dd388472392f5ce7a27b9e09d9858c26.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

Research on the Relationship between Cause. Related marketing and Consumer’s Purchase Intention: Empirical Evidence from Taiwan LOGO Presenter: Yu-Chi Lai Instructor:Dr. TZU-CHING CHEN June 02, 2010

Content I. Introduction II. Literature Review III. Methodology 2 LOGO
Introduction Background Motivation Purpose of Research 3 LOGO

Background In recent years, marketing campaigns and promotions with a social dimension have become more visible. (Mason, 2002) 4 LOGO

Background Consumers are becoming more concerned with corporate social responsibility and firms are finding that consumers’ perceptions of this responsibility influence their beliefs and attitudes about new products manufactured by a company. (Brown and Dacin, 1997) 5 LOGO

Motivation Promotions in which the amount is given to a charity by a firm is somehow tied to the purchase intention of consumers. (Varadarajan and Menon, 1988) 6 LOGO

Motivation In this context, companies have discovered the importance of strategic social alliances, particularly in the form of cause-related marketing (CRM) programs. (IEG Sponsorship Report, 2006) 7 LOGO

Purpose of Research Most of the past studies on CRM have been undertaken in the context of western countries, such as USA. Virtually no serious study has attempted to validate theory and practice about CRM in Taiwan context. 8 LOGO

Purpose of Research This research aims to examine the relationship between cause-related marketing (CRM) and purchase intention and focus on the empirical evidence from Taiwan. 9 LOGO

Literature Review Cause-Related Marketing Purchase Intention Research Model and Hypothesis 10 LOGO

Cause-Related Marketing v CRM is the transaction where firms contribute a specified amount to a designated cause when consumers buy the company’s products. (Cornwell and Coote, 2005) 11 LOGO

Cause-Related Marketing v CRM is the process of formulating and implementing marketing activities that are characterized by an offer from the firm to contribute a specified amount to a designated cause when customers engage in revenueproving exchanges that satisfy organizational and individual objectives. (Cara et al. , 2007) 12 LOGO

Cause-Related Marketing v Evidence to date suggests that CRM may provide better results than discounting prices or increasing promotional spend by up to 20 percent. (Roy, 2004) 13 LOGO

Purchase Intention v Purchase intention is one type of judgment about how an individual intends to buy a specific brand. (Poddar et al. , 2009) 14 LOGO

Purchase Intention v It is important to understand customers’ purchase intentions because customers’ behavior can usually be predicted by their intention. (Billy et al. , 2008) 15 LOGO

