06130ad791aff282afff2093feb348e1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Review Concept of Operations for an Enterprise Architecture Intelligence Center Haiping Luo June, 2005 1
Review Concept of Operations for an Enterprise Architecture Intelligence Center Haiping Luo June, 2005 1
 Settings You were members of an EA Steering Committee of a fictional company, reviewing a Concept of Operations for an EA repository Ø You would critique the Con. Ops as roles such as: Ø § § § Ø Enterprise managers Business function operators Enterprise architects Technical staff members External stakeholders (investor, customer, partner, auditor, EA evaluator, …) Please hold your comments until the critique session. During critiquing, please indicate your role and the slide number you are referring. June, 2005 2
Settings You were members of an EA Steering Committee of a fictional company, reviewing a Concept of Operations for an EA repository Ø You would critique the Con. Ops as roles such as: Ø § § § Ø Enterprise managers Business function operators Enterprise architects Technical staff members External stakeholders (investor, customer, partner, auditor, EA evaluator, …) Please hold your comments until the critique session. During critiquing, please indicate your role and the slide number you are referring. June, 2005 2
 Overview Ø EA Intelligence Center: an Introduction Ø EAIC Architecture Ø EAIC Construction Ø EAIC Operations Ø EAIC Performance Evaluation Ø Summary Ø Critique June, 2005 3
Overview Ø EA Intelligence Center: an Introduction Ø EAIC Architecture Ø EAIC Construction Ø EAIC Operations Ø EAIC Performance Evaluation Ø Summary Ø Critique June, 2005 3
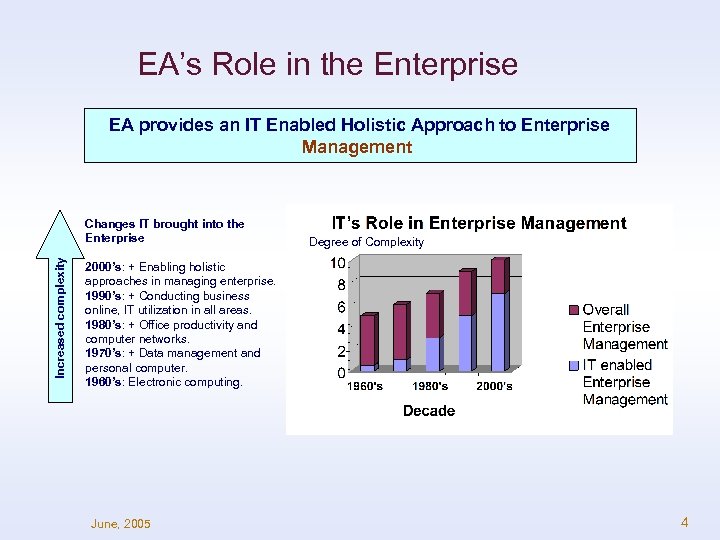 EA’s Role in the Enterprise EA provides an IT Enabled Holistic Approach to Enterprise Management. Increased complexity Changes IT brought into the Enterprise Degree of Complexity 2000’s: + Enabling holistic approaches in managing enterprise. 1990’s: + Conducting business online, IT utilization in all areas. 1980’s: + Office productivity and computer networks. 1970’s: + Data management and personal computer. 1960’s: Electronic computing. June, 2005 4
EA’s Role in the Enterprise EA provides an IT Enabled Holistic Approach to Enterprise Management. Increased complexity Changes IT brought into the Enterprise Degree of Complexity 2000’s: + Enabling holistic approaches in managing enterprise. 1990’s: + Conducting business online, IT utilization in all areas. 1980’s: + Office productivity and computer networks. 1970’s: + Data management and personal computer. 1960’s: Electronic computing. June, 2005 4
 EA Intelligence Center: an Introduction Ø The EA Intelligence Center: § § § June, 2005 Documents an enterprise’ structure, i. e. , its elements, their relationships, and their interoperations; Assembles and presents the abstract documentation and blueprints of an enterprise’ architecture; Facilitates the processes of designing, aligning, improving, and managing the architecture of an enterprise. 5
