c40f524af98ac9d448d4f818aced1379.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

 Retailing n There is no commonly accepted definition of retailing, due to its complicated and dispersed structure. n Retailing is the selling of finished goods and service to the consumer for personal or family consumption. It includes store retailing, such as department stores, nonstore retailing, such as direct selling and mail order, or service retailing, such as dry cleaning. ” - (Cross 1995, p. 312)
Retailing n There is no commonly accepted definition of retailing, due to its complicated and dispersed structure. n Retailing is the selling of finished goods and service to the consumer for personal or family consumption. It includes store retailing, such as department stores, nonstore retailing, such as direct selling and mail order, or service retailing, such as dry cleaning. ” - (Cross 1995, p. 312)
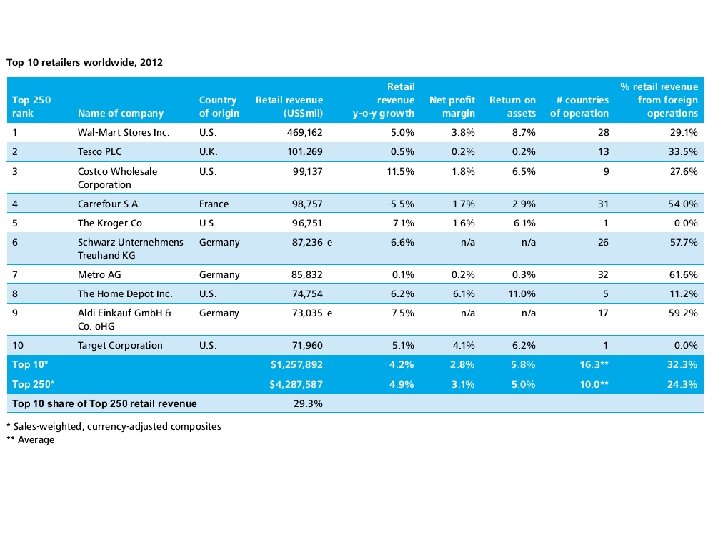
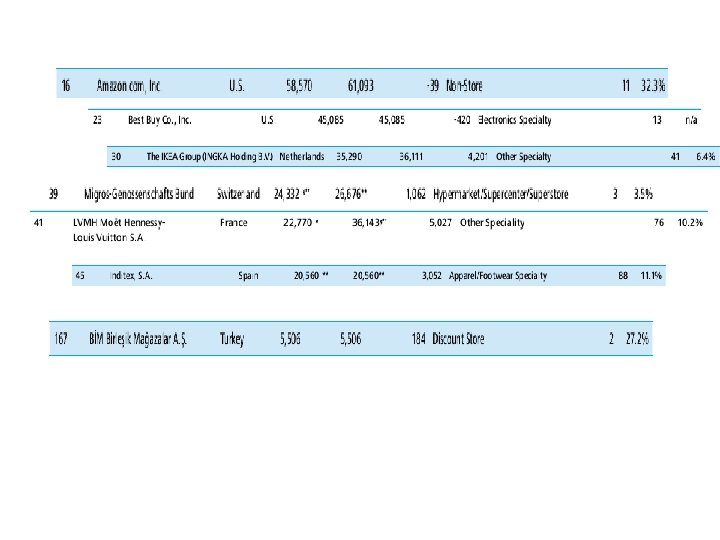
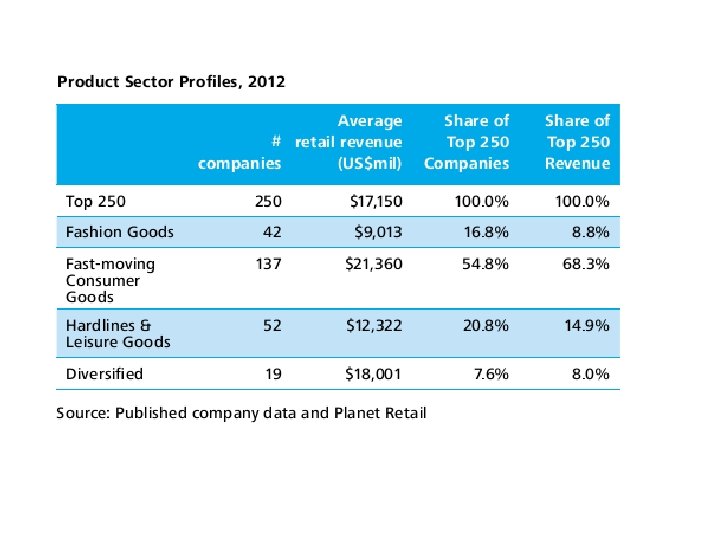
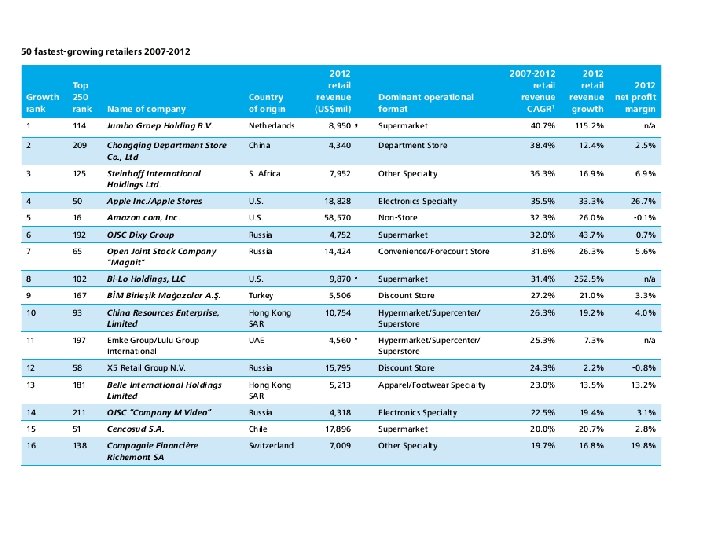
 Retail and Logistics n With the appropriate logistics, products should be of a better presentational quality, could possibly be cheaper, have a longer shelf life and there should be far fewer instances of stock out. n If a retailer gets good sales data from the checkout system, this can be used in scheduling transport and deciding levels and locations of stock holding.
Retail and Logistics n With the appropriate logistics, products should be of a better presentational quality, could possibly be cheaper, have a longer shelf life and there should be far fewer instances of stock out. n If a retailer gets good sales data from the checkout system, this can be used in scheduling transport and deciding levels and locations of stock holding.
 Wal-Mart n n the retail hub (distribution center) and spoke (individual stores) system direct procurement cross docking store-ready displays n n point-of-sales (POS) retail link system- web EDI hand-held computers voice-based order filling (VOF) system
