c53248ca70dfe18399fa19425d706656.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 Rhinosinusitis Jihan AL Maddah
Rhinosinusitis Jihan AL Maddah
 Definition • Inflammation of the mucous membrane of nose and sinuses. • One of the most common conditions presenting to clinicians worldwide, and can potentially have enormous and a devastating socioeconomic impact.
Definition • Inflammation of the mucous membrane of nose and sinuses. • One of the most common conditions presenting to clinicians worldwide, and can potentially have enormous and a devastating socioeconomic impact.
 Classification Rhinosinusitis can be categorized based on: ü Duration of infection, and then further. ü Subdivided by the cause.
Classification Rhinosinusitis can be categorized based on: ü Duration of infection, and then further. ü Subdivided by the cause.
 Duration of symptoms : symptoms <4 weeks. : 4 -12 weeks. : > 4 episodes/year.
Duration of symptoms : symptoms <4 weeks. : 4 -12 weeks. : > 4 episodes/year.
 Etiology • Viral (majority). o Rhinovirus, Para-influenza, RSV, Adenovirus • Bacterial (minority). o Non-specific o Specific (syphilis, TB) • Fungal (minority). • Allergic (Common) (ARIA) o Mild, Moderate, Severe o Persistent, Intermittent
Etiology • Viral (majority). o Rhinovirus, Para-influenza, RSV, Adenovirus • Bacterial (minority). o Non-specific o Specific (syphilis, TB) • Fungal (minority). • Allergic (Common) (ARIA) o Mild, Moderate, Severe o Persistent, Intermittent
 Etiology • Non-allergic eosinophilic rhinitis • Occupational • Hormonal • Drug induced • Gustatory • Vasomotor
Etiology • Non-allergic eosinophilic rhinitis • Occupational • Hormonal • Drug induced • Gustatory • Vasomotor
 Symptoms • Three cardinal symptoms: ü Purulent nasal discharge (purulent-cloudy) ü Nasal obstruction (congestion, blockage, or stuffiness) ü Facial pain-pressure-fullness (involves the anterior face and peri-orbital region or manifests with headache that can be localized or diffuse).
Symptoms • Three cardinal symptoms: ü Purulent nasal discharge (purulent-cloudy) ü Nasal obstruction (congestion, blockage, or stuffiness) ü Facial pain-pressure-fullness (involves the anterior face and peri-orbital region or manifests with headache that can be localized or diffuse).
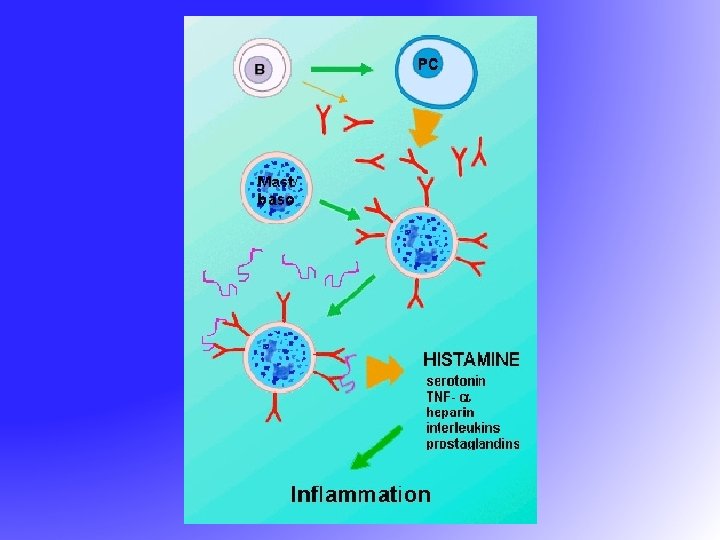
 Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) • 30% of patients with AR have asthma • The majority of patients with asthma have AR • AR is a major risk factor for poor asthma control • All patients with AR should be assessed for asthma
Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) • 30% of patients with AR have asthma • The majority of patients with asthma have AR • AR is a major risk factor for poor asthma control • All patients with AR should be assessed for asthma
