08cbd9618c21331bf9f68dea5d1b1f4e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
 Research Methods for the Social Sciences: An Introductory Course March 1 st, 2010 – More on Design: Causality Division on Addictions, Cambridge Health Alliance Harvard Medical School
Research Methods for the Social Sciences: An Introductory Course March 1 st, 2010 – More on Design: Causality Division on Addictions, Cambridge Health Alliance Harvard Medical School
 Agenda n Revisiting Research Design – Experimental vs. Quasi-Experimental – Longitudinal Designs n Prevalence vs. Incidence / Individual Trajectories n Moderation and Mediation n Sample Studies
Agenda n Revisiting Research Design – Experimental vs. Quasi-Experimental – Longitudinal Designs n Prevalence vs. Incidence / Individual Trajectories n Moderation and Mediation n Sample Studies
 Caveat: Association Does Not Equal Causation Correlate Does Not Equal Determinant
Caveat: Association Does Not Equal Causation Correlate Does Not Equal Determinant

 MMR – Autism Link?
MMR – Autism Link?
 Correlation vs. Experiment n Correlational research – Goal: To describe relationship between two or more variables. – NO CAUSALITY n Experimental research – Goal: Cause-and-effect relationship between variables Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
Correlation vs. Experiment n Correlational research – Goal: To describe relationship between two or more variables. – NO CAUSALITY n Experimental research – Goal: Cause-and-effect relationship between variables Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
 Does Caffeine Increase Blood Pressure? n WRONG Approach – Ask participants (or observe) how many cups of coffee they drink – Measure blood pressure – Calculate the correlation coefficient Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides n RIGHT Approach – Manipulate amount of coffee § Experimental group – drink § Control group – do not drink – Random group assignment – Test difference between groups
Does Caffeine Increase Blood Pressure? n WRONG Approach – Ask participants (or observe) how many cups of coffee they drink – Measure blood pressure – Calculate the correlation coefficient Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides n RIGHT Approach – Manipulate amount of coffee § Experimental group – drink § Control group – do not drink – Random group assignment – Test difference between groups
