a837e6f771ff83231cb30021a1fb0fb2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Respecting the Consumer – the Data Protection Perspective Billy Hawkes Data Protection Commissioner Association of Advertisers in Ireland 3 June 2009
Respecting the Consumer – the Data Protection Perspective Billy Hawkes Data Protection Commissioner Association of Advertisers in Ireland 3 June 2009
 Presentation Outline • • Marketing – what do people think? Data Protection – what is it? Direct Marketing – the Rules Best Practice
Presentation Outline • • Marketing – what do people think? Data Protection – what is it? Direct Marketing – the Rules Best Practice
 Importance of key issues affecting the general public (2008) Very Important Ø Ø Ø A good health service * Crime prevention Privacy of personal information Protection of consumer rights Ethics in public office (new question in 2008) 89% 87% 84% 77%
Importance of key issues affecting the general public (2008) Very Important Ø Ø Ø A good health service * Crime prevention Privacy of personal information Protection of consumer rights Ethics in public office (new question in 2008) 89% 87% 84% 77%
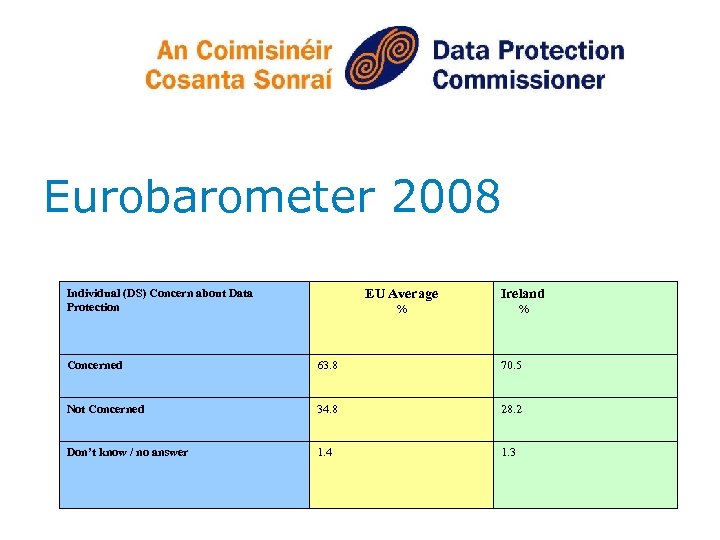 Eurobarometer 2008 Individual (DS) Concern about Data Protection EU Average Ireland % % Concerned 63. 8 70. 5 Not Concerned 34. 8 28. 2 Don’t know / no answer 1. 4 1. 3
Eurobarometer 2008 Individual (DS) Concern about Data Protection EU Average Ireland % % Concerned 63. 8 70. 5 Not Concerned 34. 8 28. 2 Don’t know / no answer 1. 4 1. 3
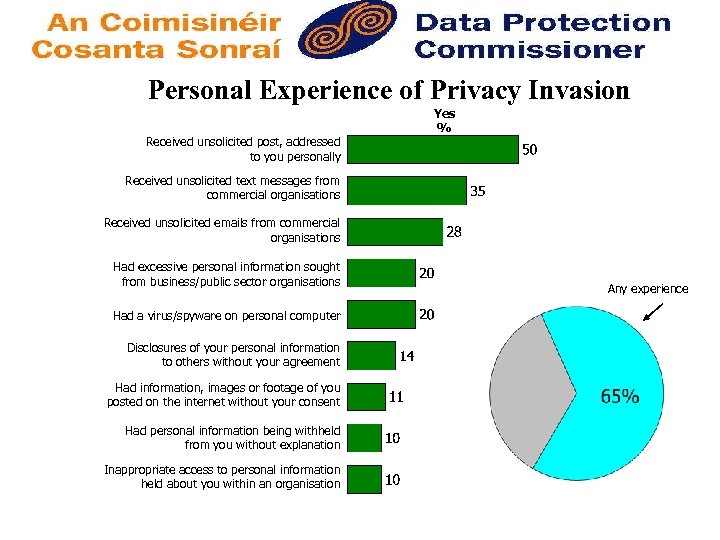 Personal Experience of Privacy Invasion Yes % Received unsolicited post, addressed to you personally Received unsolicited text messages from commercial organisations Received unsolicited emails from commercial organisations Had excessive personal information sought from business/public sector organisations Had a virus/spyware on personal computer Disclosures of your personal information to others without your agreement Had information, images or footage of you posted on the internet without your consent Had personal information being withheld from you without explanation Inappropriate access to personal information held about you within an organisation Any experience
