be631132c0c5e5e9f5bd55b663644b67.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
 Research forecast report Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 Mark H. Mortensen October 2011
Research forecast report Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 Mark H. Mortensen October 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 2 Contents Slide no. 4. List of figures and tables 5. Document map – Executive summary 6. Worldwide service fulfilment system forecast: 2010– 2015 7. Order management, inventory management and activation systems will continue their growth, providing flow through 8. The mobile and business service segments will grow the fastest, but residential broadband will still be the largest 9. Emerging markets will achieve the highest growth, while developed markets, especially Western Europe, will lag 10. Document map – Recommendations 11. Recommendations for CSPs [1] 12. Recommendations for CSPs [2] 13. Recommendations for ISVs (tactical) 14. Recommendations for ISVs (strategic) 15. Document map – Forecast 16. Emerging markets will experience the highest growth in order management systems 17. Order management systems for residential broadband services will continue to dominate the market Slide no. 18. The inventory system market will continue to grow, but will change as federation and transformation increase 19. The focus in the inventory system market will shift towards IP infrastructure, IT like equipment and services 20. Activation systems are showing stronger growth, especially in emerging markets 21. Activation systems focus on mobile and ‘over the top’ services, as well as IP and fibre infrastructure 22. The engineering tools market will continue its modest growth worldwide, with different foci in different markets 23. The engineering tools market will continue its modest growth worldwide, with different foci in different markets 24. Document map – Market drivers and inhibitors 25. Service fulfilment system market drivers [1] 26. Service fulfilment system market drivers [2] 27. Service fulfilment system market drivers [3] 28. Service fulfilment system market drivers [4] 29. Service fulfilment system market inhibitors [1] 30. Service fulfilment system market inhibitors [2] © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 2 Contents Slide no. 4. List of figures and tables 5. Document map – Executive summary 6. Worldwide service fulfilment system forecast: 2010– 2015 7. Order management, inventory management and activation systems will continue their growth, providing flow through 8. The mobile and business service segments will grow the fastest, but residential broadband will still be the largest 9. Emerging markets will achieve the highest growth, while developed markets, especially Western Europe, will lag 10. Document map – Recommendations 11. Recommendations for CSPs [1] 12. Recommendations for CSPs [2] 13. Recommendations for ISVs (tactical) 14. Recommendations for ISVs (strategic) 15. Document map – Forecast 16. Emerging markets will experience the highest growth in order management systems 17. Order management systems for residential broadband services will continue to dominate the market Slide no. 18. The inventory system market will continue to grow, but will change as federation and transformation increase 19. The focus in the inventory system market will shift towards IP infrastructure, IT like equipment and services 20. Activation systems are showing stronger growth, especially in emerging markets 21. Activation systems focus on mobile and ‘over the top’ services, as well as IP and fibre infrastructure 22. The engineering tools market will continue its modest growth worldwide, with different foci in different markets 23. The engineering tools market will continue its modest growth worldwide, with different foci in different markets 24. Document map – Market drivers and inhibitors 25. Service fulfilment system market drivers [1] 26. Service fulfilment system market drivers [2] 27. Service fulfilment system market drivers [3] 28. Service fulfilment system market drivers [4] 29. Service fulfilment system market inhibitors [1] 30. Service fulfilment system market inhibitors [2] © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 3 Contents Slide no. 31. Document map – Business environment 32. Telecoms market growth was dampened in 2010, except in emerging markets, while data grew, but ARPU did not 33. In 2010, CSPs continued to target specific service needs in service fulfilment 34. In 2010, interest in department sized transformations and federation and larger scale transformations grew 35. In 2010, major ISVs continued to expand their professional services 36. In 2010– 2011, the consolidation of service fulfilment systems continued 37. Document map – Market definition 38. Telecoms software market segmentation 39. Service fulfilment sub segment definitions 40. Service fulfilment software features 41. Market segment and revenue type definitions 42. Our comprehensive forecast model is supported by a sound knowledge of markets Slide no. 43. Document map – About the author and Analysys Mason 44. About the author 45. Copyright and disclaimer 46. About Analysys Mason 47. Research from Analysys Mason 48. Consulting from Analysys Mason © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 3 Contents Slide no. 31. Document map – Business environment 32. Telecoms market growth was dampened in 2010, except in emerging markets, while data grew, but ARPU did not 33. In 2010, CSPs continued to target specific service needs in service fulfilment 34. In 2010, interest in department sized transformations and federation and larger scale transformations grew 35. In 2010, major ISVs continued to expand their professional services 36. In 2010– 2011, the consolidation of service fulfilment systems continued 37. Document map – Market definition 38. Telecoms software market segmentation 39. Service fulfilment sub segment definitions 40. Service fulfilment software features 41. Market segment and revenue type definitions 42. Our comprehensive forecast model is supported by a sound knowledge of markets Slide no. 43. Document map – About the author and Analysys Mason 44. About the author 45. Copyright and disclaimer 46. About Analysys Mason 47. Research from Analysys Mason 48. Consulting from Analysys Mason © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 4 Contents List of tables and figures Slide no. 6. Figure 1: Service fulfilment system revenue, worldwide, 2010– 2015 7. Figure 2: Service fulfilment system revenue by sub segment, worldwide, 2010– 2015 8. Figure 3: Service fulfilment system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 9. Figure 4: Service fulfilment system revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 16. Figure 5: Order management system revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 17. Figure 6: Order management system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 18. Figure 7: Inventory management system revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 19. Figure 8: Inventory management system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 20. Figure 9: Activation system revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 21. Figure 10: Activation system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 22. Figure 11: Engineering tools revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 23. Figure 12: Engineering tools system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 Slide no. 25. Table 1 a: Service fulfilment system market drivers 26. Table 1 b: Service fulfilment system market drivers 27. Table 1 c: Service fulfilment system market drivers 28. Table 1 d: Service fulfilment system market drivers 29. Table 2 a: Service fulfilment system market inhibitors 30. Table 2 b: Service fulfilment system market inhibitors 38. Figure 13: Telecoms software market segments 39. Table 3: Definitions of service fulfilment and its sub segments 41. Table 4: Definitions of service fulfilment market segments 41. Table 5: Definitions of service fulfilment revenue types 42. Figure 14: Key factors influencing forecast assumptions © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 4 Contents List of tables and figures Slide no. 6. Figure 1: Service fulfilment system revenue, worldwide, 2010– 2015 7. Figure 2: Service fulfilment system revenue by sub segment, worldwide, 2010– 2015 8. Figure 3: Service fulfilment system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 9. Figure 4: Service fulfilment system revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 16. Figure 5: Order management system revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 17. Figure 6: Order management system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 18. Figure 7: Inventory management system revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 19. Figure 8: Inventory management system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 20. Figure 9: Activation system revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 21. Figure 10: Activation system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 22. Figure 11: Engineering tools revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 23. Figure 12: Engineering tools system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 Slide no. 25. Table 1 a: Service fulfilment system market drivers 26. Table 1 b: Service fulfilment system market drivers 27. Table 1 c: Service fulfilment system market drivers 28. Table 1 d: Service fulfilment system market drivers 29. Table 2 a: Service fulfilment system market inhibitors 30. Table 2 b: Service fulfilment system market inhibitors 38. Figure 13: Telecoms software market segments 39. Table 3: Definitions of service fulfilment and its sub segments 41. Table 4: Definitions of service fulfilment market segments 41. Table 5: Definitions of service fulfilment revenue types 42. Figure 14: Key factors influencing forecast assumptions © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 5 Document map: Executive summary Document map Executive summary Recommendations Forecast Market drivers and inhibitors Business environment Market definition About the author and Analysys Mason © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 5 Document map: Executive summary Document map Executive summary Recommendations Forecast Market drivers and inhibitors Business environment Market definition About the author and Analysys Mason © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
