d3e687854c36b6f1b5175b175a4b2088.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62
 Rethinking Welfare Economics: a direct Operationalisation of Sen’s Capability Approach Turin, Italy Department Seminar Turin December 2013 Paul Anand Economics, The Open University and Health Economics Research Centre, Oxford University
Rethinking Welfare Economics: a direct Operationalisation of Sen’s Capability Approach Turin, Italy Department Seminar Turin December 2013 Paul Anand Economics, The Open University and Health Economics Research Centre, Oxford University
 Rethinking Welfare Economics: A Capability Approach Motivation Background and Theory Measurement (Data Development) Development and Happiness of Very Young Children Conclusions
Rethinking Welfare Economics: A Capability Approach Motivation Background and Theory Measurement (Data Development) Development and Happiness of Very Young Children Conclusions
 Three Major Themes Capability approach provides a feasible way of going beyond GDP (eg Petty/Kuznets/Stone/Sen) QOL/experienced utility is highly multidimensional Capability approach permits application of production and distributional concerns to consumers/citizens/QOL and is therefore a feasible complement to Edgeworth Box welfare economics
Three Major Themes Capability approach provides a feasible way of going beyond GDP (eg Petty/Kuznets/Stone/Sen) QOL/experienced utility is highly multidimensional Capability approach permits application of production and distributional concerns to consumers/citizens/QOL and is therefore a feasible complement to Edgeworth Box welfare economics
 Capabilities Measurement Project Some Collaborators and Advisors Philosophy and Social Science Ian Carter Keith Dowding Francesco Guala Martin van Hees Graciela Tonon Maria Sigala AHRB Economics and Health Alastair Gray Graham Hunter Paula Lorgelly Jaya Krishnakumar Peter Moffat Cristina Santos Judit Simon Ron Smith Laurence Roope Amartya Sen James Heckman Leverhulme Trust
Capabilities Measurement Project Some Collaborators and Advisors Philosophy and Social Science Ian Carter Keith Dowding Francesco Guala Martin van Hees Graciela Tonon Maria Sigala AHRB Economics and Health Alastair Gray Graham Hunter Paula Lorgelly Jaya Krishnakumar Peter Moffat Cristina Santos Judit Simon Ron Smith Laurence Roope Amartya Sen James Heckman Leverhulme Trust
 Some publications… Journal of Human Development and Capabilities (2009) Chapter in Festschrift for Amartya Sen Arguments for a Better World, Oxford University Press, Basu and Kanbur, (2009) Journal of Public Economics (2011) Social Indicators Research, Journal of Health Economics, Journal of Medical Ethics, Health Economics etc
Some publications… Journal of Human Development and Capabilities (2009) Chapter in Festschrift for Amartya Sen Arguments for a Better World, Oxford University Press, Basu and Kanbur, (2009) Journal of Public Economics (2011) Social Indicators Research, Journal of Health Economics, Journal of Medical Ethics, Health Economics etc
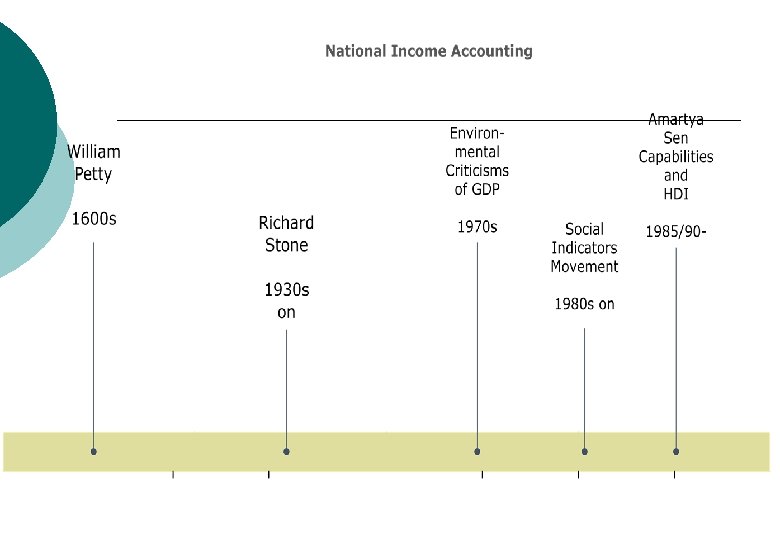
 Five Measurement Problems with GDP per head ¡ Fails to account for loss of environmental assets ¡ Excludes the value of household productive activities ¡ GDP is not a measure of human wellbeing ¡ Not all sources of wellbeing are strongly & positively related to income ¡ Average GDP says nothing about distribution
Five Measurement Problems with GDP per head ¡ Fails to account for loss of environmental assets ¡ Excludes the value of household productive activities ¡ GDP is not a measure of human wellbeing ¡ Not all sources of wellbeing are strongly & positively related to income ¡ Average GDP says nothing about distribution
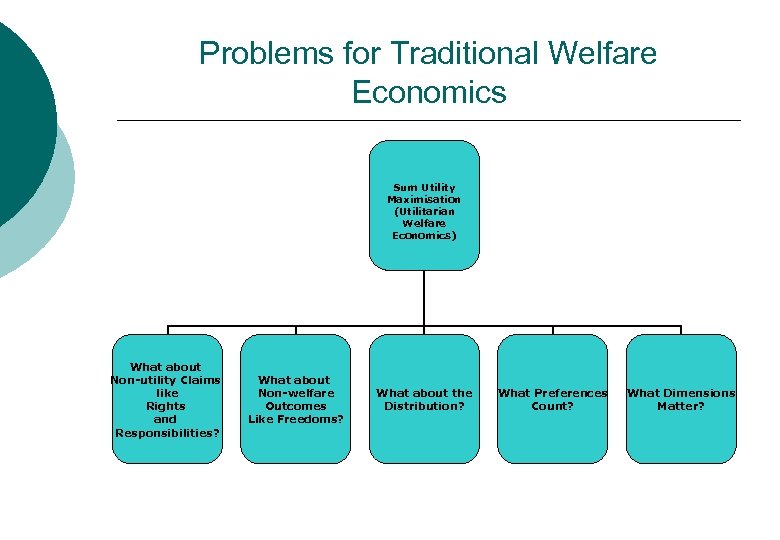 Problems for Traditional Welfare Economics Sum Utility Maximisation (Utilitarian Welfare Economics) What about Non-utility Claims like Rights and Responsibilities? What about Non-welfare Outcomes Like Freedoms? What about the Distribution? What Preferences Count? What Dimensions Matter?
Problems for Traditional Welfare Economics Sum Utility Maximisation (Utilitarian Welfare Economics) What about Non-utility Claims like Rights and Responsibilities? What about Non-welfare Outcomes Like Freedoms? What about the Distribution? What Preferences Count? What Dimensions Matter?
