Дыхательная система.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

Respiratory system DR. RAIGORODETSKYI MICHAEL ANECTHESIOLOGY DEPARTMENT BNAI-ZION MEDICAL CENTER

Respiratory Function ► Exchange of gases ► Regulation of body p. H ► Protection § Inhaled pathogens § Irritating substances ► Vocalization

Respiration ► Breathing ► External respiration ► Gas transport by blood ► Internal respiration

Respiratory System ► Conducting system § Airways ► Gas exchange surface § Alveoli ► Ventilatory assistance § Bones and muscle

Airways ► Air pathway § Mouth, nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchioles Respiratory bronchioles Alveoli ► Alveoli § Site of gas exchange § Single layer of thin exchange epithelium
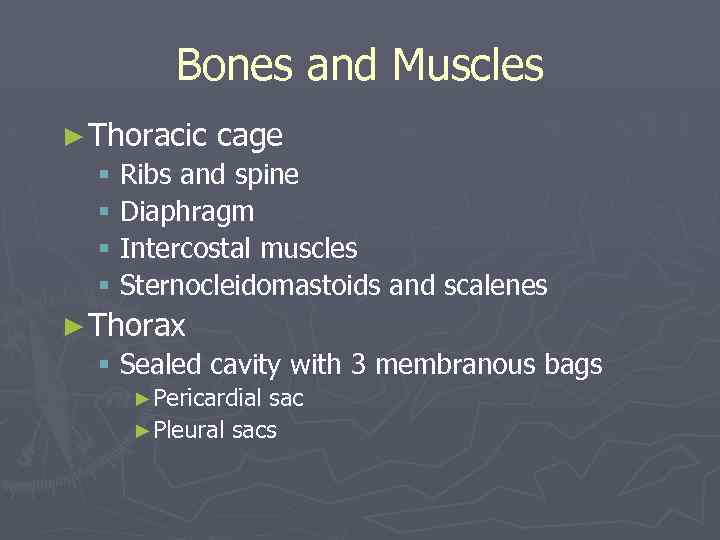
Bones and Muscles ► Thoracic cage § Ribs and spine § Diaphragm § Intercostal muscles § Sternocleidomastoids and scalenes ► Thorax § Sealed cavity with 3 membranous bags ►Pericardial sac ►Pleural sacs
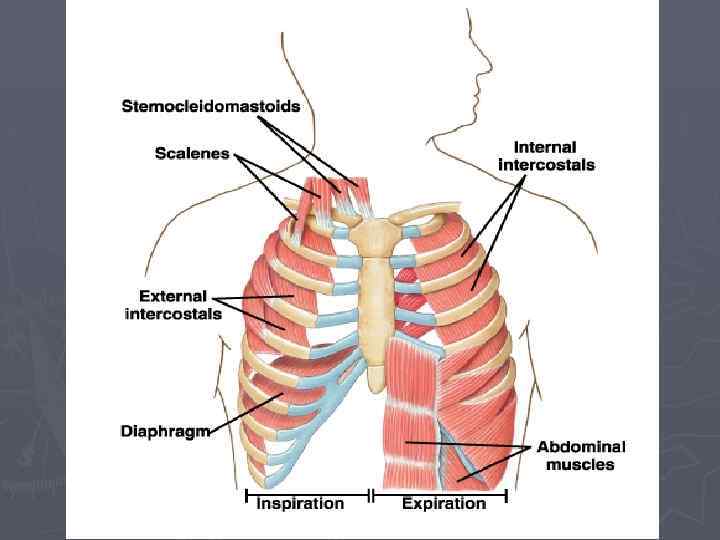