 Properties of an Experiment Manipulate at least 1 independent variable 2. Assign participants to the various conditions in a way that assures their initial equivalence 3. Control extraneous variables 1. Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
Properties of an Experiment Manipulate at least 1 independent variable 2. Assign participants to the various conditions in a way that assures their initial equivalence 3. Control extraneous variables 1. Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
 Assignment of Participants to Conditions n Simple random assignment (Between Group) – Every participant has equal probability of being placed in any experimental condition. n Matched Random assignment (Between Group) – Participants are assigned to groups based on their score on a relevant measure. n Repeated measures (Within group) – Same participant is assigned to different conditions. Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
Assignment of Participants to Conditions n Simple random assignment (Between Group) – Every participant has equal probability of being placed in any experimental condition. n Matched Random assignment (Between Group) – Participants are assigned to groups based on their score on a relevant measure. n Repeated measures (Within group) – Same participant is assigned to different conditions. Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
 Control Extraneous Variables n Eliminate or hold constant factors (confounds), other than IV that may affect the outcomes of the experiment. – If these factors are random, they create noise that can mask any effects – If they vary systematically with condition, they can create confounds Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
Control Extraneous Variables n Eliminate or hold constant factors (confounds), other than IV that may affect the outcomes of the experiment. – If these factors are random, they create noise that can mask any effects – If they vary systematically with condition, they can create confounds Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
