29c4f2897422febe9c590816d6ca9f1c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Reset and Interrupts Advanced Programming 1
Reset and Interrupts Advanced Programming 1
 Resets and Interrupts l See the Reset and Interrupts Section in the 68 HC 11 E Family Technical Data Sheet (pp. 79 -96) l For a more detailed description see the Reset and Interrupt Section of the Reference Manual (pp. 159 -196) 2
Resets and Interrupts l See the Reset and Interrupts Section in the 68 HC 11 E Family Technical Data Sheet (pp. 79 -96) l For a more detailed description see the Reset and Interrupt Section of the Reference Manual (pp. 159 -196) 2
 Interrupts l l l An interrupt is an event that causes the CPU to suspend whatever is doing (running a program) handle the interrupt (running a routine servicing the interrupt) and then resumes what it was doing To handle the interrupt the CPU jump to a special routine called an interrupt service routine (ISR) or an interrupt handler The difference from a subroutine is that ISRs are located at pre-determined starting addresses 3
Interrupts l l l An interrupt is an event that causes the CPU to suspend whatever is doing (running a program) handle the interrupt (running a routine servicing the interrupt) and then resumes what it was doing To handle the interrupt the CPU jump to a special routine called an interrupt service routine (ISR) or an interrupt handler The difference from a subroutine is that ISRs are located at pre-determined starting addresses 3
 Resets • A Reset is a special type of interrupt. • Resets do not return back to finish executing the interrupted program • Resets are used to force the MCU to assume a set of initial conditions and to begin executing instructions from a predetermined starting address • When a reset occurs, the CPU finishes executing the present instruction and then begins execution of the reset routine 4
Resets • A Reset is a special type of interrupt. • Resets do not return back to finish executing the interrupted program • Resets are used to force the MCU to assume a set of initial conditions and to begin executing instructions from a predetermined starting address • When a reset occurs, the CPU finishes executing the present instruction and then begins execution of the reset routine 4
 Types of Reset l l RESET pin Power-On Reset (POR) Computer Operating Properly (COP) Watchdog Timer Reset Clock Monitor Fail (CMF) Reset 5
Types of Reset l l RESET pin Power-On Reset (POR) Computer Operating Properly (COP) Watchdog Timer Reset Clock Monitor Fail (CMF) Reset 5
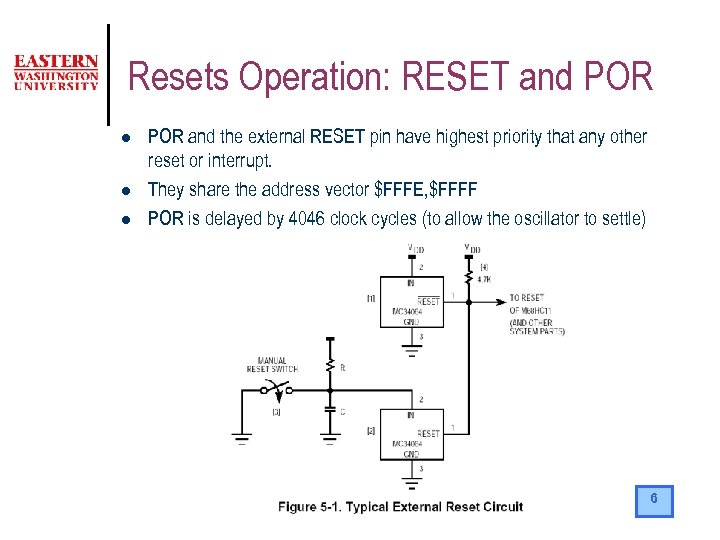 Resets Operation: RESET and POR l l l POR and the external RESET pin have highest priority that any other reset or interrupt. They share the address vector $FFFE, $FFFF POR is delayed by 4046 clock cycles (to allow the oscillator to settle) 6
Resets Operation: RESET and POR l l l POR and the external RESET pin have highest priority that any other reset or interrupt. They share the address vector $FFFE, $FFFF POR is delayed by 4046 clock cycles (to allow the oscillator to settle) 6