 Economic Theory (Sen 1985 pp 11 -4) ACTIVITES DEPEND ON RESOURCES EQ 1. fi = fi(xi) - heterogeneity in conversion HAPPINESS DEPENDS ON ACTIVITIES EQ 2. ui = hi(fi) - happiness CAPABILITIES ARE ALL THE ACTIVITIES POSSIBLE FOR A PERSON GIVEN RESOURCES EQ 3. Qi = {f 1, f 2, …fm}/endowment - advantage xi is vector of commodities possessed by i f(. ) converts resources into activities (doings/beings aka functionings) “Qi represents the freedom a person has in terms of the choice of functionings, given his personal features Fi…and his command over commodities xi. ”
Economic Theory (Sen 1985 pp 11 -4) ACTIVITES DEPEND ON RESOURCES EQ 1. fi = fi(xi) - heterogeneity in conversion HAPPINESS DEPENDS ON ACTIVITIES EQ 2. ui = hi(fi) - happiness CAPABILITIES ARE ALL THE ACTIVITIES POSSIBLE FOR A PERSON GIVEN RESOURCES EQ 3. Qi = {f 1, f 2, …fm}/endowment - advantage xi is vector of commodities possessed by i f(. ) converts resources into activities (doings/beings aka functionings) “Qi represents the freedom a person has in terms of the choice of functionings, given his personal features Fi…and his command over commodities xi. ”
 Some Early Empirical Capabilities Research ¡ Human Development Index ¡ ¡ Schokkaert and van Ootegem (1990) Enrica Chiappero Martinetti (1994, 2000) Laderchi (1997) Kuklys (2005) ¡ Andrea Brandolini (1999) ¡ ¡ “The purpose is to assess the operational content of the approach ie the empirical methods to measure functionings and capabilities…much of what one can do depends the available data…. we discussed the practical difficulties of moving to capabilities and proposed to remain in the (refined) functionings space. ” Source: Plenary paper given to the International Economics Association Congress, Buenos Aires
Some Early Empirical Capabilities Research ¡ Human Development Index ¡ ¡ Schokkaert and van Ootegem (1990) Enrica Chiappero Martinetti (1994, 2000) Laderchi (1997) Kuklys (2005) ¡ Andrea Brandolini (1999) ¡ ¡ “The purpose is to assess the operational content of the approach ie the empirical methods to measure functionings and capabilities…much of what one can do depends the available data…. we discussed the practical difficulties of moving to capabilities and proposed to remain in the (refined) functionings space. ” Source: Plenary paper given to the International Economics Association Congress, Buenos Aires
 AHRB Project to Measure Capabilities (2005) Research Question Can we measure human capabilities across a wide spectrum of life domains within the conventions applicable to national household and social surveys?
AHRB Project to Measure Capabilities (2005) Research Question Can we measure human capabilities across a wide spectrum of life domains within the conventions applicable to national household and social surveys?
 Framework for Questions The OCAP Survey Nussbaum’s List Comprehensive Robust (similar to others) Don’t require universal claims Has normative grounding
Framework for Questions The OCAP Survey Nussbaum’s List Comprehensive Robust (similar to others) Don’t require universal claims Has normative grounding
 Question Categories ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Life Bodily Health Bodily Integrity Senses Imagination and Thought Emotions Practical Reason Affiliation Nature Leisure Control over one’s Environment
Question Categories ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Life Bodily Health Bodily Integrity Senses Imagination and Thought Emotions Practical Reason Affiliation Nature Leisure Control over one’s Environment
 Bodily Health ¡ Being able to have good health, including reproductive health; to be adequately nourished; to have adequate shelter
Bodily Health ¡ Being able to have good health, including reproductive health; to be adequately nourished; to have adequate shelter
 ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ 2 Bodily Health Being able to have good health, BHEALTH (Q 57) Does your health in any way limit your daily activities compared to most people of your age? Yes, No. BHPS including reproductive health; BREPRODUCT (Q 61) Are you able to have children? Yes, No, Don't know, Prefer not to answer If No Please indicate the reason(s) you are not able to have children. I cannot have children because of: Q 62_1 My age; Q 62_2 I have had a vasectomy / hysterectomy; Q 62 -3 Another medical condition; Q 62_4 My partner being unable / unwilling; Q 62_5 Another reason; Q 62_6 Prefer not to answer. to be adequately nourished BNOURISH (Q 59) Do you eat fresh meat, chicken or fish at least twice a week? Yes/No BHPS If No Q 60 For which of the following reasons, if any, do you NOT eat fresh meat, chicken or fish at least twice a week? [Please tick all that apply] I am vegetarian/vegan, I cannot afford to, I do not like eating fresh meat, chicken or fish that often, I do not have time to prepare fresh food. , Some other reason to have adequate shelter. BSHELTER (Q 85) Is your current accommodation adequate or inadequate for your current needs? More than adequate, Adequate, Inadequate, Very inadequate BCANMOVE (Q 86) Are you prevented from moving home for any reason? Yes, No If yes Q 87 What prevents you from moving home? Lack of money/finances; The Council would be unlikely to re-house me; Family responsibilities and/or schooling; I could not move out of my current accommodation because of some other reason
¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ 2 Bodily Health Being able to have good health, BHEALTH (Q 57) Does your health in any way limit your daily activities compared to most people of your age? Yes, No. BHPS including reproductive health; BREPRODUCT (Q 61) Are you able to have children? Yes, No, Don't know, Prefer not to answer If No Please indicate the reason(s) you are not able to have children. I cannot have children because of: Q 62_1 My age; Q 62_2 I have had a vasectomy / hysterectomy; Q 62 -3 Another medical condition; Q 62_4 My partner being unable / unwilling; Q 62_5 Another reason; Q 62_6 Prefer not to answer. to be adequately nourished BNOURISH (Q 59) Do you eat fresh meat, chicken or fish at least twice a week? Yes/No BHPS If No Q 60 For which of the following reasons, if any, do you NOT eat fresh meat, chicken or fish at least twice a week? [Please tick all that apply] I am vegetarian/vegan, I cannot afford to, I do not like eating fresh meat, chicken or fish that often, I do not have time to prepare fresh food. , Some other reason to have adequate shelter. BSHELTER (Q 85) Is your current accommodation adequate or inadequate for your current needs? More than adequate, Adequate, Inadequate, Very inadequate BCANMOVE (Q 86) Are you prevented from moving home for any reason? Yes, No If yes Q 87 What prevents you from moving home? Lack of money/finances; The Council would be unlikely to re-house me; Family responsibilities and/or schooling; I could not move out of my current accommodation because of some other reason
 HEALTH STATUS Does your health in any way limit your daily activities compared to most people of your age? Yes, No. BHPS
HEALTH STATUS Does your health in any way limit your daily activities compared to most people of your age? Yes, No. BHPS
 REPRODUCTION Are you able to have children? NEW Yes, No, Don't know, Prefer not to answer If no please indicate the reason(s) you are not able to have children I cannot have children because of: Q 62_1 My age Q 62_2 I have had a vasectomy / hysterectomy Q 62_3 Another medical condition Q 62_4 My partner being unable / unwilling Q 62_5 Another reason Q 62_6 Prefer not to answer
REPRODUCTION Are you able to have children? NEW Yes, No, Don't know, Prefer not to answer If no please indicate the reason(s) you are not able to have children I cannot have children because of: Q 62_1 My age Q 62_2 I have had a vasectomy / hysterectomy Q 62_3 Another medical condition Q 62_4 My partner being unable / unwilling Q 62_5 Another reason Q 62_6 Prefer not to answer
