427f39e3ef363e458171b77aa69fa010.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49

REVIEW FOR EXAM 3 BUS 3500 - Abdou Illia, Spring 2009 1

The Internet and e. Business Part 1 2

Brief history of the Internet Make sure you know what DNS is used for. 1969 The Defense Advanced Research Projects developed ARPANET, the precursor of the Internet 1971 Ray Tomlison invents e-mail 1979 USENET newsgroups created at Duke University and the University of North Carolina 1984 Domain Name System (DNS) established 1991 Tim Berners-Lee creates the World Wide Web 1994 First online shopping mall, first spam email, first pizza ordered online, first advertisement banner 2000 A major denial of service attack brings down websites such as Yahoo!, Amazon. com, and e. Bay 2002 Denial of service attack knocks out 8/15 root DNS 3 servers

Accessing the Internet (www) Web Browser Network Packet Webserver Software Packet Router User PC needs: - Workstation Operating System - TCP/IP - Web browser (e. g. Internet Explorer) - Internet access (e. g. thru an ISP) - IP Address (e. g. 128. 150. 9) Webserver needs: - Network (or Server) Operating System - TCP/IP - Domain name (e. g. eiu. edu) - Internet access 4 - IP Address (e. g. 139. 67. 8. 3)

Internet applications/services p E-Mail p File transfers p Instant messaging (IM) p Newsgroups p Streaming audio and video p Internet telephony p World Wide Web (WWW) p Portal 5

Portal p Portal n Web site that offers a broad array of resources and services; such as email p newsgroup p Serach engines p Online shopping malls p n Example: yahoo!, msn, aol 6

Summary Questions Book 1) (a) Name some Internet applications/services (b) What is Instant Messaging? (c) What is a newsgroup? 2) (a) What does a user PC needs for accessing the World Wide Web? (b) What is needed on the webserver side? Notes 9, 14, 15 7 3) Name some Internet connection options available for residential users and businesses. 5 -6 4) What is meant by podcasting? 16 5) (a) What is an intranet? (b) an extranet? (c) a portal Refers to the slide # in class posted notes 18, 19 7

Information Systems for Business Integration: ERP Systems Part 2 8
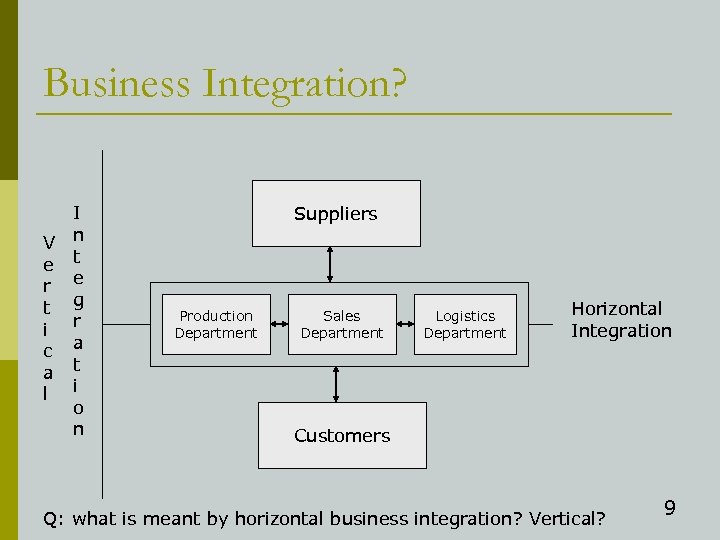
Business Integration? I V n e t r e t g i r c a a t l i o n Suppliers Production Department Sales Department Logistics Department Horizontal Integration Customers Q: what is meant by horizontal business integration? Vertical? 9

