805a6154b814540bc48d177ac2ca9318.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 Rethinking enterprise and infrastructure architecture Microsoft Infrastructure Architect Forum 24 October 2005 Neil Macehiter, Partner advising on IT-business alignment
Rethinking enterprise and infrastructure architecture Microsoft Infrastructure Architect Forum 24 October 2005 Neil Macehiter, Partner advising on IT-business alignment
 Key messages for today § IT-business alignment has never been so important § Alignment must be pursued in the context of understanding business processes, priorities § Service-orientation is not just for applications § Contracts aren’t just about function: they encapsulate and communicate business priorities to IT delivery organisations § Enterprise architecture needs to be more inclusive, sophisticated § IT governance models must take all this into account © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 2
Key messages for today § IT-business alignment has never been so important § Alignment must be pursued in the context of understanding business processes, priorities § Service-orientation is not just for applications § Contracts aren’t just about function: they encapsulate and communicate business priorities to IT delivery organisations § Enterprise architecture needs to be more inclusive, sophisticated § IT governance models must take all this into account © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 2
 Agenda Business and IT: new tensions IT-business alignment Alignment principle #1: service-oriented IT Alignment principle #2: understanding business processes and their priorities § Enterprise architecture must reflect IT-business alignment principles § A governance model for service-oriented IT § Recommendations § § © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 3
Agenda Business and IT: new tensions IT-business alignment Alignment principle #1: service-oriented IT Alignment principle #2: understanding business processes and their priorities § Enterprise architecture must reflect IT-business alignment principles § A governance model for service-oriented IT § Recommendations § § © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 3
 A brief introduction to MWD § Strategic advice and consulting § Focus on issues concerning IT-business alignment – Driving more business value out of enterprise IT – Not about the “nuts and bolts” of individual technologies § Core: two highly experienced industry analysts / practitioners – Sun, Oracle, Sybase, Ovum, Deloitte Consulting, etc § Based in UK, Europe-wide focus © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 4
A brief introduction to MWD § Strategic advice and consulting § Focus on issues concerning IT-business alignment – Driving more business value out of enterprise IT – Not about the “nuts and bolts” of individual technologies § Core: two highly experienced industry analysts / practitioners – Sun, Oracle, Sybase, Ovum, Deloitte Consulting, etc § Based in UK, Europe-wide focus © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 4
 Business and IT: new tensions © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 5 advising on IT-business alignment
Business and IT: new tensions © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 5 advising on IT-business alignment
 Business pressures are driving change in new ways § Globalisation – Customers, partners, suppliers – and competition – Connectedness driving sophisticated value chains § Transparency – Industry regulations, consumer pressure and competition driving openness § Service focus – Differentiation and shareholder value increasingly derived from service experience © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 6
Business pressures are driving change in new ways § Globalisation – Customers, partners, suppliers – and competition – Connectedness driving sophisticated value chains § Transparency – Industry regulations, consumer pressure and competition driving openness § Service focus – Differentiation and shareholder value increasingly derived from service experience © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 6
