Measurement Scales.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Research Strategies and Designs
Research Strategies and Designs
 Scientific Method This involves… q q q q q isolating the problem -- why this research is important and worth doing literature review concepts operationalization forming research questions and hypothesis/hypotheses building a research design collecting the data analyzing the data collected making generalizations writing report presenting and or publishing results
Scientific Method This involves… q q q q q isolating the problem -- why this research is important and worth doing literature review concepts operationalization forming research questions and hypothesis/hypotheses building a research design collecting the data analyzing the data collected making generalizations writing report presenting and or publishing results
 Qualitative and Quantitative methods of research (Hard and Soft methods) q Quantitative – we can estivate numerical parameters, such as quantity, number, share q Experiments (classical and quasi) q Surveys (standardized questionnaires) q Secondary data analysis q Structured observation q Hall-tests q Ghost purchaser q We can get a deeper understanding of what is happening q Interviews q Focus groups q Participant observation
Qualitative and Quantitative methods of research (Hard and Soft methods) q Quantitative – we can estivate numerical parameters, such as quantity, number, share q Experiments (classical and quasi) q Surveys (standardized questionnaires) q Secondary data analysis q Structured observation q Hall-tests q Ghost purchaser q We can get a deeper understanding of what is happening q Interviews q Focus groups q Participant observation
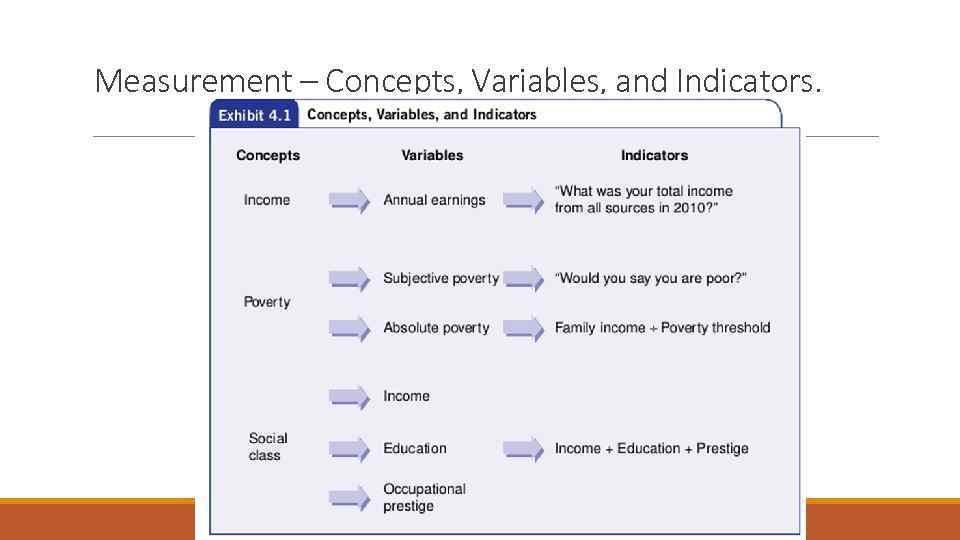 Measurement – Concepts, Variables, and Indicators.
Measurement – Concepts, Variables, and Indicators.
