103846a16d5cc5314d87177b0c234545.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Revenue administration reforms - recent trends and developments in the East AFRITAC region Andrew Okello Revenue administration Advisor 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Revenue administration reforms - recent trends and developments in the East AFRITAC region Andrew Okello Revenue administration Advisor 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 What is the East AFRITAC? ü A tripartite undertaking to strengthen capacity in East Africa in the areas of the IMF’s expertise ü An effort to promote closeness and strengthen field presence for effective technical assistance ü A result-oriented approach and an enhanced governance structure 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
What is the East AFRITAC? ü A tripartite undertaking to strengthen capacity in East Africa in the areas of the IMF’s expertise ü An effort to promote closeness and strengthen field presence for effective technical assistance ü A result-oriented approach and an enhanced governance structure 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Areas of East AFRITAC Assistance ü East AFRITAC delivers technical assistance on a grant basis in the following areas: – – – Banking supervision Monetary operations Revenue administration Macroeconomic statistics Public financial reform Macroeconomic analysis 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Areas of East AFRITAC Assistance ü East AFRITAC delivers technical assistance on a grant basis in the following areas: – – – Banking supervision Monetary operations Revenue administration Macroeconomic statistics Public financial reform Macroeconomic analysis 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Membership and Funding ü East AFRITAC covers 7 countries in East Africa: • Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Malawi, Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda ü The Center is funded by 15 bi- and multi-lateral donors, two member countries, and the IMF: • Af. DB, Canada, China PR, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Italy, Luxembourg, Norway, Russia, Sweden, Switzerland, The Netherlands, and United Kingdom ü 25 sub-Saharan countries covered by 3 AFRITACs 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Membership and Funding ü East AFRITAC covers 7 countries in East Africa: • Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Malawi, Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda ü The Center is funded by 15 bi- and multi-lateral donors, two member countries, and the IMF: • Af. DB, Canada, China PR, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Italy, Luxembourg, Norway, Russia, Sweden, Switzerland, The Netherlands, and United Kingdom ü 25 sub-Saharan countries covered by 3 AFRITACs 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Tax policy and administration ü Reform agendas full of undertakings that require major funding allocations ü Tax policy and tax administration are the means by which governments raise revenue to finance spending on public goods and services ü Tax policy – the choice of tax instruments ü Tax administration – the implementation of tax policy “Policy change without administrative change is nothing…” Milka Casanegra, 1992 ü An efficient tax system will provide the most sustainable source of government funding in the long term 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Tax policy and administration ü Reform agendas full of undertakings that require major funding allocations ü Tax policy and tax administration are the means by which governments raise revenue to finance spending on public goods and services ü Tax policy – the choice of tax instruments ü Tax administration – the implementation of tax policy “Policy change without administrative change is nothing…” Milka Casanegra, 1992 ü An efficient tax system will provide the most sustainable source of government funding in the long term 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
