RETAIL STRATEGIES ppt.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 RETAIL MARKETING STRATEGY Dr. RAMKI
RETAIL MARKETING STRATEGY Dr. RAMKI
 Retail Marketing Strategy Target Market and Retail Format Building a Sustainable Competitive Advantage Growth Strategies Strategic Retail Planning Process TESCO Case Study
Retail Marketing Strategy Target Market and Retail Format Building a Sustainable Competitive Advantage Growth Strategies Strategic Retail Planning Process TESCO Case Study

 Introduction To Retail Strategy Strategies can build a business. Strategies can also kill a business. The word strategy is derived from Greek word ‘Strategos’ which means ‘General’. A successful implementation of strategy can turn a retailer into the world’s largest company, for example, Wal-Mart. Planning strategies provide a road map for retail organisations. Strategies can also play a major role in times of uncertainty (unexpected developments on business horizon).
Introduction To Retail Strategy Strategies can build a business. Strategies can also kill a business. The word strategy is derived from Greek word ‘Strategos’ which means ‘General’. A successful implementation of strategy can turn a retailer into the world’s largest company, for example, Wal-Mart. Planning strategies provide a road map for retail organisations. Strategies can also play a major role in times of uncertainty (unexpected developments on business horizon).
 Introduction To Retail Strategy Effective strategies can guide the retail businesses in deploying funds creatively and optimally. The retail business is a people-centric business where competition between rival retailers occurs at the store level. In order to succeed, retailers should have a strong back-end support of SCM. Retaining customers and also making them shop more would be the challenge in the current scenario. Retail marketing strategies will address the issues mentioned above and provide a path for retailers to succeed in the changing dynamics of retailing today.
Introduction To Retail Strategy Effective strategies can guide the retail businesses in deploying funds creatively and optimally. The retail business is a people-centric business where competition between rival retailers occurs at the store level. In order to succeed, retailers should have a strong back-end support of SCM. Retaining customers and also making them shop more would be the challenge in the current scenario. Retail marketing strategies will address the issues mentioned above and provide a path for retailers to succeed in the changing dynamics of retailing today.
 Definition of Strategy Retail strategy comprises the competitive moves and business approaches that managers employ to attract and please customers. It also includes conducting the retail operations to grow the business successfully so as to achieve the targeted objectives. - Dr. Ramki
Definition of Strategy Retail strategy comprises the competitive moves and business approaches that managers employ to attract and please customers. It also includes conducting the retail operations to grow the business successfully so as to achieve the targeted objectives. - Dr. Ramki
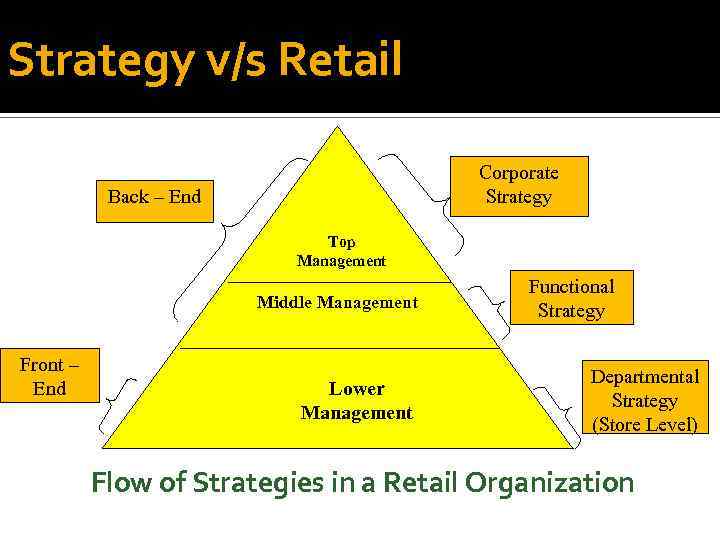 Strategy v/s Retail Corporate Strategy Back – End Top Management Middle Management Front – End Lower Management Functional Strategy Departmental Strategy (Store Level) Flow of Strategies in a Retail Organization
Strategy v/s Retail Corporate Strategy Back – End Top Management Middle Management Front – End Lower Management Functional Strategy Departmental Strategy (Store Level) Flow of Strategies in a Retail Organization
 Importance of Strategies in Retailing Cut Throat Competition. Differentiation. Dynamic Changes in the Environment. Changing Customer’s Needs and Consumption Basket. Identifying Future Trends. Helps in Store Positioning.