Personal Experience of Privacy Invasion Yes % Received unsolicited post, addressed to you personally Received unsolicited text messages from commercial organisations Received unsolicited emails from commercial organisations Had excessive personal information sought from business/public sector organisations Had a virus/spyware on personal computer Disclosures of your personal information to others without your agreement Had information, images or footage of you posted on the internet without your consent Had personal information being withheld from you without explanation Inappropriate access to personal information held about you within an organisation Any experience
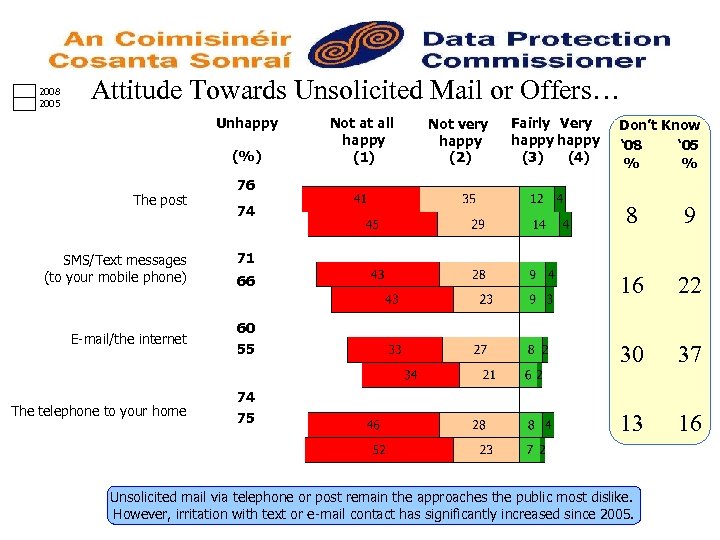 2008 2005 Attitude Towards Unsolicited Mail or Offers… Unhappy (%) The post SMS/Text messages (to your mobile phone) Not at all happy (1) Not very happy (2) Fairly Very happy (3) (4) Don’t Know ‘ 08 ‘ 05 % % 76 74 8 9 16 22 30 37 13 16 71 66 E-mail/the internet 60 55 The telephone to your home 74 75 Unsolicited mail via telephone or post remain the approaches the public most dislike. However, irritation with text or e-mail contact has significantly increased since 2005.
2008 2005 Attitude Towards Unsolicited Mail or Offers… Unhappy (%) The post SMS/Text messages (to your mobile phone) Not at all happy (1) Not very happy (2) Fairly Very happy (3) (4) Don’t Know ‘ 08 ‘ 05 % % 76 74 8 9 16 22 30 37 13 16 71 66 E-mail/the internet 60 55 The telephone to your home 74 75 Unsolicited mail via telephone or post remain the approaches the public most dislike. However, irritation with text or e-mail contact has significantly increased since 2005.
