15246378c943b4cf2a6551ff9ef5e0d1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

Reusable Software Architectures Feature Modeling for Software Product Lines SEG 3202 Nour EL-Kadri

Feature Modeling • Important aspect of Software Product Line Engineering • Feature – Requirement or characteristic provided by one or more members of the product line – Characteristic that differentiates among members of the software product line – Use to determine common and variable functionality • Software Product Lines have different kinds of features – Functional features • Functional requirement, e. g. , PIN validation – Non-functional features • Non-functional requirement (e. g. , security, performance) – Parameterized features (e. g. , red, yellow, green)

Feature Modeling • Features are categorized as – Common features • Provided by all members of product line – Optional features • Provided by some members of product line – Alternative features • Choice of features • One of the alternatives may be a default feature – Parameterized feature • Defines a product line parameter • Type, permitted values, default value
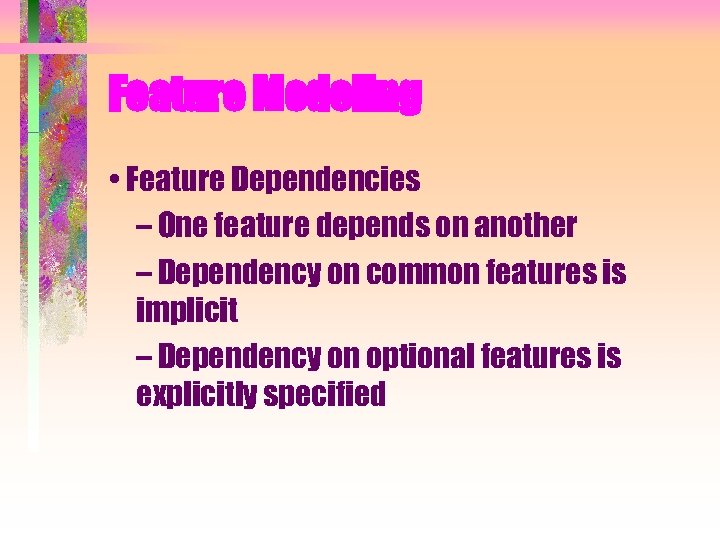
Feature Modeling • Feature Dependencies – One feature depends on another – Dependency on common features is implicit – Dependency on optional features is explicitly specified

Feature Notation • • • Uses extension mechanisms of UML – Stereotypes, tagged values, constraints «common feature» Feature Name, – «common feature» Factory Kernel « optional feature» Feature Name {prerequisite = P} – «optional feature» Light, «optional feature» Beeper «alternative feature» Feature Name {prerequisite = P} – «alternative feature» French, «alternative feature» Spanish «default feature» Feature Name {prerequisite = P} – «default feature» English « parameterized feature» Feature Name – «parameterized feature» ATM Password Length {type = integer, permitted value = 4. . 8, default value = 4}

Feature Notation • Prerequisite feature – Feature that an optional or alternative feature depends on • « optional feature» Workflow Planning User {prerequisite = Workflow Management} • «alternative feature» TOD Clock {prerequisite = Multi-line Display} • Explicit feature – Feature that can be selected individually • Implicit feature – Feature that is not allowed to be selected individually • Mutually inclusive feature could be an implicit feature – « optional feature» Recipe {mutually includes = Analog Weight}

Feature Modeling • Model feature as a use case – Can use when a feature is modeled as a use case • Model feature as a use case package – Can use when a feature is a grouping of use cases • Model feature as a class – Using UML static modeling to model metaclasses • Feature / use case dependency – Tabular representation

Use Cases and Features • Use Cases – Used to define functional requirements of a system • Features – Used to identify reusable requirements • Use cases – Can be used to determine features in Software Product Lines – Use cases relate to functional features – Use cases can also help determine parameterized features

