2ac2823cff6fcbd6a07d8c8ef0ab6236.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Revolutionizing the Delivery of Quality Healthcare through Automation AIDC 100 October 15, 2008 Manuel Lowenhaupt, MD Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
Revolutionizing the Delivery of Quality Healthcare through Automation AIDC 100 October 15, 2008 Manuel Lowenhaupt, MD Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
 “Even small healthcare institutions are complex, barely manageable places… large healthcare institutions may be the most complex organizations in human history. ” Peter Drucker Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
“Even small healthcare institutions are complex, barely manageable places… large healthcare institutions may be the most complex organizations in human history. ” Peter Drucker Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
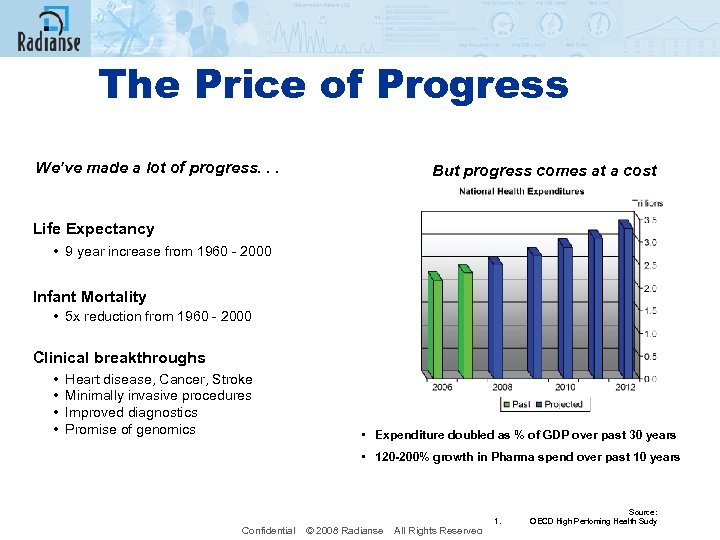 The Price of Progress We’ve made a lot of progress. . . But progress comes at a cost Life Expectancy • 9 year increase from 1960 - 2000 Infant Mortality • 5 x reduction from 1960 - 2000 Clinical breakthroughs • Heart disease, Cancer, Stroke • Minimally invasive procedures • Improved diagnostics • Promise of genomics • Expenditure doubled as % of GDP over past 30 years • 120 -200% growth in Pharma spend over past 10 years Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved 1. Source: OECD High Perfoming Health Sudy
The Price of Progress We’ve made a lot of progress. . . But progress comes at a cost Life Expectancy • 9 year increase from 1960 - 2000 Infant Mortality • 5 x reduction from 1960 - 2000 Clinical breakthroughs • Heart disease, Cancer, Stroke • Minimally invasive procedures • Improved diagnostics • Promise of genomics • Expenditure doubled as % of GDP over past 30 years • 120 -200% growth in Pharma spend over past 10 years Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved 1. Source: OECD High Perfoming Health Sudy
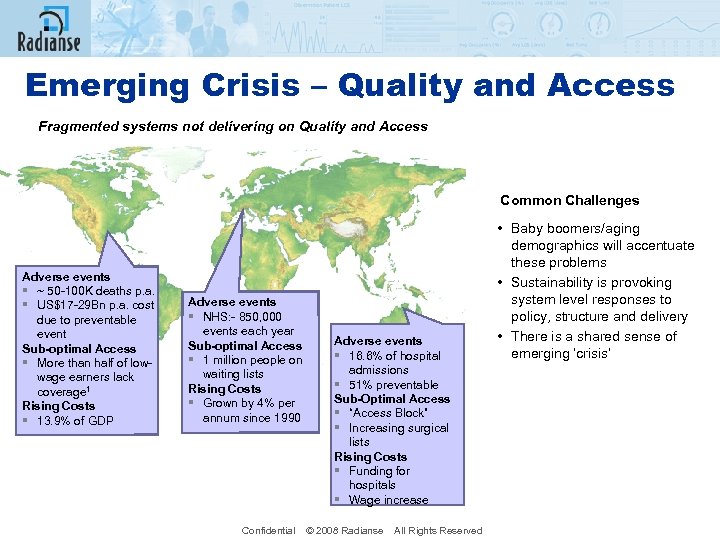 Emerging Crisis – Quality and Access Fragmented systems not delivering on Quality and Access Common Challenges Adverse events § ~ 50 -100 K deaths p. a. § US$17 -29 Bn p. a. cost due to preventable event Sub-optimal Access § More than half of lowwage earners lack coverage 1 Rising Costs § 13. 9% of GDP Adverse events § NHS: - 850, 000 events each year Sub-optimal Access § 1 million people on waiting lists Rising Costs § Grown by 4% per annum since 1990 Adverse events § 16. 6% of hospital admissions § 51% preventable Sub-Optimal Access § “Access Block” § Increasing surgical lists Rising Costs § Funding for hospitals § Wage increase Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved • Baby boomers/aging demographics will accentuate these problems • Sustainability is provoking system level responses to policy, structure and delivery • There is a shared sense of emerging ‘crisis’
