romatoid arthrites.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 28


Rheumatoid arthritis By: jawad Mahmmad Karbala University/College of Medicine

Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease in which the normal immune response is directed against an individual's own tissue, including the joints, tendons, and bones, resulting in inflammation and destruction of these tissues approximately 3 cases per 10, 000 people Women are affected by RA approximately 3 times more often than men Onset is most frequent during middle age, but people of any age can be affected
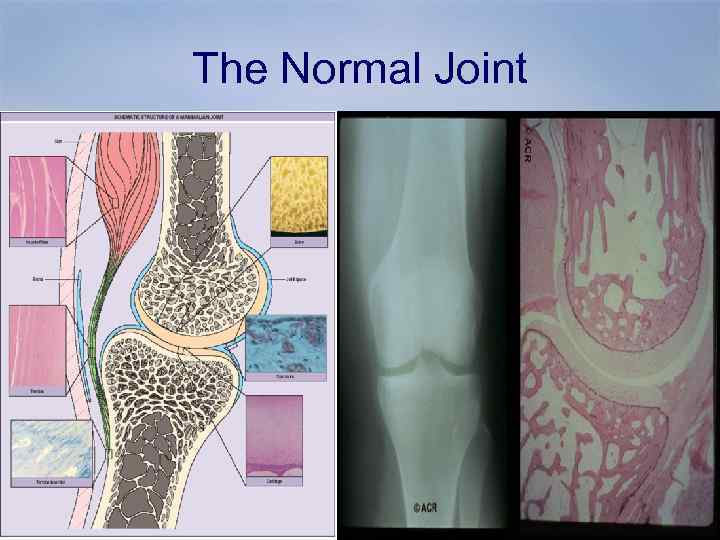
The Normal Joint
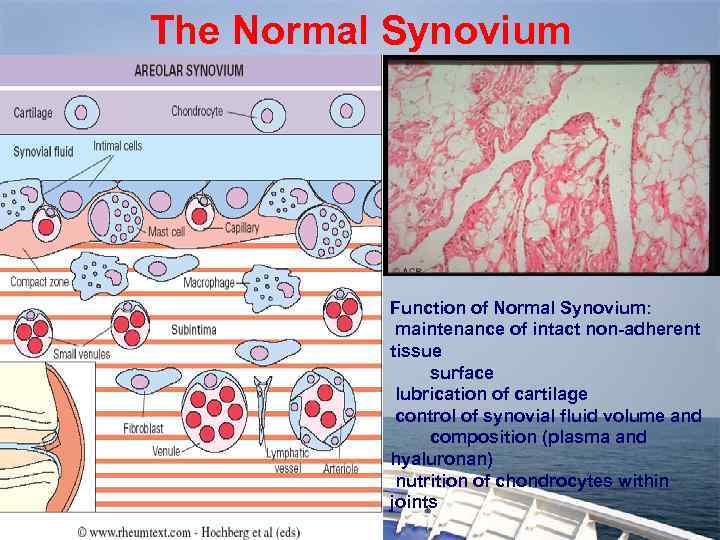
The Normal Synovium Function of Normal Synovium: maintenance of intact non-adherent tissue surface lubrication of cartilage control of synovial fluid volume and composition (plasma and hyaluronan) nutrition of chondrocytes within joints
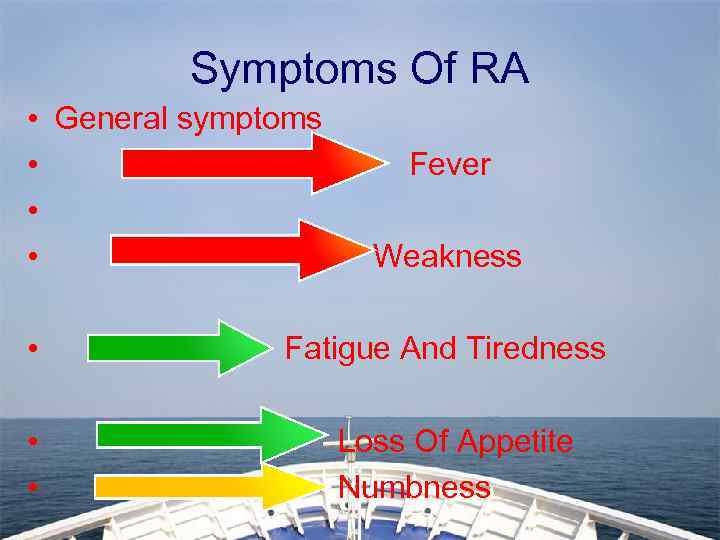