 Types of variable n Dependent variables – OBSERVED n Independent variables – MANIPULATED n Control variables – held CONSTANT Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
Types of variable n Dependent variables – OBSERVED n Independent variables – MANIPULATED n Control variables – held CONSTANT Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
 Quasi-Experiment No IV manipulation. 2. No random group assignment. 1. Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
Quasi-Experiment No IV manipulation. 2. No random group assignment. 1. Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
 Type 1. Pretest-Posttest Design n O 1 – pretest measure of students’ drug use n X – intervention n O 2 – posttest measure of drug use. O 1 X O 2 Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
Type 1. Pretest-Posttest Design n O 1 – pretest measure of students’ drug use n X – intervention n O 2 – posttest measure of drug use. O 1 X O 2 Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
 Type 1. Pretest-Posttest Design. Weaknesses. n Extraneous variables (History effect) – Something else affected the IV n Maturation effect – Students grew up. n Regression to the mean – The tendency for extreme scores to move, or regress toward the mean (because of measurement error). n Attrition – Some subjects may drop out before posttest. Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
Type 1. Pretest-Posttest Design. Weaknesses. n Extraneous variables (History effect) – Something else affected the IV n Maturation effect – Students grew up. n Regression to the mean – The tendency for extreme scores to move, or regress toward the mean (because of measurement error). n Attrition – Some subjects may drop out before posttest. Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
 Type 2. Simple Interrupted Time -Series Design n O 1 O 2 O 3 O 4 X O 5 O 6 O 7 O 8 n Taking several pretest measures of the DV before introducing an IV. And then, taking several posttest measures. Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
Type 2. Simple Interrupted Time -Series Design n O 1 O 2 O 3 O 4 X O 5 O 6 O 7 O 8 n Taking several pretest measures of the DV before introducing an IV. And then, taking several posttest measures. Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