 Resets Operation: COP l l COP failure is intended to detect software processing errors. If the CPU watchdog times out a reset is initiated. To prevent a COP failure reset from occurring the application program must “clear” the watchdog timer on a regular basis. To “clear” the COP timer the application program must follow a 2 step sequence. It must write a $55 to the COPRST (at $103 A) register followed by writing a $AA to the COPRST register. The COP system is enabled or disabled depending on the state of the NOCOP bit in the CONFIG register (at $103 F). The COP timeout period is set by the timer rate control bits CR 1 and CR 0 in the configuration OPTION register (at $1039). 7
Resets Operation: COP l l COP failure is intended to detect software processing errors. If the CPU watchdog times out a reset is initiated. To prevent a COP failure reset from occurring the application program must “clear” the watchdog timer on a regular basis. To “clear” the COP timer the application program must follow a 2 step sequence. It must write a $55 to the COPRST (at $103 A) register followed by writing a $AA to the COPRST register. The COP system is enabled or disabled depending on the state of the NOCOP bit in the CONFIG register (at $103 F). The COP timeout period is set by the timer rate control bits CR 1 and CR 0 in the configuration OPTION register (at $1039). 7
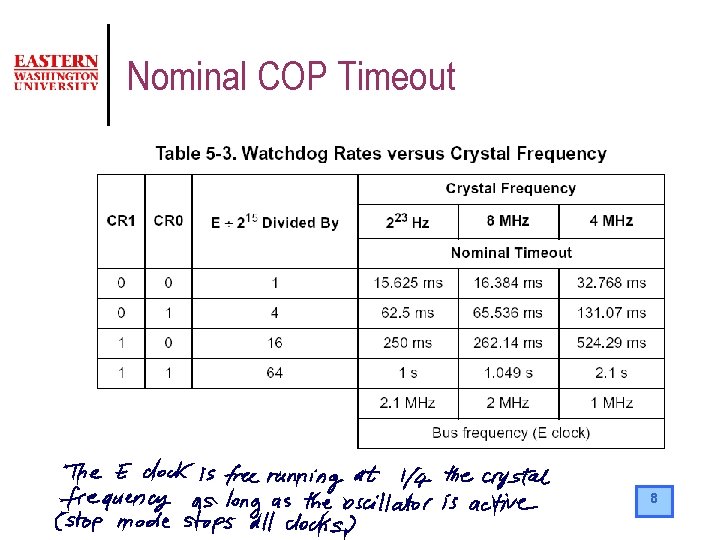 Nominal COP Timeout 8
Nominal COP Timeout 8
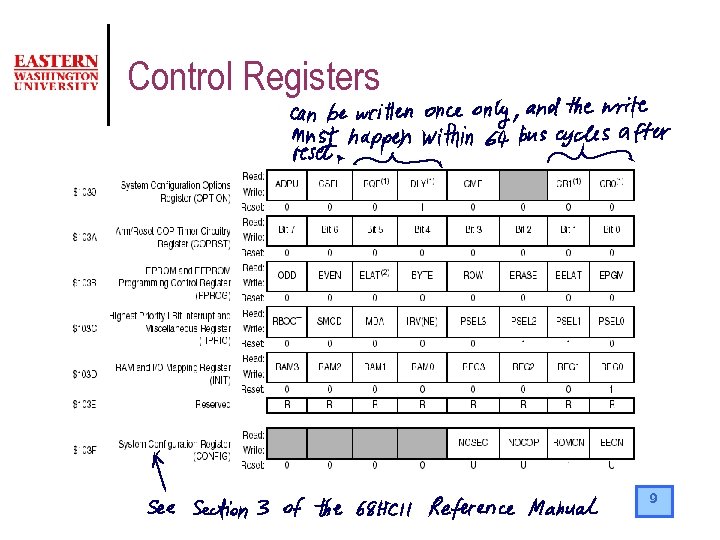 Control Registers 9
Control Registers 9
 Resets Operation: Clock Monitor l l This reset triggers if the CPU clock drops below a frequency of 10 KHz. To enable the clock monitor reset, set the clock monitor enable (CME) bit in the system’s configuration options register (OPTION at $1039) The clock monitor reset is based on an internal resistor-capacitor (RC) time delay. When a crystal fails it can still generate approximately 1000 more cycles due to its internal capacitance. 10
Resets Operation: Clock Monitor l l This reset triggers if the CPU clock drops below a frequency of 10 KHz. To enable the clock monitor reset, set the clock monitor enable (CME) bit in the system’s configuration options register (OPTION at $1039) The clock monitor reset is based on an internal resistor-capacitor (RC) time delay. When a crystal fails it can still generate approximately 1000 more cycles due to its internal capacitance. 10
 Types of Interrupt l l A microcontroller uses interrupts for “critical tasks” that cannot wait, such as I/O events. There are many separate interrupt sources Some are generated by a signal at an external pin Others are generated when special bits are set (a combination of hardware and software causes these bits to set). 11
Types of Interrupt l l A microcontroller uses interrupts for “critical tasks” that cannot wait, such as I/O events. There are many separate interrupt sources Some are generated by a signal at an external pin Others are generated when special bits are set (a combination of hardware and software causes these bits to set). 11