Symptoms Of RA • • General symptoms Fever Weakness • Fatigue And Tiredness • Loss Of Appetite • Numbness
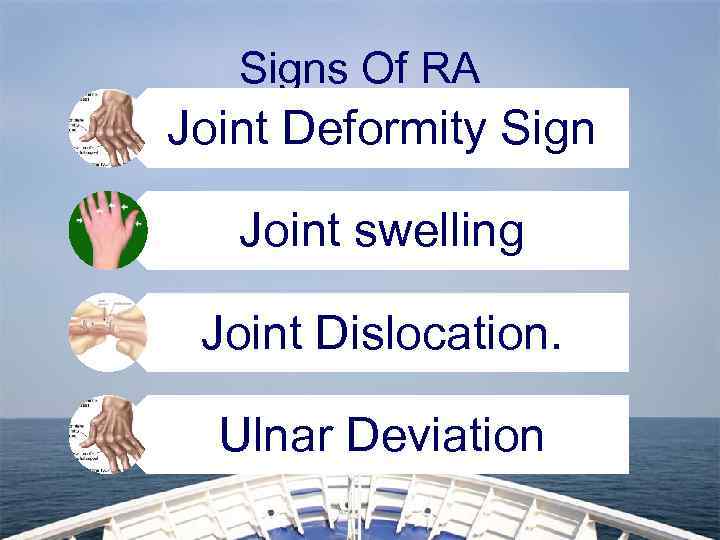
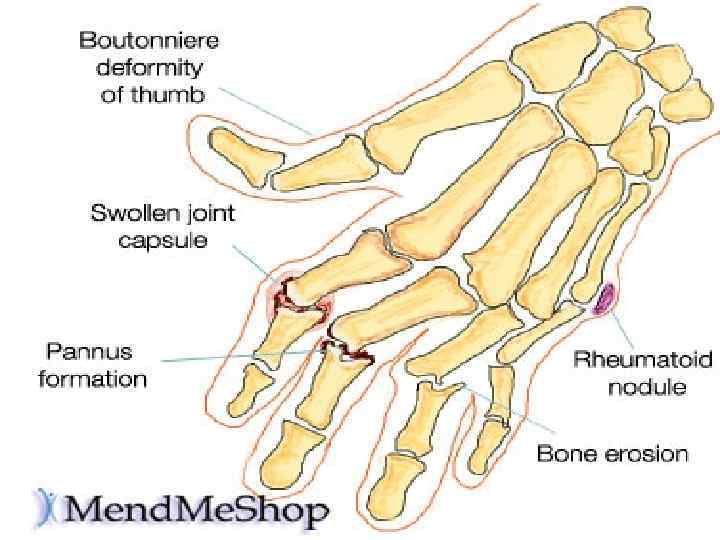
Signs Of RA Joint Deformity Sign Joint swelling Joint Dislocation. Ulnar Deviation
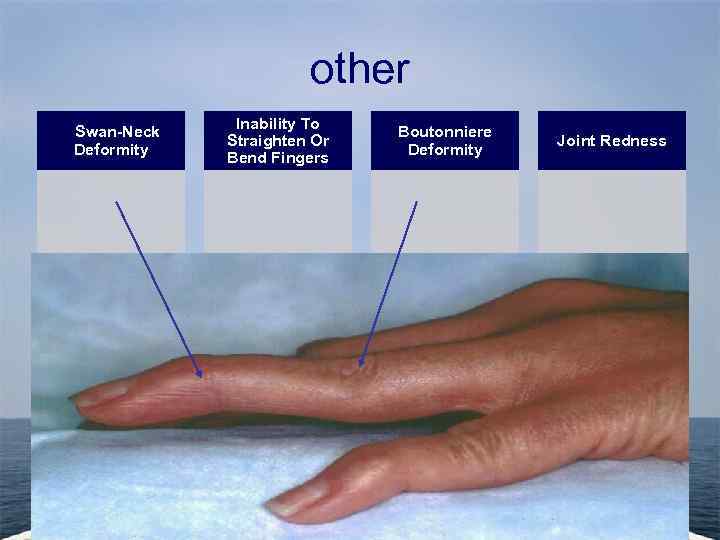
other Swan-Neck Deformity Inability To Straighten Or Bend Fingers Boutonniere Deformity Joint Redness

Rheumatoid arthritis small joints of hands and feet affected first, larger joints later
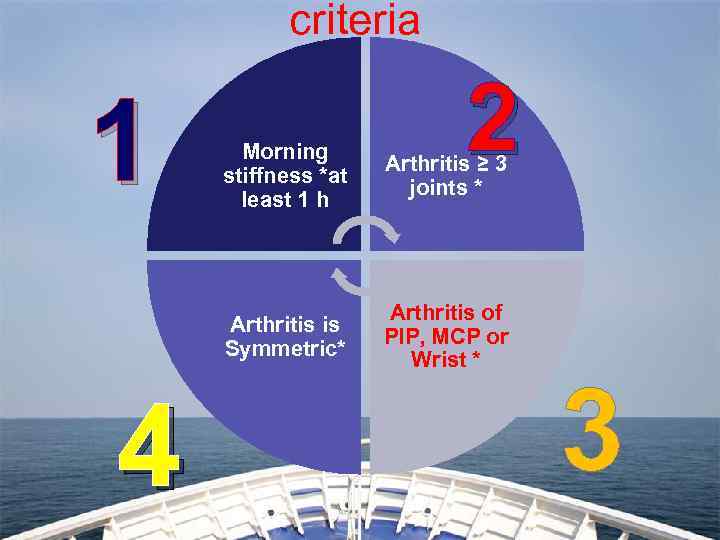
criteria 1 2 Arthritis ≥ 3 joints * Arthritis is Symmetric* 4 Morning stiffness *at least 1 h Arthritis of PIP, MCP or Wrist * 3

5 6 7 ! criteria Subcutaneous nodules. Serum RF An Auto-antibody to Self Ig. G Fc Radiographic Changes typical of RA on hand wrist radiographs A person shall be said to have rheumatoid arthritis if he or she has 4 of 7 criteria, with present for at least 6 weeks
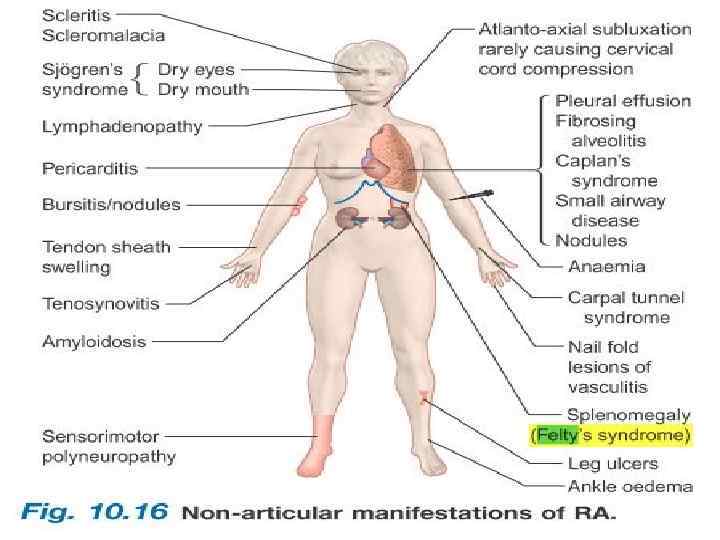