Purchase Intention v Given that the cost of retaining an existing customer is less expensive than prospecting for a new customer, purchase intention is a very important consideration for marketers. (Monroe, 1999) 16 LOGO
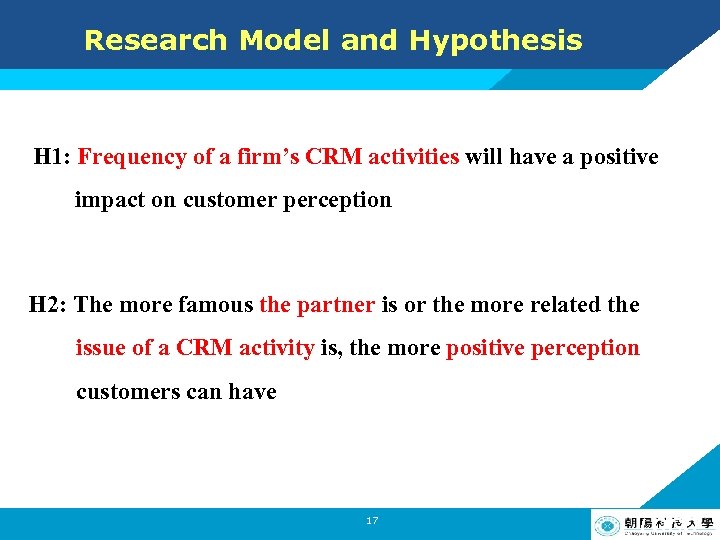
Research Model and Hypothesis H 1: Frequency of a firm’s CRM activities will have a positive impact on customer perception H 2: The more famous the partner is or the more related the issue of a CRM activity is, the more positive perception customers can have 17 LOGO
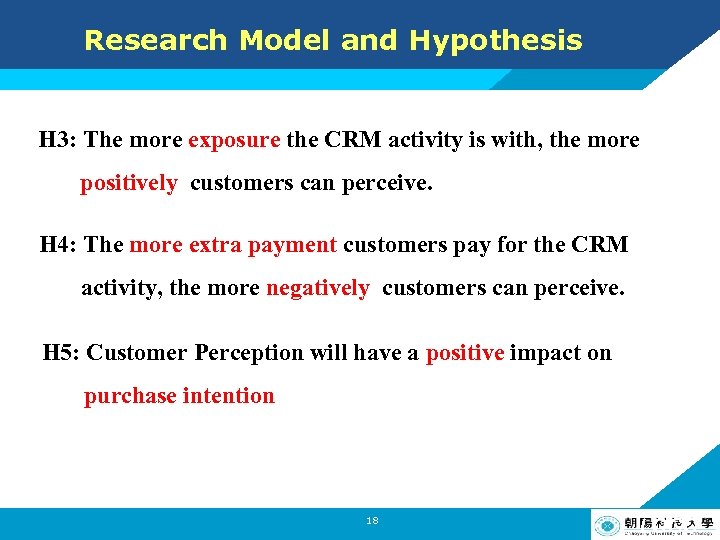
Research Model and Hypothesis H 3: The more exposure the CRM activity is with, the more positively customers can perceive. H 4: The more extra payment customers pay for the CRM activity, the more negatively customers can perceive. H 5: Customer Perception will have a positive impact on purchase intention 18 LOGO
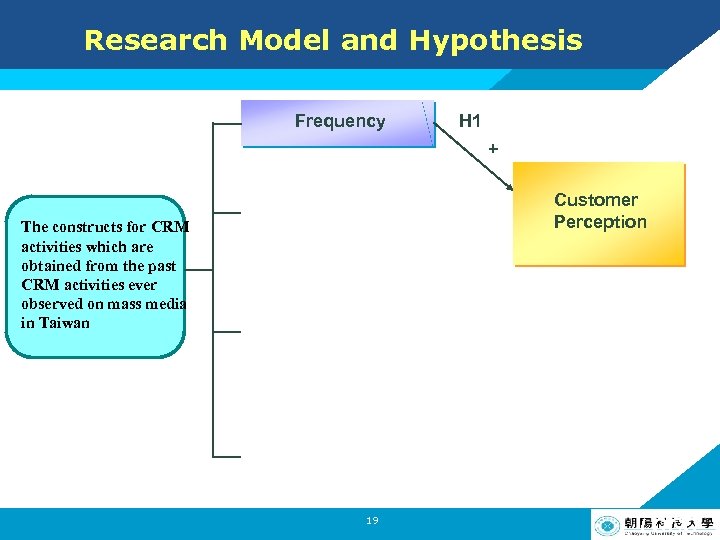