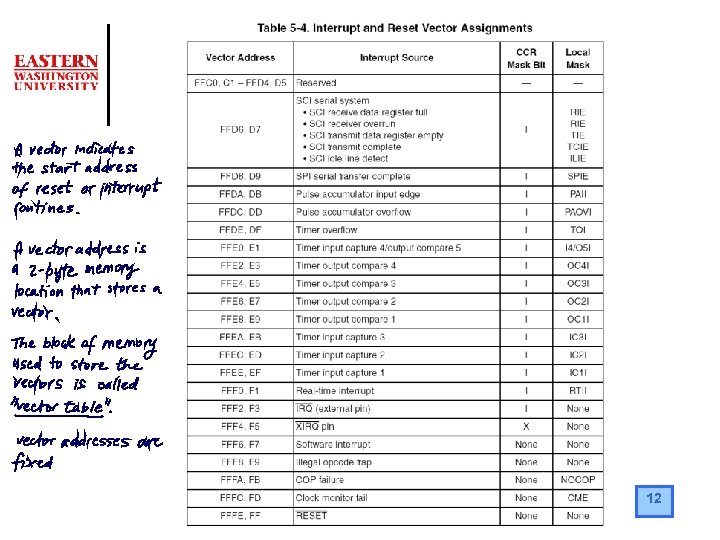 12
12
 Interrupt Vectors Customization l l The programmer can customize the service routine addresses by using a vector jump table. The “elements” of the vector jump table are called pseudo-vectors or jump vectors. The pseudo vectors are in RAM Each pseudo vector takes three bytes of RAM 13
Interrupt Vectors Customization l l The programmer can customize the service routine addresses by using a vector jump table. The “elements” of the vector jump table are called pseudo-vectors or jump vectors. The pseudo vectors are in RAM Each pseudo vector takes three bytes of RAM 13
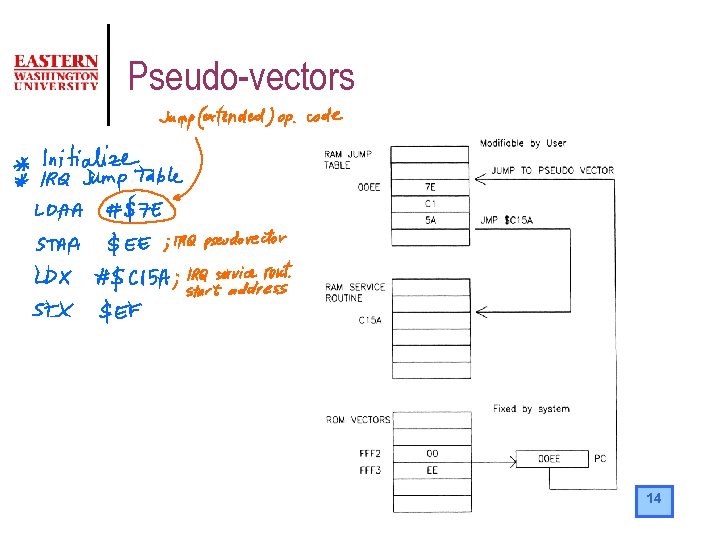 Pseudo-vectors 14
Pseudo-vectors 14
 Stacking the Registers l l l An ISR will most likely change the content of some of the CPU registers An ISR also needs to know where to return to when it has completed servicing the request When an interrupt request occurs and it is enabled the CPU will push all the CPU register values onto the stack before it fetches the vector An ISR use the instruction RTI to return control back to the program interrupted. When RTI is executed, it pulls the data from the stack to restore them to the CPU registers Resets do not stack the CPU registers, since a reset routine does not normally return control back to the program interrupted. 15
Stacking the Registers l l l An ISR will most likely change the content of some of the CPU registers An ISR also needs to know where to return to when it has completed servicing the request When an interrupt request occurs and it is enabled the CPU will push all the CPU register values onto the stack before it fetches the vector An ISR use the instruction RTI to return control back to the program interrupted. When RTI is executed, it pulls the data from the stack to restore them to the CPU registers Resets do not stack the CPU registers, since a reset routine does not normally return control back to the program interrupted. 15
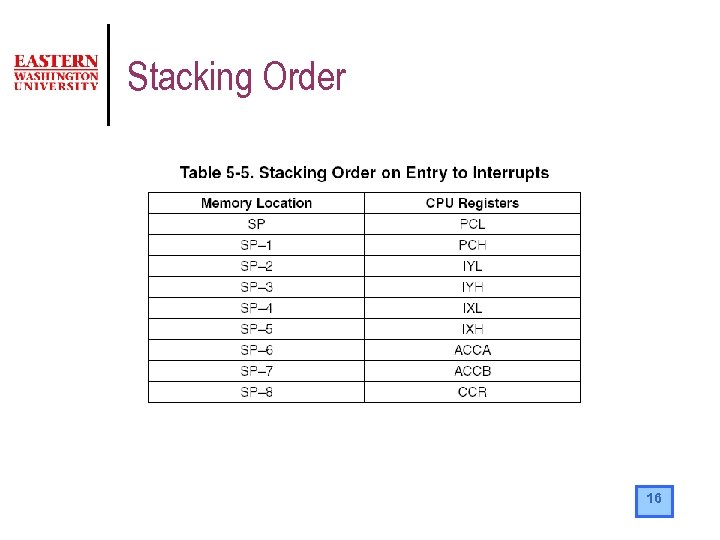 Stacking Order 16
Stacking Order 16
 Interrupt Priority 17
Interrupt Priority 17
 Interrupt Priority 18
Interrupt Priority 18
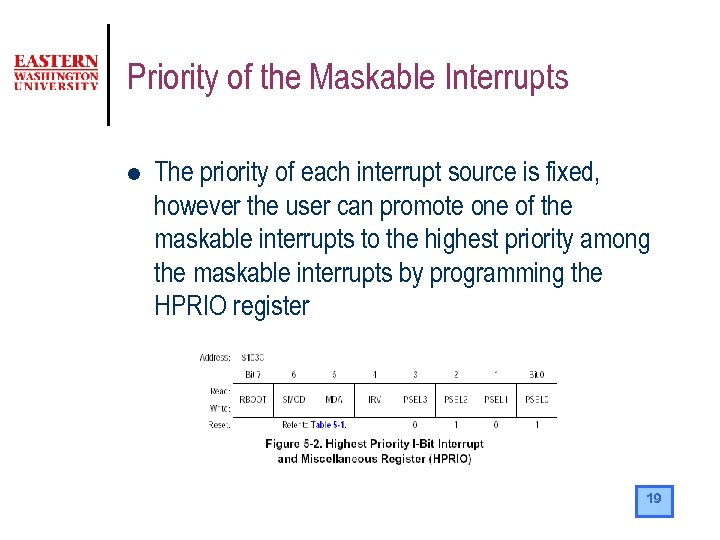 Priority of the Maskable Interrupts l The priority of each interrupt source is fixed, however the user can promote one of the maskable interrupts to the highest priority among the maskable interrupts by programming the HPRIO register 19
Priority of the Maskable Interrupts l The priority of each interrupt source is fixed, however the user can promote one of the maskable interrupts to the highest priority among the maskable interrupts by programming the HPRIO register 19
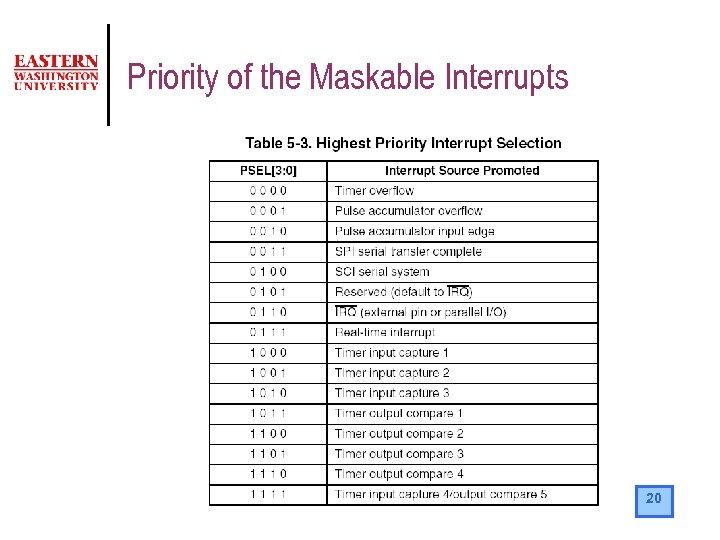 Priority of the Maskable Interrupts 20
Priority of the Maskable Interrupts 20