Wal-Mart n n the retail hub (distribution center) and spoke (individual stores) system direct procurement cross docking store-ready displays n n point-of-sales (POS) retail link system- web EDI hand-held computers voice-based order filling (VOF) system

 Franchising n The word 'franchise' is of Anglo-French derivation - from franc - meaning free. n Franchising is a contractual agreement between two parties. n The franchisor is a supplier who allows an operator, or a franchisee, to use the supplier's trademark and sale the supplier's goods. In return, the operator pays the supplier a fee.
Franchising n The word 'franchise' is of Anglo-French derivation - from franc - meaning free. n Franchising is a contractual agreement between two parties. n The franchisor is a supplier who allows an operator, or a franchisee, to use the supplier's trademark and sale the supplier's goods. In return, the operator pays the supplier a fee.
 Franchising n Franchising is founded and first applied in America. n Thirty three countries, including the United States, and Australia, have laws that explicitly regulate franchising. n The majority of all other countries having laws which have a direct or indirect impact on franchising. n There almost 60 sectors working with this system: Car Rental, Care, Services, Shoes and Accessories, Interior decoration, Computers, Cosmetics, Retail Stores, Education, Food, Medical Supplies, House Appliances, Dry Cleaning, Fast-Food, Hospitality and Restaurants.
Franchising n Franchising is founded and first applied in America. n Thirty three countries, including the United States, and Australia, have laws that explicitly regulate franchising. n The majority of all other countries having laws which have a direct or indirect impact on franchising. n There almost 60 sectors working with this system: Car Rental, Care, Services, Shoes and Accessories, Interior decoration, Computers, Cosmetics, Retail Stores, Education, Food, Medical Supplies, House Appliances, Dry Cleaning, Fast-Food, Hospitality and Restaurants.
