5dc93dfd2d37f270b2542099afebb34a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Retailing Research
Retailing Research
 Overview n Retailing What is research? Using the facts Researching the market Methods of data collection n Primary V Secondary n Quantitative V Qualitative n Consumers expectations Malcolm Kirkup’s theory The Consumer Profile Use to the retail manager The Quiz and questions n n n n
Overview n Retailing What is research? Using the facts Researching the market Methods of data collection n Primary V Secondary n Quantitative V Qualitative n Consumers expectations Malcolm Kirkup’s theory The Consumer Profile Use to the retail manager The Quiz and questions n n n n
 Definition: Retailing n “Process of selling consumer goods directly to consumers. Unlike the wholesaler, who sells goods to other businesses for resale, the retailer is the final agent through which products pass on their way from manufacturer to user. ” (Bangs 1998) n The retailer has to anticipate the needs of its present and even future consumers n Larger retail firms consist of: Discount stores, chain stores, department stores, and supermarkets.
Definition: Retailing n “Process of selling consumer goods directly to consumers. Unlike the wholesaler, who sells goods to other businesses for resale, the retailer is the final agent through which products pass on their way from manufacturer to user. ” (Bangs 1998) n The retailer has to anticipate the needs of its present and even future consumers n Larger retail firms consist of: Discount stores, chain stores, department stores, and supermarkets.
 Retailing also includes: n n n House-to-house canvassing, Mail-order selling, Vending machines, Petrol stations, and Street stalls
Retailing also includes: n n n House-to-house canvassing, Mail-order selling, Vending machines, Petrol stations, and Street stalls
 What is Research? n “Research is not simply describing what you find. ” (Marshall, 1997) n Making sense of what you find. n “The more questions a specific area or fact can answer – that is, the more scope it has – the more useful it is to science and society. ” (Marshall, I BID)
What is Research? n “Research is not simply describing what you find. ” (Marshall, 1997) n Making sense of what you find. n “The more questions a specific area or fact can answer – that is, the more scope it has – the more useful it is to science and society. ” (Marshall, I BID)
 Theories n Vital in the pre-determining of consumer behaviour patterns. n Strong Theories – Used for prediction n Weak Theories – Only sufficient for explanation
Theories n Vital in the pre-determining of consumer behaviour patterns. n Strong Theories – Used for prediction n Weak Theories – Only sufficient for explanation
 PARADIGMS n Paradigms are particular ways of thinking about and sharing information with items of a similar nature. n Assumptions Conceptualisations Values Attitudes Orientations Beliefs n n n
PARADIGMS n Paradigms are particular ways of thinking about and sharing information with items of a similar nature. n Assumptions Conceptualisations Values Attitudes Orientations Beliefs n n n
 Advantage and Disadvantage Of Paradigms n Advantage: They prevent analysts wasting time on problems they are not best equipped to solve. n Disadvantage: They blinker researchers to other valid ways of looking at the issues.
Advantage and Disadvantage Of Paradigms n Advantage: They prevent analysts wasting time on problems they are not best equipped to solve. n Disadvantage: They blinker researchers to other valid ways of looking at the issues.
 Starting with the Facts? n Induction n Deduction n Induction is the ordering of facts n Deduction is the logical leap process, always looking for the next stage past theoretical ideas.
Starting with the Facts? n Induction n Deduction n Induction is the ordering of facts n Deduction is the logical leap process, always looking for the next stage past theoretical ideas.