Emerging Crisis – Quality and Access Fragmented systems not delivering on Quality and Access Common Challenges Adverse events § ~ 50 -100 K deaths p. a. § US$17 -29 Bn p. a. cost due to preventable event Sub-optimal Access § More than half of lowwage earners lack coverage 1 Rising Costs § 13. 9% of GDP Adverse events § NHS: - 850, 000 events each year Sub-optimal Access § 1 million people on waiting lists Rising Costs § Grown by 4% per annum since 1990 Adverse events § 16. 6% of hospital admissions § 51% preventable Sub-Optimal Access § “Access Block” § Increasing surgical lists Rising Costs § Funding for hospitals § Wage increase Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved • Baby boomers/aging demographics will accentuate these problems • Sustainability is provoking system level responses to policy, structure and delivery • There is a shared sense of emerging ‘crisis’
 Identification of Leading Performance Provider Trends Trend Hypotheses High Level Trends / Characteristics of the High Performing Provider Market A. Evolution of Science, Medicine and Technology to Improve Treatment and Access B. Increasing Influence of Consumers/Patients C. Initiation of Broad-Based Health System Reform D. Shifting Care Delivery Models E. Improved Patient Flow / Demand Management F. Evolving Roles and Skills of Clinicians G. Effective Leadership and Culture Change H. Increase Investment and Effective Utilisation of Clinical IT I. Consolidation /Outsourcing of Provider Back-Office J. Improved Visibility, Reporting and Management of KPIs K. Increased Private / Public Sector Collaboration Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
Identification of Leading Performance Provider Trends Trend Hypotheses High Level Trends / Characteristics of the High Performing Provider Market A. Evolution of Science, Medicine and Technology to Improve Treatment and Access B. Increasing Influence of Consumers/Patients C. Initiation of Broad-Based Health System Reform D. Shifting Care Delivery Models E. Improved Patient Flow / Demand Management F. Evolving Roles and Skills of Clinicians G. Effective Leadership and Culture Change H. Increase Investment and Effective Utilisation of Clinical IT I. Consolidation /Outsourcing of Provider Back-Office J. Improved Visibility, Reporting and Management of KPIs K. Increased Private / Public Sector Collaboration Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