Effects on organ systems RA affects several organ systems, as follows: Cutaneous Pulmonary Cardiac Renal Gastrointestinal (GI) Vascular Hematologic Neurologic Ocular

What causes rheumatoid arthritis? • The cause of RA is not known. Yet, new research is giving us a better idea of what makes the immune system attack the body and create inflammation. In RA, the focus of the inflammation is in the synovium, the tissue that lines the joint. Immune cells release inflammation-causing chemicals. These chemicals can damage cartilage (the tissue that cushions between joints) and bone. • Other things likely play a role in RA as well. For instance, genes make some people more prone to getting RA. that affect the immune system may
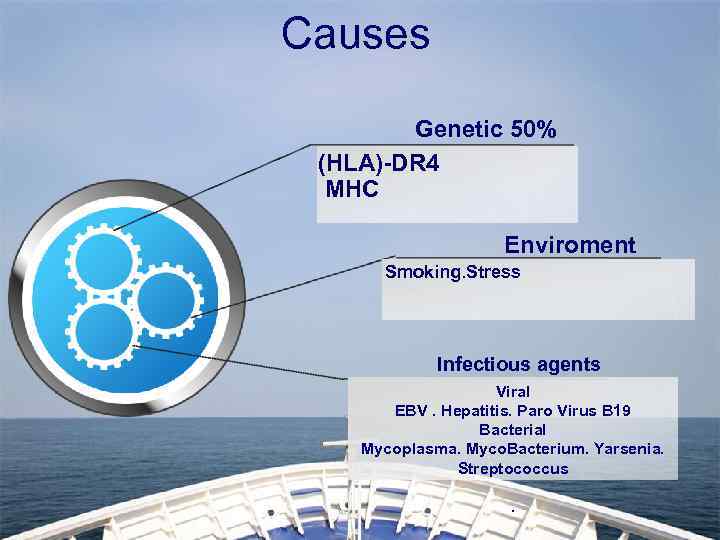
Causes Genetic 50% (HLA)-DR 4 MHC Enviroment Smoking. Stress Infectious agents Viral EBV. Hepatitis. Paro Virus B 19 Bacterial Mycoplasma. Myco. Bacterium. Yarsenia. Streptococcus.