Importance of Strategies in Retailing Cut Throat Competition. Differentiation. Dynamic Changes in the Environment. Changing Customer’s Needs and Consumption Basket. Identifying Future Trends. Helps in Store Positioning.
 Growth Strategies Multiple Formats for addressing different segments of people.
Growth Strategies Multiple Formats for addressing different segments of people.
 Growth Strategies Scaling up & Modernization of Stores
Growth Strategies Scaling up & Modernization of Stores
 Growth Strategies Entrant New Market & New Segment For Example: Rural Retail – Aadhar ( Future Group)
Growth Strategies Entrant New Market & New Segment For Example: Rural Retail – Aadhar ( Future Group)
 Growth Strategies Adopt IT in Retail – SAP, Oracle Retail for Back – End Operations.
Growth Strategies Adopt IT in Retail – SAP, Oracle Retail for Back – End Operations.
 Growth Strategies Effective CRM implementation For ex—Nordstrom, Shopper Stop 1 st citizen club, CCD
Growth Strategies Effective CRM implementation For ex—Nordstrom, Shopper Stop 1 st citizen club, CCD
 Strategic Retail Planning Process Study the Retail Environment Conduct Retail Research Analyse Consumer Behaviour Study Segmentation, Targeting & Positioning Conduct Locational Analysis Select Store Format & Layout Decide Merchandise & Category Mix Decide Pricing Strategy Plan Back End Operations (SCM) Plan Visual Merchandising & Store Ambience Plan In-Store Marketing & Out-of-Store Marketing Implement Retail Strategy
Strategic Retail Planning Process Study the Retail Environment Conduct Retail Research Analyse Consumer Behaviour Study Segmentation, Targeting & Positioning Conduct Locational Analysis Select Store Format & Layout Decide Merchandise & Category Mix Decide Pricing Strategy Plan Back End Operations (SCM) Plan Visual Merchandising & Store Ambience Plan In-Store Marketing & Out-of-Store Marketing Implement Retail Strategy
 Future Of Retail Strategies Automation of process to ensure more trained manpower. Online Retailing. Shift from shopping to ‘SHOPTAINMENT’. Art of Survival
Future Of Retail Strategies Automation of process to ensure more trained manpower. Online Retailing. Shift from shopping to ‘SHOPTAINMENT’. Art of Survival
 Case Study Jack Cohen founded Tesco in 1919 using his bonus from his services in the army during World War I. In 1924, Cohen bought a tea shipment from TE Stockwell. The first three letters of TE Stock. Well and the first two letters of Cohen were used to make up the name ‘TESCO’ The first Tesco Store opened in 1929 in Edgware, North London. By 24 th February 2007, the UK-based retailer Tesco PLC was one of the largest retailers in the world
Case Study Jack Cohen founded Tesco in 1919 using his bonus from his services in the army during World War I. In 1924, Cohen bought a tea shipment from TE Stockwell. The first three letters of TE Stock. Well and the first two letters of Cohen were used to make up the name ‘TESCO’ The first Tesco Store opened in 1929 in Edgware, North London. By 24 th February 2007, the UK-based retailer Tesco PLC was one of the largest retailers in the world
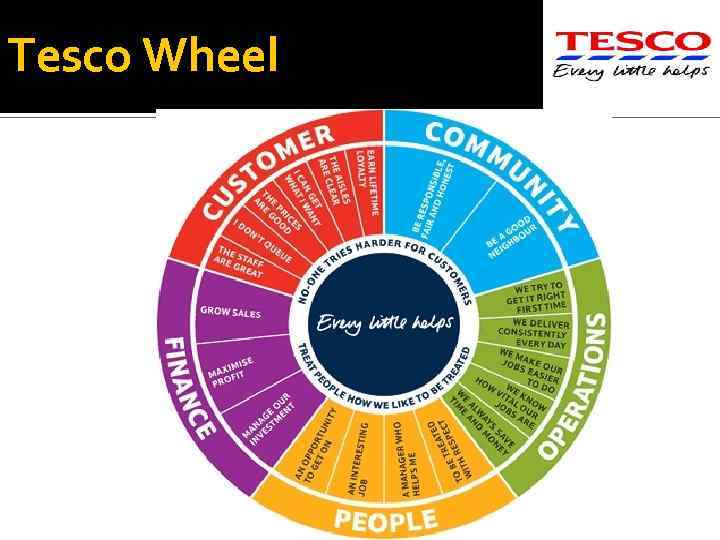
 Case Study In 1997, Terry Leahy, who was the Deputy Managing Director took over as CEO. His aim was to make Tesco a ‘Value Retailer’, by creating value for the customers and earning their lifetime loyalty. Leahy called this strategy the ‘Tesco Way’ The Tesco Way comprised of core purpose, values, principles, goals and the BALANCED SCORE CARD APPROACH, which was called the ‘Steering Wheel’ at Tesco. This system literally steers the business and the people. The Steering Wheel was a management tool that directed the focus of business initiatives on delivering the core purpose of Tesco.