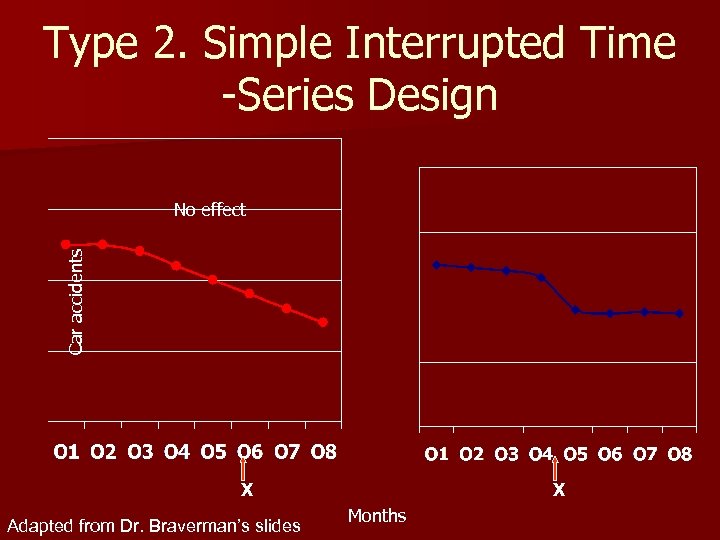 Type 2. Simple Interrupted Time -Series Design Car accidents No effect X Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides X Months
Type 2. Simple Interrupted Time -Series Design Car accidents No effect X Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides X Months
 Type 3. Longitudinal Designs O 1 O 2 O 3 O 4 IV: Time Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
Type 3. Longitudinal Designs O 1 O 2 O 3 O 4 IV: Time Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
 Longitudinal Designs. Weaknesses. 1. Attrition – Moving, lost motivation, mortality, etc. – Attrition can often introduce systematic bias 2. Researchers’ effort, time, money. Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
Longitudinal Designs. Weaknesses. 1. Attrition – Moving, lost motivation, mortality, etc. – Attrition can often introduce systematic bias 2. Researchers’ effort, time, money. Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
 Evaluating Quasi-Experimental Designs. n To conclude causality 1. The presumed causal variable preceded the effect in time. 2. The cause and the effect covary. 3. All other alternative explanations are eliminated. Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
Evaluating Quasi-Experimental Designs. n To conclude causality 1. The presumed causal variable preceded the effect in time. 2. The cause and the effect covary. 3. All other alternative explanations are eliminated. Adapted from Dr. Braverman’s slides
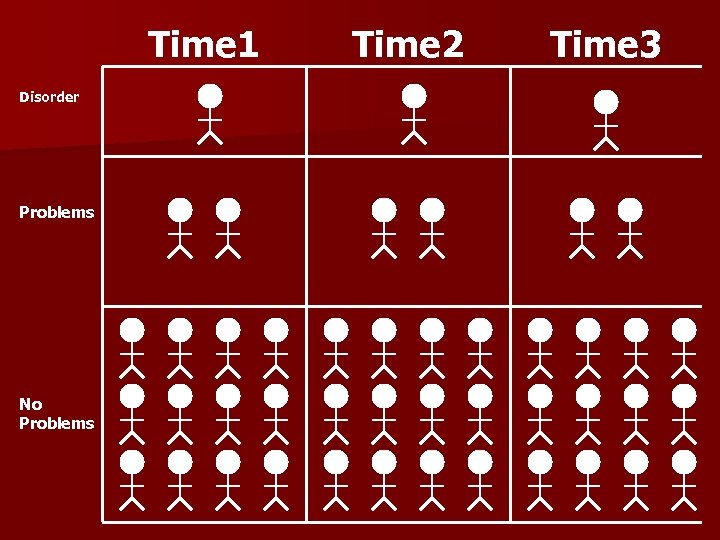
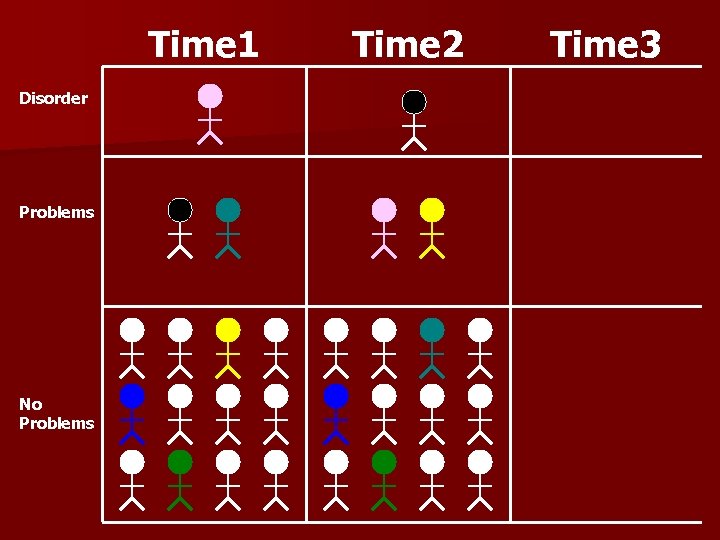
 Aggregate vs. Individual Trajectory Most of the information we collect tells us about the average behavior of groups, but not about individual patterns n Individual trajectory research explores the course of a behavior or disorder within an individual n
Aggregate vs. Individual Trajectory Most of the information we collect tells us about the average behavior of groups, but not about individual patterns n Individual trajectory research explores the course of a behavior or disorder within an individual n
 Cross-Sectional design. Comparison between different age groups. n Weaknesses: n 1. 2. Generation effect No individual development
Cross-Sectional design. Comparison between different age groups. n Weaknesses: n 1. 2. Generation effect No individual development
