6a4cc061a23a73b52b02d62ca9a9eed3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

 RFID Experts Group (REG) e. Waste: Environmental & Recycling Issues 27 October 2005 http: //www. autoid. org/presentations. htm
RFID Experts Group (REG) e. Waste: Environmental & Recycling Issues 27 October 2005 http: //www. autoid. org/presentations. htm
 Today’s REG Panel Craig K. Harmon, Q. E. D. Systems, REG Chair Ø Rich Vossel, Savi Technology Ø Angela Leith, U. S. Environmental Protection Agency Ø Clarke Mc. Allister, ADASA Ø
Today’s REG Panel Craig K. Harmon, Q. E. D. Systems, REG Chair Ø Rich Vossel, Savi Technology Ø Angela Leith, U. S. Environmental Protection Agency Ø Clarke Mc. Allister, ADASA Ø
 RFID Experts Group Craig K. Harmon, Chair Ø Bert Moore, Secretary Ø Ø Responsible for RFID Implementation Guidance
RFID Experts Group Craig K. Harmon, Chair Ø Bert Moore, Secretary Ø Ø Responsible for RFID Implementation Guidance
 RFID Experts Group Ø Formed in February 2004 to assist Do. D with RFID implementation Ø Ø Ø Current Proposed Guidelines for the Use of RFID Enabled Labels in Military Logistics: Recommendations for Revision of MIL-STD 129 Under the AIM Global umbrella in July 2004 International collaboration (1 st Intl Mtg - 9/15 -16) Ø Ø Europe Japan Korea China
RFID Experts Group Ø Formed in February 2004 to assist Do. D with RFID implementation Ø Ø Ø Current Proposed Guidelines for the Use of RFID Enabled Labels in Military Logistics: Recommendations for Revision of MIL-STD 129 Under the AIM Global umbrella in July 2004 International collaboration (1 st Intl Mtg - 9/15 -16) Ø Ø Europe Japan Korea China
 REG Terms of Reference (To. Rs) Ø Ø Ø Ø To. R 5 -I: Interrogator System Implementation & Operations To. R 5 -B: Back-up To. R 5 -L: Enabled Labels & Packaging To. R 5 -R: Recyclability To. R 5 -Q: Tag Quality To. R 5 -E: Education & Certification To. R 5 -G: Global Operation (Regulatory) To. R 5 -P: Privacy To. R 5 -F: Safety (Public Policy) To. R: 5 -C: Security To. R: 5 -T: Sensors and Transducers To. R 5 -S: Technology Selection To. R 5 -M: Software & Middleware
REG Terms of Reference (To. Rs) Ø Ø Ø Ø To. R 5 -I: Interrogator System Implementation & Operations To. R 5 -B: Back-up To. R 5 -L: Enabled Labels & Packaging To. R 5 -R: Recyclability To. R 5 -Q: Tag Quality To. R 5 -E: Education & Certification To. R 5 -G: Global Operation (Regulatory) To. R 5 -P: Privacy To. R 5 -F: Safety (Public Policy) To. R: 5 -C: Security To. R: 5 -T: Sensors and Transducers To. R 5 -S: Technology Selection To. R 5 -M: Software & Middleware
 ISO/IEC Implementation TRs Ø Ø Ø ISO/IEC 24729 -1, Information technology — Radio frequency identification for item management — Implementation guidelines – Part 1: RFID-enabled labels ISO/IEC 24729 -2, Information technology — Radio frequency identification for item management — Implementation guidelines – Part 2: Recyclability of RF tags ISO/IEC 24729 -3, Information technology — Radio frequency identification for item management — Implementation guidelines – Part 3: RFID interrogator/antenna installation
ISO/IEC Implementation TRs Ø Ø Ø ISO/IEC 24729 -1, Information technology — Radio frequency identification for item management — Implementation guidelines – Part 1: RFID-enabled labels ISO/IEC 24729 -2, Information technology — Radio frequency identification for item management — Implementation guidelines – Part 2: Recyclability of RF tags ISO/IEC 24729 -3, Information technology — Radio frequency identification for item management — Implementation guidelines – Part 3: RFID interrogator/antenna installation
 RF tags & recycling How RF tags can assist in recycling efforts Ø The effect of RF tags in the waste stream Ø
RF tags & recycling How RF tags can assist in recycling efforts Ø The effect of RF tags in the waste stream Ø
 Europe Restrictions on Hazardous Substances (Ro. HS ) & Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)
Europe Restrictions on Hazardous Substances (Ro. HS ) & Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)
 Ro. HS Ø Ø EU’s Directive 2002/95/EC Ro. HS legislation calls for the removal of lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyls, and polybrominated diphenyl ethers The National Safety Council estimates that 254 million home computers became obsolete in the U. S. between 1997 and 2003. Another 250 million are expected to become obsolete between 2004 and 2007. The Gartner Group, expects Americans to replace or junk 133, 000 PCs per day this year alone.
