1aa1ed74d712c676da287fdd073baf9d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 96

RHB Rad Prot & Fluoro Syllabus RT 244 FALL 2007

measurement 100 R = 1 C/kg 1 Rad = 1/100 Gray 1 Rem =. 01 Sievert (Rad + QF = REM) 1 REM = 10 m. Sv 1 Rem = 1000 m. Rem

• The average person in the United States receives about 360 mrem every year whole body equivalent dose. This is mostly from natural sources of radiation, such as radon
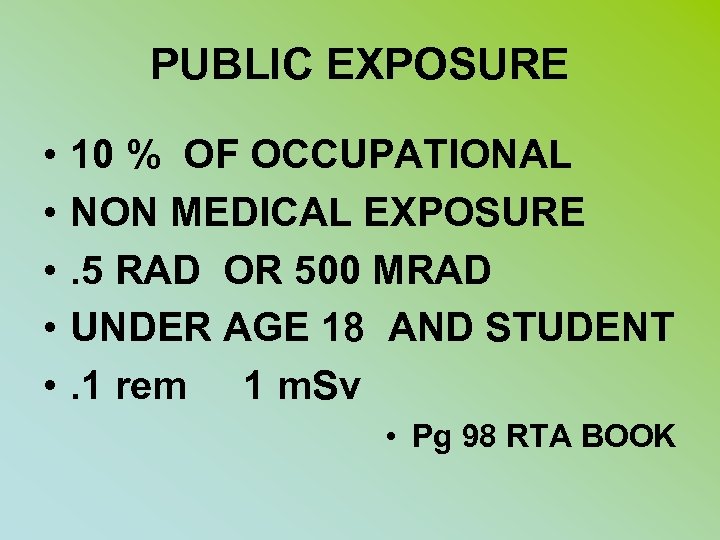
PUBLIC EXPOSURE • • • 10 % OF OCCUPATIONAL NON MEDICAL EXPOSURE. 5 RAD OR 500 MRAD UNDER AGE 18 AND STUDENT. 1 rem 1 m. Sv • Pg 98 RTA BOOK
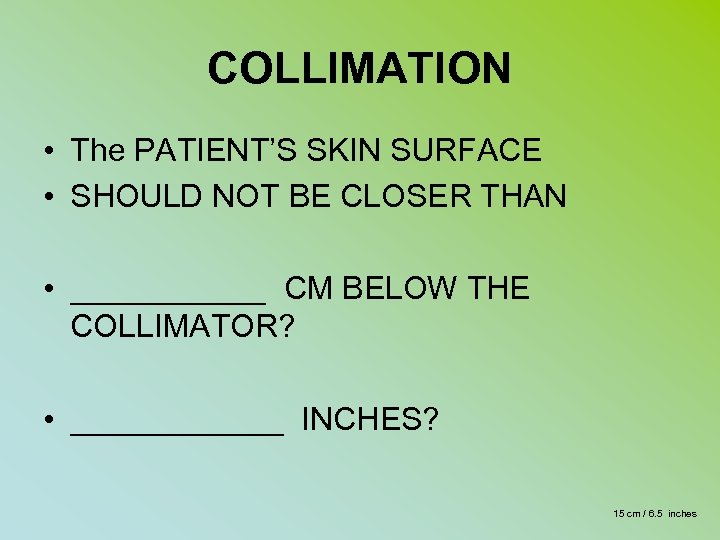
COLLIMATION • The PATIENT’S SKIN SURFACE • SHOULD NOT BE CLOSER THAN • ______ CM BELOW THE COLLIMATOR? • ______ INCHES? 15 cm / 6. 5 inches
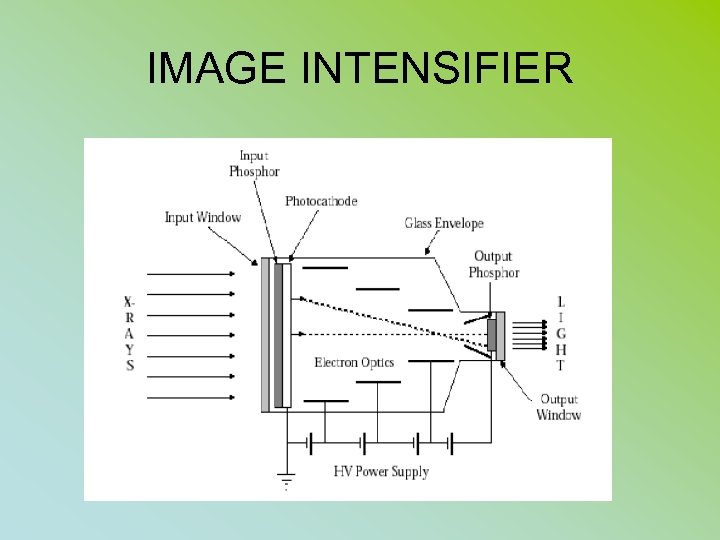
IMAGE INTENSIFIER

IMAGE INTENSIFIER • • • FUNCTION: CHANGE XRAY PHOTONS TO LIGHT PHOTONS (INPUT PHOSPHOR) TO ELECTONS (PHOTOCATHODE) ACCERATES ELECTRONS ACROSS TUBE AT 25, 000 VOLT POTIENTAL • CHANGED BACK TO LIGHT AT OUTPUT PHOSPHOR

