6a83ca6fdf8e9ed26b5ba9966a27088f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Research Methodology (UNP 0010) Semester 2 – 2012/2013 Lecturer: Dr. Nor Zairah Ab. Rahim INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
Research Methodology (UNP 0010) Semester 2 – 2012/2013 Lecturer: Dr. Nor Zairah Ab. Rahim INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
 • Designed for: – Master by Course • Runs like this - all students : – Attend all 3 meetings; 4 hours in each meeting 1. Meeting 1: Get to know the research topic and interest, lectures on several key area of research methodology Part 1, Discussion. 2. Meeting 2: Library Search, Quiz about topic in Meeting 1, continue with lectures on several key area of research methodology Part 2. 3. Meeting 3: Presentation of Proposal (First 3 Chapters of Thesis) • Assessment: i. tasks in the subject outline, ii. quizzes, iii. Presentation, iv. Written Proposal, v. Overall Participation
• Designed for: – Master by Course • Runs like this - all students : – Attend all 3 meetings; 4 hours in each meeting 1. Meeting 1: Get to know the research topic and interest, lectures on several key area of research methodology Part 1, Discussion. 2. Meeting 2: Library Search, Quiz about topic in Meeting 1, continue with lectures on several key area of research methodology Part 2. 3. Meeting 3: Presentation of Proposal (First 3 Chapters of Thesis) • Assessment: i. tasks in the subject outline, ii. quizzes, iii. Presentation, iv. Written Proposal, v. Overall Participation
 END PRODUCT? • Presentation of Proposal – PPT Slide – Hardcopy Proposal • Corrected Proposal – 15 Pages – PPT Slides For Writing Guidelines, refer to: 1. http: //www. ais. utm. my/zuraini/catego ry/documents-sharing/ 2. http: //sps. utm. my/sps/images/academi cresources/UTM%20 Thesis%20 Manu al%202007. pdf Submit Online to me. Dateline: 15 th March 2013 by 4 PM
END PRODUCT? • Presentation of Proposal – PPT Slide – Hardcopy Proposal • Corrected Proposal – 15 Pages – PPT Slides For Writing Guidelines, refer to: 1. http: //www. ais. utm. my/zuraini/catego ry/documents-sharing/ 2. http: //sps. utm. my/sps/images/academi cresources/UTM%20 Thesis%20 Manu al%202007. pdf Submit Online to me. Dateline: 15 th March 2013 by 4 PM
 Research 4
Research 4
 Research We do research in our every day life! • • • What to wear to office Punctured tyre Broken washing machine Cooking for lunch Finding new home Family problems 5
Research We do research in our every day life! • • • What to wear to office Punctured tyre Broken washing machine Cooking for lunch Finding new home Family problems 5
 Research Task Everyday thinking Identify a problem What to cook for lunch? Gather data Look what is in the fridge Analyse the data Is it enough for everybody in the house? Everybody’s favourite food? Interpret the data Need more ingredient Gather more data Where can I get the ingredient? Simple to cook? Enough time? Analyse the data The cheapest shop? Fresh ingredients? Buy readymade meals? Interpret the data Pak Ali’s shop sell fresh chicken. Everyone in the house loves chicken rendang. But preparing rendang will take a lot of time, tiring, too many ingredients Draw conclusion Go to the stall & buy readymade rendang 6