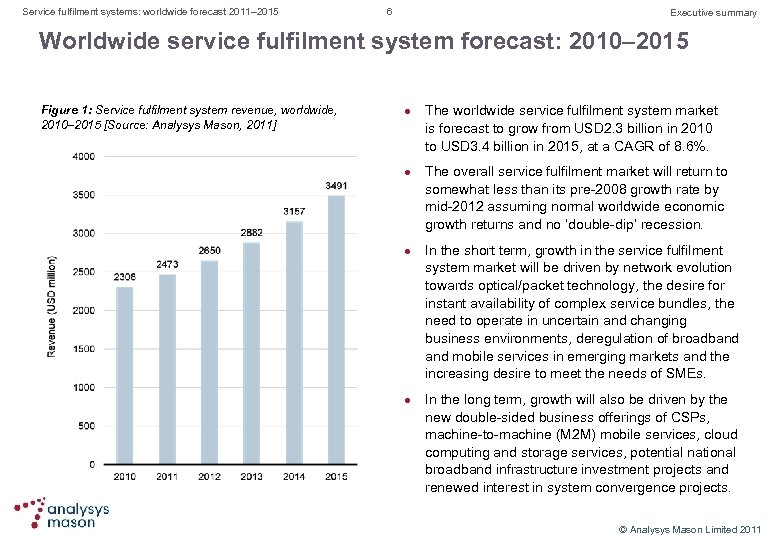 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 6 Executive summary Worldwide service fulfilment system forecast: 2010– 2015 Figure 1: Service fulfilment system revenue, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l The worldwide service fulfilment system market is forecast to grow from USD 2. 3 billion in 2010 to USD 3. 4 billion in 2015, at a CAGR of 8. 6%. The overall service fulfilment market will return to somewhat less than its pre 2008 growth rate by mid 2012 assuming normal worldwide economic growth returns and no ‘double dip’ recession. In the short term, growth in the service fulfilment system market will be driven by network evolution towards optical/packet technology, the desire for instant availability of complex service bundles, the need to operate in uncertain and changing business environments, deregulation of broadband mobile services in emerging markets and the increasing desire to meet the needs of SMEs. In the long term, growth will also be driven by the new double sided business offerings of CSPs, machine to machine (M 2 M) mobile services, cloud computing and storage services, potential national broadband infrastructure investment projects and renewed interest in system convergence projects. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 6 Executive summary Worldwide service fulfilment system forecast: 2010– 2015 Figure 1: Service fulfilment system revenue, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l The worldwide service fulfilment system market is forecast to grow from USD 2. 3 billion in 2010 to USD 3. 4 billion in 2015, at a CAGR of 8. 6%. The overall service fulfilment market will return to somewhat less than its pre 2008 growth rate by mid 2012 assuming normal worldwide economic growth returns and no ‘double dip’ recession. In the short term, growth in the service fulfilment system market will be driven by network evolution towards optical/packet technology, the desire for instant availability of complex service bundles, the need to operate in uncertain and changing business environments, deregulation of broadband mobile services in emerging markets and the increasing desire to meet the needs of SMEs. In the long term, growth will also be driven by the new double sided business offerings of CSPs, machine to machine (M 2 M) mobile services, cloud computing and storage services, potential national broadband infrastructure investment projects and renewed interest in system convergence projects. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
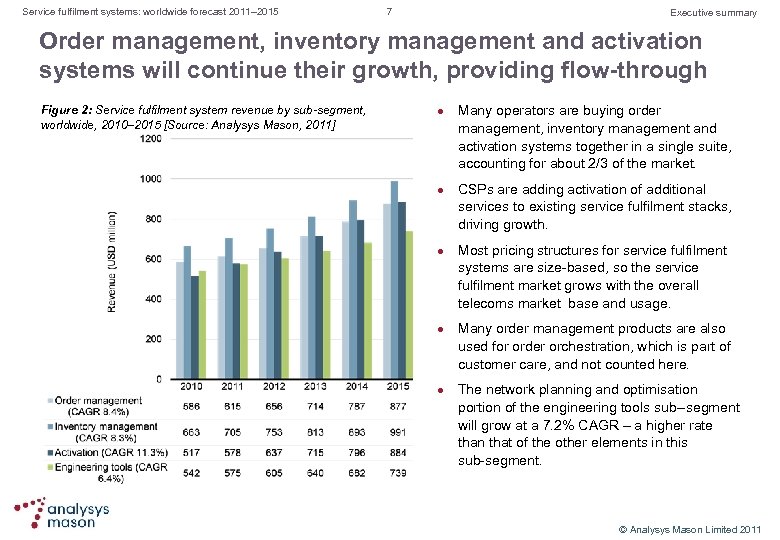 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 7 Executive summary Order management, inventory management and activation systems will continue their growth, providing flow-through Figure 2: Service fulfilment system revenue by sub-segment, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l l Many operators are buying order management, inventory management and activation systems together in a single suite, accounting for about 2/3 of the market. CSPs are adding activation of additional services to existing service fulfilment stacks, driving growth. Most pricing structures for service fulfilment systems are size based, so the service fulfilment market grows with the overall telecoms market base and usage. Many order management products are also used for order orchestration, which is part of customer care, and not counted here. The network planning and optimisation portion of the engineering tools sub segment will grow at a 7. 2% CAGR – a higher rate than that of the other elements in this sub segment. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 7 Executive summary Order management, inventory management and activation systems will continue their growth, providing flow-through Figure 2: Service fulfilment system revenue by sub-segment, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l l Many operators are buying order management, inventory management and activation systems together in a single suite, accounting for about 2/3 of the market. CSPs are adding activation of additional services to existing service fulfilment stacks, driving growth. Most pricing structures for service fulfilment systems are size based, so the service fulfilment market grows with the overall telecoms market base and usage. Many order management products are also used for order orchestration, which is part of customer care, and not counted here. The network planning and optimisation portion of the engineering tools sub segment will grow at a 7. 2% CAGR – a higher rate than that of the other elements in this sub segment. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
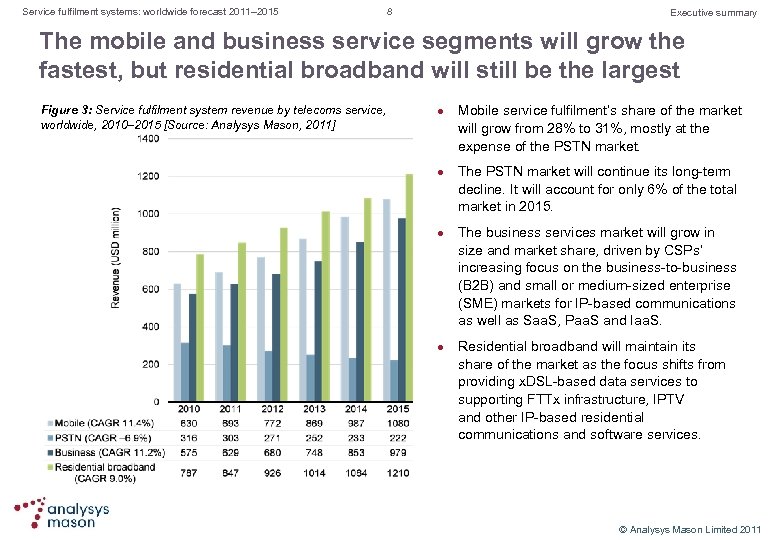 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 8 Executive summary The mobile and business service segments will grow the fastest, but residential broadband will still be the largest Figure 3: Service fulfilment system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l Mobile service fulfilment’s share of the market will grow from 28% to 31%, mostly at the expense of the PSTN market. The PSTN market will continue its long term decline. It will account for only 6% of the total market in 2015. The business services market will grow in size and market share, driven by CSPs’ increasing focus on the business to business (B 2 B) and small or medium sized enterprise (SME) markets for IP based communications as well as Saa. S, Paa. S and Iaa. S. Residential broadband will maintain its share of the market as the focus shifts from providing x. DSL based data services to supporting FTTx infrastructure, IPTV and other IP based residential communications and software services. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 8 Executive summary The mobile and business service segments will grow the fastest, but residential broadband will still be the largest Figure 3: Service fulfilment system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l Mobile service fulfilment’s share of the market will grow from 28% to 31%, mostly at the expense of the PSTN market. The PSTN market will continue its long term decline. It will account for only 6% of the total market in 2015. The business services market will grow in size and market share, driven by CSPs’ increasing focus on the business to business (B 2 B) and small or medium sized enterprise (SME) markets for IP based communications as well as Saa. S, Paa. S and Iaa. S. Residential broadband will maintain its share of the market as the focus shifts from providing x. DSL based data services to supporting FTTx infrastructure, IPTV and other IP based residential communications and software services. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
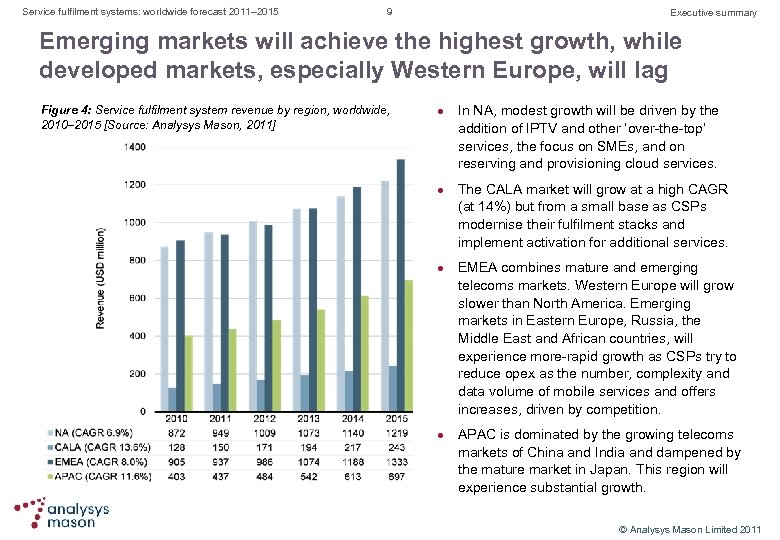 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 9 Executive summary Emerging markets will achieve the highest growth, while developed markets, especially Western Europe, will lag Figure 4: Service fulfilment system revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l In NA, modest growth will be driven by the addition of IPTV and other ‘over the top’ services, the focus on SMEs, and on reserving and provisioning cloud services. The CALA market will grow at a high CAGR (at 14%) but from a small base as CSPs modernise their fulfilment stacks and implement activation for additional services. EMEA combines mature and emerging telecoms markets. Western Europe will grow slower than North America. Emerging markets in Eastern Europe, Russia, the Middle East and African countries, will experience more rapid growth as CSPs try to reduce opex as the number, complexity and data volume of mobile services and offers increases, driven by competition. APAC is dominated by the growing telecoms markets of China and India and dampened by the mature market in Japan. This region will experience substantial growth. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 9 Executive summary Emerging markets will achieve the highest growth, while developed markets, especially Western Europe, will lag Figure 4: Service fulfilment system revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l In NA, modest growth will be driven by the addition of IPTV and other ‘over the top’ services, the focus on SMEs, and on reserving and provisioning cloud services. The CALA market will grow at a high CAGR (at 14%) but from a small base as CSPs modernise their fulfilment stacks and implement activation for additional services. EMEA combines mature and emerging telecoms markets. Western Europe will grow slower than North America. Emerging markets in Eastern Europe, Russia, the Middle East and African countries, will experience more rapid growth as CSPs try to reduce opex as the number, complexity and data volume of mobile services and offers increases, driven by competition. APAC is dominated by the growing telecoms markets of China and India and dampened by the mature market in Japan. This region will experience substantial growth. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 10 Document map: Recommendations Document map Executive summary Recommendations Forecast Market drivers and inhibitors Business environment Market definition About the author and Analysys Mason © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 10 Document map: Recommendations Document map Executive summary Recommendations Forecast Market drivers and inhibitors Business environment Market definition About the author and Analysys Mason © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
![Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 11 Recommendations for CSPs [1] l The Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 11 Recommendations for CSPs [1] l The](https://present5.com/presentation/be631132c0c5e5e9f5bd55b663644b67/image-11.jpg) Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 11 Recommendations for CSPs [1] l The drive for scale – implementation for effective use is paramount. l CSPs that are still using manual procedures for service fulfilment should implement integrated service fulfilment suites from leading ISVs or NEMs who have multivendor suites. This will allow them to manage the complexity of the new services and service bundles economically. CSPs should look to vendors that not only provide integrated systems, but also have predefined processes, service templates and workflows that they can implement quickly and without costly and time consuming customisation. CSPs should engage an SI that is highly experienced in process design to address changes in organisation and business processes. This will enable them to achieve the required benefits from service fulfilment technology. Many CSPs have failed to realise much of the potential benefit of investment in service fulfilment systems because they have been unable to align the goals and processes of different groups within their organisations. CSPs should integrate network inventory databases with fault, performance and workforce management systems to avoid costly dispatches and reduce mean time to resolution. The digital consumer – new systems to support new services and then expand their footprint. In the short term, CSPs’ projects in service fulfilment should focus primarily on supporting new digital service roll outs , rather than on trying to achieve consolidation. The solution should support both new and future services, because CSPs are continually introducing services. It should also have an extremely open architecture and substantial capabilities to federate data and integrate into enterprise level service and product catalogues. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 11 Recommendations for CSPs [1] l The drive for scale – implementation for effective use is paramount. l CSPs that are still using manual procedures for service fulfilment should implement integrated service fulfilment suites from leading ISVs or NEMs who have multivendor suites. This will allow them to manage the complexity of the new services and service bundles economically. CSPs should look to vendors that not only provide integrated systems, but also have predefined processes, service templates and workflows that they can implement quickly and without costly and time consuming customisation. CSPs should engage an SI that is highly experienced in process design to address changes in organisation and business processes. This will enable them to achieve the required benefits from service fulfilment technology. Many CSPs have failed to realise much of the potential benefit of investment in service fulfilment systems because they have been unable to align the goals and processes of different groups within their organisations. CSPs should integrate network inventory databases with fault, performance and workforce management systems to avoid costly dispatches and reduce mean time to resolution. The digital consumer – new systems to support new services and then expand their footprint. In the short term, CSPs’ projects in service fulfilment should focus primarily on supporting new digital service roll outs , rather than on trying to achieve consolidation. The solution should support both new and future services, because CSPs are continually introducing services. It should also have an extremely open architecture and substantial capabilities to federate data and integrate into enterprise level service and product catalogues. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
![Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 12 Recommendations for CSPs [2] l Cloud Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 12 Recommendations for CSPs [2] l Cloud](https://present5.com/presentation/be631132c0c5e5e9f5bd55b663644b67/image-12.jpg) Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 12 Recommendations for CSPs [2] l Cloud computing – automated operations are a necessity. l Introduction of new business models – interfaces to third parties will be key. l CSPs must implement new service fulfilment infrastructures, or extend existing ones, to support the reservation and service provisioning needs of its cloud offerings (Iaa. S and Paa. S) to large and medium enterprises. These must be highly automated and under the control of the customers. They must work together with complementary functions in the customer care and billing arenas, sharing a common product catalogue and subscriber data. CSPs that offer Saa. S to consumers, SMEs, and/or large enterprises need to implement service fulfilment stacks as well as order orchestration and other customer care functions to support these IT like services. With many of these services being provided by third parties, especially in the early years, interfaces between the third party’s systems and the CSP’s systems will be required. CSPs that offer the functions of their network to third parties for bundling with other services (network as a service) will also have to offer interfaces to those third parties’ systems for automated provisioning and control. The Internet of things (M 2 M) – low average revenue per device (ARPD) requires automation. The large scale of M 2 M services and the low average revenue per device will require that CSPs implement fully automated operations under the control of the device owning entities. This will probably require new service fulfilment systems, specialised to the task. Interfaces to the systems belonging to the business entities that operate the M 2 M networks will be required. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 12 Recommendations for CSPs [2] l Cloud computing – automated operations are a necessity. l Introduction of new business models – interfaces to third parties will be key. l CSPs must implement new service fulfilment infrastructures, or extend existing ones, to support the reservation and service provisioning needs of its cloud offerings (Iaa. S and Paa. S) to large and medium enterprises. These must be highly automated and under the control of the customers. They must work together with complementary functions in the customer care and billing arenas, sharing a common product catalogue and subscriber data. CSPs that offer Saa. S to consumers, SMEs, and/or large enterprises need to implement service fulfilment stacks as well as order orchestration and other customer care functions to support these IT like services. With many of these services being provided by third parties, especially in the early years, interfaces between the third party’s systems and the CSP’s systems will be required. CSPs that offer the functions of their network to third parties for bundling with other services (network as a service) will also have to offer interfaces to those third parties’ systems for automated provisioning and control. The Internet of things (M 2 M) – low average revenue per device (ARPD) requires automation. The large scale of M 2 M services and the low average revenue per device will require that CSPs implement fully automated operations under the control of the device owning entities. This will probably require new service fulfilment systems, specialised to the task. Interfaces to the systems belonging to the business entities that operate the M 2 M networks will be required. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 13 Recommendations for ISVs (tactical) l l l Service fulfilment suites are the future. With two thirds of the market buying service fulfilment suites, not individual systems, ISVs should attempt to provide a suite, or be a pre configured component of another vendor’s suite. If this is not possible, ISVs should seek out CSPs that are technology focused and are looking to achieve a competitive advantage with a best in class architecture. Basic pre-configured systems for smaller operators. For small CSPs, ISVs should work to solve the current fulfilment problems quickly with systems that are relatively simple to deploy and that are pre configured for their basic use. Saa. S models are useful, especially in the early years for the CSP. Expect moderate transformation projects, growing in the future. For the next year, ISVs should target transformation projects (such as the consolidation of order and inventory management systems) at the department level, not the whole enterprise where the risks of project failure are much higher. They should also prepare for when CSPs will begin funding larger transformation and federation projects again in 2012. Extend order management systems into customer care. ISVs that offer order management systems should also look to extend the use of these systems into the CRM arena to offer complex service bundles and enhanced customer facing functions. Offer services, too. ISVs with strong selling abilities should seek to win as much revenue as possible from each sale by offering additional services, such as systems integration, data loading, and business process development and optimisation. The combination is difficult to manage, but ISVs that succeed will reap significant rewards. Standards are becoming important. ISVs should comply with the Tele. Management Forum’s SID and the e. TOM framework, which is rapidly becoming a requirement for many CSPs. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 13 Recommendations for ISVs (tactical) l l l Service fulfilment suites are the future. With two thirds of the market buying service fulfilment suites, not individual systems, ISVs should attempt to provide a suite, or be a pre configured component of another vendor’s suite. If this is not possible, ISVs should seek out CSPs that are technology focused and are looking to achieve a competitive advantage with a best in class architecture. Basic pre-configured systems for smaller operators. For small CSPs, ISVs should work to solve the current fulfilment problems quickly with systems that are relatively simple to deploy and that are pre configured for their basic use. Saa. S models are useful, especially in the early years for the CSP. Expect moderate transformation projects, growing in the future. For the next year, ISVs should target transformation projects (such as the consolidation of order and inventory management systems) at the department level, not the whole enterprise where the risks of project failure are much higher. They should also prepare for when CSPs will begin funding larger transformation and federation projects again in 2012. Extend order management systems into customer care. ISVs that offer order management systems should also look to extend the use of these systems into the CRM arena to offer complex service bundles and enhanced customer facing functions. Offer services, too. ISVs with strong selling abilities should seek to win as much revenue as possible from each sale by offering additional services, such as systems integration, data loading, and business process development and optimisation. The combination is difficult to manage, but ISVs that succeed will reap significant rewards. Standards are becoming important. ISVs should comply with the Tele. Management Forum’s SID and the e. TOM framework, which is rapidly becoming a requirement for many CSPs. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 14 Recommendations for ISVs (strategic) l Meet architectural requirements for strategic initiatives. Prepare to support CSPs’ strategic initiatives of cloud computing, new business models and M 2 M offerings by demonstrating that your systems, either existing or new, meet their increasing requirements for: open interfaces for controlling, or being controlled by, third party systems completely automated operations ability to support new IT like services quickly. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 14 Recommendations for ISVs (strategic) l Meet architectural requirements for strategic initiatives. Prepare to support CSPs’ strategic initiatives of cloud computing, new business models and M 2 M offerings by demonstrating that your systems, either existing or new, meet their increasing requirements for: open interfaces for controlling, or being controlled by, third party systems completely automated operations ability to support new IT like services quickly. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 15 Document map: Forecast Document map Executive summary Recommendations Forecast Market drivers and inhibitors Business environment Market definition About the author and Analysys Mason © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 15 Document map: Forecast Document map Executive summary Recommendations Forecast Market drivers and inhibitors Business environment Market definition About the author and Analysys Mason © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
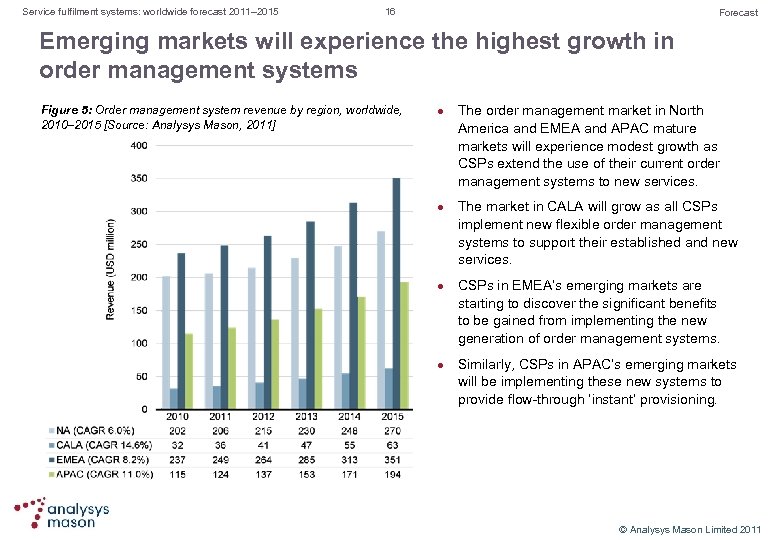 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 16 Forecast Emerging markets will experience the highest growth in order management systems Figure 5: Order management system revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l The order management market in North America and EMEA and APAC mature markets will experience modest growth as CSPs extend the use of their current order management systems to new services. The market in CALA will grow as all CSPs implement new flexible order management systems to support their established and new services. CSPs in EMEA’s emerging markets are starting to discover the significant benefits to be gained from implementing the new generation of order management systems. Similarly, CSPs in APAC’s emerging markets will be implementing these new systems to provide flow through ‘instant’ provisioning. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 16 Forecast Emerging markets will experience the highest growth in order management systems Figure 5: Order management system revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l The order management market in North America and EMEA and APAC mature markets will experience modest growth as CSPs extend the use of their current order management systems to new services. The market in CALA will grow as all CSPs implement new flexible order management systems to support their established and new services. CSPs in EMEA’s emerging markets are starting to discover the significant benefits to be gained from implementing the new generation of order management systems. Similarly, CSPs in APAC’s emerging markets will be implementing these new systems to provide flow through ‘instant’ provisioning. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