• The ratio of the number of light photons striking the output screen to the ratio of the number of x-ray photons striking the input screen is called fluxgain
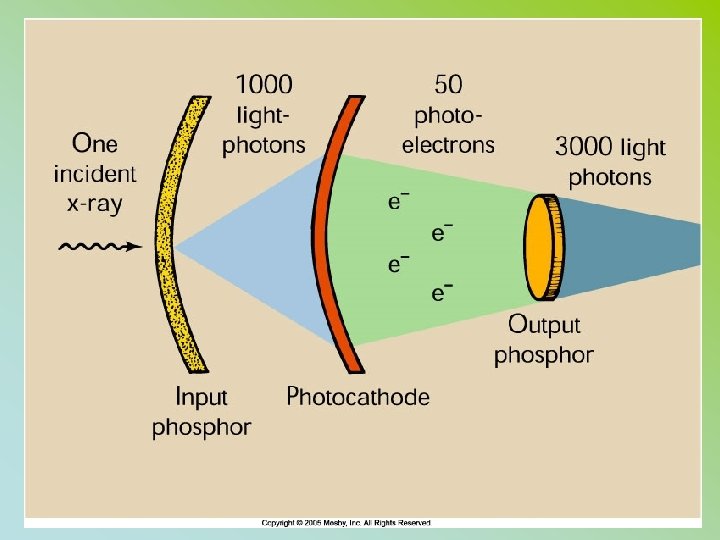
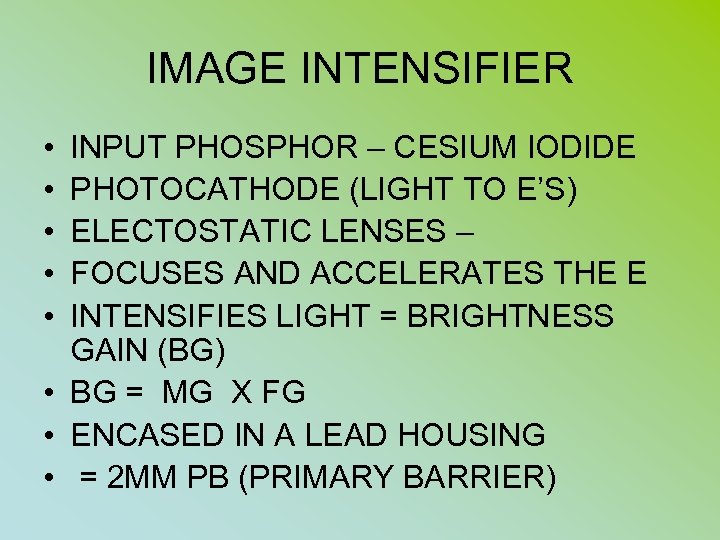
IMAGE INTENSIFIER • • • INPUT PHOSPHOR – CESIUM IODIDE PHOTOCATHODE (LIGHT TO E’S) ELECTOSTATIC LENSES – FOCUSES AND ACCELERATES THE E INTENSIFIES LIGHT = BRIGHTNESS GAIN (BG) • BG = MG X FG • ENCASED IN A LEAD HOUSING • = 2 MM PB (PRIMARY BARRIER)
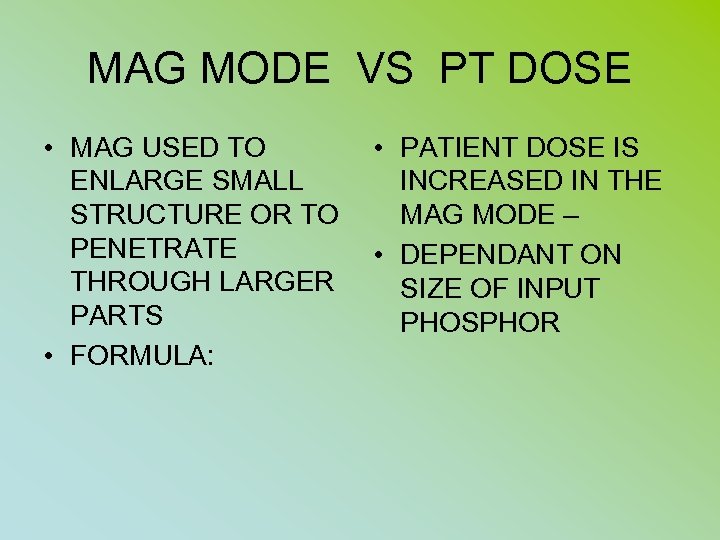
MAG MODE VS PT DOSE • MAG USED TO ENLARGE SMALL STRUCTURE OR TO PENETRATE THROUGH LARGER PARTS • FORMULA: • PATIENT DOSE IS INCREASED IN THE MAG MODE – • DEPENDANT ON SIZE OF INPUT PHOSPHOR

MAG MODE FORMULA IP OLD SIZE IP NEW SIZE = MAG

MORE FORMULAS BG = MG X FG • BG = MINIFICATION GAIN X FLUX GAIN • MINIFICATION GAIN – same # e at input condensed to output phosphor – ratio of surface area on input screen over surface area of output screen IP SIZE OP SIZE 2 2

BG = MG X FG • FLUX GAIN – increase of light brightness due to the conversion efficiency of the output screen • 1 electron = 50 light photons is 50 FG • Can decrease as II ages • Output phosphor almost always 1 inch • Zinc cadnium phosphot • Flux gain is almost always 50