Research Task Everyday thinking Identify a problem What to cook for lunch? Gather data Look what is in the fridge Analyse the data Is it enough for everybody in the house? Everybody’s favourite food? Interpret the data Need more ingredient Gather more data Where can I get the ingredient? Simple to cook? Enough time? Analyse the data The cheapest shop? Fresh ingredients? Buy readymade meals? Interpret the data Pak Ali’s shop sell fresh chicken. Everyone in the house loves chicken rendang. But preparing rendang will take a lot of time, tiring, too many ingredients Draw conclusion Go to the stall & buy readymade rendang 6
 Research • Creation of new knowledge, using an appropriate process to the satisfaction of the users of the research – learn how to cook rendang, learn the best stall that sell cheap & tasty rendang Everyday thinking Good academic research • Poor data • Incomplete data • Hasty thinking • • Sufficient data sources Appropriate data sources Accurately recorded Properly analysed No hidden assumption Conclusion well-founded Properly presented As judged by the users of the research 7
Research • Creation of new knowledge, using an appropriate process to the satisfaction of the users of the research – learn how to cook rendang, learn the best stall that sell cheap & tasty rendang Everyday thinking Good academic research • Poor data • Incomplete data • Hasty thinking • • Sufficient data sources Appropriate data sources Accurately recorded Properly analysed No hidden assumption Conclusion well-founded Properly presented As judged by the users of the research 7
 What is Research? Research is a human activity based on intellectual investigation and aimed at discovering, interpreting, and revising human knowledge on different aspects of the world. Research is the method used to accumulate scientific knowledge. Roscoe, J. T. (1975) 8 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
What is Research? Research is a human activity based on intellectual investigation and aimed at discovering, interpreting, and revising human knowledge on different aspects of the world. Research is the method used to accumulate scientific knowledge. Roscoe, J. T. (1975) 8 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
 What is Research? Research is any conscious premeditated (planned/ intended/ studied) inquiry – any investigation which seeks to increase one’s knowledge of a given situation. Goldhor, H. (1972) 9 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
What is Research? Research is any conscious premeditated (planned/ intended/ studied) inquiry – any investigation which seeks to increase one’s knowledge of a given situation. Goldhor, H. (1972) 9 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
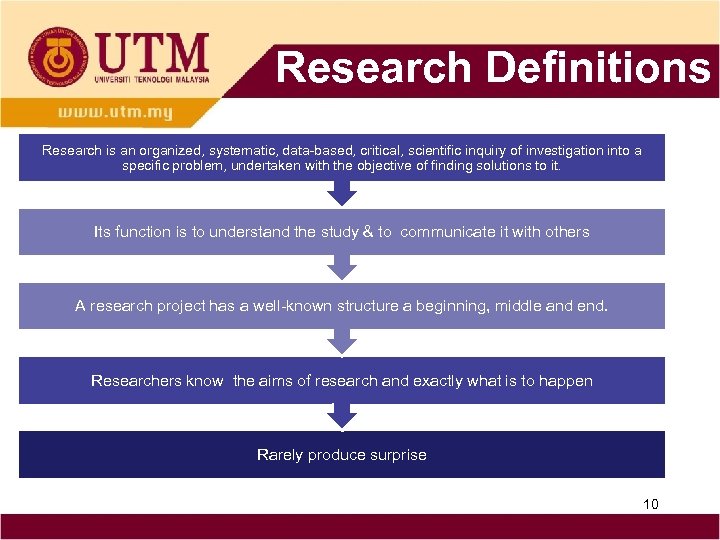 Research Definitions Research is an organized, systematic, data-based, critical, scientific inquiry of investigation into a specific problem, undertaken with the objective of finding solutions to it. Its function is to understand the study & to communicate it with others A research project has a well-known structure a beginning, middle and end. Researchers know the aims of research and exactly what is to happen Rarely produce surprise 10
Research Definitions Research is an organized, systematic, data-based, critical, scientific inquiry of investigation into a specific problem, undertaken with the objective of finding solutions to it. Its function is to understand the study & to communicate it with others A research project has a well-known structure a beginning, middle and end. Researchers know the aims of research and exactly what is to happen Rarely produce surprise 10
