19651798287f4f8b16ebe34fa8a6fe8a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: Why we need to take action in (insert your region)? R. William Field, Ph. D. , M. S. Associate Professor ist 0 L Department of Occupational p 1 and Environmental Health To Department of Epidemiology College of Public Health 104 IREH University of Iowa City, IA 52242 Bill-field@uiowa. edu
Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: Why we need to take action in (insert your region)? R. William Field, Ph. D. , M. S. Associate Professor ist 0 L Department of Occupational p 1 and Environmental Health To Department of Epidemiology College of Public Health 104 IREH University of Iowa City, IA 52242 Bill-field@uiowa. edu
 Why is the evidence ignored or not accepted ? ? M Invisible, odorless, colorless M Naturally occurring (no villains) M Can not link deaths to radon exposure M Long latency period M Not a dread hazard M Cancers occur one at a time M Voluntary risk M Lack of press – no sensational story M No sensory reminders to repetitively stimulate us to think about it M Lung cancer does not occur in children
Why is the evidence ignored or not accepted ? ? M Invisible, odorless, colorless M Naturally occurring (no villains) M Can not link deaths to radon exposure M Long latency period M Not a dread hazard M Cancers occur one at a time M Voluntary risk M Lack of press – no sensational story M No sensory reminders to repetitively stimulate us to think about it M Lung cancer does not occur in children
 Radon Mines
Radon Mines
 Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #1 There is widespread potential for radon exposure in homes coast to coast as well as workplaces!
Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #1 There is widespread potential for radon exposure in homes coast to coast as well as workplaces!
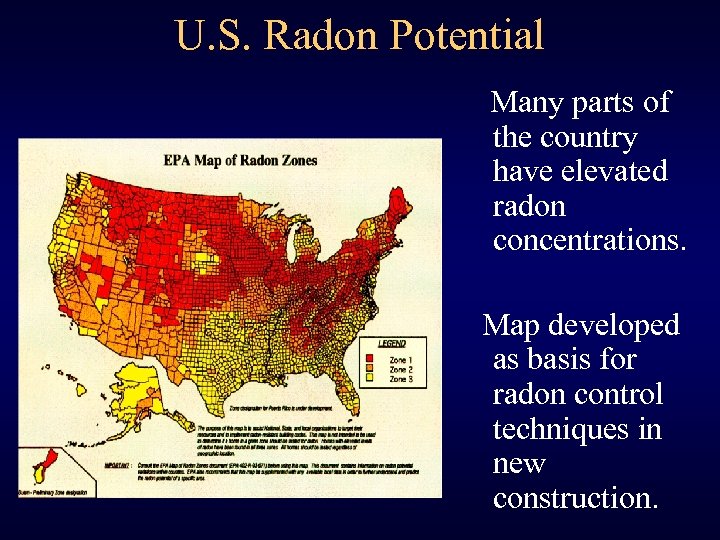 U. S. Radon Potential Many parts of the country have elevated radon concentrations. Map developed as basis for radon control techniques in new construction.
U. S. Radon Potential Many parts of the country have elevated radon concentrations. Map developed as basis for radon control techniques in new construction.
 Insert slide here describing radon occurrence in year area of interest Radon maps can be found here: http: //www. epa. gov/radon/zonemap. html
Insert slide here describing radon occurrence in year area of interest Radon maps can be found here: http: //www. epa. gov/radon/zonemap. html
 What Is Radon – 222 (radon)? • Radon is a gas • It is naturally occurring Radon • You can not see or smell it 3. 8 days Radium 1, 600 years Uranium 4. 5 billion years • It enters buildings from the soil beneath them
What Is Radon – 222 (radon)? • Radon is a gas • It is naturally occurring Radon • You can not see or smell it 3. 8 days Radium 1, 600 years Uranium 4. 5 billion years • It enters buildings from the soil beneath them
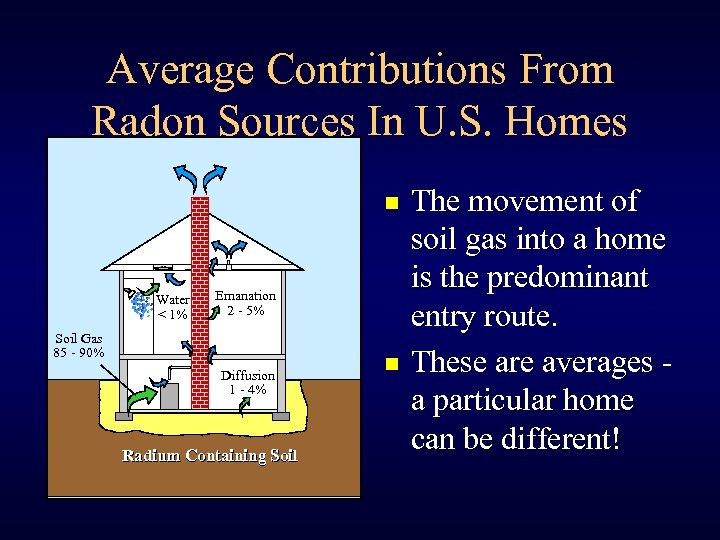 Average Contributions From Radon Sources In U. S. Homes n Water < 1% Emanation 2 - 5% Soil Gas 85 - 90% Diffusion 1 - 4% Radium Containing Soil n The movement of soil gas into a home is the predominant entry route. These are averages a particular home can be different!