 Nested Interrupts l l l After Stacking the registers, the CPU sets the I bit in the CCR to prevent any other interrupts from occurring If the interrupt service routine does not clear the I bit, only nonmaskable interrupts can interrupt the routine When interrupt routines are interrupted, a condition of nested interrupts is said to exist Many systems try to avoid nested interrupts because it makes the software more complicated and there is a danger of stack overflow Nonmaskable interrupts and resets will always be able to interrupt a low-priority maskable interrupt It is possible to change the priority level of any one of the maskable (I-bit related) interrupts using the highest priority interrupt (HPRIO at $103 C) register 21
Nested Interrupts l l l After Stacking the registers, the CPU sets the I bit in the CCR to prevent any other interrupts from occurring If the interrupt service routine does not clear the I bit, only nonmaskable interrupts can interrupt the routine When interrupt routines are interrupted, a condition of nested interrupts is said to exist Many systems try to avoid nested interrupts because it makes the software more complicated and there is a danger of stack overflow Nonmaskable interrupts and resets will always be able to interrupt a low-priority maskable interrupt It is possible to change the priority level of any one of the maskable (I-bit related) interrupts using the highest priority interrupt (HPRIO at $103 C) register 21
 Interrupt masking and enabling · · · · Microcontrollers can be programmed to ignore some interrupt sources. This is achieved by not setting a special bit called the interrupt’s enable bit. The process of ignoring an interrupt is called masking. Interrupts that can be enabled/disabled are called maskable. Each maskable interrupt has its own corresponding enable or mask bit. Typically, an enable/mask bit is set or cleared by writing to a specific I/O control or status register When an enable bit is set to 1, the CPU will respond to the interrupt request, when is set to 0, the CPU will ignore the request. When a mask bit is set to 1, the CPU will ignore the interrupt request, when is set to 1, the CPU will respond to the request. 22
Interrupt masking and enabling · · · · Microcontrollers can be programmed to ignore some interrupt sources. This is achieved by not setting a special bit called the interrupt’s enable bit. The process of ignoring an interrupt is called masking. Interrupts that can be enabled/disabled are called maskable. Each maskable interrupt has its own corresponding enable or mask bit. Typically, an enable/mask bit is set or cleared by writing to a specific I/O control or status register When an enable bit is set to 1, the CPU will respond to the interrupt request, when is set to 0, the CPU will ignore the request. When a mask bit is set to 1, the CPU will ignore the interrupt request, when is set to 1, the CPU will respond to the request. 22
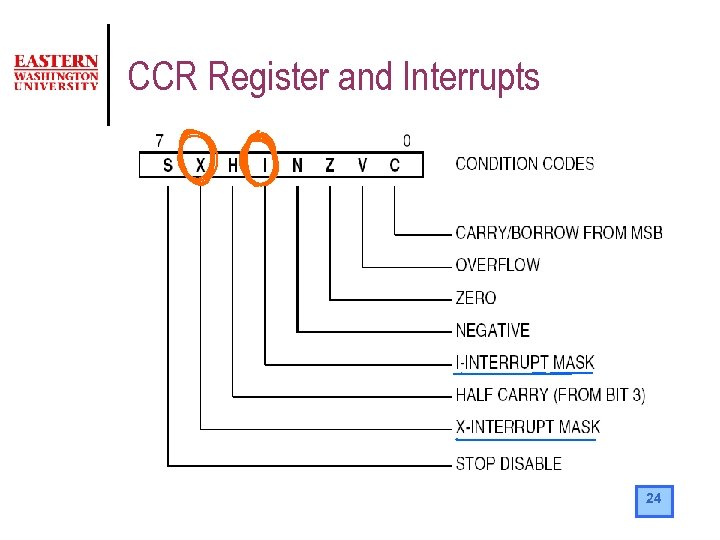
 CCR Register and Interrupts · · · Most interrupts are maskable by the I bit in the CCR. If the I bit is set, all the associated interrupts are masked. The SEI instruction set the I bit of the CCR. It disables interrupt globally. The CLI instruction clear the I bit of the CCR. It enables interrupt globally. To mask only some of the interrupts covered by the I bit, the I bit is cleared using the CLI instruction and then each interrupt is individually masked by writing to the associated control register. 23