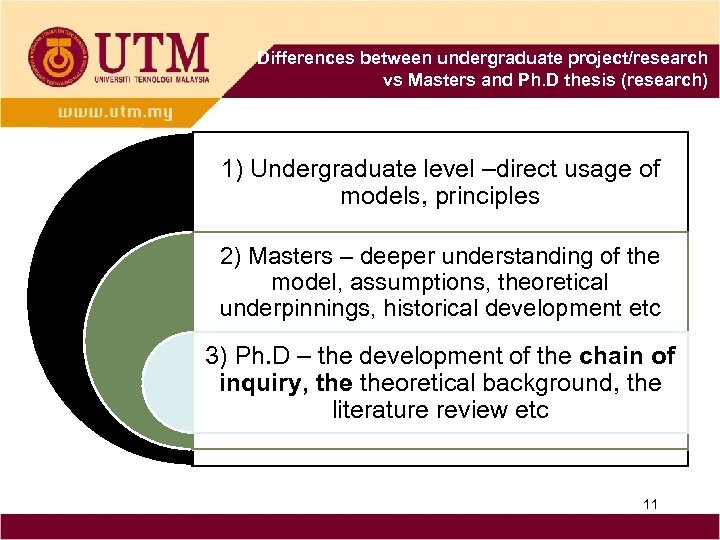 Differences between undergraduate project/research vs Masters and Ph. D thesis (research) 1) Undergraduate level –direct usage of models, principles 2) Masters – deeper understanding of the model, assumptions, theoretical underpinnings, historical development etc 3) Ph. D – the development of the chain of inquiry, theoretical background, the literature review etc 11
Differences between undergraduate project/research vs Masters and Ph. D thesis (research) 1) Undergraduate level –direct usage of models, principles 2) Masters – deeper understanding of the model, assumptions, theoretical underpinnings, historical development etc 3) Ph. D – the development of the chain of inquiry, theoretical background, the literature review etc 11
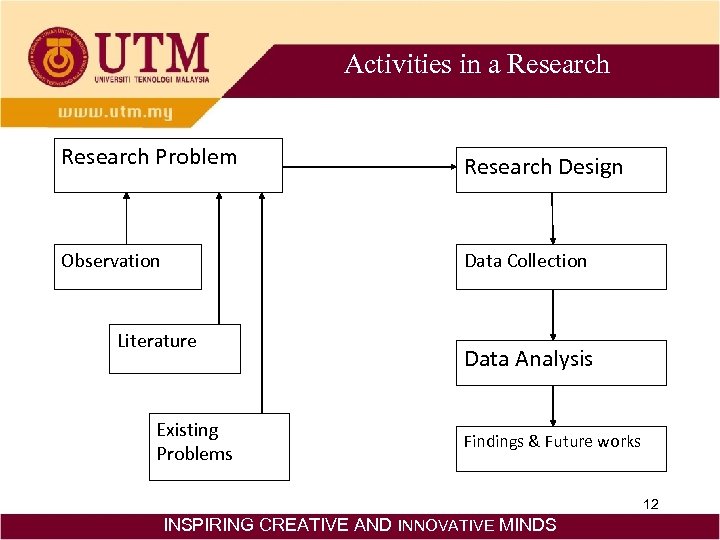 Activities in a Research Problem Research Design Observation Data Collection Literature Existing Problems Data Analysis Findings & Future works 12 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
Activities in a Research Problem Research Design Observation Data Collection Literature Existing Problems Data Analysis Findings & Future works 12 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
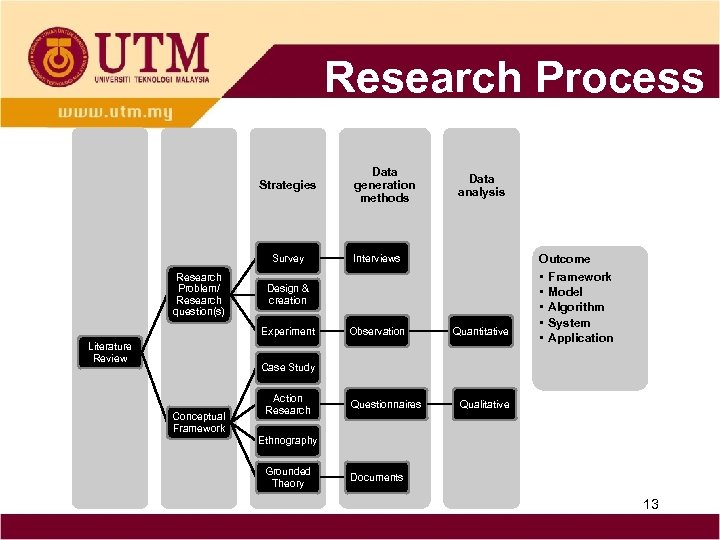 Research Process Strategies Survey Research Problem/ Research question(s) Data analysis Interviews Outcome Design & creation Experiment Literature Review Data generation methods Observation Quantitative • • • Framework Model Algorithm System Application Case Study Conceptual Framework Action Research Questionnaires Qualitative Ethnography Grounded Theory Documents 13
Research Process Strategies Survey Research Problem/ Research question(s) Data analysis Interviews Outcome Design & creation Experiment Literature Review Data generation methods Observation Quantitative • • • Framework Model Algorithm System Application Case Study Conceptual Framework Action Research Questionnaires Qualitative Ethnography Grounded Theory Documents 13
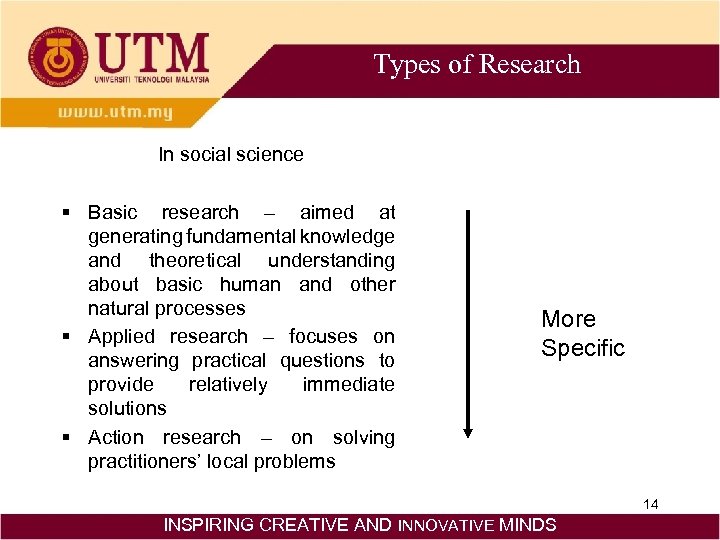 Types of Research In social science § Basic research – aimed at generating fundamental knowledge and theoretical understanding about basic human and other natural processes § Applied research – focuses on answering practical questions to provide relatively immediate solutions § Action research – on solving practitioners’ local problems More Specific 14 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
Types of Research In social science § Basic research – aimed at generating fundamental knowledge and theoretical understanding about basic human and other natural processes § Applied research – focuses on answering practical questions to provide relatively immediate solutions § Action research – on solving practitioners’ local problems More Specific 14 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
 Computing Discipline The Computing Discipline § Hardware – Electrical Engineering, Computer Engineering. § Software – Computer Science, Software engineering. § Organizational – Information Systems Information Technology 15 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