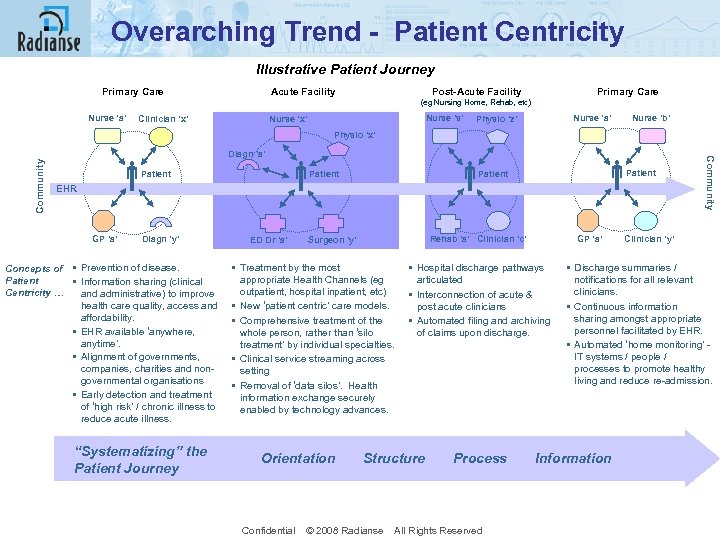 Overarching Trend - Patient Centricity Illustrative Patient Journey Primary Care Acute Facility Post-Acute Facility Primary Care (eg Nursing Home, Rehab, etc) Nurse ‘a’ Clinician ‘x’ Nurse ‘s’ Nurse ‘x’ Nurse ‘a’ Physio ‘z’ Nurse ‘b’ Patient EHR GP ‘a’ Diagn ‘y’ Concepts of • Prevention of disease. Patient • Information sharing (clinical Centricity … and administrative) to improve health care quality, access and affordability. • EHR available ‘anywhere, anytime’. • Alignment of governments, companies, charities and nongovernmental organisations • Early detection and treatment of ‘high risk’ / chronic illness to reduce acute illness. “Systematizing” the Patient Journey Diagn ‘a’ GP ‘a’ Rehab ‘a’ Clinician ‘c’ Surgeon ‘y’ • Treatment by the most appropriate Health Channels (eg outpatient, hospital inpatient, etc) • New ‘patient centric’ care models. • Comprehensive treatment of the whole person, rather than ‘silo treatment’ by individual specialties. • Clinical service streaming across setting • Removal of ‘data silos’. Health information exchange securely enabled by technology advances. Orientation Patient ED Dr ‘a’ • Hospital discharge pathways articulated • Interconnection of acute & post acute clinicians • Automated filing and archiving of claims upon discharge. Structure Process Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved Community Physio ‘x’ Clinician ‘y’ • Discharge summaries / notifications for all relevant clinicians. • Continuous information sharing amongst appropriate personnel facilitated by EHR. • Automated ‘home monitoring’ - IT systems / people / processes to promote healthy living and reduce re-admission. Information
Overarching Trend - Patient Centricity Illustrative Patient Journey Primary Care Acute Facility Post-Acute Facility Primary Care (eg Nursing Home, Rehab, etc) Nurse ‘a’ Clinician ‘x’ Nurse ‘s’ Nurse ‘x’ Nurse ‘a’ Physio ‘z’ Nurse ‘b’ Patient EHR GP ‘a’ Diagn ‘y’ Concepts of • Prevention of disease. Patient • Information sharing (clinical Centricity … and administrative) to improve health care quality, access and affordability. • EHR available ‘anywhere, anytime’. • Alignment of governments, companies, charities and nongovernmental organisations • Early detection and treatment of ‘high risk’ / chronic illness to reduce acute illness. “Systematizing” the Patient Journey Diagn ‘a’ GP ‘a’ Rehab ‘a’ Clinician ‘c’ Surgeon ‘y’ • Treatment by the most appropriate Health Channels (eg outpatient, hospital inpatient, etc) • New ‘patient centric’ care models. • Comprehensive treatment of the whole person, rather than ‘silo treatment’ by individual specialties. • Clinical service streaming across setting • Removal of ‘data silos’. Health information exchange securely enabled by technology advances. Orientation Patient ED Dr ‘a’ • Hospital discharge pathways articulated • Interconnection of acute & post acute clinicians • Automated filing and archiving of claims upon discharge. Structure Process Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved Community Physio ‘x’ Clinician ‘y’ • Discharge summaries / notifications for all relevant clinicians. • Continuous information sharing amongst appropriate personnel facilitated by EHR. • Automated ‘home monitoring’ - IT systems / people / processes to promote healthy living and reduce re-admission. Information
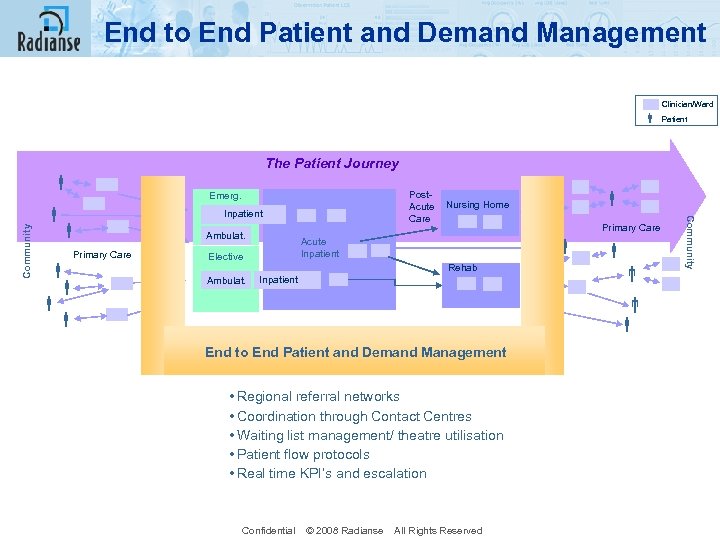 End to End Patient and Demand Management Clinician/Ward Patient The Patient Journey Post- Acute Nursing Home Care Emerg. Primary Care Inpatient Ambulat. Acute Inpatient Elective Primary Care Rehab Ambulat. Inpatient End to End Patient and Demand Management • Regional referral networks • Coordination through Contact Centres • Waiting list management/ theatre utilisation • Patient flow protocols • Real time KPI’s and escalation Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved Community
End to End Patient and Demand Management Clinician/Ward Patient The Patient Journey Post- Acute Nursing Home Care Emerg. Primary Care Inpatient Ambulat. Acute Inpatient Elective Primary Care Rehab Ambulat. Inpatient End to End Patient and Demand Management • Regional referral networks • Coordination through Contact Centres • Waiting list management/ theatre utilisation • Patient flow protocols • Real time KPI’s and escalation Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved Community
 Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
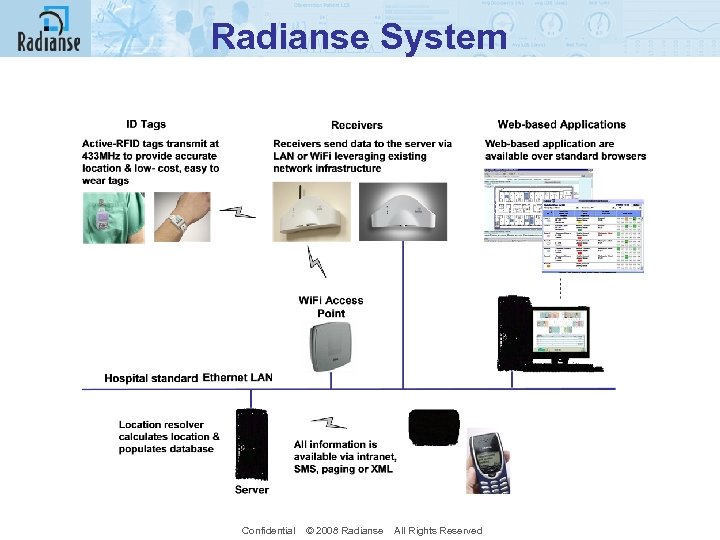 Radianse System Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
Radianse System Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
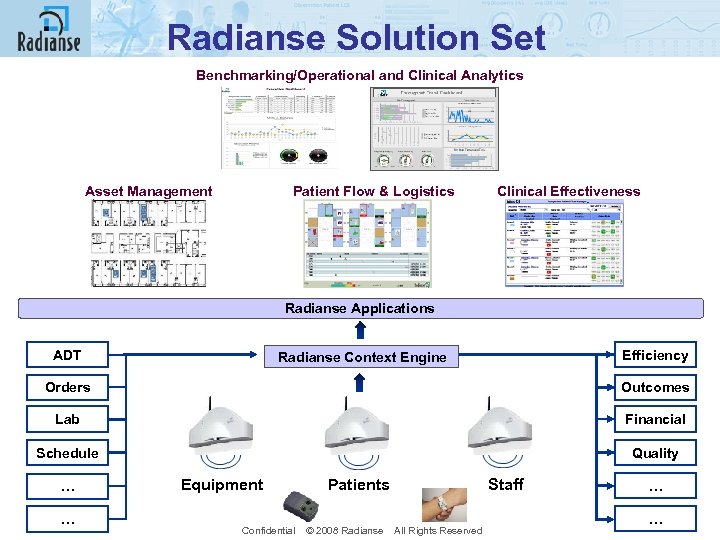 Radianse Solution Set Benchmarking/Operational and Clinical Analytics Asset Management Patient Flow & Logistics Clinical Effectiveness Radianse Applications ADT Efficiency Radianse Context Engine Orders Outcomes Lab Financial Schedule Quality … … Equipment Patients Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved Staff … …