CCR Register and Interrupts · · · Most interrupts are maskable by the I bit in the CCR. If the I bit is set, all the associated interrupts are masked. The SEI instruction set the I bit of the CCR. It disables interrupt globally. The CLI instruction clear the I bit of the CCR. It enables interrupt globally. To mask only some of the interrupts covered by the I bit, the I bit is cleared using the CLI instruction and then each interrupt is individually masked by writing to the associated control register. 23
 CCR Register and Interrupts 24
CCR Register and Interrupts 24
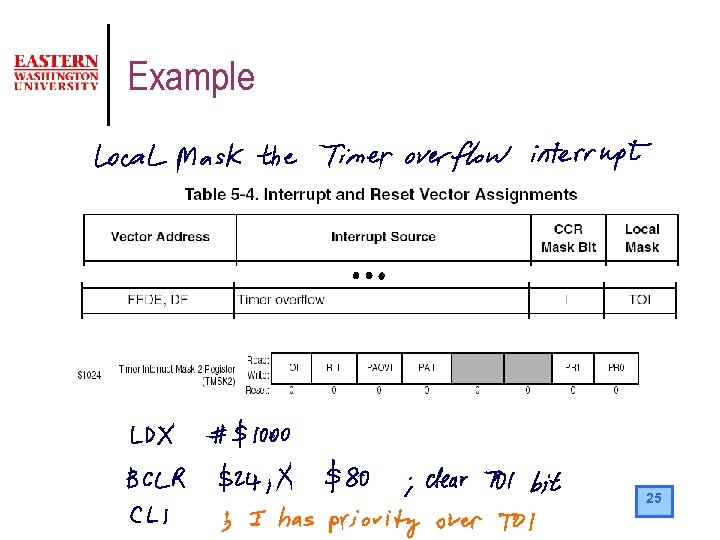 Example 25
Example 25
 Hardware Interrupts l l l Illegal Opcode Trap Non-Maskable Interrupt (XIRQ) Interrupt Request (IRQ) 26
Hardware Interrupts l l l Illegal Opcode Trap Non-Maskable Interrupt (XIRQ) Interrupt Request (IRQ) 26
 Illegal Op code Trap l l A trap is the part of a program that catches an error condition and indicate to the user that an error has occurred. In many cases, the errors are of such a nature that program execution must be aborted. It is up to the programmer to decide what error conditions are to be trapped and how they are to be handled. For example a divide by zero error may be a trap. The 68 HC 11 comes with a built in trapfor illegal op codes. If the fetched code does not correspond to any instruction the illegal op code trap (IOP) interrupt takes place. What the IOP interrupt routine should do depends on the application. 27
Illegal Op code Trap l l A trap is the part of a program that catches an error condition and indicate to the user that an error has occurred. In many cases, the errors are of such a nature that program execution must be aborted. It is up to the programmer to decide what error conditions are to be trapped and how they are to be handled. For example a divide by zero error may be a trap. The 68 HC 11 comes with a built in trapfor illegal op codes. If the fetched code does not correspond to any instruction the illegal op code trap (IOP) interrupt takes place. What the IOP interrupt routine should do depends on the application. 27
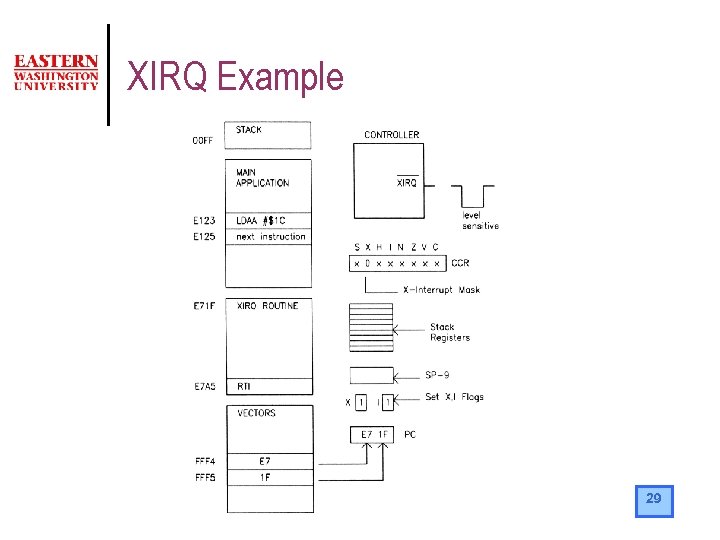
 Non maskable interrupt (XIRQ) l l By default when you power up or reset the microcontroller, XIRQ is masked. That is, the X bit in the CCR is set. To unmask XIRQ, you use the TAP instruction to clear bit X. TPA ; get original CCR ANDA #$BF ; reset bit 6, (X) TAP ; put it back in CCR Once the program has cleared X, executing another TAP will not set X again. The only way to set X again is through a reset. While the service routine is executing, the CPU will set bit X and I. Unless the service routine reset the I bit or the X bit this prevents other interrupts from interfering. When the service routine executes RTI the original CCR contents is recovered. 28