Computing Discipline The Computing Discipline § Hardware – Electrical Engineering, Computer Engineering. § Software – Computer Science, Software engineering. § Organizational – Information Systems Information Technology 15 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
 Categories of Research in CS § Application-Based Research § How knowledge areas of CS can contribute to other fields eg Bioinformatics, Healthcare, tsunami detection system, earthquake prediction system § Theory-Based Research § How knowledge of Cs can be enhanced, improved, formulated eg Fuzzy Set Theory, Pattern recognition. § Industry-based Research § Practical usage eg CAD, QC Dept, Human resource dept. 16 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
Categories of Research in CS § Application-Based Research § How knowledge areas of CS can contribute to other fields eg Bioinformatics, Healthcare, tsunami detection system, earthquake prediction system § Theory-Based Research § How knowledge of Cs can be enhanced, improved, formulated eg Fuzzy Set Theory, Pattern recognition. § Industry-based Research § Practical usage eg CAD, QC Dept, Human resource dept. 16 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
 Reasons for doing research • • • To add to the body of knowledge To solve a problem To find out what happen To find evidence to inform practice To develop a greater understanding of people or their world To predict, plan and control To contribute to other people’s well-being To contribute to personal needs To test or disprove a theory To come out with a better way To understand another person’s point of view To create more interest in the researcher 17
Reasons for doing research • • • To add to the body of knowledge To solve a problem To find out what happen To find evidence to inform practice To develop a greater understanding of people or their world To predict, plan and control To contribute to other people’s well-being To contribute to personal needs To test or disprove a theory To come out with a better way To understand another person’s point of view To create more interest in the researcher 17
 The outcome of the research • • • A new or improved product A new theory A re-interpretation of an existing theory New or improved research tool or technique A new or improved model or perspective An in-depth study of a particular situation An exploration of a topic, area or field A critical analysis Unanticipated outcomes 18
The outcome of the research • • • A new or improved product A new theory A re-interpretation of an existing theory New or improved research tool or technique A new or improved model or perspective An in-depth study of a particular situation An exploration of a topic, area or field A critical analysis Unanticipated outcomes 18
 Sources of research ideas • Suggestions from people • Past research students’ work • Recent conference & journal paper (www. scholar. google. com) • Call for papers • Current issues • Clients needs • To support or refute certain statements e. g: - Green computing is the future - Social networking is the future communication - Baby dumping is the result of new year events 19
Sources of research ideas • Suggestions from people • Past research students’ work • Recent conference & journal paper (www. scholar. google. com) • Call for papers • Current issues • Clients needs • To support or refute certain statements e. g: - Green computing is the future - Social networking is the future communication - Baby dumping is the result of new year events 19
