Retro Transcr Vir.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Retro- transcribing viruses
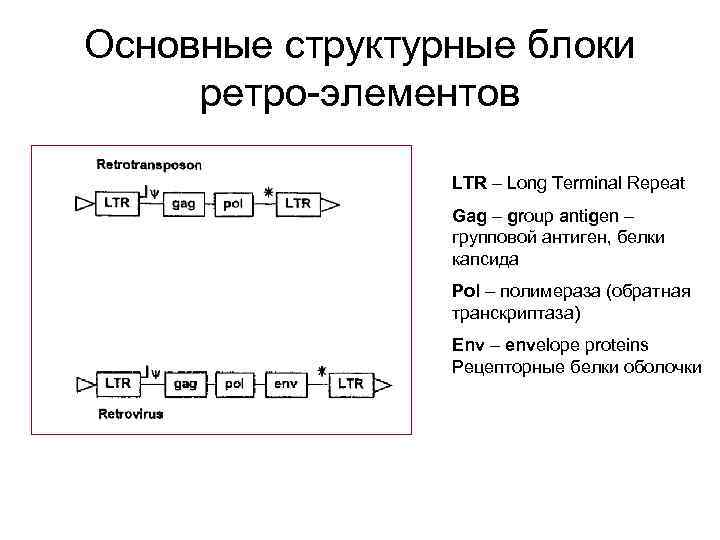
Основные структурные блоки ретро-элементов LTR – Long Terminal Repeat Gag – group antigen – групповой антиген, белки капсида Pol – полимераза (обратная транскриптаза) Env – envelope proteins Рецепторные белки оболочки
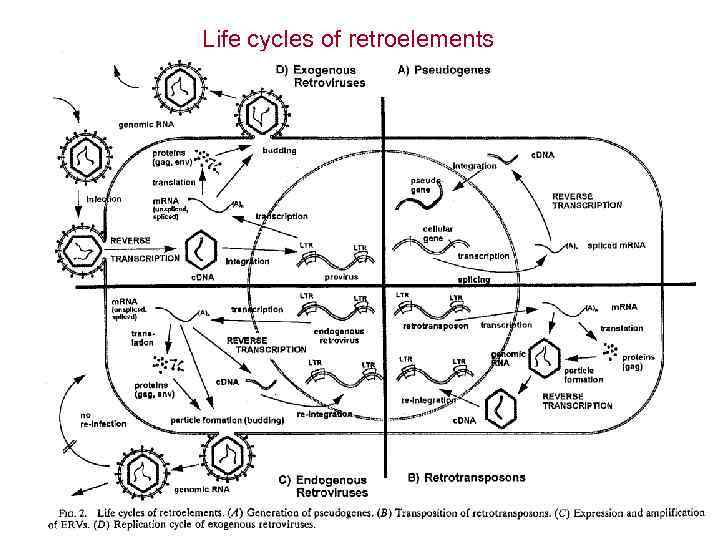
Life cycles of retroelements
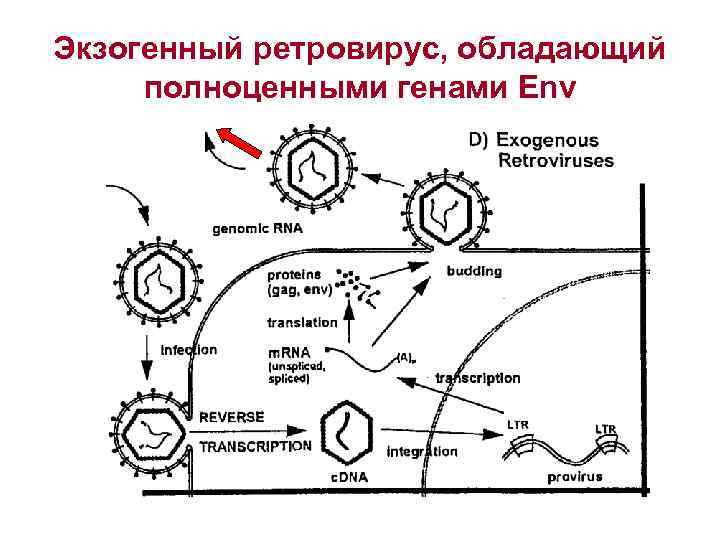
Экзогенный ретровирус, обладающий полноценными генами Env
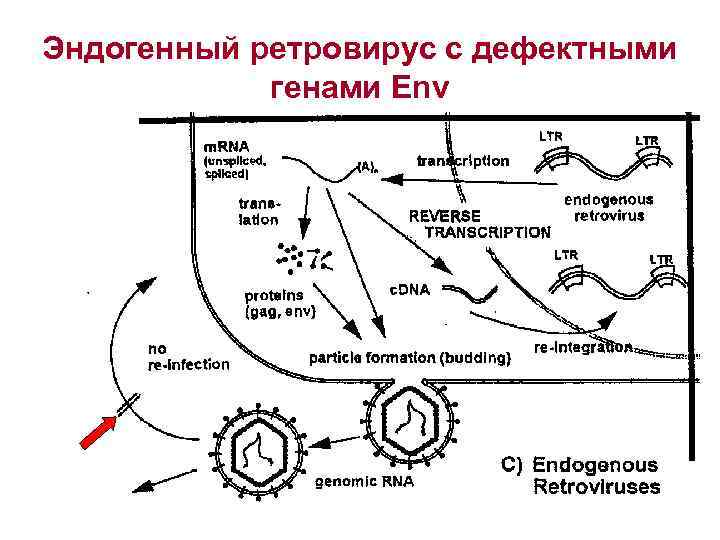
Эндогенный ретровирус с дефектными генами Env
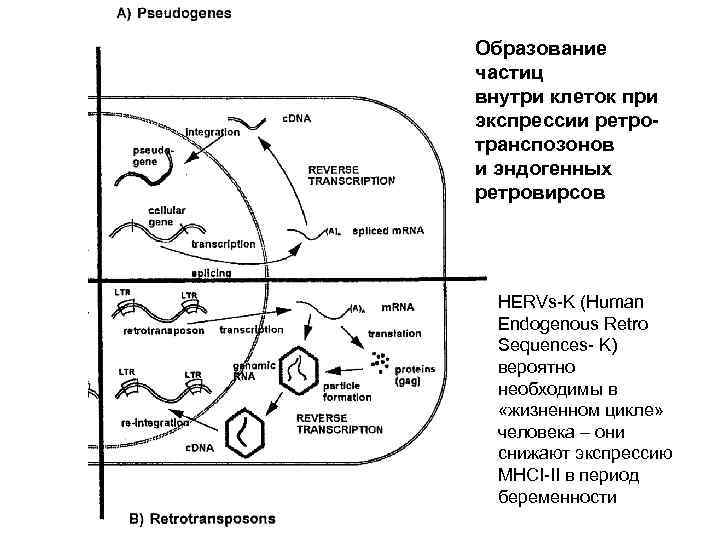