 Measurement – multi-item scale
Measurement – multi-item scale
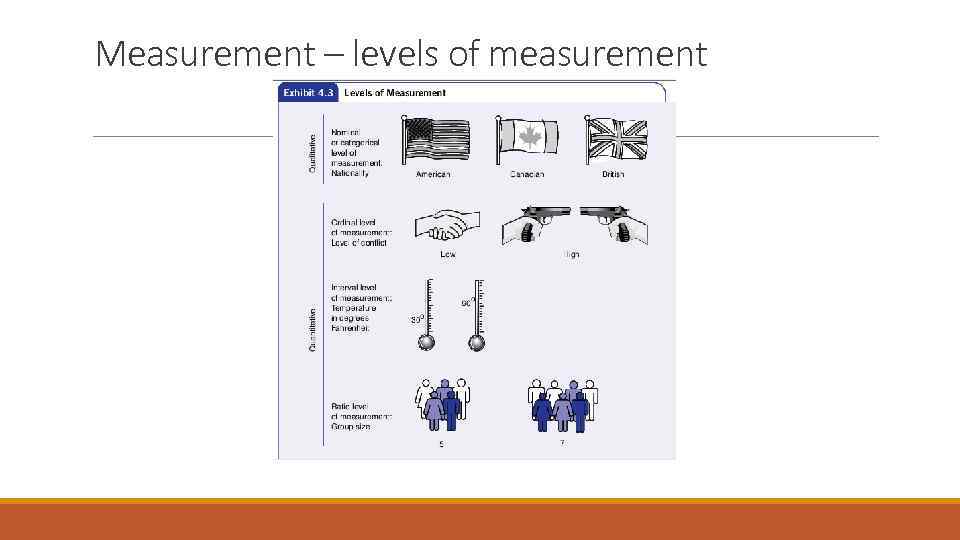 Measurement – levels of measurement
Measurement – levels of measurement
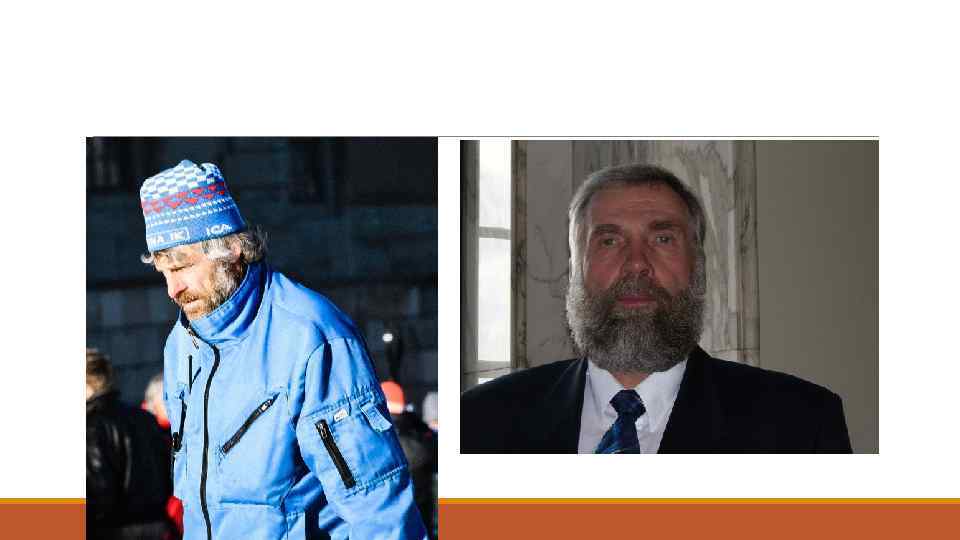

 At the 1980 Winter Olympics in Lake Placid, Wassberg edged out Finland's Juha Mieto by 0. 01 seconds in the 15 km, the closest cross-country skiing race in Olympic history. Wassberg subsequently suggested to Mieto that the gold medal should be split between them "as one-hundredth of a second is nothing in a 15 -kilometer race". This incident led the FIS to change their timing to the nearest one-tenth of a second. It also resulted in an apocryphal urban legend that Wassberg and Mieto's medals were cut in half and re-welded into half-gold, half-silver medals. [2] At the 1984 Winter Olympics, Wassberg beat out fellow Swede Gunde Svan by 4. 9 seconds in the 50 km, the closest margin of victory ever in that event until Giorgio Di Centa(Italy) edged out Yevgeny Dementyev (Russia) by 0. 8 seconds at the 2006 Winter Olympics though the 2006 event was a mass start event while the 1984 event was an interval start event.