Average Contributions From Radon Sources In U. S. Homes n Water < 1% Emanation 2 - 5% Soil Gas 85 - 90% Diffusion 1 - 4% Radium Containing Soil n The movement of soil gas into a home is the predominant entry route. These are averages a particular home can be different!
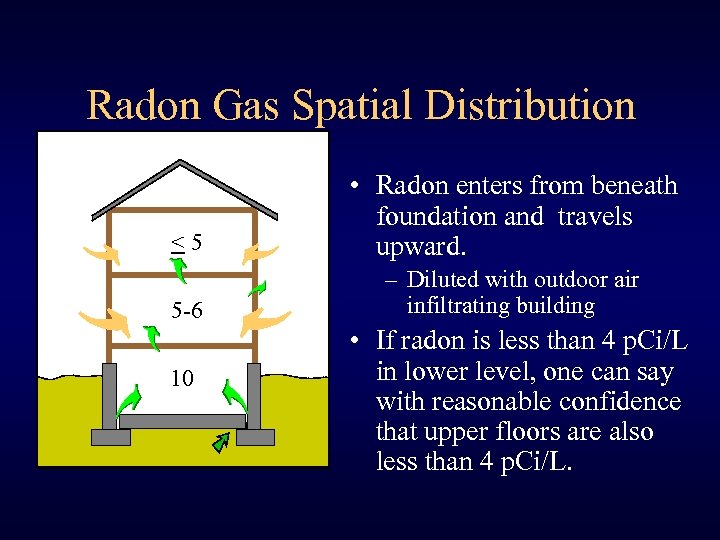 Radon Gas Spatial Distribution <5 • Radon enters from beneath foundation and travels upward. 5 -6 – Diluted with outdoor air infiltrating building 10 • If radon is less than 4 p. Ci/L in lower level, one can say with reasonable confidence that upper floors are also less than 4 p. Ci/L.
Radon Gas Spatial Distribution <5 • Radon enters from beneath foundation and travels upward. 5 -6 – Diluted with outdoor air infiltrating building 10 • If radon is less than 4 p. Ci/L in lower level, one can say with reasonable confidence that upper floors are also less than 4 p. Ci/L.
 Occupational Exposure to Radon – Very Common • Mine workers, including uranium, hard rock, and vanadium • Workers remediating radioactive contaminated sites, including uranium mill sites and mill tailings • Workers at underground nuclear waste repositories • Radon mitigation contractors and testers • Employees of natural caves • Phosphate fertilizer plant workers • Oil refinery workers • Utility tunnel workers
Occupational Exposure to Radon – Very Common • Mine workers, including uranium, hard rock, and vanadium • Workers remediating radioactive contaminated sites, including uranium mill sites and mill tailings • Workers at underground nuclear waste repositories • Radon mitigation contractors and testers • Employees of natural caves • Phosphate fertilizer plant workers • Oil refinery workers • Utility tunnel workers
 • Subway tunnel workers • Construction excavators • Power plant workers, including geothermal power and coal • Employees of radon health mines • Employees of radon balneotherapy spas (waterborne 222 Rn source) • Water plant operators (waterborne 222 Rn source) • Fish hatchery attendants (waterborne 222 Rn source) • Employees who come in contact with technologically enhanced sources of naturally occurring radioactive materials • Incidental exposure in almost any occupation from local geologic 222 Rn sources • Plowing?
• Subway tunnel workers • Construction excavators • Power plant workers, including geothermal power and coal • Employees of radon health mines • Employees of radon balneotherapy spas (waterborne 222 Rn source) • Water plant operators (waterborne 222 Rn source) • Fish hatchery attendants (waterborne 222 Rn source) • Employees who come in contact with technologically enhanced sources of naturally occurring radioactive materials • Incidental exposure in almost any occupation from local geologic 222 Rn sources • Plowing?
 Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #2 Outdoor radon exposure can be significant!
Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #2 Outdoor radon exposure can be significant!
 Outdoor 222 Rn Concentrations
Outdoor 222 Rn Concentrations
 Outdoor Radon in Iowa National INDOOR Average 1. 4 p. Ci/L
Outdoor Radon in Iowa National INDOOR Average 1. 4 p. Ci/L
 Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #3 Alpha particles are very effective at causing DNA damage!
Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #3 Alpha particles are very effective at causing DNA damage!
 Why Is Radon A Concern? Radon Decay Products Radon • Radon decays into radioactive particles known as radon decay products. • These particles are easily inhaled and deposited in the lungs where they can damage sensitive lung tissue.