 Comorbidities: • Up to 80% of patients with bilateral chronic sinusitis have AR • Otitis media • Conjunctivitis • Lower respiratory tract infections • Dental problems – malocclusion, discoloration • Sleep disorders
Comorbidities: • Up to 80% of patients with bilateral chronic sinusitis have AR • Otitis media • Conjunctivitis • Lower respiratory tract infections • Dental problems – malocclusion, discoloration • Sleep disorders
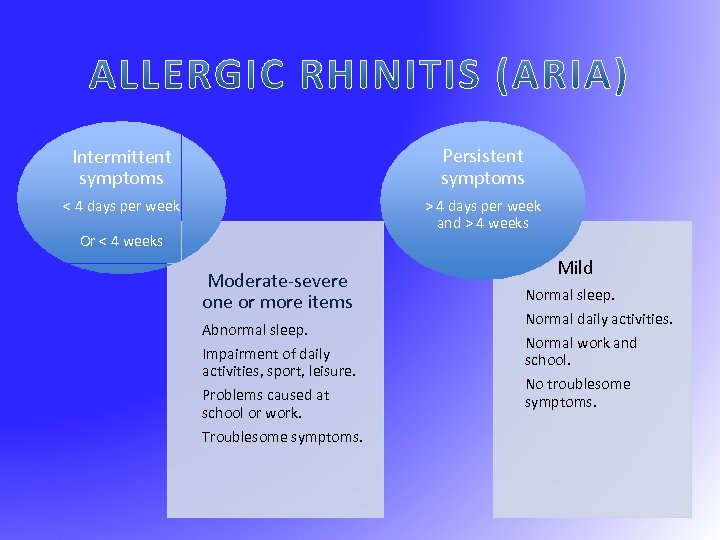 Intermittent symptoms Persistent symptoms < 4 days per week > 4 days per week and > 4 weeks Or < 4 weeks Moderate-severe one or more items Abnormal sleep. Impairment of daily activities, sport, leisure. Problems caused at school or work. Troublesome symptoms. Mild Normal sleep. Normal daily activities. Normal work and school. No troublesome symptoms.
Intermittent symptoms Persistent symptoms < 4 days per week > 4 days per week and > 4 weeks Or < 4 weeks Moderate-severe one or more items Abnormal sleep. Impairment of daily activities, sport, leisure. Problems caused at school or work. Troublesome symptoms. Mild Normal sleep. Normal daily activities. Normal work and school. No troublesome symptoms.
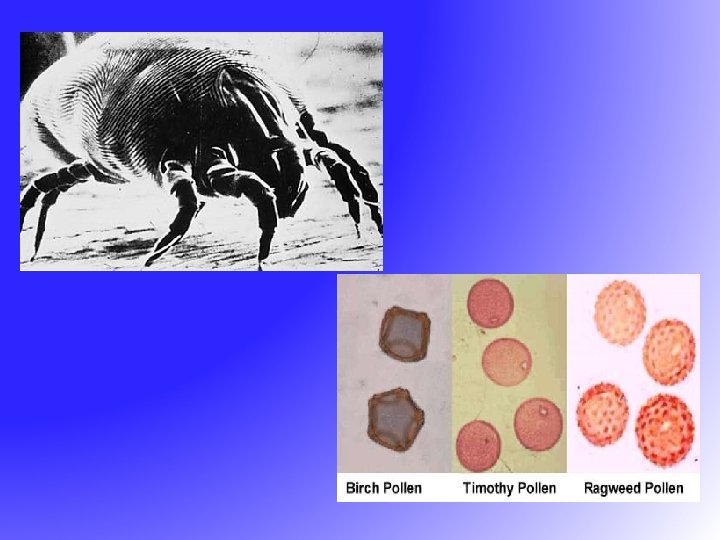
 Allergic Rhinitis - Causes Seasonal (Intermittent) • Pollen from ü Grasses ü Weeds ü Trees • • • Perennial (Persistent) House dust mites Mold and fungus spores Cockroaches Animal dander Food Chemicals
Allergic Rhinitis - Causes Seasonal (Intermittent) • Pollen from ü Grasses ü Weeds ü Trees • • • Perennial (Persistent) House dust mites Mold and fungus spores Cockroaches Animal dander Food Chemicals

 Allergic Rhinitis ü +ve family history ü Personal history of atopic disease e. g eczema, urticaria and asthma
Allergic Rhinitis ü +ve family history ü Personal history of atopic disease e. g eczema, urticaria and asthma
 Allergic Rhinitis - Symptoms Sensitive to specific allergens ( dust mites, pollens) ü Pruritus of the nose, eyes, palate, ears ü Sneezing > 2 at a time ü Watery rhinorrhoea ü Coexistant asthma or eczema ü Seasonal symptoms ü Family history of allergies
Allergic Rhinitis - Symptoms Sensitive to specific allergens ( dust mites, pollens) ü Pruritus of the nose, eyes, palate, ears ü Sneezing > 2 at a time ü Watery rhinorrhoea ü Coexistant asthma or eczema ü Seasonal symptoms ü Family history of allergies
 Diagnosis – Present illness, past medical history, family history, environmental history and impact on quality of life. Lungs and Skin – Nose, Eyes, Ears, – edematous Inferior turbinate, polyps
Diagnosis – Present illness, past medical history, family history, environmental history and impact on quality of life. Lungs and Skin – Nose, Eyes, Ears, – edematous Inferior turbinate, polyps
 Investigations Blood test : Ig. E ( total & specific), eosinophilia Nasal biopsy for differential dx Skin test ( In vivo) RAST (radio-allergosorbent test) ( In vitro)