At the 1980 Winter Olympics in Lake Placid, Wassberg edged out Finland's Juha Mieto by 0. 01 seconds in the 15 km, the closest cross-country skiing race in Olympic history. Wassberg subsequently suggested to Mieto that the gold medal should be split between them "as one-hundredth of a second is nothing in a 15 -kilometer race". This incident led the FIS to change their timing to the nearest one-tenth of a second. It also resulted in an apocryphal urban legend that Wassberg and Mieto's medals were cut in half and re-welded into half-gold, half-silver medals. [2] At the 1984 Winter Olympics, Wassberg beat out fellow Swede Gunde Svan by 4. 9 seconds in the 50 km, the closest margin of victory ever in that event until Giorgio Di Centa(Italy) edged out Yevgeny Dementyev (Russia) by 0. 8 seconds at the 2006 Winter Olympics though the 2006 event was a mass start event while the 1984 event was an interval start event.
 What we can observe? Physical activity and behavior ◦ How customers move in the supermarket (EKEA decision) Verbal activity ◦ Talks in a line for registration in an airport ◦ Spouses’ talks in a shop Expressive behavior (mimics, intonations, poses, gestures) ◦ Poligraph and 25 th frame ◦ Lie to Me, Paul Ekman) Recoded information (graphical, audio and video) Barcodes on the packages Notes people make at arts exhibitions Наблюдение 2010
What we can observe? Physical activity and behavior ◦ How customers move in the supermarket (EKEA decision) Verbal activity ◦ Talks in a line for registration in an airport ◦ Spouses’ talks in a shop Expressive behavior (mimics, intonations, poses, gestures) ◦ Poligraph and 25 th frame ◦ Lie to Me, Paul Ekman) Recoded information (graphical, audio and video) Barcodes on the packages Notes people make at arts exhibitions Наблюдение 2010
 What we can observe? Spacial parameters and traces ◦ Behavior in elevators, other public places ◦ Arts exhibitions – who comes close to paintings Temporal characteristics (simultaneous or sequential, what time does it take) ◦ Fast-food, registration – how long people have to wait in a line ◦ What time it takes to attract attention Physical objects ◦ ◦ What brands of canned food or clothes respondents have Garbage on the parking lot Наблюдение 2010
What we can observe? Spacial parameters and traces ◦ Behavior in elevators, other public places ◦ Arts exhibitions – who comes close to paintings Temporal characteristics (simultaneous or sequential, what time does it take) ◦ Fast-food, registration – how long people have to wait in a line ◦ What time it takes to attract attention Physical objects ◦ ◦ What brands of canned food or clothes respondents have Garbage on the parking lot Наблюдение 2010
 Advantages of observation v No direct contact is needed v Less distortions, because an object of observation does not interpret his/her actions and motives (not concerned with social desirability). v You do not have to rely on respondents’ memory v We can get data about nonverbal behavior v We can get some kinds of information faster and cheaper compared to other methods v It is quite compatible with other methods (surveys etc. ) Наблюдение 2010
Advantages of observation v No direct contact is needed v Less distortions, because an object of observation does not interpret his/her actions and motives (not concerned with social desirability). v You do not have to rely on respondents’ memory v We can get data about nonverbal behavior v We can get some kinds of information faster and cheaper compared to other methods v It is quite compatible with other methods (surveys etc. ) Наблюдение 2010
 Limitations of observation q We cannot observe psychological process (to learn, what people think). q Sometimes it is difficult to interpret data, we can make mistakes. q We can miss some behaviors, acts, exchanges etc. -- they will be absent in our records. q We can observe only for a limited period of time q An observer could be a prejudiced person q Risk to invade people’s private life. Наблюдение 2010
Limitations of observation q We cannot observe psychological process (to learn, what people think). q Sometimes it is difficult to interpret data, we can make mistakes. q We can miss some behaviors, acts, exchanges etc. -- they will be absent in our records. q We can observe only for a limited period of time q An observer could be a prejudiced person q Risk to invade people’s private life. Наблюдение 2010
 Participant observation q Entering the field – legend q Blanche Geer – “GPA mentality” q Andrei Alexeev – Lenpoligraphmash. q Michael Burawoy -- furniture factory in Syktyvkar q Anna Govorova – “liquid currency” at Svetlana radio-electronics plant q Behaving in the field – making records. q Debriefing and ethics q Presenting and publishing q Advantages and benefits.
