Rheumatic endocarditis RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE •

























- Размер: 927.5 Кб
- Количество слайдов: 29
Описание презентации Rheumatic endocarditis RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE • по слайдам
 Rheumatic endocarditis
Rheumatic endocarditis
 RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE • Rheumatic fever is a post-streptococcal immune-mediated inflammatory disease affect heart and extra-cardiac sites e. g. joints, skin, brain…. • The incidence and mortality of rheumatic fever has declined over the past 30 years (due to improved socioeconomic condition and rapid diagnosis and treatment of strep. pharyngitis).
RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE • Rheumatic fever is a post-streptococcal immune-mediated inflammatory disease affect heart and extra-cardiac sites e. g. joints, skin, brain…. • The incidence and mortality of rheumatic fever has declined over the past 30 years (due to improved socioeconomic condition and rapid diagnosis and treatment of strep. pharyngitis).
 * Pathogenesis: • An acute attack of streptococcal pharyngitis by group A beta-hemolytic streptococci. • Within 2 -4 weeks after this attack anti-streptococcal antibodies are formed and attack the heart and the extra-cardiac sites. • The mechanism of this immune reaction is not yet understood, however, the most accepted hypothesis is antigenic similarity hypothesis.
* Pathogenesis: • An acute attack of streptococcal pharyngitis by group A beta-hemolytic streptococci. • Within 2 -4 weeks after this attack anti-streptococcal antibodies are formed and attack the heart and the extra-cardiac sites. • The mechanism of this immune reaction is not yet understood, however, the most accepted hypothesis is antigenic similarity hypothesis.
 vegetations Aschoff body pericarditis. Strep throat Antibody production Antibody cross-reaction with heart
vegetations Aschoff body pericarditis. Strep throat Antibody production Antibody cross-reaction with heart
 * Pathological features of Rheumatic Heart disease: • The characteristic lesion of acute rheumatic fever is the Aschoff body , consisting of a focus of necrosis (representing the site of antigen – antibody reaction) surrounded by activated histiocytes and lymphocytes. The histiocytes may be mononuclear or multinuclear, and are referred to as Anitschkow’s or Aschoff cells.
* Pathological features of Rheumatic Heart disease: • The characteristic lesion of acute rheumatic fever is the Aschoff body , consisting of a focus of necrosis (representing the site of antigen – antibody reaction) surrounded by activated histiocytes and lymphocytes. The histiocytes may be mononuclear or multinuclear, and are referred to as Anitschkow’s or Aschoff cells.
 • These foci may be found in the pericardium, the myocardium, or uncommonly in the valves. • They ultimately «heal» by fibrosis.
• These foci may be found in the pericardium, the myocardium, or uncommonly in the valves. • They ultimately «heal» by fibrosis.
 — The disease passes into two phases; A. Acute phase: acute rheumatic pancarditis (inflammation of endocardium, myocardium and pericardium) 1. Myocarditis. 2. Pericarditis: «bread and butter», due to fibrinous inflammation 3. Endocarditis: edema, inflammation and fibrin deposits on valve leaflets (vegetations) along lines of closure. Mostly mitral and aortic valves. Aschoff nodules are uncommon in the valves.
— The disease passes into two phases; A. Acute phase: acute rheumatic pancarditis (inflammation of endocardium, myocardium and pericardium) 1. Myocarditis. 2. Pericarditis: «bread and butter», due to fibrinous inflammation 3. Endocarditis: edema, inflammation and fibrin deposits on valve leaflets (vegetations) along lines of closure. Mostly mitral and aortic valves. Aschoff nodules are uncommon in the valves.
 B. Chronic phase: Acute changes may resolve completely or progress to scarring and development of chronic valvular deformities many years after the acute disease.
B. Chronic phase: Acute changes may resolve completely or progress to scarring and development of chronic valvular deformities many years after the acute disease.