Investigations Blood test : Ig. E ( total & specific), eosinophilia Nasal biopsy for differential dx Skin test ( In vivo) RAST (radio-allergosorbent test) ( In vitro)
 Treatment Avoidance of allergen Normal Saline douching Local and/or antihistamine Local and/or steroids Sublingual / Subcutaneous Immunotherapy (Desensitization)
Treatment Avoidance of allergen Normal Saline douching Local and/or antihistamine Local and/or steroids Sublingual / Subcutaneous Immunotherapy (Desensitization)
 Treatment-Surgical - for nasal obstruction only Septoplasty Turbinate reduction Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS)
Treatment-Surgical - for nasal obstruction only Septoplasty Turbinate reduction Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS)
 Vasomotor Rhinitis ü Autonomic disturbance – excessive parasympathetic activity ü No specific cause found ü Symptoms : rhinorrhoea, sneezing, nasal obstruction ü Treatment: Local nasal steroids, anticholinergic medication
Vasomotor Rhinitis ü Autonomic disturbance – excessive parasympathetic activity ü No specific cause found ü Symptoms : rhinorrhoea, sneezing, nasal obstruction ü Treatment: Local nasal steroids, anticholinergic medication
 Rhinitis Medicamentosa Avoid prolong use of vasoconstrictor nose drop Treatment: stop vasoconstrictors, local/systemic steroids
Rhinitis Medicamentosa Avoid prolong use of vasoconstrictor nose drop Treatment: stop vasoconstrictors, local/systemic steroids
 • Sinusitis is characterized by inflammation of the lining of the paranasal sinuses. Because the nasal mucosa is simultaneously involved and because sinusitis rarely occurs without concurrent rhinitis, rhinosinusitis is now the preferred term for this condition. • Rhinosinusitis affects an estimated 35 million people per year in the United States and accounts for close to 16 million office visits per year
• Sinusitis is characterized by inflammation of the lining of the paranasal sinuses. Because the nasal mucosa is simultaneously involved and because sinusitis rarely occurs without concurrent rhinitis, rhinosinusitis is now the preferred term for this condition. • Rhinosinusitis affects an estimated 35 million people per year in the United States and accounts for close to 16 million office visits per year
 • The vast majority of rhinosinusitis episodes are caused by viral infection. • Most viral upper respiratory tract infections are caused by rhinovirus, but coronavirus, influenza A and B, parainfluenza, respiratory syncytial virus, adenovirus, and enterovirus are also causative agents. Rhinovirus, influenza, and parainfluenza viruses are the primary pathogens in 3 -15% of patients with acute sinusitis. • In about 0. 5 -2% of cases, viral sinusitis can progress to acute bacterial sinusitis.