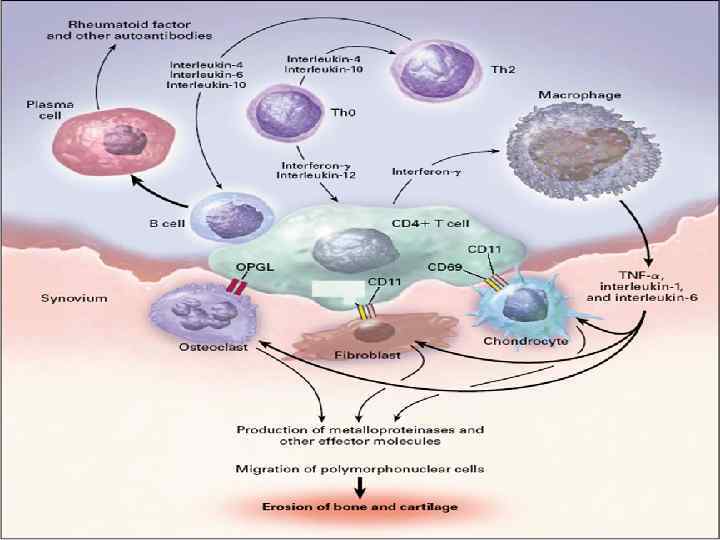
Pathophysiology • The pathogenesis of RA is not completely understood. An external trigger (eg, cigarette smoking, infection, or trauma) that triggers an autoimmune reaction, leading to synovial hypertrophy and chronic joint inflammation along with the potential for extra-articular manifestations, is theorized to occur in genetically susceptible individuals. • Synovial cell hyperplasia and endothelial cell activation are early events in the pathologic process that progresses to uncontrolled inflammation and consequent cartilage and bone destruction. Genetic factors and immune system abnormalities contribute to disease propagation.

Ø Foreign substance such as V OR B Ø Activation (B-cell. T-cell. Macrophage. Synovial fibroblast ) Ø Secretion Cytokines (TNF-alph. IL-1. IL-6. VEGF Ø VEGF(essentiol to blood vessel