Systems for Horizontal Integration p Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems n integrate all the internal processes through a common information system (or an integrated set of info systems) Production Department Process 1 Warehousing Process 2 Process 1 Sales Department Process 1 Process 2 Common Database Marketing Department Process 1 Process 2 Logistics Department Process 1 Process 2 Accounting Department Process 2 Process 1 ERP system Process 2 10
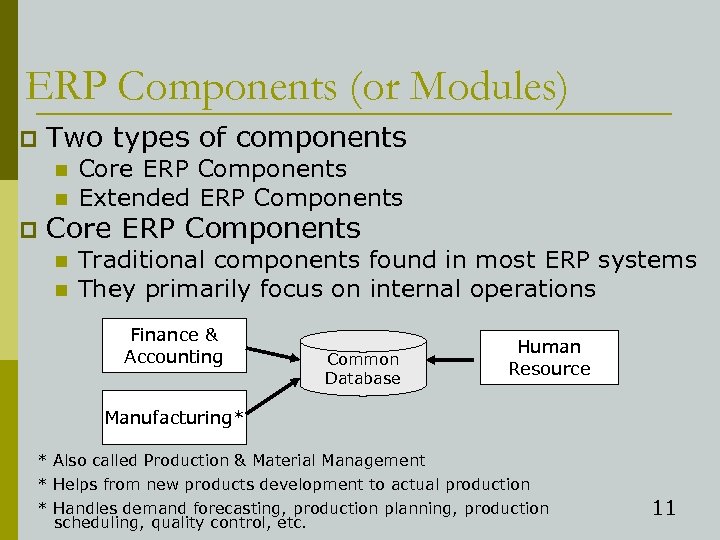
ERP Components (or Modules) p Two types of components n n p Core ERP Components Extended ERP Components Core ERP Components n n Traditional components found in most ERP systems They primarily focus on internal operations Finance & Accounting Common Database Human Resource Manufacturing* * Also called Production & Material Management * Helps from new products development to actual production * Handles demand forecasting, production planning, production scheduling, quality control, etc. 11

ERP Components (or Modules) p Extended ERP Components n n Extra components that might be included They primarily focus on external operations Customer Relationship Management Supply Chain Management Business Intelligence 1 Common Database E-Business 2 1 Provide information that help users in decision-making 1 Collects info used throughout the organization, organize it, and uses analytical tools to help decision-making process 2 Includes e-logistics (managing transportation & storage of goods over the Internet) and e-procurement (B 2 B purchase & sale of supplies & services over the Internet) 12

ERP Components (or Modules) p ERP mainly used by medium and large businesses n n Average lifetime cost: $15 Million (2003 surveys) Implementation process: up to 5 years The largest vendors worldwide in 2005 according to Gartner Dataquest # Vendor Revenue (million $) Market share (%) 1 SAP 4726 28. 7 2 Oracle Applications* 1674 10. 2 3 The Sage Group 1221 7. 4 4 Microsoft Dynamics 616 3. 7 5 SSA Global Technologies 464 2. 8 * In January 2005, Oracle bought People. Soft the 3 rd player until then. 13

Factors in ERP System Success Active support of upper management p Having the best people on the implementation team p Managing the time line well p User involvement in the planning and implementing ERP systems p 14

Summary Questions Book 1) What is the difference between Horizontal integration and Vertical integration? What could be the consequences of a bad horizontal integration? 2) What kind of information system is typically used by organizations for horizontal integration? Notes 5, 6 7 3) What are the core modules found in ERP systems? . ? 10 4) What does the Manufacturing ERP component allow? Name some of the activities it handles 10 5) Name the major three ERP software vendors 12 6) What are the success factors of ERP implementation? 14 Refers to the slide # in class posted notes 15

Review Questions p Make sure you can answer the following questions about ERP: n Chapter 10 Review Questions available in the Notes’ section of the course web site. 16

Information Systems for Business Integration: EDI, SCM, CRM Systems Part 2 (Cont. ) 17