 NOURISHMENT Do you eat fresh meat, chicken or fish at least twice a week? Yes/No BHPS with additions If No (Q 60) For which of the following reasons, if any, do you NOT eat fresh meat, chicken or fish at least twice a week? [Please tick all that apply] I am vegetarian/vegan I cannot afford to I do not like eating fresh meat, chicken or fish that often I do not have time to prepare fresh food Some other reason
NOURISHMENT Do you eat fresh meat, chicken or fish at least twice a week? Yes/No BHPS with additions If No (Q 60) For which of the following reasons, if any, do you NOT eat fresh meat, chicken or fish at least twice a week? [Please tick all that apply] I am vegetarian/vegan I cannot afford to I do not like eating fresh meat, chicken or fish that often I do not have time to prepare fresh food Some other reason
 ADEQUATE SHELTER BSHELTER (Q 85) Is your current accommodation adequate or inadequate for your current needs? More than adequate, Adequate, Inadequate, Very inadequate BCANMOVE (Q 86) Are you prevented from moving home for any reason? Yes, No If yes (Q 87) What prevents you from moving home? Lack of money/finances; The Council would be unlikely to re-house me; Family responsibilities and/or schooling; I could not move out of my current accommodation because of some other reason
ADEQUATE SHELTER BSHELTER (Q 85) Is your current accommodation adequate or inadequate for your current needs? More than adequate, Adequate, Inadequate, Very inadequate BCANMOVE (Q 86) Are you prevented from moving home for any reason? Yes, No If yes (Q 87) What prevents you from moving home? Lack of money/finances; The Council would be unlikely to re-house me; Family responsibilities and/or schooling; I could not move out of my current accommodation because of some other reason
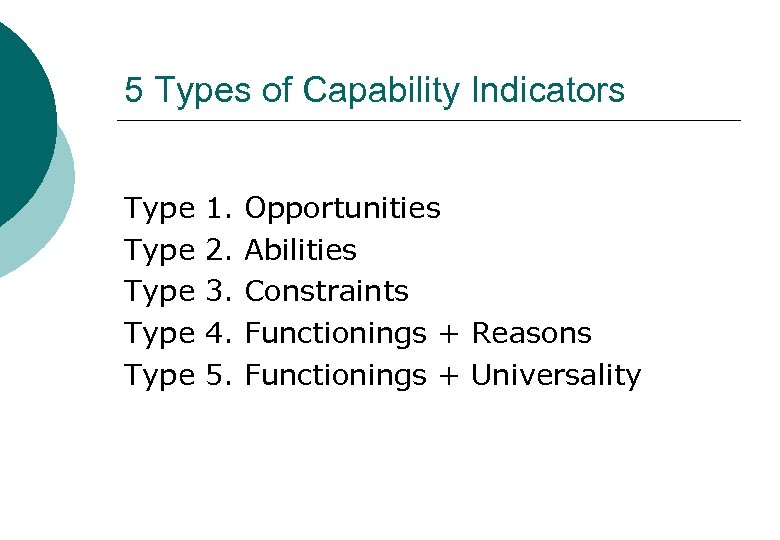 5 Types of Capability Indicators Type 1. Opportunities Type 2. Abilities Type 3. Constraints Type 4. Functionings + Reasons Type 5. Functionings + Universality
5 Types of Capability Indicators Type 1. Opportunities Type 2. Abilities Type 3. Constraints Type 4. Functionings + Reasons Type 5. Functionings + Universality
 Analyses ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Multiple Dimensions of Wellbeing Deprivation and the Identification of the Poor Marginalisation and the Clustering of Disadvantage Health and Wellbeing in Other Dimensions Nature and Costs of Domestic Violence Wellbeing in Older Age Happiness and Development of Very Young Children
Analyses ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Multiple Dimensions of Wellbeing Deprivation and the Identification of the Poor Marginalisation and the Clustering of Disadvantage Health and Wellbeing in Other Dimensions Nature and Costs of Domestic Violence Wellbeing in Older Age Happiness and Development of Very Young Children
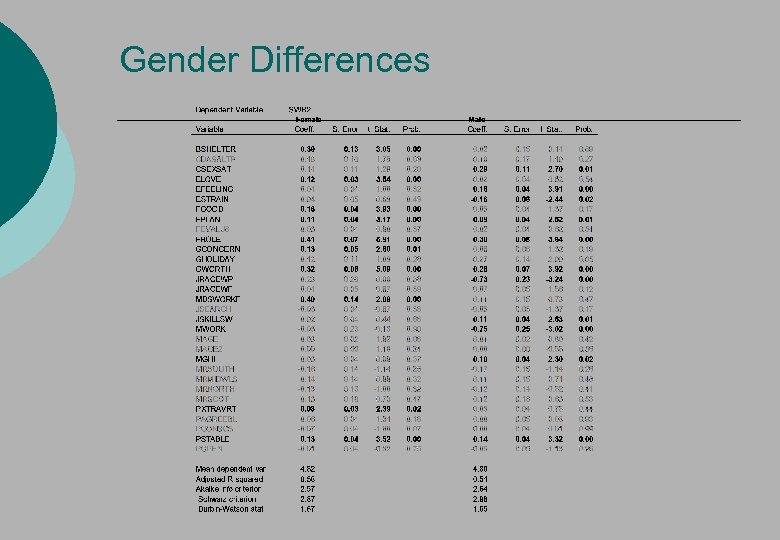 Gender Differences
Gender Differences
 Our Latest Data 2012 -3 Home UK HOME I am able to share domestic tasks within the household fairly I am able to socialise with others in the family as I would wish USA 6. 11 6. 64 6. 40 6. 96 I am able to make ends meet 6. 28 6. 36 I am able to achieve a good work-life balance 5. 81 5. 98 I am able to find a home suitable for my needs 6. 52 6. 96 I am able to enjoy the kinds of personal relationships that I want 6. 16 6. 40 I have good opportunities to feel valued and loved 6. 26 6. 92
Our Latest Data 2012 -3 Home UK HOME I am able to share domestic tasks within the household fairly I am able to socialise with others in the family as I would wish USA 6. 11 6. 64 6. 40 6. 96 I am able to make ends meet 6. 28 6. 36 I am able to achieve a good work-life balance 5. 81 5. 98 I am able to find a home suitable for my needs 6. 52 6. 96 I am able to enjoy the kinds of personal relationships that I want 6. 16 6. 40 I have good opportunities to feel valued and loved 6. 26 6. 92
 Work UK WORK USA I am able to find work when I need to 6. 50 6. 97 I am able to use my talents and skills at work 6. 51 7. 07 I am able to work under a good manager at the moment 6. 10 6. 79 I am always treated as an equal (and not discriminated against) by people at work 6. 78 7. 39 I have good opportunities for promotion or recognition at work 4. 77 5. 90 I have good opportunities to socialise at work 5. 58 6. 72
Work UK WORK USA I am able to find work when I need to 6. 50 6. 97 I am able to use my talents and skills at work 6. 51 7. 07 I am able to work under a good manager at the moment 6. 10 6. 79 I am always treated as an equal (and not discriminated against) by people at work 6. 78 7. 39 I have good opportunities for promotion or recognition at work 4. 77 5. 90 I have good opportunities to socialise at work 5. 58 6. 72
 Community UK USA 4. 95 5. 94 I am treated by people where I live as an equal (and not discriminated against) 7. 09 7. 60 I am able to practice my religious beliefs (including atheism/agnosticism) 7. 59 8. 12 I am able to express my political views when I wish 7. 23 7. 56 COMMUNITY I have good opportunities to take part in local social events
Community UK USA 4. 95 5. 94 I am treated by people where I live as an equal (and not discriminated against) 7. 09 7. 60 I am able to practice my religious beliefs (including atheism/agnosticism) 7. 59 8. 12 I am able to express my political views when I wish 7. 23 7. 56 COMMUNITY I have good opportunities to take part in local social events
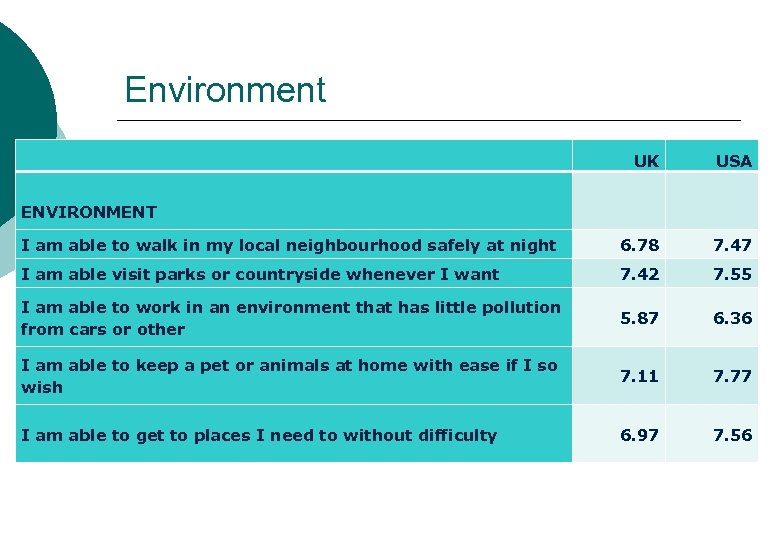 Environment UK USA I am able to walk in my local neighbourhood safely at night 6. 78 7. 47 I am able visit parks or countryside whenever I want 7. 42 7. 55 I am able to work in an environment that has little pollution from cars or other 5. 87 6. 36 I am able to keep a pet or animals at home with ease if I so wish 7. 11 7. 77 I am able to get to places I need to without difficulty 6. 97 7. 56 ENVIRONMENT
Environment UK USA I am able to walk in my local neighbourhood safely at night 6. 78 7. 47 I am able visit parks or countryside whenever I want 7. 42 7. 55 I am able to work in an environment that has little pollution from cars or other 5. 87 6. 36 I am able to keep a pet or animals at home with ease if I so wish 7. 11 7. 77 I am able to get to places I need to without difficulty 6. 97 7. 56 ENVIRONMENT
 Access to Services UK USA Make use of banking and personal finance services 7. 62 7. 92 Get my rubbish cleared away 7. 45 8. 25 Get trades people or the landlord to help fix problems in the house 6. 69 7. 15 Be treated by a doctor or nurse 7. 27 7. 52 Get help from the police 6. 81 7. 67 Get help from a solicitor 6. 78 6. 36 Get to a range of shops 7. 60 7. 76 ACCESS TO SERVICES
Access to Services UK USA Make use of banking and personal finance services 7. 62 7. 92 Get my rubbish cleared away 7. 45 8. 25 Get trades people or the landlord to help fix problems in the house 6. 69 7. 15 Be treated by a doctor or nurse 7. 27 7. 52 Get help from the police 6. 81 7. 67 Get help from a solicitor 6. 78 6. 36 Get to a range of shops 7. 60 7. 76 ACCESS TO SERVICES
 2011 -2 dataset ¡ ¡ To obtain a measure of activity participation, or functionings, we collected binary indicators of 30 activities individuals may or may not have been involved in “yesterday. ” l Attending an evening class, caring for someone ill (unpaid), commuting, cooking, DIY, drinking alcohol, exercising, housework, internet (personal use), internet (paid employment), intimate relations, listening to music, looking after a pet, other outdoor activities, paid employment, playing a musical instrument, praying or meditating, relaxing or napping, reading for pleasure, self-care, smoking, socialising, shopping, time with children, visiting a park or countryside, visiting a cinema/concert/gallery/museum, volunteering, watching TV, other The choice of activities was largely influenced by work by Kahneman et al. (2004, AER).