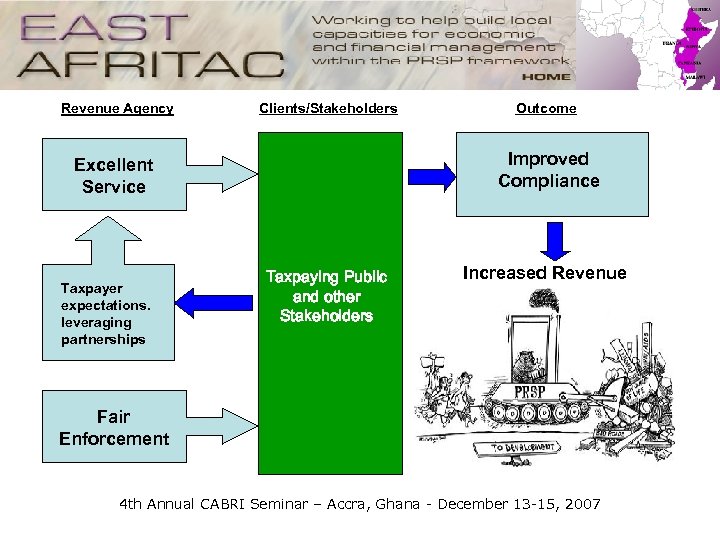 Revenue Agency Clients/Stakeholders Improved Compliance Excellent Service Taxpayer expectations. leveraging partnerships Outcome Taxpaying Public and other Stakeholders Increased Revenue Fair Enforcement 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Revenue Agency Clients/Stakeholders Improved Compliance Excellent Service Taxpayer expectations. leveraging partnerships Outcome Taxpaying Public and other Stakeholders Increased Revenue Fair Enforcement 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
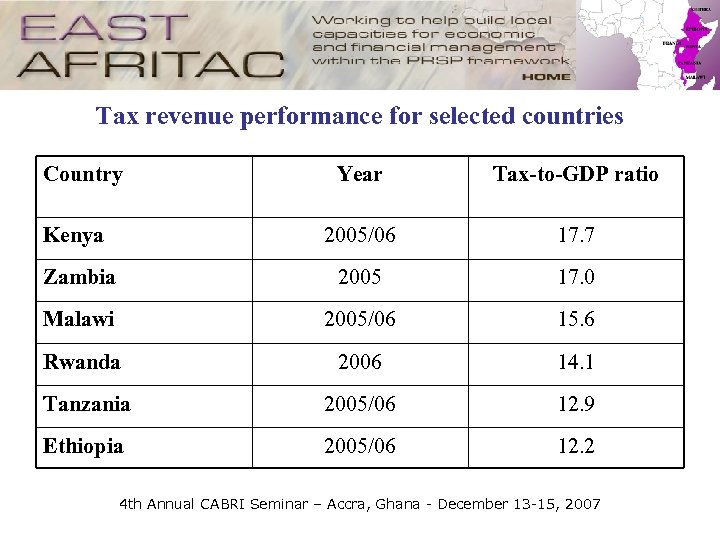 Tax revenue performance for selected countries Country Year Tax-to-GDP ratio Kenya 2005/06 17. 7 Zambia 2005 17. 0 Malawi 2005/06 15. 6 Rwanda 2006 14. 1 Tanzania 2005/06 12. 9 Ethiopia 2005/06 12. 2 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Tax revenue performance for selected countries Country Year Tax-to-GDP ratio Kenya 2005/06 17. 7 Zambia 2005 17. 0 Malawi 2005/06 15. 6 Rwanda 2006 14. 1 Tanzania 2005/06 12. 9 Ethiopia 2005/06 12. 2 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Revenue administration reform drivers ü ü ü Enhance revenue Modernize administration/improve service Reduce compliance burden Reduce administration costs Facilitate trade and investment Improve integrity 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Revenue administration reform drivers ü ü ü Enhance revenue Modernize administration/improve service Reduce compliance burden Reduce administration costs Facilitate trade and investment Improve integrity 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Establishment of semi-autonomous revenue collection agencies ü The advert of the semi-autonomous revenue authorities (RA) over the past 2 decades has been a distinguishing feature of revenue administration Anglophone Africa – Ghana, Nigeria ü In the region, Uganda established, (1991) the first incarnation of the model that became widely emulated over the next 15 years in East and Southern Africa (Kenya, Tanzania, Rwanda, Malawi) ü This RA model brings all major central government revenue collection activities, particularly tax and customs administration under one umbrella 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Establishment of semi-autonomous revenue collection agencies ü The advert of the semi-autonomous revenue authorities (RA) over the past 2 decades has been a distinguishing feature of revenue administration Anglophone Africa – Ghana, Nigeria ü In the region, Uganda established, (1991) the first incarnation of the model that became widely emulated over the next 15 years in East and Southern Africa (Kenya, Tanzania, Rwanda, Malawi) ü This RA model brings all major central government revenue collection activities, particularly tax and customs administration under one umbrella 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Establishment of semi-autonomous revenue collection agencies cont… ü The RA model broadly provides a degree of operational autonomy through a governance arrangement that is distinct from the ministry of finance unlike the traditional government department ü Key issues – Reforms without RA – Autonomy? ? – Independent funding – Reduce corruption? ? – Internal audit function 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Establishment of semi-autonomous revenue collection agencies cont… ü The RA model broadly provides a degree of operational autonomy through a governance arrangement that is distinct from the ministry of finance unlike the traditional government department ü Key issues – Reforms without RA – Autonomy? ? – Independent funding – Reduce corruption? ? – Internal audit function 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Outsourcing revenue administration • Uncommon in the region, however in the pursuit of savings and efficiency gains some functions have been outsourced. • Core tax administration functions rarely outsourced – audit of refund claims, exemptions? ? ? • Private sector support in customs on the decline, PSI services phased out, only Tanzania replaced PSI services with DI services 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Outsourcing revenue administration • Uncommon in the region, however in the pursuit of savings and efficiency gains some functions have been outsourced. • Core tax administration functions rarely outsourced – audit of refund claims, exemptions? ? ? • Private sector