Supply Chain Management SCM 18
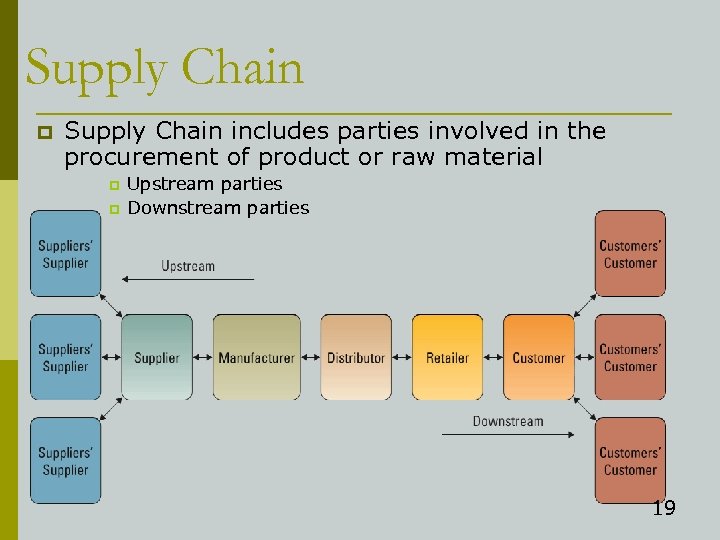
Supply Chain p Supply Chain includes parties involved in the procurement of product or raw material p p Upstream parties Downstream parties 19

Supply Chain Management SCM p p SCM implies the management of information flow between a company and upstream and downstream parties of the supply chain Which of the following is NOT a potential benefit of SCM? a) It helps avoid shortage of raw material b) It could shorten the time for delivering finished products to distributors c) It could help organizations better forecast their production of goods and services d) It could help organizations better forecast the needs of their distributors e) None of the above 20

SCM Process p Stages of SCM (SC Council’s Reference Model): 1) Planning: develop and implement processes that attempt to forecast demand for products and services § 2) Sourcing: determine who should supply the items required § 3) 2) Schedule production Ensure raw materials are on hand when needed Product delivery (logistics) 1) 2) 5) Goal: Be supplied on time, within budget Production: make the product 1) 4) Goal: Balance demand with supply of raw material Everything from receiving a customer inquiry to invoicing Warehouse management is one very important factor Returns: managing returns of raw materials as well as 21 finished goods

EDI: a SCM Technology p Electronic Data Interchange (EDI): n A network technology that allows the transfer and processing of business documents (usually orders) between a company and its suppliers Suppliers EDI Sys. Value Added Network (VAN) or Private network connection EDI System Company’s Internal processes Production Department Process 1 Process 2 Sales Department Process 1 Process 2 Delivery Department Process 1 Process 2 22

EDI: SCM Technology p EDI documents must be formatted according to specific standards n n p Advantages: n n n p ANSI X 12 – used in North America EDIFACT – international, but widely used in Europe Eliminates paperwork Reduces errors Speeds supply process Disadvantages: n n Provides connection only between two companies Limits freedom of comparing prices. 23
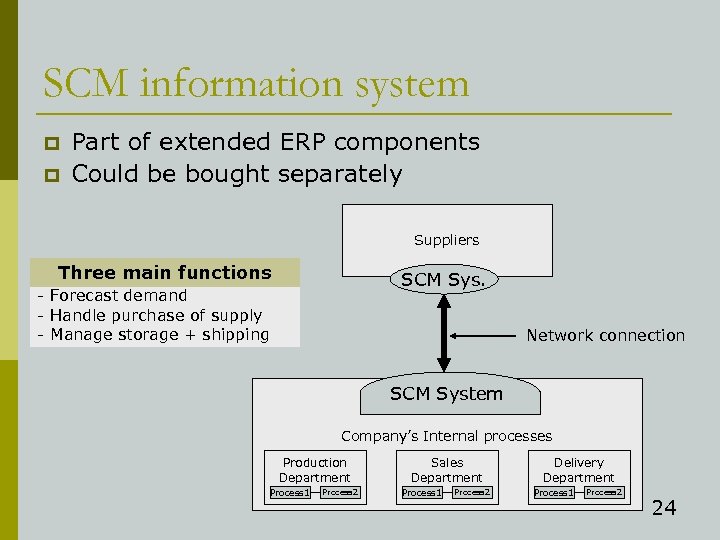
SCM information system p p Part of extended ERP components Could be bought separately Suppliers Three main functions SCM Sys. - Forecast demand - Handle purchase of supply - Manage storage + shipping Network connection SCM System Company’s Internal processes Production Department Process 1 Process 2 Sales Department Process 1 Process 2 Delivery Department Process 1 Process 2 24