Ro. HS Ø Ø EU’s Directive 2002/95/EC Ro. HS legislation calls for the removal of lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyls, and polybrominated diphenyl ethers The National Safety Council estimates that 254 million home computers became obsolete in the U. S. between 1997 and 2003. Another 250 million are expected to become obsolete between 2004 and 2007. The Gartner Group, expects Americans to replace or junk 133, 000 PCs per day this year alone.
 Ø Ø The electronics industry must fully comply with the Ro. HS directive by July 1, 2006 Companies that aren’t in compliance with the Ro. HS directive by the deadline will not be able to sell their products into EU countries.
Ø Ø The electronics industry must fully comply with the Ro. HS directive by July 1, 2006 Companies that aren’t in compliance with the Ro. HS directive by the deadline will not be able to sell their products into EU countries.
 China Ø Ø Ø China’s Regulation for Pollution Control of Electronic Products (RPCEP) Ministry of Information Industry (MII) has been working on lead -free legislation, and its Article 11 requires manufacturers to restrict the use of the same substances targeted by Europe in certain consumer electronic products. Six Chinese ministries have contributed to writing the Management Regulation on the Recycling and Treatment of Disposed Appliances and Electronics Products regulation, including the State Environment Protection Administration (SEPA). Significantly, the Chinese directive will cover all electrical and electronic products produced in, or imported to, China. Noncompliance could mean heavy fines and/or losing the right to do business in China.
China Ø Ø Ø China’s Regulation for Pollution Control of Electronic Products (RPCEP) Ministry of Information Industry (MII) has been working on lead -free legislation, and its Article 11 requires manufacturers to restrict the use of the same substances targeted by Europe in certain consumer electronic products. Six Chinese ministries have contributed to writing the Management Regulation on the Recycling and Treatment of Disposed Appliances and Electronics Products regulation, including the State Environment Protection Administration (SEPA). Significantly, the Chinese directive will cover all electrical and electronic products produced in, or imported to, China. Noncompliance could mean heavy fines and/or losing the right to do business in China.
 Japan Ø Ø Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law governs the use and control of hazardous substances in products sold in the marketplace. Japan believes its environmental laws already comply with global directives, including the Ro. HS and WEEE, and isn’t expected to introduce any additional legislation. (In fact, Japanese manufacturers, particularly in the consumer electronics sector, started to place lead-free restrictions on its suppliers a few years ago. ) Japan already has several environmental laws in place, including the Promotion of Utilization of Recycled Resources, which regulates computers and other electronic products and rechargeable battery recycling. Most Japanese companies expect to be Ro. HS-compliant by March 1, 2006, four months before the EU-imposed deadline.
Japan Ø Ø Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law governs the use and control of hazardous substances in products sold in the marketplace. Japan believes its environmental laws already comply with global directives, including the Ro. HS and WEEE, and isn’t expected to introduce any additional legislation. (In fact, Japanese manufacturers, particularly in the consumer electronics sector, started to place lead-free restrictions on its suppliers a few years ago. ) Japan already has several environmental laws in place, including the Promotion of Utilization of Recycled Resources, which regulates computers and other electronic products and rechargeable battery recycling. Most Japanese companies expect to be Ro. HS-compliant by March 1, 2006, four months before the EU-imposed deadline.