BG = MG X FG • • Brightness gain BG = MINIFICATION GAIN X FLUX GAIN (old Patterson B-2 fluoro –obsolete) Brightness gain is a measure of the conversion factor that is the ratio of the intensity of the output phosphor to the input phosphor • conversion factor = intensity of OP Ø • m. R/sec


KELL FACTOR VERTICAL RESOLUTION ABILITY TO RESOLVE OBJECTS SPACED APART IN A VERTICAL DIRECTION MORE DOTS(GLOBULES) = MORE SCAN LINES = MORE/BETTER RESOLUTION • RATIO OF VERTICAL RESOLUITON • # OF SCAN LINES • KELL FACTOR FOR 525 LINE SYSTEM • IS 0. 7

ESE FOR FLUORO • TLD PLACED AT SKIN ENTRACE POINT • 1 – 5 R/MINUTE AVE IS 4 R/MIN • INTERGRAL DOSE – • 100 ERGS OF TISSUE = 1 RAD EXPOSURE • OR 1 GM RAD = 100 ERGS

SSD – TUBE TO SKIN DISTANCE • FIXED UNITS • 18” PREFERRED • 15 “ MINIMUM MOBILE UNITS ( C-ARMS) • 12’ MINIMUM

PATIENT PROTECTION • • LIMIT SIZE OF BEAM ON TIME DISTANCE OF SOURCE TO SKIN PBL FILTRATION (2. 5 mm Al eq) @ 70 SHEILDING SCREEN/FILM COMBO
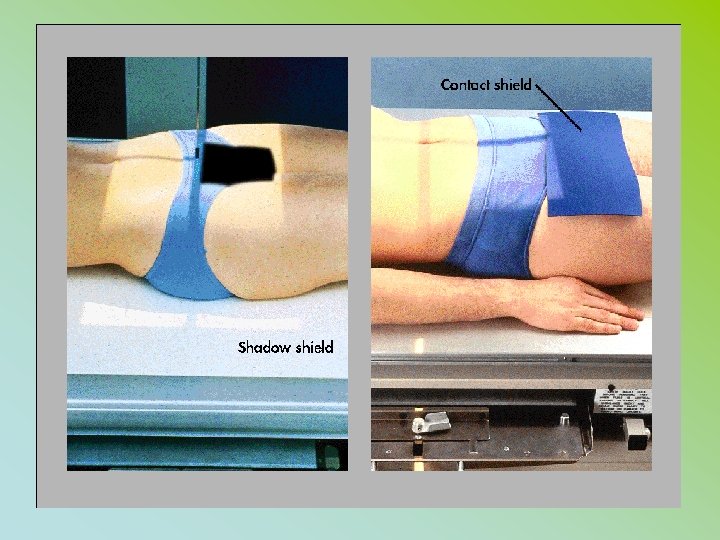

GONAD SHIELDING • MUST BE. 5 MM OF LEAD • MUST BE USED WHEN GONADS WILL LIE WITHING 5 CM OF THE COLLIMATED AREA (RHB) • KUB. Lumbar Spine Pelvis • male vs female shielding