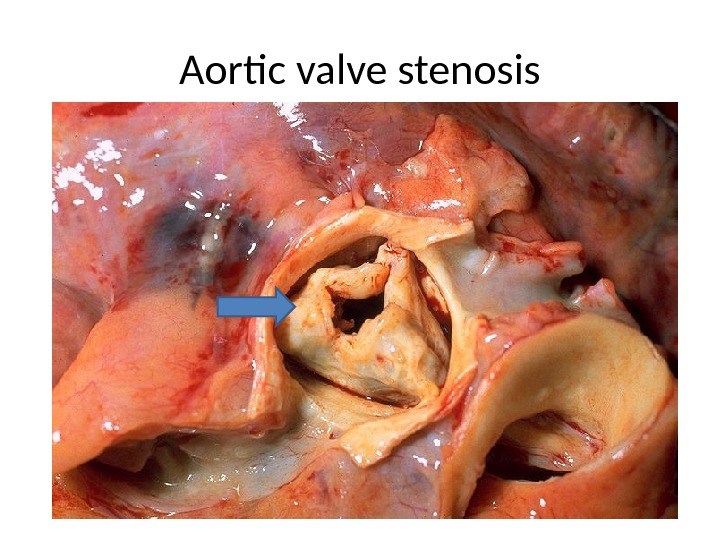
 Aortic valve stenosis
Aortic valve stenosis
 * Extra-cardiac lesions of rheumatic fever: • These lesions are acute and resolve completely without disability. 1. Migratory polyarthritis: It causes «fleeting arthritis» in the large joints, self limited, no chronic deformities. 2. Skin: skin rheumatic nodules, erythema marginatum. 3. Sydenham chorea: a neurologic disorder with involuntary purposeless, rapid movements.
* Extra-cardiac lesions of rheumatic fever: • These lesions are acute and resolve completely without disability. 1. Migratory polyarthritis: It causes «fleeting arthritis» in the large joints, self limited, no chronic deformities. 2. Skin: skin rheumatic nodules, erythema marginatum. 3. Sydenham chorea: a neurologic disorder with involuntary purposeless, rapid movements.
 * Clinical features of Acute Rheumatic Fever: • Occurs 10 days to 6 weeks after pharyngitis • Peak incidence: 5 -15 years. • Cardiac manifestations: pericardial friction rubs, weak heart sounds, tachycardia and arrhythmias. • Extra-cardiac: fever, migratory polyarthritis of large joints, arthralgia, skin lesions, chorea. • Pharyngeal culture may be negative, but anti streptolysin O (ASO) titer will be high.
* Clinical features of Acute Rheumatic Fever: • Occurs 10 days to 6 weeks after pharyngitis • Peak incidence: 5 -15 years. • Cardiac manifestations: pericardial friction rubs, weak heart sounds, tachycardia and arrhythmias. • Extra-cardiac: fever, migratory polyarthritis of large joints, arthralgia, skin lesions, chorea. • Pharyngeal culture may be negative, but anti streptolysin O (ASO) titer will be high.
 * Jones criteria: A. Major criteria: – Carditis. – Polyarthritis – Sydenham’s chorea. – Erythema marginatum. – Subcutaneous nodules. B. Minor criteria: – Previous history of rheumatic fever. – Arthralgia. – Fever. – Lab tests indicative of inflammation : ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate), CRP (C-Reactive protein), leukocytosis. – ECG changes.
* Jones criteria: A. Major criteria: – Carditis. – Polyarthritis – Sydenham’s chorea. – Erythema marginatum. – Subcutaneous nodules. B. Minor criteria: – Previous history of rheumatic fever. – Arthralgia. – Fever. – Lab tests indicative of inflammation : ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate), CRP (C-Reactive protein), leukocytosis. – ECG changes.
 * Diagnosis of rheumatic fever: • Need 2 major criteria or 1 major and 2 minor criteria.