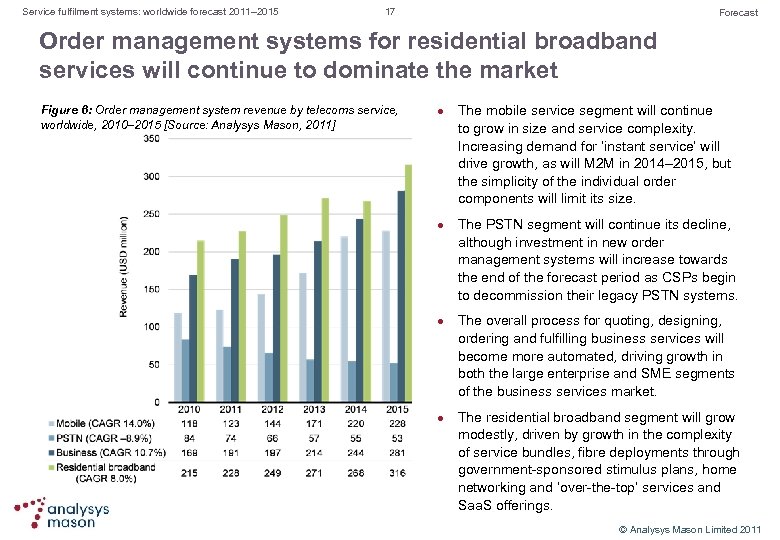 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 17 Forecast Order management systems for residential broadband services will continue to dominate the market Figure 6: Order management system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l The mobile service segment will continue to grow in size and service complexity. Increasing demand for ‘instant service’ will drive growth, as will M 2 M in 2014– 2015, but the simplicity of the individual order components will limit its size. The PSTN segment will continue its decline, although investment in new order management systems will increase towards the end of the forecast period as CSPs begin to decommission their legacy PSTN systems. The overall process for quoting, designing, ordering and fulfilling business services will become more automated, driving growth in both the large enterprise and SME segments of the business services market. The residential broadband segment will grow modestly, driven by growth in the complexity of service bundles, fibre deployments through government sponsored stimulus plans, home networking and ‘over the top’ services and Saa. S offerings. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 17 Forecast Order management systems for residential broadband services will continue to dominate the market Figure 6: Order management system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l The mobile service segment will continue to grow in size and service complexity. Increasing demand for ‘instant service’ will drive growth, as will M 2 M in 2014– 2015, but the simplicity of the individual order components will limit its size. The PSTN segment will continue its decline, although investment in new order management systems will increase towards the end of the forecast period as CSPs begin to decommission their legacy PSTN systems. The overall process for quoting, designing, ordering and fulfilling business services will become more automated, driving growth in both the large enterprise and SME segments of the business services market. The residential broadband segment will grow modestly, driven by growth in the complexity of service bundles, fibre deployments through government sponsored stimulus plans, home networking and ‘over the top’ services and Saa. S offerings. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
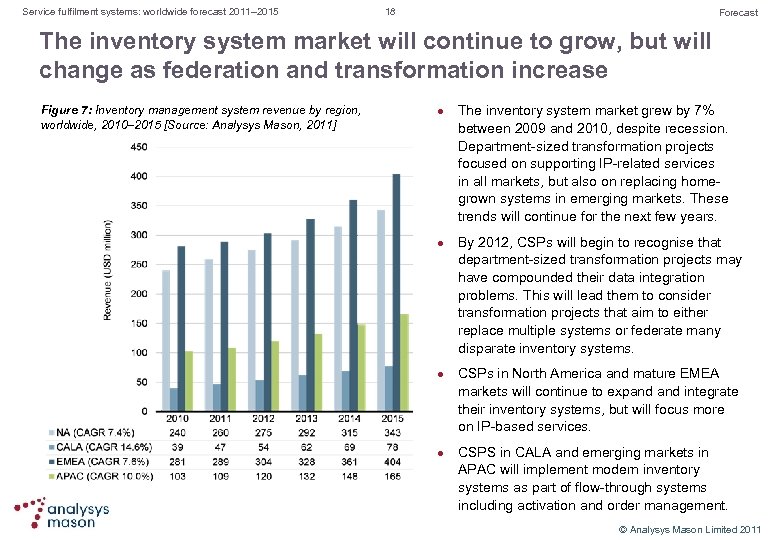 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 18 Forecast The inventory system market will continue to grow, but will change as federation and transformation increase Figure 7: Inventory management system revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l The inventory system market grew by 7% between 2009 and 2010, despite recession. Department sized transformation projects focused on supporting IP related services in all markets, but also on replacing home grown systems in emerging markets. These trends will continue for the next few years. By 2012, CSPs will begin to recognise that department sized transformation projects may have compounded their data integration problems. This will lead them to consider transformation projects that aim to either replace multiple systems or federate many disparate inventory systems. CSPs in North America and mature EMEA markets will continue to expand integrate their inventory systems, but will focus more on IP based services. CSPS in CALA and emerging markets in APAC will implement modern inventory systems as part of flow through systems including activation and order management. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 18 Forecast The inventory system market will continue to grow, but will change as federation and transformation increase Figure 7: Inventory management system revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l The inventory system market grew by 7% between 2009 and 2010, despite recession. Department sized transformation projects focused on supporting IP related services in all markets, but also on replacing home grown systems in emerging markets. These trends will continue for the next few years. By 2012, CSPs will begin to recognise that department sized transformation projects may have compounded their data integration problems. This will lead them to consider transformation projects that aim to either replace multiple systems or federate many disparate inventory systems. CSPs in North America and mature EMEA markets will continue to expand integrate their inventory systems, but will focus more on IP based services. CSPS in CALA and emerging markets in APAC will implement modern inventory systems as part of flow through systems including activation and order management. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
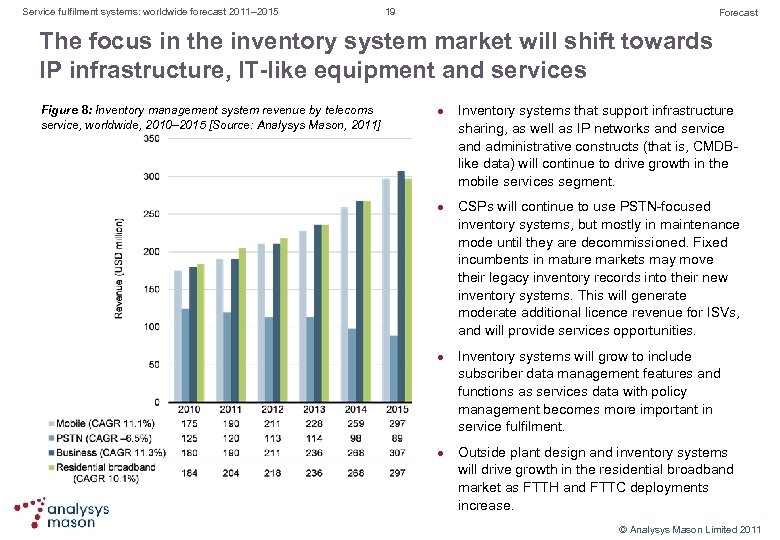 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 19 Forecast The focus in the inventory system market will shift towards IP infrastructure, IT-like equipment and services Figure 8: Inventory management system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l Inventory systems that support infrastructure sharing, as well as IP networks and service and administrative constructs (that is, CMDB like data) will continue to drive growth in the mobile services segment. CSPs will continue to use PSTN focused inventory systems, but mostly in maintenance mode until they are decommissioned. Fixed incumbents in mature markets may move their legacy inventory records into their new inventory systems. This will generate moderate additional licence revenue for ISVs, and will provide services opportunities. Inventory systems will grow to include subscriber data management features and functions as services data with policy management becomes more important in service fulfilment. Outside plant design and inventory systems will drive growth in the residential broadband market as FTTH and FTTC deployments increase. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 19 Forecast The focus in the inventory system market will shift towards IP infrastructure, IT-like equipment and services Figure 8: Inventory management system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l Inventory systems that support infrastructure sharing, as well as IP networks and service and administrative constructs (that is, CMDB like data) will continue to drive growth in the mobile services segment. CSPs will continue to use PSTN focused inventory systems, but mostly in maintenance mode until they are decommissioned. Fixed incumbents in mature markets may move their legacy inventory records into their new inventory systems. This will generate moderate additional licence revenue for ISVs, and will provide services opportunities. Inventory systems will grow to include subscriber data management features and functions as services data with policy management becomes more important in service fulfilment. Outside plant design and inventory systems will drive growth in the residential broadband market as FTTH and FTTC deployments increase. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
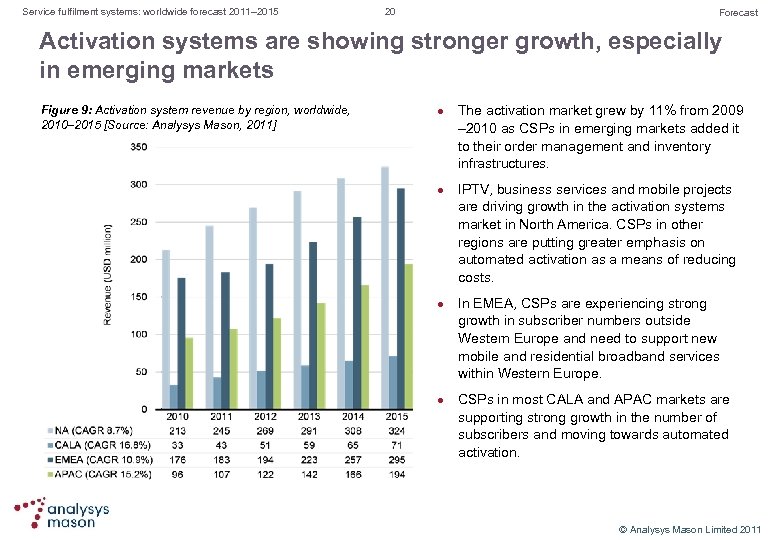 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 20 Forecast Activation systems are showing stronger growth, especially in emerging markets Figure 9: Activation system revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l The activation market grew by 11% from 2009 – 2010 as CSPs in emerging markets added it to their order management and inventory infrastructures. IPTV, business services and mobile projects are driving growth in the activation systems market in North America. CSPs in other regions are putting greater emphasis on automated activation as a means of reducing costs. In EMEA, CSPs are experiencing strong growth in subscriber numbers outside Western Europe and need to support new mobile and residential broadband services within Western Europe. CSPs in most CALA and APAC markets are supporting strong growth in the number of subscribers and moving towards automated activation. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 20 Forecast Activation systems are showing stronger growth, especially in emerging markets Figure 9: Activation system revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l The activation market grew by 11% from 2009 – 2010 as CSPs in emerging markets added it to their order management and inventory infrastructures. IPTV, business services and mobile projects are driving growth in the activation systems market in North America. CSPs in other regions are putting greater emphasis on automated activation as a means of reducing costs. In EMEA, CSPs are experiencing strong growth in subscriber numbers outside Western Europe and need to support new mobile and residential broadband services within Western Europe. CSPs in most CALA and APAC markets are supporting strong growth in the number of subscribers and moving towards automated activation. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
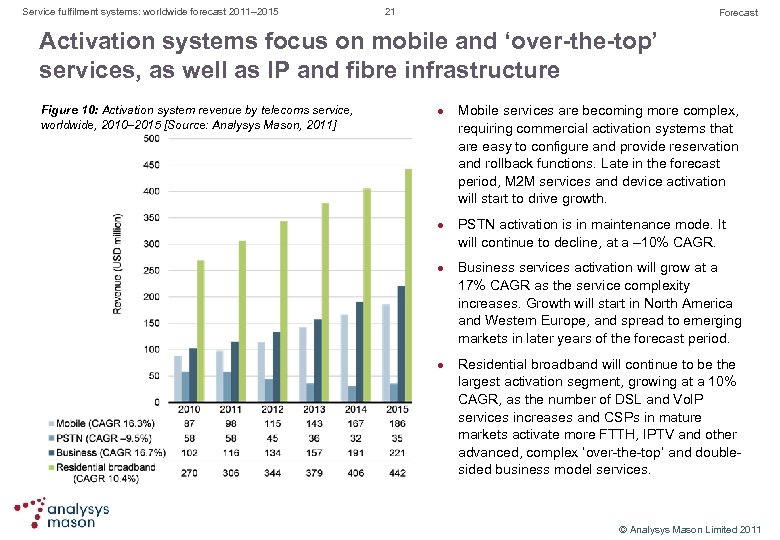 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 21 Forecast Activation systems focus on mobile and ‘over-the-top’ services, as well as IP and fibre infrastructure Figure 10: Activation system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l Mobile services are becoming more complex, requiring commercial activation systems that are easy to configure and provide reservation and rollback functions. Late in the forecast period, M 2 M services and device activation will start to drive growth. PSTN activation is in maintenance mode. It will continue to decline, at a – 10% CAGR. Business services activation will grow at a 17% CAGR as the service complexity increases. Growth will start in North America and Western Europe, and spread to emerging markets in later years of the forecast period. Residential broadband will continue to be the largest activation segment, growing at a 10% CAGR, as the number of DSL and Vo. IP services increases and CSPs in mature markets activate more FTTH, IPTV and other advanced, complex ‘over the top’ and double sided business model services. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 21 Forecast Activation systems focus on mobile and ‘over-the-top’ services, as well as IP and fibre infrastructure Figure 10: Activation system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l Mobile services are becoming more complex, requiring commercial activation systems that are easy to configure and provide reservation and rollback functions. Late in the forecast period, M 2 M services and device activation will start to drive growth. PSTN activation is in maintenance mode. It will continue to decline, at a – 10% CAGR. Business services activation will grow at a 17% CAGR as the service complexity increases. Growth will start in North America and Western Europe, and spread to emerging markets in later years of the forecast period. Residential broadband will continue to be the largest activation segment, growing at a 10% CAGR, as the number of DSL and Vo. IP services increases and CSPs in mature markets activate more FTTH, IPTV and other advanced, complex ‘over the top’ and double sided business model services. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