 Time 1 Disorder Problems No Problems Time 2 Time 3
Time 1 Disorder Problems No Problems Time 2 Time 3
 Time 1 Disorder Problems No Problems Time 2 Time 3
Time 1 Disorder Problems No Problems Time 2 Time 3
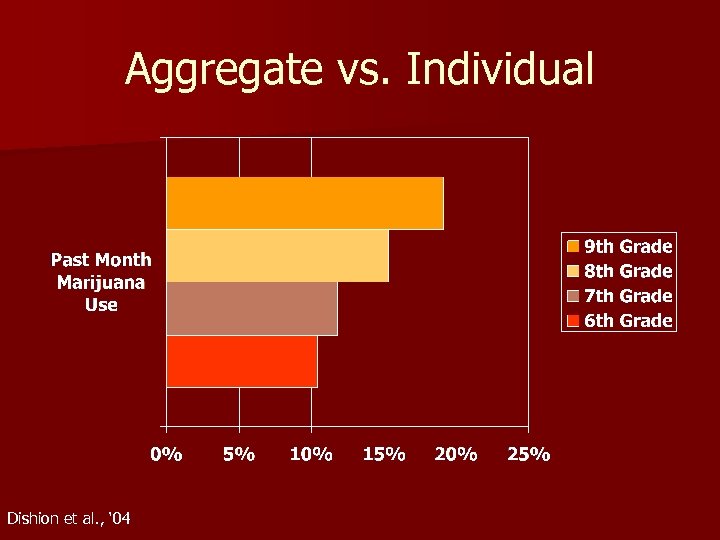 Aggregate vs. Individual Dishion et al. , ‘ 04
Aggregate vs. Individual Dishion et al. , ‘ 04
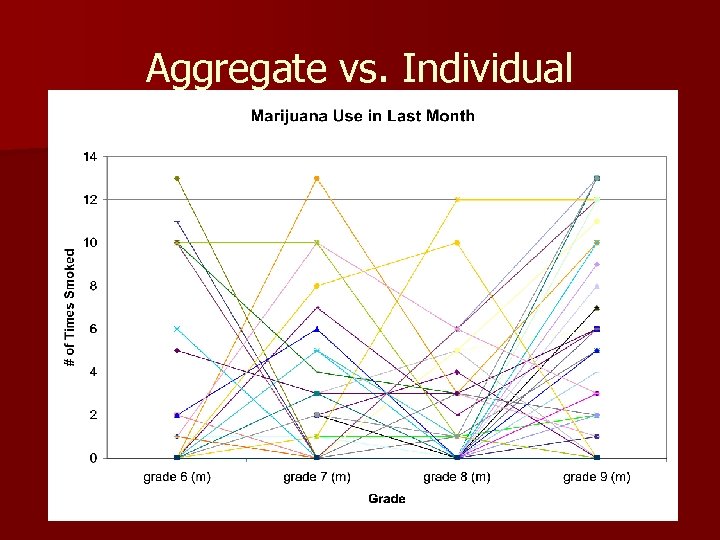 Aggregate vs. Individual
Aggregate vs. Individual
 Moderation and Mediation n Once we have found an effect: X Y, we can ask two questions – What mediates the effect – What moderates the effect
Moderation and Mediation n Once we have found an effect: X Y, we can ask two questions – What mediates the effect – What moderates the effect
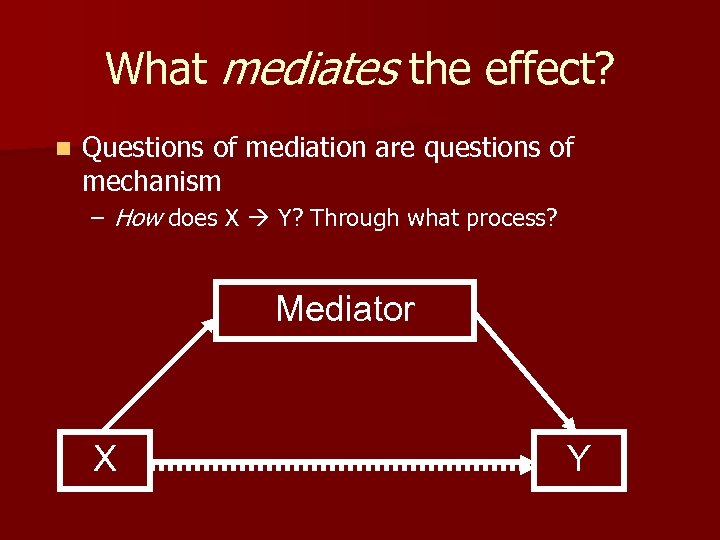 What mediates the effect? n Questions of mediation are questions of mechanism – How does X Y? Through what process? Mediator X Y
What mediates the effect? n Questions of mediation are questions of mechanism – How does X Y? Through what process? Mediator X Y
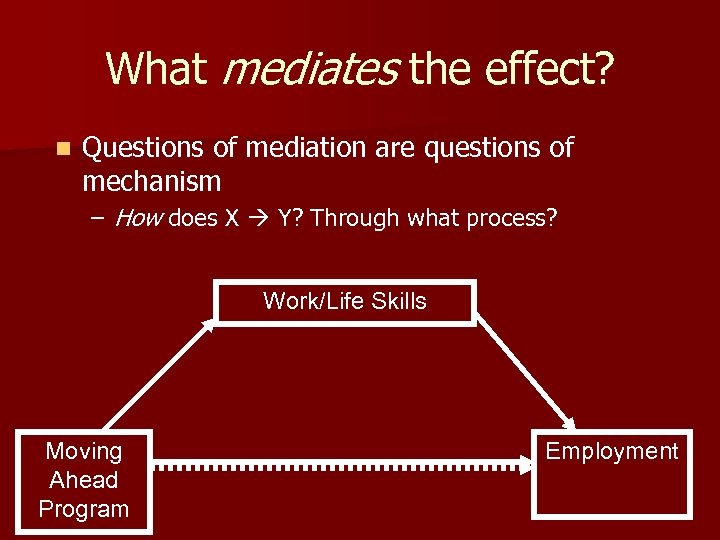 What mediates the effect? n Questions of mediation are questions of mechanism – How does X Y? Through what process? Work/Life Skills Moving Ahead Program Employment
What mediates the effect? n Questions of mediation are questions of mechanism – How does X Y? Through what process? Work/Life Skills Moving Ahead Program Employment
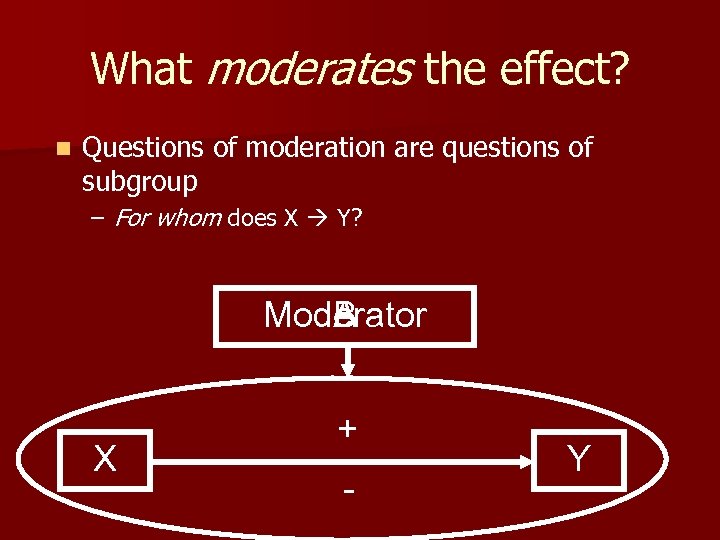 What moderates the effect? n Questions of moderation are questions of subgroup – For whom does X Y? Moderator B A X + - Y
What moderates the effect? n Questions of moderation are questions of subgroup – For whom does X Y? Moderator B A X + - Y
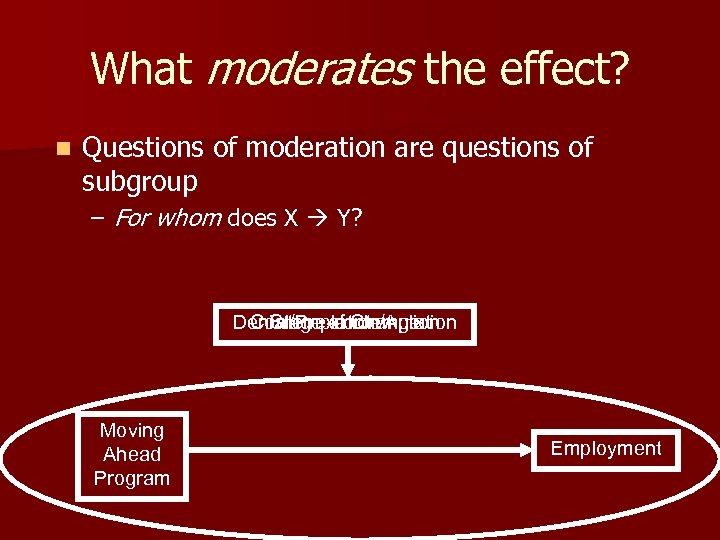 What moderates the effect? n Questions of moderation are questions of subgroup – For whom does X Y? Denial/Pre-contemplation Contemplation/Action Stage of Change Moving Ahead Program Employment
What moderates the effect? n Questions of moderation are questions of subgroup – For whom does X Y? Denial/Pre-contemplation Contemplation/Action Stage of Change Moving Ahead Program Employment
 How Can We Really Know Causality? n Sure, science is okay, but the true measure of truth in our society? . . . WDOT? n WHAT DOES OPRAH THINK?