 Common resulting business/technology change projects/scenarios § Managing and proving regulatory compliance § Refinement of approaches to business and technology outsourcing § Integration of processes horizontally across organisations § Integration of processes, products and offerings between organisations © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 7
Common resulting business/technology change projects/scenarios § Managing and proving regulatory compliance § Refinement of approaches to business and technology outsourcing § Integration of processes horizontally across organisations § Integration of processes, products and offerings between organisations © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 7
 The challenge: IT often fails to support these types of changes effectively § Technology integration is costly, risky and complicated § Information is everywhere, but getting access to the right information at the right time is very difficult § Modifying system behaviour takes too long and changes are difficult to communicate and implement effectively § Much of IT system and operations expenditure is bloated and fixed - operations run with excess redundant capacity The result: IT seen as a cost centre, not a source of business value © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 8
The challenge: IT often fails to support these types of changes effectively § Technology integration is costly, risky and complicated § Information is everywhere, but getting access to the right information at the right time is very difficult § Modifying system behaviour takes too long and changes are difficult to communicate and implement effectively § Much of IT system and operations expenditure is bloated and fixed - operations run with excess redundant capacity The result: IT seen as a cost centre, not a source of business value © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 8
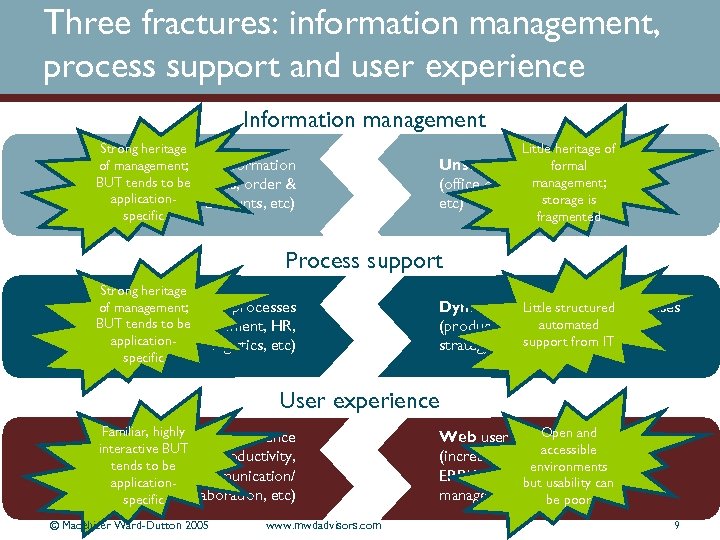 Three fractures: information management, process support and user experience Information management Strong heritage of management; Structured information BUT tends to be (customer records, order & applicationfulfilment records, accounts, etc) specific Little heritage of Unstructured information formal management; (office documents, web content storage is etc) fragmented Process support Strong heritage of management; Stable, predictable processes BUT tends order (accounting, to be fulfilment, HR, applicationlogistics, etc) specific Dynamic, collaborative processes Little structured automated (product innovation, marketing, support strategy setting, etc)from IT User experience Familiar, highly user experience Desktop interactive BUT (office productivity, tends to be application- communication/ specific collaboration, etc) © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com Open and Web user experience accessible (increasing numbers of environments ERP/CRM applications, content but usability can management, etc) poor be 9
Three fractures: information management, process support and user experience Information management Strong heritage of management; Structured information BUT tends to be (customer records, order & applicationfulfilment records, accounts, etc) specific Little heritage of Unstructured information formal management; (office documents, web content storage is etc) fragmented Process support Strong heritage of management; Stable, predictable processes BUT tends order (accounting, to be fulfilment, HR, applicationlogistics, etc) specific Dynamic, collaborative processes Little structured automated (product innovation, marketing, support strategy setting, etc)from IT User experience Familiar, highly user experience Desktop interactive BUT (office productivity, tends to be application- communication/ specific collaboration, etc) © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com Open and Web user experience accessible (increasing numbers of environments ERP/CRM applications, content but usability can management, etc) poor be 9