EA Intelligence Center: an Introduction Ø The EA Intelligence Center: § § § June, 2005 Documents an enterprise’ structure, i. e. , its elements, their relationships, and their interoperations; Assembles and presents the abstract documentation and blueprints of an enterprise’ architecture; Facilitates the processes of designing, aligning, improving, and managing the architecture of an enterprise. 5
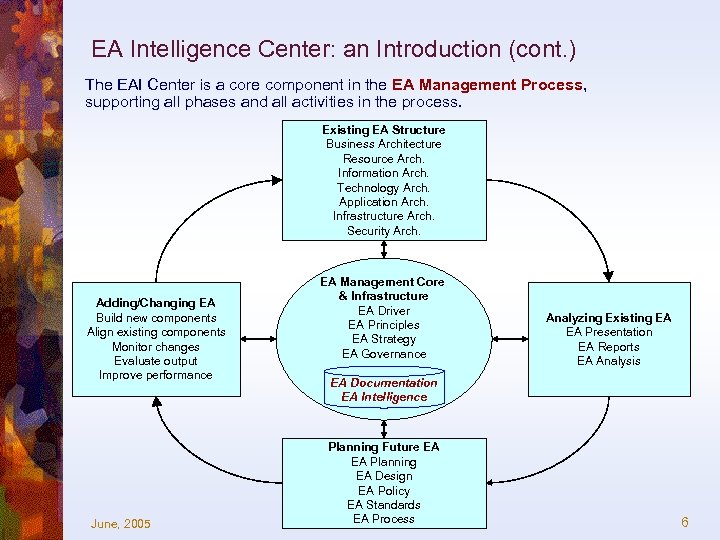 EA Intelligence Center: an Introduction (cont. ) The EAI Center is a core component in the EA Management Process, supporting all phases and all activities in the process. Existing EA Structure Business Architecture Resource Arch. Information Arch. Technology Arch. Application Arch. Infrastructure Arch. Security Arch. Adding/Changing EA Build new components Align existing components Monitor changes Evaluate output Improve performance June, 2005 EA Management Core & Infrastructure EA Driver EA Principles EA Strategy EA Governance Analyzing Existing EA EA Presentation EA Reports EA Analysis EA Documentation EA Intelligence Planning Future EA EA Planning EA Design EA Policy EA Standards EA Process 6
EA Intelligence Center: an Introduction (cont. ) The EAI Center is a core component in the EA Management Process, supporting all phases and all activities in the process. Existing EA Structure Business Architecture Resource Arch. Information Arch. Technology Arch. Application Arch. Infrastructure Arch. Security Arch. Adding/Changing EA Build new components Align existing components Monitor changes Evaluate output Improve performance June, 2005 EA Management Core & Infrastructure EA Driver EA Principles EA Strategy EA Governance Analyzing Existing EA EA Presentation EA Reports EA Analysis EA Documentation EA Intelligence Planning Future EA EA Planning EA Design EA Policy EA Standards EA Process 6
 EA Intelligence Center: an Introduction (cont. ) Ø The key characteristics of the EA Intelligence Center is that its information assembling activities focus on an ultimate goal: Providing EA Intelligence to support enterprise management decision making June, 2005 7
EA Intelligence Center: an Introduction (cont. ) Ø The key characteristics of the EA Intelligence Center is that its information assembling activities focus on an ultimate goal: Providing EA Intelligence to support enterprise management decision making June, 2005 7
 Concept: EA Intelligence Enterprise Architecture Intelligence is the process of enhancing enterprise metadata into information and then into actionable knowledge to support enterprise management decision making. June, 2005 8
Concept: EA Intelligence Enterprise Architecture Intelligence is the process of enhancing enterprise metadata into information and then into actionable knowledge to support enterprise management decision making. June, 2005 8
 Concept Comparison: EA Intelligence vs. Business Intelligence Ø Similarities: § § assemble scattered information; turn data into actionable knowledge; facilitate self-service reporting; support decision making. June, 2005 9