 South Korea & Taiwan Ø South Korea and Taiwan are also working on Ro. HS-type legislation, and Mexico has proposed legislation with provisions similar to the Ro. HS
South Korea & Taiwan Ø South Korea and Taiwan are also working on Ro. HS-type legislation, and Mexico has proposed legislation with provisions similar to the Ro. HS
 Rich Vossel AIM REG Recycling To. R Ø Strategic Systems – Savi Technology Ø
Rich Vossel AIM REG Recycling To. R Ø Strategic Systems – Savi Technology Ø
 RFID & Recycling
RFID & Recycling
 RFID & Recycling Ø Ø How Big a Deal is RFID? Supply Chain Mandates Walmart, Do. D, Albertsons, Best Buy, Metro, Tesco Walmart - $125 Billion in US. ØAverage Case sells for $50 Ø 2. 5 Billion Tagged Case Ø Ø Albertson, Target, etc. – Guess 10 Billion Tagged Case Next - Guess 10 X Items per Case 100 Billion Tags
RFID & Recycling Ø Ø How Big a Deal is RFID? Supply Chain Mandates Walmart, Do. D, Albertsons, Best Buy, Metro, Tesco Walmart - $125 Billion in US. ØAverage Case sells for $50 Ø 2. 5 Billion Tagged Case Ø Ø Albertson, Target, etc. – Guess 10 Billion Tagged Case Next - Guess 10 X Items per Case 100 Billion Tags
 RFID & Recycling Ø Ø How Big a Deal is RFID? Healthcare Ø Ø Ø e. Pedigree – Rx Units of Sale 3 Billion Prescriptions per year Next - Medical Devices, Unit Dose, Instruments, Staff
RFID & Recycling Ø Ø How Big a Deal is RFID? Healthcare Ø Ø Ø e. Pedigree – Rx Units of Sale 3 Billion Prescriptions per year Next - Medical Devices, Unit Dose, Instruments, Staff
 RFID & Recycling Ø Where will all these tags end up? Ø Ø Supply Chain Mandates Ø Ø In someone's trash. . . because most are attached to PACKAGING Pallets and Cases e. Pedigree Ø Bottles, syringe vials, blister packs, tubes
RFID & Recycling Ø Where will all these tags end up? Ø Ø Supply Chain Mandates Ø Ø In someone's trash. . . because most are attached to PACKAGING Pallets and Cases e. Pedigree Ø Bottles, syringe vials, blister packs, tubes
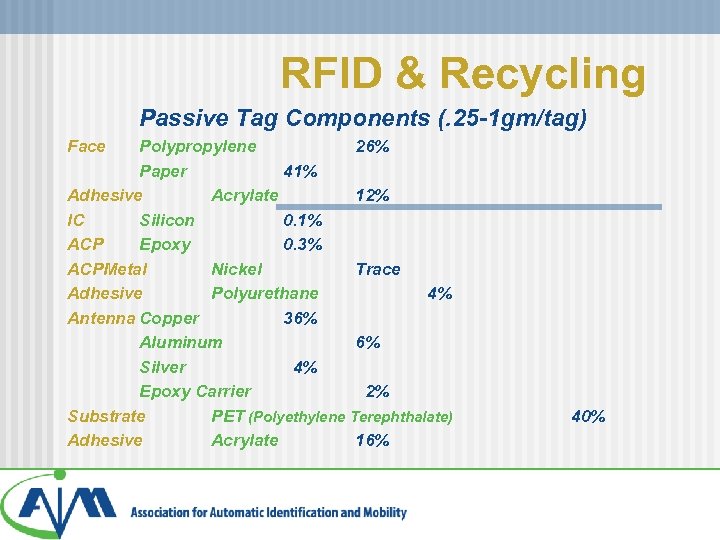 RFID & Recycling Passive Tag Components (. 25 -1 gm/tag) Face Polypropylene 26% Paper 41% Adhesive Acrylate 12% IC Silicon 0. 1% ACP Epoxy 0. 3% ACPMetal Nickel Trace Adhesive Polyurethane 4% Antenna Copper 36% Aluminum 6% Silver 4% Epoxy Carrier 2% Substrate PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) Adhesive Acrylate 16% 40%
RFID & Recycling Passive Tag Components (. 25 -1 gm/tag) Face Polypropylene 26% Paper 41% Adhesive Acrylate 12% IC Silicon 0. 1% ACP Epoxy 0. 3% ACPMetal Nickel Trace Adhesive Polyurethane 4% Antenna Copper 36% Aluminum 6% Silver 4% Epoxy Carrier 2% Substrate PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) Adhesive Acrylate 16% 40%
 RFID & Recycling What are the affected Waste Streams? Ø Ø Ø Corrugate, Carton Board Plastic Glass Steel Aluminum
RFID & Recycling What are the affected Waste Streams? Ø Ø Ø Corrugate, Carton Board Plastic Glass Steel Aluminum
 RFID & Recycling Ø Ø What are the Issues with RFID tags and Recycling? Tainting Existing Waste Streams ØRecycle Materials are Raw Materials ØPurity and Quality = Price Ø Regulations focusing on e. Wastes ØEnough Ø Ø Ø electronics to be e. Waste? Recycle Industry Game Changer Ownership Mark Automated Separation