2011 -2 dataset ¡ ¡ To obtain a measure of activity participation, or functionings, we collected binary indicators of 30 activities individuals may or may not have been involved in “yesterday. ” l Attending an evening class, caring for someone ill (unpaid), commuting, cooking, DIY, drinking alcohol, exercising, housework, internet (personal use), internet (paid employment), intimate relations, listening to music, looking after a pet, other outdoor activities, paid employment, playing a musical instrument, praying or meditating, relaxing or napping, reading for pleasure, self-care, smoking, socialising, shopping, time with children, visiting a park or countryside, visiting a cinema/concert/gallery/museum, volunteering, watching TV, other The choice of activities was largely influenced by work by Kahneman et al. (2004, AER).
 2011 -2 Data We also collected data on a wide range of resources and personal characteristics. ¡ Resource variables included income, education, health and a number of other socio-economic attributes. ¡ For personal characteristics we collected data on ‘soft skills’ personality traits. ¡
2011 -2 Data We also collected data on a wide range of resources and personal characteristics. ¡ Resource variables included income, education, health and a number of other socio-economic attributes. ¡ For personal characteristics we collected data on ‘soft skills’ personality traits. ¡
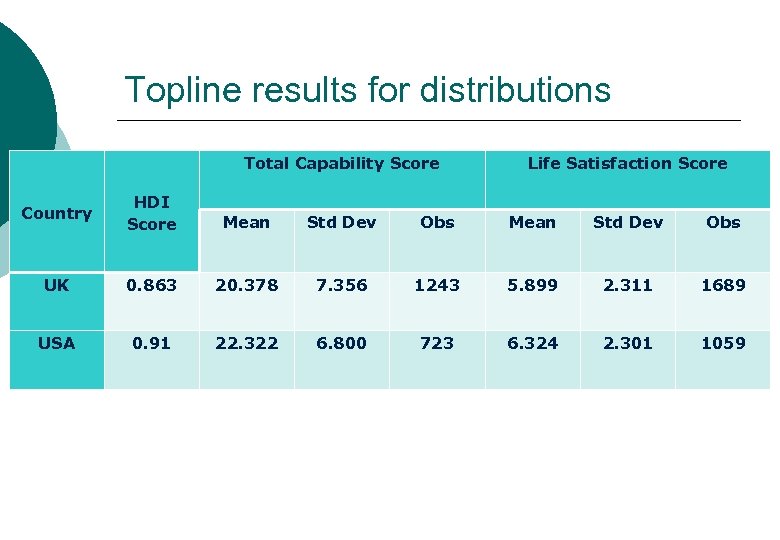 Topline results for distributions Total Capability Score Life Satisfaction Score Country HDI Score Mean Std Dev Obs UK 0. 863 20. 378 7. 356 1243 5. 899 2. 311 1689 USA 0. 91 22. 322 6. 800 723 6. 324 2. 301 1059
Topline results for distributions Total Capability Score Life Satisfaction Score Country HDI Score Mean Std Dev Obs UK 0. 863 20. 378 7. 356 1243 5. 899 2. 311 1689 USA 0. 91 22. 322 6. 800 723 6. 324 2. 301 1059
 Distribution of wellbeing variables How we might compare wellbeing outcomes in the two countries when the measures are based on ordinal data? ¡ We draw on recent work by Yalonetzky (2013, Econometric Rev), which provides stochastic dominance conditions for ordinal variables ¡ l analogous results to those in a seminal paper by Atkinson and Bourguignon (1982, Rev Econ Stud) in the context of continuous variables
Distribution of wellbeing variables How we might compare wellbeing outcomes in the two countries when the measures are based on ordinal data? ¡ We draw on recent work by Yalonetzky (2013, Econometric Rev), which provides stochastic dominance conditions for ordinal variables ¡ l analogous results to those in a seminal paper by Atkinson and Bourguignon (1982, Rev Econ Stud) in the context of continuous variables
 Distribution of wellbeing variables ¡ USA FOSD the UK for Total capabilities. l ¡ USA FOSD the UK for Work and Community capabilities. l ¡ However, even SOSD is not statistically significant FOSD is statistically significant at the 1% level. USA FOSD the UK for Home capabilities. l l FOSD is statistically significant, but only at the 10% level. SOSD is achieved at the 5% level.
Distribution of wellbeing variables ¡ USA FOSD the UK for Total capabilities. l ¡ USA FOSD the UK for Work and Community capabilities. l ¡ However, even SOSD is not statistically significant FOSD is statistically significant at the 1% level. USA FOSD the UK for Home capabilities. l l FOSD is statistically significant, but only at the 10% level. SOSD is achieved at the 5% level.