Breathing ► Inspiration: § Contraction of diaphragm / intercostal muscles § Expansion of thorax expansion of lungs § Pressure in lungs ↓ § Air inflow ► Expiration: § Relaxation of muscles § Thorax / lung recoil back § Pressure in lungs ↑ § Air outflow
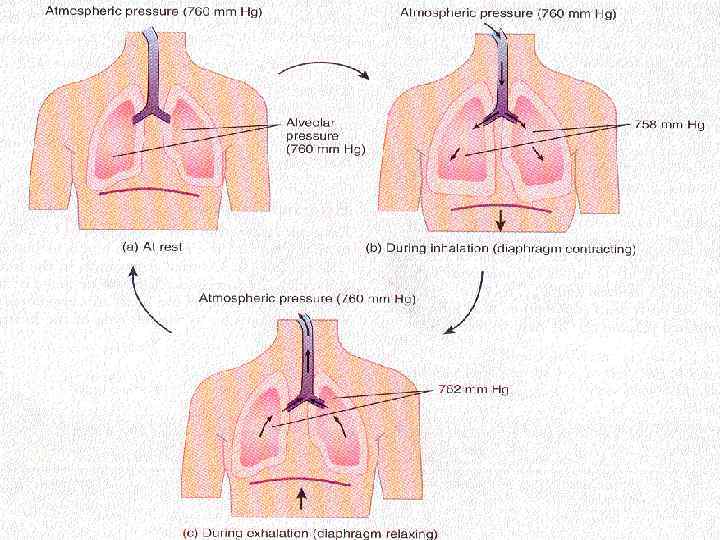

Forceful breathing ► Inspiration: § Contraction of accessory muscles extra expansion of thorax extra air inflow ► Expiration: § Contraction abdominal muscles abdominal contents move up diaphragm moves up § Abdominal muscles retract rib cage § Internal intercostal muscles retract rib cage
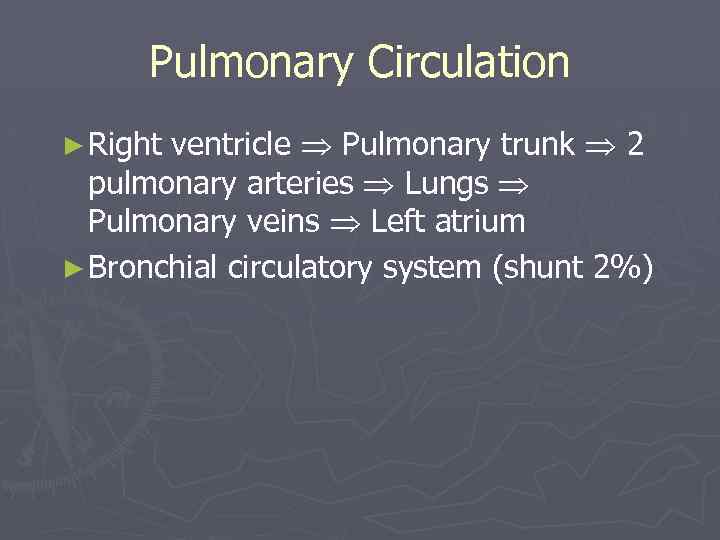
Pulmonary Circulation ventricle Pulmonary trunk 2 pulmonary arteries Lungs Pulmonary veins Left atrium ► Bronchial circulatory system (shunt 2%) ► Right
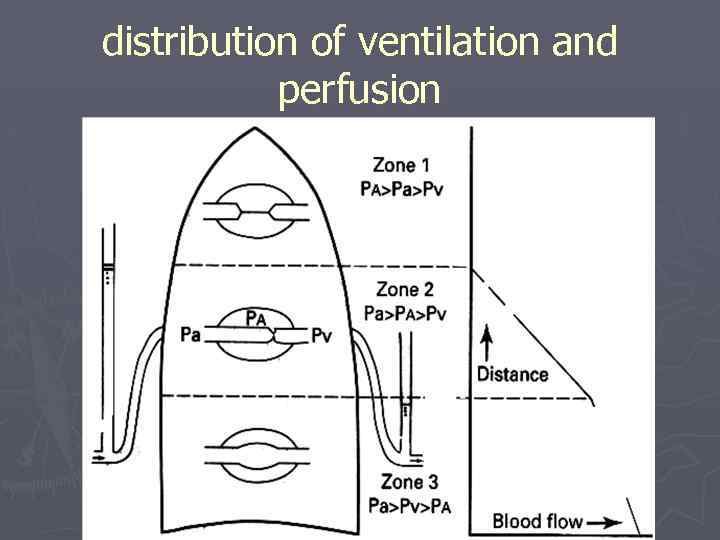
distribution of ventilation and perfusion