 Franchising n Various tangibles and intangibles such as national or international advertising, training and other support services are commonly made available by the franchisor. n Single unit (solus ) franchising- Multi unit franchising n Based EFF- Turkey has the first rank in franchised chain number in Europe-1876 chain stores (% 78 of total chain stores in Turkey) (1375 brands in France, 960 brands in Germany)
Franchising n Various tangibles and intangibles such as national or international advertising, training and other support services are commonly made available by the franchisor. n Single unit (solus ) franchising- Multi unit franchising n Based EFF- Turkey has the first rank in franchised chain number in Europe-1876 chain stores (% 78 of total chain stores in Turkey) (1375 brands in France, 960 brands in Germany)
 Why become a franchisee? n n n Set up assistance/supervision Management and employee training Enforcement of norms Worldwide supply Marketing strategy (Marketing communication) Brand awareness… Why become a franchisor? n n n Renting brand name Raising financial and managerial capital to grow fast Harnessing the entrepreneurial spirit
Why become a franchisee? n n n Set up assistance/supervision Management and employee training Enforcement of norms Worldwide supply Marketing strategy (Marketing communication) Brand awareness… Why become a franchisor? n n n Renting brand name Raising financial and managerial capital to grow fast Harnessing the entrepreneurial spirit
 The Franchise Contract Definition of terms Organizational structure Term of initial agreement Term of renewal Causes for termination or nonrenewal Territorial exclusivity Intellectual property protection Assignment of responsibilities Ability to sub-franchise Mutual agreement of pro forma cash flows Development schedule and associated penalties Fees: front end, ongoing Currency and remittance restrictions Remedies in case of disagreement
The Franchise Contract Definition of terms Organizational structure Term of initial agreement Term of renewal Causes for termination or nonrenewal Territorial exclusivity Intellectual property protection Assignment of responsibilities Ability to sub-franchise Mutual agreement of pro forma cash flows Development schedule and associated penalties Fees: front end, ongoing Currency and remittance restrictions Remedies in case of disagreement
 Mc Donald’s Franchising System in Turkey n n n n n Administration is being given to individuals. No allowance for corporates. Success in 5 -6 months of training The operator should not have any other responsibilities rather than managing the franchised restaurant. The franchising agreement is limited with one restaurant, no territorial exclusivity is given. Investment cost on average is (depends on type of restaurant and bigness) 400. 000 - 500. 000 USD + KDV. Duration of the contract: 10 years Franchise fee: 30. 000 USD + KDV During the franchising period, operator should pay contribution margin for the ads, development and royalty. Mc. Donald's based on the growth strategies, is deciding and ranking the places to open restaurants-sometimes they buy or rent the real estate.
Mc Donald’s Franchising System in Turkey n n n n n Administration is being given to individuals. No allowance for corporates. Success in 5 -6 months of training The operator should not have any other responsibilities rather than managing the franchised restaurant. The franchising agreement is limited with one restaurant, no territorial exclusivity is given. Investment cost on average is (depends on type of restaurant and bigness) 400. 000 - 500. 000 USD + KDV. Duration of the contract: 10 years Franchise fee: 30. 000 USD + KDV During the franchising period, operator should pay contribution margin for the ads, development and royalty. Mc. Donald's based on the growth strategies, is deciding and ranking the places to open restaurants-sometimes they buy or rent the real estate.