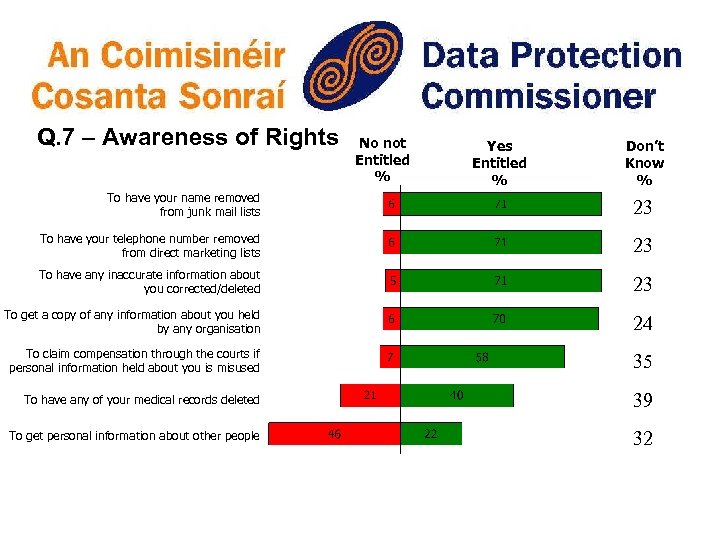 Q. 7 – Awareness of Rights No not Entitled % Yes Entitled % Don’t Know % To have your name removed from junk mail lists 23 To have your telephone number removed from direct marketing lists 23 To have any inaccurate information about you corrected/deleted 23 To get a copy of any information about you held by any organisation 24 To claim compensation through the courts if personal information held about you is misused 35 To have any of your medical records deleted 39 To get personal information about other people 32
Q. 7 – Awareness of Rights No not Entitled % Yes Entitled % Don’t Know % To have your name removed from junk mail lists 23 To have your telephone number removed from direct marketing lists 23 To have any inaccurate information about you corrected/deleted 23 To get a copy of any information about you held by any organisation 24 To claim compensation through the courts if personal information held about you is misused 35 To have any of your medical records deleted 39 To get personal information about other people 32
 Complaints to DPC 2008 • 1031 formal complaints • Many more enquiries dealt with informally TYPE Direct Marketing* Access Rights Disclosure Accuracy Other % 35 30 16 2 17 * Mainly electronic (SMS etc). Direct Marketing accounted for 57% of complaints in 2007
Complaints to DPC 2008 • 1031 formal complaints • Many more enquiries dealt with informally TYPE Direct Marketing* Access Rights Disclosure Accuracy Other % 35 30 16 2 17 * Mainly electronic (SMS etc). Direct Marketing accounted for 57% of complaints in 2007
 Unsolicited Marketing – DPC Annual Report Case Studies • Unsolicited Text Messages (12/2005; 5/2006 – deletion of database ordered) • Unsolicited Faxes (20/2008) • Unsolicited e-mails (8/2008; 17/2008 – database deleted and marketing suspended) • “Cold-Calling”/Failing to respect right to “optout” including via NDD (11/2005 (prosecution); 1/2006; 2/2006; 4/2007 – order to suspend marketing; 11/2008) • Postal Marketing (15/2007: supermarket)
Unsolicited Marketing – DPC Annual Report Case Studies • Unsolicited Text Messages (12/2005; 5/2006 – deletion of database ordered) • Unsolicited Faxes (20/2008) • Unsolicited e-mails (8/2008; 17/2008 – database deleted and marketing suspended) • “Cold-Calling”/Failing to respect right to “optout” including via NDD (11/2005 (prosecution); 1/2006; 2/2006; 4/2007 – order to suspend marketing; 11/2008) • Postal Marketing (15/2007: supermarket)
 Case Studies 2008 : Direct Marketing • • 123. 1 e (insurance) Interactive Voice Technologies Buy-as-you-Fly Celtic Water Solutions Matrix Internet Dell 2 Cases where we found in favour of DC
Case Studies 2008 : Direct Marketing • • 123. 1 e (insurance) Interactive Voice Technologies Buy-as-you-Fly Celtic Water Solutions Matrix Internet Dell 2 Cases where we found in favour of DC
 Presentation Outline • Marketing – what do people think? • Data Protection – what is it? • Direct Marketing – the Rules • Best Practice
Presentation Outline • Marketing – what do people think? • Data Protection – what is it? • Direct Marketing – the Rules • Best Practice
 Data Protection: a Human Right • Part of Right to Personal Privacy • Personal Privacy: necessary in a Democratic Society (but not absolute) • Un-enumerated right under Irish Constitution • Explicit right under European Convention on Human Rights: ECHR Act 2003
Data Protection: a Human Right • Part of Right to Personal Privacy • Personal Privacy: necessary in a Democratic Society (but not absolute) • Un-enumerated right under Irish Constitution • Explicit right under European Convention on Human Rights: ECHR Act 2003
 EU Charter of Fundamental Rights: Article 8 • • Protection of personal data 1. Everyone has the right to the protection of personal data concerning him or her. 2. Such data must be processed fairly for specified purposes and on the basis of the consent of the person concerned or some other legitimate basis laid down by law. Everyone has the right of access to data which has been collected concerning him or her, and the right to have it rectified. 3. Compliance with these rules shall be subject to control by an independent authority.