How Can We Really Know Causality? n Sure, science is okay, but the true measure of truth in our society? . . . WDOT? n WHAT DOES OPRAH THINK?
 Oprah and Jenny Mc. Carthy
Oprah and Jenny Mc. Carthy
 From Oprah Interview n “In recent years, the number of children diagnosed with autism has risen from 1 in every 500 children to 1 in 150—and science has not discovered a reason why. Jenny says she believes that childhood vaccinations may play a part. "What number will it take for people just to start listening to what the mothers of children who have seen autism have been saying for years, which is, 'We vaccinated our baby and something happened. ”
From Oprah Interview n “In recent years, the number of children diagnosed with autism has risen from 1 in every 500 children to 1 in 150—and science has not discovered a reason why. Jenny says she believes that childhood vaccinations may play a part. "What number will it take for people just to start listening to what the mothers of children who have seen autism have been saying for years, which is, 'We vaccinated our baby and something happened. ”
 From Oprah Interview n “Jenny says even before Evan received his vaccines, she tried to talk to her pediatrician about it. "Right before his MMR shot, I said to the doctor, 'I have a very bad feeling about this shot. This is the autism shot, isn't it? ' And he said, 'No, that is ridiculous. It is a mother's desperate attempt to blame something, ' and he swore at me, and then the nurse gave [Evan] the shot, " she says. "And I remember going, 'Oh, God, I hope he's right. ' And soon thereafter —boom—the soul's gone from his eyes. "
From Oprah Interview n “Jenny says even before Evan received his vaccines, she tried to talk to her pediatrician about it. "Right before his MMR shot, I said to the doctor, 'I have a very bad feeling about this shot. This is the autism shot, isn't it? ' And he said, 'No, that is ridiculous. It is a mother's desperate attempt to blame something, ' and he swore at me, and then the nurse gave [Evan] the shot, " she says. "And I remember going, 'Oh, God, I hope he's right. ' And soon thereafter —boom—the soul's gone from his eyes. "
 Freed et al. , 2009 Online survey of parents of children up to age 17 n 1 in 4 parents agree that “some vaccines cause autism in healthy children” n
Freed et al. , 2009 Online survey of parents of children up to age 17 n 1 in 4 parents agree that “some vaccines cause autism in healthy children” n
 Perceived Link n n Autism diagnoses have increased as MMR vaccines have increased Autism develops around the same age as the MMR vaccine is given Autism used to be confined to upper classes and did not cross class lines until vaccination did so Symptoms of autism mirror symptoms of mercury poisoning
Perceived Link n n Autism diagnoses have increased as MMR vaccines have increased Autism develops around the same age as the MMR vaccine is given Autism used to be confined to upper classes and did not cross class lines until vaccination did so Symptoms of autism mirror symptoms of mercury poisoning
 History of the MMR – Autism Link (reviewed by Gerber and Offit, 2009) n Wakefield et al. , 1998 – 12 Consecutively referred patients to pediatric GI department with pervasive developmental disorders – In 8 of these patients, parents or doctors identified the onset of problems as occurring immediately after MMR vaccination. n Gerber & Offit Analysis – Because of the timing of emergence of autism, and the number of children who develop autism, Gerber & Offit point out that the number of children Wakefield saw with autism developing shortly after MMR vaccination could occur by chance.