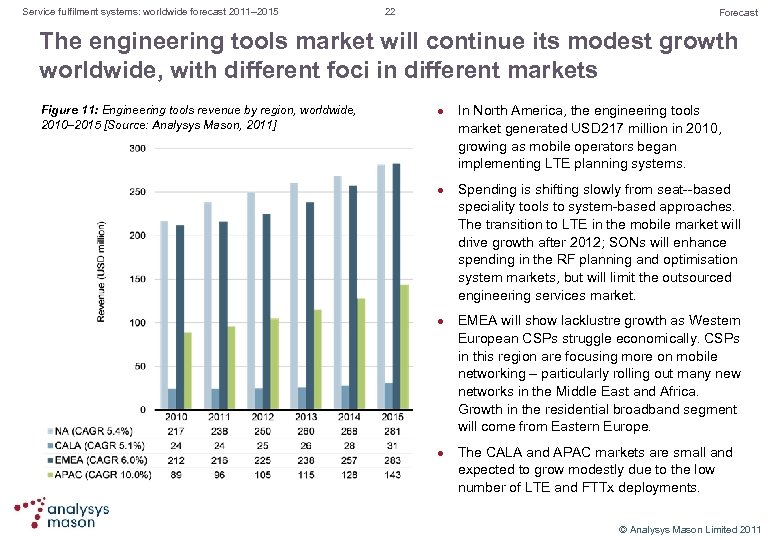 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 22 Forecast The engineering tools market will continue its modest growth worldwide, with different foci in different markets Figure 11: Engineering tools revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l In North America, the engineering tools market generated USD 217 million in 2010, growing as mobile operators began implementing LTE planning systems. Spending is shifting slowly from seat based speciality tools to system based approaches. The transition to LTE in the mobile market will drive growth after 2012; SONs will enhance spending in the RF planning and optimisation system markets, but will limit the outsourced engineering services market. EMEA will show lacklustre growth as Western European CSPs struggle economically. CSPs in this region are focusing more on mobile networking – particularly rolling out many new networks in the Middle East and Africa. Growth in the residential broadband segment will come from Eastern Europe. The CALA and APAC markets are small and expected to grow modestly due to the low number of LTE and FTTx deployments. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 22 Forecast The engineering tools market will continue its modest growth worldwide, with different foci in different markets Figure 11: Engineering tools revenue by region, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l In North America, the engineering tools market generated USD 217 million in 2010, growing as mobile operators began implementing LTE planning systems. Spending is shifting slowly from seat based speciality tools to system based approaches. The transition to LTE in the mobile market will drive growth after 2012; SONs will enhance spending in the RF planning and optimisation system markets, but will limit the outsourced engineering services market. EMEA will show lacklustre growth as Western European CSPs struggle economically. CSPs in this region are focusing more on mobile networking – particularly rolling out many new networks in the Middle East and Africa. Growth in the residential broadband segment will come from Eastern Europe. The CALA and APAC markets are small and expected to grow modestly due to the low number of LTE and FTTx deployments. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
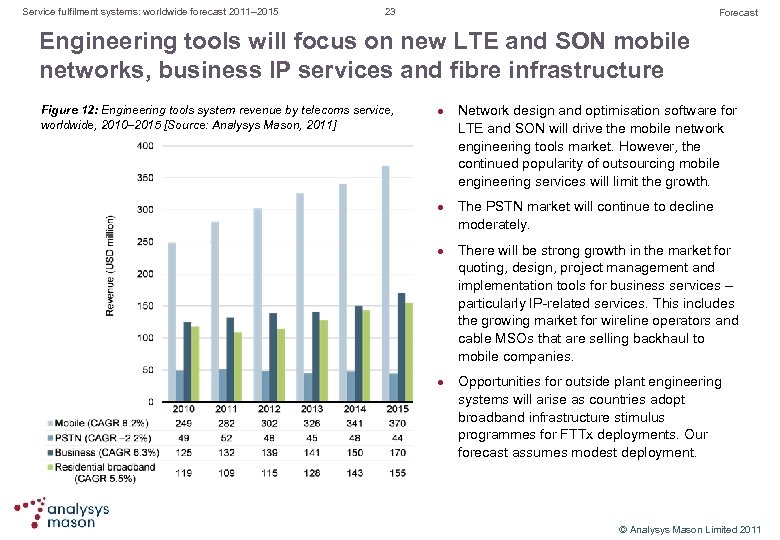 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 23 Forecast Engineering tools will focus on new LTE and SON mobile networks, business IP services and fibre infrastructure Figure 12: Engineering tools system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l Network design and optimisation software for LTE and SON will drive the mobile network engineering tools market. However, the continued popularity of outsourcing mobile engineering services will limit the growth. The PSTN market will continue to decline moderately. There will be strong growth in the market for quoting, design, project management and implementation tools for business services – particularly IP related services. This includes the growing market for wireline operators and cable MSOs that are selling backhaul to mobile companies. Opportunities for outside plant engineering systems will arise as countries adopt broadband infrastructure stimulus programmes for FTTx deployments. Our forecast assumes modest deployment. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 23 Forecast Engineering tools will focus on new LTE and SON mobile networks, business IP services and fibre infrastructure Figure 12: Engineering tools system revenue by telecoms service, worldwide, 2010– 2015 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] l l Network design and optimisation software for LTE and SON will drive the mobile network engineering tools market. However, the continued popularity of outsourcing mobile engineering services will limit the growth. The PSTN market will continue to decline moderately. There will be strong growth in the market for quoting, design, project management and implementation tools for business services – particularly IP related services. This includes the growing market for wireline operators and cable MSOs that are selling backhaul to mobile companies. Opportunities for outside plant engineering systems will arise as countries adopt broadband infrastructure stimulus programmes for FTTx deployments. Our forecast assumes modest deployment. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 24 Document map: Market drivers and inhibitors Document map Executive summary Recommendations Forecast Market drivers and inhibitors Business environment Market definition About the author and Analysys Mason © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 24 Document map: Market drivers and inhibitors Document map Executive summary Recommendations Forecast Market drivers and inhibitors Business environment Market definition About the author and Analysys Mason © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
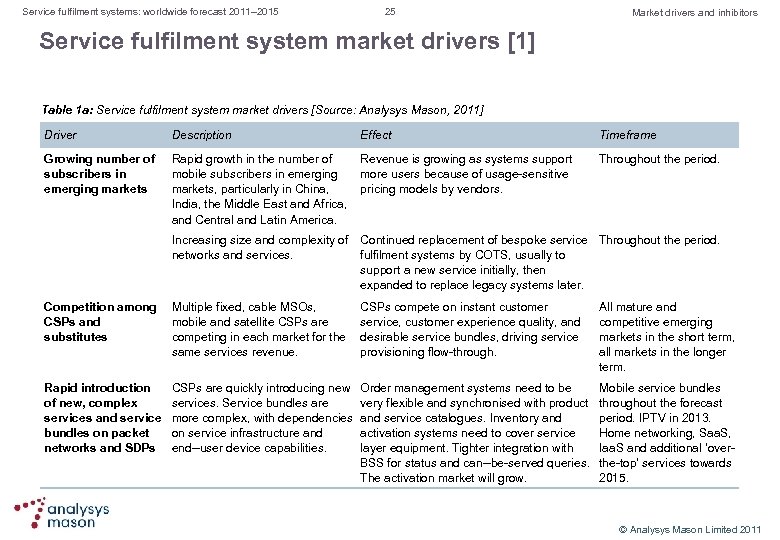 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 25 Market drivers and inhibitors Service fulfilment system market drivers [1] Table 1 a: Service fulfilment system market drivers [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Driver Description Effect Growing number of subscribers in emerging markets Rapid growth in the number of Revenue is growing as systems support mobile subscribers in emerging more users because of usage sensitive markets, particularly in China, pricing models by vendors. India, the Middle East and Africa, and Central and Latin America. Timeframe Throughout the period. Increasing size and complexity of Continued replacement of bespoke service Throughout the period. networks and services. fulfilment systems by COTS, usually to support a new service initially, then expanded to replace legacy systems later. Competition among Multiple fixed, cable MSOs, CSPs and mobile and satellite CSPs are substitutes competing in each market for the same services revenue. CSPs compete on instant customer service, customer experience quality, and desirable service bundles, driving service provisioning flow through. All mature and competitive emerging markets in the short term, all markets in the longer term. Rapid introduction of new, complex services and service bundles on packet networks and SDPs Order management systems need to be very flexible and synchronised with product and service catalogues. Inventory and activation systems need to cover service layer equipment. Tighter integration with BSS for status and can be served queries. The activation market will grow. Mobile service bundles throughout the forecast period. IPTV in 2013. Home networking, Saa. S, Iaa. S and additional ‘over the top’ services towards 2015. CSPs are quickly introducing new services. Service bundles are more complex, with dependencies on service infrastructure and end user device capabilities. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 25 Market drivers and inhibitors Service fulfilment system market drivers [1] Table 1 a: Service fulfilment system market drivers [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Driver Description Effect Growing number of subscribers in emerging markets Rapid growth in the number of Revenue is growing as systems support mobile subscribers in emerging more users because of usage sensitive markets, particularly in China, pricing models by vendors. India, the Middle East and Africa, and Central and Latin America. Timeframe Throughout the period. Increasing size and complexity of Continued replacement of bespoke service Throughout the period. networks and services. fulfilment systems by COTS, usually to support a new service initially, then expanded to replace legacy systems later. Competition among Multiple fixed, cable MSOs, CSPs and mobile and satellite CSPs are substitutes competing in each market for the same services revenue. CSPs compete on instant customer service, customer experience quality, and desirable service bundles, driving service provisioning flow through. All mature and competitive emerging markets in the short term, all markets in the longer term. Rapid introduction of new, complex services and service bundles on packet networks and SDPs Order management systems need to be very flexible and synchronised with product and service catalogues. Inventory and activation systems need to cover service layer equipment. Tighter integration with BSS for status and can be served queries. The activation market will grow. Mobile service bundles throughout the forecast period. IPTV in 2013. Home networking, Saa. S, Iaa. S and additional ‘over the top’ services towards 2015. CSPs are quickly introducing new services. Service bundles are more complex, with dependencies on service infrastructure and end user device capabilities. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
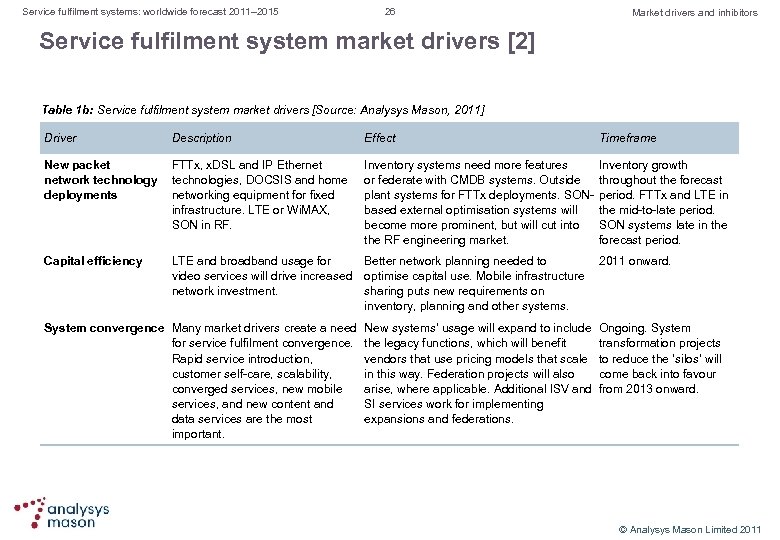 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 26 Market drivers and inhibitors Service fulfilment system market drivers [2] Table 1 b: Service fulfilment system market drivers [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Driver Description New packet FTTx, x. DSL and IP Ethernet network technology technologies, DOCSIS and home deployments networking equipment for fixed infrastructure. LTE or Wi. MAX, SON in RF. Capital efficiency Effect Timeframe Inventory systems need more features Inventory growth or federate with CMDB systems. Outside throughout the forecast plant systems for FTTx deployments. SON period. FTTx and LTE in based external optimisation systems will the mid to late period. become more prominent, but will cut into SON systems late in the RF engineering market. forecast period. LTE and broadband usage for Better network planning needed to 2011 onward. video services will drive increased optimise capital use. Mobile infrastructure network investment. sharing puts new requirements on inventory, planning and other systems. System convergence Many market drivers create a need for service fulfilment convergence. Rapid service introduction, customer self care, scalability, converged services, new mobile services, and new content and data services are the most important. New systems’ usage will expand to include Ongoing. System the legacy functions, which will benefit transformation projects vendors that use pricing models that scale to reduce the ‘silos’ will in this way. Federation projects will also come back into favour arise, where applicable. Additional ISV and from 2013 onward. SI services work for implementing expansions and federations. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 26 Market drivers and inhibitors Service fulfilment system market drivers [2] Table 1 b: Service fulfilment system market drivers [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Driver Description New packet FTTx, x. DSL and IP Ethernet network technology technologies, DOCSIS and home deployments networking equipment for fixed infrastructure. LTE or Wi. MAX, SON in RF. Capital efficiency Effect Timeframe Inventory systems need more features Inventory growth or federate with CMDB systems. Outside throughout the forecast plant systems for FTTx deployments. SON period. FTTx and LTE in based external optimisation systems will the mid to late period. become more prominent, but will cut into SON systems late in the RF engineering market. forecast period. LTE and broadband usage for Better network planning needed to 2011 onward. video services will drive increased optimise capital use. Mobile infrastructure network investment. sharing puts new requirements on inventory, planning and other systems. System convergence Many market drivers create a need for service fulfilment convergence. Rapid service introduction, customer self care, scalability, converged services, new mobile services, and new content and data services are the most important. New systems’ usage will expand to include Ongoing. System the legacy functions, which will benefit transformation projects vendors that use pricing models that scale to reduce the ‘silos’ will in this way. Federation projects will also come back into favour arise, where applicable. Additional ISV and from 2013 onward. SI services work for implementing expansions and federations. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