EU Charter of Fundamental Rights: Article 8 • • Protection of personal data 1. Everyone has the right to the protection of personal data concerning him or her. 2. Such data must be processed fairly for specified purposes and on the basis of the consent of the person concerned or some other legitimate basis laid down by law. Everyone has the right of access to data which has been collected concerning him or her, and the right to have it rectified. 3. Compliance with these rules shall be subject to control by an independent authority.
 Lisbon Treaty Article 16 Treaty on the Functioning of the Union • 1. Everyone has the right to the protection of personal data concerning them. • 2. The European Parliament and the Council, acting in accordance with the ordinary legislative procedure, shall lay down the rules relating to the protection of individuals with regard to the processing of personal data by Union institutions, bodies, offices and agencies, and by the Member States when carrying out activities which fall within the scope of Union law, and the rules relating to the free movement of such data. • Compliance with these rules shall be subject to the control of independent authorities.
Lisbon Treaty Article 16 Treaty on the Functioning of the Union • 1. Everyone has the right to the protection of personal data concerning them. • 2. The European Parliament and the Council, acting in accordance with the ordinary legislative procedure, shall lay down the rules relating to the protection of individuals with regard to the processing of personal data by Union institutions, bodies, offices and agencies, and by the Member States when carrying out activities which fall within the scope of Union law, and the rules relating to the free movement of such data. • Compliance with these rules shall be subject to the control of independent authorities.
 EU & Irish Legislation • Data Protection Directive 95/46/EC • Electronic Privacy Directive 2002/58/EC • EUROPOL etc • Data Protection Acts 1988 & 2003 • EC Electronic Privacy Regulations 2003 (SI 535/2003) and 2008 (SI 526/2008) • Corresponding Acts • Good Friday Agreement • Disability Act 2005
EU & Irish Legislation • Data Protection Directive 95/46/EC • Electronic Privacy Directive 2002/58/EC • EUROPOL etc • Data Protection Acts 1988 & 2003 • EC Electronic Privacy Regulations 2003 (SI 535/2003) and 2008 (SI 526/2008) • Corresponding Acts • Good Friday Agreement • Disability Act 2005
 Rights and Obligations • • Rights of “data subject” (= identifiable, living individual) to control the use of their “personal data” (very broad definition) Obligations on “data controllers” (“a person who controls the contents and use of personal data”) and “data processors” (“A person who processes personal data on behalf of a data controller”)
Rights and Obligations • • Rights of “data subject” (= identifiable, living individual) to control the use of their “personal data” (very broad definition) Obligations on “data controllers” (“a person who controls the contents and use of personal data”) and “data processors” (“A person who processes personal data on behalf of a data controller”)
 The Data Protection Rules 1. Fair obtaining & processing • Consent 2. Specified purpose 3. No disclosure • unless “compatible” 4. Safe and secure 5. 6. 7. 8. Accurate, up-to-date Relevant, not excessive Retention period Right of access
The Data Protection Rules 1. Fair obtaining & processing • Consent 2. Specified purpose 3. No disclosure • unless “compatible” 4. Safe and secure 5. 6. 7. 8. Accurate, up-to-date Relevant, not excessive Retention period Right of access
 Sensitive Data (special protection) • • Physical or mental health Racial origin Political opinions Religious or other beliefs Sexual life Criminal convictions Alleged commission of offence Trade Union membership
Sensitive Data (special protection) • • Physical or mental health Racial origin Political opinions Religious or other beliefs Sexual life Criminal convictions Alleged commission of offence Trade Union membership
 Rule 1 Obtain & Process Fairly I • Data controller must give full information about identity Ø purposes Ø disclosees Ø any other data necessary for “fairness” Ø • Third party data controllers must contact data subject to provide these details Ø must give name of original data controller Ø
Rule 1 Obtain & Process Fairly I • Data controller must give full information about identity Ø purposes Ø disclosees Ø any other data necessary for “fairness” Ø • Third party data controllers must contact data subject to provide these details Ø must give name of original data controller Ø