 Happiness regressions ¡ ¡ ¡ Being unemployed is negatively and highly statistically significantly associated with life satisfaction in both countries. Being married / living with partner is positively associated with life satisfaction l statistically significant at the 1% level in the USA and at the 5% level in the UK. Being white and having an above school level education are also both positively related to life satisfaction in the UK
Happiness regressions ¡ ¡ ¡ Being unemployed is negatively and highly statistically significantly associated with life satisfaction in both countries. Being married / living with partner is positively associated with life satisfaction l statistically significant at the 1% level in the USA and at the 5% level in the UK. Being white and having an above school level education are also both positively related to life satisfaction in the UK
 Happiness regressions ¡ ¡ ¡ Capabilities are novel in the happiness literature and their inclusion leads to some striking observations. In each country, both health and Home and Work capabilities are positively and statistically significantly related to life satisfaction at the 1% level. Community capabilities are also positively related to life satisfaction in both countries (5%UK, 10%US)
Happiness regressions ¡ ¡ ¡ Capabilities are novel in the happiness literature and their inclusion leads to some striking observations. In each country, both health and Home and Work capabilities are positively and statistically significantly related to life satisfaction at the 1% level. Community capabilities are also positively related to life satisfaction in both countries (5%UK, 10%US)
 Happiness regressions ¡ ¡ After controlling for capabilities, the positive effect of household income becomes insignificant in both the USA and the UK. l suggests that development of capabilities may be an important mechanism via which higher levels of income can boost life satisfaction. Similarly, the significance of being married or living with partner disappears after controlling for capabilities l suggests that development of good health and certain capabilities, particularly in the Home and Work, may be important transmission mechanisms
Happiness regressions ¡ ¡ After controlling for capabilities, the positive effect of household income becomes insignificant in both the USA and the UK. l suggests that development of capabilities may be an important mechanism via which higher levels of income can boost life satisfaction. Similarly, the significance of being married or living with partner disappears after controlling for capabilities l suggests that development of good health and certain capabilities, particularly in the Home and Work, may be important transmission mechanisms
 Happiness regressions ¡ ¡ ¡ …increases in R-squared values after including Health and capabilities - to 0. 548 in the USA and 0. 571 in the UK (In the happiness literature, it is rare to see Rsquared values above around 0. 25. ) …results suggest that capabilities have been important missing variables in that literature (further corroborated by large reductions in AIC and BIC). …relationship between life satisfaction and capabilities is likely to be highly endogenous (reverse causality)
Happiness regressions ¡ ¡ ¡ …increases in R-squared values after including Health and capabilities - to 0. 548 in the USA and 0. 571 in the UK (In the happiness literature, it is rare to see Rsquared values above around 0. 25. ) …results suggest that capabilities have been important missing variables in that literature (further corroborated by large reductions in AIC and BIC). …relationship between life satisfaction and capabilities is likely to be highly endogenous (reverse causality)
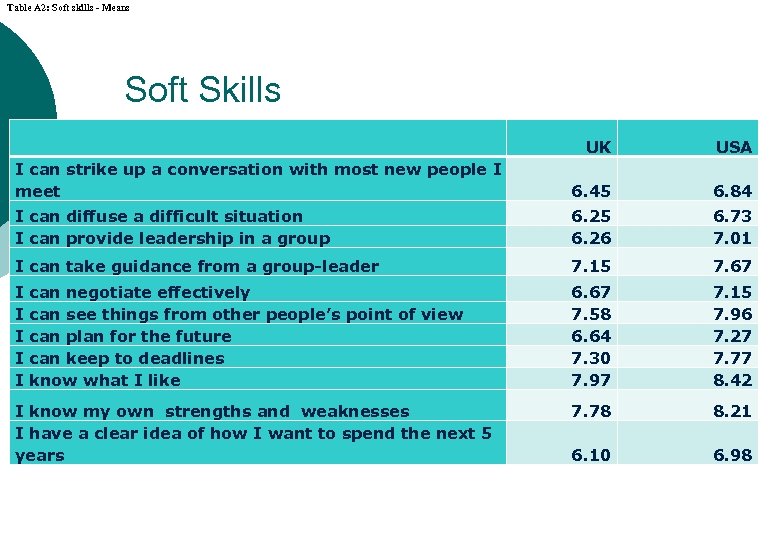 Table A 2: Soft skills - Means Soft Skills UK USA I can strike up a conversation with most new people I meet 6. 45 6. 84 I can diffuse a difficult situation I can provide leadership in a group 6. 25 6. 26 6. 73 7. 01 I can take guidance from a group-leader 7. 15 7. 67 I can negotiate effectively I can see things from other people’s point of view I can plan for the future I can keep to deadlines I know what I like 6. 67 7. 58 6. 64 7. 30 7. 97 7. 15 7. 96 7. 27 7. 77 8. 42 I know my own strengths and weaknesses I have a clear idea of how I want to spend the next 5 years 7. 78 8. 21 6. 10 6. 98
Table A 2: Soft skills - Means Soft Skills UK USA I can strike up a conversation with most new people I meet 6. 45 6. 84 I can diffuse a difficult situation I can provide leadership in a group 6. 25 6. 26 6. 73 7. 01 I can take guidance from a group-leader 7. 15 7. 67 I can negotiate effectively I can see things from other people’s point of view I can plan for the future I can keep to deadlines I know what I like 6. 67 7. 58 6. 64 7. 30 7. 97 7. 15 7. 96 7. 27 7. 77 8. 42 I know my own strengths and weaknesses I have a clear idea of how I want to spend the next 5 years 7. 78 8. 21 6. 10 6. 98
 1 A Health ARGENTINA 2007 LIFE SATISFACTION AFO CAPABILITIES Does health limit daily activities compared to age group? Coef Signif Sign Correct -0. 16 -1. 947 YES Have you recently felt constantly under strain? -1. 66 -1. 408 YES 0. 122 1. 463 YES 0. 121 0. 83 YES 0. 252 2. 513 YES I have a clear plan of how I would like my life to be 0. 025 0. 239 YES At present, how easy or difficult do you find it to enjoy 0. 135 1. 427 YES the love care and support of your immediate family? Have you recently been able to enjoy your normal day to day activities? 0. 013 0. 136 YES Do you tend to find it easy or difficult to imagine the situation of other people (ie to put yourself in others's shoes) Religion 0. 696 Have you recently lost much sleep over worry? Political 0. 166 0. 369 4. 118 YES Please indicate how safe you feel walking alone in the area near your home after dark? Please indicate how vulnerable you feel to domestic violence in the future -0. 01 -0. 157 -0. 05 -0. 51 I am free to participate in political activities that affect my life if I want to I am free to practice my religion as I want to Imagination My idea of a good life is based on my own judgement /Thought Emotional Safety BUT SAFETY DURING DAY IS SIGNIFICANT AT CLOSE TO 5%
1 A Health ARGENTINA 2007 LIFE SATISFACTION AFO CAPABILITIES Does health limit daily activities compared to age group? Coef Signif Sign Correct -0. 16 -1. 947 YES Have you recently felt constantly under strain? -1. 66 -1. 408 YES 0. 122 1. 463 YES 0. 121 0. 83 YES 0. 252 2. 513 YES I have a clear plan of how I would like my life to be 0. 025 0. 239 YES At present, how easy or difficult do you find it to enjoy 0. 135 1. 427 YES the love care and support of your immediate family? Have you recently been able to enjoy your normal day to day activities? 0. 013 0. 136 YES Do you tend to find it easy or difficult to imagine the situation of other people (ie to put yourself in others's shoes) Religion 0. 696 Have you recently lost much sleep over worry? Political 0. 166 0. 369 4. 118 YES Please indicate how safe you feel walking alone in the area near your home after dark? Please indicate how vulnerable you feel to domestic violence in the future -0. 01 -0. 157 -0. 05 -0. 51 I am free to participate in political activities that affect my life if I want to I am free to practice my religion as I want to Imagination My idea of a good life is based on my own judgement /Thought Emotional Safety BUT SAFETY DURING DAY IS SIGNIFICANT AT CLOSE TO 5%
 ARGENTINA 2007 LIFE SATISFACTION = f (CAPABILITIES) 1 B Environment coef signif Sign correct I appreciate and value plants animals and the world of nature 0. 419 1. 027 -0. 25 -1. 978 0. 089 0. 585 YES Have you recently been thinking of yourself as a worthless person? -0. 61 -2. 811 ? YES I respect value and appreciate other people Do you normally have at least one week's (seven days) annual holiday away from home? -0. 36 -1. 318 0. 334 1. 5 -0. 55 -1. 575 -0. 45 -2. 055 Social How difficult do you find it to make friendships which last with people Relations outside work Outside of work, have you recently felt that you were playing a useful part in things? Housing Work Is your current accommodation adequate or inadequate for your current needs? While seeking work in the future, do you think is it is likely you will be discriminated against because of your race? YES YES
ARGENTINA 2007 LIFE SATISFACTION = f (CAPABILITIES) 1 B Environment coef signif Sign correct I appreciate and value plants animals and the world of nature 0. 419 1. 027 -0. 25 -1. 978 0. 089 0. 585 YES Have you recently been thinking of yourself as a worthless person? -0. 61 -2. 811 ? YES I respect value and appreciate other people Do you normally have at least one week's (seven days) annual holiday away from home? -0. 36 -1. 318 0. 334 1. 5 -0. 55 -1. 575 -0. 45 -2. 055 Social How difficult do you find it to make friendships which last with people Relations outside work Outside of work, have you recently felt that you were playing a useful part in things? Housing Work Is your current accommodation adequate or inadequate for your current needs? While seeking work in the future, do you think is it is likely you will be discriminated against because of your race? YES YES
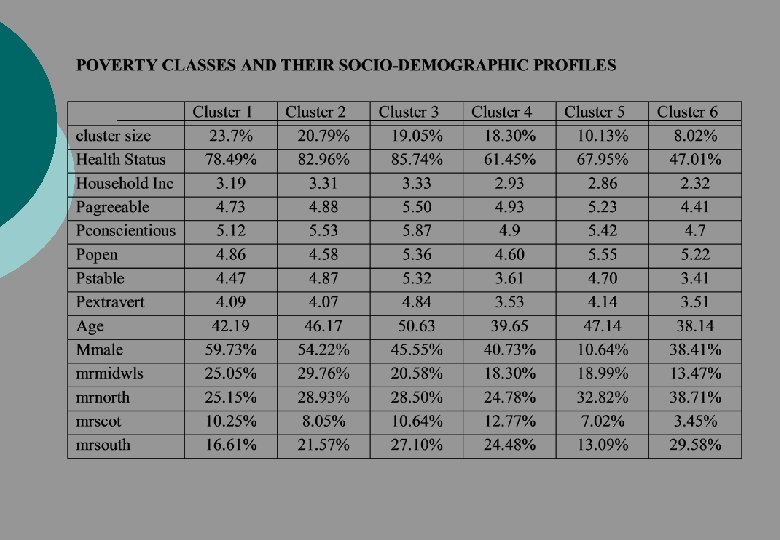
 Health and Deprivation Data ¡ ¡ Does health limit your daily activities for your age All capabilities, life satisfaction and socio-economic covariates Analysis (latent class) ¡ Can we identify a group deprived on multiple dimensions? ¡ What are capability classes related to?