Radianse Solution Set Benchmarking/Operational and Clinical Analytics Asset Management Patient Flow & Logistics Clinical Effectiveness Radianse Applications ADT Efficiency Radianse Context Engine Orders Outcomes Lab Financial Schedule Quality … … Equipment Patients Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved Staff … …
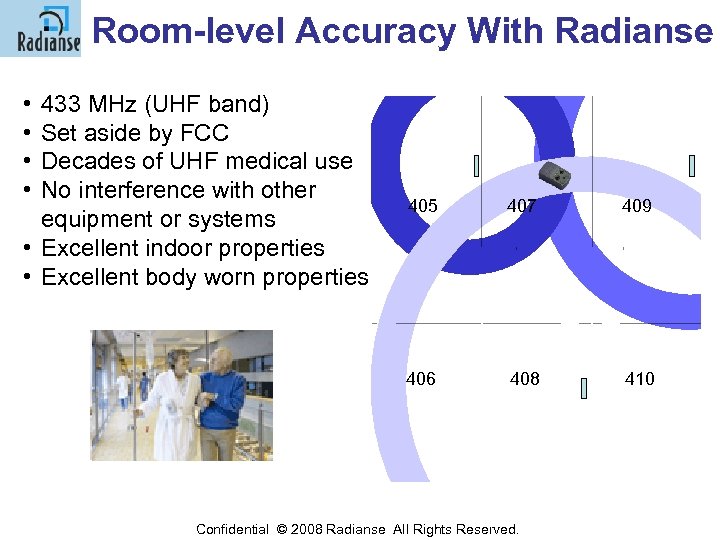 Room-level Accuracy With Radianse • • 433 MHz (UHF band) Set aside by FCC Decades of UHF medical use No interference with other 401 403 405 407 409 equipment or systems • Excellent indoor properties • Excellent body worn properties 402 404 406 408 410 Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved. Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
Room-level Accuracy With Radianse • • 433 MHz (UHF band) Set aside by FCC Decades of UHF medical use No interference with other 401 403 405 407 409 equipment or systems • Excellent indoor properties • Excellent body worn properties 402 404 406 408 410 Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved. Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
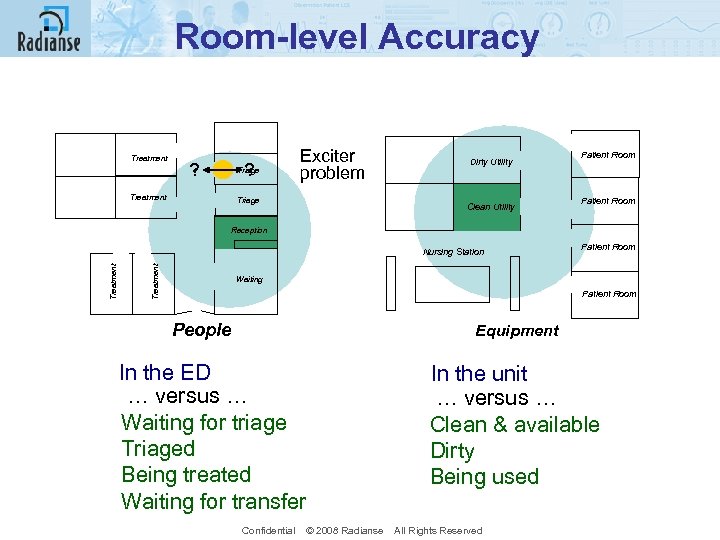 Room-level Accuracy Treatment ? Triage Exciter problem Triage ED Dirty Utility Clean Utility Treatment Patient Room Reception Nursing Station Treatment Patient Room UNIT Patient Room Waiting Patient Room People Equipment In the ED … versus … Waiting for triage Triaged Being treated Waiting for transfer In the unit … versus … Clean & available Dirty Being used Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
Room-level Accuracy Treatment ? Triage Exciter problem Triage ED Dirty Utility Clean Utility Treatment Patient Room Reception Nursing Station Treatment Patient Room UNIT Patient Room Waiting Patient Room People Equipment In the ED … versus … Waiting for triage Triaged Being treated Waiting for transfer In the unit … versus … Clean & available Dirty Being used Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
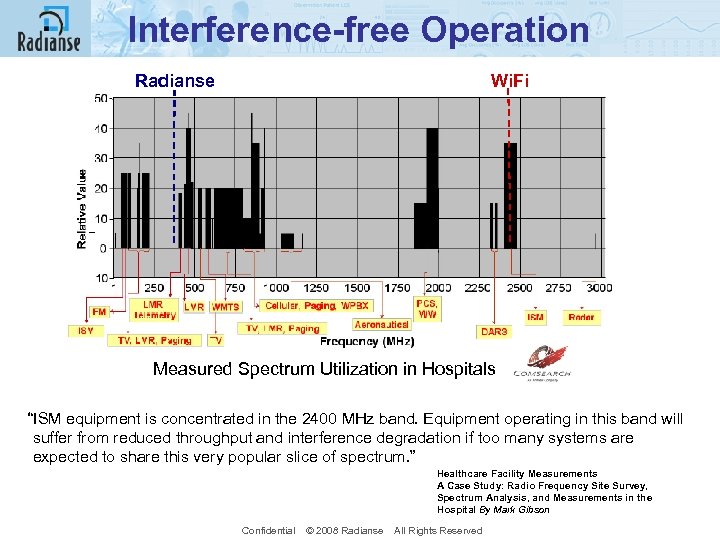 Interference-free Operation Radianse Wi. Fi Measured Spectrum Utilization in Hospitals “ISM equipment is concentrated in the 2400 MHz band. Equipment operating in this band will suffer from reduced throughput and interference degradation if too many systems are expected to share this very popular slice of spectrum. ” Healthcare Facility Measurements A Case Study: Radio Frequency Site Survey, Spectrum Analysis, and Measurements in the Hospital By Mark Gibson Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