Innervation Parasympathetic - constrict bronchioles Sympathetic -dilates bronchioles
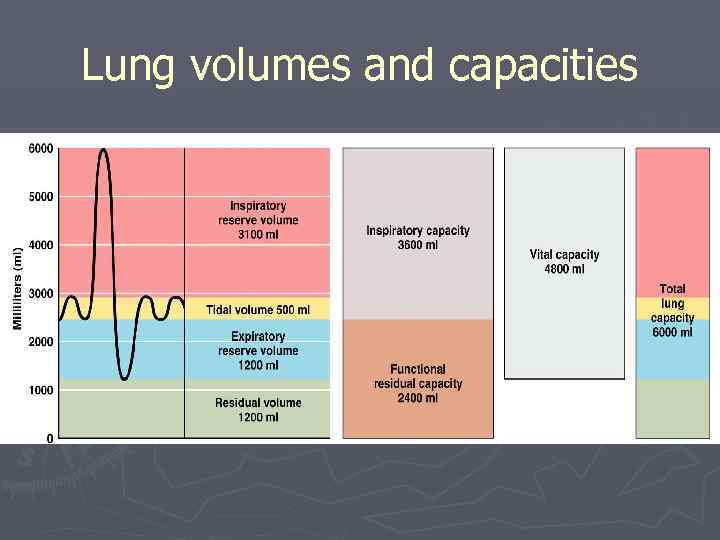
Lung volumes and capacities

Airway Resistance ► Airway diameter § Decrease diameter, increase resistance § Bronchiole diameter adjustable ►Controls ► Control resistance of bronchoconstriction § CO 2 § Histamine § Parasympathetic neurons § Beta-2 adrenergic receptors
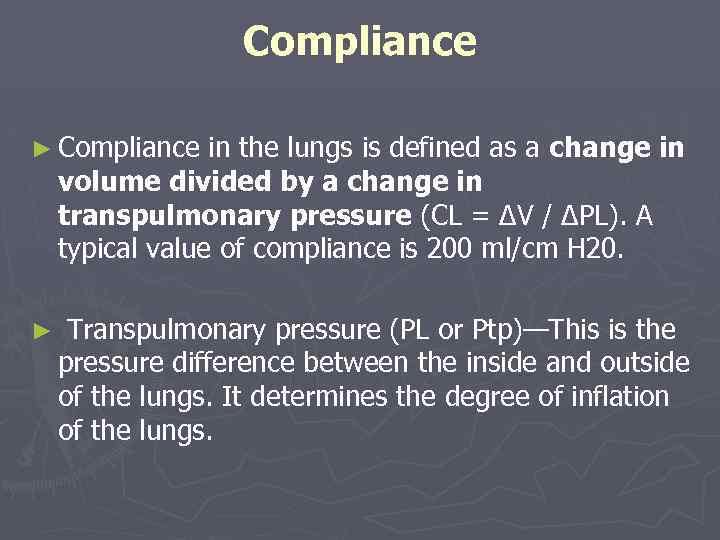
Compliance ► Compliance in the lungs is defined as a change in volume divided by a change in transpulmonary pressure (CL = ΔV / ΔPL). A typical value of compliance is 200 ml/cm H 20. ► Transpulmonary pressure (PL or Ptp)—This is the pressure difference between the inside and outside of the lungs. It determines the degree of inflation of the lungs.