* Diagnosis of rheumatic fever: • Need 2 major criteria or 1 major and 2 minor criteria.
 CHRONIC RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE — Endocarditis heals by progressive fibrosis. Chronic scarring of the valves constitutes the most important long-term sequelae of rheumatic fever, and usually becomes clinically manifest decades after the acute process. • Left sided valves (mitral and aortic) are more commonly involved than the right. • Fibrosis of valve leaflets —> stenosis.
CHRONIC RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE — Endocarditis heals by progressive fibrosis. Chronic scarring of the valves constitutes the most important long-term sequelae of rheumatic fever, and usually becomes clinically manifest decades after the acute process. • Left sided valves (mitral and aortic) are more commonly involved than the right. • Fibrosis of valve leaflets —> stenosis.
 • Fibrosis of chordae tendonae —> regurgitation (improper closure). • Other cardiac complications: 1. Subacute bacterial endocarditis. 2. Arrhythmia. 3. Chronic heart failure.
• Fibrosis of chordae tendonae —> regurgitation (improper closure). • Other cardiac complications: 1. Subacute bacterial endocarditis. 2. Arrhythmia. 3. Chronic heart failure.
 • In valve stenosis: Leaflets are thickened, fibrotic, shrunken with fusion Dilatation and hypertrophy of left atrium. Secondary deposition of Ca++ fish mouth (button hole) stenosis — i. e. the stenosed valve looks like a fish’s mouth Lungs are firm and heavy (chronic passive congestion).
• In valve stenosis: Leaflets are thickened, fibrotic, shrunken with fusion Dilatation and hypertrophy of left atrium. Secondary deposition of Ca++ fish mouth (button hole) stenosis — i. e. the stenosed valve looks like a fish’s mouth Lungs are firm and heavy (chronic passive congestion).
 Pulmonary hypertension Right side of the heart may be affected later (right ventricular hypertrophy). • In valve incompetence (regurgitation): – Retracted leaflets. – Left ventricular hypertrophy and dilatation.
Pulmonary hypertension Right side of the heart may be affected later (right ventricular hypertrophy). • In valve incompetence (regurgitation): – Retracted leaflets. – Left ventricular hypertrophy and dilatation.
 * Mitral valve stenosis: • Leads to left atrial dilatation and failure, chronic venous congestion of the lung, lung fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension and chronic right sided heart failure.
* Mitral valve stenosis: • Leads to left atrial dilatation and failure, chronic venous congestion of the lung, lung fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension and chronic right sided heart failure.
 * Mitral valve incompetence: • Leads to left ventricular dilatation and failure, left atrial dilatation and failure, chronic pulmonary congestion, lung fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension and chronic right sided heart failure.
* Mitral valve incompetence: • Leads to left ventricular dilatation and failure, left atrial dilatation and failure, chronic pulmonary congestion, lung fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension and chronic right sided heart failure.
 Infective Endocarditis
Infective Endocarditis
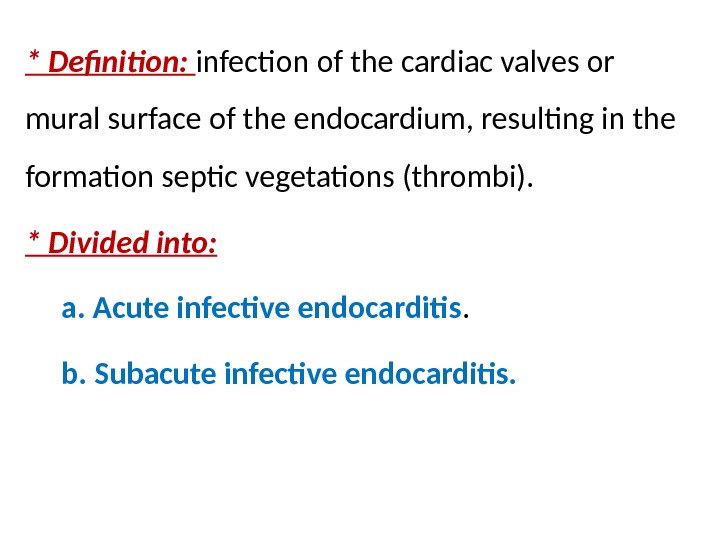
 * Definition: infection of the cardiac valves or mural surface of the endocardium, resulting in the formation septic vegetations (thrombi). * Divided into: a. Acute infective endocarditis. b. Subacute infective endocarditis.