 Never stop writing… • Keep notes of: – Possible research questions – Anything that came across your mind in relation to the research; thoughts problems, insights, plans, emerging analysis, interpretation • Helps to clarify your ideas – esp when you meet your SV • Exercise for your proposal/thesis writing 20
Never stop writing… • Keep notes of: – Possible research questions – Anything that came across your mind in relation to the research; thoughts problems, insights, plans, emerging analysis, interpretation • Helps to clarify your ideas – esp when you meet your SV • Exercise for your proposal/thesis writing 20
 What Research is NOT? • Research is not information gathering – Gathering information from resources such as books or magazines. – No contribution to new knowledge • Research is not the transformation of facts – No contribution to new knowledge although this might make knowledge more accessible. 21 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
What Research is NOT? • Research is not information gathering – Gathering information from resources such as books or magazines. – No contribution to new knowledge • Research is not the transformation of facts – No contribution to new knowledge although this might make knowledge more accessible. 21 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
 Who is a Researcher? • • Matured Ability to focus and concentrate Disciplined Independent Hardworking Innovative & Creative Critical Thinking Available (time) 22 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
Who is a Researcher? • • Matured Ability to focus and concentrate Disciplined Independent Hardworking Innovative & Creative Critical Thinking Available (time) 22 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
 Research Skills • To prepare effective proposal • To generate results • To communicate results : presentation & publication 23 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
Research Skills • To prepare effective proposal • To generate results • To communicate results : presentation & publication 23 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
 Think Like A Researcher • An investigation (an inquiry) to find something out. • Controlled inquiry concerning certain events. • Problem solving. • Application of the scientific approach to study a problem • Systematic , controlled, empirical and critical investigation guided by theory and hypothesis. 24 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
Think Like A Researcher • An investigation (an inquiry) to find something out. • Controlled inquiry concerning certain events. • Problem solving. • Application of the scientific approach to study a problem • Systematic , controlled, empirical and critical investigation guided by theory and hypothesis. 24 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
 Think Like A Researcher • • Encounter problems State problems Propose hypotheses Deduce outcomes Formulate rival hypotheses Devise and conduct empirical tests Draw conclusions 25
Think Like A Researcher • • Encounter problems State problems Propose hypotheses Deduce outcomes Formulate rival hypotheses Devise and conduct empirical tests Draw conclusions 25
