320 49% Rice Cornell SSRs 524 228 44%
Alignment Totals DATASET TOTAL COMPARED TOTAL MAPPED % MAPPED Rice Complete CDSs 1, 358 505 37% Rice TIGR Gis 12, 354 6, 290 51% Rice BGI EST Clusters 24, 179 12, 135 50% Rice db. ESTs 104, 549 49, 773 48% Rice BGI ESTs 86, 623 40, 049 46% Maize Unigene Clusters 10, 678 3, 972 37% Maize TIGR Gis 27, 642 6, 941 25% Maize db. ESTs 147, 657 38, 718 26% Barley db. ESTs 148, 651 50, 579 34% Wheat db. ESTs 166, 513 49, 146 29% Sorghum db. ESTs 84, 711 28, 044 33% Rice CUGI BAC ends 88, 053 18, 260 21% Rice JRGP/Cornell RFLP Markers 2, 682 1, 320 49% Rice Cornell SSRs 524 228 44%
 Automating Alignments: For each group of data sets, there is a script to automatically: • Run psl. Reps • Load results into the database • Discard low-quality matches • Update documentation
Automating Alignments: For each group of data sets, there is a script to automatically: • Run psl. Reps • Load results into the database • Discard low-quality matches • Update documentation
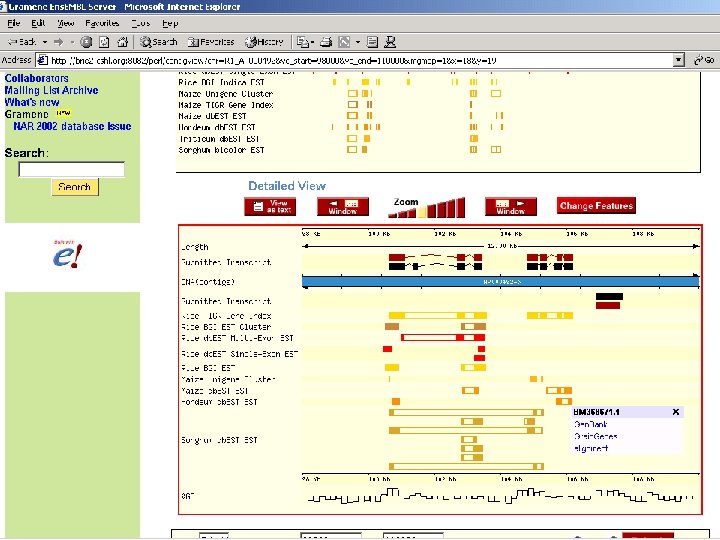
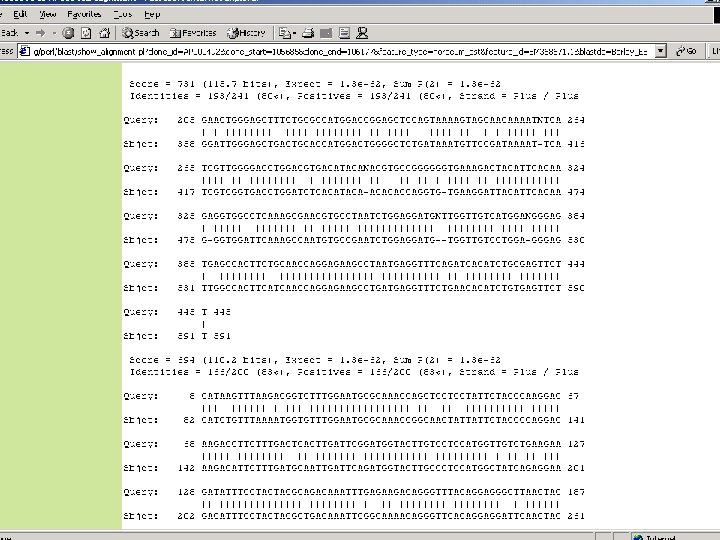
 Comparative Maps
Comparative Maps
 Map Correspondences Same marker on multiple mapping studies • Name-identity • Curated evidence Sequence-based correspondences for JRGP and Cornell markers: • BLAT search & alignment • Utilize genetic mapping information, accepting matches on same chromosome and less than 30 c. M apart.