Research Model and Hypothesis Frequency H 1 + Customer Perception The constructs for CRM activities which are obtained from the past CRM activities ever observed on mass media in Taiwan 19 LOGO
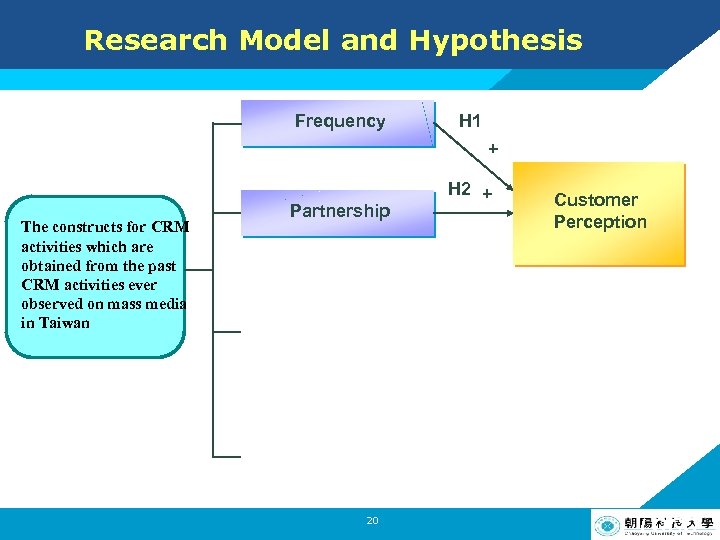
Research Model and Hypothesis Frequency H 1 + The constructs for CRM activities which are obtained from the past CRM activities ever observed on mass media in Taiwan Partnership 20 H 2 + Customer Perception LOGO
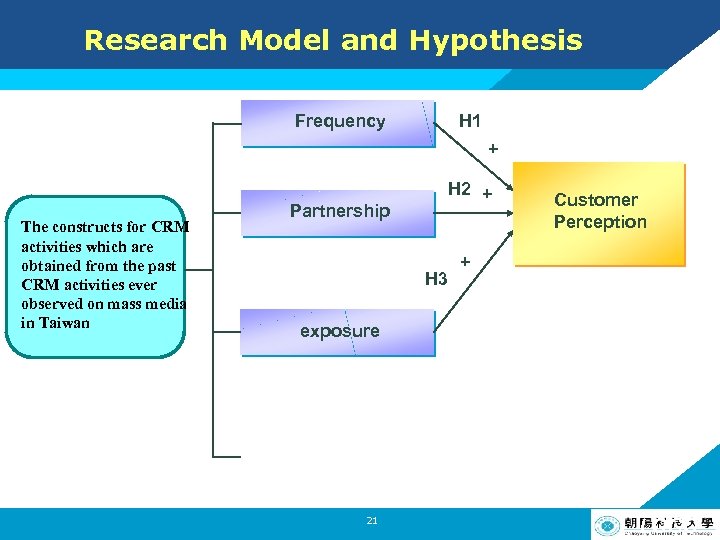
Research Model and Hypothesis Frequency H 1 + The constructs for CRM activities which are obtained from the past CRM activities ever observed on mass media in Taiwan Partnership H 2 + H 3 Customer Perception + exposure 21 LOGO
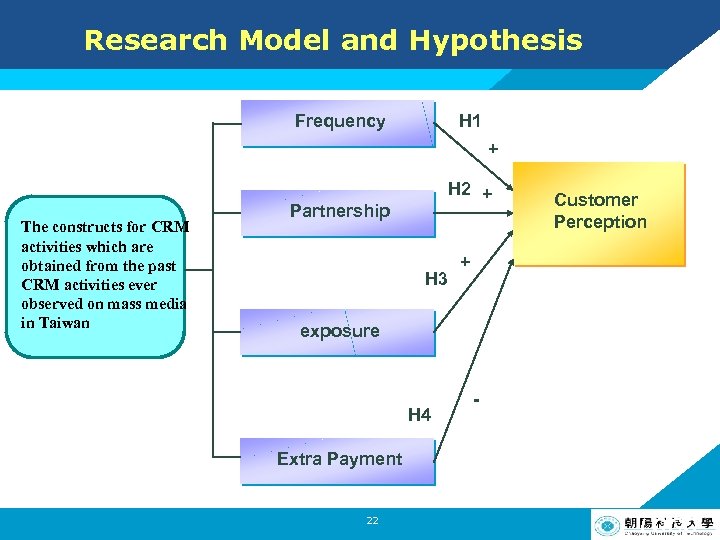
Research Model and Hypothesis Frequency H 1 + The constructs for CRM activities which are obtained from the past CRM activities ever observed on mass media in Taiwan H 2 + Partnership H 3 Customer Perception + exposure H 4 - Extra Payment 22 LOGO
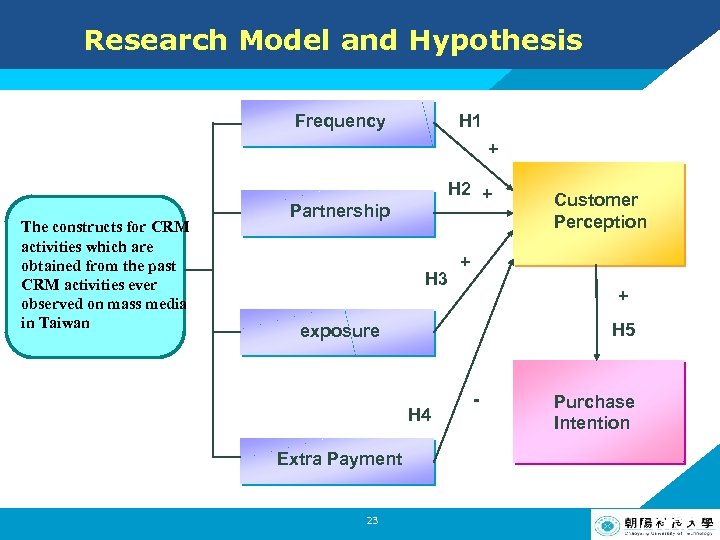
