6614289e3a0901347a4dd6bba21c16cf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

Research: Theory, Method, Practice Stefan Arnborg, KTH

Courses FD 3001: 7. 5 hp DA 2205: 3 hp of 7. 5 Examination: Presence on lectures with external lecturer Homework: 2 papers: DA 2205: 2 from list FDD 3001: 2 from list, except 1 and 2 1: Self-presentation 2: Press Release 3: Grant Application 4: Paper Analysis 5: Fraud Investigation 6: Proposal Review 7: Media Event 8: Self presentation and press release 9: Elective (must be approved by me)

Norms of Academic Science: Merton 1942 • C communism (or communitarianism) • U universality: universal knowledge • D disinterestedness: no personal stakes(except honour) • O originality: NEW knowledge • S scepticism: try to falsify • Merton’s context: relation between power and scientist in dictatorships (Hitler, Stalin). Border between society and science demarcated.

Post-Academic Science: Ziman 2000 • • • P proprietarian ( IP, business opportunity) L local: related to local network of stakeholders A authoritarian: hierarchical control C commissioned (researcher is ’consultant’) E expert: role is problem-solver • Ziman’s context: Universities are like any corporations, and output directly economically measurable. Globalization • Etzkowitz: Triple Helix: Academy/Region/Industry

CUDOS, PLACE, or both? Fuller(2000) criticized the idea that an ancient CUDOS system was recently replaced by Mode 2 or PLACE or triple helix, since the two sets of norms have (almost) always co-existed, as they do today with occasional outburst of activity to ‘change the balance’. EXAMPLE: Kaiser Wilhelm Institute, now Fraunhofer Institute.

What is Truth? • Plato: Rationalistic, Cave simile, observations unreliable. Cf Meno. • Aristotle: Deductive truth: What follows from true assumptions is true. Whats opposite can be deductively refuted is true. (cf proof by contradiction, statistical hypothesis tests) Aristotle: Inductive truth: What regularly obtains is true (cf statistical inference) • Peirce: What a community of scholars eventually agrees upon is Truth. • Latour: Something is True if it cannot be resisted, tied into a network of irresistible microsociological relations between humans, ideas and material artefacts. (ANT)

Progress of Science • Accumulation of observations, experiments and theories (Francis Bacon, Comté). Naive positivism. • Theories are prior to observations, the latter Confirm (Carnap) or Falsify (Popper) theories. Logical Positivism • Scientific progress is revolutionary (Kuhn, Feyerabend). Paradigms, or ANYTHING GOES.

Kuhn: Paradigms in Science • Normal Science: Exemplar to take after, filling in gaps, ’goldplating’ • Anomalies: Try to explain anomalies by interpretation of experiments and observations. No rejection of theory • Crisis: Anomalies are serious enough to reject theory and force a new PARADIGM. • Typically, a new paradigm is not universally but only gradually accepted.

Feyerabend - Against Method Science is an essentially anarchistic enterprise The only principle that does not inhibit progress is: ANYTHING GOES Hypotheses contradicting well-confirmed theories give us evidence that cannot be obtained in other ways If there is a driving force in science, it is aesthetics.

Hawthorne and Placebo • Clients of Healers & Homeopathists, subjects in the ‘no-intervention’ group can also see positive changes • Is this pseudoscience? (Kathy Sykes TV programmes) • Brain’s reward system releases signal substances that have the same type of effect as drugs?
Paradigm shifts in mathematics? • Environment: Computer and Biology challenge. Internalized. • Scientific Computing, SIMULATION • Stochastic computations (MCMC) • Neural and bioinspired computation?

This book argues that conceptual metaphor plays a central, defining role in mathematical ideas within the cognitive unconsciousfrom arithmetic and algebra to sets and logic to infinity in all of its forms: transfinite numbers, points at infinity, infinitesimals, and so on.

Is Praxiteles’ work already in the marble? NO: Structure of Science (and Truth) is the outcome of a practice Which claims can be resisted? Which can be made? Which allies can be brought in? Which links resist? Scientific truth defined in centers of calculation and verified in galleries of a community of practice extending through society as an actor network Callon, Latour ca 1985

Lyotard • The post-modern condition: Commissioned work for Montreal Education authority - prophetic • Fight against concept of ’Grand Narrative’ as opposed to complex web of ’micro-narratives’

Goals in Research, sketch: • Humanities: Understanding Phenomena • Social Sciences: Improve society • Natural Science: Predict outcome of experiments • Mathematics: 1: Solve problems - prove theorems 2: Create Landscape in which theorems can be defined and proved.

Qualitative Research • Margaret Mead: Best known (to American public) scientist before Einstein • Coming of Age in Samoa, ≈1925 - controversies settled or not? • Immersion, constructing

Three Inconvenient Germans • Karl Marx (1818 -1883) Class, Organization of Production, Revolution Founder of latest state religions • Friedrich Nietzsche (1844 -1900). Aesthetics revolutionized, existentialist and post-modernity icon • Sigmund Freud (1856 -1938), discoverer of the unconscious

Why Greek science? ? • Well studied and documented • Greek classicism shapes our way of seeing the world. • Greek society cruel: Slaves, Wars, Racism, Oppression of women (i. e. , like Europe)
Thales-585 Anaximander 611 -547 Anaximenes -502 Pythagoras 570 -508 Parmenides 510 Zenon 488 Empedokles 450 Herakleitos 540 -480 Anaxagoras 500 -428 Protagoras 420 Demokritos 460 -370 Sokrates 469 -399, Antisthenes Platon 428 -348 Aristarkos Aristoteles 384 -322 Herodotos 425 Arkimedes -300 E Euklides Appolonius Epikureos 342 -270 Selevkos Epiktetus 50 -125 Hipparkos Poseidonius 100

Theory of Evolution • First account by Anaximandros, including sketch of natural selection • Based on mechanistic view, not Intelligent Design • Restated by Empedocles • Rejected by Aristotle as implausible. Teleological explanation. Important paradim shift (in ’wrong’ direction).