Use Cases and Features • Functional feature modeled as – One or more use cases • Use cases that are reused together can be grouped into use case package • Feature modeled as use case package
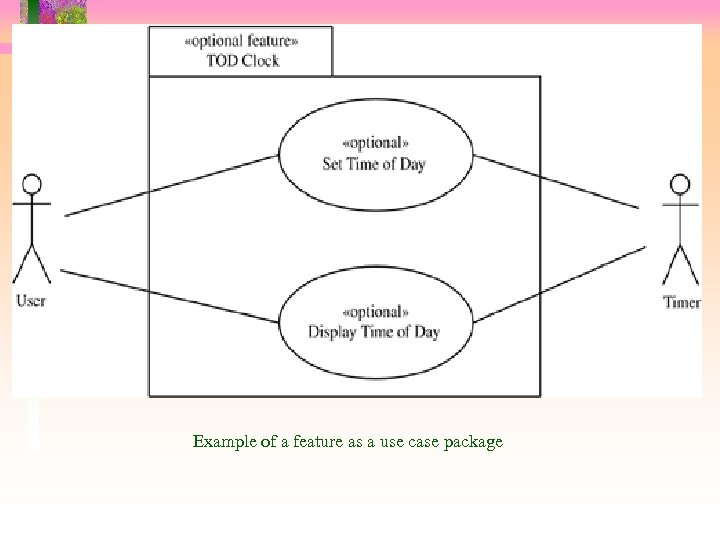
Example of a feature as a use case package
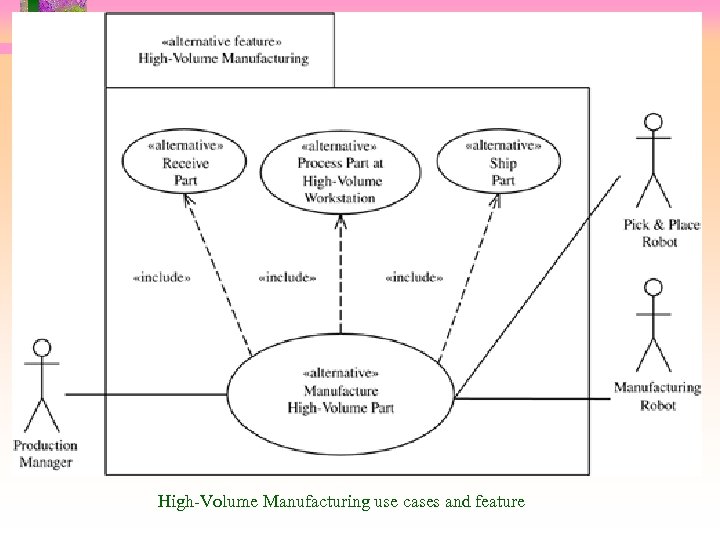
High-Volume Manufacturing use cases and feature

Use Cases and Features • Use cases can be used to model feature dependencies • Use case relationships can be specified <<include>> • Common functionality split off into abstract use case <<extend>> • One use case extends another when certain conditions hold • Use case dependency can be modeled as feature dependency
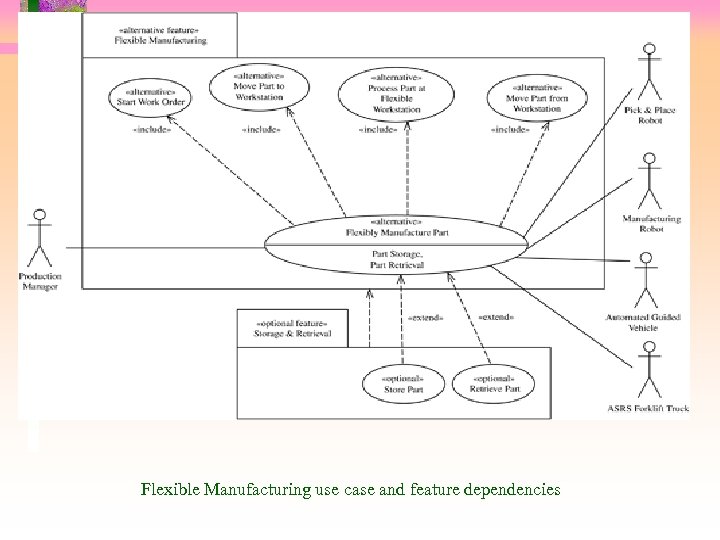
Flexible Manufacturing use case and feature dependencies