Research Model and Hypothesis Frequency H 1 + The constructs for CRM activities which are obtained from the past CRM activities ever observed on mass media in Taiwan H 2 + Partnership H 3 Customer Perception + + H 5 exposure H 4 - Purchase Intention Extra Payment 23 LOGO
Methodology Data Collection Instrument Estimation Methods 24 LOGO
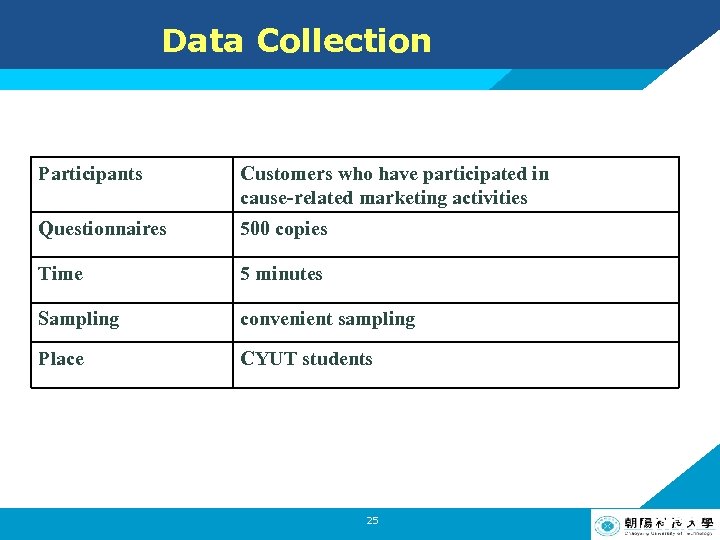
Data Collection Participants Customers who have participated in cause-related marketing activities Questionnaires 500 copies Time 5 minutes Sampling convenient sampling Place CYUT students 25 LOGO
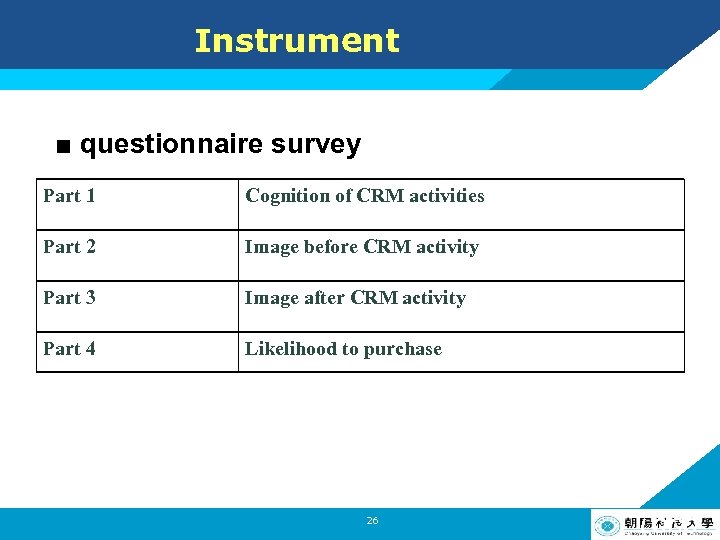
Instrument ■ questionnaire survey Part 1 Cognition of CRM activities Part 2 Image before CRM activity Part 3 Image after CRM activity Part 4 Likelihood to purchase 26 LOGO
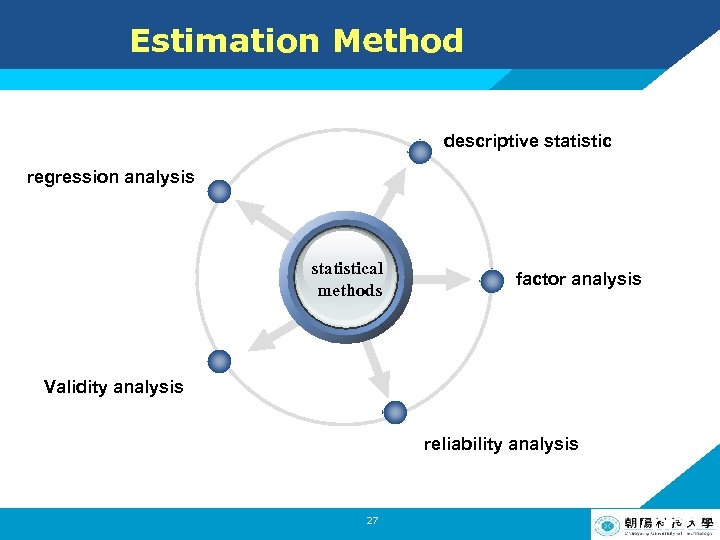
Estimation Method descriptive statistic Add Your Text regression analysis statistical methods factor analysis Validity analysis reliability analysis 27 LOGO

LOGO
dd388472392f5ce7a27b9e09d9858c26.ppt