 Obtain & Process Fairly II One of these conditions required: Ø Consent Ø Legal obligation Ø Contract with individual Ø Necessary to protect vital interests Ø Necessary for a public function (Justice) Ø necessary for ‘legitimate interests’
Obtain & Process Fairly II One of these conditions required: Ø Consent Ø Legal obligation Ø Contract with individual Ø Necessary to protect vital interests Ø Necessary for a public function (Justice) Ø necessary for ‘legitimate interests’
 Processing Sensitive Data One of these additional conditions is required Ø Explicit consent Ø Necessary under employment law Ø To prevent injury or protect vital interests Ø Process the data of members/clients of nonprofit orgs. Ø Legal advice Ø For Medical Purposes Ø Statutory function
Processing Sensitive Data One of these additional conditions is required Ø Explicit consent Ø Necessary under employment law Ø To prevent injury or protect vital interests Ø Process the data of members/clients of nonprofit orgs. Ø Legal advice Ø For Medical Purposes Ø Statutory function
 Rule 2 Specified Purpose • Part of obligations when obtaining to specify purpose • Cannot expand purpose without reverting to individual
Rule 2 Specified Purpose • Part of obligations when obtaining to specify purpose • Cannot expand purpose without reverting to individual
 Rule 3 Disclose only if compatible • General rule – no disclosure for different purpose • Exceptions made, to balance other interests of society • Section 8 exceptions Ø Ø Ø Investigation of crime Collection of taxes Security of the State Protect life & limb Law or court order Legal advice and legal proceedings • No general “public interest” test
Rule 3 Disclose only if compatible • General rule – no disclosure for different purpose • Exceptions made, to balance other interests of society • Section 8 exceptions Ø Ø Ø Investigation of crime Collection of taxes Security of the State Protect life & limb Law or court order Legal advice and legal proceedings • No general “public interest” test
 Presentation Outline • Marketing – what do people think? • Data Protection – what is it? • Direct Marketing – the Rules • Best Practice
Presentation Outline • Marketing – what do people think? • Data Protection – what is it? • Direct Marketing – the Rules • Best Practice
 Direct Marketing Legislation • The Data Protection Acts 1988 and 2003 Ø Mainly Section 2 • SI 535 of 2003 European Communities (Electronic Communications Networks and Services) Data Protection and Privacy) Regulations as amended by SI 526 of 2008 Ø Mainly Regulation 13 (Unsolicited Communications) • Other Legislation: Consumer Protection, ECommerce, Financial Regulation etc
Direct Marketing Legislation • The Data Protection Acts 1988 and 2003 Ø Mainly Section 2 • SI 535 of 2003 European Communities (Electronic Communications Networks and Services) Data Protection and Privacy) Regulations as amended by SI 526 of 2008 Ø Mainly Regulation 13 (Unsolicited Communications) • Other Legislation: Consumer Protection, ECommerce, Financial Regulation etc
 Direct Marketing Definition • “direct marketing” includes direct mailing other than direct mailing carried out in the course of political activities by a political party or its members, or a body established by or under statute or a candidate for election to, or a holder of, elective political office;
Direct Marketing Definition • “direct marketing” includes direct mailing other than direct mailing carried out in the course of political activities by a political party or its members, or a body established by or under statute or a candidate for election to, or a holder of, elective political office;
 Direct Marketing – the Golden Rule of Consent • Only market willing customers • Strong Irish customer resistance to “junk mail” or “spam” • Failure to respect consumer choice is against the law Ø Criminal offence where electronic means used
Direct Marketing – the Golden Rule of Consent • Only market willing customers • Strong Irish customer resistance to “junk mail” or “spam” • Failure to respect consumer choice is against the law Ø Criminal offence where electronic means used
 Mailing lists • Legal Right to opt-out of direct marketing Ø Delete data subject from mailing list Ø Notify the data subject within 40 days • Failure is breach of Data Protection Acts (S. 2(7)) Ø Complaint to Commissioner Ø Enforcement Action (e. g. delete database)
Mailing lists • Legal Right to opt-out of direct marketing Ø Delete data subject from mailing list Ø Notify the data subject within 40 days • Failure is breach of Data Protection Acts (S. 2(7)) Ø Complaint to Commissioner Ø Enforcement Action (e. g. delete database)