Concept Comparison: EA Intelligence vs. Business Intelligence Ø Similarities: § § assemble scattered information; turn data into actionable knowledge; facilitate self-service reporting; support decision making. June, 2005 9
 Concept Comparison: EA Intelligence vs. Business Intelligence Ø Differences: § § § focuses on metadata rather than data; processes mainly descriptive text rather than numerical / categorical values; utilizes mainly qualitative / structural / reasoning methods rather than quantitative methods; targets at improving structure more than amount; outputs mainly modeling diagrams & context tables rather than statistical values & charts. June, 2005 10
Concept Comparison: EA Intelligence vs. Business Intelligence Ø Differences: § § § focuses on metadata rather than data; processes mainly descriptive text rather than numerical / categorical values; utilizes mainly qualitative / structural / reasoning methods rather than quantitative methods; targets at improving structure more than amount; outputs mainly modeling diagrams & context tables rather than statistical values & charts. June, 2005 10
 Possible Types of EA Intelligence Analyses • • • Change impact analysis (related, what if, quantitative, …) Redundancy / reusability analysis Process analysis (bottleneck, work flow, point of failure, …) Vulnerability analysis (roles & responsibility, process, point of failure, …) Performance analysis (roles, responsibility, and accountability; performance metrics, …) Interoperation analysis (exchange of information, standardization, …) Structural analysis (degree of centralization, standardization, capacity analysis, …) Culture analysis (communication, philosophy, leadership assumptions, methodology, …) Semantic reasoning and inference June, 2005 11
Possible Types of EA Intelligence Analyses • • • Change impact analysis (related, what if, quantitative, …) Redundancy / reusability analysis Process analysis (bottleneck, work flow, point of failure, …) Vulnerability analysis (roles & responsibility, process, point of failure, …) Performance analysis (roles, responsibility, and accountability; performance metrics, …) Interoperation analysis (exchange of information, standardization, …) Structural analysis (degree of centralization, standardization, capacity analysis, …) Culture analysis (communication, philosophy, leadership assumptions, methodology, …) Semantic reasoning and inference June, 2005 11
 EA Intelligence Center: an Introduction (cont. ) Ø Who may benefit from the EA Intelligence Center? § § § June, 2005 Enterprise managers Business function operators Enterprise architects Technical staff members External stakeholders 12
EA Intelligence Center: an Introduction (cont. ) Ø Who may benefit from the EA Intelligence Center? § § § June, 2005 Enterprise managers Business function operators Enterprise architects Technical staff members External stakeholders 12