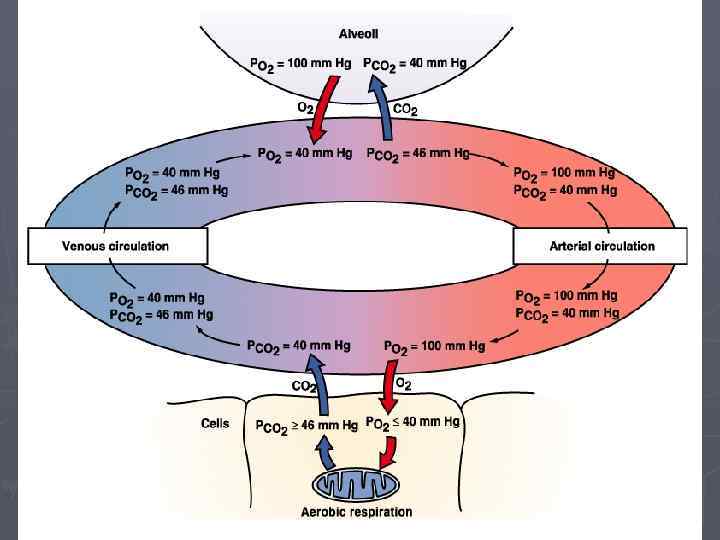
Gas Exchange ► Exchange of O 2 and CO 2 between alveolar air and blood occurs via passive diffusion ► Governed by § Dalton’s Law § Total pressure is the sum of individual gas pressures § Partial pressure § Henry’s Law ► when a mixture of gases is in contact with a liquid, each gas will dissolve in the liquid in proportion to its partial pressure gradient § Solubility of CO 2 greater than O 2 (24 x)

Gas Exchange ► Simple diffusion ► Rate of diffusion § Partial pressure gradient ►Higher to lower pressure § Surface area § Thickness of membrane ►Inversely proportional to distance

Movement of Gas into a Liquid ► Dependent on: § Pressure ►Moves from higher to lower § Solubility ►More soluble, less pressure required § Temperature
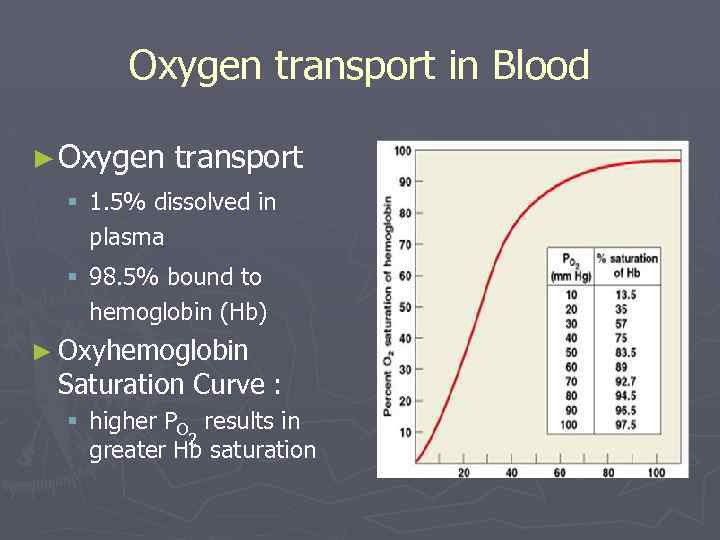
Oxygen transport in Blood ► Oxygen transport § 1. 5% dissolved in plasma § 98. 5% bound to hemoglobin (Hb) ► Oxyhemoglobin Saturation Curve : § higher PO results in 2 greater Hb saturation

oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve ► right shift - Decreased Affinity, more O 2 unloaded ► left shift- Increased Affinity, less O 2 unloaded
Effects of Temperature ► HIGHER Temperature --> Decreased Affinity (right) ► 2. LOWER Temperature --> Increased Affinity (left)
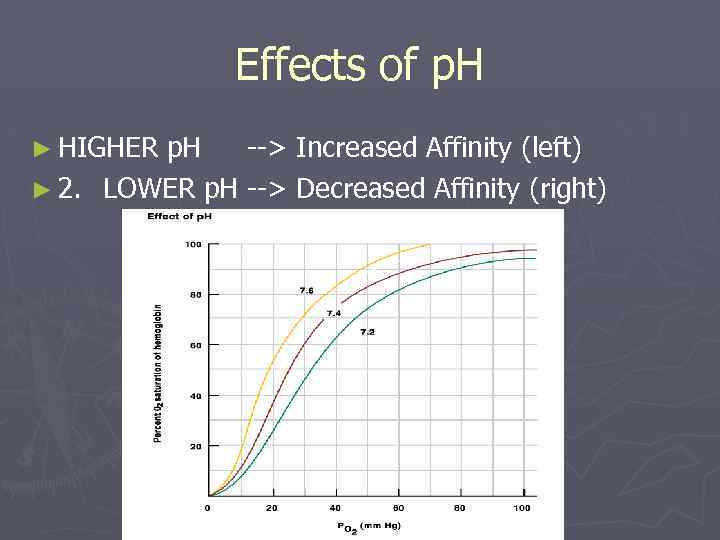
Effects of p. H ► HIGHER p. H --> Increased Affinity (left) ► 2. LOWER p. H --> Decreased Affinity (right)

Effects of Diphosphoglycerate (DPG) ► DPG - produced by anaerobic processes in RBCs ► 2. HIGHER DPG > Decreased Affinity (right) ► 3. thyroxine, testosterone, epinephrine, increase RBC metabolism and DPG production, cause RIGHT shift

Carbondioxide transport ► 7 -10 % dissolved in plasma ► 22 % bound to Hb ► 70 % transported as HCO 3 CO 2 + H 2 O H 2 CO 3 H+ + HCO 3 -
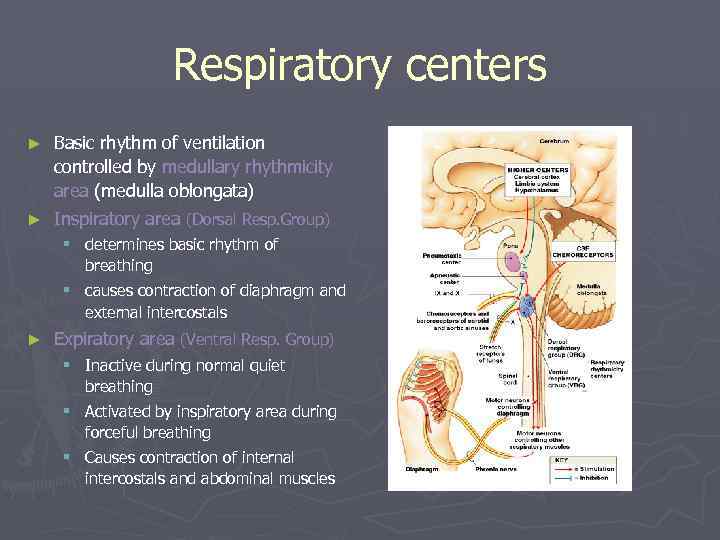
Respiratory centers ► Basic rhythm of ventilation controlled by medullary rhythmicity area (medulla oblongata) ► Inspiratory area (Dorsal Resp. Group) § determines basic rhythm of breathing § causes contraction of diaphragm and external intercostals ► Expiratory area (Ventral Resp. Group) § Inactive during normal quiet breathing § Activated by inspiratory area during forceful breathing § Causes contraction of internal intercostals and abdominal muscles
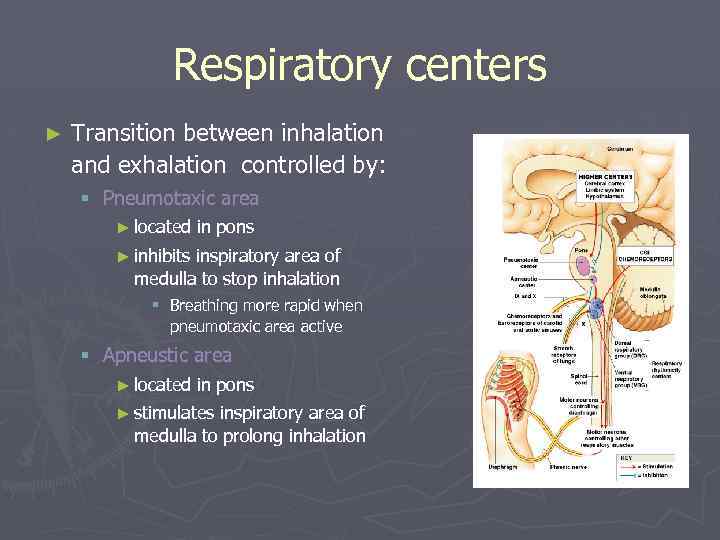
Respiratory centers ► Transition between inhalation and exhalation controlled by: § Pneumotaxic area ► located in pons ► inhibits inspiratory area of medulla to stop inhalation § Breathing more rapid when pneumotaxic area active § Apneustic area ► located in pons ► stimulates inspiratory area of medulla to prolong inhalation