Features and Variation Points • Model variation point as feature • Use Case Variation Point – Location in a use case where a change can take place – VP as Optional functional requirement within a use case • Optional feature • E. g. , Variation points in Microwave Oven SPL – Turntable VP -> «optional feature» Turntable – Beeper VP -> «optional feature» Beeper – VP as Alternative functional requirement within a use case • Alternative features • E. g. , Display variation point in Microwave Oven SPL – «alternative feature» Multi-Line Display – «default feature» One-Line Display

Features and Variation Points • Parameterized features – Parameter identified in use case – Different values of parameter in different members of product line • Variation point identifies location in use case – where parameterized functionality is inserted • «parameterized feature» ATM Password Length {type = integer, permitted value = 4. . 8, default value = 4}
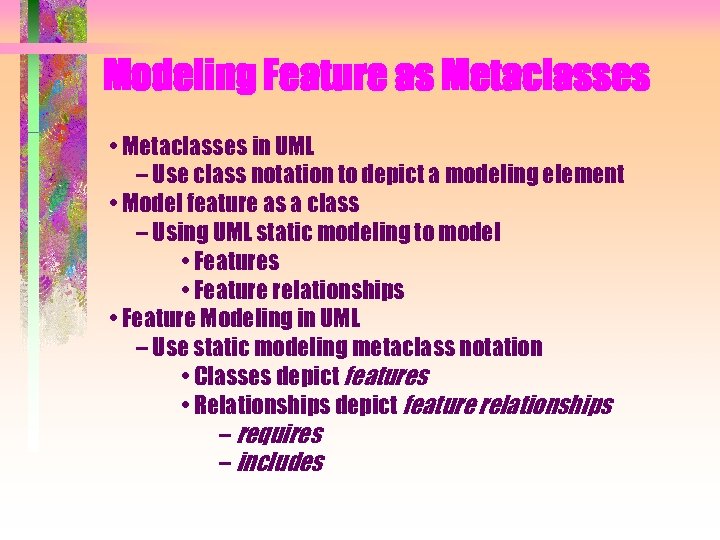
Modeling Feature as Metaclasses • Metaclasses in UML – Use class notation to depict a modeling element • Model feature as a class – Using UML static modeling to model • Features • Feature relationships • Feature Modeling in UML – Use static modeling metaclass notation • Classes depict features • Relationships depict feature relationships – requires – includes
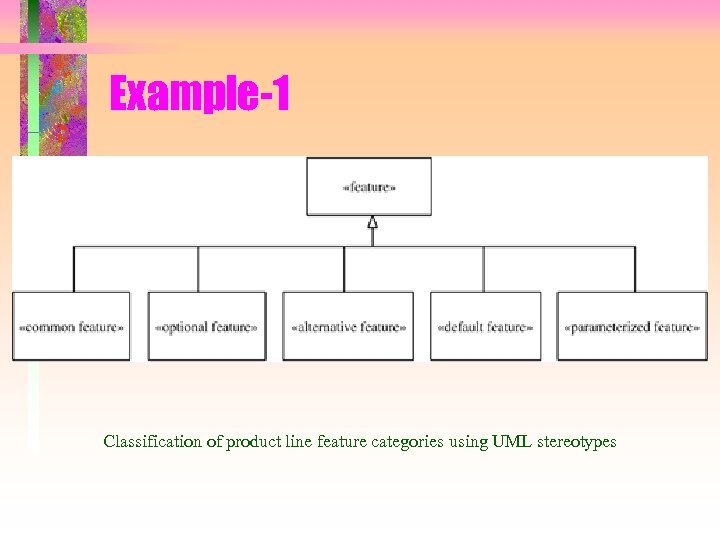
Example-1 Classification of product line feature categories using UML stereotypes
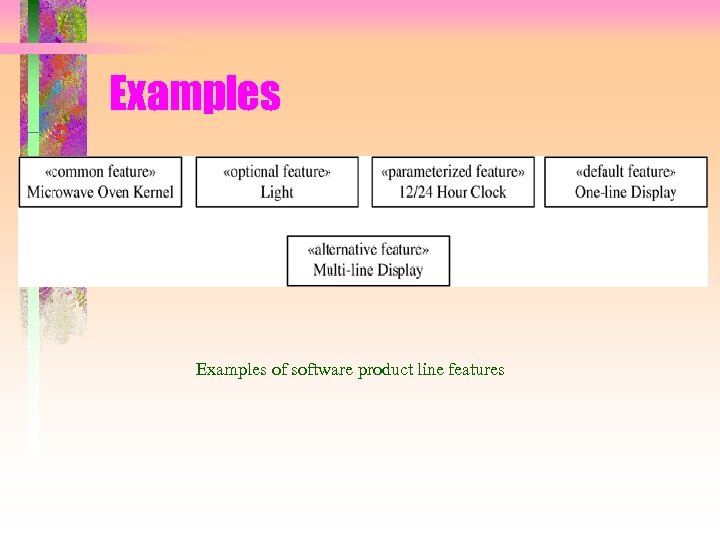
Examples of software product line features
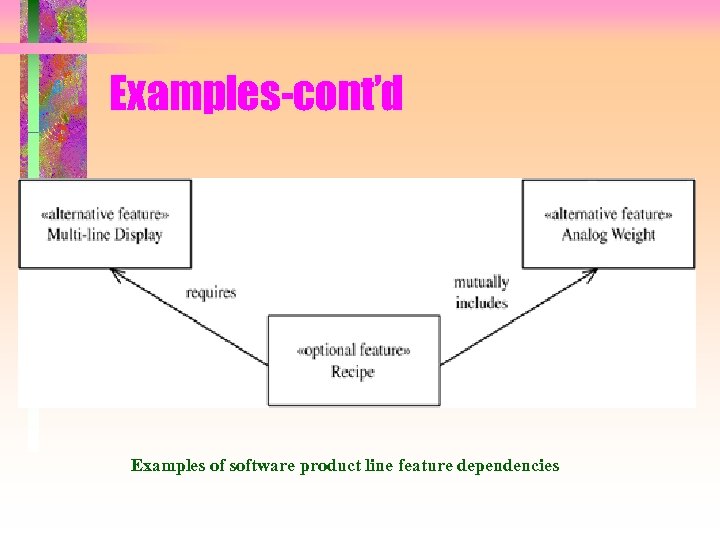
Examples-cont’d Examples of software product line feature dependencies