 EA Intelligence Center: an Introduction (cont. ) In short, the EA Intelligence Center’s mission is to assemble EA information to support a wide range of enterprise decision making. Ø With this mission in mind, the EA intelligence capacity needs to be: Ø § § § June, 2005 built into EAIC’ design; implemented in its construction; carried out in its operations; embedded in its processes; evaluated in its performance evaluations. 13
EA Intelligence Center: an Introduction (cont. ) In short, the EA Intelligence Center’s mission is to assemble EA information to support a wide range of enterprise decision making. Ø With this mission in mind, the EA intelligence capacity needs to be: Ø § § § June, 2005 built into EAIC’ design; implemented in its construction; carried out in its operations; embedded in its processes; evaluated in its performance evaluations. 13
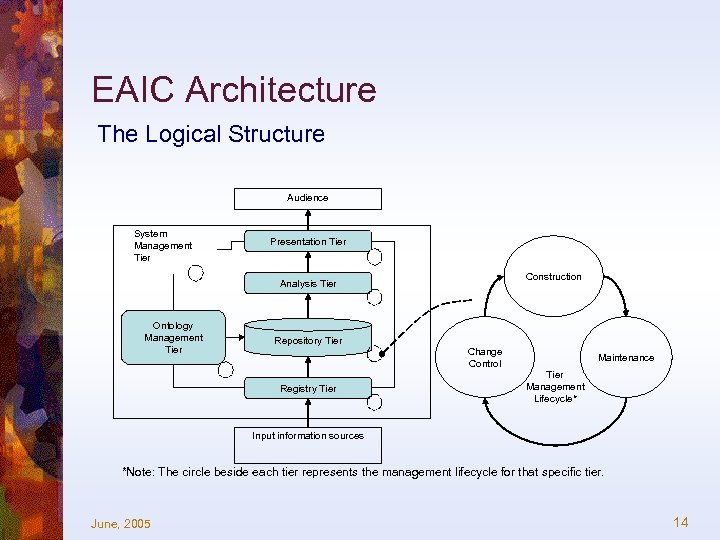 EAIC Architecture The Logical Structure Audience System Management Tier Presentation Tier Construction Analysis Tier Ontology Management Tier Repository Tier Registry Tier Change Control Maintenance Tier Management Lifecycle* Input information sources *Note: The circle beside each tier represents the management lifecycle for that specific tier. June, 2005 14
EAIC Architecture The Logical Structure Audience System Management Tier Presentation Tier Construction Analysis Tier Ontology Management Tier Repository Tier Registry Tier Change Control Maintenance Tier Management Lifecycle* Input information sources *Note: The circle beside each tier represents the management lifecycle for that specific tier. June, 2005 14
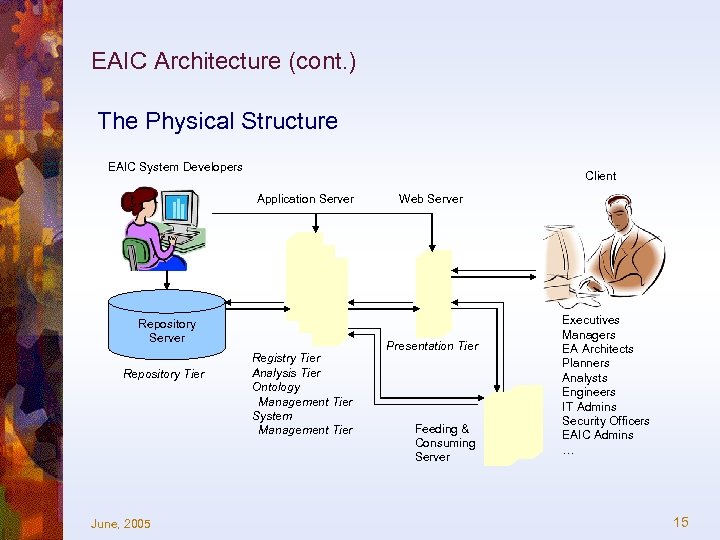 EAIC Architecture (cont. ) The Physical Structure EAIC System Developers Client Application Server Repository Tier June, 2005 Registry Tier Analysis Tier Ontology Management Tier System Management Tier Web Server Presentation Tier Feeding & Consuming Server Executives Managers EA Architects Planners Analysts Engineers IT Admins Security Officers EAIC Admins … 15
EAIC Architecture (cont. ) The Physical Structure EAIC System Developers Client Application Server Repository Tier June, 2005 Registry Tier Analysis Tier Ontology Management Tier System Management Tier Web Server Presentation Tier Feeding & Consuming Server Executives Managers EA Architects Planners Analysts Engineers IT Admins Security Officers EAIC Admins … 15
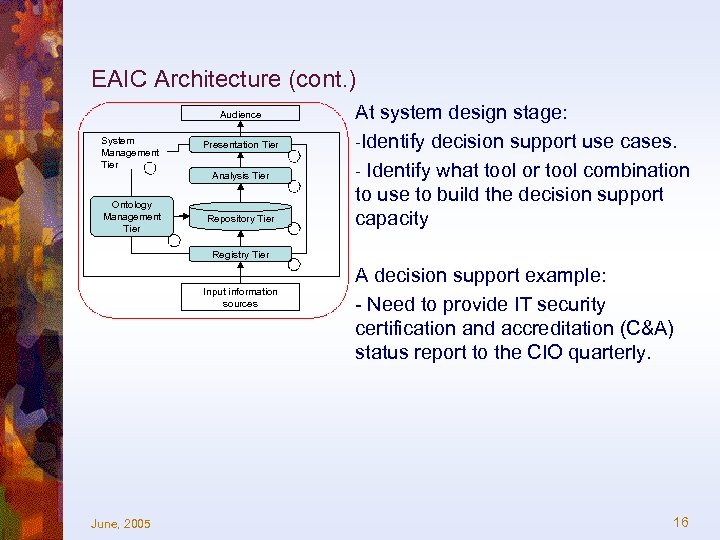 EAIC Architecture (cont. ) Audience System Management Tier Ontology Management Tier Presentation Tier Analysis Tier Repository Tier At system design stage: -Identify decision support use cases. - Identify what tool or tool combination to use to build the decision support capacity Registry Tier Input information sources June, 2005 A decision support example: - Need to provide IT security certification and accreditation (C&A) status report to the CIO quarterly. 16
EAIC Architecture (cont. ) Audience System Management Tier Ontology Management Tier Presentation Tier Analysis Tier Repository Tier At system design stage: -Identify decision support use cases. - Identify what tool or tool combination to use to build the decision support capacity Registry Tier Input information sources June, 2005 A decision support example: - Need to provide IT security certification and accreditation (C&A) status report to the CIO quarterly. 16