Map Correspondences Same marker on multiple mapping studies • Name-identity • Curated evidence Sequence-based correspondences for JRGP and Cornell markers: • BLAT search & alignment • Utilize genetic mapping information, accepting matches on same chromosome and less than 30 c. M apart.
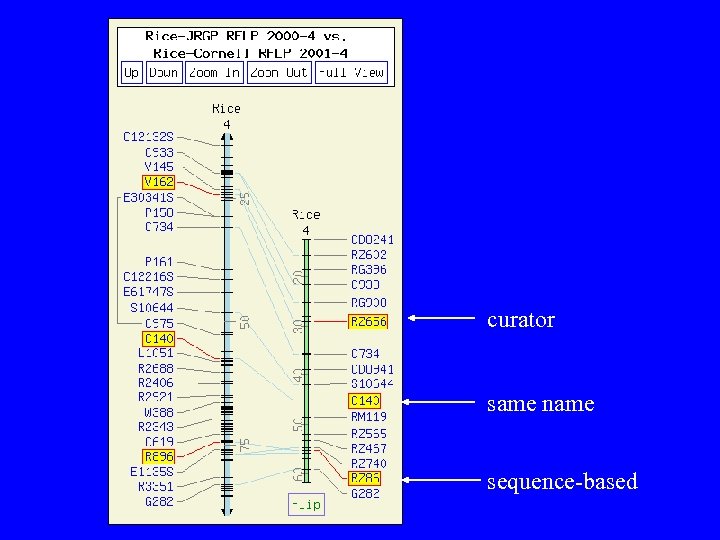 curator same name sequence-based
curator same name sequence-based
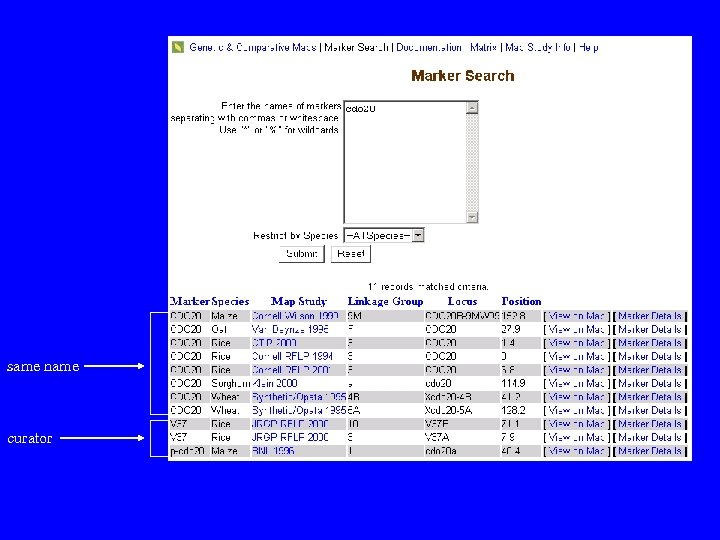 same name curator
same name curator
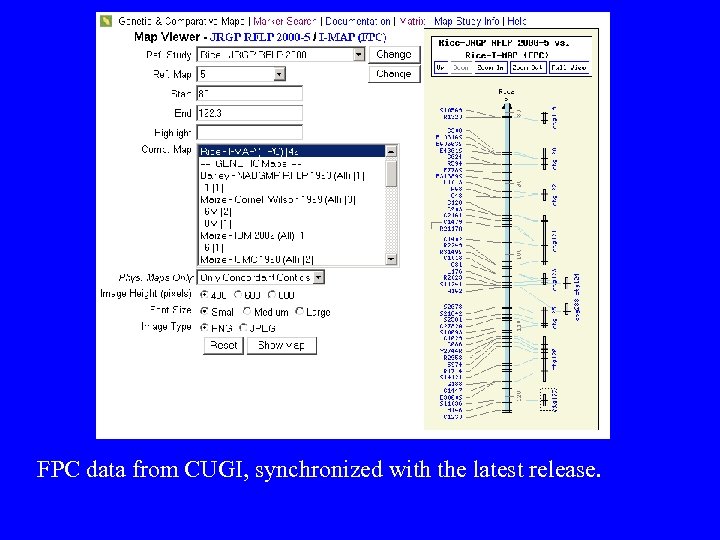 FPC data from CUGI, synchronized with the latest release.