Why Is Radon A Concern? Radon Decay Products Radon • Radon decays into radioactive particles known as radon decay products. • These particles are easily inhaled and deposited in the lungs where they can damage sensitive lung tissue.
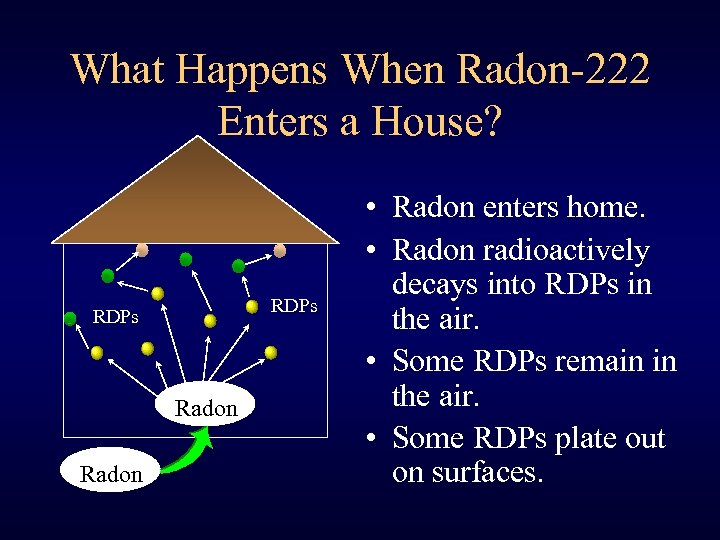 What Happens When Radon-222 Enters a House? RDPs Radon • Radon enters home. • Radon radioactively decays into RDPs in the air. • Some RDPs remain in the air. • Some RDPs plate out on surfaces.
What Happens When Radon-222 Enters a House? RDPs Radon • Radon enters home. • Radon radioactively decays into RDPs in the air. • Some RDPs remain in the air. • Some RDPs plate out on surfaces.
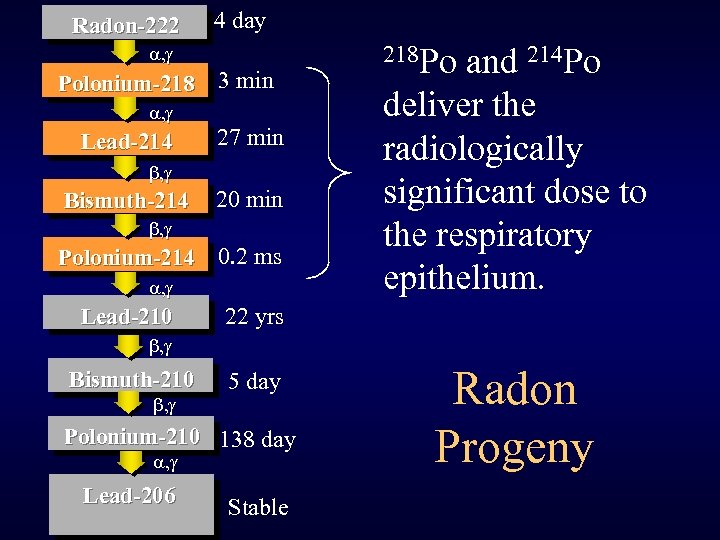 Radon-222 4 day a, g Polonium-218 a, g Lead-214 3 min 27 min b, g Bismuth-214 20 min b, g Polonium-214 0. 2 ms a, g Lead-210 218 Po and 214 Po deliver the radiologically significant dose to the respiratory epithelium. 22 yrs b, g Bismuth-210 b, g 5 day Polonium-210 138 day a, g Lead-206 Stable Radon Progeny
Radon-222 4 day a, g Polonium-218 a, g Lead-214 3 min 27 min b, g Bismuth-214 20 min b, g Polonium-214 0. 2 ms a, g Lead-210 218 Po and 214 Po deliver the radiologically significant dose to the respiratory epithelium. 22 yrs b, g Bismuth-210 b, g 5 day Polonium-210 138 day a, g Lead-206 Stable Radon Progeny
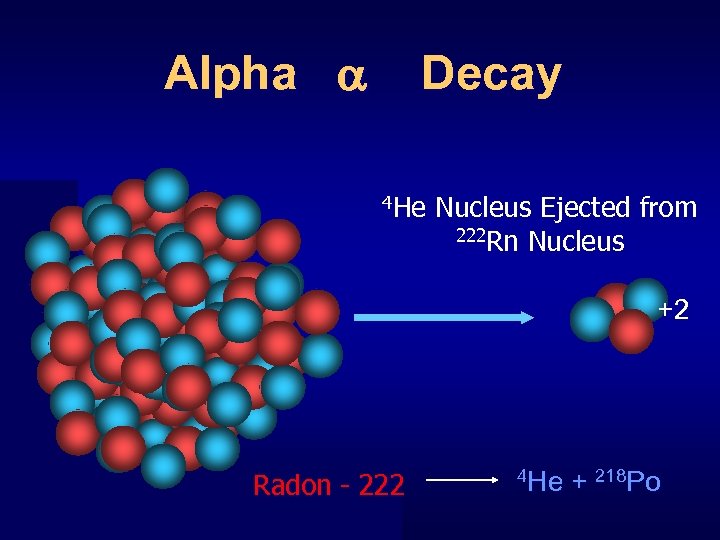 Alpha Decay 4 He + + Nucleus Ejected from 222 Rn Nucleus + + +2 + + + Radon - 222 4 He He + 218 Po
Alpha Decay 4 He + + Nucleus Ejected from 222 Rn Nucleus + + +2 + + + Radon - 222 4 He He + 218 Po
 What Happens When Radon Decay Products Are Inhaled? n n Double Strand Breaks Highly radioactive particles adhere to lung tissue, where they can irradiate sensitive cells. Radiation can alter the cells, increasing the potential for cancer.