 IT-business alignment © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 10 advising on IT-business alignment
IT-business alignment © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 10 advising on IT-business alignment
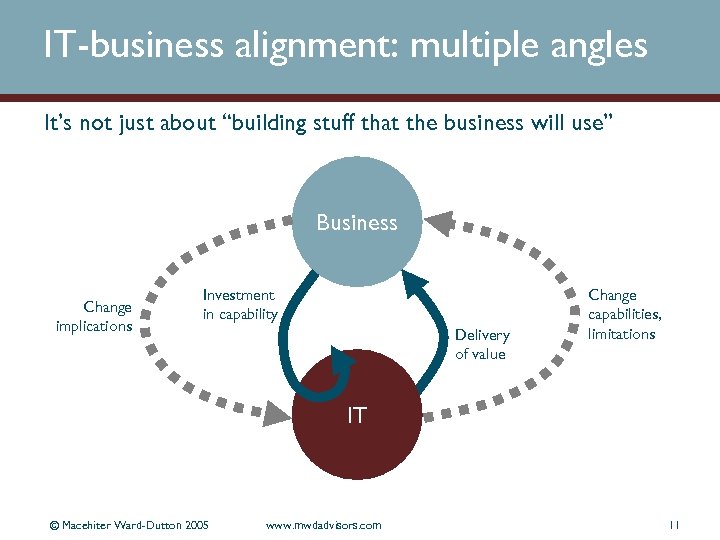 IT-business alignment: multiple angles It’s not just about “building stuff that the business will use” Business Change implications Investment in capability Delivery of value Change capabilities, limitations IT © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 11
IT-business alignment: multiple angles It’s not just about “building stuff that the business will use” Business Change implications Investment in capability Delivery of value Change capabilities, limitations IT © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 11
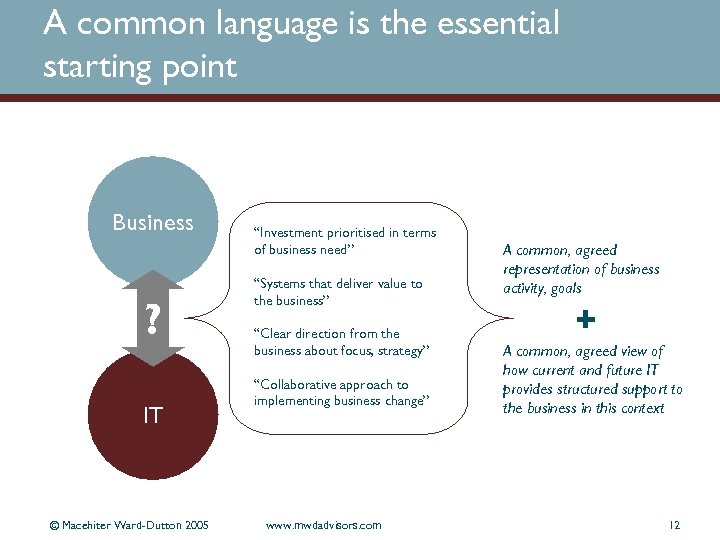 A common language is the essential starting point Business ? IT © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 “Investment prioritised in terms of business need” “Systems that deliver value to the business” “Clear direction from the business about focus, strategy” “Collaborative approach to implementing business change” www. mwdadvisors. com A common, agreed representation of business activity, goals + A common, agreed view of how current and future IT provides structured support to the business in this context 12
A common language is the essential starting point Business ? IT © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 “Investment prioritised in terms of business need” “Systems that deliver value to the business” “Clear direction from the business about focus, strategy” “Collaborative approach to implementing business change” www. mwdadvisors. com A common, agreed representation of business activity, goals + A common, agreed view of how current and future IT provides structured support to the business in this context 12
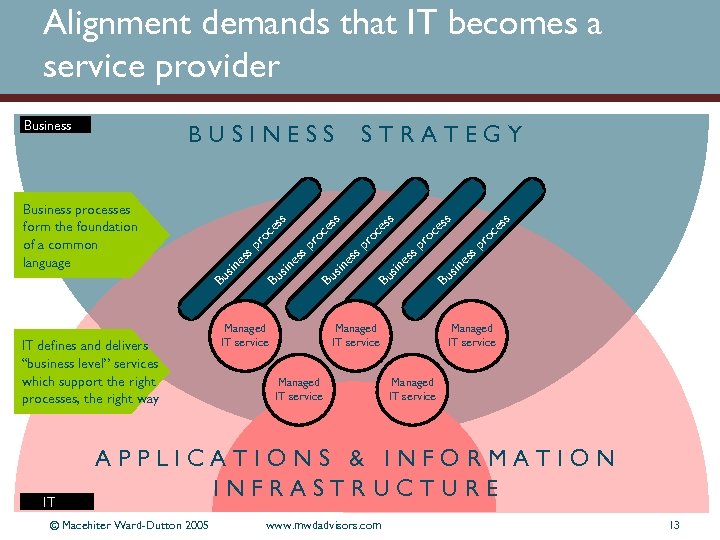 Alignment demands that IT becomes a service provider IT defines and delivers “business level” services which support the right processes, the right way IT Managed IT service sp ro ce ss Bu sin es sp ro ce ss sp es Bu sin es Bu s in es sp ro ce ss Business processes form the foundation of a common language STRATEGY sp ro ce ss BUSINESS Bu sin es Business Managed IT service APPLICATIONS & INFORMATION INFRASTRUCTURE © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 13
Alignment demands that IT becomes a service provider IT defines and delivers “business level” services which support the right processes, the right way IT Managed IT service sp ro ce ss Bu sin es sp ro ce ss sp es Bu sin es Bu s in es sp ro ce ss Business processes form the foundation of a common language STRATEGY sp ro ce ss BUSINESS Bu sin es Business Managed IT service APPLICATIONS & INFORMATION INFRASTRUCTURE © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 13
 Alignment principle #1: understanding service-oriented IT © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 14 advising on IT-business alignment
Alignment principle #1: understanding service-oriented IT © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 14 advising on IT-business alignment
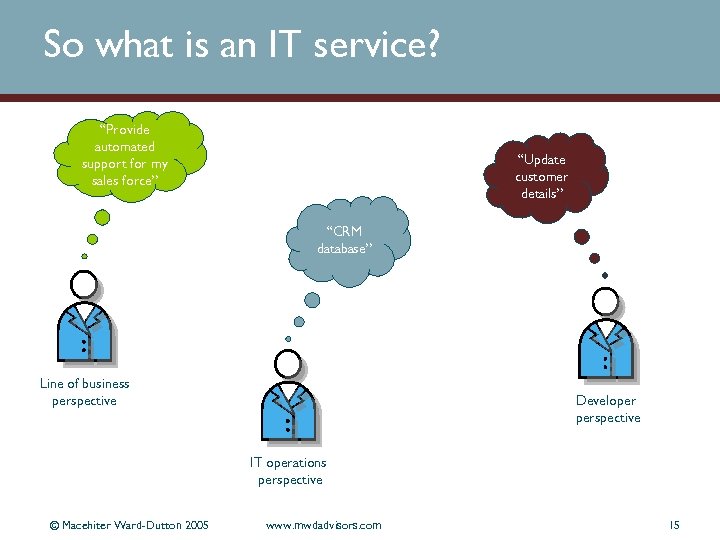 So what is an IT service? “Provide automated support for my sales force” “Update customer details” “CRM database” Line of business perspective Developer perspective IT operations perspective © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 15
So what is an IT service? “Provide automated support for my sales force” “Update customer details” “CRM database” Line of business perspective Developer perspective IT operations perspective © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 15