Non maskable interrupt (XIRQ) l l By default when you power up or reset the microcontroller, XIRQ is masked. That is, the X bit in the CCR is set. To unmask XIRQ, you use the TAP instruction to clear bit X. TPA ; get original CCR ANDA #$BF ; reset bit 6, (X) TAP ; put it back in CCR Once the program has cleared X, executing another TAP will not set X again. The only way to set X again is through a reset. While the service routine is executing, the CPU will set bit X and I. Unless the service routine reset the I bit or the X bit this prevents other interrupts from interfering. When the service routine executes RTI the original CCR contents is recovered. 28
 XIRQ Example 29
XIRQ Example 29
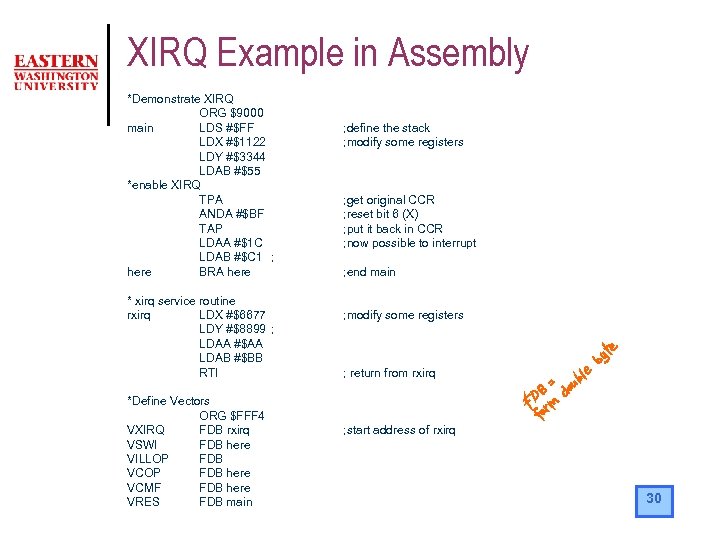 XIRQ Example in Assembly *Demonstrate XIRQ ORG $9000 main LDS #$FF LDX #$1122 LDY #$3344 LDAB #$55 *enable XIRQ TPA ANDA #$BF TAP LDAA #$1 C LDAB #$C 1 ; here BRA here * xirq service routine rxirq LDX #$6677 LDY #$8899 ; LDAA #$AA LDAB #$BB RTI *Define Vectors ORG $FFF 4 VXIRQ FDB rxirq VSWI FDB here VILLOP FDB VCOP FDB here VCMF FDB here VRES FDB main ; define the stack ; modify some registers ; get original CCR ; reset bit 6 (X) ; put it back in CCR ; now possible to interrupt ; end main ; modify some registers ; return from rxirq ; start address of rxirq 30
XIRQ Example in Assembly *Demonstrate XIRQ ORG $9000 main LDS #$FF LDX #$1122 LDY #$3344 LDAB #$55 *enable XIRQ TPA ANDA #$BF TAP LDAA #$1 C LDAB #$C 1 ; here BRA here * xirq service routine rxirq LDX #$6677 LDY #$8899 ; LDAA #$AA LDAB #$BB RTI *Define Vectors ORG $FFF 4 VXIRQ FDB rxirq VSWI FDB here VILLOP FDB VCOP FDB here VCMF FDB here VRES FDB main ; define the stack ; modify some registers ; get original CCR ; reset bit 6 (X) ; put it back in CCR ; now possible to interrupt ; end main ; modify some registers ; return from rxirq ; start address of rxirq 30
 XIRQ Example in C /* XIRQ Example */ unsigned int data; /* data to increment */ void main(void) { data = 0; /* initialize data */ /* setup jump vector */ asm(“ldaa #0 x 7 E”); /*opcode of jump (extended) */ asm(“staa 0 x. F 1”); /* the jump instr. is put at address $00 F 1*/ asm(“ldd #rxirq); asm(“std 0 x. F 2”); /*enable XIRQ */ asm(“tpa”); asm(“anda #0 x. BF”); asm(“tap”); while(1); /* loop forever */ } void rxirq(void) /* interrupt service routine for XIRQ */ { data++; asm(“rti”); } 31
XIRQ Example in C /* XIRQ Example */ unsigned int data; /* data to increment */ void main(void) { data = 0; /* initialize data */ /* setup jump vector */ asm(“ldaa #0 x 7 E”); /*opcode of jump (extended) */ asm(“staa 0 x. F 1”); /* the jump instr. is put at address $00 F 1*/ asm(“ldd #rxirq); asm(“std 0 x. F 2”); /*enable XIRQ */ asm(“tpa”); asm(“anda #0 x. BF”); asm(“tap”); while(1); /* loop forever */ } void rxirq(void) /* interrupt service routine for XIRQ */ { data++; asm(“rti”); } 31
 Interrupt Request (IRQ) l l l Interrupt request is maskable by setting bit 1 in the CCR You can mask IRQ using the instruction SEI You can unmask IRQ using CLI It is also possible to program IRQ to be edge sensitive or level sensitive To make IRQ edge sensitive only you have to set the IRQE bit (bit 5) in the OPTION register (at $1039). Some bits in OPTION are time protected. They can be changed only within the first 64 clock cycles after a reset. 32