History of the MMR – Autism Link (reviewed by Gerber and Offit, 2009) n Wakefield et al. , 1998 – 12 Consecutively referred patients to pediatric GI department with pervasive developmental disorders – In 8 of these patients, parents or doctors identified the onset of problems as occurring immediately after MMR vaccination. n Gerber & Offit Analysis – Because of the timing of emergence of autism, and the number of children who develop autism, Gerber & Offit point out that the number of children Wakefield saw with autism developing shortly after MMR vaccination could occur by chance.
 History of the MMR – Autism Link (reviewed by Gerber and Offit, 2009) n Epidemiological Studies that followed – Rates of autism diagnosis did not increase significantly after introduction of MMR vaccine in 1987 – No clustering of autism diagnoses around time of vaccination – Vaccinated and unvaccinated children just as likely to develop autism – There has been an increase in autism diagnosis from 1988 to 1999 though vaccination rates have remained stable.
History of the MMR – Autism Link (reviewed by Gerber and Offit, 2009) n Epidemiological Studies that followed – Rates of autism diagnosis did not increase significantly after introduction of MMR vaccine in 1987 – No clustering of autism diagnoses around time of vaccination – Vaccinated and unvaccinated children just as likely to develop autism – There has been an increase in autism diagnosis from 1988 to 1999 though vaccination rates have remained stable.
 Article 2: Hobfoll et al. , 2009. Trajectories of resilience, resistance, and distress during ongoing terrorism: The case of Jews and Arabs in Israel n Research Question: – What is the prevalence of different mental health trajectories in a population exposed to ongoing terrorism and what predicts those trajectories? n This is a question that attempts to identify psychosocial factors that influence mental health in a given context.
Article 2: Hobfoll et al. , 2009. Trajectories of resilience, resistance, and distress during ongoing terrorism: The case of Jews and Arabs in Israel n Research Question: – What is the prevalence of different mental health trajectories in a population exposed to ongoing terrorism and what predicts those trajectories? n This is a question that attempts to identify psychosocial factors that influence mental health in a given context.
 Article 2: Hobfoll et al. , 2009. Trajectories of resilience, resistance, and distress during ongoing terrorism: The case of Jews and Arabs in Israel n Trajectories – Resistant (no symptoms at T 1 or T 2) – Resilient (symptoms at T 1 but not T 2) – Delayed distress (symptoms at T 1 but not T 2) – Chronic distress (symptoms at both T 1 and T 2)
Article 2: Hobfoll et al. , 2009. Trajectories of resilience, resistance, and distress during ongoing terrorism: The case of Jews and Arabs in Israel n Trajectories – Resistant (no symptoms at T 1 or T 2) – Resilient (symptoms at T 1 but not T 2) – Delayed distress (symptoms at T 1 but not T 2) – Chronic distress (symptoms at both T 1 and T 2)
 Article 2: Hobfoll et al. , 2009. Trajectories of resilience, resistance, and distress during ongoing terrorism: The case of Jews and Arabs in Israel n Hypotheses: – Greater economic resources will distinguish resistant and resilient individuals from distressed individuals. – Greater social support, less resource loss, less exposure, and less positive psychological change will distinguish resistant and resilient individuals from distressed individuals – Non-religious individuals will be more likely to belong to the resistant and resilient trajectories (compared to the distressed trajectory) than religious individuals. – Fewer resources and greater loss of resources will distinguish delayed distress individuals from resistant individuals.