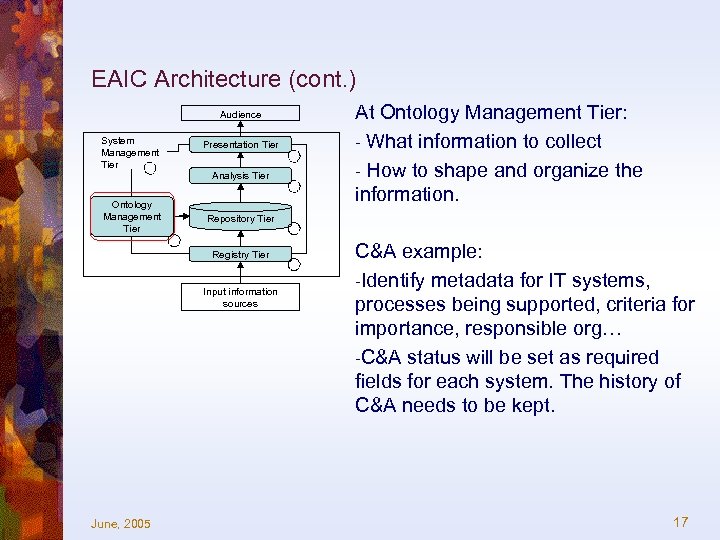 EAIC Architecture (cont. ) Audience System Management Tier Ontology Management Tier Presentation Tier Analysis Tier Repository Tier Registry Tier Input information sources June, 2005 At Ontology Management Tier: - What information to collect - How to shape and organize the information. C&A example: -Identify metadata for IT systems, processes being supported, criteria for importance, responsible org… -C&A status will be set as required fields for each system. The history of C&A needs to be kept. 17
EAIC Architecture (cont. ) Audience System Management Tier Ontology Management Tier Presentation Tier Analysis Tier Repository Tier Registry Tier Input information sources June, 2005 At Ontology Management Tier: - What information to collect - How to shape and organize the information. C&A example: -Identify metadata for IT systems, processes being supported, criteria for importance, responsible org… -C&A status will be set as required fields for each system. The history of C&A needs to be kept. 17
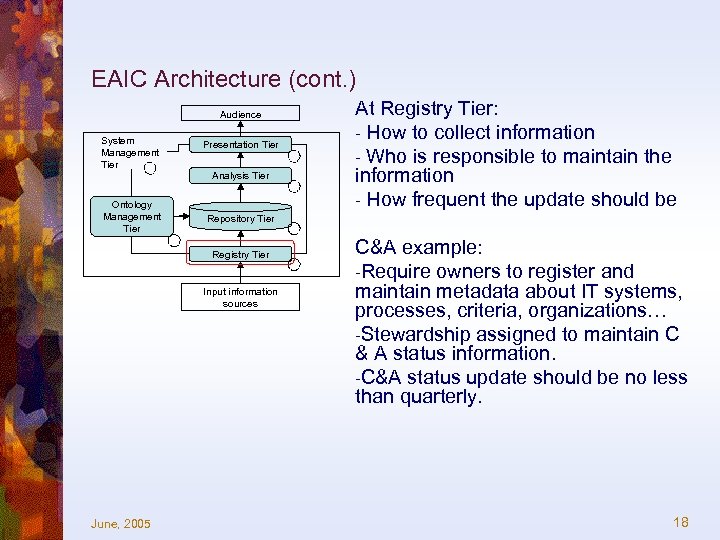 EAIC Architecture (cont. ) Audience System Management Tier Ontology Management Tier Presentation Tier Analysis Tier Repository Tier Registry Tier Input information sources June, 2005 At Registry Tier: - How to collect information - Who is responsible to maintain the information - How frequent the update should be C&A example: -Require owners to register and maintain metadata about IT systems, processes, criteria, organizations… -Stewardship assigned to maintain C & A status information. -C&A status update should be no less than quarterly. 18
EAIC Architecture (cont. ) Audience System Management Tier Ontology Management Tier Presentation Tier Analysis Tier Repository Tier Registry Tier Input information sources June, 2005 At Registry Tier: - How to collect information - Who is responsible to maintain the information - How frequent the update should be C&A example: -Require owners to register and maintain metadata about IT systems, processes, criteria, organizations… -Stewardship assigned to maintain C & A status information. -C&A status update should be no less than quarterly. 18
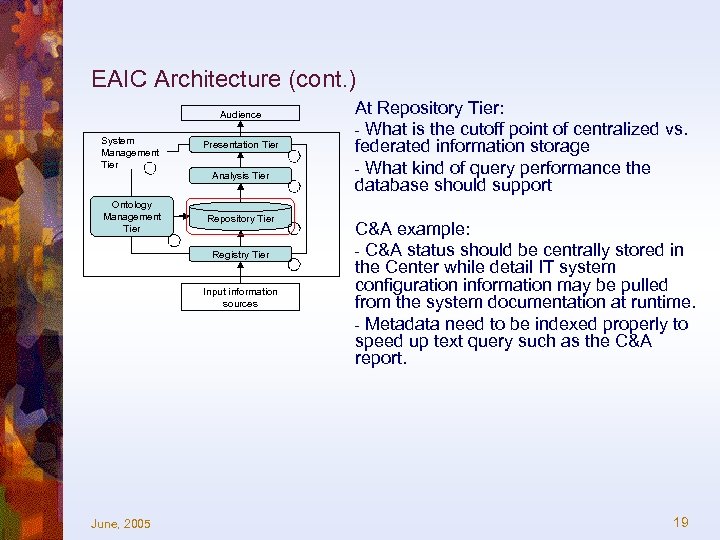 EAIC Architecture (cont. ) Audience System Management Tier Ontology Management Tier Presentation Tier Analysis Tier Repository Tier Registry Tier Input information sources June, 2005 At Repository Tier: - What is the cutoff point of centralized vs. federated information storage - What kind of query performance the database should support C&A example: - C&A status should be centrally stored in the Center while detail IT system configuration information may be pulled from the system documentation at runtime. - Metadata need to be indexed properly to speed up text query such as the C&A report. 19