• The vast majority of rhinosinusitis episodes are caused by viral infection. • Most viral upper respiratory tract infections are caused by rhinovirus, but coronavirus, influenza A and B, parainfluenza, respiratory syncytial virus, adenovirus, and enterovirus are also causative agents. Rhinovirus, influenza, and parainfluenza viruses are the primary pathogens in 3 -15% of patients with acute sinusitis. • In about 0. 5 -2% of cases, viral sinusitis can progress to acute bacterial sinusitis.
 • Rarely, sinusitis is caused by fungi. • Fungal sinusitis (eg, allergic fungal sinusitis) may appear similar to lower airway disorder and allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. • Fungal agents associated with this condition include: ü Aspergillus and Alternaria species (60%). ü Bipolaris and Curvularia (20%).
• Rarely, sinusitis is caused by fungi. • Fungal sinusitis (eg, allergic fungal sinusitis) may appear similar to lower airway disorder and allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. • Fungal agents associated with this condition include: ü Aspergillus and Alternaria species (60%). ü Bipolaris and Curvularia (20%).
 Viral Bacterial Dental origin – 10% Fungal Anatomical Allergy Polyps Immune deficiency
Viral Bacterial Dental origin – 10% Fungal Anatomical Allergy Polyps Immune deficiency
 u 75% bacterial isolates, most commonly in adults: ü 35% coagulase-negative staphylococci (CNS) ü 23% Corynebacterium species ü 8% Staph aureus Low numbers of these species were present. u In children, the most common organisms: ü 40% H influenzae ü 34% M catarrhalis ü 50% S pneumoniae
u 75% bacterial isolates, most commonly in adults: ü 35% coagulase-negative staphylococci (CNS) ü 23% Corynebacterium species ü 8% Staph aureus Low numbers of these species were present. u In children, the most common organisms: ü 40% H influenzae ü 34% M catarrhalis ü 50% S pneumoniae
 Pathophysiology The pathophysiology of rhinosinusitis is related to 3 factors: 1. Obstruction of sinus drainage pathways (sinus ostia) (trauma, rhinitis) 2. Ciliary impairment (Primary ciliary dyskinesia) 3. Altered mucus quantity and quality ( Cystic fibrosis).
Pathophysiology The pathophysiology of rhinosinusitis is related to 3 factors: 1. Obstruction of sinus drainage pathways (sinus ostia) (trauma, rhinitis) 2. Ciliary impairment (Primary ciliary dyskinesia) 3. Altered mucus quantity and quality ( Cystic fibrosis).