Gonad shielding & dose • ♀ receive 3 x more dose than • ♂ for pelvic x-rays • 1 mm lead will reduce exposure (primary) by about 50% ♀ • by about 90 – 95 % ♂
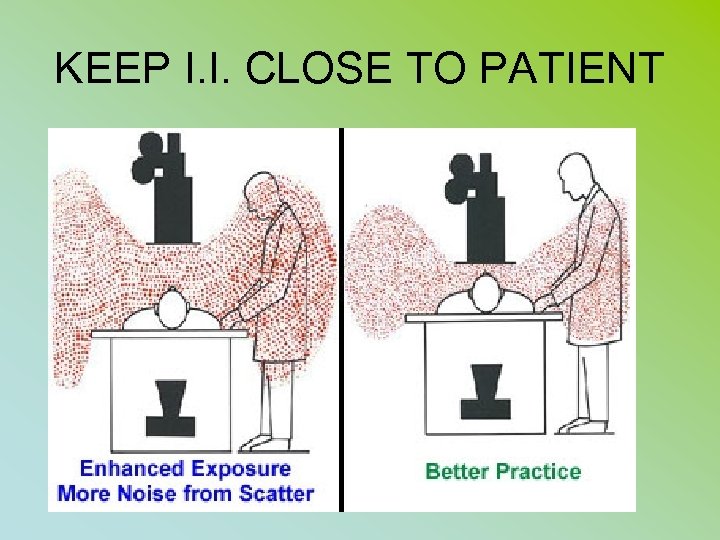
KEEP I. I. CLOSE TO PATIENT
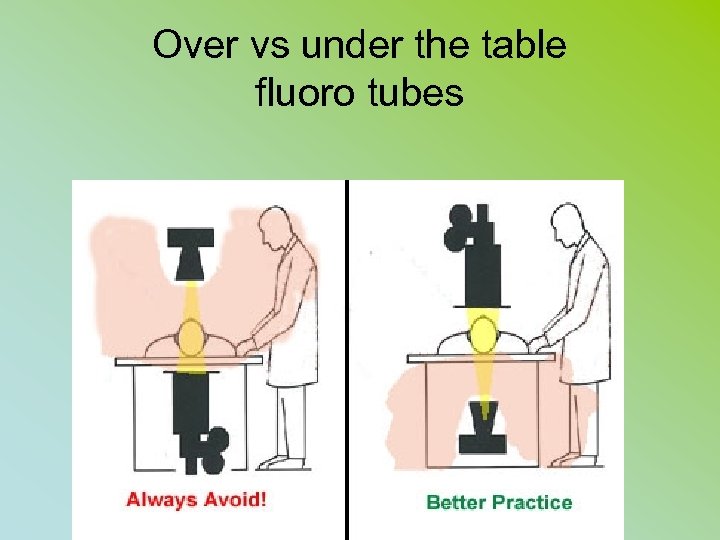
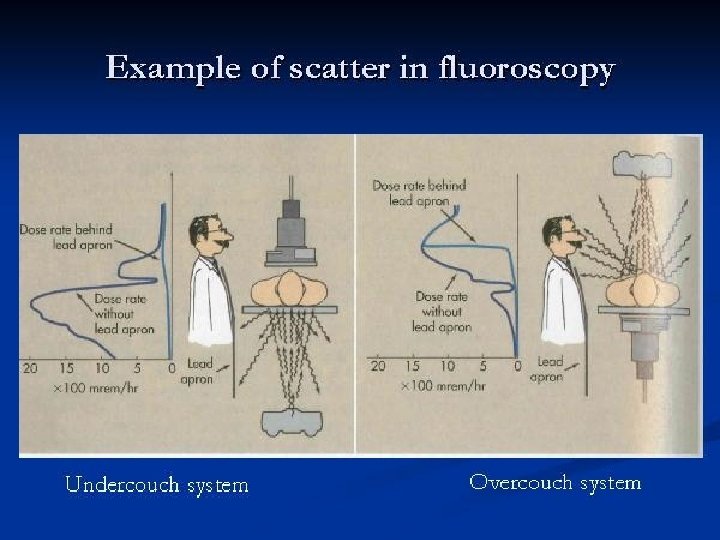
Over vs under the table fluoro tubes
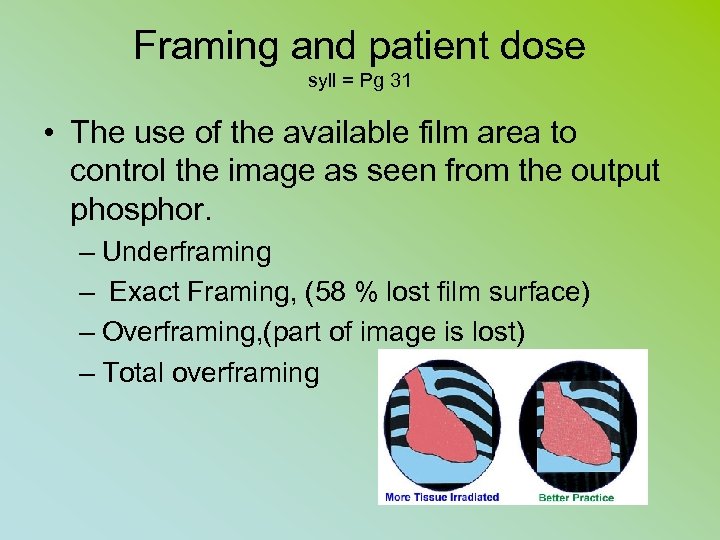
Framing and patient dose syll = Pg 31 • The use of the available film area to control the image as seen from the output phosphor. – Underframing – Exact Framing, (58 % lost film surface) – Overframing, (part of image is lost) – Total overframing

EXPOSURE RATES FLUORO • MA IS 0. 5 MA TO 5 MA PER MIN • AVE DOSE IS 4 R / MIN • IF MACHINE OUTPUT IS 2 R/MA/MIN = WHAT IS PT DOSE AT 1. 5 MA FOR 5 MIN STUDY? • 15 R

EXPOSURE RATES FOR FLUORO • • • CURRENT STANDARD 10 R/MIN (INTENSIFIED UNITS) HLC: BOOST MODE 20 R/MIN OLD (1974) NO ABC NON IMAGE INTES 5 R/MIN

DOSE REGULATIONS • BEFORE 1974 - AT TABLETOP • 5 R/MIN (WITHOUT AEC) – BOOST MODE • After 1974 with AEC • 10 R/MIN 20 R/MIN BOOST

RADIATION PROTECTION The Patient is the largest scattering object • Lower at a 90 DEGREE ANGLE from the patient + PRIMARY BEAM AT 1 METER DISTANCE • 1/1000 OF INTENSITY PRIMARY XRAY or 0. 1%

BUCKY SLOT COVER. 25 MM LEAD
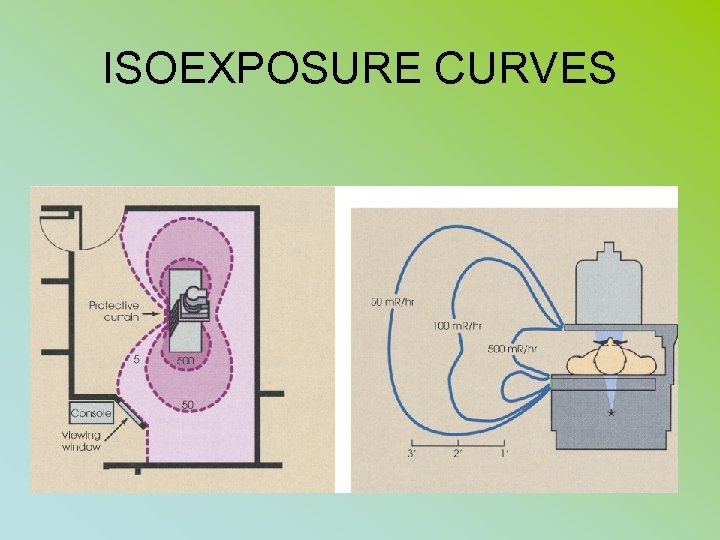
ISOEXPOSURE CURVES