RFID & Recycling Ø Ø What are the Issues with RFID tags and Recycling? Tainting Existing Waste Streams ØRecycle Materials are Raw Materials ØPurity and Quality = Price Ø Regulations focusing on e. Wastes ØEnough Ø Ø Ø electronics to be e. Waste? Recycle Industry Game Changer Ownership Mark Automated Separation
 RFID & Recycling What are the issues? ØCorrugate, Carton Board ØClogging Filters, Residual Silver in Cellulose ØPlastic ØDegrading all recycle plastic to park benches ØGlass ØSilicon stones start cracks, Cu fouls furnaces ØSteel ØCu/Al degrade the quality of scrap metal ØAluminum ØLittle concern, especially with Al antenna
RFID & Recycling What are the issues? ØCorrugate, Carton Board ØClogging Filters, Residual Silver in Cellulose ØPlastic ØDegrading all recycle plastic to park benches ØGlass ØSilicon stones start cracks, Cu fouls furnaces ØSteel ØCu/Al degrade the quality of scrap metal ØAluminum ØLittle concern, especially with Al antenna
 RFID & Recycling What does the RFID Industry want relative to Recycling? Ø Create no negative impact on present recycling Ø Provide recycling improvement if possible Ø How are some in the RFID Industry achieving this? ØUse waste stream subject matter experts – trade association ØWork a waste stream before tags are prolific ØKeep the regulators informed
RFID & Recycling What does the RFID Industry want relative to Recycling? Ø Create no negative impact on present recycling Ø Provide recycling improvement if possible Ø How are some in the RFID Industry achieving this? ØUse waste stream subject matter experts – trade association ØWork a waste stream before tags are prolific ØKeep the regulators informed
 RFID & Recycling 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Process Being Practiced by AIM Theoretical Assessment of affect on present recycling processes Pilot testing that present/proposed processes are sufficient. Draft guidelines for tagging and waste recycle entities. Submit to a knowledgeable 3 rd party to validate Submit the 3 rd Party reviewed guidelines to the EPA for approval Issuance of guidelines to the RFID tagging community Have some entity certify that particular RFID tags meet the guidelines Ask the Fiber Box Association for their study as the best example
RFID & Recycling 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Process Being Practiced by AIM Theoretical Assessment of affect on present recycling processes Pilot testing that present/proposed processes are sufficient. Draft guidelines for tagging and waste recycle entities. Submit to a knowledgeable 3 rd party to validate Submit the 3 rd Party reviewed guidelines to the EPA for approval Issuance of guidelines to the RFID tagging community Have some entity certify that particular RFID tags meet the guidelines Ask the Fiber Box Association for their study as the best example
 RFID & Recycling Ø Ø Are RFID Components e. Waste? Readers and Printers Are e. Waste Ø Ø Ø Local Disposal Regulations WEEE - Ro. HS Passive Tags Generally Are Not e. Waste Ø Local Disposal Regulations § direct landfill § thermal recycling with energy and constituent recovery, landfill ash § mechanical/chemical separation for constituent reuse Ø WEEE