proliferation)Angiogenesis Ø This conterepute to form Pannus(Cell. angiogenesis. chondrocyte. osteoclast ) Ø Lead to Vilous projection access to cartilage and bone

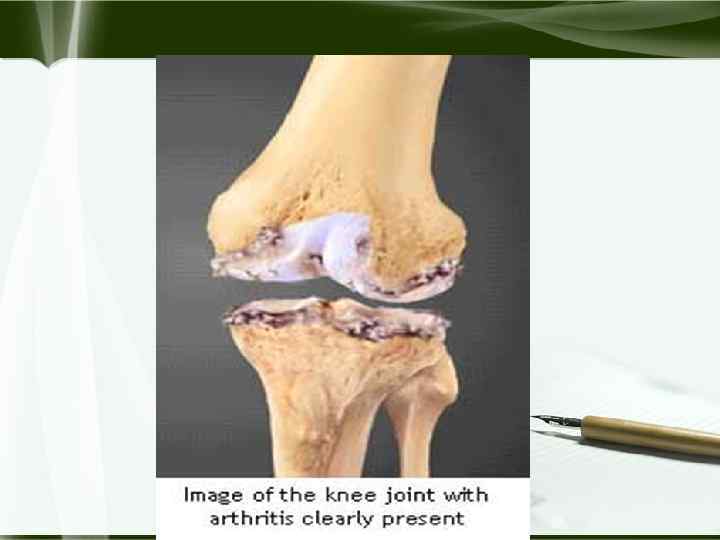
Cartilage Distraction u Activation cell in Pannus relese Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPS) …. . Lead Cartilage Distraction u Chondrocytes in cartilage (activation By TNFalph. . IL 1) ……. . u TNF-a-mediated apoptosis in chondrocytes u Cartilage damage and joint space narrowing
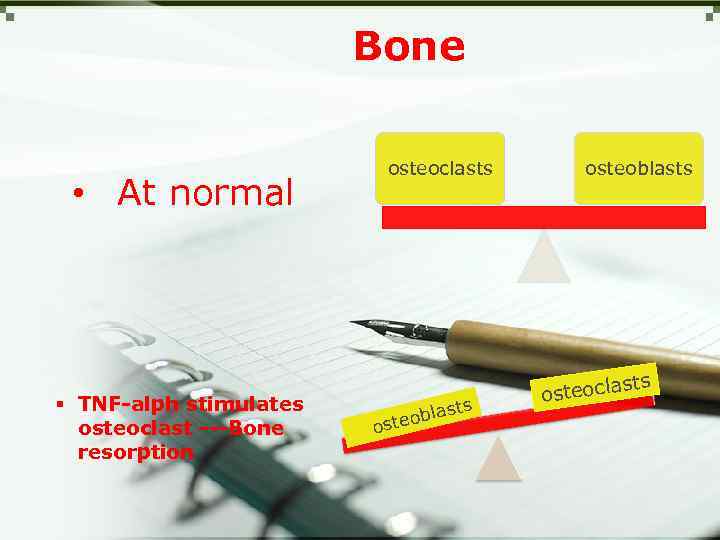
Bone • At normal § TNF-alph stimulates osteoclast ---Bone resorption osteoclasts st eobla ost s osteoblasts osteocla
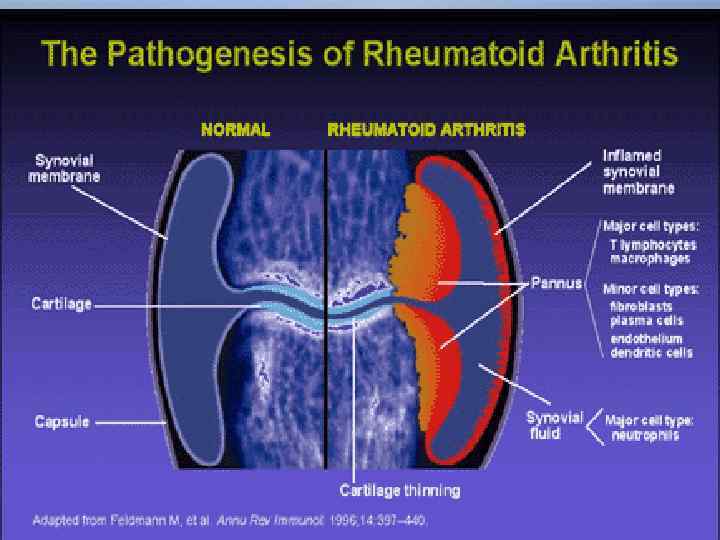
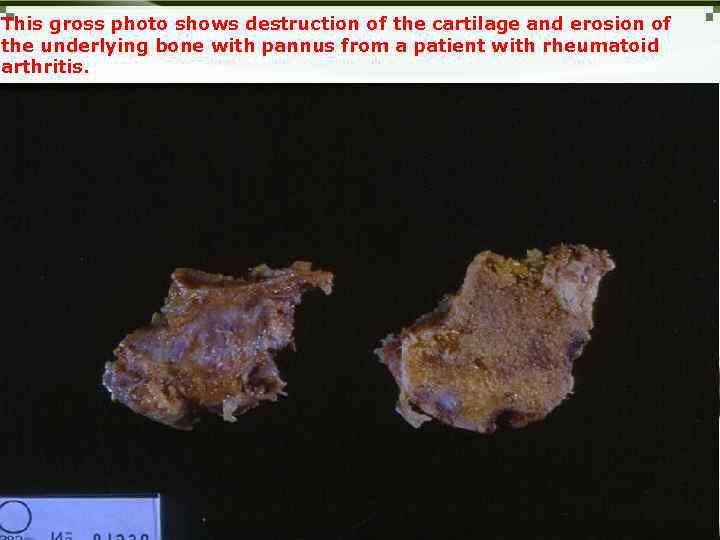
This gross photo shows destruction of the cartilage and erosion of the underlying bone with pannus from a patient with rheumatoid arthritis.