What Happens When Radon Decay Products Are Inhaled? n n Double Strand Breaks Highly radioactive particles adhere to lung tissue, where they can irradiate sensitive cells. Radiation can alter the cells, increasing the potential for cancer.
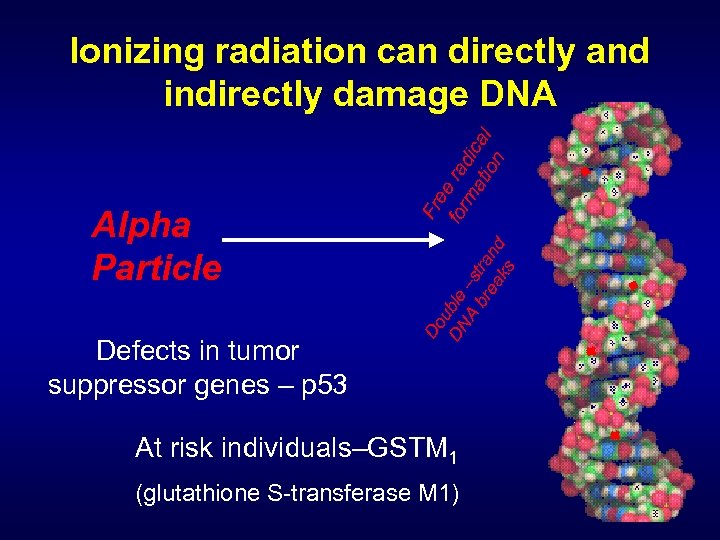 Alpha Particle Defects in tumor suppressor genes – p 53 Fr Do ee ub DN le for ra –s ma dic A br tra tio al ea nd n ks Ionizing radiation can directly and indirectly damage DNA At risk individuals–GSTM 1 (glutathione S-transferase M 1)
Alpha Particle Defects in tumor suppressor genes – p 53 Fr Do ee ub DN le for ra –s ma dic A br tra tio al ea nd n ks Ionizing radiation can directly and indirectly damage DNA At risk individuals–GSTM 1 (glutathione S-transferase M 1)
 Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #4 For the average individual in the United States – Radon decay products (radon) deliver over 50% of our average radiation dose! For the average, Iowan it represents well over 75%!!
Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #4 For the average individual in the United States – Radon decay products (radon) deliver over 50% of our average radiation dose! For the average, Iowan it represents well over 75%!!
 Annual Effective Dose Equivalent to Member of the U. S. Population NCRP 93 (1987) Natural (mrem) Radon Cosmic 200 27 Terrestrial: -external -internal 28 39 Artificial (mrem) -Diag. X-rays 39 -Nuc. Med. 14 -Consumer Pro. 10 -Other ~1 TOTAL ~360
Annual Effective Dose Equivalent to Member of the U. S. Population NCRP 93 (1987) Natural (mrem) Radon Cosmic 200 27 Terrestrial: -external -internal 28 39 Artificial (mrem) -Diag. X-rays 39 -Nuc. Med. 14 -Consumer Pro. 10 -Other ~1 TOTAL ~360
 Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #5 Waterborne radon also contributes to our overall radon exposure!
Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #5 Waterborne radon also contributes to our overall radon exposure!