Образование частиц внутри клеток при экспрессии ретротранспозонов и эндогенных ретровирсов HERVs-K (Human Endogenous Retro Sequences- K) вероятно необходимы в «жизненном цикле» человека – они снижают экспресcию MHCI-II в период беременности

RETROVIRIDAE • Orthoretrovirinae – Alpharetrovirus. Avian leukosis virus. Rous sarcoma virus. – Betaretrovirus. Mouse mammary tumor virus. – Deltaretrovirus. Bovine leukemia virus. HTLV-1, HTLV 2, HTLV-3. – Epsilon retrovirus. Fish retroviruses – Gammaretrovirus. Feline leukemia virus – Lentivirus. HIV-1, HIV-2, • Spumaretrovirinae. Feline foamy virus. Human foamy viruses- «пенящие» вирусы
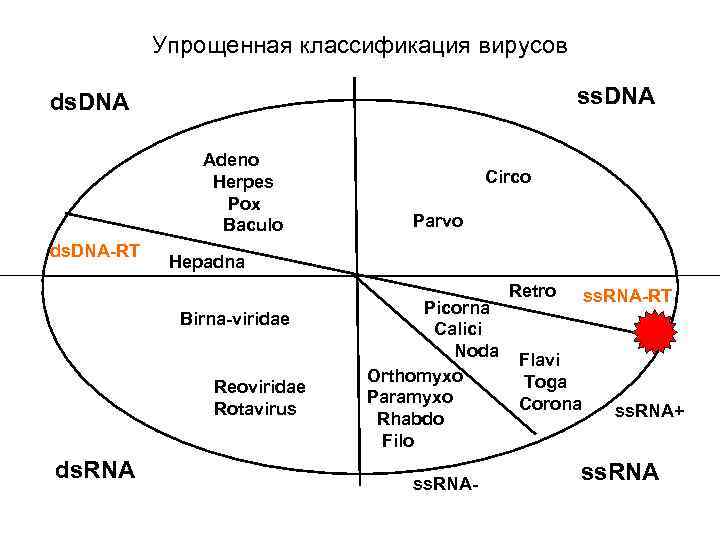
Упрощенная классификация вирусов ss. DNA ds. DNA Adeno Herpes Pox Baculo ds. DNA-RT Parvo Hepadna Birna-viridae Reoviridae Rotavirus ds. RNA Circo Picorna Calici Noda Orthomyxo Paramyxo Rhabdo Filo ss. RNA- Retro ss. RNA-RT Flavi Toga Corona ss. RNA+ ss. RNA