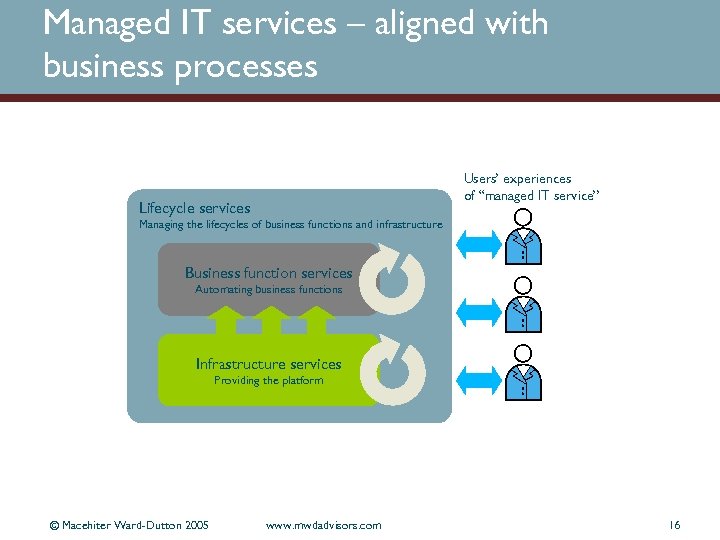 Managed IT services – aligned with business processes Users’ experiences of “managed IT service” Lifecycle services Managing the lifecycles of business functions and infrastructure Business function services Automating business functions Infrastructure services Providing the platform © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 16
Managed IT services – aligned with business processes Users’ experiences of “managed IT service” Lifecycle services Managing the lifecycles of business functions and infrastructure Business function services Automating business functions Infrastructure services Providing the platform © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 16
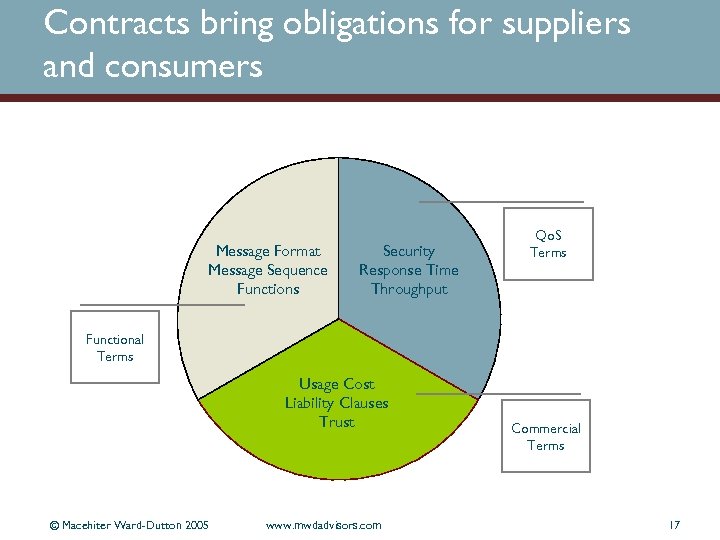 Contracts bring obligations for suppliers and consumers Message Format Message Sequence Functions Security Response Time Throughput Qo. S Terms Functional Terms Usage Cost Liability Clauses Trust © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com Commercial Terms 17
Contracts bring obligations for suppliers and consumers Message Format Message Sequence Functions Security Response Time Throughput Qo. S Terms Functional Terms Usage Cost Liability Clauses Trust © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com Commercial Terms 17
 Alignment principle #2: understanding business processes and their priorities © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 18 advising on IT-business alignment
Alignment principle #2: understanding business processes and their priorities © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 18 advising on IT-business alignment
![A universe of business processes [1] A hierarchy of business processes S M E A universe of business processes [1] A hierarchy of business processes S M E](https://present5.com/presentation/805a6154b814540bc48d177ac2ca9318/image-19.jpg) A universe of business processes [1] A hierarchy of business processes S M E E © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 M “Strategy” processes – instances oversee instances of management processes M E www. mwdadvisors. com E “Management” processes – instances oversee instances of execution processes E “Execution” processes – instances handle particular units of work within business activities 19
A universe of business processes [1] A hierarchy of business processes S M E E © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 M “Strategy” processes – instances oversee instances of management processes M E www. mwdadvisors. com E “Management” processes – instances oversee instances of execution processes E “Execution” processes – instances handle particular units of work within business activities 19
![A universe of business processes [2] Contribution to competitive differentiation S S M M A universe of business processes [2] Contribution to competitive differentiation S S M M](https://present5.com/presentation/805a6154b814540bc48d177ac2ca9318/image-20.jpg) A universe of business processes [2] Contribution to competitive differentiation S S M M E E E Non-differentiating Differentiating (focus should be on efficiency) (focus should be on flexibility) © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 20
A universe of business processes [2] Contribution to competitive differentiation S S M M E E E Non-differentiating Differentiating (focus should be on efficiency) (focus should be on flexibility) © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 20
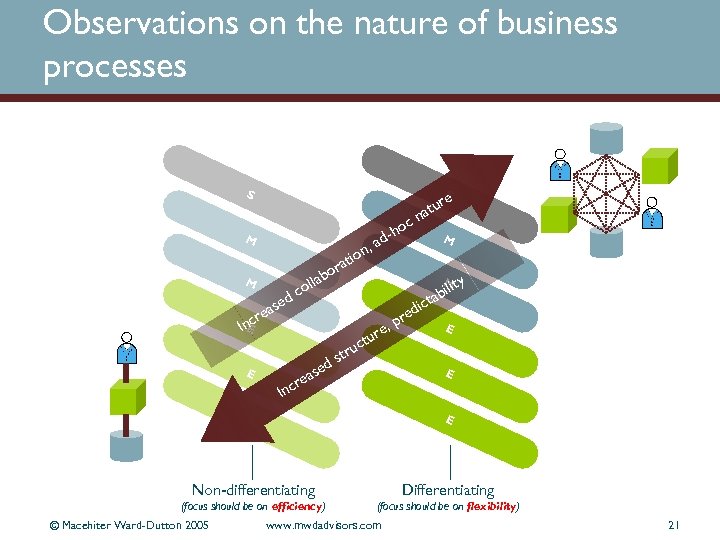 Observations on the nature of business processes S S M M s r ea c e o dc ll r abo at , ad io n as cre E e M M E In tr ds ho e t ur a cn u , ure ct d pre ic lit abi t y E E In E E Non-differentiating Differentiating (focus should be on efficiency) (focus should be on flexibility) © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 21