Interrupt Request (IRQ) l l l Interrupt request is maskable by setting bit 1 in the CCR You can mask IRQ using the instruction SEI You can unmask IRQ using CLI It is also possible to program IRQ to be edge sensitive or level sensitive To make IRQ edge sensitive only you have to set the IRQE bit (bit 5) in the OPTION register (at $1039). Some bits in OPTION are time protected. They can be changed only within the first 64 clock cycles after a reset. 32
 Interrupt Configuration l l l To set up interrupt operation, it is necessary to do some configuration (“ritual”) During the configuration steps it is prudent to disable interrupts Typically, after configuration is complete, interrupts are enabled 33
Interrupt Configuration l l l To set up interrupt operation, it is necessary to do some configuration (“ritual”) During the configuration steps it is prudent to disable interrupts Typically, after configuration is complete, interrupts are enabled 33
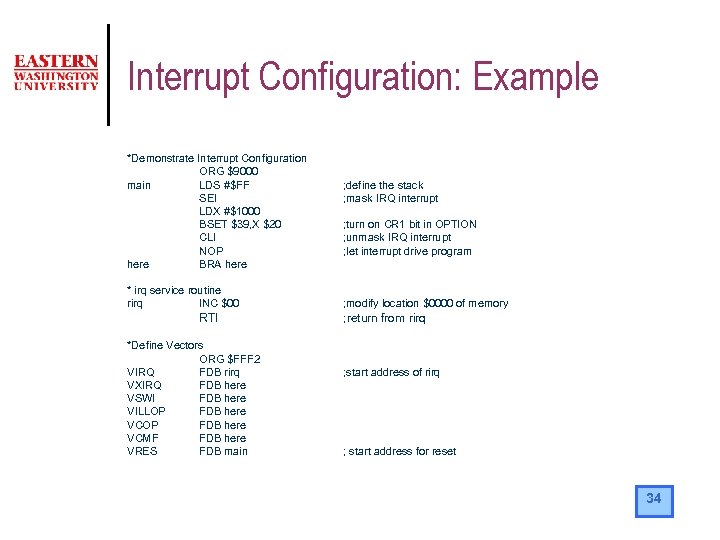 Interrupt Configuration: Example *Demonstrate Interrupt Configuration ORG $9000 main LDS #$FF SEI LDX #$1000 BSET $39, X $20 CLI NOP here BRA here * irq service routine rirq INC $00 RTI *Define Vectors ORG $FFF 2 VIRQ FDB rirq VXIRQ FDB here VSWI FDB here VILLOP FDB here VCMF FDB here VRES FDB main ; define the stack ; mask IRQ interrupt ; turn on CR 1 bit in OPTION ; unmask IRQ interrupt ; let interrupt drive program ; modify location $0000 of memory ; return from rirq ; start address of rirq ; start address for reset 34
Interrupt Configuration: Example *Demonstrate Interrupt Configuration ORG $9000 main LDS #$FF SEI LDX #$1000 BSET $39, X $20 CLI NOP here BRA here * irq service routine rirq INC $00 RTI *Define Vectors ORG $FFF 2 VIRQ FDB rirq VXIRQ FDB here VSWI FDB here VILLOP FDB here VCMF FDB here VRES FDB main ; define the stack ; mask IRQ interrupt ; turn on CR 1 bit in OPTION ; unmask IRQ interrupt ; let interrupt drive program ; modify location $0000 of memory ; return from rirq ; start address of rirq ; start address for reset 34
 Interrupt Polling l l Interrupt polling is a way to determine which one of multiple devices has requested the interrupt. If several devices are all connected through external logic circuitry to the interrupt pin of the microcontroller, there is no immediate way to know which device requested the interrupt. The microcontroller reads the status register of each device to find the one that requested the interrupt. It can then call the appropriate service routine for that device. 35
Interrupt Polling l l Interrupt polling is a way to determine which one of multiple devices has requested the interrupt. If several devices are all connected through external logic circuitry to the interrupt pin of the microcontroller, there is no immediate way to know which device requested the interrupt. The microcontroller reads the status register of each device to find the one that requested the interrupt. It can then call the appropriate service routine for that device. 35