Customer Relationship Management CRM 25

CRM systems p p CRM systems are systems that can help manage all aspects of organizations’ relation with their customers. Which of the following is NOT a potential benefit of CRM systems? a) b) c) d) e) f) Provide better customer service Make call centers more efficient Help sales staff close deals faster Simplify marketing and sales processes Discover new customers None of the above 26

Goals of CRM systems p Goal of CRM is to increase sales and repeat business by learning the customer n n n p Determine the customer’s needs and preferences Determine the customer’s satisfaction with service Determine which customers are in the magic 20 percent (or have the potential to become part of it) Recency, Frequency, Monetary value (RFM) at heart of CRM systems n n n How recently a customer purchased items (Recency) How frequently a customer purchased items (Frequency) How much a customer spends on each purchase (Monetary Value 27
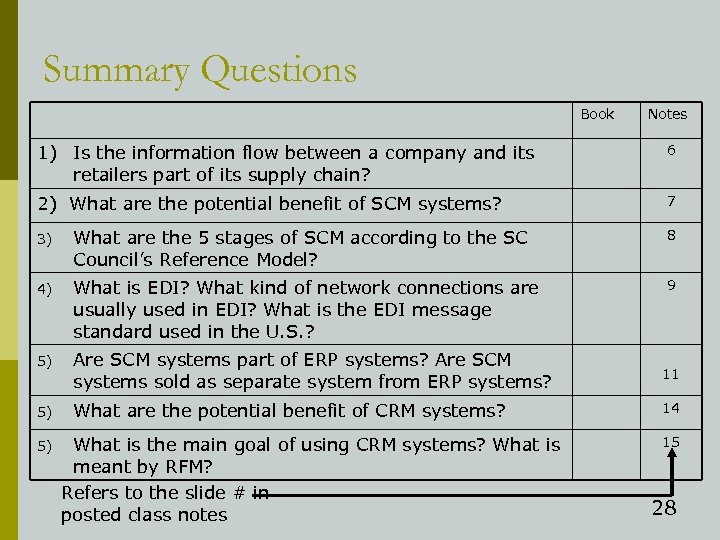
Summary Questions Book Notes 1) Is the information flow between a company and its retailers part of its supply chain? 6 2) What are the potential benefit of SCM systems? 7 3) What are the 5 stages of SCM according to the SC Council’s Reference Model? 8 4) What is EDI? What kind of network connections are usually used in EDI? What is the EDI message standard used in the U. S. ? 9 5) Are SCM systems part of ERP systems? Are SCM systems sold as separate system from ERP systems? 11 5) What are the potential benefit of CRM systems? 14 5) What is the main goal of using CRM systems? What is meant by RFM? Refers to the slide # in posted class notes 15 28

Review Questions p Make sure you can answer the following questions: n Chapter 8 -9 review Questions posted to the Review section of the course web site. 29

Managing Security Part 3 30

Best way to prepare p Review the ppt notes or chapter 4 in the book to make sure you can answer the following questions n n Chapter 4 Review Questions available in the Review section of course web site Quiz 3 questions posted to the Review section of the course web site). 31