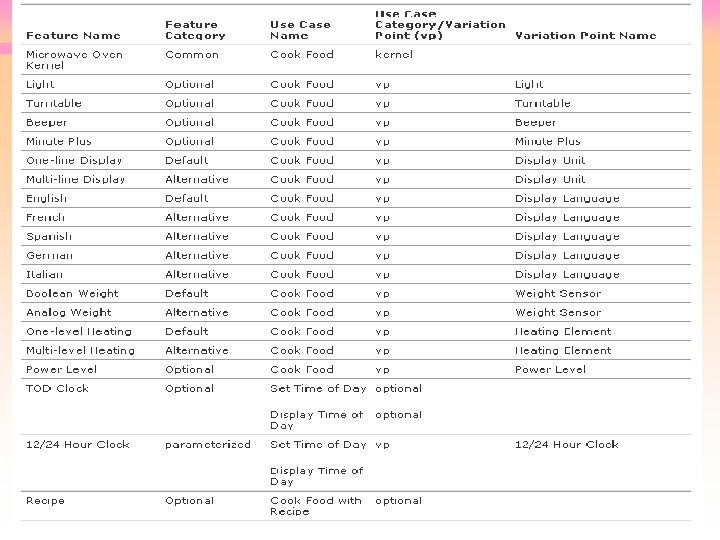
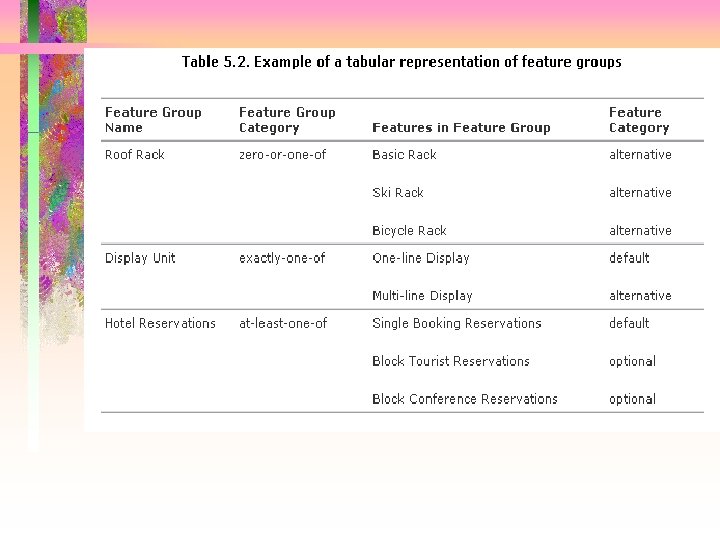
Representing Features in Tables • Can use tables to depict – Features • One row per feature – Feature / use case dependencies • Columns of table • Feature Name • Feature Category • Use Case Name • Use Category or Variation Point (vp) • Variation Point Name The following slide shows a Tabular representation of feature/use case relationships: microwave oven software product line