Interference-free Operation Radianse Wi. Fi Measured Spectrum Utilization in Hospitals “ISM equipment is concentrated in the 2400 MHz band. Equipment operating in this band will suffer from reduced throughput and interference degradation if too many systems are expected to share this very popular slice of spectrum. ” Healthcare Facility Measurements A Case Study: Radio Frequency Site Survey, Spectrum Analysis, and Measurements in the Hospital By Mark Gibson Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
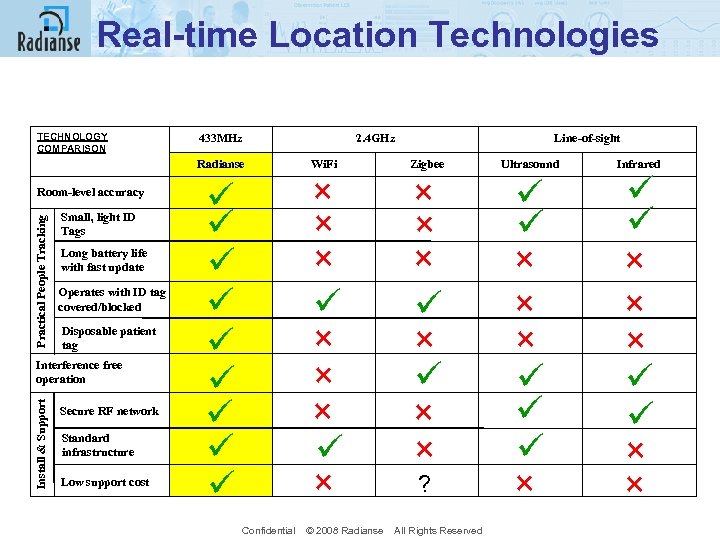 Real-time Location Technologies TECHNOLOGY COMPARISON 433 MHz 2. 4 GHz Radianse Small, light ID Tags Long battery life with fast update Operates with ID tag covered/blocked Disposable patient tag Interference free operation Install & Support Practical People Tracking Room-level accuracy Secure RF network Standard infrastructure Low support cost ü ü ü ü ü Wi. Fi × × × ü × Line-of-sight Zigbee × × × ü × × ? Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved Ultrasound ü ü × × × ü ü ü × Infrared ü ü × × × ü ü × ×
Real-time Location Technologies TECHNOLOGY COMPARISON 433 MHz 2. 4 GHz Radianse Small, light ID Tags Long battery life with fast update Operates with ID tag covered/blocked Disposable patient tag Interference free operation Install & Support Practical People Tracking Room-level accuracy Secure RF network Standard infrastructure Low support cost ü ü ü ü ü Wi. Fi × × × ü × Line-of-sight Zigbee × × × ü × × ? Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved Ultrasound ü ü × × × ü ü ü × Infrared ü ü × × × ü ü × ×
 Find Application Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
Find Application Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
 Patient Flow Application Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
Patient Flow Application Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
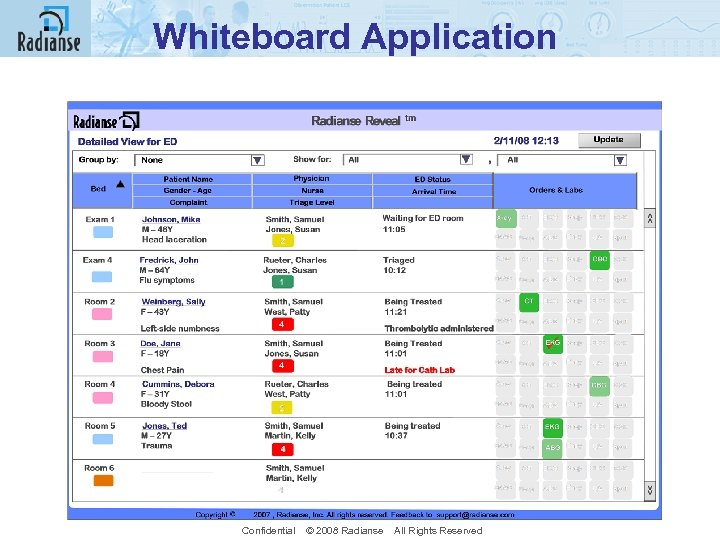 Whiteboard Application Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
Whiteboard Application Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
 Clinical Effectiveness Radianse managed workflow Target door-to-balloon time = n minutes Patient arrives with chest pain Registered & paired with Radianse ID tag Arrival time and patient location captured MI protocol initiated, alerts cath lab team Assets for cath lab are automatically inventoried Doctor located & alerted to cath lab Auto match of right patient, equipment, staff & device made in cath lab Interventionist performs procedure Family-centric view of progress & timeliness of care Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved Time in minutes