Health and Deprivation Data ¡ ¡ Does health limit your daily activities for your age All capabilities, life satisfaction and socio-economic covariates Analysis (latent class) ¡ Can we identify a group deprived on multiple dimensions? ¡ What are capability classes related to?
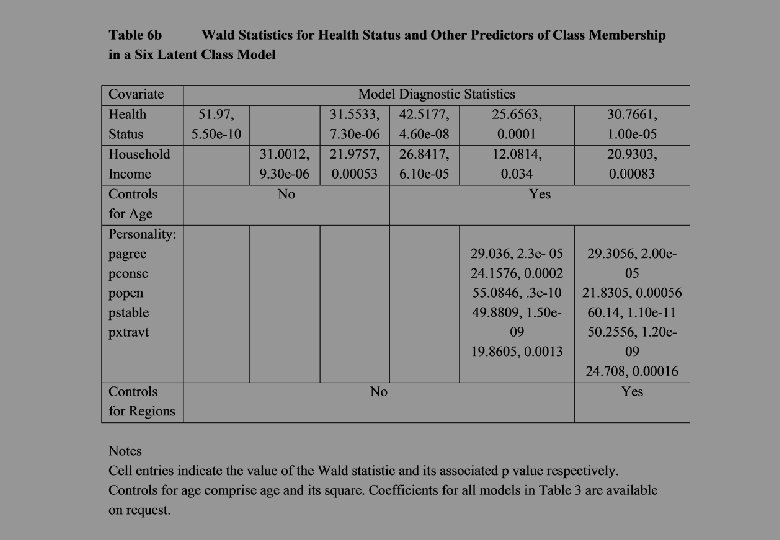
 Violent Crime, Gender Inequalities and Life Satisfaction (Anand Santos 2007, Santos 2013) Data ¡ Past Experience/Future vulnerability to domestic, sexual and other forms of assault ¡ Current experience of Safety in local area during day and night Findings 1. Violence in general has a negative impact on life satisfaction whether you use self report or local area reports 2. Self-reported vulnerability to future assault drives out past experience of violence in happiness equations 3. Some evidence that higher relative earning females are more at risk of domestic violence 4. Happiness based estimates of costs of violence as two times higher
Violent Crime, Gender Inequalities and Life Satisfaction (Anand Santos 2007, Santos 2013) Data ¡ Past Experience/Future vulnerability to domestic, sexual and other forms of assault ¡ Current experience of Safety in local area during day and night Findings 1. Violence in general has a negative impact on life satisfaction whether you use self report or local area reports 2. Self-reported vulnerability to future assault drives out past experience of violence in happiness equations 3. Some evidence that higher relative earning females are more at risk of domestic violence 4. Happiness based estimates of costs of violence as two times higher
 Housing and Minorities (Anand Coates and Norris 2013) Issue ¡ Irish Travellers
Housing and Minorities (Anand Coates and Norris 2013) Issue ¡ Irish Travellers
 Housing and Minorities (Anand Coates and Norris 2013) Issue ¡ Irish Travellers Findings – A Problem of Housing? 1. Health Problems 2. Unemployment 3. Education Adds to a vicious circle of disavantage
Housing and Minorities (Anand Coates and Norris 2013) Issue ¡ Irish Travellers Findings – A Problem of Housing? 1. Health Problems 2. Unemployment 3. Education Adds to a vicious circle of disavantage
 Some Current Work:
Some Current Work:
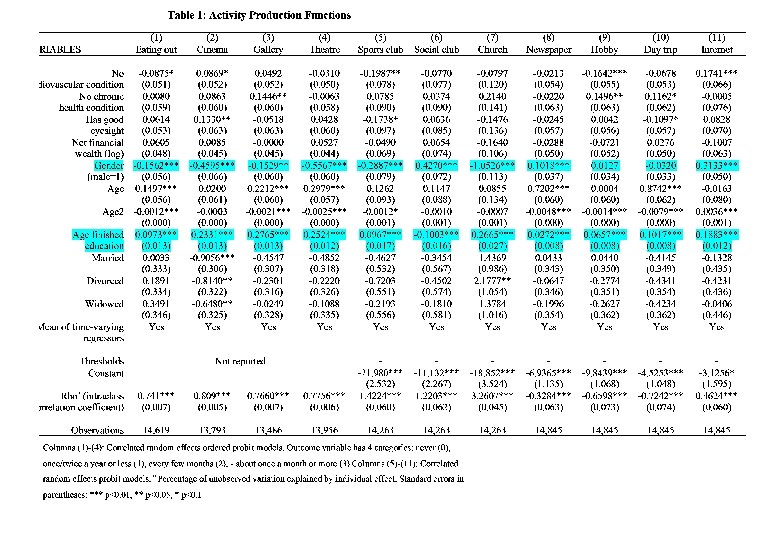
 Wellbeing Over the Life Span 11 Functionings Depend on Resources Including Particularly Gender Health and Education Happiness Depends on a Variety of Activities with Interneting Being Positive for Males and Negative for Females 4 Capabilities – Women adapt and Men don’t?
Wellbeing Over the Life Span 11 Functionings Depend on Resources Including Particularly Gender Health and Education Happiness Depends on a Variety of Activities with Interneting Being Positive for Males and Negative for Females 4 Capabilities – Women adapt and Men don’t?