EAIC Architecture (cont. ) Audience System Management Tier Ontology Management Tier Presentation Tier Analysis Tier Repository Tier Registry Tier Input information sources June, 2005 At Repository Tier: - What is the cutoff point of centralized vs. federated information storage - What kind of query performance the database should support C&A example: - C&A status should be centrally stored in the Center while detail IT system configuration information may be pulled from the system documentation at runtime. - Metadata need to be indexed properly to speed up text query such as the C&A report. 19
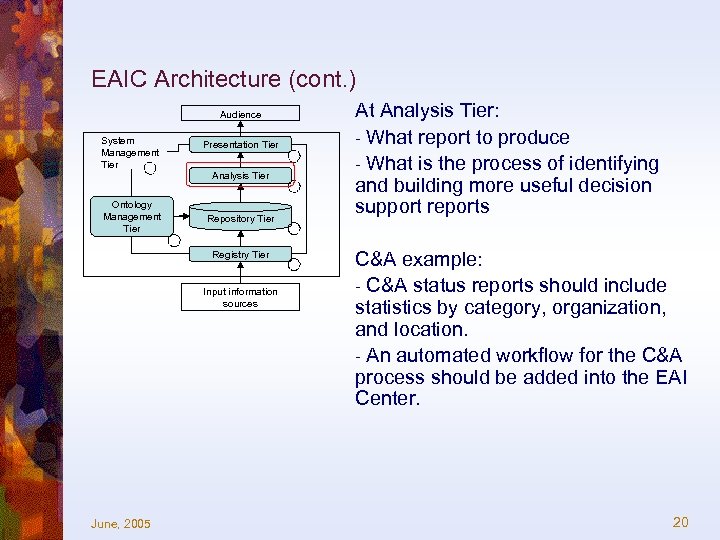 EAIC Architecture (cont. ) Audience System Management Tier Ontology Management Tier Presentation Tier Analysis Tier Repository Tier Registry Tier Input information sources June, 2005 At Analysis Tier: - What report to produce - What is the process of identifying and building more useful decision support reports C&A example: - C&A status reports should include statistics by category, organization, and location. - An automated workflow for the C&A process should be added into the EAI Center. 20
EAIC Architecture (cont. ) Audience System Management Tier Ontology Management Tier Presentation Tier Analysis Tier Repository Tier Registry Tier Input information sources June, 2005 At Analysis Tier: - What report to produce - What is the process of identifying and building more useful decision support reports C&A example: - C&A status reports should include statistics by category, organization, and location. - An automated workflow for the C&A process should be added into the EAI Center. 20
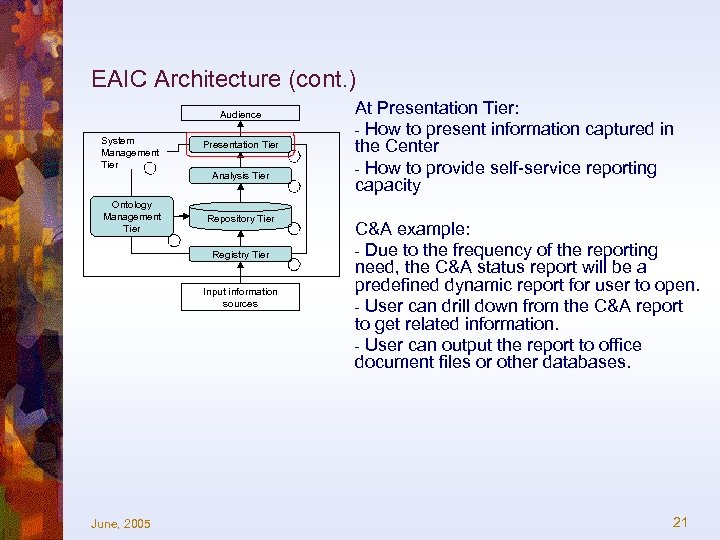 EAIC Architecture (cont. ) Audience System Management Tier Ontology Management Tier Presentation Tier Analysis Tier Repository Tier Registry Tier Input information sources June, 2005 At Presentation Tier: - How to present information captured in the Center - How to provide self-service reporting capacity C&A example: - Due to the frequency of the reporting need, the C&A status report will be a predefined dynamic report for user to open. - User can drill down from the C&A report to get related information. - User can output the report to office document files or other databases. 21
EAIC Architecture (cont. ) Audience System Management Tier Ontology Management Tier Presentation Tier Analysis Tier Repository Tier Registry Tier Input information sources June, 2005 At Presentation Tier: - How to present information captured in the Center - How to provide self-service reporting capacity C&A example: - Due to the frequency of the reporting need, the C&A status report will be a predefined dynamic report for user to open. - User can drill down from the C&A report to get related information. - User can output the report to office document files or other databases. 21