 SMS and email • Non- Customers (Individuals) Ø Must Opt-in Ø Must include the name of sender Ø Must include valid address for opt-out Ø Opt-in must be in the last 12 Months
SMS and email • Non- Customers (Individuals) Ø Must Opt-in Ø Must include the name of sender Ø Must include valid address for opt-out Ø Opt-in must be in the last 12 Months
 SMS/e-mail Continued • Customer (Individuals) Ø Opportunity to object at point of collection Ø Must include identity of sender Ø Valid opt out instructions Ø Only Similar and Related Services
SMS/e-mail Continued • Customer (Individuals) Ø Opportunity to object at point of collection Ø Must include identity of sender Ø Valid opt out instructions Ø Only Similar and Related Services
 SMS/email Continued • Businesses Ø Do not need opt-in consent Ø Must respect any opt-out request Ø Must include valid instructions on opt-out Ø Must include name of sender
SMS/email Continued • Businesses Ø Do not need opt-in consent Ø Must respect any opt-out request Ø Must include valid instructions on opt-out Ø Must include name of sender
 Phone • Non-customers Ø Ø All marketing calls must be screened against the National Directory Database opt-out list (NDD) marketing calls made to numbers recorded on the NDD opt-out list are an offence Company must record any individual opt-out requests All marketing calls must be screened against internal do not call list
Phone • Non-customers Ø Ø All marketing calls must be screened against the National Directory Database opt-out list (NDD) marketing calls made to numbers recorded on the NDD opt-out list are an offence Company must record any individual opt-out requests All marketing calls must be screened against internal do not call list
 Phone Continued • Customers Ø Provide an opt-out at time of collection Ø Must respect any opt-out request Ø Can only market them for related or similar products
Phone Continued • Customers Ø Provide an opt-out at time of collection Ø Must respect any opt-out request Ø Can only market them for related or similar products
 Faxes • Individuals Ø Ø Must receive prior consent Must respect any opt-out received • Businesses Ø Ø Must respect any preference on the NDD opt-out list Must respect any opt-out given directly to the company
Faxes • Individuals Ø Ø Must receive prior consent Must respect any opt-out received • Businesses Ø Ø Must respect any preference on the NDD opt-out list Must respect any opt-out given directly to the company
 Penalties • Postal Ø Enforcement action by Data Protection Commissioner (deletion of database etc) • Electronic Ø Criminal Offence: € 5, 000 per message, up to 10% of turnover Ø 350 prosecutions going through Courts
Penalties • Postal Ø Enforcement action by Data Protection Commissioner (deletion of database etc) • Electronic Ø Criminal Offence: € 5, 000 per message, up to 10% of turnover Ø 350 prosecutions going through Courts
 Presentation Outline • Marketing – what do people think? • Data Protection – what is it? • Direct Marketing – the Rules • Best Practice
Presentation Outline • Marketing – what do people think? • Data Protection – what is it? • Direct Marketing – the Rules • Best Practice
 Best Practice (1) • Treat Consumer with Respect Ø Respect their right to be “let alone” • Marketing that respects the Consumer’s preferences is more likely to be successful • The more intrusive the marketing, the more likely Consumer will be upset • Don’t abuse public information (electoral register etc)
Best Practice (1) • Treat Consumer with Respect Ø Respect their right to be “let alone” • Marketing that respects the Consumer’s preferences is more likely to be successful • The more intrusive the marketing, the more likely Consumer will be upset • Don’t abuse public information (electoral register etc)
 Best Practice (2) • IDMA Consumer Guide (www. idma. ie) • FEDMA Direct Marketing Guide (www. fedma. org) Ø Approved at EU level Ø On-Line Annex in preparation • Irish DPA Guidance (www. dataprotection. ie)
Best Practice (2) • IDMA Consumer Guide (www. idma. ie) • FEDMA Direct Marketing Guide (www. fedma. org) Ø Approved at EU level Ø On-Line Annex in preparation • Irish DPA Guidance (www. dataprotection. ie)
 DPC Contact Details Office of the Data Protection Commissioner Canal House Station Road Portarlington Co Laois Phone: Lo. Call 1890 252231 057 8684800 Fax: 057 8684757 Email: info@dataprotection. ie Website: www. dataprotection. ie
DPC Contact Details Office of the Data Protection Commissioner Canal House Station Road Portarlington Co Laois Phone: Lo. Call 1890 252231 057 8684800 Fax: 057 8684757 Email: info@dataprotection. ie Website: www. dataprotection. ie