FPC data from CUGI, synchronized with the latest release.
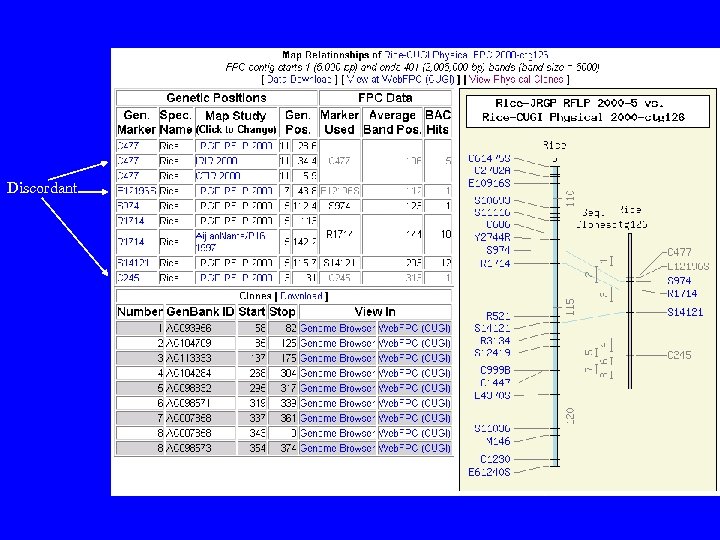 Discordant
Discordant
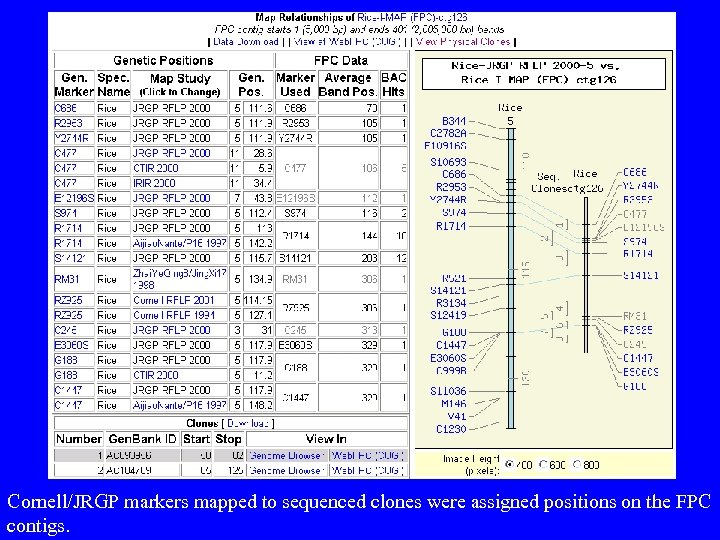 Cornell/JRGP markers mapped to sequenced clones were assigned positions on the FPC contigs.
Cornell/JRGP markers mapped to sequenced clones were assigned positions on the FPC contigs.