Modern theory of Evolution • Based on careful collection of supporting observations (many of which can also be found in Aristotle: Parts of animals) • Refutable by age of earth (Kelvin could not know about heating by radioactivity ) and lack of understanding of genetics (Mendel’s work had been unnoticed) • Still considered somewhat daring, but (almost) only remaining hypothesis.

Greek Astronomy • • Relied on Eastern knowledge (Persia, India, …) Predict eclipses (Thales, 585 BC) Sizes of earth, moon, the zodiac to within 1% Size of sun : Aristarkos 180 times earth -> Heliocentrism as a plausible model • Poseidonius (teacher of Cicero): Size of sun 6000 tim earth (50% low) es Explanation of tidal water (sun, moon) made possible tidal water tables

Greek Astronomy • • Relied on Eastern knowledge (Persia, India, …) Predict eclipses (Thales, 585 BC) Sizes of earth, moon, the zodiac to within 1% Size of sun : Aristarkos 180 times earth -> Heliocentrism as a plausible model • Poseidonius (teacher of Cicero): Size of sun 6000 tim earth (50% low) es Explanation of tidal water (sun, moon) made possible tidal water tables

Astronomy • Aristotle Hipparkus and Ptolemai geocentrists • Appolonius: Defined both conic sections and the epicycle system. … and in the west? • Copernicus: Sun might be the center because of its majestic appearance? • However, predictions based on heliocentrism inferior • It took more than 100 years before Kepler saved the heliocentric view by using Appolonius conic sections instead of his epicycles. If the heliocentricists had followed a scientific method, they should have rejected their hypothesis.
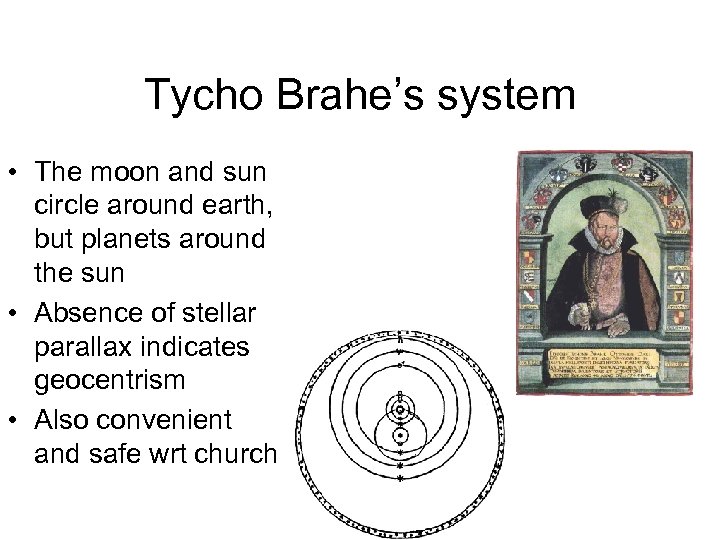
Tycho Brahe’s system • The moon and sun circle around earth, but planets around the sun • Absence of stellar parallax indicates geocentrism • Also convenient and safe wrt church

Atomism • Not unique for Greek philosophers • Democrit, Leukippos, from observations of life cycles and chemical processes • Epikuros combined it with an ethics of no after -life, explicated in one of the great antique works of literature, Lucretius ‘ De Rerum Natura’, On the Order of Nature.

The ‘Dark ages’ • Greek science and literature survived in the Byzantine and Muslim worlds • Applied to rational analysis of theological problems (Ibn Rushd, Ibn Sina, Ibn Khaldun) • Grinding halt after destruction of Baghdad (1258) and conquest of Constantinople (1453) • Translated to Latin from Greek and Arabic (Plato, Aristotle) • Aristotle surpasses Plato as ‘the Philosopher’, treated as semi-god rather than human. • Scholasticism - fascinating, but not in line with course

Islamic Science • The first islamic law schools (ca 800) developed the academic degree system and CV concept (Doctor’s degree, promotion and hat) which were taken over by Bologna and Padua, and still exist

Islamic Scholars • Ibn Sina (Avicenna), ca 1000, practice based medicine (antibiotics, vaccines (inoculation). • Ibn Rushd (Averroes), ca 1200, precursor of scholasticism, mixing ‘axioms’ in the form of Quran statements with observations, deriving new truth by syllogism. Saved Aristotle.

Ibn Khaldun (ca 1360): Muqqadimah • Politician, social scientist, historian, economist. • First statements of market theory, importance of stable institutions, property right, stable currency • First scientific Marxist (without political program): Power and wealth distribution depends on how production is organized • ‘Anyone can have ideas, but only through words and language can you convince’

Newton, (1642 -1727) 1665 - Alchemy 1666 - Calculus 1667 - Fellow, Trinity College 1669 - professor 1682 -4 Principia 1689 - Parlamentarian 1692 - Opticks 1696 - Royal Mint 1703 - Royal Society 1733 - Daniel and Apocalypse First modern or last ancient? ?


Cambridge Wranglers -Created the math you studied: Green, Stokes, Macauly, Routh Maxwell, Larmor, Cunningham, Dirac… -Competitive math examination aimed at ranking candidates for fellowships --Appointments for life with no particular duties -- often awarded at age 20 -25
6614289e3a0901347a4dd6bba21c16cf.ppt