support in customs on the decline, PSI services phased out, only Tanzania replaced PSI services with DI services 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Integrated customs and tax administration functions • Degree of integration varies • Shared functions – planning, HR, administration, finance, legal, IT, taxpayer service? , investigation? • Separate functions – debt collection, audit, • Pros and cons of integrated tax and customs administration • LTU 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Integrated customs and tax administration functions • Degree of integration varies • Shared functions – planning, HR, administration, finance, legal, IT, taxpayer service? , investigation? • Separate functions – debt collection, audit, • Pros and cons of integrated tax and customs administration • LTU 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Revenue authorities – other issues • Tax policy formulation • Delegation to sub-national levels 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Revenue authorities – other issues • Tax policy formulation • Delegation to sub-national levels 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 A modern tax administration is characterized by… ü An integrated organization with a function-based structure ü A strong headquarters function ü Effective businesses processes, based on self assessment ü Risk-based compliance programs ü Skilled and professional staff acting with fairness, honesty, and transparency 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
A modern tax administration is characterized by… ü An integrated organization with a function-based structure ü A strong headquarters function ü Effective businesses processes, based on self assessment ü Risk-based compliance programs ü Skilled and professional staff acting with fairness, honesty, and transparency 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
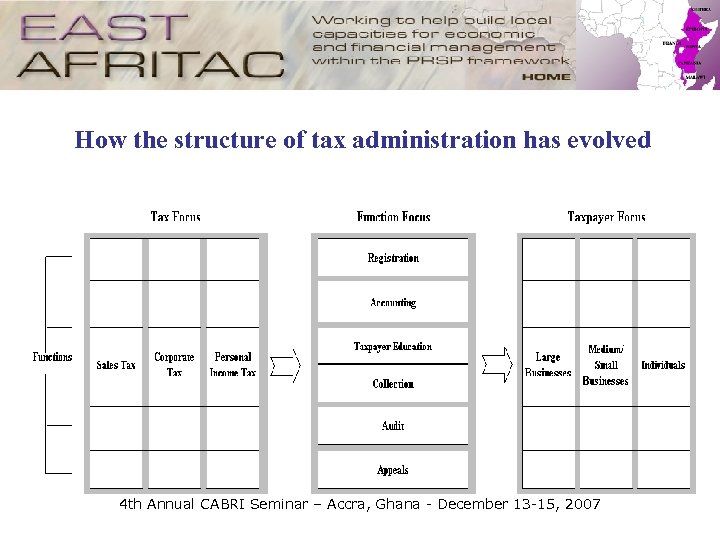 How the structure of tax administration has evolved 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
How the structure of tax administration has evolved 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Development of self-assessment ü Self-assessment – A system where taxpayers comply with their basic tax obligations without intervention of a tax official – Tax officials provide taxpayer with information and education about their obligations – Taxpayers complete their return accurately and submit them voluntarily with their payments – Failing that, enforcement actions is taken and penalties applied ü VAT was the impetus ü Income tax now mostly self-assessed ü However, while most countries have adopted self-assessment, the practice in reality falls far short 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Development of self-assessment ü Self-assessment – A system where taxpayers comply with their basic tax obligations without intervention of a tax official – Tax officials provide taxpayer with information and education about their obligations – Taxpayers complete their return accurately and submit them voluntarily with their payments – Failing that, enforcement actions is taken and penalties applied ü VAT was the impetus ü Income tax now mostly self-assessed ü However, while most countries have adopted self-assessment, the practice in reality falls far short 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Conditions for self assessment ü ü ü ü Simple and stable tax law Good services to taxpayers Simple filing and payment procedures Effective collection enforcement Selective risk-based audit programs Fairly applied penalties Fair and timely dispute resolution 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Conditions for self assessment ü ü ü ü Simple and stable tax law Good services to taxpayers Simple filing and payment procedures Effective collection enforcement Selective risk-based audit programs Fairly applied penalties Fair and timely dispute resolution 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Integration of domestic tax administration ü Traditional Anglophone influence in the region - split of direct and indirect tax administration ü RA and VAT – missed integration opportunities ü VAT, income tax, and