PERSONNEL PROTECTION • SCATTER FROM THE PATIENT • TABLE TOP, COLLIMATOR, TUBE HOUSING, BUCKY • STRAY RADIATION – LEAKAGE OR SCATTER RADIATION

TOWER CURTAIN. 25 MM LEAD EQ

PERSONNEL PROTECTION • STANDING BEHIND A PROTECTIVE PRIMARY (1/16 TH pb) BARRIER: • PRIMARY RADIATION EXPOSURE – 99. 87% REDUCED • PORTABLE BARRIER = 99 % REDUCTION

PERSONNEL PROTECTION • • • PROTECTIVE APRONS – 0. 25 PB = 97% ↓ TO SCATTER 0. 5 PB = 99. 9% ↓ TO SCATTER THYROID SHEILDS (0. 25 & 0. 5) GLOVES (0. 25 & 0. 5)

PERSONNEL PROTECTION MONITORING • FILM BADGE • TLD • POSL • POCKET DOSIMETER • RING BADGE

PERSONNEL PROTECTION MONITORING • • DOSE LIMITS WHOLE BODY EYES EXTREMITIES (BELOW ELBOW/KNEES)

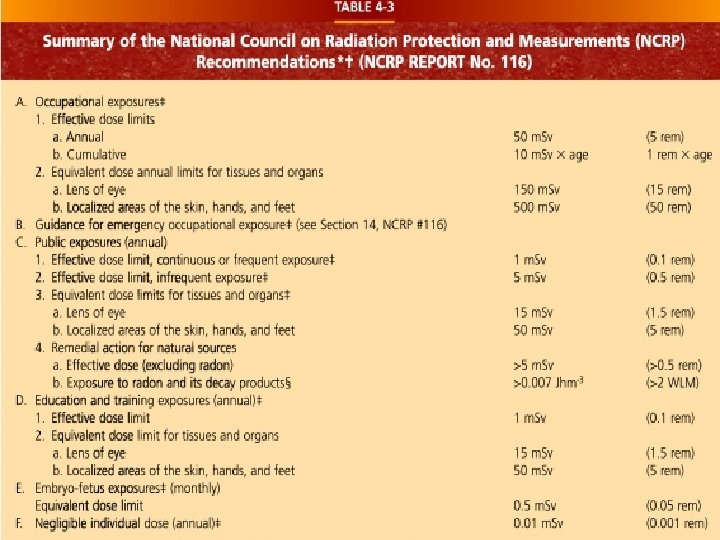
Occupational Dose ANNUAL LIMITS • WHOLE BODY = 5 REMS / 5000 m. Rem • LENS OF THE EYE = 15 REMS • EXTREMITIES = 50 REMS



TLD
Report at least every quarter Preserved for a minimum of 3 years

RHB NOTIFICATION (EXP IN 24 HOURS) • • IMMEDIATE – WITHIN 24 HOURS TOTAL DOSE OF 25 rems Eye dose – 75 rem Extremity – 250 RADS OVEREXPOSURE – WITHIN 30 DAYS TOTAL DOSE OF 5 rems Eye dose – 15 rem Extremity - 50 REMS

LICENSE RENEWAL • WITHIN 30 DAYS OF EXPRIATION • NOTIFICATION OF CHANGE OF ADDRESS
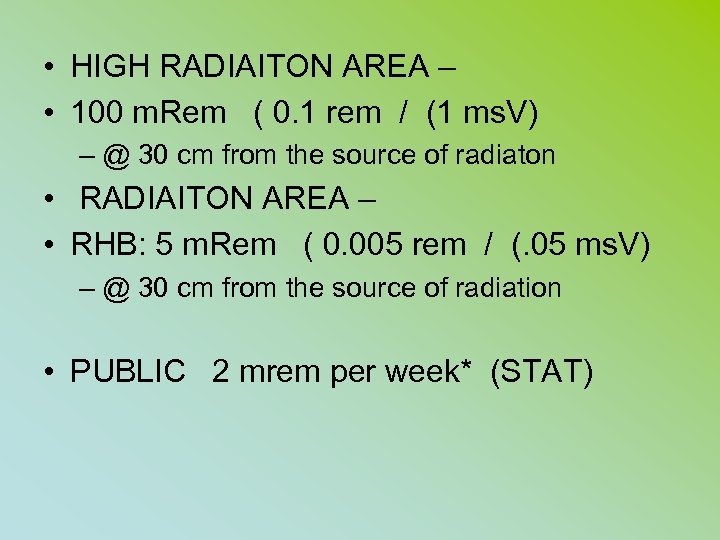
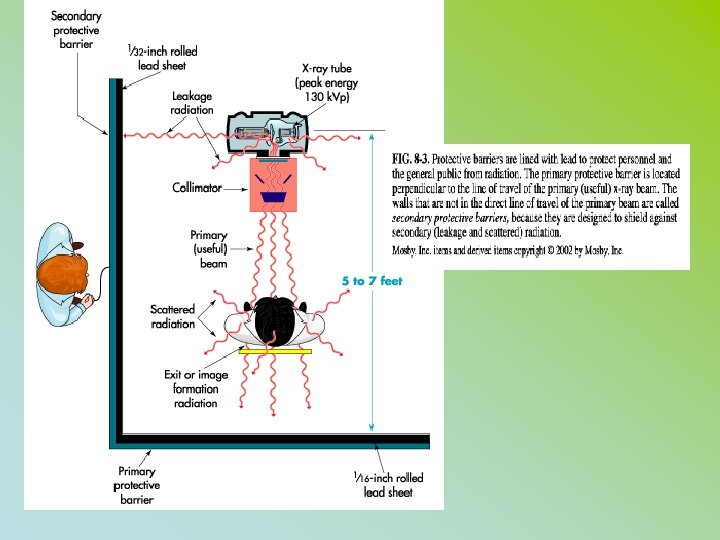
• HIGH RADIAITON AREA – • 100 m. Rem ( 0. 1 rem / (1 ms. V) – @ 30 cm from the source of radiaton • RADIAITON AREA – • RHB: 5 m. Rem ( 0. 005 rem / (. 05 ms. V) – @ 30 cm from the source of radiation • PUBLIC 2 mrem per week* (STAT)