Observations on the nature of business processes S S M M s r ea c e o dc ll r abo at , ad io n as cre E e M M E In tr ds ho e t ur a cn u , ure ct d pre ic lit abi t y E E In E E Non-differentiating Differentiating (focus should be on efficiency) (focus should be on flexibility) © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 21
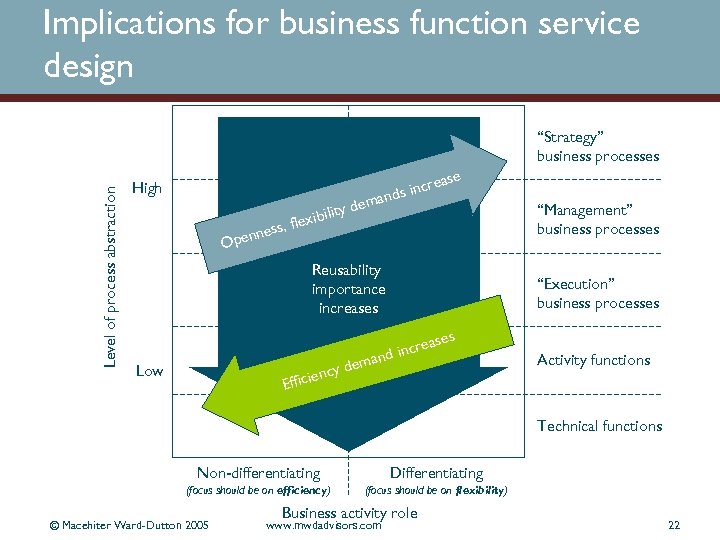 Implications for business function service design Level of process abstraction “Strategy” business processes High d ibility x ss, fle ase cre ds in n ema ne Open Reusability importance increases ncy d fficie E Low “Management” business processes “Execution” business processes a incre nd ema Activity functions Technical functions Non-differentiating Differentiating (focus should be on efficiency) (focus should be on flexibility) © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 Business activity role www. mwdadvisors. com 22
Implications for business function service design Level of process abstraction “Strategy” business processes High d ibility x ss, fle ase cre ds in n ema ne Open Reusability importance increases ncy d fficie E Low “Management” business processes “Execution” business processes a incre nd ema Activity functions Technical functions Non-differentiating Differentiating (focus should be on efficiency) (focus should be on flexibility) © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 Business activity role www. mwdadvisors. com 22
 Enterprise architecture must reflect IT-business alignment principles © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 23 advising on IT-business alignment
Enterprise architecture must reflect IT-business alignment principles © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 23 advising on IT-business alignment
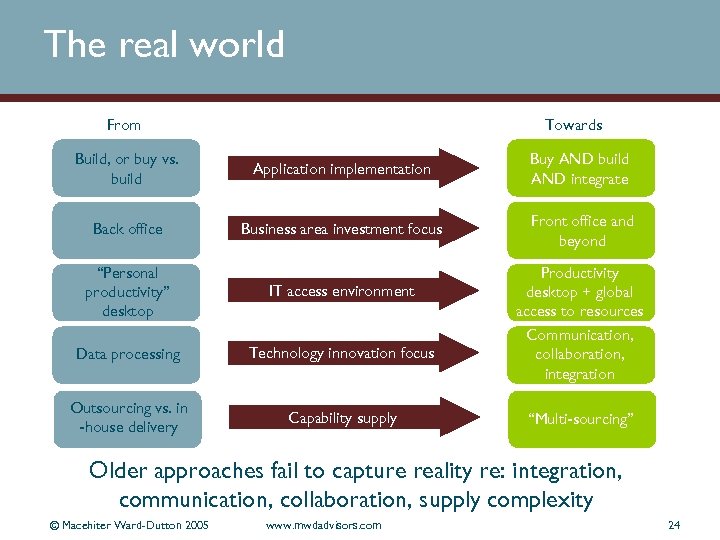 The real world From Towards Build, or buy vs. build Application implementation Buy AND build AND integrate Back office Business area investment focus Front office and beyond “Personal productivity” desktop IT access environment Data processing Technology innovation focus Outsourcing vs. in -house delivery Capability supply Productivity desktop + global access to resources Communication, collaboration, integration “Multi-sourcing” Older approaches fail to capture reality re: integration, communication, collaboration, supply complexity © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 24
The real world From Towards Build, or buy vs. build Application implementation Buy AND build AND integrate Back office Business area investment focus Front office and beyond “Personal productivity” desktop IT access environment Data processing Technology innovation focus Outsourcing vs. in -house delivery Capability supply Productivity desktop + global access to resources Communication, collaboration, integration “Multi-sourcing” Older approaches fail to capture reality re: integration, communication, collaboration, supply complexity © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 24
![A “traditional” view of EA [1]: The Zachman framework Source: John Zachman, ZIFA © A “traditional” view of EA [1]: The Zachman framework Source: John Zachman, ZIFA ©](https://present5.com/presentation/805a6154b814540bc48d177ac2ca9318/image-25.jpg) A “traditional” view of EA [1]: The Zachman framework Source: John Zachman, ZIFA © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 25
A “traditional” view of EA [1]: The Zachman framework Source: John Zachman, ZIFA © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 25
![A “traditional” view of EA [2]: TOGAF ADM Source: Open Group © Macehiter Ward-Dutton A “traditional” view of EA [2]: TOGAF ADM Source: Open Group © Macehiter Ward-Dutton](https://present5.com/presentation/805a6154b814540bc48d177ac2ca9318/image-26.jpg) A “traditional” view of EA [2]: TOGAF ADM Source: Open Group © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 26
A “traditional” view of EA [2]: TOGAF ADM Source: Open Group © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 26