The Discovery of HIV as the Cause of AIDS in 1984 Robert C. Gallo, M. D. , and Luc Montagnier, M. D. Surface of a T Lymphocyte Infected by HIV. Photograph by Lennart Nilsson, M. D. , Stockholm, Sweden, 1985.
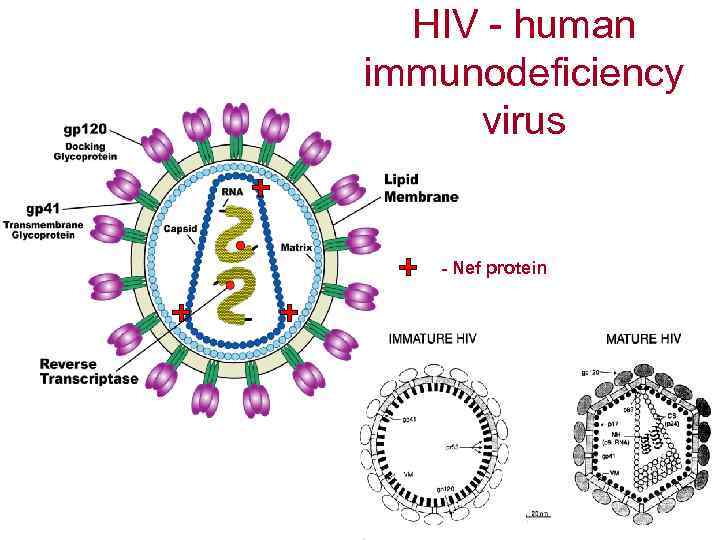
HIV - human immunodeficiency virus - Nef protein
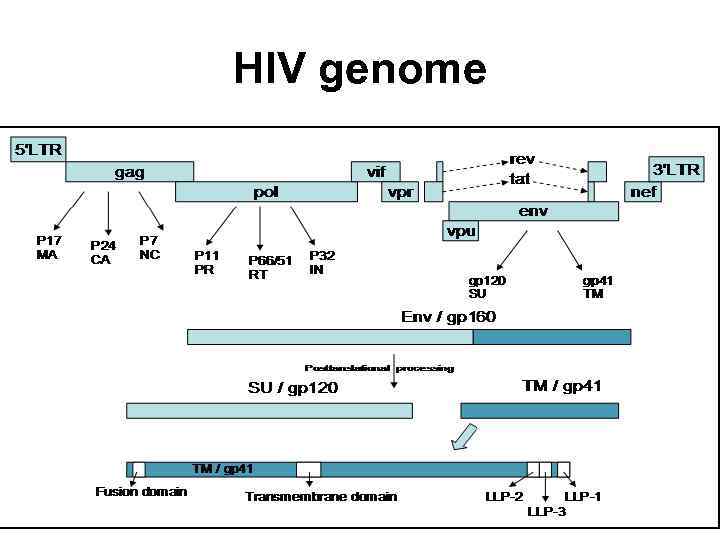
HIV genome
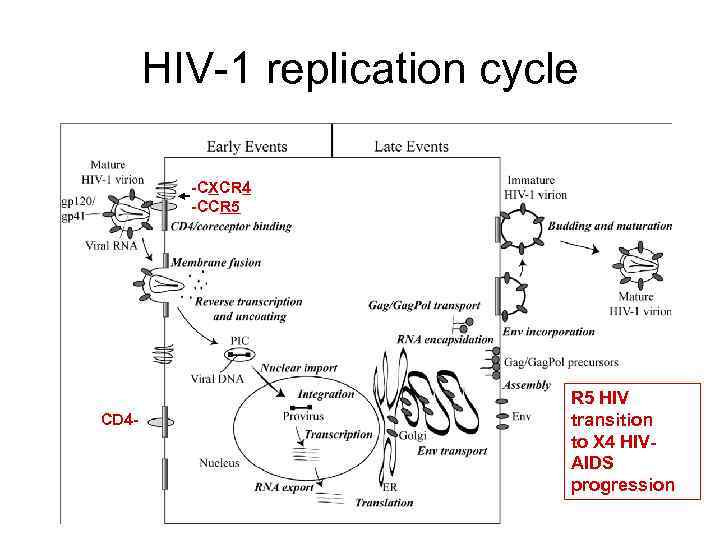
HIV-1 replication cycle -CXCR 4 -CCR 5 CD 4 - R 5 HIV transition to X 4 HIVAIDS progression
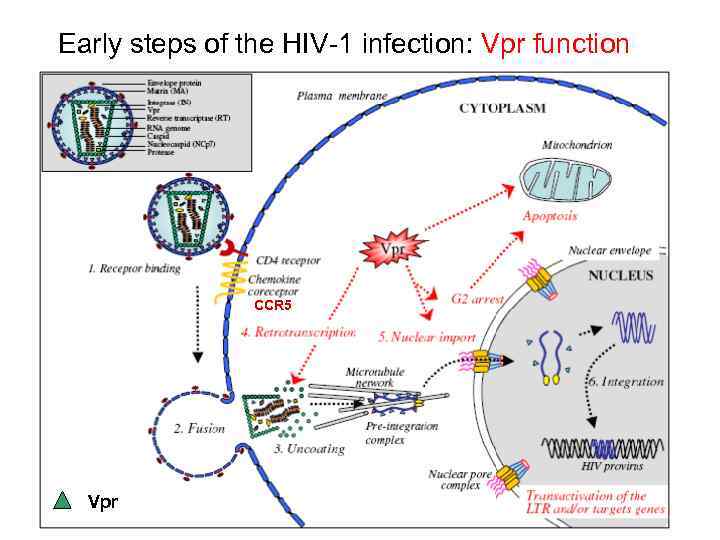
Early steps of the HIV-1 infection: Vpr function CCR 5 Vpr
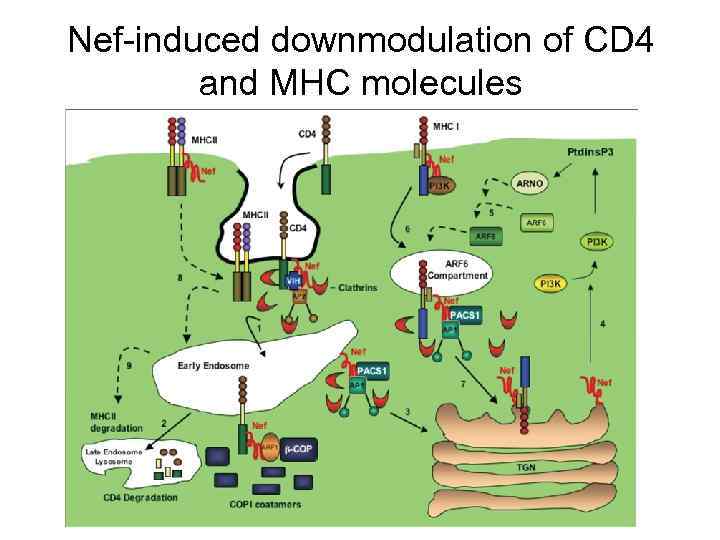
Nef-induced downmodulation of CD 4 and MHC molecules
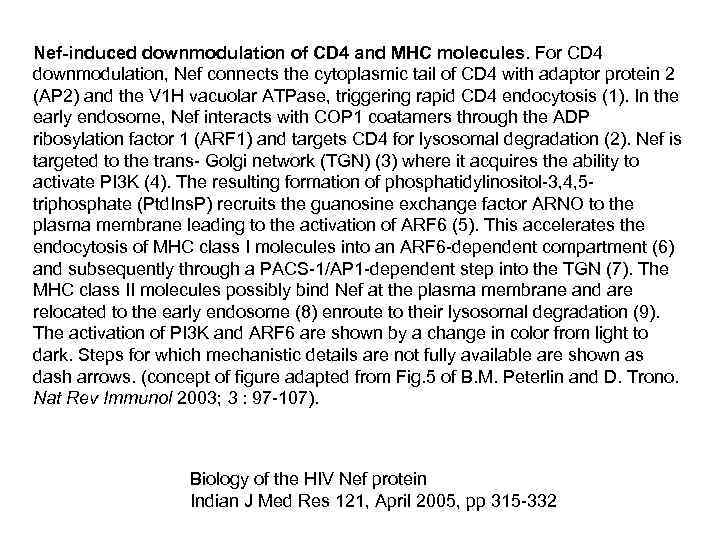