Article 2: Hobfoll et al. , 2009. Trajectories of resilience, resistance, and distress during ongoing terrorism: The case of Jews and Arabs in Israel n Hypotheses: – Greater economic resources will distinguish resistant and resilient individuals from distressed individuals. – Greater social support, less resource loss, less exposure, and less positive psychological change will distinguish resistant and resilient individuals from distressed individuals – Non-religious individuals will be more likely to belong to the resistant and resilient trajectories (compared to the distressed trajectory) than religious individuals. – Fewer resources and greater loss of resources will distinguish delayed distress individuals from resistant individuals.
 Article 2: Hobfoll et al. , 2009. Trajectories of resilience, resistance, and distress during ongoing terrorism: The case of Jews and Arabs in Israel n Sample and Design: – Nationally representative telephone survey of adult Israelis, stratified by region (N = 1, 613) – Initial response rate of 57% at T 1 and 44% of the sample provided data at T 2, so analyses are based on one quarter of potential respondents 2, 830 1, 613 (57%) 897 drop-outs (56%) 709 T 2 Data (44%) 7 insufficient data
Article 2: Hobfoll et al. , 2009. Trajectories of resilience, resistance, and distress during ongoing terrorism: The case of Jews and Arabs in Israel n Sample and Design: – Nationally representative telephone survey of adult Israelis, stratified by region (N = 1, 613) – Initial response rate of 57% at T 1 and 44% of the sample provided data at T 2, so analyses are based on one quarter of potential respondents 2, 830 1, 613 (57%) 897 drop-outs (56%) 709 T 2 Data (44%) 7 insufficient data
 Article 2: Hobfoll et al. , 2009. Trajectories of resilience, resistance, and distress during ongoing terrorism: The case of Jews and Arabs in Israel n Measures: Predictors n Measures: Outcome – Demographics: Age, gender, income, education, ethnicity, religiousness, marital status – Terrorism exposure (# of types: 0, 1, 2+) – Loss of resources (economic or psychosocial) – Post-terrorism growth (e. g. , hope, intimacy, etc. ) – Social support – – – PTSD symptoms Depression symptoms 2+ PTSD or depressive symptoms used as the cut to classify participants as resistant or not at a given timepoint
Article 2: Hobfoll et al. , 2009. Trajectories of resilience, resistance, and distress during ongoing terrorism: The case of Jews and Arabs in Israel n Measures: Predictors n Measures: Outcome – Demographics: Age, gender, income, education, ethnicity, religiousness, marital status – Terrorism exposure (# of types: 0, 1, 2+) – Loss of resources (economic or psychosocial) – Post-terrorism growth (e. g. , hope, intimacy, etc. ) – Social support – – – PTSD symptoms Depression symptoms 2+ PTSD or depressive symptoms used as the cut to classify participants as resistant or not at a given timepoint
 Article 2: Hobfoll et al. , 2009. Trajectories of resilience, resistance, and distress during ongoing terrorism: The case of Jews and Arabs in Israel n Analysis Plan – Descriptives for each trajectory – Logistic Regressions – Resistant vs. Distressed – Gender, ethnicity, religiousness, income, education, psychosocial resource loss at T 1 & T 2, T 2 social support – Resilient vs. Distressed – Ethnicity, income, T 2 psychosocial resource loss, T 2 posttraumatic growth – Delayed Distress vs. Resistant – Education, T 2 psychosocial resource loss
Article 2: Hobfoll et al. , 2009. Trajectories of resilience, resistance, and distress during ongoing terrorism: The case of Jews and Arabs in Israel n Analysis Plan – Descriptives for each trajectory – Logistic Regressions – Resistant vs. Distressed – Gender, ethnicity, religiousness, income, education, psychosocial resource loss at T 1 & T 2, T 2 social support – Resilient vs. Distressed – Ethnicity, income, T 2 psychosocial resource loss, T 2 posttraumatic growth – Delayed Distress vs. Resistant – Education, T 2 psychosocial resource loss