 Waterborne Radon Primarily from groundwater sources (wells) rather than rivers Waterborne radon to air ratio 10, 000 : 1
Waterborne Radon Primarily from groundwater sources (wells) rather than rivers Waterborne radon to air ratio 10, 000 : 1
 Proposed Waterborne Radon Standard • EPA proposed new regulations November 2, 1999 (64 FR 59246). • 300 p. Ci/L standard for public water supplies • Multimedia Mitigation (MMM) programs - while individual water systems reduce radon levels in drinking water to 4, 000 p. Ci/L or lower
Proposed Waterborne Radon Standard • EPA proposed new regulations November 2, 1999 (64 FR 59246). • 300 p. Ci/L standard for public water supplies • Multimedia Mitigation (MMM) programs - while individual water systems reduce radon levels in drinking water to 4, 000 p. Ci/L or lower
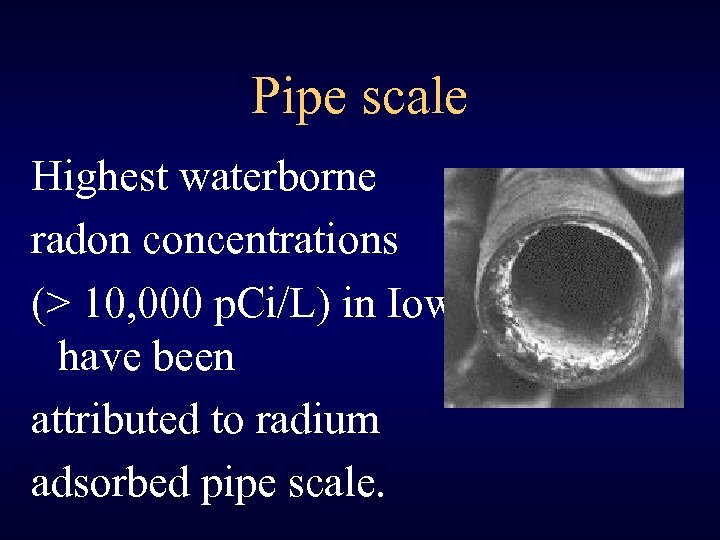 Pipe scale Highest waterborne radon concentrations (> 10, 000 p. Ci/L) in Iowa have been attributed to radium adsorbed pipe scale.
Pipe scale Highest waterborne radon concentrations (> 10, 000 p. Ci/L) in Iowa have been attributed to radium adsorbed pipe scale.
 Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #6 National and International Public Health Agencies support the contention that radon is a leading environmental health risk!
Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #6 National and International Public Health Agencies support the contention that radon is a leading environmental health risk!
 EPA & Surgeon General Recommend Take action if a home is at or above 4. 0 p. Ci/L (year long average) 4. 0 p. Ci/L EPA ACTION LEVEL Average indoor: 1. 3 – 1. 4 p. Ci/L Average outdoor: 0. 4 p. Ci/L
EPA & Surgeon General Recommend Take action if a home is at or above 4. 0 p. Ci/L (year long average) 4. 0 p. Ci/L EPA ACTION LEVEL Average indoor: 1. 3 – 1. 4 p. Ci/L Average outdoor: 0. 4 p. Ci/L
 How Does Radon Rank As A Cancer Causing Agent? • Radon is ranked as a Group A carcinogen – Highest ranking for cancer potential – Known to cause cancer in humans – Tobacco smoke and tobacco products in same category International Agency for Research on Cancer
How Does Radon Rank As A Cancer Causing Agent? • Radon is ranked as a Group A carcinogen – Highest ranking for cancer potential – Known to cause cancer in humans – Tobacco smoke and tobacco products in same category International Agency for Research on Cancer
 “Radon Is A Serious National Health Problem” • • • American Lung Association American Medical Association Environmental Protection Agency National Academy of Sciences National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurement • U. S. Surgeon General • World Health Organization, and others…. .
“Radon Is A Serious National Health Problem” • • • American Lung Association American Medical Association Environmental Protection Agency National Academy of Sciences National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurement • U. S. Surgeon General • World Health Organization, and others…. .
 Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #7 Laboratory studies using different species of radon-exposed animals clearly show a linear doseresponse relationship between radon and lung cancer.
Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #7 Laboratory studies using different species of radon-exposed animals clearly show a linear doseresponse relationship between radon and lung cancer.
 Animal Studies • Confirm carcinogenicity of radon. • Exposure to ore dusts and diesel fumes, simultaneously with radon, did not increase incidence of lung cancer above that produced by radon progeny exposures alone. (DOE/OER 1988)
Animal Studies • Confirm carcinogenicity of radon. • Exposure to ore dusts and diesel fumes, simultaneously with radon, did not increase incidence of lung cancer above that produced by radon progeny exposures alone. (DOE/OER 1988)
 Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #8 Studies of occupationally-exposed miners clearly show a linear relationship between radon exposure and lung cancer!
Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #8 Studies of occupationally-exposed miners clearly show a linear relationship between radon exposure and lung cancer!