RHB “RULES” RHB RP PG 61 • LICENTIATES OF THE HEALING ARTS (MD, DO, DC, DPM) • MUST HAVE A • RADIOLOGY SUPERVISOR & OPERATORS PERMIT & CERTIFICATE • TO OPERATE OR SUPERVISE THE USE OF X-RAYS ON HUMANS • SUPEVISORS MUST POST THEIR LICENSES

RHB “RULES” RHB RP PG 62 • ALL XRAYS MUST BE ORDERED BY A PHYSICIAN • VERBAL OR WRITTEN PRESCRIPTION • See Section C – “Technologist Restrictions”

Declared Pregnant Worker • Must declare pregnancy – 2 badges provided • 1 worn at collar (Mother’s exposure) • 1 worn inside apron at waist level Under 5 rad – negligible risk Risk increases above 15 rad Recommend abortion (spontaneous) 25 rad • (“Baby exposure” approx 1/1000 of ESE) • www. ntc. gov/NRC/RG/08/08 -013. html

CARDINAL RULES • TIME • DISTANCE • SHEILDING

HVL TVL • The amount of material required to reduce the energy of the beam by……. . • ____________ • Examples 100 – 50 - 25 – 12. 5 – 6. 25 - 3. 12 • ? How many to reduce to 1/2 ? 1/10 th ?

SHEILDING PG 72 RHB • HVL – expressed 2 ways • HOW MUCH IT REDUCES THE ORGINAL BEAM INTENSITY • HOW MUCH IS REQUIRED FOR BARRIER THICKNESS (amount needed to attenuated the beam
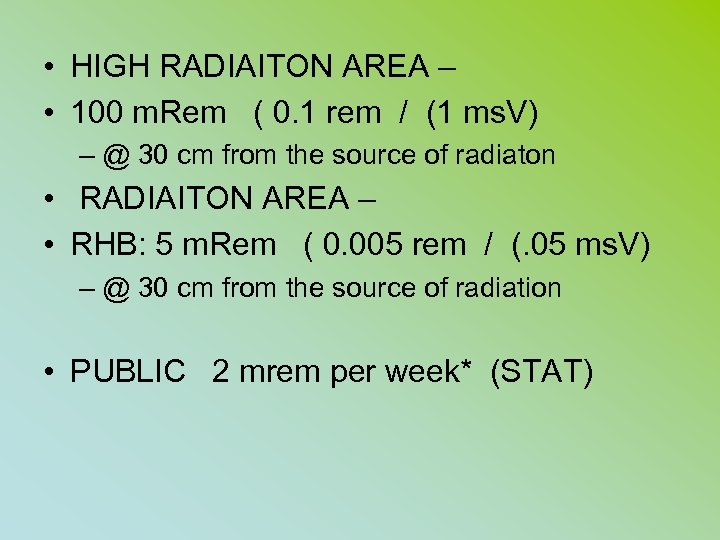
• HIGH RADIAITON AREA – • 100 m. Rem ( 0. 1 rem / (1 ms. V) – @ 30 cm from the source of radiaton • RADIAITON AREA – • RHB: 5 m. Rem ( 0. 005 rem / (. 05 ms. V) – @ 30 cm from the source of radiation • PUBLIC 2 mrem per week* (STAT)

A “controlled area” is defined as one • that is occupied by people trained in radiologic safety • that is occupied by people who wear radiation monitors • whose occupancy factor is 1

Room Sheilding Ch. 9 • Workload Factor (W) -ma/sec/week – how much time during the week is the beam on • Occupancy Factor (T) - # of people in room - beyond the barrier • Use Factor (U) - % of time beam will strike a barrier (table pg 242) Primary vs Secondary • Leakage Radiation

We recall that as an occupationally exposed individual, federal law limits annual occupational whole body radiation dose to 5 rem (5000 mrem or 50 m. Sv) However …. .