 Think Like A Researcher • Concepts: Accepted collection of meanings or characteristics associated with certain events, objects, conditions, situations and behaviors. An Idea expressed as symbol or in words (e. g: s=d/t; s=speed, d=distance, t=time) • Constructs: A definition specially invented to represent an abstract phenomenon for a given research project. • Operational Definitions: Stated in terms of specific criteria for testing or measurement. E. g: if the concept is "weight", an operational definition could be "the weight of an object as measured on a scale". • Theory: A set of systematically interrelated concepts, definitions and propositions that are advanced to explain and predict phenomenon. 26 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
Think Like A Researcher • Concepts: Accepted collection of meanings or characteristics associated with certain events, objects, conditions, situations and behaviors. An Idea expressed as symbol or in words (e. g: s=d/t; s=speed, d=distance, t=time) • Constructs: A definition specially invented to represent an abstract phenomenon for a given research project. • Operational Definitions: Stated in terms of specific criteria for testing or measurement. E. g: if the concept is "weight", an operational definition could be "the weight of an object as measured on a scale". • Theory: A set of systematically interrelated concepts, definitions and propositions that are advanced to explain and predict phenomenon. 26 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
 Examples of constructs Ideas Ageism, sexism, racism, self-esteem, poverty, social capital, trust, philanthropy, affluence, morality, tolerance, air pollution, genetic engineering, euthanasia, marriage, taboos People Age, gender, ethnicity, height, obesity, morbidity, energy, muscle soreness, fatigue Organisations Financial performance, corporate social responsibility, firm survival, organisational culture, service quality, corporate governance, outsourcing, alliances Events Armageddon, famine, urban regeneration, Jihad, secularism Objects/Things Sun, hurricanes, tsunamis, trees, flowers, amino acids, stem cells ULP 0010: Research Methodology 27
Examples of constructs Ideas Ageism, sexism, racism, self-esteem, poverty, social capital, trust, philanthropy, affluence, morality, tolerance, air pollution, genetic engineering, euthanasia, marriage, taboos People Age, gender, ethnicity, height, obesity, morbidity, energy, muscle soreness, fatigue Organisations Financial performance, corporate social responsibility, firm survival, organisational culture, service quality, corporate governance, outsourcing, alliances Events Armageddon, famine, urban regeneration, Jihad, secularism Objects/Things Sun, hurricanes, tsunamis, trees, flowers, amino acids, stem cells ULP 0010: Research Methodology 27
 Research is NOT a SIMPLE Linear Activity • Never more in a straight line. • Always loops back & forth. • Manage the parts in order to manage the whole. • Searching for something you won’t know until you find it. • Nobody can solve the world’s great problems in a tiny project. 28 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
Research is NOT a SIMPLE Linear Activity • Never more in a straight line. • Always loops back & forth. • Manage the parts in order to manage the whole. • Searching for something you won’t know until you find it. • Nobody can solve the world’s great problems in a tiny project. 28 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