 Acute sinusitis - Symptoms Proceeding URTI or Dental infection Pain - depends on the involving sinus throbbing aggravated by coughing Nasal obstruction Purulent rhinorrhoea
Acute sinusitis - Symptoms Proceeding URTI or Dental infection Pain - depends on the involving sinus throbbing aggravated by coughing Nasal obstruction Purulent rhinorrhoea
 Acute Sinusitis - Signs Fever Local tenderness Mucous in nose or nasopharynx Dental origin X-ray with opacity or fluid level
Acute Sinusitis - Signs Fever Local tenderness Mucous in nose or nasopharynx Dental origin X-ray with opacity or fluid level
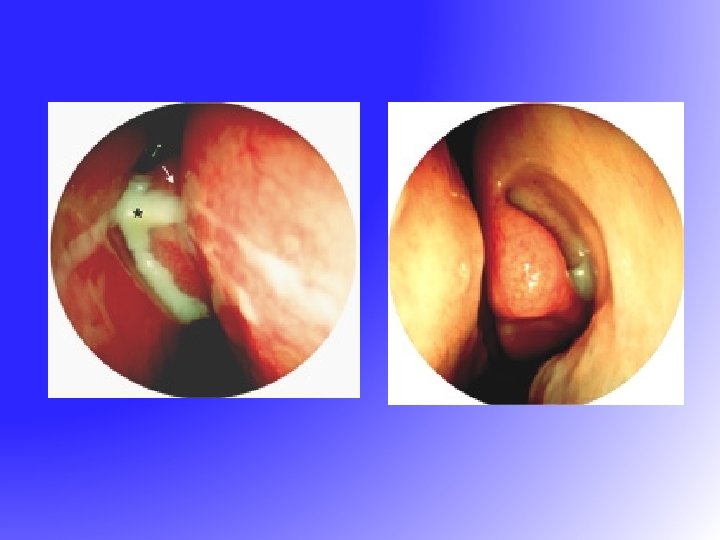
 Acute Sinusitis Streptococcus pneumoniae Haemophilus Influenza Staphylococcus Anaerobes
Acute Sinusitis Streptococcus pneumoniae Haemophilus Influenza Staphylococcus Anaerobes
 However, the evaluation might include the following laboratory tests : . Nasal cytology (allergy) Nasal-sinus biopsy (mass, polyp, tumor) Tests for immunodeficiency (recurrent sinusitis associated with other infections) Sweat chloride test and electron microscopy in cystic fibrosis, or ciliary dysfunction
However, the evaluation might include the following laboratory tests : . Nasal cytology (allergy) Nasal-sinus biopsy (mass, polyp, tumor) Tests for immunodeficiency (recurrent sinusitis associated with other infections) Sweat chloride test and electron microscopy in cystic fibrosis, or ciliary dysfunction