excise domestic operations have been merged in Kenya, Rwanda, Tanzania, Uganda, Malawi ü The revenue agencies have established fully integrated domestic tax administrations that are organized around the key functions at the operational and headquarters level ü Advantages of integrating domestic tax administration: • Reduces tax administration and taxpayers’ compliance costs • Allows implementation of a unified, function-based organization • Increases effectiveness of tax administration (common registration, collection, and audit functions) ü Head office/field office functions 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Integration of domestic tax administration ü Traditional Anglophone influence in the region - split of direct and indirect tax administration ü RA and VAT – missed integration opportunities ü VAT, income tax, and excise domestic operations have been merged in Kenya, Rwanda, Tanzania, Uganda, Malawi ü The revenue agencies have established fully integrated domestic tax administrations that are organized around the key functions at the operational and headquarters level ü Advantages of integrating domestic tax administration: • Reduces tax administration and taxpayers’ compliance costs • Allows implementation of a unified, function-based organization • Increases effectiveness of tax administration (common registration, collection, and audit functions) ü Head office/field office functions 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
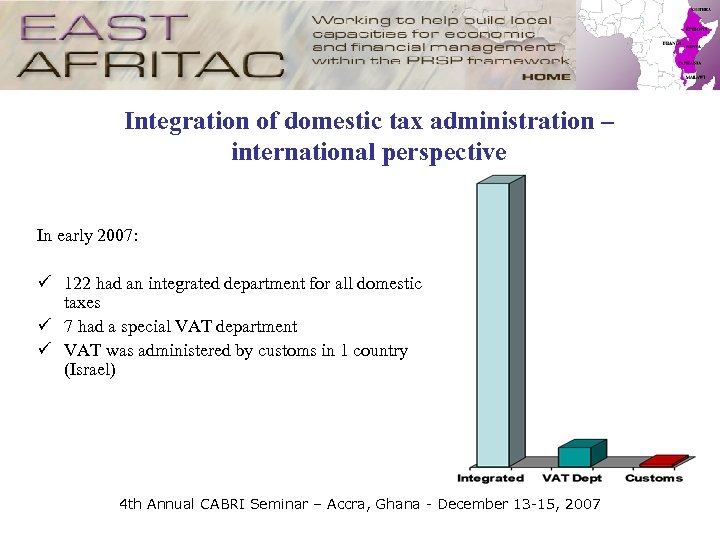 Integration of domestic tax administration – international perspective In early 2007: ü 122 had an integrated department for all domestic taxes ü 7 had a special VAT department ü VAT was administered by customs in 1 country (Israel) 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Integration of domestic tax administration – international perspective In early 2007: ü 122 had an integrated department for all domestic taxes ü 7 had a special VAT department ü VAT was administered by customs in 1 country (Israel) 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Integration of domestic tax administration – key issues ü ü Legislative review and development of common tax procedures code Business process review and improvement Integrated tax administration system (ITAS) Change management, training and capacity building 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Integration of domestic tax administration – key issues ü ü Legislative review and development of common tax procedures code Business process review and improvement Integrated tax administration system (ITAS) Change management, training and capacity building 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Taxpayer segmentation ü Taxpayers are not homogeneous ü In the past decade, many tax administrations have moved away from a one -size fits all approach and developed organizational structures on the basis of taxpayer segments ü Initially in the OECD countries (the Netherlands in 1990, New Zealand in 1994, and more recently Australia, France, and the UK) ü Several countries in the region have also developed the concept to improve their organization and tax compliance programs (Kenya, Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda) ü Tax administrations categorize their taxpayer population into 4 main categories: large business, medium businesses, small businesses and micro businesses 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Taxpayer segmentation ü Taxpayers are not homogeneous ü In the past decade, many tax administrations have moved away from a one -size fits all approach and developed organizational structures on the basis of taxpayer segments ü Initially in the OECD countries (the Netherlands in 1990, New Zealand in 1994, and more recently Australia, France, and the UK) ü Several countries in the region have also developed the concept to improve their organization and tax compliance programs (Kenya, Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda) ü Tax administrations categorize their taxpayer population into 4 main categories: large business, medium businesses, small businesses and micro businesses 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