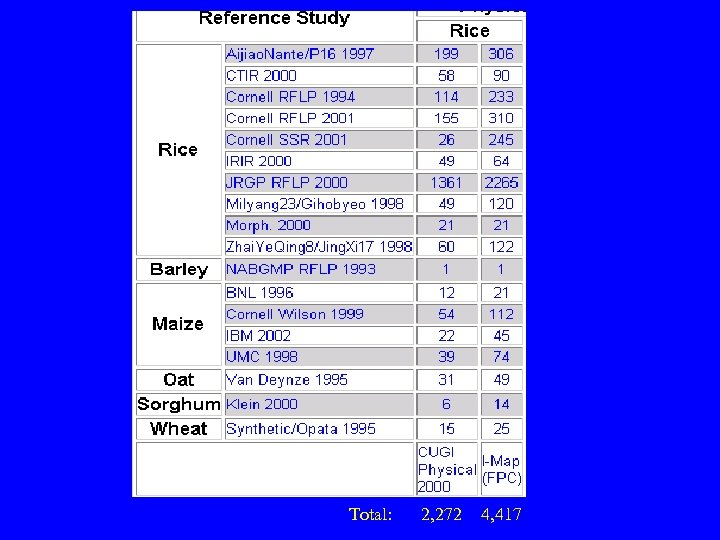 Total: 2, 272 4, 417
Total: 2, 272 4, 417
 Ens. EMBL Pipeline in a Nutshell
Ens. EMBL Pipeline in a Nutshell
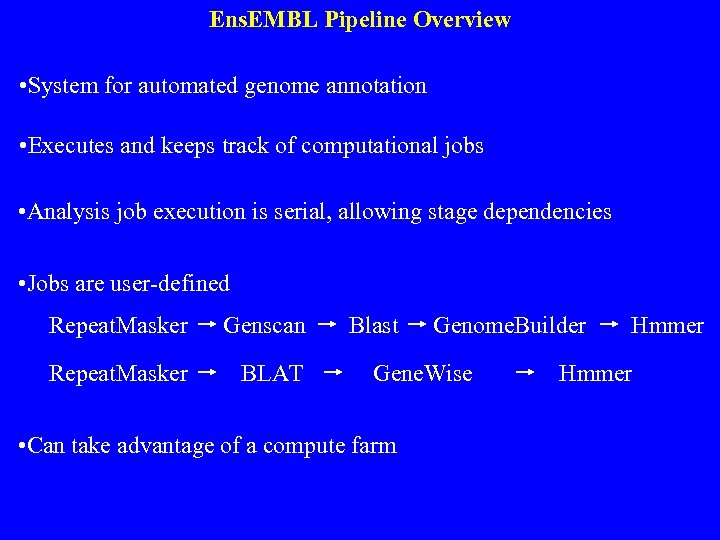 Ens. EMBL Pipeline Overview • System for automated genome annotation • Executes and keeps track of computational jobs • Analysis job execution is serial, allowing stage dependencies • Jobs are user-defined Repeat. Masker Genscan Repeat. Masker BLAT Blast Genome. Builder Gene. Wise • Can take advantage of a compute farm Hmmer
Ens. EMBL Pipeline Overview • System for automated genome annotation • Executes and keeps track of computational jobs • Analysis job execution is serial, allowing stage dependencies • Jobs are user-defined Repeat. Masker Genscan Repeat. Masker BLAT Blast Genome. Builder Gene. Wise • Can take advantage of a compute farm Hmmer
 Organization • Utilizes and expands on the Ens. EMBL-core modules and database schema • Database stores: • analysis program names and parameters • analysis results • rules for job dependencies • and progress status for each job • Perl modules: • access the database • execute specified analysis programs • parse and load into the database the analysis results
Organization • Utilizes and expands on the Ens. EMBL-core modules and database schema • Database stores: • analysis program names and parameters • analysis results • rules for job dependencies • and progress status for each job • Perl modules: • access the database • execute specified analysis programs • parse and load into the database the analysis results
 Cluster Utilization • How to split up tasks? • Contig-by-contig approach • How to execute jobs on slave nodes? • Load management an scheduling (LSF, PBS, etc) • Management of management: • Automatic job submission • Error/completion checking
Cluster Utilization • How to split up tasks? • Contig-by-contig approach • How to execute jobs on slave nodes? • Load management an scheduling (LSF, PBS, etc) • Management of management: • Automatic job submission • Error/completion checking