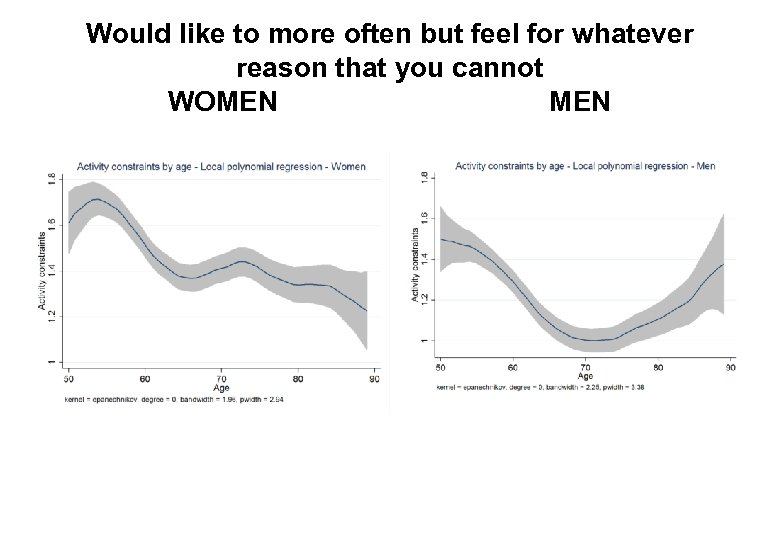 Would like to more often but feel for whatever reason that you cannot WOMEN
Would like to more often but feel for whatever reason that you cannot WOMEN
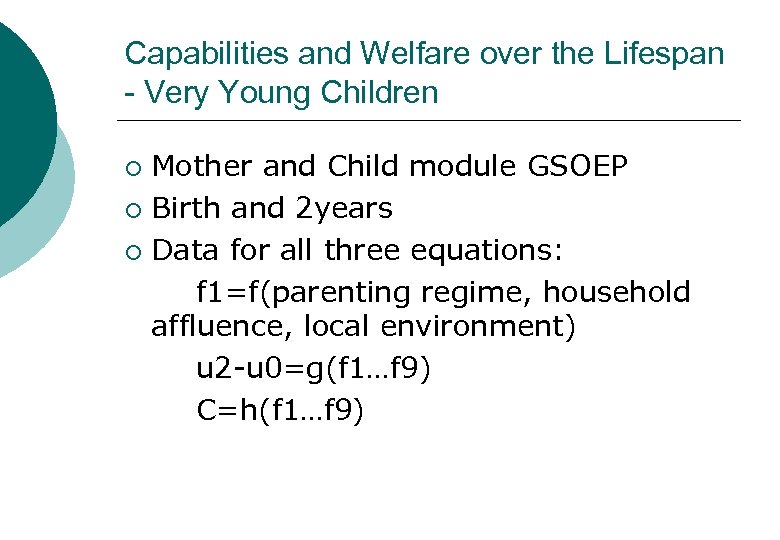 Capabilities and Welfare over the Lifespan - Very Young Children Mother and Child module GSOEP ¡ Birth and 2 years ¡ Data for all three equations: f 1=f(parenting regime, household affluence, local environment) u 2 -u 0=g(f 1…f 9) C=h(f 1…f 9) ¡
Capabilities and Welfare over the Lifespan - Very Young Children Mother and Child module GSOEP ¡ Birth and 2 years ¡ Data for all three equations: f 1=f(parenting regime, household affluence, local environment) u 2 -u 0=g(f 1…f 9) C=h(f 1…f 9) ¡
 Capabilities and Welfare over the Lifespan - Very Young Children Data for all three equations: Functionings ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Sing Walk Paint Read Look Play Visit Shop Watch Singing children’s songs with or to the child Talking walks outdoors Painting or doing arts and crafts Reading or telling stories Looking at picture books Going to the playground Visiting other families with children Going shopping with the child Watching television or videos with the child
Capabilities and Welfare over the Lifespan - Very Young Children Data for all three equations: Functionings ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Sing Walk Paint Read Look Play Visit Shop Watch Singing children’s songs with or to the child Talking walks outdoors Painting or doing arts and crafts Reading or telling stories Looking at picture books Going to the playground Visiting other families with children Going shopping with the child Watching television or videos with the child

 Capabilities and Welfare over the Lifespan - Very Young Children Data for all three equations: Capabilities Talking, Everyday Skills, Movement, Social Skills ¡ Talking ¡ t 1 Understands brief instructions such as ‘go get your shoes’ ¡ t 2 Forms sentences with at least two words ¡ t 3 Speaks in full sentences (with four or more words) ¡ t 4 Listens attentively to a story for five minutes or longer ¡ t 5 Passes on simple message such as dinner is ready ¡ Eskills ¡ e 1 Uses a spoon to eat, without assistance and without dripping ¡ e 2 Blows his/her nose without assistance ¡ e 3 Uses the toilet to do ‘number two’ ¡ e 4 Puts on pants and underpants the right way around ¡ e 5 Brushes his/her teeth without assistance f 1=f(parenting regime, household affluence, local environment) u 2 -u 0=g(f 1…f 9) C=h(f 1…f 9)
Capabilities and Welfare over the Lifespan - Very Young Children Data for all three equations: Capabilities Talking, Everyday Skills, Movement, Social Skills ¡ Talking ¡ t 1 Understands brief instructions such as ‘go get your shoes’ ¡ t 2 Forms sentences with at least two words ¡ t 3 Speaks in full sentences (with four or more words) ¡ t 4 Listens attentively to a story for five minutes or longer ¡ t 5 Passes on simple message such as dinner is ready ¡ Eskills ¡ e 1 Uses a spoon to eat, without assistance and without dripping ¡ e 2 Blows his/her nose without assistance ¡ e 3 Uses the toilet to do ‘number two’ ¡ e 4 Puts on pants and underpants the right way around ¡ e 5 Brushes his/her teeth without assistance f 1=f(parenting regime, household affluence, local environment) u 2 -u 0=g(f 1…f 9) C=h(f 1…f 9)
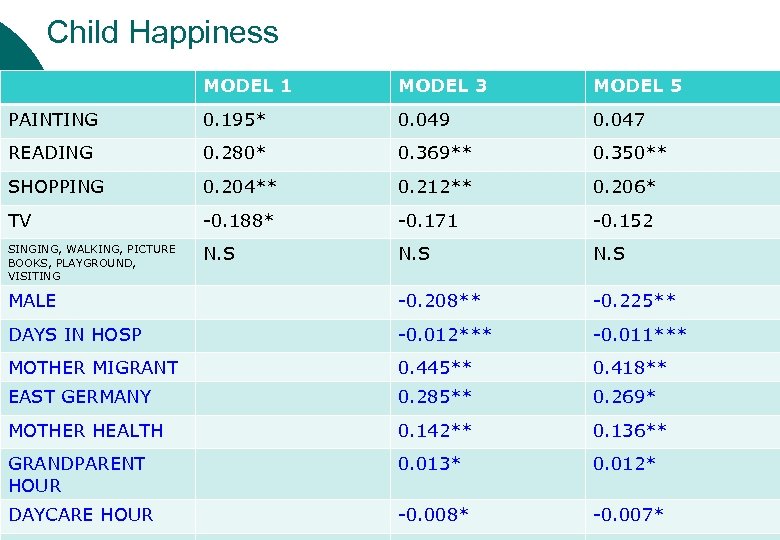 Child Happiness MODEL 1 MODEL 3 MODEL 5 PAINTING 0. 195* 0. 049 0. 047 READING 0. 280* 0. 369** 0. 350** SHOPPING 0. 204** 0. 212** 0. 206* TV -0. 188* -0. 171 -0. 152 SINGING, WALKING, PICTURE BOOKS, PLAYGROUND, VISITING N. S MALE -0. 208** -0. 225** DAYS IN HOSP -0. 012*** -0. 011*** MOTHER MIGRANT 0. 445** 0. 418** EAST GERMANY 0. 285** 0. 269* MOTHER HEALTH 0. 142** 0. 136** GRANDPARENT HOUR 0. 013* 0. 012* DAYCARE HOUR -0. 008* -0. 007*
Child Happiness MODEL 1 MODEL 3 MODEL 5 PAINTING 0. 195* 0. 049 0. 047 READING 0. 280* 0. 369** 0. 350** SHOPPING 0. 204** 0. 212** 0. 206* TV -0. 188* -0. 171 -0. 152 SINGING, WALKING, PICTURE BOOKS, PLAYGROUND, VISITING N. S MALE -0. 208** -0. 225** DAYS IN HOSP -0. 012*** -0. 011*** MOTHER MIGRANT 0. 445** 0. 418** EAST GERMANY 0. 285** 0. 269* MOTHER HEALTH 0. 142** 0. 136** GRANDPARENT HOUR 0. 013* 0. 012* DAYCARE HOUR -0. 008* -0. 007*