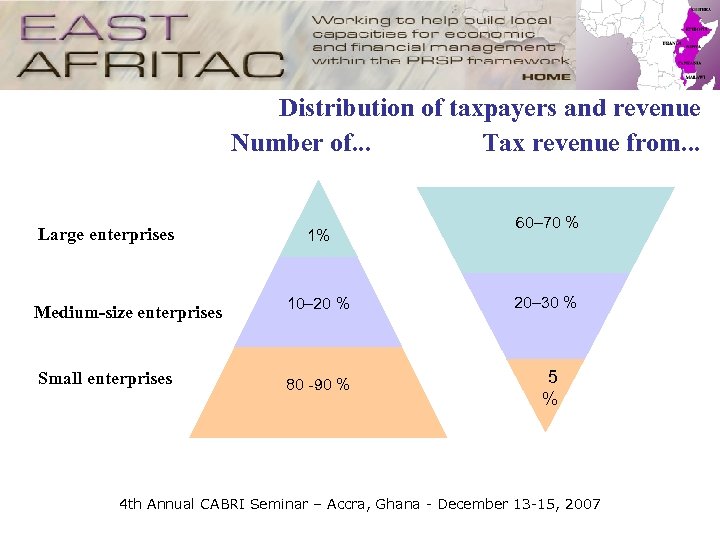 Distribution of taxpayers and revenue Number of. . . Tax revenue from. . . Large enterprises 1% 60– 70 % Medium-size enterprises 10– 20 % 20– 30 % Small enterprises 80 -90 % 5 % 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Distribution of taxpayers and revenue Number of. . . Tax revenue from. . . Large enterprises 1% 60– 70 % Medium-size enterprises 10– 20 % 20– 30 % Small enterprises 80 -90 % 5 % 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Why the move towards taxpayer segmentation? ü Developing compliance strategies that take into account “risk management” concepts ü Providing services to taxpayers according to their needs (better focus on “client” needs) ü Allocating enforcement and audit resources to areas of greatest risks 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Why the move towards taxpayer segmentation? ü Developing compliance strategies that take into account “risk management” concepts ü Providing services to taxpayers according to their needs (better focus on “client” needs) ü Allocating enforcement and audit resources to areas of greatest risks 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Creation of large taxpayers units (LTU) ü Large taxpayers units established in all countries, as a first step in adopting a taxpayer segmentation approach ü Secure 60+ percent of total tax revenue ü Expected benefits of LTUs • • • Reduce level of non compliance among large taxpayers Provide better services to large taxpayers Use LTU as a pilot to introduce major changes (e. g. , integration and self-assessment) Use LTU to secure implementation of major policy reform Signal government’s commitment to enforce tax laws to the taxpayer community ü Centers of excellence? ? ? ü ü Functional and integrated organization Simplified procedures New approaches – risk analysis, self-assessment Computerization 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Creation of large taxpayers units (LTU) ü Large taxpayers units established in all countries, as a first step in adopting a taxpayer segmentation approach ü Secure 60+ percent of total tax revenue ü Expected benefits of LTUs • • • Reduce level of non compliance among large taxpayers Provide better services to large taxpayers Use LTU as a pilot to introduce major changes (e. g. , integration and self-assessment) Use LTU to secure implementation of major policy reform Signal government’s commitment to enforce tax laws to the taxpayer community ü Centers of excellence? ? ? ü ü Functional and integrated organization Simplified procedures New approaches – risk analysis, self-assessment Computerization 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
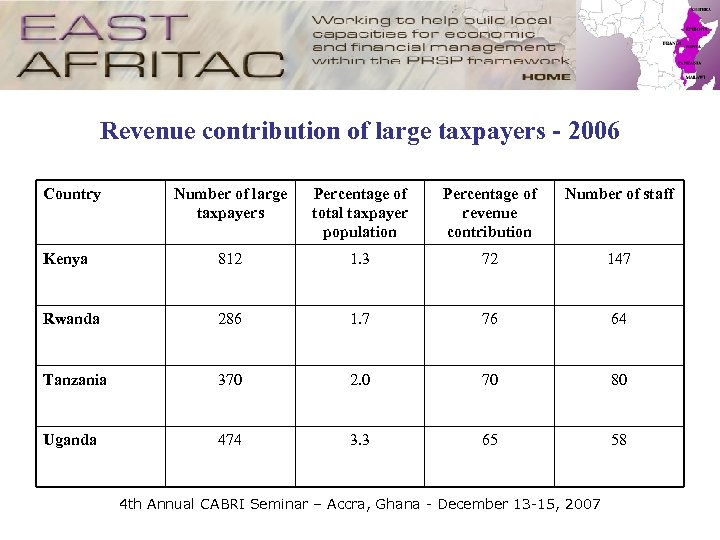 Revenue contribution of large taxpayers - 2006 Country Number of large taxpayers Percentage of total taxpayer population Percentage of revenue contribution Number of staff Kenya 812 1. 3 72 147 Rwanda 286 1. 7 76 64 Tanzania 370 2. 0 70 80 Uganda 474 3. 3 65 58 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Revenue contribution of large taxpayers - 2006 Country Number of large taxpayers Percentage of total taxpayer population Percentage of revenue contribution Number of staff Kenya 812 1. 3 72 147 Rwanda 286 1. 7 76 64 Tanzania 370 2. 0 70 80 Uganda 474 3. 3 65 58 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Creation of medium taxpayers units ü Definition ü Early steps taken in identifying taxpayers in the next most important group by revenue potential – i. e. medium-size enterprises ü Some countries are developing dedicated offices and/or programs for the administration of medium-size taxpayers ü However, management of medium taxpayers still weak and concept of medium tax offices not yet developed ü Critical focal area for the medium term 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Creation of medium taxpayers units ü Definition ü Early steps taken in identifying taxpayers in the next most important group by revenue potential – i. e. medium-size enterprises ü Some countries are developing dedicated offices and/or programs for the administration of medium-size taxpayers ü However, management of medium taxpayers still weak and concept of medium tax offices not yet developed ü Critical focal area for the medium term 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Administration of small and micro taxpayers ü The very large number of small and micro-businesses pose many challenges for tax administrations ü Is a key sector that must be tapped if tax base is to be expanded ü Simplified tax administration regime for small businesses – Eritrea, Ethiopia, Rwanda, Uganda, Tanzania, Kenya ü Use of withholding systems ü Block management system in Tanzania ü Issues – design, resource allocation, cost. . 