Regulation of Respiratory centers ► Basic rhythm of ventilation coordinated by inspiratory area of respiratory centre, but modified by: § Cortical influences ► Voluntary control over breathing § Hypothalamus and limbic system ► Emotional stimuli § Proprioceptors ► Upper motor neurons of primary motor cortex also stimulate inspiratory area § Inflation (Hering-Breuer) reflex ► Stretch receptors in walls of bronchi and bronchioles § Inhibit inspiratory and apneustic areas ► causes exhalation to begin to protect against overinflation
Regulation of Respiratory centers ► Chemoreceptors: § Central (in medulla oblongata): responds to CO 2 ↑ ► CO 2 passes blood brain barrier ► CO 2 + H 2 O H 2 CO 3 H+ + HCO 3► H+ stimulates receptors breathing depth ↑ + rate ↑ § Peripheral (in aortic / carotid bodies): ► responds when O 2 < 60 mm Hg increase ventilation ► Responds to p. H ↓ increase ventilation
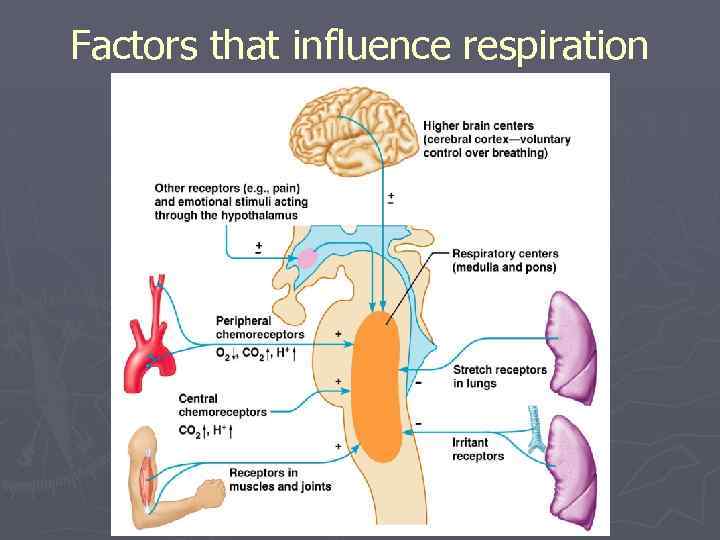
Factors that influence respiration
Дыхательная система.ppt