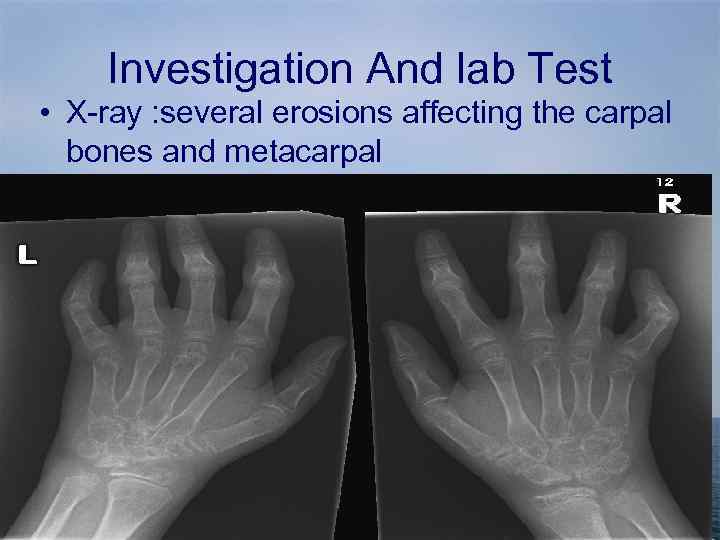
Investigation And lab Test • X-ray : several erosions affecting the carpal bones and metacarpal
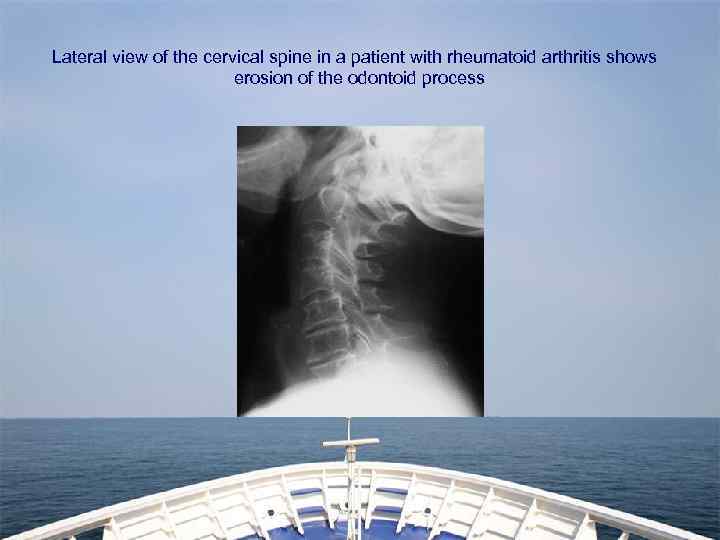
Lateral view of the cervical spine in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis shows erosion of the odontoid process
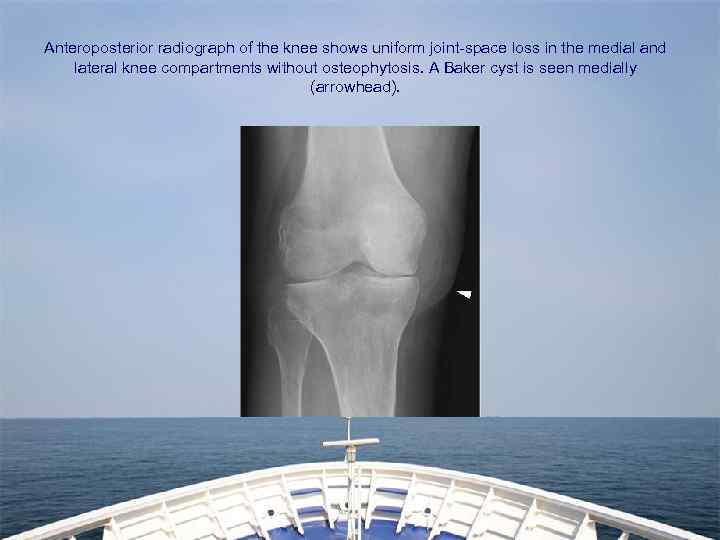
Anteroposterior radiograph of the knee shows uniform joint-space loss in the medial and lateral knee compartments without osteophytosis. A Baker cyst is seen medially (arrowhead).

• MRI And CAT scan • Blood Examination Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) C-reactive protein (CRP) level Complete blood count (CBC) Rheumatoid factor (RF) assay Antinuclear antibody (ANA) assay • synovial fluid analysis • • •
romatoid arthrites.pptx