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Administration of small and micro taxpayers ü The very large number of small and micro-businesses pose many challenges for tax administrations ü Is a key sector that must be tapped if tax base is to be expanded ü Simplified tax administration regime for small businesses – Eritrea, Ethiopia, Rwanda, Uganda, Tanzania, Kenya ü Use of withholding systems ü Block management system in Tanzania ü Issues – design, resource allocation, cost. . 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Customs Administration reforms ü Key issues – The changing role of customs – Traditional versus modern customs – Performance indicators for customs services – Integrity issues in customs – Links to risk management 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Customs Administration reforms ü Key issues – The changing role of customs – Traditional versus modern customs – Performance indicators for customs services – Integrity issues in customs – Links to risk management 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Customs Administration reform strategies ü Reorganization of program delivery in customs – distinction between policy and operations ü A service orientation including greater information to and engagement of the private sector ü Automation of transactions processing and management information support ü Self-assessment and use of risk-based approached to compliance management 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Customs Administration reform strategies ü Reorganization of program delivery in customs – distinction between policy and operations ü A service orientation including greater information to and engagement of the private sector ü Automation of transactions processing and management information support ü Self-assessment and use of risk-based approached to compliance management 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Customs Administration reform strategies ü Use of trader segmentation to implement appropriate compliance and trade facilitation strategies ü Simplified procedures for authorized economic operators/traders (Tanzania, initiatives in other countries) • Pre-approved traders deemed to be highly compliant and low risk • Formal application by these traders for the privilege • Trader required to keep books and records that are periodically audited by customs • An agreement is signed between customs and the trader detailing responsibilities and obligation of BOTH parties – revocable for non -compliance 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Customs Administration reform strategies ü Use of trader segmentation to implement appropriate compliance and trade facilitation strategies ü Simplified procedures for authorized economic operators/traders (Tanzania, initiatives in other countries) • Pre-approved traders deemed to be highly compliant and low risk • Formal application by these traders for the privilege • Trader required to keep books and records that are periodically audited by customs • An agreement is signed between customs and the trader detailing responsibilities and obligation of BOTH parties – revocable for non -compliance 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Customs Administration reform strategies ü Use audit-based controls – Post clearance audits of trader records and systems is superior to transactions-based controls – Joint audits with VAT and income take place – Training and capacity building - accounting systems, IT systems and auditing techniques 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Customs Administration reform strategies ü Use audit-based controls – Post clearance audits of