Case Study In 1997, Terry Leahy, who was the Deputy Managing Director took over as CEO. His aim was to make Tesco a ‘Value Retailer’, by creating value for the customers and earning their lifetime loyalty. Leahy called this strategy the ‘Tesco Way’ The Tesco Way comprised of core purpose, values, principles, goals and the BALANCED SCORE CARD APPROACH, which was called the ‘Steering Wheel’ at Tesco. This system literally steers the business and the people. The Steering Wheel was a management tool that directed the focus of business initiatives on delivering the core purpose of Tesco.
 Tesco Wheel
Tesco Wheel
 Case Study The steering wheel approach guides Tesco to manage the running of daily activities while allow it to meet changing customer demands. The ‘Steering Wheel’ has four quadrants, namely OPERATIONS, PEOPLE, CUSTOMERS and FINANCE. Forming the focal point of the steering wheel were the two values that guide Tesco: ‘No one tries harder for the customers’ and ‘Treat people how we like to be treated’.
Case Study The steering wheel approach guides Tesco to manage the running of daily activities while allow it to meet changing customer demands. The ‘Steering Wheel’ has four quadrants, namely OPERATIONS, PEOPLE, CUSTOMERS and FINANCE. Forming the focal point of the steering wheel were the two values that guide Tesco: ‘No one tries harder for the customers’ and ‘Treat people how we like to be treated’.
 Case Study Each of these quadrants were divided into different segments. For e. g. The People Quadrant covered issues like Recruitment Development Of Employees Maintaining High Morale Retention Levels
Case Study Each of these quadrants were divided into different segments. For e. g. The People Quadrant covered issues like Recruitment Development Of Employees Maintaining High Morale Retention Levels
 Case Study The progress of the priorities were monitored by the Key Performance Indicators (KPI). KPI’s were used to channel Tesco’s resources around its people, customers, operations and finance. The steering wheel approach helped Tesco to communicate its strategy to all the levels of the organization in order to align its goals. The overall company performance at the highest level was managed using the ‘Corporate Steering Wheel’ strategy with specific deliverables.
Case Study The progress of the priorities were monitored by the Key Performance Indicators (KPI). KPI’s were used to channel Tesco’s resources around its people, customers, operations and finance. The steering wheel approach helped Tesco to communicate its strategy to all the levels of the organization in order to align its goals. The overall company performance at the highest level was managed using the ‘Corporate Steering Wheel’ strategy with specific deliverables.
 Case Study The steering wheel was prominently displayed in all the stores, corporate office and the departments. All the stores conducted a meeting every week called the ‘Steering Wheel’ meeting, which reviewed the store performance. The Steering Wheel was used to measure the operational efficiency, customer service, satisfaction of the employees and financial parameters of the Tesco stores. Earlier corporate social responsibility (CSR) was a part of operations, but by putting it in a separate quadrant
Case Study The steering wheel was prominently displayed in all the stores, corporate office and the departments. All the stores conducted a meeting every week called the ‘Steering Wheel’ meeting, which reviewed the store performance. The Steering Wheel was used to measure the operational efficiency, customer service, satisfaction of the employees and financial parameters of the Tesco stores. Earlier corporate social responsibility (CSR) was a part of operations, but by putting it in a separate quadrant
 Steering Tesco Ahead
Steering Tesco Ahead