 Early Radon Related Epidemiology 1556 Agricola - Miners in Europe 1879 Harting & Hesse - Lung Cancer in Miners 1921 Uhlig - Radium Emanations & Lung Cancer 1950 s Peller - First Review of Mining Related Cancers 1970 s (ongoing) – Studies of Underground Miners
Early Radon Related Epidemiology 1556 Agricola - Miners in Europe 1879 Harting & Hesse - Lung Cancer in Miners 1921 Uhlig - Radium Emanations & Lung Cancer 1950 s Peller - First Review of Mining Related Cancers 1970 s (ongoing) – Studies of Underground Miners
 Original Scientific Basis For Radon Risk Estimates • Studies on miners. –Uranium miners in U. S. and other countries
Original Scientific Basis For Radon Risk Estimates • Studies on miners. –Uranium miners in U. S. and other countries
 EPIDEMIOLOGIC MINER STUDIES China (Tin Miners) Czechoslovakia (Uranium) Colorado (Uranium) Ontario (Uranium) Newfoundland (Florspar) Sweden (Iron) New Mexico (Uranium) Beaverlodge (Uranium) Port Radium (Uranium) Radium Hill (Uranium) France (Uranium)
EPIDEMIOLOGIC MINER STUDIES China (Tin Miners) Czechoslovakia (Uranium) Colorado (Uranium) Ontario (Uranium) Newfoundland (Florspar) Sweden (Iron) New Mexico (Uranium) Beaverlodge (Uranium) Port Radium (Uranium) Radium Hill (Uranium) France (Uranium)
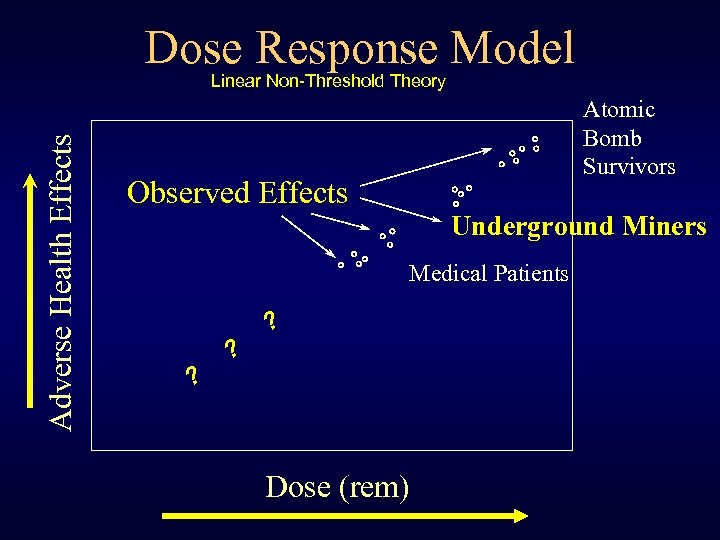 Dose Response Model Adverse Health Effects Linear Non-Threshold Theory Atomic Bomb Survivors Observed Effects Underground Miners Medical Patients ? ? ? Dose (rem)
Dose Response Model Adverse Health Effects Linear Non-Threshold Theory Atomic Bomb Survivors Observed Effects Underground Miners Medical Patients ? ? ? Dose (rem)
 Occupational Miner Studies • Linear dose response relationship was found for all the occupational studies. • A 1994 NCI pooled analyses of 68, 000 miners concluded that about 39% of the lung cancer deaths among smokers and 73% of the lung cancer deaths among never-smokers may have been due to their occupational radon progeny exposure. • Projecting risks to the residential setting they concluded that radon progeny may be responsible for 10 – 12% of lung cancers in smokers and 28 -31% in never-smokers.
Occupational Miner Studies • Linear dose response relationship was found for all the occupational studies. • A 1994 NCI pooled analyses of 68, 000 miners concluded that about 39% of the lung cancer deaths among smokers and 73% of the lung cancer deaths among never-smokers may have been due to their occupational radon progeny exposure. • Projecting risks to the residential setting they concluded that radon progeny may be responsible for 10 – 12% of lung cancers in smokers and 28 -31% in never-smokers.
 National Academy of Sciences BEIR VI 1999 Ø Risk estimates based primarily on radonexposed miners Ø Estimated 18, 600 lung cancer deaths each year in the U. S. from residential radon exposure EPA Estimates 21, 000
National Academy of Sciences BEIR VI 1999 Ø Risk estimates based primarily on radonexposed miners Ø Estimated 18, 600 lung cancer deaths each year in the U. S. from residential radon exposure EPA Estimates 21, 000
 Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #9 Case-control studies of individuals exposed to radon in their homes show an increased lung cancer risk even at or below the EPA’s action level of 4 p. Ci/L (150 Bq/m 3).
Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #9 Case-control studies of individuals exposed to radon in their homes show an increased lung cancer risk even at or below the EPA’s action level of 4 p. Ci/L (150 Bq/m 3).