 Treatment of acute sinusitis consists of providing adequate drainage of the involved sinus and appropriate systemic treatment of the likely bacterial pathogens. can be achieved surgically with sinus puncture and irrigation techniques. Options for medical drainage are as follows: alpha-adrenergic days 10 -14 days for a maximum of 3 -5 treatment is usually given for 14 days. Usual first-line therapy is Amoxicillin, Clarithromycin Azithromycin
Treatment of acute sinusitis consists of providing adequate drainage of the involved sinus and appropriate systemic treatment of the likely bacterial pathogens. can be achieved surgically with sinus puncture and irrigation techniques. Options for medical drainage are as follows: alpha-adrenergic days 10 -14 days for a maximum of 3 -5 treatment is usually given for 14 days. Usual first-line therapy is Amoxicillin, Clarithromycin Azithromycin
 Acute Sinusitis - Treatment • Antibiotics x 2 weeks Amoxycillin Augmentin Cefuroxime + metronidazole • Vasoconstrictor nose drops – aid drainage • Antral washout – for resistance case – both diagnostic and therapeutic • Functional endoscopic sinus surgery
Acute Sinusitis - Treatment • Antibiotics x 2 weeks Amoxycillin Augmentin Cefuroxime + metronidazole • Vasoconstrictor nose drops – aid drainage • Antral washout – for resistance case – both diagnostic and therapeutic • Functional endoscopic sinus surgery
 Chronic Sinusitis - Symptoms Usually less - no pain Nasal obstruction Nasal/Post nasal purulnt discharge Cacosmia
Chronic Sinusitis - Symptoms Usually less - no pain Nasal obstruction Nasal/Post nasal purulnt discharge Cacosmia
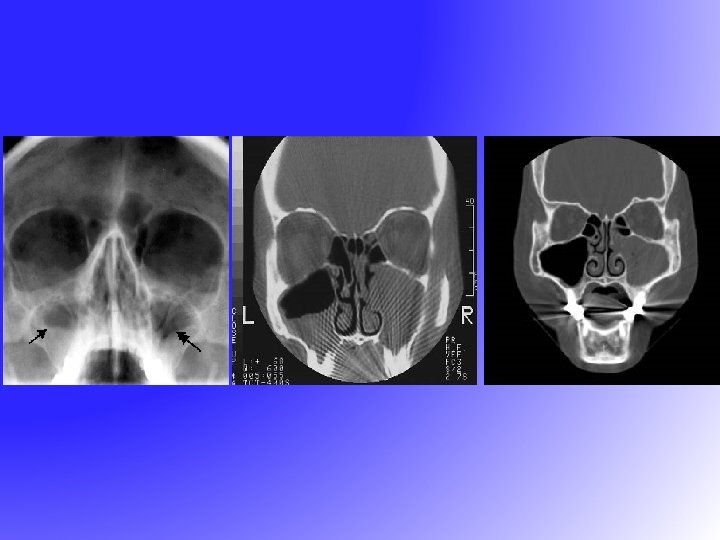
 Chronic Sinusitis - Signs Mucopus in the meati Nasal mucosa congested X-ray show fluid level or opacity