 Chapter 12 Wholesaling
Chapter 12 Wholesaling
 Wholesaling n Businesses that ¨ do not sell products to a significant degree to ultimate household consumers ¨ sell products primarily to other businesses: retailers, industrial users, commercial users… n Creating an efficient infrastructure to exploit ¨ economies of scope (operating across brands and product categories) ¨ economies of scale (high volume)
Wholesaling n Businesses that ¨ do not sell products to a significant degree to ultimate household consumers ¨ sell products primarily to other businesses: retailers, industrial users, commercial users… n Creating an efficient infrastructure to exploit ¨ economies of scope (operating across brands and product categories) ¨ economies of scale (high volume)
 n Source of Revenue ¨ A wholesaler's main source of revenue is the discount charged on products (purchase products in bulk at a lower price from producers and sell them to retailers with higher prices) ¨ distributors charge service fees (a percentage of the net sales for rendering their services). n Customer Focus ¨ Wholesalers view retailers as their key customers. ¨ Distributors view producers as the primary clients. n Services Offered ¨ A wholesaler has a warehouse and is a passive company that resells (only fulfils orders from retailers ). ¨ A distributor also stores, picks, ships, invoices and handles returns/ customr service on manufacturer’s behalf ¨ And offer sales and marketing services as well
n Source of Revenue ¨ A wholesaler's main source of revenue is the discount charged on products (purchase products in bulk at a lower price from producers and sell them to retailers with higher prices) ¨ distributors charge service fees (a percentage of the net sales for rendering their services). n Customer Focus ¨ Wholesalers view retailers as their key customers. ¨ Distributors view producers as the primary clients. n Services Offered ¨ A wholesaler has a warehouse and is a passive company that resells (only fulfils orders from retailers ). ¨ A distributor also stores, picks, ships, invoices and handles returns/ customr service on manufacturer’s behalf ¨ And offer sales and marketing services as well
 Digitalization in Retailing “What is going on? ”
Digitalization in Retailing “What is going on? ”
 barrier to online shopping • Fear factor ¨ ¨ ¨ n Feel factor ¨ n Feel, see, try out/on Fulfillment factor ¨ ¨ n Credit card safety (69%), then privacy (61%) Returns Customer service questions answered Not willing to pay shipping/handling Don’t want to wait for products Frustration factor ¨ ¨ Difficult to shop online Completing transaction takes too long
barrier to online shopping • Fear factor ¨ ¨ ¨ n Feel factor ¨ n Feel, see, try out/on Fulfillment factor ¨ ¨ n Credit card safety (69%), then privacy (61%) Returns Customer service questions answered Not willing to pay shipping/handling Don’t want to wait for products Frustration factor ¨ ¨ Difficult to shop online Completing transaction takes too long
 Consumer side of e-tailing -attributes of favorite shopping web sitesn trust n n n n fulfillment/reliability (the precise presentation of a product and delivery of the right product at the right time promised), security/privacy (security of payments and privacy of given information), customer service (ready and supportive service that is quick to respond customer inquiries). web site design (information search, order processing, personalization, ease of navigation, , price knowledge, site aesthetics and product selection), perceived usefulness (convenience, competitive pricing, and greater access to information) good product assortment/ wide variety enjoyment ¨ self-gratification and social experiences
Consumer side of e-tailing -attributes of favorite shopping web sitesn trust n n n n fulfillment/reliability (the precise presentation of a product and delivery of the right product at the right time promised), security/privacy (security of payments and privacy of given information), customer service (ready and supportive service that is quick to respond customer inquiries). web site design (information search, order processing, personalization, ease of navigation, , price knowledge, site aesthetics and product selection), perceived usefulness (convenience, competitive pricing, and greater access to information) good product assortment/ wide variety enjoyment ¨ self-gratification and social experiences
 mobile marketing n the two-way or multi-way communication and promotion of an offer between a firm and its customers using a mobile devices, such as mobile phones, digital music players, and handheld Internet access devices. n With the help of GPS and new technological tools, retailers can detect the active mobile devices in their stores and transmit location-specific promotions n Better store layouts based on the detected in-store traffic.
mobile marketing n the two-way or multi-way communication and promotion of an offer between a firm and its customers using a mobile devices, such as mobile phones, digital music players, and handheld Internet access devices. n With the help of GPS and new technological tools, retailers can detect the active mobile devices in their stores and transmit location-specific promotions n Better store layouts based on the detected in-store traffic.