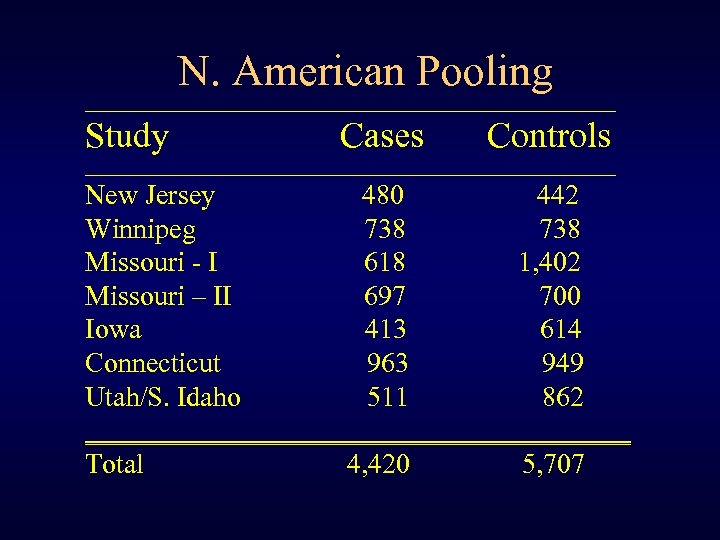 N. American Pooling ______________________________ Study Cases Controls ______________________________ New Jersey 480 442 Winnipeg 738 Missouri - I 618 1, 402 Missouri – II 697 700 Iowa 413 614 Connecticut 963 949 Utah/S. Idaho 511 862 ____________________ Total 4, 420 5, 707
N. American Pooling ______________________________ Study Cases Controls ______________________________ New Jersey 480 442 Winnipeg 738 Missouri - I 618 1, 402 Missouri – II 697 700 Iowa 413 614 Connecticut 963 949 Utah/S. Idaho 511 862 ____________________ Total 4, 420 5, 707
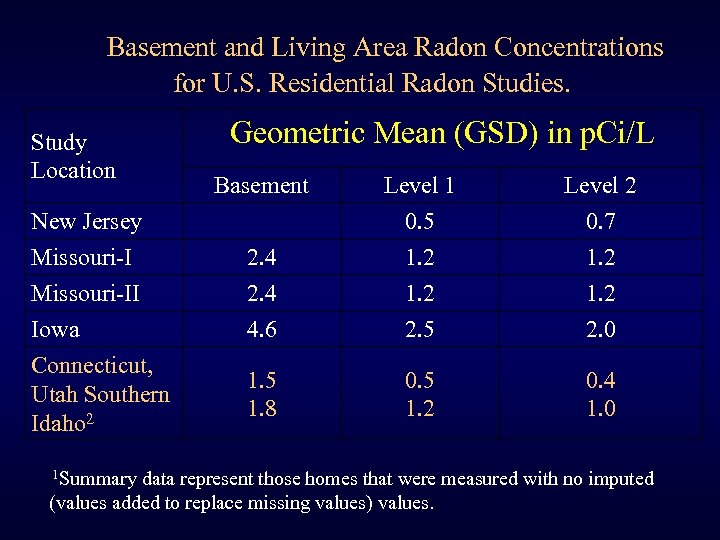 Basement and Living Area Radon Concentrations for U. S. Residential Radon Studies. Study Location Geometric Mean (GSD) in p. Ci/L Basement Level 1 0. 5 Level 2 0. 7 2. 4 4. 6 1. 2 2. 5 1. 2 2. 0 1. 5 1. 8 0. 5 1. 2 0. 4 1. 0 New Jersey Missouri-II Iowa Connecticut, Utah Southern Idaho 2 1 Summary data represent those homes that were measured with no imputed (values added to replace missing values) values.
Basement and Living Area Radon Concentrations for U. S. Residential Radon Studies. Study Location Geometric Mean (GSD) in p. Ci/L Basement Level 1 0. 5 Level 2 0. 7 2. 4 4. 6 1. 2 2. 5 1. 2 2. 0 1. 5 1. 8 0. 5 1. 2 0. 4 1. 0 New Jersey Missouri-II Iowa Connecticut, Utah Southern Idaho 2 1 Summary data represent those homes that were measured with no imputed (values added to replace missing values) values.
 International Pooling of Residential Radon Case-Control Studies New Jersey, Missouri I, Canada, Iowa, Missouri II, a combined study from Connecticut, Utah and S. Idaho 18% – 0% 1 Shenyang, China, Stockholm, Sweden, Swedish nationwide, Winnipeg, Canada, S. Finland, Finnish nationwide, SW England, W. Germany, Sweden, Czech Republic, Italy. Trento, Spain, Austria, France, China - Gansu Province, E. Germany 16%
International Pooling of Residential Radon Case-Control Studies New Jersey, Missouri I, Canada, Iowa, Missouri II, a combined study from Connecticut, Utah and S. Idaho 18% – 0% 1 Shenyang, China, Stockholm, Sweden, Swedish nationwide, Winnipeg, Canada, S. Finland, Finnish nationwide, SW England, W. Germany, Sweden, Czech Republic, Italy. Trento, Spain, Austria, France, China - Gansu Province, E. Germany 16%
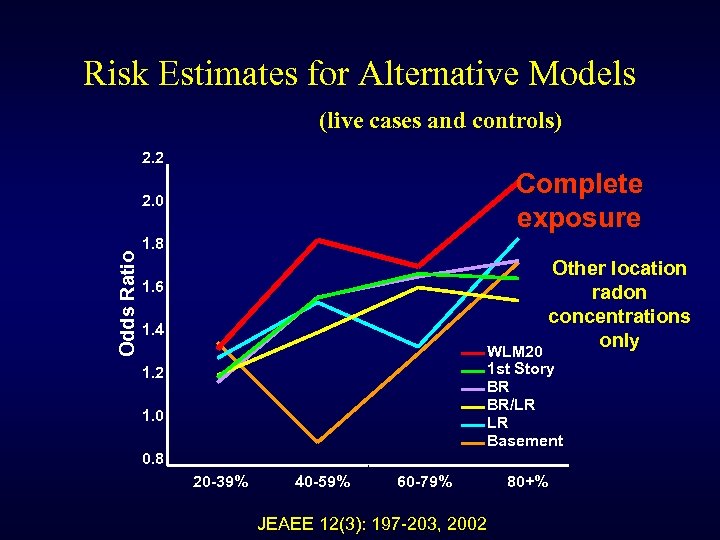 Risk Estimates for Alternative Models (live cases and controls) 2. 2 Complete exposure Odds Ratio 2. 0 1. 8 Other location radon concentrations only WLM 20 1. 6 1. 4 1 st Story BR BR/LR LR Basement 1. 2 1. 0 0. 8 20 -39% 40 -59% 60 -79% JEAEE 12(3): 197 -203, 2002 80+%
Risk Estimates for Alternative Models (live cases and controls) 2. 2 Complete exposure Odds Ratio 2. 0 1. 8 Other location radon concentrations only WLM 20 1. 6 1. 4 1 st Story BR BR/LR LR Basement 1. 2 1. 0 0. 8 20 -39% 40 -59% 60 -79% JEAEE 12(3): 197 -203, 2002 80+%
 Iowa Study Summary • The findings suggest that prolonged exposure to radon, even at 4 p. Ci/L, increases lung cancer risk. • These findings indicate that radon is a major environmental carcinogen.