 The good and the bad of EA frameworks The good The bad § The frameworks give us a useful “language” for communicating and sharing ideas about how IT systems can/should support business needs § Methodologies like the TOGAF ADM give solid templates for EA process work § Starting to consider more dynamic aspects of EA § The roots of most frameworks are in the creation or change of transactional information processing systems § The real world of IT is much more ugly and complicated § Still documentation-oriented – not focused on the process of architecture evolution & governance – as-is, to-be, vision views © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 27
The good and the bad of EA frameworks The good The bad § The frameworks give us a useful “language” for communicating and sharing ideas about how IT systems can/should support business needs § Methodologies like the TOGAF ADM give solid templates for EA process work § Starting to consider more dynamic aspects of EA § The roots of most frameworks are in the creation or change of transactional information processing systems § The real world of IT is much more ugly and complicated § Still documentation-oriented – not focused on the process of architecture evolution & governance – as-is, to-be, vision views © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 27
 The challenge Business process Applications The business Activities, processes Data The real world doesn’t “decompose” nicely – and IT isn’t just about things you build in-house © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 28
The challenge Business process Applications The business Activities, processes Data The real world doesn’t “decompose” nicely – and IT isn’t just about things you build in-house © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 28
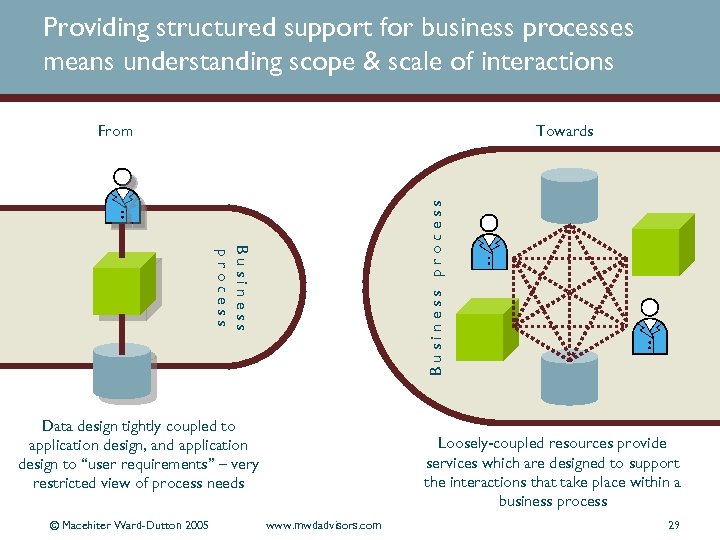 Providing structured support for business processes means understanding scope & scale of interactions Towards Business process From Data design tightly coupled to application design, and application design to “user requirements” – very restricted view of process needs © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 Loosely-coupled resources provide services which are designed to support the interactions that take place within a business process www. mwdadvisors. com 29
Providing structured support for business processes means understanding scope & scale of interactions Towards Business process From Data design tightly coupled to application design, and application design to “user requirements” – very restricted view of process needs © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 Loosely-coupled resources provide services which are designed to support the interactions that take place within a business process www. mwdadvisors. com 29
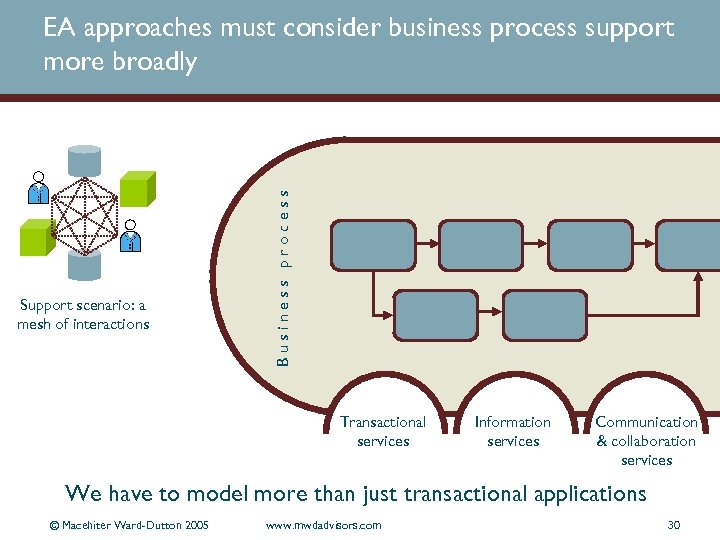 Support scenario: a mesh of interactions Business process EA approaches must consider business process support more broadly Transactional services Information services Communication & collaboration services We have to model more than just transactional applications © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 30
Support scenario: a mesh of interactions Business process EA approaches must consider business process support more broadly Transactional services Information services Communication & collaboration services We have to model more than just transactional applications © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 30
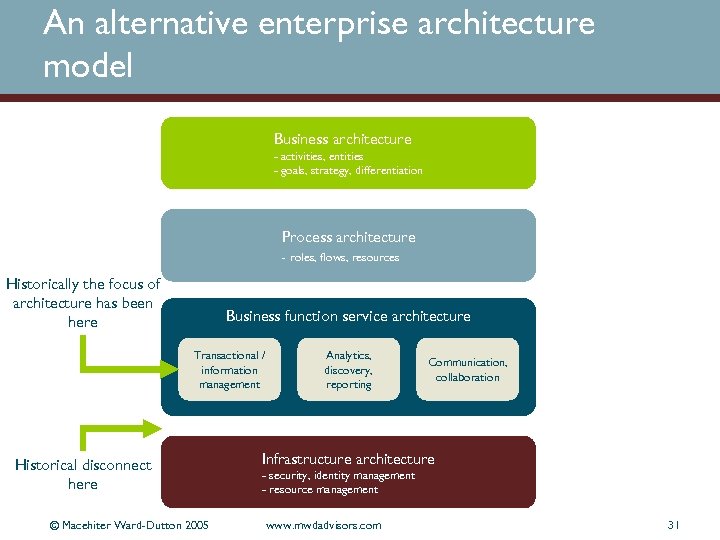 An alternative enterprise architecture model Business architecture - activities, entities - goals, strategy, differentiation Process architecture - roles, flows, resources Historically the focus of architecture has been here Business function service architecture Transactional / information management Historical disconnect here © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 Analytics, discovery, reporting Communication, collaboration Infrastructure architecture - security, identity management - resource management www. mwdadvisors. com 31