Managing the Development and Purchase of IS Part 4 32

Systems Development Methodology? p The process companies go through to develop and maintain an information system p Framework for successful IS development p A System Development Methodology is used n n p For building a new system Or for modifying an existing system Examples of SDM: n System Development Life Cycle ■ Prototyping n Joint Application Development ■ Rapid Application Development 33

Questions p Which of the following is true about SDM? 1) They provide guidelines for developing IS and maintaining them which includes upgrading and improving them. 2) SDM are needed when a brand new IS has to be developed, but you don’t need to use a SDM when it comes to modifying an existing IS. 3) When a company is engaged in developing an IS, the process involves the company’s employees who would be the future users of the IS, and IS professionals like system analysts and programmers. But it doesn’t involve the company’s management 4) All of the above 34
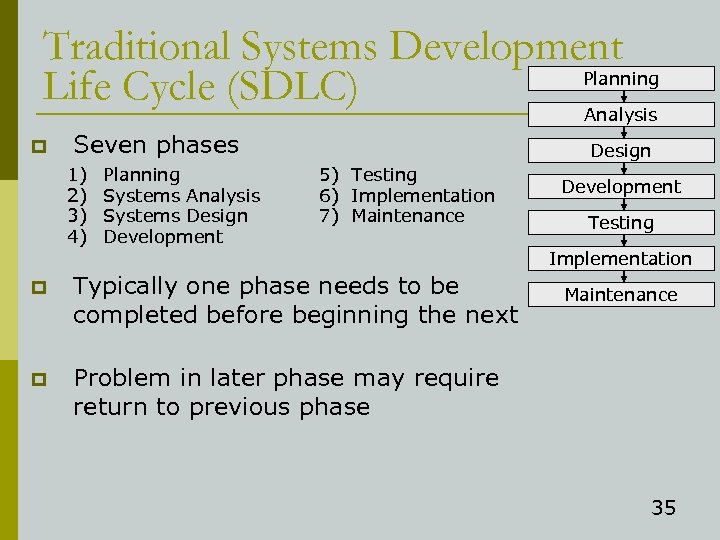
Traditional Systems Development Planning Life Cycle (SDLC) Analysis p Seven phases 1) 2) 3) 4) Planning Systems Analysis Systems Design Development Design 5) Testing 6) Implementation 7) Maintenance Development Testing Implementation p Typically one phase needs to be completed before beginning the next p Problem in later phase may require return to previous phase Maintenance 35

Question p In SDLC, the 7 phases are typically followed in a sequential order, which means we don’t return to a previous phase in any circumstances q True q False 36

Feasibility Analyses Planning p Feasibility analyses n Technical Analysis p n Can the organization afford the system? Will it provide an adequate Benefit? Operational Analysis (i. e. assessing the human element of the proposed system) p p Resistance to change Organizational politics System development schedule n n p Do the technologies exist to develop the system? Economic Analysis p p System Development Schedule Is the proposed development time line realistic? Is the programming team available during Programming step? Planning performed by Project Manager using n n n Search and investigation (e. g. for technical analysis step) Total Cost of Ownership analysis 37 Project Management software
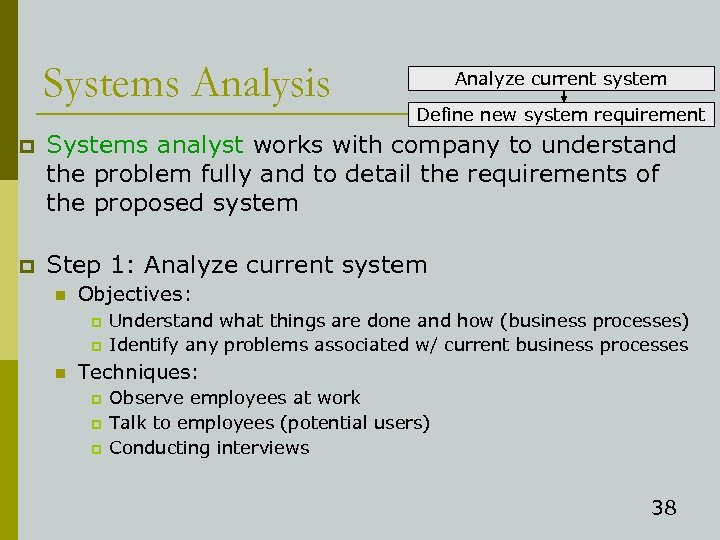
Systems Analysis Analyze current system Define new system requirement p Systems analyst works with company to understand the problem fully and to detail the requirements of the proposed system p Step 1: Analyze current system n Objectives: p p n Understand what things are done and how (business processes) Identify any problems associated w/ current business processes Techniques: p p p Observe employees at work Talk to employees (potential users) Conducting interviews 38

