874970ac2d39130ba963f9d2ac791229.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10

Results-Based Management (RBM) terminology and definitions Bruce Gracie International Telecommunication Union

Results Based Management (source ADB) § Results Based Management (RBM) can mean different things to different people. (Asian Development Bank) § Definition: RBM is the way an organization applies processes and resources to achieve targeted results. Results refer to outcomes that convey a benefit or positive ‘result’ Results also encompass the service outputs that make those outcomes possible Results can also refer to internal outputs such as services provided by one part of the organization for use by another. § § The key issue is that results differ from ‘activities’ or ‘functions’. (i. e. result – well organized WTDC; activity – travel to India to review facilities) § Many people when asked what they produce (services) describe what they do (activities).

RBM dimensions (ADB) § RBM encompasses four dimensions, namely: § specified results that are measurable, monitorable and relevant § resources that are adequate for achieving the targeted results § organizational arrangements which ensure that authority and responsibility are aligned with results and resources § processes for planning, monitoring, communicating and releasing resources that enable the organization to convert resources into the desired results.
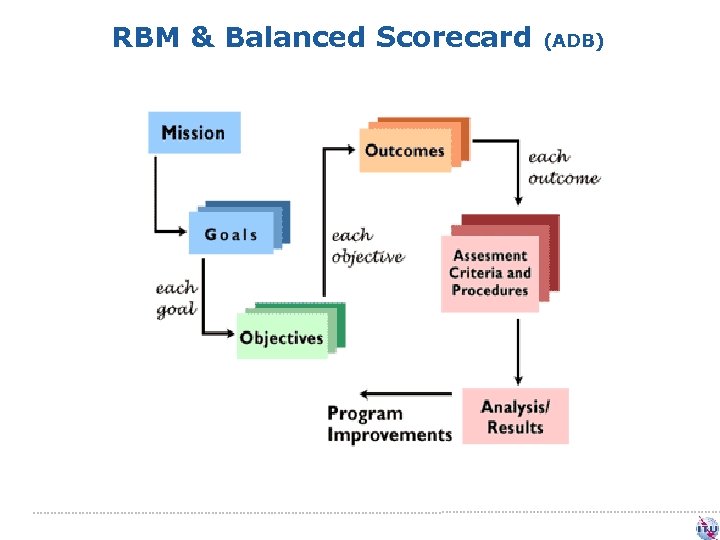
RBM & Balanced Scorecard (ADB)
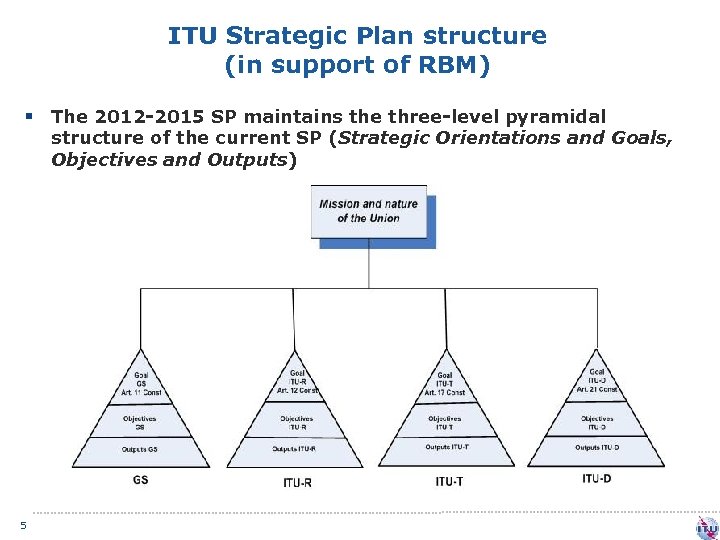
ITU Strategic Plan structure (in support of RBM) § The 2012 -2015 SP maintains the three-level pyramidal structure of the current SP (Strategic Orientations and Goals, Objectives and Outputs) 5

Goals – ITU definition (Note: all definitions presented are from ITU Budget document) Goals refer to the Union’s high-level targets to which the objectives of the Sectors and the ITU General Secretariat contribute, directly or indirectly Examples BDT – Work in co-operation with governments and industry to expand benefits of information society to developing countries. . . GS – Effectiveness and efficiency in the planning, management, coordination and delivery of services to support the Union and its Membership. . .

Objective - – ITU definition Objectives refer to the specific purposes and aims of individual Sectors and of the ITU General Secretariat. Examples BDT: Obj’tive 1 – Coordinating / International Cooperation GS: Obj’tive 1: Efficient planning, coordination and execution of the corporate, strategic, external relations, communications and inter-sectoral activities of the Union.

Outputs – ITU definition Outputs refer to the final products or services delivered by the ITU (e. g. deliverables of a programme) Examples BDT: Objective 1 / Output 1 World Telecommunications Development Conference 2014 GS: Objective 1 / Output 1 Provision of inputs for (major) ITU events (generic) (In GS Operational Plan – for 2014: WTDC, PP-10, etc. )
KPI – ITU definition (abbreviated) Key performance indicators (KPIs) are the criteria used to measure the achievement of outputs. These indicators can be qualitative or quantitative. Examples Qualitative BDT – Obj. 1 / Outcome 1 – Survey results of satisfaction of participants with the organization of the WTDC Quantitative GS – Obj. 1 / Outcome 1 – All documents translated and issued by the due date for the WTDC

Linking financial and strategic planning Roles of major meetings (groups) PP - Strategic Plan Sets the strategic framework, (Goals, Objectives, Outputs) relative spending targets, interprets BI into work plans Council – Budget (Results-based) Allocates actual resources by objective, monitors progress (using KPIs) and reallocates resources to maximize results Sector Assemblies / Conferences – Action Plans Establish Sector Action Plans and prioritize the objectives Advisory Groups Monitor and advise on progress against AP 10
874970ac2d39130ba963f9d2ac791229.ppt