 Research Paradigm • Positivist Paradigm – Attempts to test hypothesis, precise quantitative data by using experiments, surveys and statistical analysis. Independent variables & dependent variables, cause & effect. • Interpretive Paradigm – To understand phenomenon • Critical Paradigm – To help subjects to change & improve current conditions eg creating strategies, empowering & initiating actions. 29
Research Paradigm • Positivist Paradigm – Attempts to test hypothesis, precise quantitative data by using experiments, surveys and statistical analysis. Independent variables & dependent variables, cause & effect. • Interpretive Paradigm – To understand phenomenon • Critical Paradigm – To help subjects to change & improve current conditions eg creating strategies, empowering & initiating actions. 29
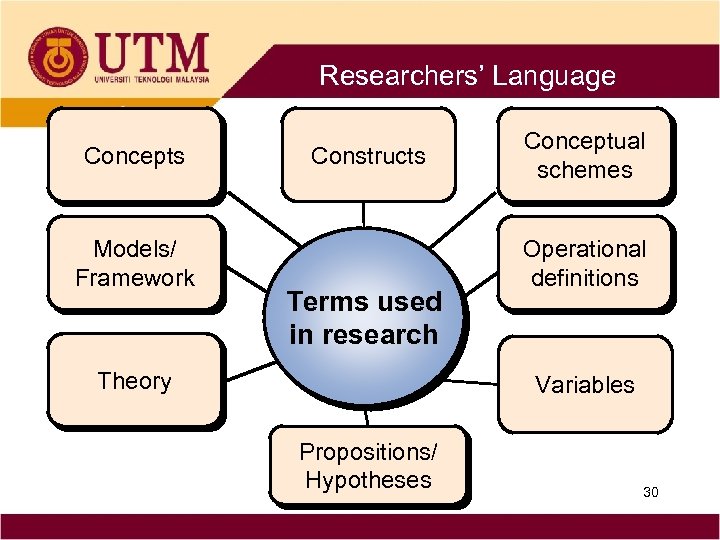 Researchers’ Language Concepts Models/ Framework Constructs Terms used in research Theory Conceptual schemes Operational definitions Variables Propositions/ Hypotheses 30
Researchers’ Language Concepts Models/ Framework Constructs Terms used in research Theory Conceptual schemes Operational definitions Variables Propositions/ Hypotheses 30
 Theoretical Framework • Is a conceptual model of how one theorizes or makes logical sense of the relationships among the several factors that have been identified as important to the problem. • LR identifies the variables that might be important as determined by previous research findings. • From TF then testable hypothesis can be developed to examine whether theory formulated valid or not. 31 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
Theoretical Framework • Is a conceptual model of how one theorizes or makes logical sense of the relationships among the several factors that have been identified as important to the problem. • LR identifies the variables that might be important as determined by previous research findings. • From TF then testable hypothesis can be developed to examine whether theory formulated valid or not. 31 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
 Variables • A variable is an entity that can take on different values. Anything that can vary can be considered a variable. 32 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
Variables • A variable is an entity that can take on different values. Anything that can vary can be considered a variable. 32 INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS
 References • Oates, B. J (2006) Researching Information Systems and Computing. Sage Publication. London • "Academy of Management Review"; What Constitutes a Theoretical Contribution? ; David A. Whetton; 1989 • "Human Resource Management"; HRM: A Map, Model or Theory? ; Mike Noon; 1999 • SPS Research Methodology Slides (Prof Dr. Muhd Rashid Rajuddin, Prof Dr. Noor Azlan Ahmad Zanzali, etc. ) • Slides from previous semester (Prof. Dr. Bob Colomb, Dr. Noorminshah I. Ahad, PM Dr. Zuraini Ismail) 33
References • Oates, B. J (2006) Researching Information Systems and Computing. Sage Publication. London • "Academy of Management Review"; What Constitutes a Theoretical Contribution? ; David A. Whetton; 1989 • "Human Resource Management"; HRM: A Map, Model or Theory? ; Mike Noon; 1999 • SPS Research Methodology Slides (Prof Dr. Muhd Rashid Rajuddin, Prof Dr. Noor Azlan Ahmad Zanzali, etc. ) • Slides from previous semester (Prof. Dr. Bob Colomb, Dr. Noorminshah I. Ahad, PM Dr. Zuraini Ismail) 33