Clinical Effectiveness Radianse managed workflow Target door-to-balloon time = n minutes Patient arrives with chest pain Registered & paired with Radianse ID tag Arrival time and patient location captured MI protocol initiated, alerts cath lab team Assets for cath lab are automatically inventoried Doctor located & alerted to cath lab Auto match of right patient, equipment, staff & device made in cath lab Interventionist performs procedure Family-centric view of progress & timeliness of care Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved Time in minutes
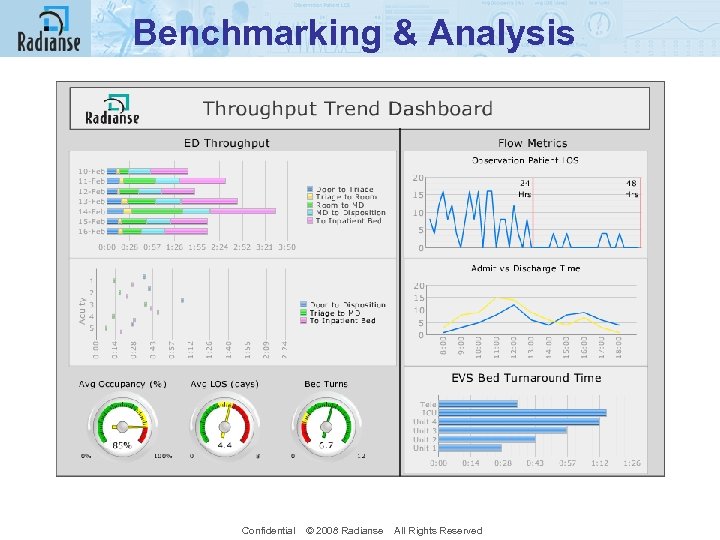 Benchmarking & Analysis Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
Benchmarking & Analysis Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
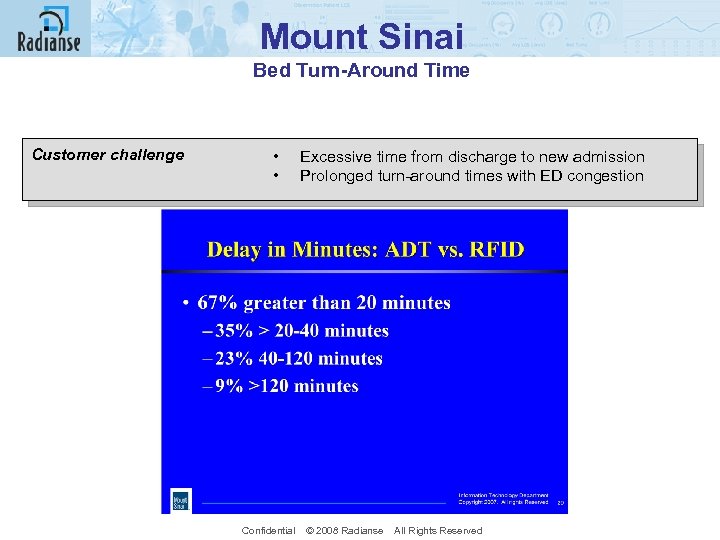 Mount Sinai Bed Turn-Around Time Customer challenge • • Excessive time from discharge to new admission Prolonged turn-around times with ED congestion Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
Mount Sinai Bed Turn-Around Time Customer challenge • • Excessive time from discharge to new admission Prolonged turn-around times with ED congestion Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
 Providence Hospital Bed Management and Turnover Customer challenge • • ED diversions, wait times, left-without-being-seen Multiple phone calls to coordinate patient placement • Before (measured): Weekday (mode): 45 min Weekend (mode): 60 min Range: 15 -> 525 min • Tracking towards: Weekday (mode): 35 min (20%) Weekend (mode): 45 min (25%) Range: 15 -> 500 min Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
Providence Hospital Bed Management and Turnover Customer challenge • • ED diversions, wait times, left-without-being-seen Multiple phone calls to coordinate patient placement • Before (measured): Weekday (mode): 45 min Weekend (mode): 60 min Range: 15 -> 525 min • Tracking towards: Weekday (mode): 35 min (20%) Weekend (mode): 45 min (25%) Range: 15 -> 500 min Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
 Massachusetts General Hospital Complex Care Delivery Customer challenge • • • Difficult to monitor, complex care processes Provider information overload Limited resources leading to delays in care • Real-time tracking of equipment, patients and staff – “OR of the Future” • 40% improvement in OR throughput • Billing for Anesthesia time • “Zone of Patient Safety” – “Office of the Future” – Performance Improvement – workflow studies • Stroke pathway adherence • Needle localization for breast-biopsy Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