RFID & Recycling Ø Ø Are RFID Components e. Waste? Readers and Printers Are e. Waste Ø Ø Ø Local Disposal Regulations WEEE - Ro. HS Passive Tags Generally Are Not e. Waste Ø Local Disposal Regulations § direct landfill § thermal recycling with energy and constituent recovery, landfill ash § mechanical/chemical separation for constituent reuse Ø WEEE
 RFID & Recycling Ø Can RFID Tagging Improve Recycling? ØMixed Consumer Waste Separation ØWaste Stream Identifier Ø Ø Ø Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive in the European Union (WEEE) Restriction of Hazardous Substances (addendum to WEEE) (Ro. HS) End of Life Vehicle (ELV) in the European Union Home Electronics Recycling Law (HERL) in Japan Extended Producer Responsibility Program(EPRP) in Korea
RFID & Recycling Ø Can RFID Tagging Improve Recycling? ØMixed Consumer Waste Separation ØWaste Stream Identifier Ø Ø Ø Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive in the European Union (WEEE) Restriction of Hazardous Substances (addendum to WEEE) (Ro. HS) End of Life Vehicle (ELV) in the European Union Home Electronics Recycling Law (HERL) in Japan Extended Producer Responsibility Program(EPRP) in Korea
 Angela Leith Ø U. S. Environmental Protection Agency
Angela Leith Ø U. S. Environmental Protection Agency
 Clarke Mc. Allister ADASA Ø RFID Tags in OCC* Ø The Future of OCC Recycling Ø Future Value of Tagged OCC Ø Action Items Ø *OCC = Old Corrugated Cartons
Clarke Mc. Allister ADASA Ø RFID Tags in OCC* Ø The Future of OCC Recycling Ø Future Value of Tagged OCC Ø Action Items Ø *OCC = Old Corrugated Cartons
 Old Corrugated Cartons (OCC) 1. Internationally traded commodity. 2. Worth $40 to $60 per bale for the fiber. 3. Worth an additional amount for the RFID tags. OCC bales contain up to ~1000 tags.
Old Corrugated Cartons (OCC) 1. Internationally traded commodity. 2. Worth $40 to $60 per bale for the fiber. 3. Worth an additional amount for the RFID tags. OCC bales contain up to ~1000 tags.
 The Future of OCC Recycling Ø Problem: Billions of valuable RFID tags will be wasted: Ø Ø Ø Filter Screens Sludge (Solid Waste) Effluent (Liquids) Cumulatively into paper products Solution: A fifth vector – Recycled RFID Tags
The Future of OCC Recycling Ø Problem: Billions of valuable RFID tags will be wasted: Ø Ø Ø Filter Screens Sludge (Solid Waste) Effluent (Liquids) Cumulatively into paper products Solution: A fifth vector – Recycled RFID Tags
 Ten-Year OCC Futures Model Conclusion: The total value mined from OCC bales will increase for ADASA-licensed paper mills.
Ten-Year OCC Futures Model Conclusion: The total value mined from OCC bales will increase for ADASA-licensed paper mills.
 Realizing the Benefits of Tag Reuse Ø Ø Ø You don’t have to waste billions of RFID tags Consider buying recycled RFID tags Provide tag passwords to authorized tag recyclers
Realizing the Benefits of Tag Reuse Ø Ø Ø You don’t have to waste billions of RFID tags Consider buying recycled RFID tags Provide tag passwords to authorized tag recyclers
 Questions?
Questions?
 Thank You!
Thank You!