Iowa Study Summary • The findings suggest that prolonged exposure to radon, even at 4 p. Ci/L, increases lung cancer risk. • These findings indicate that radon is a major environmental carcinogen.
 Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #10 Radon exposure represents a major source of cancer mortality in the United States!
Residential Radon Exposure – A Leading Environmental Health Risk: What is the Evidence? WHAT IS THE EVIDENCE #10 Radon exposure represents a major source of cancer mortality in the United States!
 LUNG CANCER DEATHS Per Year Estimated 163, 510 Lung Cancer Deaths in 2005* *CA: A Journal for Clinicians - 2005 Attributed to Radon Approximately 21, 000 EPA 2003
LUNG CANCER DEATHS Per Year Estimated 163, 510 Lung Cancer Deaths in 2005* *CA: A Journal for Clinicians - 2005 Attributed to Radon Approximately 21, 000 EPA 2003
 Should we be concerned about radon-induced lung cancer given that the risk pales in comparison to the risk posed by smoking?
Should we be concerned about radon-induced lung cancer given that the risk pales in comparison to the risk posed by smoking?
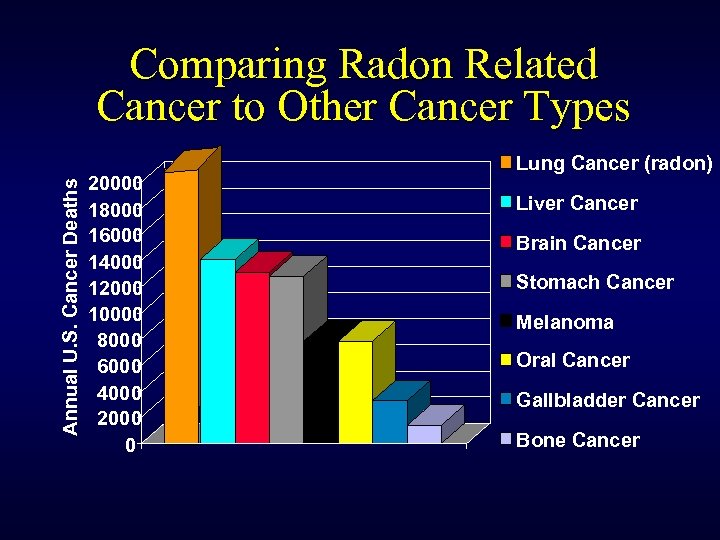 Annual U. S. Cancer Deaths Comparing Radon Related Cancer to Other Cancer Types 20000 18000 16000 14000 12000 10000 8000 6000 4000 2000 0 Lung Cancer (radon) Liver Cancer Brain Cancer Stomach Cancer Melanoma Oral Cancer Gallbladder Cancer Bone Cancer
Annual U. S. Cancer Deaths Comparing Radon Related Cancer to Other Cancer Types 20000 18000 16000 14000 12000 10000 8000 6000 4000 2000 0 Lung Cancer (radon) Liver Cancer Brain Cancer Stomach Cancer Melanoma Oral Cancer Gallbladder Cancer Bone Cancer

 Is Radon a Leading Environmental Health Risk ? Radon Decay Products Radon
Is Radon a Leading Environmental Health Risk ? Radon Decay Products Radon
 Further Information on Radon EPA 1 -800 -SOS-RADON http: //www. epa. gov/radon/ Bill Field 319 -335 -4413 bill-field@uiowa. edu
Further Information on Radon EPA 1 -800 -SOS-RADON http: //www. epa. gov/radon/ Bill Field 319 -335 -4413 bill-field@uiowa. edu