 Top digital activitiy by store type
Top digital activitiy by store type
 digital retailing Virtual product demonstrations n Highly designated fitting rooms n Name on fitting room door n In-room camera with 360 degree views n Virtual models (jcpenney. com) (http: //www. dailydooh. com/archives/30991) n Fit guides and comparisons (pants@gap. com) n Mobile checkout n Electronic receipt n QR code ordering n
digital retailing Virtual product demonstrations n Highly designated fitting rooms n Name on fitting room door n In-room camera with 360 degree views n Virtual models (jcpenney. com) (http: //www. dailydooh. com/archives/30991) n Fit guides and comparisons (pants@gap. com) n Mobile checkout n Electronic receipt n QR code ordering n
 Future of retailing RFID n n n automated transaction without the cost of checkout. permanent security tag for the product. It can also be a web address for any product information; a virtual label, assembly instructions, reviews, repair, replacement, recycling, etc. ¨ in July 2003, Wal-Mart asked its top 100 suppliers to be RFID compliant by January, 2005. ¨ To make themselves RFID compliant, the suppliers needed to incur an estimated $20 Million.
Future of retailing RFID n n n automated transaction without the cost of checkout. permanent security tag for the product. It can also be a web address for any product information; a virtual label, assembly instructions, reviews, repair, replacement, recycling, etc. ¨ in July 2003, Wal-Mart asked its top 100 suppliers to be RFID compliant by January, 2005. ¨ To make themselves RFID compliant, the suppliers needed to incur an estimated $20 Million.
 Future of retailing 3 D Printing n Additive Manufacturing, is a technique in which products are built layer-by-layer. n If 3 D printers are networked to consumers and to a database of design specifications, this would open a number of possibilities: ¨ Product development and prototyping ---changing the lead time for product development and speed to market zero inventory. ¨ Customization to order and personalization: Garments could be manufactured to the exact fit or the stored fit for a consumer.
Future of retailing 3 D Printing n Additive Manufacturing, is a technique in which products are built layer-by-layer. n If 3 D printers are networked to consumers and to a database of design specifications, this would open a number of possibilities: ¨ Product development and prototyping ---changing the lead time for product development and speed to market zero inventory. ¨ Customization to order and personalization: Garments could be manufactured to the exact fit or the stored fit for a consumer.
 n http: //www. mmaglobal. com/case-studyhub/case_studies/view/27155
n http: //www. mmaglobal. com/case-studyhub/case_studies/view/27155
 Evoque m-marketing campaign results n With APP (working with Apple’s gyroscope, accelerometer, compass, and GPS features) customers are transported inside the car, with a 360 -degree view of the interior. n locating the nearest retailer, opting in for more information about the car, or customizing their very own Evoque. Results n Users averaged 77. 5 seconds on the i. Phone i. Ad, beating the industry average of 60 seconds. n Consumers spent an average of 80. 1 seconds on the i. Pad, compared to the industry average of 60 seconds. n 0. 59 percent tap-through rate, compared to industry 0. 50 percent standard. n Views per visit reached 8. 10, compared to average of 3.
Evoque m-marketing campaign results n With APP (working with Apple’s gyroscope, accelerometer, compass, and GPS features) customers are transported inside the car, with a 360 -degree view of the interior. n locating the nearest retailer, opting in for more information about the car, or customizing their very own Evoque. Results n Users averaged 77. 5 seconds on the i. Phone i. Ad, beating the industry average of 60 seconds. n Consumers spent an average of 80. 1 seconds on the i. Pad, compared to the industry average of 60 seconds. n 0. 59 percent tap-through rate, compared to industry 0. 50 percent standard. n Views per visit reached 8. 10, compared to average of 3.
 Social network effect on retailing n ‘the use of social technologies to connect, listen, understand, and engage to improve the shopping experience’ n Facebook, Twitter, . . . Like button-Foursquare n socially powered applications ¨ the Kraft i. Food Assistant offers recipes, shopping lists and Community support and feedback. n Social networks are sending an increasing amount of traffic to retailers (up 13% in 2010) such that 9. 1 per cent of visits to eshopping sites now come from social media.
Social network effect on retailing n ‘the use of social technologies to connect, listen, understand, and engage to improve the shopping experience’ n Facebook, Twitter, . . . Like button-Foursquare n socially powered applications ¨ the Kraft i. Food Assistant offers recipes, shopping lists and Community support and feedback. n Social networks are sending an increasing amount of traffic to retailers (up 13% in 2010) such that 9. 1 per cent of visits to eshopping sites now come from social media.