An alternative enterprise architecture model Business architecture - activities, entities - goals, strategy, differentiation Process architecture - roles, flows, resources Historically the focus of architecture has been here Business function service architecture Transactional / information management Historical disconnect here © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 Analytics, discovery, reporting Communication, collaboration Infrastructure architecture - security, identity management - resource management www. mwdadvisors. com 31
 Enterprise Architecture and IT Governance © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 32 advising on IT-business alignment
Enterprise Architecture and IT Governance © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 32 advising on IT-business alignment
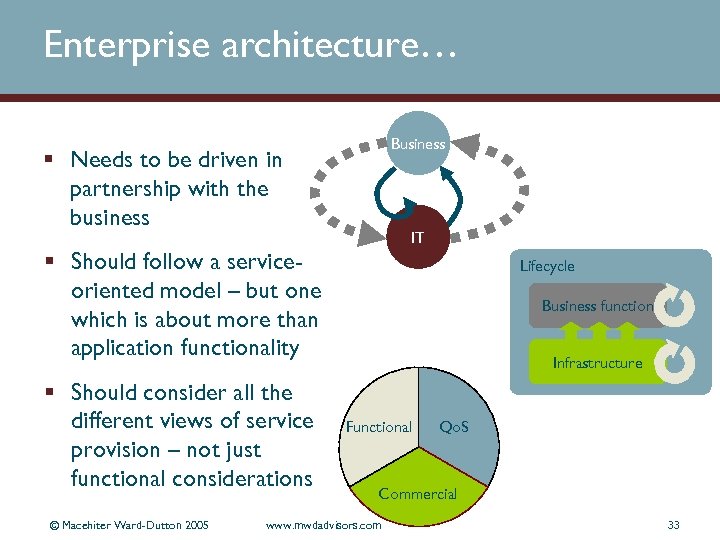 Enterprise architecture… Business § Needs to be driven in partnership with the business IT § Should follow a serviceoriented model – but one which is about more than application functionality § Should consider all the different views of service provision – not just functional considerations © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 Lifecycle Business function Infrastructure Functional Qo. S Commercial www. mwdadvisors. com 33
Enterprise architecture… Business § Needs to be driven in partnership with the business IT § Should follow a serviceoriented model – but one which is about more than application functionality § Should consider all the different views of service provision – not just functional considerations © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 Lifecycle Business function Infrastructure Functional Qo. S Commercial www. mwdadvisors. com 33
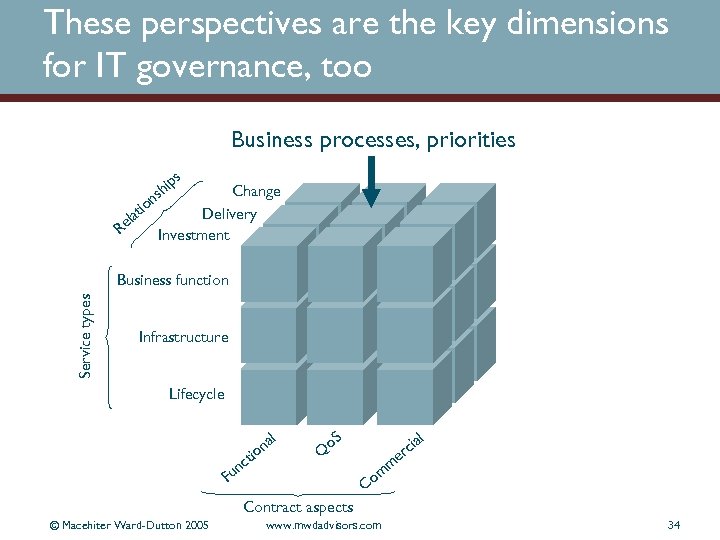 These perspectives are the key dimensions for IT governance, too Business processes, priorities s Change Delivery Investment n tio la Re ip sh Service types Business function Infrastructure Lifecycle l na io t nc Fu o. S ia rc Q l e m m Co Contract aspects © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 34
These perspectives are the key dimensions for IT governance, too Business processes, priorities s Change Delivery Investment n tio la Re ip sh Service types Business function Infrastructure Lifecycle l na io t nc Fu o. S ia rc Q l e m m Co Contract aspects © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 34
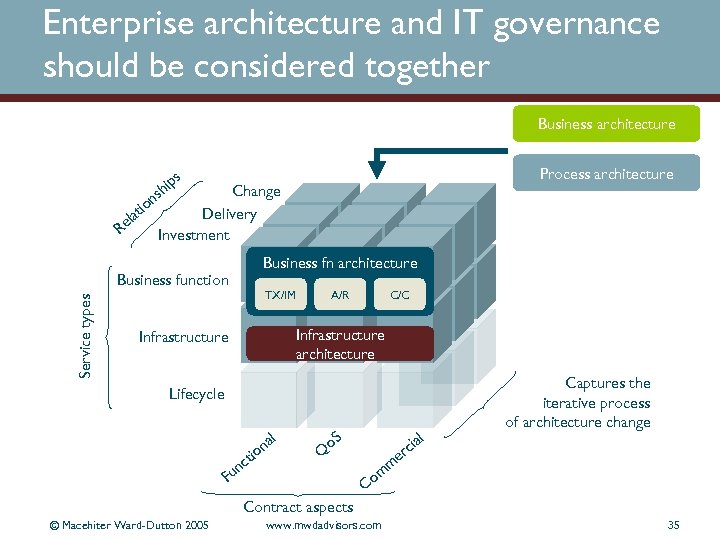 Enterprise architecture and IT governance should be considered together Business architecture Change Delivery Investment n tio la Re s Business function Service types Process architecture s hip Business fn architecture TX/IM A/R C/C Infrastructure architecture Infrastructure Lifecycle l na io t nc Fu o. S ia rc Q l Captures the iterative process of architecture change e m m Co Contract aspects © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 35
Enterprise architecture and IT governance should be considered together Business architecture Change Delivery Investment n tio la Re s Business function Service types Process architecture s hip Business fn architecture TX/IM A/R C/C Infrastructure architecture Infrastructure Lifecycle l na io t nc Fu o. S ia rc Q l Captures the iterative process of architecture change e m m Co Contract aspects © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 35
 You can use the model to… § Identify strengths and weaknesses in your current IT governance approach § Identify the contributions made by particular technologies to business objectives § As above for IT vendors § Consider the dimensions that affect sourcing decisions © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 36