Participant observation q Entering the field – legend q Blanche Geer – “GPA mentality” q Andrei Alexeev – Lenpoligraphmash. q Michael Burawoy -- furniture factory in Syktyvkar q Anna Govorova – “liquid currency” at Svetlana radio-electronics plant q Behaving in the field – making records. q Debriefing and ethics q Presenting and publishing q Advantages and benefits.
 Laud Humphreys – Tearoom Trade 1970 q The study is an analysis of homosexual acts taking place in public toilets. q Humphreys observes and describes various social cues (body language, hand language, etc. ) developed and used by participants in those places. q 38% of Humphreys' subjects were neither bisexual nor homosexual; 24% were clearly bisexual; 24% were single and were covert homosexuals, and only 14% corresponded to the popular stereotype of homosexuality - clear members of the gay community interested in primarily homosexual relationships. q Important thesis of Tearoom Trade is the incongruity between the private self and the social self for many of the men engaging in this form of homosexual activity. q Humphreys' rationale was that because of public stigma associated with the homosexual activities in question, and his subjects' desires to keep their activities secret, many were unlikely to allow him an opportunity for observation and follow-up interview were he to reveal himself as a researcher. q Ethical considerations: half of Humphreys’ colleagues left department in protest. (He recoded car license plates and was able to identify his subjects).
Laud Humphreys – Tearoom Trade 1970 q The study is an analysis of homosexual acts taking place in public toilets. q Humphreys observes and describes various social cues (body language, hand language, etc. ) developed and used by participants in those places. q 38% of Humphreys' subjects were neither bisexual nor homosexual; 24% were clearly bisexual; 24% were single and were covert homosexuals, and only 14% corresponded to the popular stereotype of homosexuality - clear members of the gay community interested in primarily homosexual relationships. q Important thesis of Tearoom Trade is the incongruity between the private self and the social self for many of the men engaging in this form of homosexual activity. q Humphreys' rationale was that because of public stigma associated with the homosexual activities in question, and his subjects' desires to keep their activities secret, many were unlikely to allow him an opportunity for observation and follow-up interview were he to reveal himself as a researcher. q Ethical considerations: half of Humphreys’ colleagues left department in protest. (He recoded car license plates and was able to identify his subjects).
 Наблюдение 2010
Наблюдение 2010
 Issues in Qualitative Research Generalisability Enriching understanding and generating theory Validity Often concerns: honesty, credibility, richness, authenticity, Fuzzy Generalisations depth, scope, subjectivity, strength of Falsification feeling, capturing ◦ Using extreme uniqueness, idiographic (most/least likely to fit statements, fidelity to theory), atypical, and participants’ accounts critical cases Reliability Dependability, consistency, comprehensiveness, ‘checkability’, empathy, uniqueness, explanatory and descriptive potential, confirmability, “neutrality”, applicability, transferability
Issues in Qualitative Research Generalisability Enriching understanding and generating theory Validity Often concerns: honesty, credibility, richness, authenticity, Fuzzy Generalisations depth, scope, subjectivity, strength of Falsification feeling, capturing ◦ Using extreme uniqueness, idiographic (most/least likely to fit statements, fidelity to theory), atypical, and participants’ accounts critical cases Reliability Dependability, consistency, comprehensiveness, ‘checkability’, empathy, uniqueness, explanatory and descriptive potential, confirmability, “neutrality”, applicability, transferability
 Strategies for. . . GENERALISABILITY Careful, sometimes strategic selection of cases Intense participation and effort to develop valid and rich descriptions Challenging theories, conventional wisdom, and prior assumptions Letting the case “talk back” – sensitivity to diversity, uniqueness, history and context RELIABILITY Good preparation for fieldwork Piloting and peer and participant debriefing Justification of decisions (e. g. transcription; recording; types of questions; extent of ‘mapping’ and ‘summarising’ in case presentation etc. ) Awareness of transcriber selectivity and other limitations Independent audits and audit trails Multiple coders