For female workers of child bearing age who are or may be pregnant, this occupational dose limit is reduced (with respect to the fetus) to: 0. 5 rem (500 mrem or 5 m. Sv) Preferably distributed evenly over the entire gestation period

Pregnancy & Embryo Mother – occupational worker (5 rem) • Baby – (500 m. Rem) • . 5 rem/ year. 05 rem/month • 5 m. Sv / month

PREGNANCY DOSE • “ 10 day rule” (no longer used) • No threshold for exposure • Leukemia , congential abnormailies cander induction, resportion or death of the embryo and genetic effects • Therapetuic Abortion “not justified” • 15 rads (risk is increased) • 25 rads or less – no injury seen • ABSORBED DOSES – 50 RADS – could result in a spontaneous abortion

• The NCRP states that: the risk (to the embryo/fetus) is considered to be negligible at 5 rads or less when compared to the other risks of pregnancy • and the risk of malformation is significantly increased above control levels only at doses above 15 rads

This latter dose limit refers to radiation dose received by the fetus, not the dose received by the mother. Note: This may or may not be the dose to the mother, depending upon the type and energy of the radiation to which the mother was exposed.

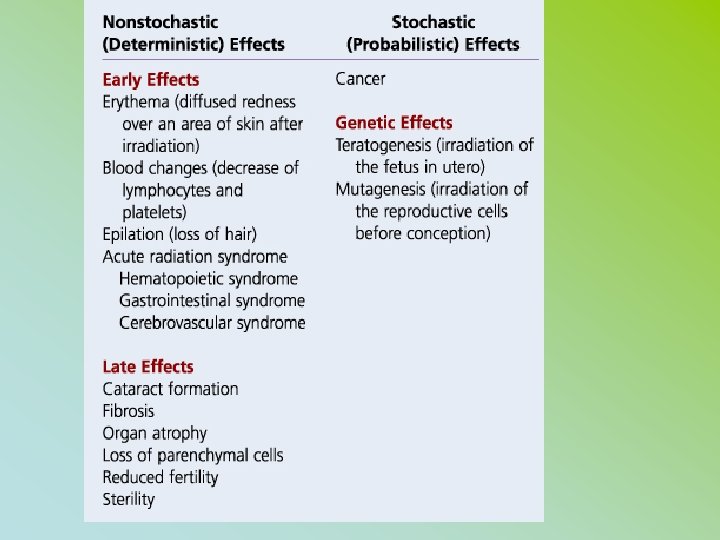
RHB – Rad Prot – CH. IX p 51 • ALARA (no minimum threshold) • STOCHASTIC EFFECTS – NON TRESHOLD (CA + GENETIC) • NON STHOCAHSTIC (DETERMINISTIC) SEVERITY OF EFFECTS VARIES WITH RADIATION DOSE (THRESHOLD) (CATARACTS, SKIN, BONE MARROW, STERILITY
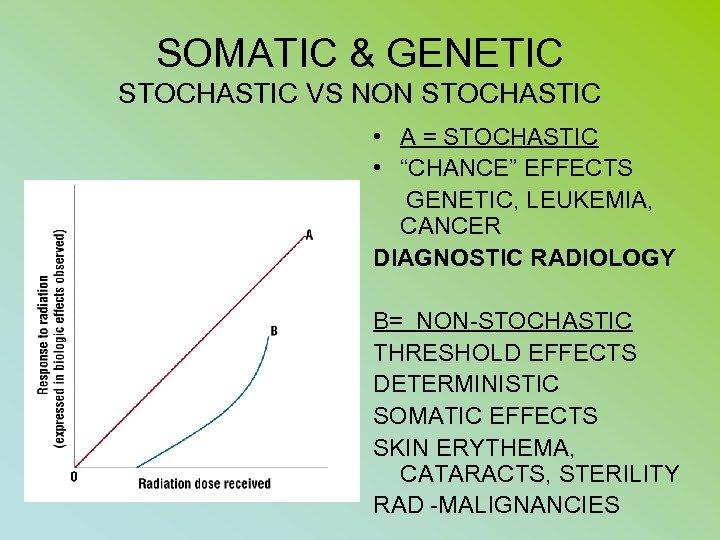
SOMATIC & GENETIC STOCHASTIC VS NON STOCHASTIC • A = STOCHASTIC • “CHANCE” EFFECTS GENETIC, LEUKEMIA, CANCER DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY B= NON-STOCHASTIC THRESHOLD EFFECTS DETERMINISTIC SOMATIC EFFECTS SKIN ERYTHEMA, CATARACTS, STERILITY RAD -MALIGNANCIES
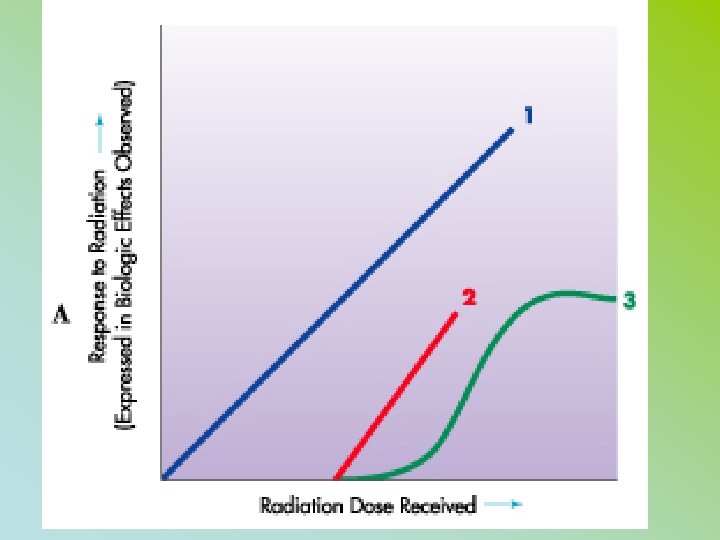

#7 – Dose Response Relationships LINEAR NON THRESHOLD • ASSUMES ANY AMOUNT OF RADIATION IS CAPABLE OF CAUSING A BIOLOGIC RESPONSE • THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE RADIATION DOSE AND BIOLOGIC RESPONSE IS CONSIDERED TO BE DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL

If at any time you have questions regarding radiation protection, do not hesitate to contact your institution’s Radiation Safety Officer (RSO)


DOSE • CINE - 2 m. R per frame (60 f/sec) • 400 mr per “look”

FLUORO RAD PROTECTION REVIEW QUESTIONS Handouts Return answers on scantron

• If at ½ foot from the radiation source the intensity of exposure is 240 m. R per hour and you remain at this location for 10 minutes, you then moved 2 feet away from the radiation source and remained there for 20 minutes? What is your total exposure?