Feature Groups • Feature group – A group of features with a particular constraint on their usage in a SPL member • Feature groups in PLUS – Mutually exclusive features • Zero or One out of a group of features – Exactly one of a group of features • One and only one out of a group of features – One or more of a group of features • One or more out of a group of features – Mutually inclusive • If one feature is picked, the other must be picked

Modeling Feature Groups in UML • Mutually exclusive features – «zero-or-one-of feature group» Feature Group Name {Alternative = A 1…An, Prerequisite = P} – «zero-or-one-of feature group» Roof Rack {alternative = Basic Rack, Ski Rack, Bicycle Rack} • Must select one feature – «exactly-one-of feature group» Feature Group Name {default = D, alternative = A 1…An, prerequisite = P} – «exactly-one-of feature group» Display Unit {default = One-line Display, alternative = Multi-line Display} • Feature groups as metaclasses
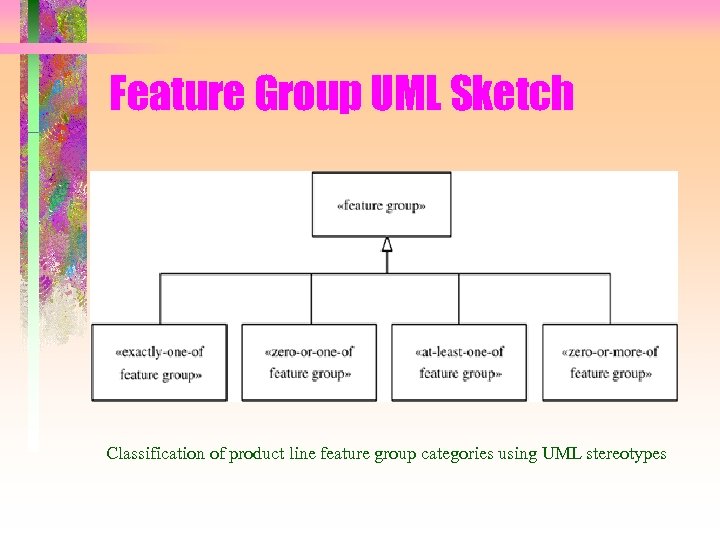
Feature Group UML Sketch Classification of product line feature group categories using UML stereotypes
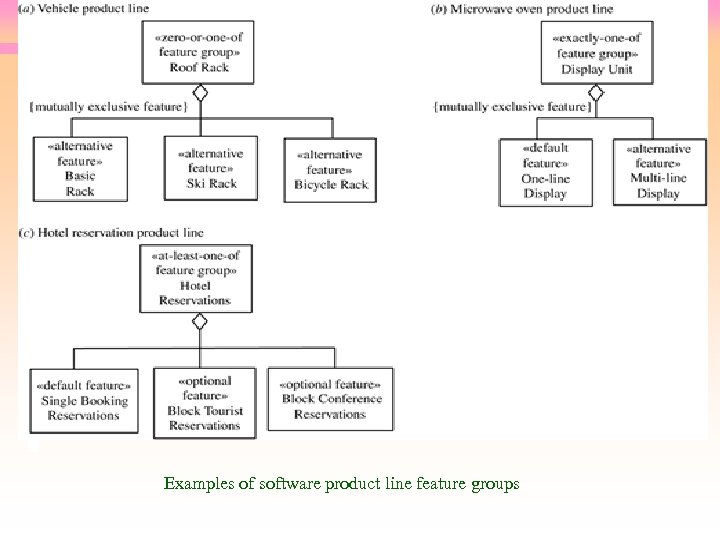
Examples of software product line feature groups