Massachusetts General Hospital Complex Care Delivery Customer challenge • • • Difficult to monitor, complex care processes Provider information overload Limited resources leading to delays in care • Real-time tracking of equipment, patients and staff – “OR of the Future” • 40% improvement in OR throughput • Billing for Anesthesia time • “Zone of Patient Safety” – “Office of the Future” – Performance Improvement – workflow studies • Stroke pathway adherence • Needle localization for breast-biopsy Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
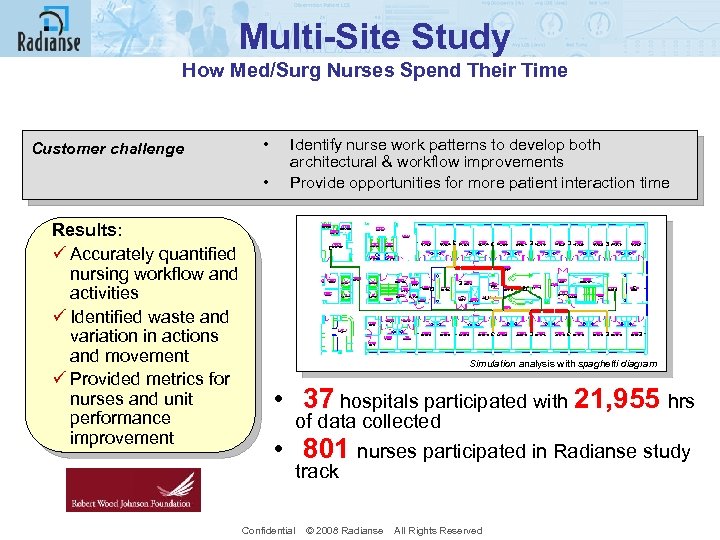 Multi-Site Study How Med/Surg Nurses Spend Their Time • Customer challenge • Results: ü Accurately quantified nursing workflow and activities ü Identified waste and variation in actions and movement ü Provided metrics for nurses and unit performance improvement Identify nurse work patterns to develop both architectural & workflow improvements Provide opportunities for more patient interaction time Simulation analysis with spaghetti diagram • 37 hospitals participated with 21, 955 hrs of data collected • 801 nurses participated in Radianse study track Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
Multi-Site Study How Med/Surg Nurses Spend Their Time • Customer challenge • Results: ü Accurately quantified nursing workflow and activities ü Identified waste and variation in actions and movement ü Provided metrics for nurses and unit performance improvement Identify nurse work patterns to develop both architectural & workflow improvements Provide opportunities for more patient interaction time Simulation analysis with spaghetti diagram • 37 hospitals participated with 21, 955 hrs of data collected • 801 nurses participated in Radianse study track Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
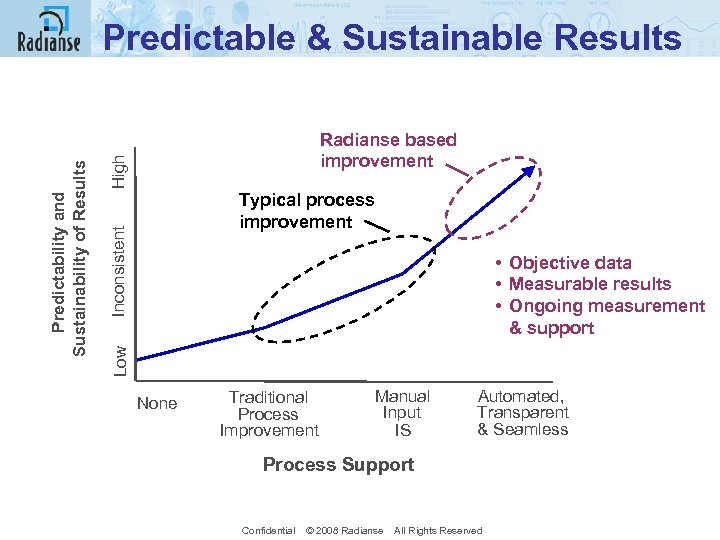 High Radianse based improvement Inconsistent Typical process improvement • Objective data • Measurable results • Ongoing measurement & support Low Predictability and Sustainability of Results Predictable & Sustainable Results None Traditional Process Improvement Manual Input IS Automated, Transparent & Seamless Process Support Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved
High Radianse based improvement Inconsistent Typical process improvement • Objective data • Measurable results • Ongoing measurement & support Low Predictability and Sustainability of Results Predictable & Sustainable Results None Traditional Process Improvement Manual Input IS Automated, Transparent & Seamless Process Support Confidential © 2008 Radianse All Rights Reserved