Nef-induced downmodulation of CD 4 and MHC molecules. For CD 4 downmodulation, Nef connects the cytoplasmic tail of CD 4 with adaptor protein 2 (AP 2) and the V 1 H vacuolar ATPase, triggering rapid CD 4 endocytosis (1). In the early endosome, Nef interacts with COP 1 coatamers through the ADP ribosylation factor 1 (ARF 1) and targets CD 4 for lysosomal degradation (2). Nef is targeted to the trans- Golgi network (TGN) (3) where it acquires the ability to activate PI 3 K (4). The resulting formation of phosphatidylinositol-3, 4, 5 triphosphate (Ptd. Ins. P) recruits the guanosine exchange factor ARNO to the plasma membrane leading to the activation of ARF 6 (5). This accelerates the endocytosis of MHC class I molecules into an ARF 6 -dependent compartment (6) and subsequently through a PACS-1/AP 1 -dependent step into the TGN (7). The MHC class II molecules possibly bind Nef at the plasma membrane and are relocated to the early endosome (8) enroute to their lysosomal degradation (9). The activation of PI 3 K and ARF 6 are shown by a change in color from light to dark. Steps for which mechanistic details are not fully available are shown as dash arrows. (concept of figure adapted from Fig. 5 of B. M. Peterlin and D. Trono. Nat Rev Immunol 2003; 3 : 97 -107). Biology of the HIV Nef protein Indian J Med Res 121, April 2005, pp 315 -332
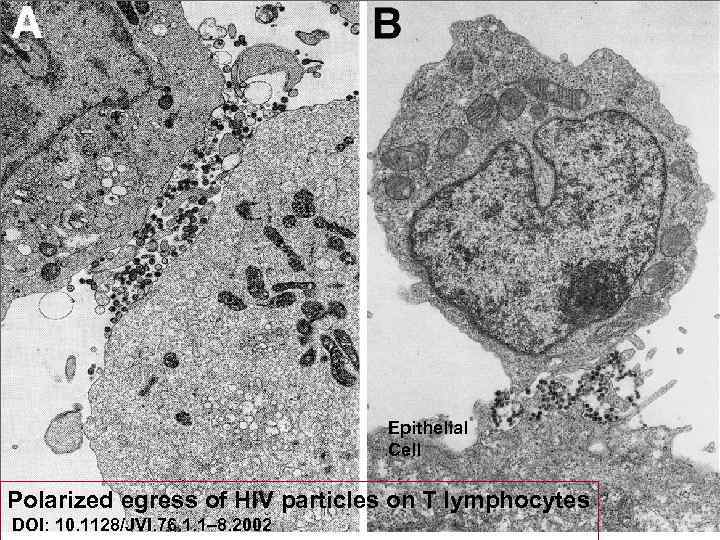
Epithelial Cell Polarized egress of HIV particles on T lymphocytes DOI: 10. 1128/JVI. 76. 1. 1– 8. 2002
Retro Transcr Vir.ppt