* Definition: infection of the cardiac valves or mural surface of the endocardium, resulting in the formation septic vegetations (thrombi). * Divided into: a. Acute infective endocarditis. b. Subacute infective endocarditis.
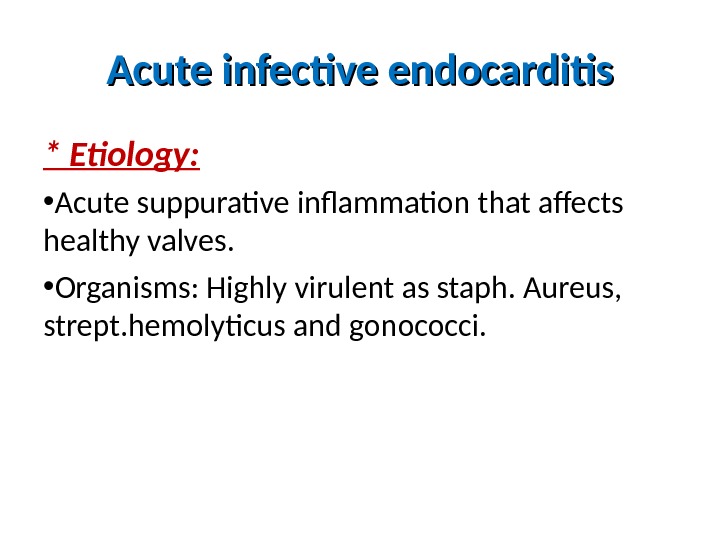
 Acute infective endocarditis * Etiology: • Acute suppurative inflammation that affects healthy valves. • Organisms: Highly virulent as staph. Aureus, strept. hemolyticus and gonococci.
Acute infective endocarditis * Etiology: • Acute suppurative inflammation that affects healthy valves. • Organisms: Highly virulent as staph. Aureus, strept. hemolyticus and gonococci.
 * Lesions: • Mitral & aortic valves are most commonly affected. Tricuspid is affected in IV drug abusers. • The mural endocardium may be also affected. • The affected valve and mural endocardium show acute suppurative inflammation + vegetations.
* Lesions: • Mitral & aortic valves are most commonly affected. Tricuspid is affected in IV drug abusers. • The mural endocardium may be also affected. • The affected valve and mural endocardium show acute suppurative inflammation + vegetations.
 * Complications: 1. Embolic complications: • Detached septic vegetations leads to systemic pyemia. 2. Toxemic complications: • Severe toxemia
* Complications: 1. Embolic complications: • Detached septic vegetations leads to systemic pyemia. 2. Toxemic complications: • Severe toxemia
 * Prognosis: • Rapidly fatal due to; 1. Severe toxemia (septicemia). 2. Cusp perforation (acute heart failure).
* Prognosis: • Rapidly fatal due to; 1. Severe toxemia (septicemia). 2. Cusp perforation (acute heart failure).