Systems Analysis p Analyze current system Define new system requirements Step 2: Define new system’s requirements n Main Objective: p n To be defined: p p n Specify What need to be done (not how to do it) Input requirements (nature of data, source, etc. ) Processing requirements Output requirements (Types of reports, content, etc. ) Storage requirements Tools and techniques p Data flow diagrams (DFD) § Start with high level process § Add more levels with increased levels of detail p Computer-Aided Software Engineering (CASE) tools § Software that eases the systems development process 39
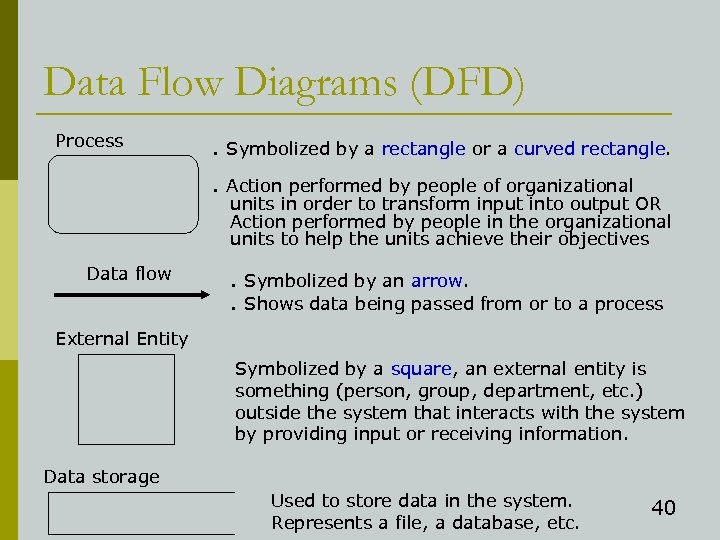
Data Flow Diagrams (DFD) Process . Symbolized by a rectangle or a curved rectangle. . Action performed by people of organizational units in order to transform input into output OR Action performed by people in the organizational units to help the units achieve their objectives Data flow . Symbolized by an arrow. . Shows data being passed from or to a process External Entity Symbolized by a square, an external entity is something (person, group, department, etc. ) outside the system that interacts with the system by providing input or receiving information. Data storage Used to store data in the system. Represents a file, a database, etc. 40

DFD Exercise p You should be able to answer Questions 1, 2, and 3 of the Lincoln Pizza’s ordering system DFD exercise. Hardcopies were given in class. You can also get a copy in the Notes’ section or in the Review section of the course web site. 41

Systems Design p Using the requirements from Systems Analysis phase to design the new or modified system. n Logical systems design p p p n Specifies all of the actual components (hardware, network, etc) used to implement the logical design The design must be frozen at end of this phase to prevent the to system grow indefinitely in terms of its scope and features p p p Uses System flowcharts to show relationships between modules Physical systems design p n Details the system’s functionality (what it should do? ) Uses Structure charts to create top-down representation of system’s modules Scope creep Feature creep Performed by system designer or (system analyst in 42 some case)