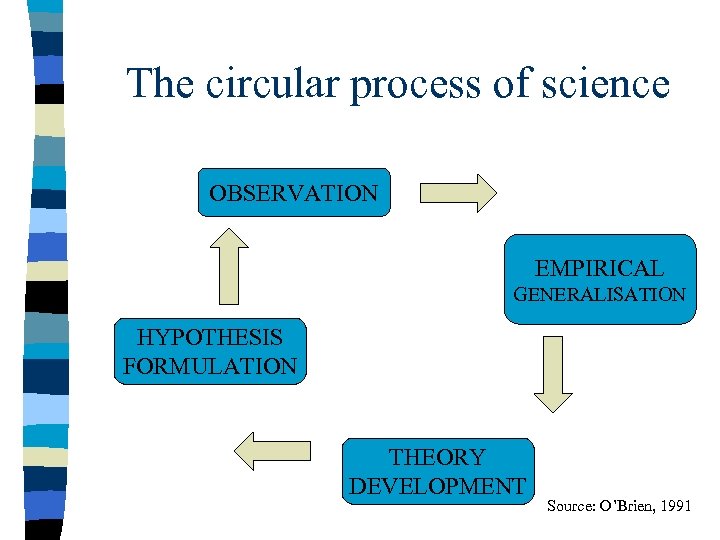 The circular process of science OBSERVATION EMPIRICAL GENERALISATION HYPOTHESIS FORMULATION THEORY DEVELOPMENT Source: O’Brien, 1991
The circular process of science OBSERVATION EMPIRICAL GENERALISATION HYPOTHESIS FORMULATION THEORY DEVELOPMENT Source: O’Brien, 1991
 Researching the market Retailers need to know who is buying what, where and when. n Analysing till receipts is useful, but can only give retailer information on what has happened and not what is going to happen. n
Researching the market Retailers need to know who is buying what, where and when. n Analysing till receipts is useful, but can only give retailer information on what has happened and not what is going to happen. n
 Next Associated with edited retailing n Edited retailing: “The involvement of offering for sale a limited range of coordinated products for a specific client group. ” (O’Brien et al. 1988) n New Next lines: n “Women who care about fashion first and price second” (Ody 1998) Men, Interiors, Jewellery.
Next Associated with edited retailing n Edited retailing: “The involvement of offering for sale a limited range of coordinated products for a specific client group. ” (O’Brien et al. 1988) n New Next lines: n “Women who care about fashion first and price second” (Ody 1998) Men, Interiors, Jewellery.
 Methods of data collection n Primary research: “This type of data must be gathered by observing phenomena or surveying respondents. ” Dibb et al. 2000
Methods of data collection n Primary research: “This type of data must be gathered by observing phenomena or surveying respondents. ” Dibb et al. 2000
 Primary Research Techniques n Experimentation – “Data collection that involves maintaining certain variables constant so that the effects of the experimental variables can be measured” n Marketing experimentation – “A set of rules and procedures by which data gathering is organised to analyse and interpret key marketing variables. ” n Sampling – “The selection of representative units from a total population. ” n n RANDOM SAMPLING STRATIFIED SAMPLING AREA SAMPLING QUOTA SAMPLING
Primary Research Techniques n Experimentation – “Data collection that involves maintaining certain variables constant so that the effects of the experimental variables can be measured” n Marketing experimentation – “A set of rules and procedures by which data gathering is organised to analyse and interpret key marketing variables. ” n Sampling – “The selection of representative units from a total population. ” n n RANDOM SAMPLING STRATIFIED SAMPLING AREA SAMPLING QUOTA SAMPLING
 Primary Research Techniques n Survey methods – “Interviews by mail and personal interviews. ” 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. cont’d. . Mail surveys Mail panels Consumer purchase diaries Telephone surveys Computer assisted telephone interviewing
Primary Research Techniques n Survey methods – “Interviews by mail and personal interviews. ” 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. cont’d. . Mail surveys Mail panels Consumer purchase diaries Telephone surveys Computer assisted telephone interviewing
 Primary Research Techniques 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Personal interview surveys Depth interviews Shopping mall/pavement intercept interviews On-site computer interviewing Focus group interviews Quali-depth interviews and IN-home interviews. cont’d. .
Primary Research Techniques 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Personal interview surveys Depth interviews Shopping mall/pavement intercept interviews On-site computer interviewing Focus group interviews Quali-depth interviews and IN-home interviews. cont’d. .
 Primary Research Techniques § Questionnaire construction cont’d. . – “Base document for research purposes, providing the questions and structure for an interview or self-completion and providing space for respondents’ answers. ” § Observation methods – “Methods by which researchers record respondents’ overt behaviour and take note of physical conditions and events. ”
Primary Research Techniques § Questionnaire construction cont’d. . – “Base document for research purposes, providing the questions and structure for an interview or self-completion and providing space for respondents’ answers. ” § Observation methods – “Methods by which researchers record respondents’ overt behaviour and take note of physical conditions and events. ”
 Methods of data collection n Secondary research: “Information compiled inside or outside the organisation for some purpose other than the current investigation. ” Dibb et al. I BID
Methods of data collection n Secondary research: “Information compiled inside or outside the organisation for some purpose other than the current investigation. ” Dibb et al. I BID
 Syndicated Data Services n BARB – Supply television stations with viewing estimates for any specific time of day. n Nielsen AGB – Provide data about products primarily sold in the retail industry; such as product sales, own brand sales and competing brands.