You can use the model to… § Identify strengths and weaknesses in your current IT governance approach § Identify the contributions made by particular technologies to business objectives § As above for IT vendors § Consider the dimensions that affect sourcing decisions © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 36
 A worked example: the role of DSI © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 37 advising on IT-business alignment
A worked example: the role of DSI © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 37 advising on IT-business alignment
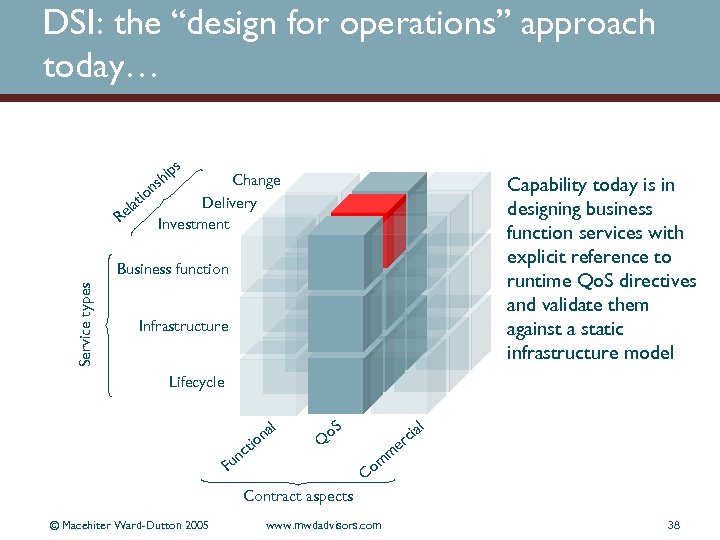 DSI: the “design for operations” approach today… s Change Delivery Investment n tio la Re ip sh Capability today is in designing business function services with explicit reference to runtime Qo. S directives and validate them against a static infrastructure model Service types Business function Infrastructure Lifecycle a on ti nc l o. S ia rc Q l e m om C Fu Contract aspects © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 38
DSI: the “design for operations” approach today… s Change Delivery Investment n tio la Re ip sh Capability today is in designing business function services with explicit reference to runtime Qo. S directives and validate them against a static infrastructure model Service types Business function Infrastructure Lifecycle a on ti nc l o. S ia rc Q l e m om C Fu Contract aspects © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 38
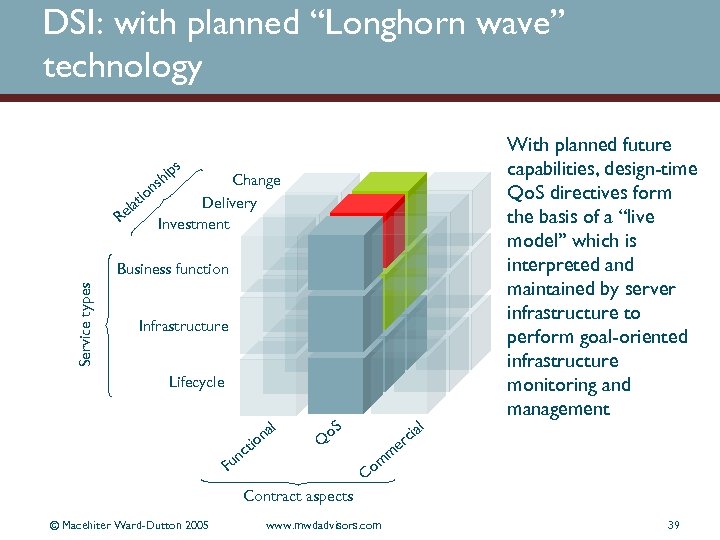 DSI: with planned “Longhorn wave” technology s Change Delivery Investment n tio la Re ip sh Service types Business function Infrastructure Lifecycle a on ti nc l o. S ia rc Q l With planned future capabilities, design-time Qo. S directives form the basis of a “live model” which is interpreted and maintained by server infrastructure to perform goal-oriented infrastructure monitoring and management e m om C Fu Contract aspects © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 39
DSI: with planned “Longhorn wave” technology s Change Delivery Investment n tio la Re ip sh Service types Business function Infrastructure Lifecycle a on ti nc l o. S ia rc Q l With planned future capabilities, design-time Qo. S directives form the basis of a “live model” which is interpreted and maintained by server infrastructure to perform goal-oriented infrastructure monitoring and management e m om C Fu Contract aspects © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 39
 A call to action § For architecture to contribute to IT-business alignment, you have to follow a holistic approach – Not just applications but infrastructure and lifecycle services – Proactively consider the links between all three – Look for technologies and patterns which support the linkages § Set up an architecture governance practice which doesn’t just allow change, but promotes it – Not a project-focused approach but an ongoing process with senior level sponsorship – Close links to business stakeholders and their priorities – Think about using contracts, policies and processes as the foundation of a common language © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 40
A call to action § For architecture to contribute to IT-business alignment, you have to follow a holistic approach – Not just applications but infrastructure and lifecycle services – Proactively consider the links between all three – Look for technologies and patterns which support the linkages § Set up an architecture governance practice which doesn’t just allow change, but promotes it – Not a project-focused approach but an ongoing process with senior level sponsorship – Close links to business stakeholders and their priorities – Think about using contracts, policies and processes as the foundation of a common language © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 40
 Thank you © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 41 advising on IT-business alignment
Thank you © Macehiter Ward-Dutton 2005 www. mwdadvisors. com 41 advising on IT-business alignment