Development p p p Programming process is usually the most difficult and time consuming in the Development process. Development performed by programmers, database developers, and network engineers Programmers use Program Development Cycle 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Review the input, processing, output, and storage requirements Develop the logic of the programs (using Flowcharts and Pseudo code) Write the programs using code generators & programming languages Test and debug the programs Complete the programs documentation 43

Development tools Program Flowchart: Graphical illustration of the problem-solving logic within a program Pseudocode: English-language statements that describe the processing steps of a program in paragraph form. Code generators: Software that generate programs that programmers could modify. Programming languages: -Java -C++ -Visual Basic -Etc. 44

Testing p Programmers test modules p p p Development team do unit testing p p Do they return proper outputs? Do they handle incorrect data appropriately? i. e. testing how modules work together System testing (software along with database and network component) n n Verification: Testing system in simulated environment with simulated data Validation: Testing system in real working environment with real data 45

Implementation p Implementation strategies n n Parallel conversion: Old and new systems used in parallel for a while. n Pilot testing: New system installed at only one location or one department n p Direct cutover: Quick change to new system Staged conversion: Only one part of the system installed, then another part is installed. User training 46

Maintenance counts for as much as 80% of the total cost of an information system p Tasks p n n Correct errors found during implementation System enhancements Incremental upgrades p Addition of major new features p 47

Summary Questions Book Notes 1) What is a System Development Methodology? What is it used for? 2) What are the 7 phases of the SDLC methodology? 3) What kind of Feasibility analyses need to be performed during the Planning phase? Why is the system development schedule important? 4) What are the two steps in the Systems Analysis phase? What techniques and tools are used during the Systems Analysis phase? 5) What tools do programmers usually use during the Development phase? 6) What is the difference between the Verification and the Validation tests performed during systems testing? 48
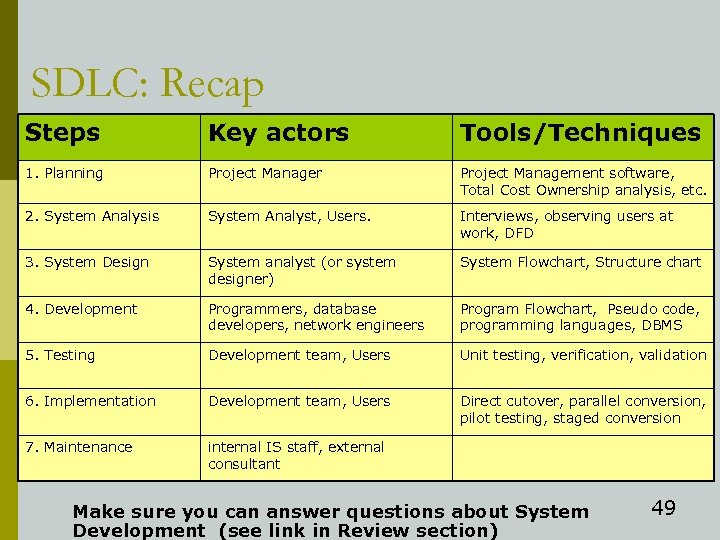
SDLC: Recap Steps Key actors Tools/Techniques 1. Planning Project Manager Project Management software, Total Cost Ownership analysis, etc. 2. System Analysis System Analyst, Users. Interviews, observing users at work, DFD 3. System Design System analyst (or system designer) System Flowchart, Structure chart 4. Development Programmers, database developers, network engineers Program Flowchart, Pseudo code, programming languages, DBMS 5. Testing Development team, Users Unit testing, verification, validation 6. Implementation Development team, Users Direct cutover, parallel conversion, pilot testing, staged conversion 7. Maintenance internal IS staff, external consultant Make sure you can answer questions about System Development (see link in Review section) 49
427f39e3ef363e458171b77aa69fa010.ppt