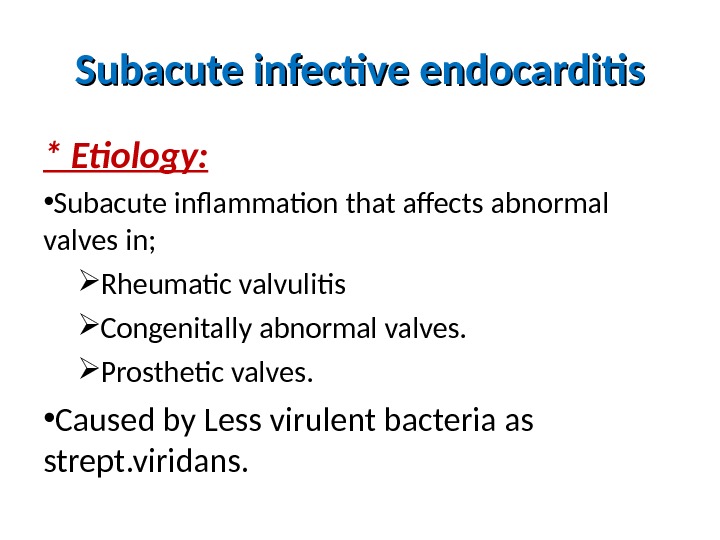
 Subacute infective endocarditis * Etiology: • Subacute inflammation that affects abnormal valves in; Rheumatic valvulitis Congenitally abnormal valves. Prosthetic valves. • Caused by Less virulent bacteria as strept. viridans.
Subacute infective endocarditis * Etiology: • Subacute inflammation that affects abnormal valves in; Rheumatic valvulitis Congenitally abnormal valves. Prosthetic valves. • Caused by Less virulent bacteria as strept. viridans.
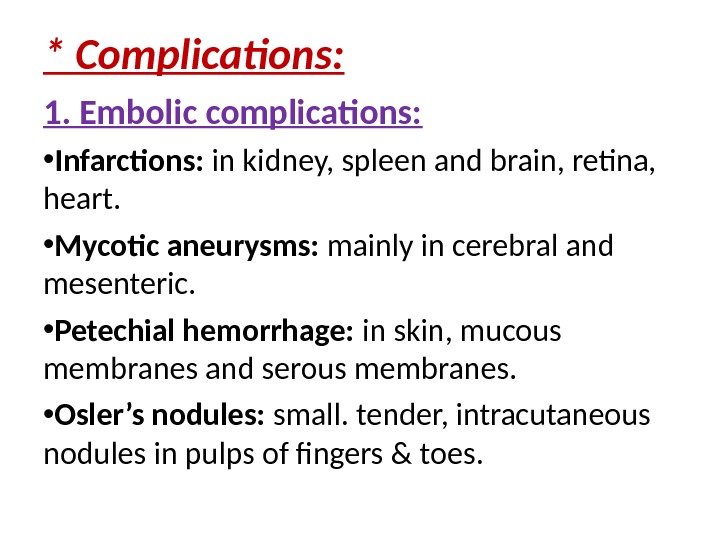
 * Complications: 1. Embolic complications: • Infarctions: in kidney, spleen and brain, retina, heart. • Mycotic aneurysms: mainly in cerebral and mesenteric. • Petechial hemorrhage: in skin, mucous membranes and serous membranes. • Osler’s nodules: small. tender, intracutaneous nodules in pulps of fingers & toes.
* Complications: 1. Embolic complications: • Infarctions: in kidney, spleen and brain, retina, heart. • Mycotic aneurysms: mainly in cerebral and mesenteric. • Petechial hemorrhage: in skin, mucous membranes and serous membranes. • Osler’s nodules: small. tender, intracutaneous nodules in pulps of fingers & toes.
 2. Toxemic complications: • Moderate toxemia: fever, anemia, clubbing of fingers, splenomegaly, petechial hemorrhage and focal glomerulonephritis (flea bitten kidney)
2. Toxemic complications: • Moderate toxemia: fever, anemia, clubbing of fingers, splenomegaly, petechial hemorrhage and focal glomerulonephritis (flea bitten kidney)
 * Prognosis: • Heal by fibrosis leads to valve lesion either stenosis or incompetence.
* Prognosis: • Heal by fibrosis leads to valve lesion either stenosis or incompetence.