trader records and systems is superior to transactions-based controls – Joint audits with VAT and income take place – Training and capacity building - accounting systems, IT systems and auditing techniques 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Focal areas ü ü Revenue administration reform has taken hold in the region RAs were a major development Reforms have been steady, sometimes based on international experience Not effective without system and procedural modernization, integration, and segmentation ü Challenge – To increase the tax-to-GDP ratio while reducing cost of collection, and improving services and support to taxpayers ü Requires achieving higher levels of voluntary compliance of taxpayers ü Development of compliance management programs that are structured around taxpayer segments the focal area 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Focal areas ü ü Revenue administration reform has taken hold in the region RAs were a major development Reforms have been steady, sometimes based on international experience Not effective without system and procedural modernization, integration, and segmentation ü Challenge – To increase the tax-to-GDP ratio while reducing cost of collection, and improving services and support to taxpayers ü Requires achieving higher levels of voluntary compliance of taxpayers ü Development of compliance management programs that are structured around taxpayer segments the focal area 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Compliance Management program for medium taxpayers Risks Interventions • Concealing sales through cash and barter transaction. • Late and non filers, and nil filers. • Poor record keeping, and false records. • VAT fraud. • Failure to comply with employer obligations. • Use of third-party information (e. g, from banks and service providers). • Establishment of quantitative benchmarks for trades and other businesses. • Elimination of inactive taxpayers from the taxpayer register. • Taxpayer education and publicity campaign to impress on taxpayers their filing obligations, closely monitor filing performance. • Make early contact with late/non filers. Also review nil filers. • Field operations should include reviewing record-keeping practices. • Apply appropriate mix of audit techniques. • Distinguish between taxpayers with a history of compliance and those with poor or unknown compliance history. • Manual screening of VAT refunds using generic criteria/ITAS can aid screening of VAT refunds. 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Compliance Management program for medium taxpayers Risks Interventions • Concealing sales through cash and barter transaction. • Late and non filers, and nil filers. • Poor record keeping, and false records. • VAT fraud. • Failure to comply with employer obligations. • Use of third-party information (e. g, from banks and service providers). • Establishment of quantitative benchmarks for trades and other businesses. • Elimination of inactive taxpayers from the taxpayer register. • Taxpayer education and publicity campaign to impress on taxpayers their filing obligations, closely monitor filing performance. • Make early contact with late/non filers. Also review nil filers. • Field operations should include reviewing record-keeping practices. • Apply appropriate mix of audit techniques. • Distinguish between taxpayers with a history of compliance and those with poor or unknown compliance history. • Manual screening of VAT refunds using generic criteria/ITAS can aid screening of VAT refunds. 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
 Other issues ü Taxation of small business - a challenge ü Other emerging issues - transfer to RAs of the collection responsibility of other government levies such as social contributions, natural resource taxation and accountability issues THE END 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007
Other issues ü Taxation of small business - a challenge ü Other emerging issues - transfer to RAs of the collection responsibility of other government levies such as social contributions, natural resource taxation and accountability issues THE END 4 th Annual CABRI Seminar – Accra, Ghana - December 13 -15, 2007