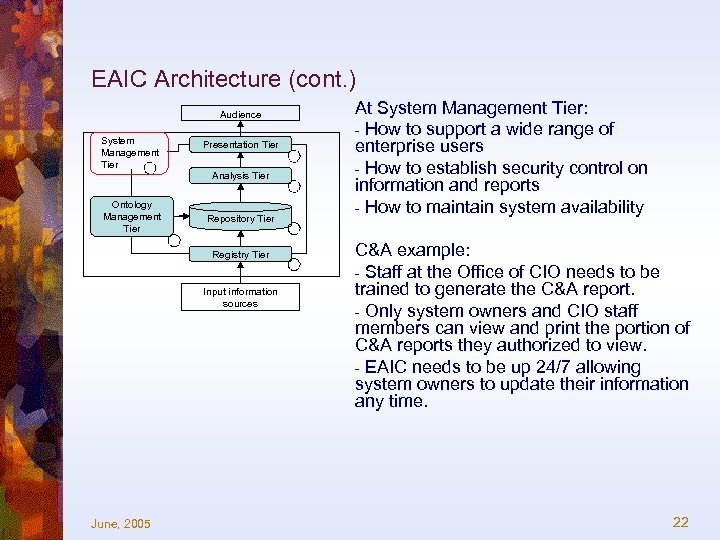 EAIC Architecture (cont. ) Audience System Management Tier Ontology Management Tier Presentation Tier Analysis Tier Repository Tier Registry Tier Input information sources June, 2005 At System Management Tier: - How to support a wide range of enterprise users - How to establish security control on information and reports - How to maintain system availability C&A example: - Staff at the Office of CIO needs to be trained to generate the C&A report. - Only system owners and CIO staff members can view and print the portion of C&A reports they authorized to view. - EAIC needs to be up 24/7 allowing system owners to update their information any time. 22
EAIC Architecture (cont. ) Audience System Management Tier Ontology Management Tier Presentation Tier Analysis Tier Repository Tier Registry Tier Input information sources June, 2005 At System Management Tier: - How to support a wide range of enterprise users - How to establish security control on information and reports - How to maintain system availability C&A example: - Staff at the Office of CIO needs to be trained to generate the C&A report. - Only system owners and CIO staff members can view and print the portion of C&A reports they authorized to view. - EAIC needs to be up 24/7 allowing system owners to update their information any time. 22
 User participation EAIC Construction Development Phases: I. Plan II. Design and Prototype III. Initial Inventory of EA contents IV. Full Construction i. iii. V. Continuous Improvement in Supporting EA Management i. iii. June, 2005 In depth baseline inventory (collect, decompose, connect) Architectural analysis and construction Intelligence insertion Maintain and update information Design target EA Improve EA Intelligence Center 23
User participation EAIC Construction Development Phases: I. Plan II. Design and Prototype III. Initial Inventory of EA contents IV. Full Construction i. iii. V. Continuous Improvement in Supporting EA Management i. iii. June, 2005 In depth baseline inventory (collect, decompose, connect) Architectural analysis and construction Intelligence insertion Maintain and update information Design target EA Improve EA Intelligence Center 23
 EAIC Construction (cont. ) Content and Capacity Building Scope Simple Abstract Stage 2. Expansion Stage 3. Enrichment Stage 1. June, 2005 24
EAIC Construction (cont. ) Content and Capacity Building Scope Simple Abstract Stage 2. Expansion Stage 3. Enrichment Stage 1. June, 2005 24
 EAIC Operations Content Management Ø System Management Ø Development Management Ø June, 2005 25
EAIC Operations Content Management Ø System Management Ø Development Management Ø June, 2005 25
 EAIC Operations (cont. ) Content Management Principles ü Ensure wide participation and clear stewardship; ü Establish policy, ownership, content manager, and content management process; ü Manage the entire content lifecycle, ad infinitum; ü Use the correct criteria for quality control; ü Be realistic in update requirement; and ü Enable automatically gathering contents as much as feasible. June, 2005 26
EAIC Operations (cont. ) Content Management Principles ü Ensure wide participation and clear stewardship; ü Establish policy, ownership, content manager, and content management process; ü Manage the entire content lifecycle, ad infinitum; ü Use the correct criteria for quality control; ü Be realistic in update requirement; and ü Enable automatically gathering contents as much as feasible. June, 2005 26