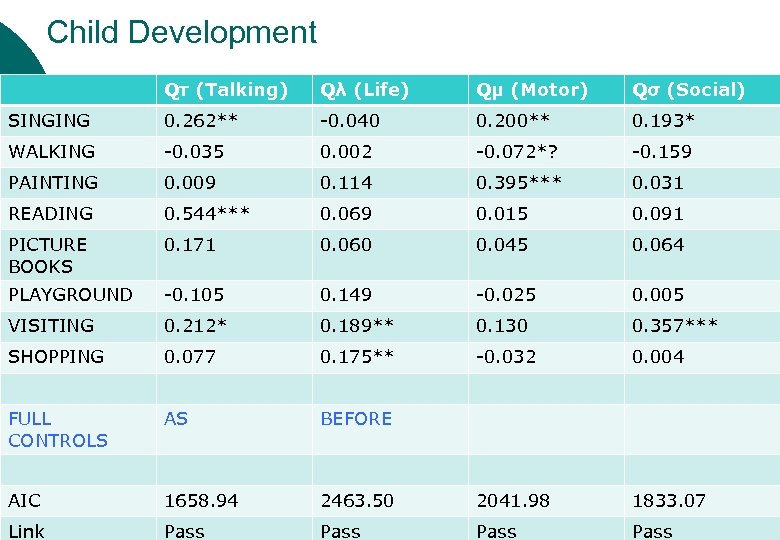 Child Development Qτ (Talking) Qλ (Life) Qμ (Motor) Qσ (Social) SINGING 0. 262** -0. 040 0. 200** 0. 193* WALKING -0. 035 0. 002 -0. 072*? -0. 159 PAINTING 0. 009 0. 114 0. 395*** 0. 031 READING 0. 544*** 0. 069 0. 015 0. 091 PICTURE BOOKS 0. 171 0. 060 0. 045 0. 064 PLAYGROUND -0. 105 0. 149 -0. 025 0. 005 VISITING 0. 212* 0. 189** 0. 130 0. 357*** SHOPPING 0. 077 0. 175** -0. 032 0. 004 FULL CONTROLS AS BEFORE AIC 1658. 94 2463. 50 2041. 98 1833. 07 Link Pass
Child Development Qτ (Talking) Qλ (Life) Qμ (Motor) Qσ (Social) SINGING 0. 262** -0. 040 0. 200** 0. 193* WALKING -0. 035 0. 002 -0. 072*? -0. 159 PAINTING 0. 009 0. 114 0. 395*** 0. 031 READING 0. 544*** 0. 069 0. 015 0. 091 PICTURE BOOKS 0. 171 0. 060 0. 045 0. 064 PLAYGROUND -0. 105 0. 149 -0. 025 0. 005 VISITING 0. 212* 0. 189** 0. 130 0. 357*** SHOPPING 0. 077 0. 175** -0. 032 0. 004 FULL CONTROLS AS BEFORE AIC 1658. 94 2463. 50 2041. 98 1833. 07 Link Pass
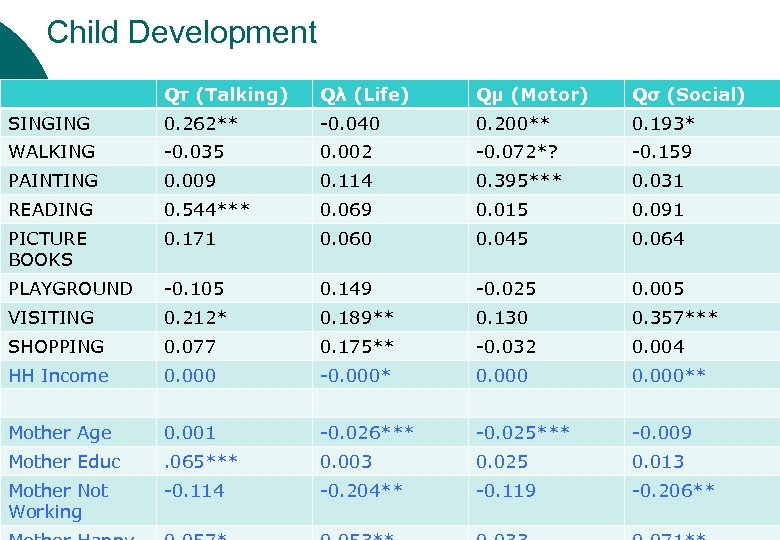 Child Development Qτ (Talking) Qλ (Life) Qμ (Motor) Qσ (Social) SINGING 0. 262** -0. 040 0. 200** 0. 193* WALKING -0. 035 0. 002 -0. 072*? -0. 159 PAINTING 0. 009 0. 114 0. 395*** 0. 031 READING 0. 544*** 0. 069 0. 015 0. 091 PICTURE BOOKS 0. 171 0. 060 0. 045 0. 064 PLAYGROUND -0. 105 0. 149 -0. 025 0. 005 VISITING 0. 212* 0. 189** 0. 130 0. 357*** SHOPPING 0. 077 0. 175** -0. 032 0. 004 HH Income 0. 000 -0. 000** Mother Age 0. 001 -0. 026*** -0. 025*** -0. 009 Mother Educ . 065*** 0. 003 0. 025 0. 013 Mother Not Working -0. 114 -0. 204** -0. 119 -0. 206**
Child Development Qτ (Talking) Qλ (Life) Qμ (Motor) Qσ (Social) SINGING 0. 262** -0. 040 0. 200** 0. 193* WALKING -0. 035 0. 002 -0. 072*? -0. 159 PAINTING 0. 009 0. 114 0. 395*** 0. 031 READING 0. 544*** 0. 069 0. 015 0. 091 PICTURE BOOKS 0. 171 0. 060 0. 045 0. 064 PLAYGROUND -0. 105 0. 149 -0. 025 0. 005 VISITING 0. 212* 0. 189** 0. 130 0. 357*** SHOPPING 0. 077 0. 175** -0. 032 0. 004 HH Income 0. 000 -0. 000** Mother Age 0. 001 -0. 026*** -0. 025*** -0. 009 Mother Educ . 065*** 0. 003 0. 025 0. 013 Mother Not Working -0. 114 -0. 204** -0. 119 -0. 206**
 Index or Dashboard? Indexes capture the imagination and measurement is expressive Dashboards carry information needed for understanding drivers Wellbeing across the age range involves issues that are partly incommensurable And… Measurement does not imply government intervention
Index or Dashboard? Indexes capture the imagination and measurement is expressive Dashboards carry information needed for understanding drivers Wellbeing across the age range involves issues that are partly incommensurable And… Measurement does not imply government intervention
 The Capabilities Measurement Project Some Concluding Observations Wellbeing comprises many very different dimensions AND it is possible to develop direct monitors of aspects of wellbeing Sen’s approach to welfare economics can be operationalised ACROSS the LIFE COURSE Countries (FRA, UK, GER), international organisations (OECD EU) and local governments are adopting the multi-dimensional measurement approach (USA interested in time use and subjective indicators) TICK! Next steps – currently there is a search for policy applications but in some areas measurement is reflecting policy eg: Labour, Education, Health, Environment, Inclusion and Equity including Tax THANK YOU!
The Capabilities Measurement Project Some Concluding Observations Wellbeing comprises many very different dimensions AND it is possible to develop direct monitors of aspects of wellbeing Sen’s approach to welfare economics can be operationalised ACROSS the LIFE COURSE Countries (FRA, UK, GER), international organisations (OECD EU) and local governments are adopting the multi-dimensional measurement approach (USA interested in time use and subjective indicators) TICK! Next steps – currently there is a search for policy applications but in some areas measurement is reflecting policy eg: Labour, Education, Health, Environment, Inclusion and Equity including Tax THANK YOU!


