 Resuscitation Teaching Day
Resuscitation Teaching Day
 Documentation • • • Experience looking through notes at C 15 - Nil written - No diagnosis/differential/plan - Chest pain with no ECG - Names, Dates, Triage Not written = Not done
Documentation • • • Experience looking through notes at C 15 - Nil written - No diagnosis/differential/plan - Chest pain with no ECG - Names, Dates, Triage Not written = Not done
 Why Write Anything? • • PRIDE in work despite environment Crunching Numbers Quality Care Acceptable Management Follow up of patient Front page of newspapers! Litigation
Why Write Anything? • • PRIDE in work despite environment Crunching Numbers Quality Care Acceptable Management Follow up of patient Front page of newspapers! Litigation
 What is our job? • • Employed to treat patients. No-one can be turned away by us. Walk-ins: Hx/Assess/Triage/Document Ambulance: Assess/Triage/Document Then may divert patient Report problems after the fact Adverse incident reports to HOD
What is our job? • • Employed to treat patients. No-one can be turned away by us. Walk-ins: Hx/Assess/Triage/Document Ambulance: Assess/Triage/Document Then may divert patient Report problems after the fact Adverse incident reports to HOD
 Reassessment • • After seeing patient, need to go back: Reassess 30 min-2 hrs - Observations - Triage - Treatment: Ab/Analgesia and effect - Ix: U dipstix/CXR/Serial ECGs - Referral or D/C or Handover
Reassessment • • After seeing patient, need to go back: Reassess 30 min-2 hrs - Observations - Triage - Treatment: Ab/Analgesia and effect - Ix: U dipstix/CXR/Serial ECGs - Referral or D/C or Handover
 Chain of Information • • • History is essential for our diagnosis Ambulance often only source Who can read Drs writing? Take on arrival and give on transfer De: Demographics M: Mechanism I: Injuries S: Signs (Obs) T: Treatment
Chain of Information • • • History is essential for our diagnosis Ambulance often only source Who can read Drs writing? Take on arrival and give on transfer De: Demographics M: Mechanism I: Injuries S: Signs (Obs) T: Treatment
 Post Cardiac Arrest Syndrome • Post. Cardiac Arrest Syndrome: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Treatment, and Prognostication A Consensus Statement From the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation • Circulation 2008; 118; 2452 -2483
Post Cardiac Arrest Syndrome • Post. Cardiac Arrest Syndrome: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Treatment, and Prognostication A Consensus Statement From the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation • Circulation 2008; 118; 2452 -2483
 Post Cardiac Arrest Syndrome • Poor prognosis: • Mortality 50 -80% • Optimization of Care • ROSC after Cardiac Arrest
Post Cardiac Arrest Syndrome • Poor prognosis: • Mortality 50 -80% • Optimization of Care • ROSC after Cardiac Arrest
 What is it? • 1. Brain injury • 2. Myocardial Dysfunction • 3. Systemic ischemia/reperfusion • 4. Underlying pathological cause
What is it? • 1. Brain injury • 2. Myocardial Dysfunction • 3. Systemic ischemia/reperfusion • 4. Underlying pathological cause
 Prognostication • • Difficult Need 72 hours at least Use of resources False hope for family
Prognostication • • Difficult Need 72 hours at least Use of resources False hope for family
 Therapeutic Strategies • • - Monitoring: ICU - EGDT: Optimize O 2 delivery (? Targets) - Oxygenation: Sats 94 -96% - Normocarbia - Lung Protective Ventilation - Manage Dysrythmias (elecs normal etc) - Hypotension: IVF then Inotropes (Echo) - Mechanical support: IABP
Therapeutic Strategies • • - Monitoring: ICU - EGDT: Optimize O 2 delivery (? Targets) - Oxygenation: Sats 94 -96% - Normocarbia - Lung Protective Ventilation - Manage Dysrythmias (elecs normal etc) - Hypotension: IVF then Inotropes (Echo) - Mechanical support: IABP
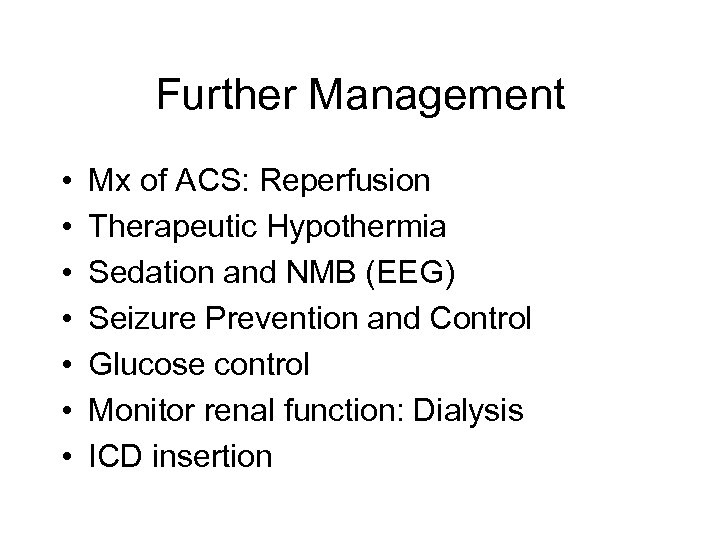 Further Management • • Mx of ACS: Reperfusion Therapeutic Hypothermia Sedation and NMB (EEG) Seizure Prevention and Control Glucose control Monitor renal function: Dialysis ICD insertion
Further Management • • Mx of ACS: Reperfusion Therapeutic Hypothermia Sedation and NMB (EEG) Seizure Prevention and Control Glucose control Monitor renal function: Dialysis ICD insertion
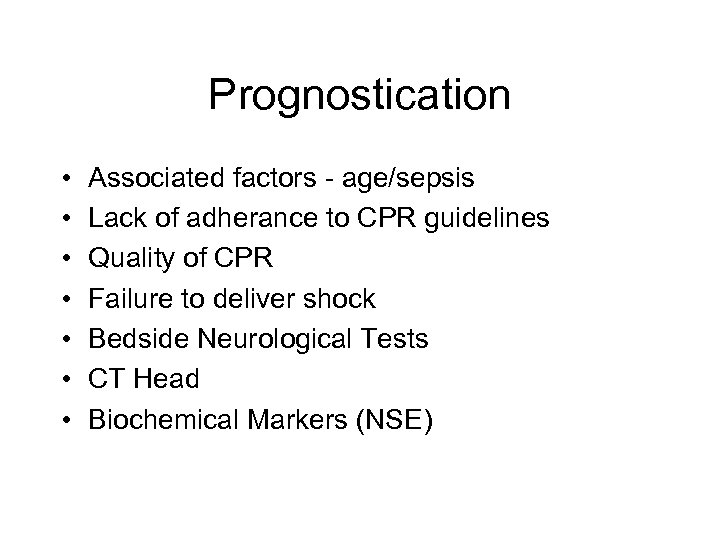 Prognostication • • Associated factors - age/sepsis Lack of adherance to CPR guidelines Quality of CPR Failure to deliver shock Bedside Neurological Tests CT Head Biochemical Markers (NSE)
Prognostication • • Associated factors - age/sepsis Lack of adherance to CPR guidelines Quality of CPR Failure to deliver shock Bedside Neurological Tests CT Head Biochemical Markers (NSE)