 EAIC Operations (cont. ) System Management Requirements ü Following system administration principles and industry best practice ü Establishing Proper Security Policy ü Documenting System Configuration June, 2005 27
EAIC Operations (cont. ) System Management Requirements ü Following system administration principles and industry best practice ü Establishing Proper Security Policy ü Documenting System Configuration June, 2005 27
 EAIC Operations (cont. ) Development Management Ongoing Tasks ü Automating content collection and update; ü Providing web services to feed consuming systems; ü Enhancing EA intelligence capacity through integrating more tools and creating own utilities; and ü Upgrading EAIC system hardware and software. June, 2005 28
EAIC Operations (cont. ) Development Management Ongoing Tasks ü Automating content collection and update; ü Providing web services to feed consuming systems; ü Enhancing EA intelligence capacity through integrating more tools and creating own utilities; and ü Upgrading EAIC system hardware and software. June, 2005 28
 EAIC Performance Evaluation Sample questions and metrics ü How well EAIC reaches EA documentation goals? -% of planned elements documented. ; ü How well EAIC is received by the enterprise? -Ave. daily users and accesses. ü How well EAIC is supporting enterprise decision making? - # of predefined reports - score of user satisfaction on DS capacity ü How well EAIC is administrated? - % up time - ave. resolution time for help calls - security C&A score June, 2005 29
EAIC Performance Evaluation Sample questions and metrics ü How well EAIC reaches EA documentation goals? -% of planned elements documented. ; ü How well EAIC is received by the enterprise? -Ave. daily users and accesses. ü How well EAIC is supporting enterprise decision making? - # of predefined reports - score of user satisfaction on DS capacity ü How well EAIC is administrated? - % up time - ave. resolution time for help calls - security C&A score June, 2005 29
 Summary Ø EAIC is a powerful tool to help managing the enterprise with a holistic approach Ø Building EA intelligence capacity is a critical requirement for an EA repository Ø Stakeholders participation is the key to EAIC success June, 2005 30
Summary Ø EAIC is a powerful tool to help managing the enterprise with a holistic approach Ø Building EA intelligence capacity is a critical requirement for an EA repository Ø Stakeholders participation is the key to EAIC success June, 2005 30
 Critique Ø Usefulness Ø Feasibility Ø Enhancement June, 2005 31
Critique Ø Usefulness Ø Feasibility Ø Enhancement June, 2005 31
 Contact Information Haiping Luo haiping. luo@va. gov This presentation will be at http: //www. aeajournal. org/Chapter_DC. asp June, 2005 32
Contact Information Haiping Luo haiping. luo@va. gov This presentation will be at http: //www. aeajournal. org/Chapter_DC. asp June, 2005 32