Strategies for. . . GENERALISABILITY Careful, sometimes strategic selection of cases Intense participation and effort to develop valid and rich descriptions Challenging theories, conventional wisdom, and prior assumptions Letting the case “talk back” – sensitivity to diversity, uniqueness, history and context RELIABILITY Good preparation for fieldwork Piloting and peer and participant debriefing Justification of decisions (e. g. transcription; recording; types of questions; extent of ‘mapping’ and ‘summarising’ in case presentation etc. ) Awareness of transcriber selectivity and other limitations Independent audits and audit trails Multiple coders
 Strategies for validity Prolonged engagement in the field Making contrast/comparisons Persistent observation Ruling out spurious relations Rich and thick description Following up surprises Leaving an audit trail Using extreme cases Reflexive diaries Assessing rival explanations Respondent validation Triangulation Peer debriefing Back translation Checking for researcher effects
Strategies for validity Prolonged engagement in the field Making contrast/comparisons Persistent observation Ruling out spurious relations Rich and thick description Following up surprises Leaving an audit trail Using extreme cases Reflexive diaries Assessing rival explanations Respondent validation Triangulation Peer debriefing Back translation Checking for researcher effects

 Some issues in Quantitative Research Generalisability Can findings be generalised outside the sample? Importance of sample Validity Reliability Fundamentally concerned Measurement validity, face with the reliability of validity, concurrent validity measures. predictive validity, construct validity, convergent validity Stability Role of confidence intervals Dependability Replicability Concept of statistical probability Internal reliability Inter-observer consistency
Some issues in Quantitative Research Generalisability Can findings be generalised outside the sample? Importance of sample Validity Reliability Fundamentally concerned Measurement validity, face with the reliability of validity, concurrent validity measures. predictive validity, construct validity, convergent validity Stability Role of confidence intervals Dependability Replicability Concept of statistical probability Internal reliability Inter-observer consistency
 Strategies for. . . Generalisability Validity Careful sample selection. Appropriate instrumentation, Random selection can be useful because of known properties. Appropriate treatment of statistical data Be cautious with making inferences. Careful sampling At best strive to minimize invalidity and maximize validity Reliability Test – Retest Chronbach Alpha Multiple coders Consider the consistency of your observations. Controllable, predictable, consistent, replicable. (Cohen et al. 2007)
Strategies for. . . Generalisability Validity Careful sample selection. Appropriate instrumentation, Random selection can be useful because of known properties. Appropriate treatment of statistical data Be cautious with making inferences. Careful sampling At best strive to minimize invalidity and maximize validity Reliability Test – Retest Chronbach Alpha Multiple coders Consider the consistency of your observations. Controllable, predictable, consistent, replicable. (Cohen et al. 2007)

 Whyte's insights • He had to learn how to conduct himself. • Acceptance in the district depended on the personal relationships. • If he was alright, then his project was alright. • Not to argue with people or pass moral judgements upon them. • Avoid expressing opinions on sensitive topics. • One has to learn when to ask questions and when not to question, as well as what questions to ask. • You'll learn the answers in the long run without even having to ask the question. • You can learn the answers to questions that you would not even have had the sense to ask. • Notice that acting on these insights all contributed to increasing the validity of Whyte's work and they can be claimed as positive benefits associated with qualitative research methods.
Whyte's insights • He had to learn how to conduct himself. • Acceptance in the district depended on the personal relationships. • If he was alright, then his project was alright. • Not to argue with people or pass moral judgements upon them. • Avoid expressing opinions on sensitive topics. • One has to learn when to ask questions and when not to question, as well as what questions to ask. • You'll learn the answers in the long run without even having to ask the question. • You can learn the answers to questions that you would not even have had the sense to ask. • Notice that acting on these insights all contributed to increasing the validity of Whyte's work and they can be claimed as positive benefits associated with qualitative research methods.
 Participant and nonparticipant (direct) observation q Nonparticipant observation is studying a social process without becoming a part of it in any way.
Participant and nonparticipant (direct) observation q Nonparticipant observation is studying a social process without becoming a part of it in any way.