Chronic Sinusitis - Signs Mucopus in the meati Nasal mucosa congested X-ray show fluid level or opacity
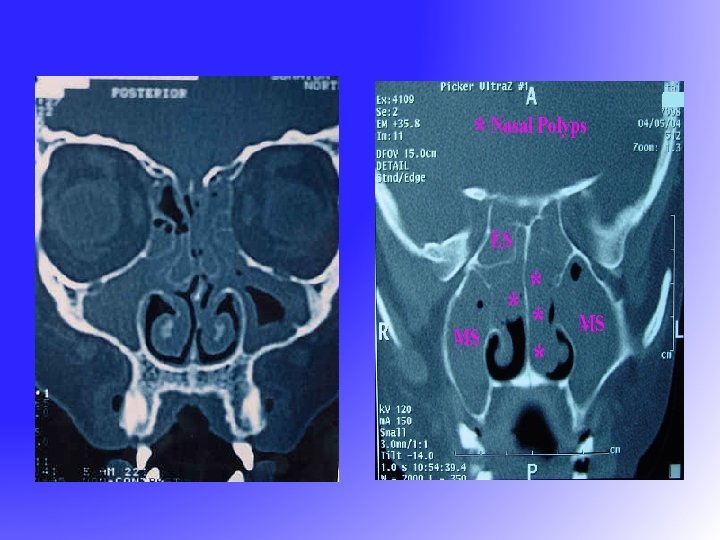
 Chronic Sinusitis - Treatment Medical Antibiotic Nasal Decongestant Topical steroid
Chronic Sinusitis - Treatment Medical Antibiotic Nasal Decongestant Topical steroid
 Chronic Sinusitis - Treatment • Surgical – Open-depends on the site • Caldwell-Luc Operation • Osteoplastic flap – Endoscopic-FESS
Chronic Sinusitis - Treatment • Surgical – Open-depends on the site • Caldwell-Luc Operation • Osteoplastic flap – Endoscopic-FESS
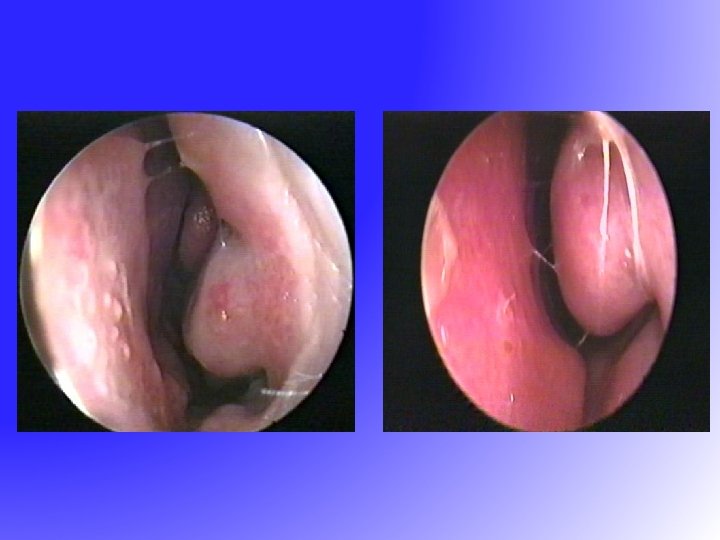
 FESS • Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery – resume the normal function of sinus • drainage • ventilation • Messerklinger 1960 s – sinus mucus drain in a genetically determined path to the natural ostium
FESS • Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery – resume the normal function of sinus • drainage • ventilation • Messerklinger 1960 s – sinus mucus drain in a genetically determined path to the natural ostium
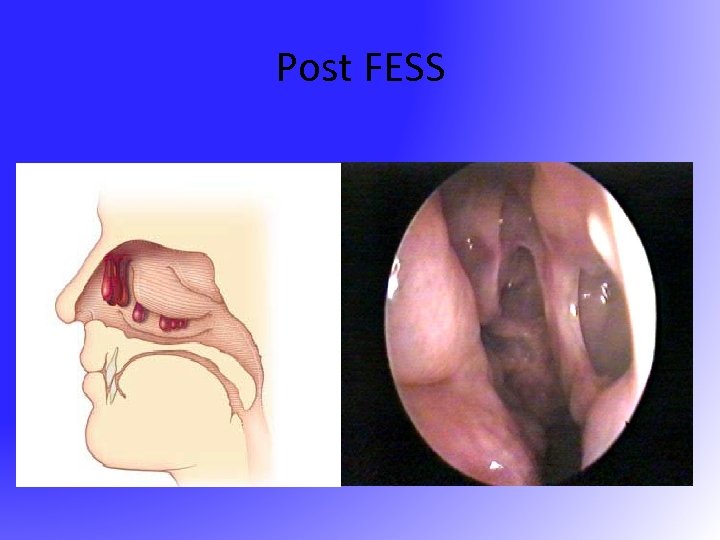 Post FESS
Post FESS
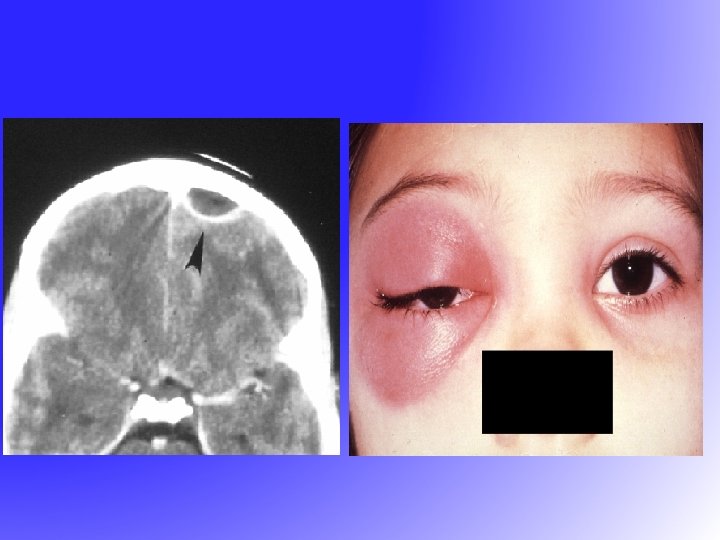
 Complications of Sinusitis • Local – Mucocele – Osteomyelitis-Pott’s tumor • Orbital – Orbital cellulitis – Orbital abscess – Cavernous sinus thrombosis • Intracranial – Epidural abscess – Subdural abscess – Intracerebral abscess
Complications of Sinusitis • Local – Mucocele – Osteomyelitis-Pott’s tumor • Orbital – Orbital cellulitis – Orbital abscess – Cavernous sinus thrombosis • Intracranial – Epidural abscess – Subdural abscess – Intracerebral abscess