Syndicated Data Services n BARB – Supply television stations with viewing estimates for any specific time of day. n Nielsen AGB – Provide data about products primarily sold in the retail industry; such as product sales, own brand sales and competing brands.
 Quantitative V Qualitative n Quantitative: Meaning the research aimed at producing statistical data to be expressed numerically. n Qualitative: Information too difficult or expensive to quantify. Includes subjective opinions and personal judgements not accessible using quantitative methods.
Quantitative V Qualitative n Quantitative: Meaning the research aimed at producing statistical data to be expressed numerically. n Qualitative: Information too difficult or expensive to quantify. Includes subjective opinions and personal judgements not accessible using quantitative methods.
 Consumer Expectations n Consumers expect more n Improvements in quality and selection of products within one retailer n Lower prices, due to higher sales n More choice at reasonable cost n ASDA Wal-Mart use buying power to lower costs at all levels of the supply chain
Consumer Expectations n Consumers expect more n Improvements in quality and selection of products within one retailer n Lower prices, due to higher sales n More choice at reasonable cost n ASDA Wal-Mart use buying power to lower costs at all levels of the supply chain
 Malcolm Kirkup’s theory n “A store is a ‘locus of social and informational, as well as material exchanges’, and therefore, methods are needed to capture the social exchanges within this arena” (Kirkup, p 3, 1998)
Malcolm Kirkup’s theory n “A store is a ‘locus of social and informational, as well as material exchanges’, and therefore, methods are needed to capture the social exchanges within this arena” (Kirkup, p 3, 1998)
 Kirkup’s theory continued. If the environment is right, the customers will keep coming back n Every consumer wants to feel special n Retailer must stay in touch with consumer demands/needs n
Kirkup’s theory continued. If the environment is right, the customers will keep coming back n Every consumer wants to feel special n Retailer must stay in touch with consumer demands/needs n
 Building a consumer profile n EDI – Electronic Data Interchange n IOS – Inter-organisational information systems n Allows the retailer to be constantly up-to -date with the minimum amount of human intervention
Building a consumer profile n EDI – Electronic Data Interchange n IOS – Inter-organisational information systems n Allows the retailer to be constantly up-to -date with the minimum amount of human intervention
 Other methods n Loyalty cards n Store cards n Credit card transactions n Need to know the consumer’s every move
Other methods n Loyalty cards n Store cards n Credit card transactions n Need to know the consumer’s every move
 The result… n More specific promotional activities n More consumer focussed n Making the consumer feel special n Increasing the sales volume of the business n Continually innovating techniques n Making sure they will be there in the future!
The result… n More specific promotional activities n More consumer focussed n Making the consumer feel special n Increasing the sales volume of the business n Continually innovating techniques n Making sure they will be there in the future!
 THE QUIZ!
THE QUIZ!
 Answers… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Observation, Empirical Generalisation, Theory development, Hypothesis Formulation. Nielsen AGB Random, stratified, area and quota sampling Mail Surveys, Mail panels, Consumer purchase diaries, Telephone surveys, Computer assisted telephone interviewing, Personal interview surveys, Depth interviews, Shopping mall/pavement intercept interviews, On-site computer interviewing, Focus Group interviews, Quali-depth interviews and IN-home interviews Providing and understanding how to create the correct purchasing environment, not just knowing WHAT they buy. Electronic Data Interchange
Answers… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Observation, Empirical Generalisation, Theory development, Hypothesis Formulation. Nielsen AGB Random, stratified, area and quota sampling Mail Surveys, Mail panels, Consumer purchase diaries, Telephone surveys, Computer assisted telephone interviewing, Personal interview surveys, Depth interviews, Shopping mall/pavement intercept interviews, On-site computer interviewing, Focus Group interviews, Quali-depth interviews and IN-home interviews Providing and understanding how to create the correct purchasing environment, not just knowing WHAT they buy. Electronic Data Interchange