Modeling Feature Groups in UML • Can select one or more features – «at-least-one-of feature group» Feature Group Name {default = D, feature = O 1, …, On, prerequisite = P} – «at-least-one-of feature group» Hotel Reservations {default = Single Booking Reservations, feature = Block Tourist Reservations, Block Conference Reservations} • A group of optional features depend on another optional feature – «zero-or-more-of feature group» Feature Group Name {feature = First Optional Feature Name, …, Nth Optional Feature Name, prerequisite = Prerequisite Feature Name} – «zero-or-more-of feature group» Automated Drive Control {feature = Cruise Control, Automatic Traction, prerequisite = Automatic Transmission}

Example of Feature Modeling Microwave Oven Product Line • Kernel first approach • Kernel use case – Cook Food • Optional use cases – Set Time of Day – Cook Food with Recipe • Product Line use case variability – Several variation points • Use case diagram (next Slide)
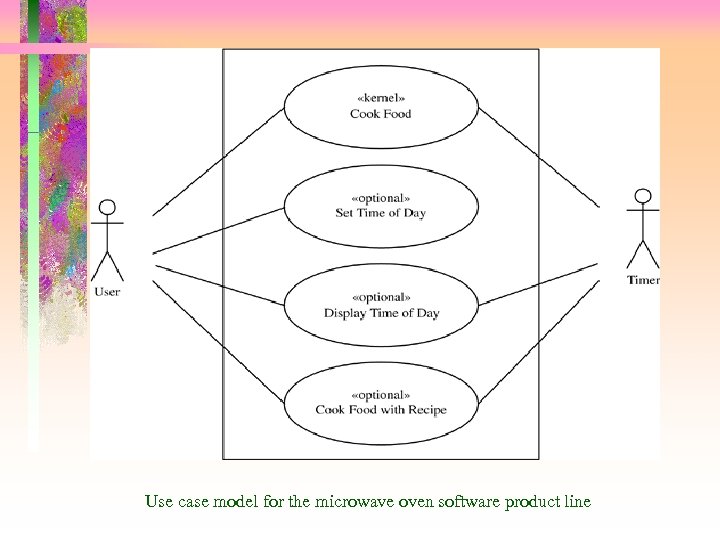
Use case model for the microwave oven software product line

Feature Model for Microwave Oven SPL Optional Features • Optional feature corresponding to use case package – <<optional feature>> TOD Clock • Optional features derived from use case variation points – Light feature • <<optional feature>> Light – Turntable feature • <<optional feature>> Turntable – Beeper feature • <<optional feature>> Beeper – Minute plus feature • <<optional feature>> Minute Plus

Feature Model for Microwave Oven SPL Feature Groups • Feature groups derived from use case variation points • Display Unit - One line / multi-line – <<exactly-one-of feature set>> Display Unit {default = One-line Display, alternative = Multi-line Display} • Display Language – <<exactly-one-of feature set>> Display Language {default = English, alternative = French, Spanish, German, Italian} • Weight Sensor - Boolean / Analog – <<exactly-one-of feature set>> Weight Sensor {default = Boolean Weight, alternative = Analog Weight} • Heating Element – one-level / multi-level – <<exactly-one-of feature set>> Heating Element {default = One-level Heating, alternative = Multi-level Heating}

Feature Model for Microwave Oven SPL Optional Functional Features with Prerequisites and Mutually Inclusive Features • Power Level buttons – <<optional feature>> Power Level {mutually includes = Multi-level Heating} • Recipe – <<optional feature>> Recipe {prerequisite = Multi-line Display, mutually includes = Analog Weight, Multi-level Heating} • TOD Clock – <<optional feature>> TOD Clock {prerequisite = Multiline Display

Feature Model for Microwave Oven SPL • Parameterized feature – 12/24 Hour Clock – «parameterized feature» 12/24 Hour Clock {type = Time, permitted value = 12: 00, 24: 00, default value = 12: 00, mutually includes = TOD Clock} • Feature Tables • Feature Dependency Diagram
15246378c943b4cf2a6551ff9ef5e0d1.ppt