 Software Interrupt l l Software interrupt (SWI) is a special instruction that has several aplications When executed, it behaves like an interrupt by stacking the registers, setting the I bit in the CCR, and fetching the contents of address $FFF 6, $FFF 7. It can be used to simulate hardware interrupts during system development It can be used for debugging programs (setting breakpoints in your program) 36
Software Interrupt l l Software interrupt (SWI) is a special instruction that has several aplications When executed, it behaves like an interrupt by stacking the registers, setting the I bit in the CCR, and fetching the contents of address $FFF 6, $FFF 7. It can be used to simulate hardware interrupts during system development It can be used for debugging programs (setting breakpoints in your program) 36
 CPU Control and Monitoring l l l COP failure reset Clock monitor fail reset The Real Time Interrupt (RTII) generates an interrupt whenever a specifies period of time expire. 37
CPU Control and Monitoring l l l COP failure reset Clock monitor fail reset The Real Time Interrupt (RTII) generates an interrupt whenever a specifies period of time expire. 37
 Real Time Interrupt (RTII) l l Some application do not need to be executing a program all the time but need to be “woken up” when required. The RTII is useful for programs that don’t need to be executing code all the time RTII can be used to “wake up” the program The microcontroller can reduce power consumption while waiting to be woken up. 38
Real Time Interrupt (RTII) l l Some application do not need to be executing a program all the time but need to be “woken up” when required. The RTII is useful for programs that don’t need to be executing code all the time RTII can be used to “wake up” the program The microcontroller can reduce power consumption while waiting to be woken up. 38
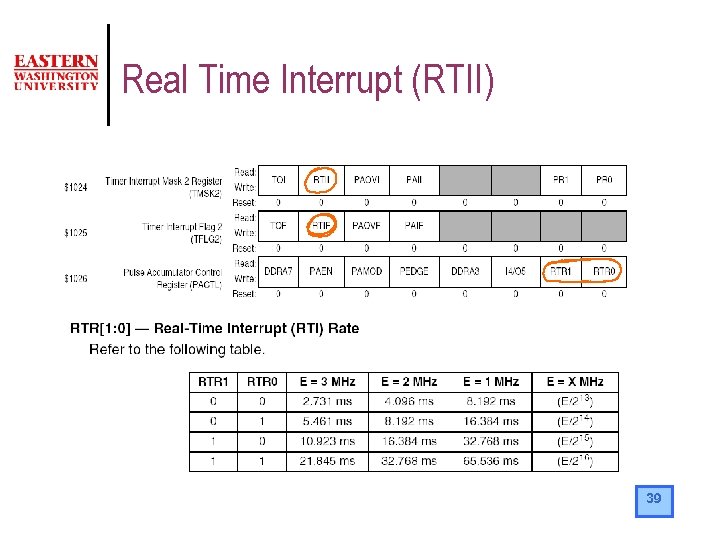 Real Time Interrupt (RTII) 39
Real Time Interrupt (RTII) 39
 WAI and STOP instruction l The WAI stacks the registers and waits for an unmasked interrupt, suspending execution l The effect of executing STOP depends on the S bit in the CCR If the S bit is set. The CPU treats STOP like a NOP and continues on to execute any instructions following the STOP. If the S bit is reset all internal clocks in the CPU halt, thus halting execution. This puts the microcontroller in the state of lowest power consumption. To wake up the controller, a RESET, XIRQ or IRQ is needed. l l l 40
WAI and STOP instruction l The WAI stacks the registers and waits for an unmasked interrupt, suspending execution l The effect of executing STOP depends on the S bit in the CCR If the S bit is set. The CPU treats STOP like a NOP and continues on to execute any instructions following the STOP. If the S bit is reset all internal clocks in the CPU halt, thus halting execution. This puts the microcontroller in the state of lowest power consumption. To wake up the controller, a RESET, XIRQ or IRQ is needed. l l l 40