The greatest contribution of unnecessary radiation exposure to the patient comes from the x-ray operator’s failure to

The greatest contribution of unnecessary radiation exposure to the patient comes from the x-ray operator’s failure to – collimate the x-ray beam to the area of clinical interest only – use proper gonadal shielding – use past screens and films – use proper exposure (technical factors

• . All of the following must be posted in areas where x-ray production machines • are utilized except: • each x-ray supervisor and operator permit • each certified radiologic technologist certificate and technologist fluoroscopy permit • Radiologic Health Department Form RH-2364, “Notice to Employee” • each physician’s license for the healing arts

– • During a 2 minute (fluoroscopy exposure time) routine upper GI series examination; a typical x-ray exposure to the patient is:

– For a fluoroscopic system equipped with and automatic brightness control • • (automatic exposure control) mechanism and where the x-ray tube is fixed below the table, moving the image intensifier way from the patient will:

– If at one foot from the radiation source the intensity of exposure is 240 • • milliroentgens (m. R) per hour and you remain at this location for 10 minutes you will receive and exposure of 40 milliroentgens (m. R). What source and remained there for 20 minutes?

• When the target to panel (tube to patient) distance is increased from 12 to 18 inches the ESE to patient is approximately: • a. Increased by 45 % • c. Decreased by 100 % • b. Increased by 25 % • d. Decreased by 45%

• At 1 foot from a source the output intensity is 300 m. R/hr and you were there for 20 minutes. • What is the intensity total if you moved 2 feet away and remained for an additional 40 minutes?

• Fluoro equipment made after 1974 with AEC shall not produce an exposure rate to the patient in excess of : • a. 1 R/ min c. 5 R/min • b. 10 R/min d. 20 R/min

– • • • You are fluoroscoping a patient using 80 kilivolt peak (kvp) technique. At this Kilovolt peak (kvp) the intensity of the x-ray beam at table top should not exceed how many roentgens per minute for each milliampere (ma) of current? 0. 2 roentgens per minute 1. 0 roentgens per minute 2. 2 roentgens per minute 5. 0 roentgens per minute

• The NCRP states that: the risk (to the embryo/fetus) is considered to be negligible at 5 rads or less when compared to the other risks of pregnancy , • and the risk of malformation is significantly increased above control levels only at doses above how many rads: a. 7 b. 10 c. 15 d. 25

• A “high radiation” area is any area , accessible to individuals, in which there exists radiation at such levels that an individual could receive in any one hour a dose to the whole body in excess of how many millirems ? • a. 5 b. 10 c. 50 d. 100

• Which of the following technical factors will create the highest skin entrance dose to the patient? • A. 80 kvp 300 ma. 5 s no filter B. 80 kvp 300 ma 1/10 s no filter • C. 80 kvp 1000 ma 1/20 s 2. 5 mm al eq. filter • D. 80 kvp 800 ma 1/60 sec. 05 mm al eq filter

• The exposure rate to a tech at 4 feet from the source is 240 m R/hr. What distance would be necessary to reduced the rate below 60 m. R/hr? • A. 1 foot • B. 6 feet • C. 2 feet • D. 9 feet

• If 85 kvp, 400 ma 0. 12 s = 150 m. R - what is the mr/mas? • A. 0. 32 • B. 3. 1 • C. 33. 1 • D. 17. 6

• Each time an x-ray beam scatters, its intensity at 1 meter from the scattering object is what fraction of its original intensity? • A. 1/10 • B. 1/100 • C. 1/500 • D. 1/1000

The California Radiation Control. Regulations define dose to mean radiation absorbed per unit mass. Whole-Body dose means exposure to which of the following: • I Major portions of the whole body • II Head and trunk • III Gonads • IV Lens of the eye • V Active blood-forming organs • VI Whole body excluding extremities a. I only b. I, III, IV & VI only c. I & IV only d. all of the above

• Which of the following gives the least patient exposure? • a. mirror optical system • b. vidicon TV camera • c plumicon TV camera • d. image orthicon

• During a CINE exam in which 35 mm film and a frame rate of 30 frames per second are utilized, what is the approximate skin exposure in roentgens/minutes? • a. 1 (given 2 mr/frame) • b. 2 – 5 • c. 5 – 10 • d. over 10

• It may be advisable to wear a second personal monitoring device if a worker is: • 1. performing routine radiological procedures • 2. pregnant • 3. a student • 4. performing special procedure • examinations

• • • All of the following must be posted in areas where x-ray producing machines are utilized EXCEPT: a each x-ray supervisor and operator permit b. each certified radiologic and operator permit c RHB – form “Notice to Employees” d. each physician’s license for the healing arts
1aa1ed74d712c676da287fdd073baf9d.ppt