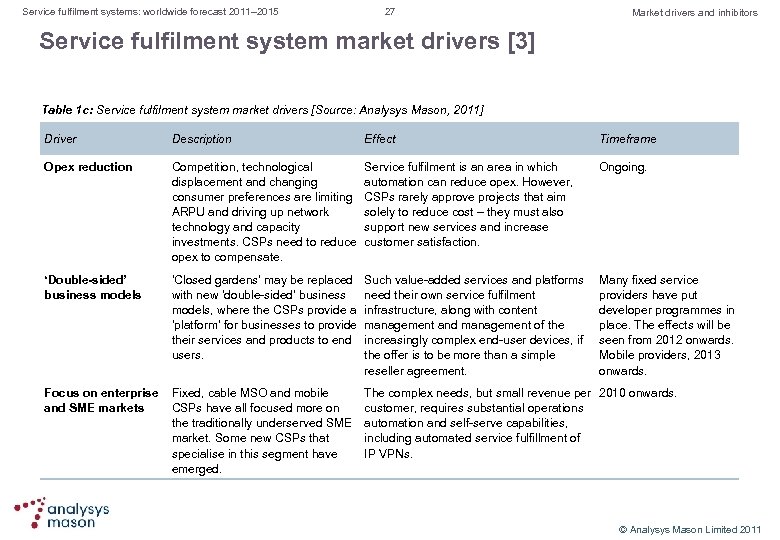 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 27 Market drivers and inhibitors Service fulfilment system market drivers [3] Table 1 c: Service fulfilment system market drivers [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Driver Description Effect Timeframe Opex reduction Competition, technological displacement and changing consumer preferences are limiting ARPU and driving up network technology and capacity investments. CSPs need to reduce opex to compensate. Service fulfilment is an area in which automation can reduce opex. However, CSPs rarely approve projects that aim solely to reduce cost – they must also support new services and increase customer satisfaction. Ongoing. ‘Double-sided’ business models ‘Closed gardens’ may be replaced with new ‘double sided’ business models, where the CSPs provide a ‘platform’ for businesses to provide their services and products to end users. Such value added services and platforms need their own service fulfilment infrastructure, along with content management and management of the increasingly complex end user devices, if the offer is to be more than a simple reseller agreement. Many fixed service providers have put developer programmes in place. The effects will be seen from 2012 onwards. Mobile providers, 2013 onwards. Focus on enterprise Fixed, cable MSO and mobile and SME markets CSPs have all focused more on the traditionally underserved SME market. Some new CSPs that specialise in this segment have emerged. The complex needs, but small revenue per 2010 onwards. customer, requires substantial operations automation and self serve capabilities, including automated service fulfillment of IP VPNs. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 27 Market drivers and inhibitors Service fulfilment system market drivers [3] Table 1 c: Service fulfilment system market drivers [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Driver Description Effect Timeframe Opex reduction Competition, technological displacement and changing consumer preferences are limiting ARPU and driving up network technology and capacity investments. CSPs need to reduce opex to compensate. Service fulfilment is an area in which automation can reduce opex. However, CSPs rarely approve projects that aim solely to reduce cost – they must also support new services and increase customer satisfaction. Ongoing. ‘Double-sided’ business models ‘Closed gardens’ may be replaced with new ‘double sided’ business models, where the CSPs provide a ‘platform’ for businesses to provide their services and products to end users. Such value added services and platforms need their own service fulfilment infrastructure, along with content management and management of the increasingly complex end user devices, if the offer is to be more than a simple reseller agreement. Many fixed service providers have put developer programmes in place. The effects will be seen from 2012 onwards. Mobile providers, 2013 onwards. Focus on enterprise Fixed, cable MSO and mobile and SME markets CSPs have all focused more on the traditionally underserved SME market. Some new CSPs that specialise in this segment have emerged. The complex needs, but small revenue per 2010 onwards. customer, requires substantial operations automation and self serve capabilities, including automated service fulfillment of IP VPNs. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
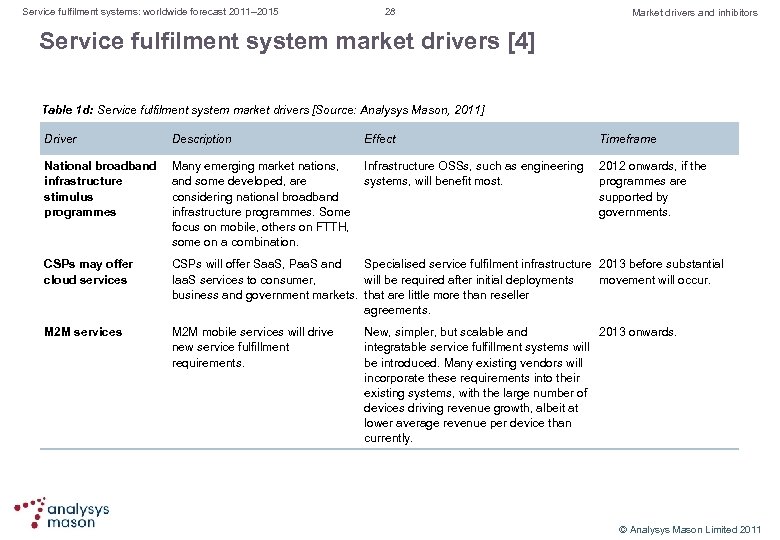 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 28 Market drivers and inhibitors Service fulfilment system market drivers [4] Table 1 d: Service fulfilment system market drivers [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Driver Description Effect Timeframe National broadband infrastructure stimulus programmes Many emerging market nations, Infrastructure OSSs, such as engineering and some developed, are systems, will benefit most. considering national broadband infrastructure programmes. Some focus on mobile, others on FTTH, some on a combination. CSPs may offer cloud services CSPs will offer Saa. S, Paa. S and Specialised service fulfilment infrastructure 2013 before substantial Iaa. S services to consumer, will be required after initial deployments movement will occur. business and government markets. that are little more than reseller agreements. M 2 M services M 2 M mobile services will drive new service fulfillment requirements. 2012 onwards, if the programmes are supported by governments. New, simpler, but scalable and 2013 onwards. integratable service fulfillment systems will be introduced. Many existing vendors will incorporate these requirements into their existing systems, with the large number of devices driving revenue growth, albeit at lower average revenue per device than currently. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 28 Market drivers and inhibitors Service fulfilment system market drivers [4] Table 1 d: Service fulfilment system market drivers [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Driver Description Effect Timeframe National broadband infrastructure stimulus programmes Many emerging market nations, Infrastructure OSSs, such as engineering and some developed, are systems, will benefit most. considering national broadband infrastructure programmes. Some focus on mobile, others on FTTH, some on a combination. CSPs may offer cloud services CSPs will offer Saa. S, Paa. S and Specialised service fulfilment infrastructure 2013 before substantial Iaa. S services to consumer, will be required after initial deployments movement will occur. business and government markets. that are little more than reseller agreements. M 2 M services M 2 M mobile services will drive new service fulfillment requirements. 2012 onwards, if the programmes are supported by governments. New, simpler, but scalable and 2013 onwards. integratable service fulfillment systems will be introduced. Many existing vendors will incorporate these requirements into their existing systems, with the large number of devices driving revenue growth, albeit at lower average revenue per device than currently. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
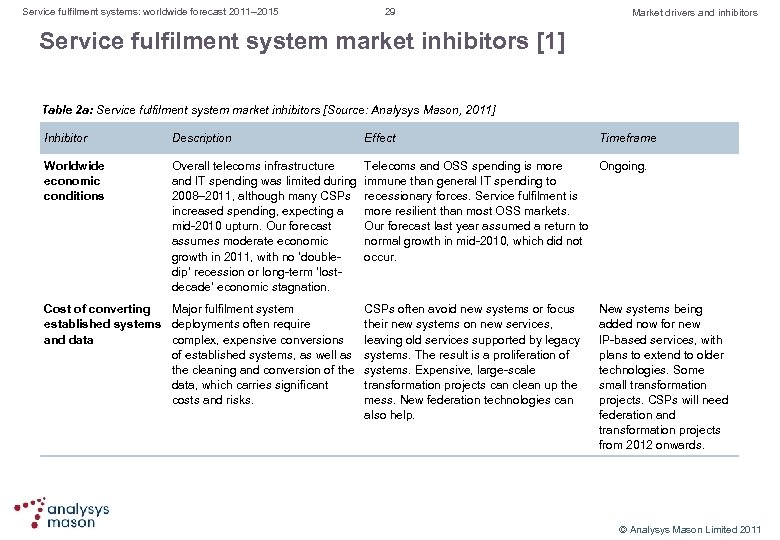 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 29 Market drivers and inhibitors Service fulfilment system market inhibitors [1] Table 2 a: Service fulfilment system market inhibitors [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Inhibitor Description Effect Worldwide economic conditions Overall telecoms infrastructure and IT spending was limited during 2008– 2011, although many CSPs increased spending, expecting a mid 2010 upturn. Our forecast assumes moderate economic growth in 2011, with no ‘double dip’ recession or long term ‘lost decade’ economic stagnation. Telecoms and OSS spending is more Ongoing. immune than general IT spending to recessionary forces. Service fulfilment is more resilient than most OSS markets. Our forecast last year assumed a return to normal growth in mid 2010, which did not occur. Cost of converting Major fulfilment system established systems deployments often require and data complex, expensive conversions of established systems, as well as the cleaning and conversion of the data, which carries significant costs and risks. CSPs often avoid new systems or focus their new systems on new services, leaving old services supported by legacy systems. The result is a proliferation of systems. Expensive, large scale transformation projects can clean up the mess. New federation technologies can also help. Timeframe New systems being added now for new IP based services, with plans to extend to older technologies. Some small transformation projects. CSPs will need federation and transformation projects from 2012 onwards. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 29 Market drivers and inhibitors Service fulfilment system market inhibitors [1] Table 2 a: Service fulfilment system market inhibitors [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Inhibitor Description Effect Worldwide economic conditions Overall telecoms infrastructure and IT spending was limited during 2008– 2011, although many CSPs increased spending, expecting a mid 2010 upturn. Our forecast assumes moderate economic growth in 2011, with no ‘double dip’ recession or long term ‘lost decade’ economic stagnation. Telecoms and OSS spending is more Ongoing. immune than general IT spending to recessionary forces. Service fulfilment is more resilient than most OSS markets. Our forecast last year assumed a return to normal growth in mid 2010, which did not occur. Cost of converting Major fulfilment system established systems deployments often require and data complex, expensive conversions of established systems, as well as the cleaning and conversion of the data, which carries significant costs and risks. CSPs often avoid new systems or focus their new systems on new services, leaving old services supported by legacy systems. The result is a proliferation of systems. Expensive, large scale transformation projects can clean up the mess. New federation technologies can also help. Timeframe New systems being added now for new IP based services, with plans to extend to older technologies. Some small transformation projects. CSPs will need federation and transformation projects from 2012 onwards. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
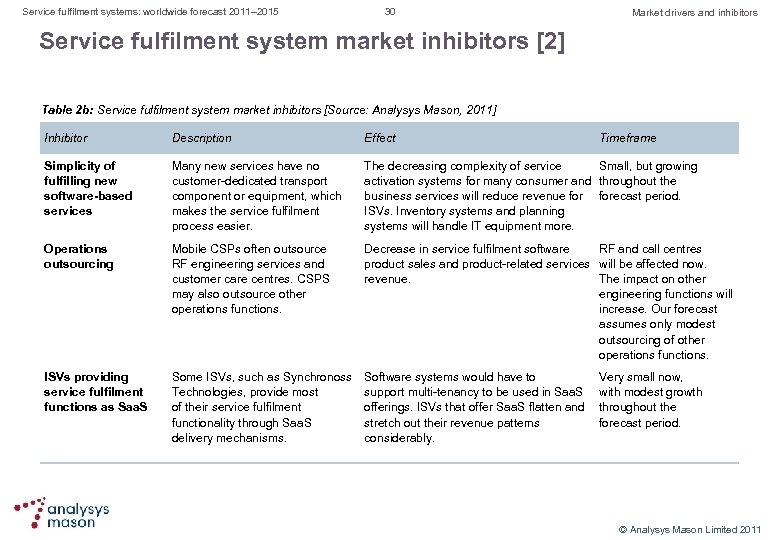 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 30 Market drivers and inhibitors Service fulfilment system market inhibitors [2] Table 2 b: Service fulfilment system market inhibitors [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Inhibitor Description Effect Timeframe Simplicity of fulfilling new software-based services Many new services have no customer dedicated transport component or equipment, which makes the service fulfilment process easier. The decreasing complexity of service Small, but growing activation systems for many consumer and throughout the business services will reduce revenue forecast period. ISVs. Inventory systems and planning systems will handle IT equipment more. Operations outsourcing Mobile CSPs often outsource RF engineering services and customer care centres. CSPS may also outsource other operations functions. Decrease in service fulfilment software RF and call centres product sales and product related services will be affected now. revenue. The impact on other engineering functions will increase. Our forecast assumes only modest outsourcing of other operations functions. ISVs providing service fulfilment functions as Saa. S Some ISVs, such as Synchronoss Technologies, provide most of their service fulfilment functionality through Saa. S delivery mechanisms. Software systems would have to support multi tenancy to be used in Saa. S offerings. ISVs that offer Saa. S flatten and stretch out their revenue patterns considerably. Very small now, with modest growth throughout the forecast period. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 30 Market drivers and inhibitors Service fulfilment system market inhibitors [2] Table 2 b: Service fulfilment system market inhibitors [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Inhibitor Description Effect Timeframe Simplicity of fulfilling new software-based services Many new services have no customer dedicated transport component or equipment, which makes the service fulfilment process easier. The decreasing complexity of service Small, but growing activation systems for many consumer and throughout the business services will reduce revenue forecast period. ISVs. Inventory systems and planning systems will handle IT equipment more. Operations outsourcing Mobile CSPs often outsource RF engineering services and customer care centres. CSPS may also outsource other operations functions. Decrease in service fulfilment software RF and call centres product sales and product related services will be affected now. revenue. The impact on other engineering functions will increase. Our forecast assumes only modest outsourcing of other operations functions. ISVs providing service fulfilment functions as Saa. S Some ISVs, such as Synchronoss Technologies, provide most of their service fulfilment functionality through Saa. S delivery mechanisms. Software systems would have to support multi tenancy to be used in Saa. S offerings. ISVs that offer Saa. S flatten and stretch out their revenue patterns considerably. Very small now, with modest growth throughout the forecast period. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 31 Document map: Business environment Document map Executive summary Recommendations Forecast Market drivers and inhibitors Business environment Market definition About the author and Analysys Mason © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 31 Document map: Business environment Document map Executive summary Recommendations Forecast Market drivers and inhibitors Business environment Market definition About the author and Analysys Mason © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 32 Business environment Telecoms market growth was dampened in 2010, except in emerging markets, while data grew, but ARPU did not Economic weakness in Europe, Japan, and NA continues l l l Consumer demand continues to be weak because of unemployment, the decline in house prices and the poor performance of retirement funds. A reduced rate of GDP growth in developed economies is impacting the telecoms industry revenue. Telecoms investments were made primarily in projects to increase revenue, with very few seeking operational cost reductions. Evolution to IP-based networks and services l l l Growth in data services l l New multimedia services delivered via fixed broadband, such as IPTV, Vo. IP and video conferencing, drove the need for higher capacity NGA infrastructure such as GPON and FTTx, and the service fulfilment functions to support them Mobile CSPs experienced increased volumes of data traffic, but decreasing ARPU, as competition depressed prices. They moved away from unlimited usage plans towards tiered usage pricing structures. Traditional voice, data and video services are all now available over IP. NGN evolution is underway in nearly all CSPs – few are attempting revolutionary change. IP based networks provide easier and more flexible network planning, configuration, optimisation and quality of service management. The focus of new services has shifted from the network layer to the services layer, and from managing individual services to managing increasingly complex service bundles. Emerging market growth opportunities l l CSPs in emerging markets continued to invest in telecoms software because they faced increasing operational complexity as a result of growth in subscriber numbers and increased competition. Small (Tier 3) CSPs are adopting integrated service fulfilment solutions with pre configured systems. These CSPs are adapting their operations to the software and, over time, adapting the software to meet their needs. They are also buying Saa. S versions at first, then bringing the systems in house over time. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 32 Business environment Telecoms market growth was dampened in 2010, except in emerging markets, while data grew, but ARPU did not Economic weakness in Europe, Japan, and NA continues l l l Consumer demand continues to be weak because of unemployment, the decline in house prices and the poor performance of retirement funds. A reduced rate of GDP growth in developed economies is impacting the telecoms industry revenue. Telecoms investments were made primarily in projects to increase revenue, with very few seeking operational cost reductions. Evolution to IP-based networks and services l l l Growth in data services l l New multimedia services delivered via fixed broadband, such as IPTV, Vo. IP and video conferencing, drove the need for higher capacity NGA infrastructure such as GPON and FTTx, and the service fulfilment functions to support them Mobile CSPs experienced increased volumes of data traffic, but decreasing ARPU, as competition depressed prices. They moved away from unlimited usage plans towards tiered usage pricing structures. Traditional voice, data and video services are all now available over IP. NGN evolution is underway in nearly all CSPs – few are attempting revolutionary change. IP based networks provide easier and more flexible network planning, configuration, optimisation and quality of service management. The focus of new services has shifted from the network layer to the services layer, and from managing individual services to managing increasingly complex service bundles. Emerging market growth opportunities l l CSPs in emerging markets continued to invest in telecoms software because they faced increasing operational complexity as a result of growth in subscriber numbers and increased competition. Small (Tier 3) CSPs are adopting integrated service fulfilment solutions with pre configured systems. These CSPs are adapting their operations to the software and, over time, adapting the software to meet their needs. They are also buying Saa. S versions at first, then bringing the systems in house over time. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 33 Business environment In 2010, CSPs continued to target specific service needs in service fulfilment l l l CSPs use a wide variety of methods to implement service fulfilment. Even the most sophisticated CSPs use many manual steps to manage low volume, complex services. However, all modern CSPs implement automated fulfilment systems for high volume services, such as residential voice, mobile voice and data, Vo. IP, x. DSL and FTTx. Large, established CSPs have a legacy of department specific approaches to service fulfilment. These CSPs find it easier to implement specific ‘best of breed’ systems from different vendors than to implement a complete change in service fulfilment processes and support systems. New CSPs and some older CSPs that are facing high growth with few support systems in place are more inclined to implement complete, integrated service fulfilment systems. Such CSPs are very cost conscious, but make quicker decisions and depend on an SI, or, increasingly, on a full solution ISV to solve problems. CSPs are deploying systems that can support multiple network technologies for converged services. They have focused the most attention on inventory management systems because of the need to understand the capabilities of available resources and the configuration of these resources in serving their customers. CSPs are making a strategic move towards consolidation of fulfilment systems, but this consolidation will maintain four distinct environments in most CSPs in the short term: PSTN, residential broadband, mobile and business services. CSPs initiated fewer projects between 2008 and 2010 than in previous years, but did not halt established projects and, in some cases, expanded them. All industry participants were under significant price pressure during 2008– 2010, and margins were tight. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 33 Business environment In 2010, CSPs continued to target specific service needs in service fulfilment l l l CSPs use a wide variety of methods to implement service fulfilment. Even the most sophisticated CSPs use many manual steps to manage low volume, complex services. However, all modern CSPs implement automated fulfilment systems for high volume services, such as residential voice, mobile voice and data, Vo. IP, x. DSL and FTTx. Large, established CSPs have a legacy of department specific approaches to service fulfilment. These CSPs find it easier to implement specific ‘best of breed’ systems from different vendors than to implement a complete change in service fulfilment processes and support systems. New CSPs and some older CSPs that are facing high growth with few support systems in place are more inclined to implement complete, integrated service fulfilment systems. Such CSPs are very cost conscious, but make quicker decisions and depend on an SI, or, increasingly, on a full solution ISV to solve problems. CSPs are deploying systems that can support multiple network technologies for converged services. They have focused the most attention on inventory management systems because of the need to understand the capabilities of available resources and the configuration of these resources in serving their customers. CSPs are making a strategic move towards consolidation of fulfilment systems, but this consolidation will maintain four distinct environments in most CSPs in the short term: PSTN, residential broadband, mobile and business services. CSPs initiated fewer projects between 2008 and 2010 than in previous years, but did not halt established projects and, in some cases, expanded them. All industry participants were under significant price pressure during 2008– 2010, and margins were tight. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 34 Business environment In 2010, interest in department-sized transformations and federation and larger-scale transformations grew l l The general market is showing more interest in convergent fulfilment systems that can support immediate service needs and, at the same time, provide a basis for supporting future services. Few CSPs are converting or consolidating old fulfilment systems that work for the services they support, although pressure is growing to do so as they seek to reduce costs by standardising technologies and training people in multiple technology areas. Many CSPs are adopting a federated approach to addressing the need for regional consolidation and functional integration. Instead of selecting one system and converting the others, they are focusing on a subset of functionality and data that must be held in common. They implement a complementary, usually new, system that provides the common functionality and controls the shared data. They then migrate data to this system from the established systems, which continue to manage their own unique needs. Over time, the common system takes over more functions, but a forced conversion is not necessary. This approach has been used in the billing arena for some time and is finding its way into the service catalogue and the inventory and order management markets. Spend on service fulfilment goes to many small ISVs. This segment is slowly consolidating, as CSPs pursue larger projects using multiple technologies. In the past few years, Amdocs has acquired Cramer Systems and Jacobs. Rimell, CSG Systems has bought Telution, Oracle purchased Meta. Solv Software and Netsure Telecom, and Subex acquired Syndesis then sold it to NEC, among others. In 2010, a number of vendors that had recently entered the inventory, order management and network planning areas for the first time expanded their business. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 34 Business environment In 2010, interest in department-sized transformations and federation and larger-scale transformations grew l l The general market is showing more interest in convergent fulfilment systems that can support immediate service needs and, at the same time, provide a basis for supporting future services. Few CSPs are converting or consolidating old fulfilment systems that work for the services they support, although pressure is growing to do so as they seek to reduce costs by standardising technologies and training people in multiple technology areas. Many CSPs are adopting a federated approach to addressing the need for regional consolidation and functional integration. Instead of selecting one system and converting the others, they are focusing on a subset of functionality and data that must be held in common. They implement a complementary, usually new, system that provides the common functionality and controls the shared data. They then migrate data to this system from the established systems, which continue to manage their own unique needs. Over time, the common system takes over more functions, but a forced conversion is not necessary. This approach has been used in the billing arena for some time and is finding its way into the service catalogue and the inventory and order management markets. Spend on service fulfilment goes to many small ISVs. This segment is slowly consolidating, as CSPs pursue larger projects using multiple technologies. In the past few years, Amdocs has acquired Cramer Systems and Jacobs. Rimell, CSG Systems has bought Telution, Oracle purchased Meta. Solv Software and Netsure Telecom, and Subex acquired Syndesis then sold it to NEC, among others. In 2010, a number of vendors that had recently entered the inventory, order management and network planning areas for the first time expanded their business. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 35 Business environment In 2010, major ISVs continued to expand their professional services l l l A service fulfilment installation involves a significant amount of software and services. Typically, the value of the associated professional services is three to five times that of the software, when customised features, integration with other OSS and data migration are included. The CSP’s IT staff often manages many of the services. Local IT integration firms frequently play a large role, as do the major SIs, such as Accenture and IBM Global Services. These obtain significant amounts of revenue from professional services for service fulfilment – more than do the software vendors, in many situations. However, a notable minority of ISVs, including Amdocs, Net. Cracker Technology (a part of NEC), and several vendors in emerging markets, including Asia. Info Linkage, Clarity, Comarch and Comptel, have also successfully sought this work. Some of the ISVs that provide service fulfilment also provide outsourced operations, often as an option. In an outsourced operation, the CSP makes a contract with the vendor to provide software and the IT systems to run the software and the operations personnel to manage orders. This approach has been popular in cable billing and mobile RF engineering for many years, and shows some signs of migrating into other operational areas. The re emergence of start up CSPs with little infrastructure and limited expertise creates the greatest demand for outsourced service fulfilment or Saa. S. Synchronoss Technologies is the largest vendor of outsourced service fulfilment in the USA. Some vendors are using Saa. S as a temporary measure to provide functionality quickly, until the CSPs’ data centres are ready to implement the software. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 35 Business environment In 2010, major ISVs continued to expand their professional services l l l A service fulfilment installation involves a significant amount of software and services. Typically, the value of the associated professional services is three to five times that of the software, when customised features, integration with other OSS and data migration are included. The CSP’s IT staff often manages many of the services. Local IT integration firms frequently play a large role, as do the major SIs, such as Accenture and IBM Global Services. These obtain significant amounts of revenue from professional services for service fulfilment – more than do the software vendors, in many situations. However, a notable minority of ISVs, including Amdocs, Net. Cracker Technology (a part of NEC), and several vendors in emerging markets, including Asia. Info Linkage, Clarity, Comarch and Comptel, have also successfully sought this work. Some of the ISVs that provide service fulfilment also provide outsourced operations, often as an option. In an outsourced operation, the CSP makes a contract with the vendor to provide software and the IT systems to run the software and the operations personnel to manage orders. This approach has been popular in cable billing and mobile RF engineering for many years, and shows some signs of migrating into other operational areas. The re emergence of start up CSPs with little infrastructure and limited expertise creates the greatest demand for outsourced service fulfilment or Saa. S. Synchronoss Technologies is the largest vendor of outsourced service fulfilment in the USA. Some vendors are using Saa. S as a temporary measure to provide functionality quickly, until the CSPs’ data centres are ready to implement the software. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 36 Business environment In 2010– 2011, the consolidation of service fulfilment systems continued l l l The service fulfilment market has been consolidating for many years as major ISVs gain market share with their service fulfilment suites and integrate these suites into larger BSS/OSS offerings. In 2011, NEMs further consolidated the market; Ericsson bought Telcordia and NEC bought Subex’s service fulfilment products previously acquired from Syndesis. We do not expect consolidation to affect the forecast to any great extent. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 36 Business environment In 2010– 2011, the consolidation of service fulfilment systems continued l l l The service fulfilment market has been consolidating for many years as major ISVs gain market share with their service fulfilment suites and integrate these suites into larger BSS/OSS offerings. In 2011, NEMs further consolidated the market; Ericsson bought Telcordia and NEC bought Subex’s service fulfilment products previously acquired from Syndesis. We do not expect consolidation to affect the forecast to any great extent. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 37 Document map: Market definition Document map Executive summary Recommendations Forecast Market drivers and inhibitors Business environment Market definition About the author and Analysys Mason © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 37 Document map: Market definition Document map Executive summary Recommendations Forecast Market drivers and inhibitors Business environment Market definition About the author and Analysys Mason © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
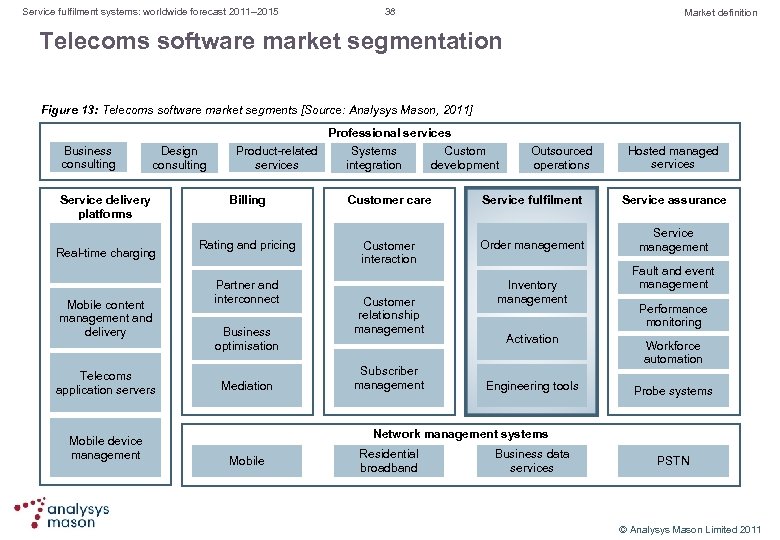 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 38 Market definition Telecoms software market segmentation Figure 13: Telecoms software market segments [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Professional services Business consulting Design consulting Service delivery platforms Real time charging Mobile content management and delivery Telecoms application servers Mobile device management Product related services Systems integration Custom development Outsourced operations Hosted managed services Billing Customer care Service fulfilment Service assurance Rating and pricing Customer interaction Order management Service management Partner and interconnect Business optimisation Mediation Customer relationship management Subscriber management Inventory management Activation Engineering tools Fault and event management Performance monitoring Workforce automation Probe systems Network management systems Mobile Residential broadband Business data services PSTN © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 38 Market definition Telecoms software market segmentation Figure 13: Telecoms software market segments [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Professional services Business consulting Design consulting Service delivery platforms Real time charging Mobile content management and delivery Telecoms application servers Mobile device management Product related services Systems integration Custom development Outsourced operations Hosted managed services Billing Customer care Service fulfilment Service assurance Rating and pricing Customer interaction Order management Service management Partner and interconnect Business optimisation Mediation Customer relationship management Subscriber management Inventory management Activation Engineering tools Fault and event management Performance monitoring Workforce automation Probe systems Network management systems Mobile Residential broadband Business data services PSTN © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
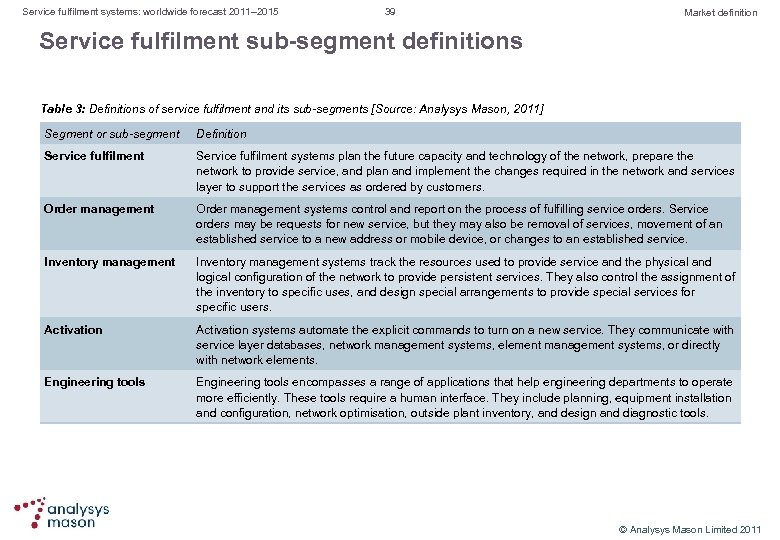 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 39 Market definition Service fulfilment sub-segment definitions Table 3: Definitions of service fulfilment and its sub-segments [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Segment or sub-segment Definition Service fulfilment systems plan the future capacity and technology of the network, prepare the network to provide service, and plan and implement the changes required in the network and services layer to support the services as ordered by customers. Order management systems control and report on the process of fulfilling service orders. Service orders may be requests for new service, but they may also be removal of services, movement of an established service to a new address or mobile device, or changes to an established service. Inventory management systems track the resources used to provide service and the physical and logical configuration of the network to provide persistent services. They also control the assignment of the inventory to specific uses, and design special arrangements to provide special services for specific users. Activation systems automate the explicit commands to turn on a new service. They communicate with service layer databases, network management systems, element management systems, or directly with network elements. Engineering tools encompasses a range of applications that help engineering departments to operate more efficiently. These tools require a human interface. They include planning, equipment installation and configuration, network optimisation, outside plant inventory, and design and diagnostic tools. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 39 Market definition Service fulfilment sub-segment definitions Table 3: Definitions of service fulfilment and its sub-segments [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Segment or sub-segment Definition Service fulfilment systems plan the future capacity and technology of the network, prepare the network to provide service, and plan and implement the changes required in the network and services layer to support the services as ordered by customers. Order management systems control and report on the process of fulfilling service orders. Service orders may be requests for new service, but they may also be removal of services, movement of an established service to a new address or mobile device, or changes to an established service. Inventory management systems track the resources used to provide service and the physical and logical configuration of the network to provide persistent services. They also control the assignment of the inventory to specific uses, and design special arrangements to provide special services for specific users. Activation systems automate the explicit commands to turn on a new service. They communicate with service layer databases, network management systems, element management systems, or directly with network elements. Engineering tools encompasses a range of applications that help engineering departments to operate more efficiently. These tools require a human interface. They include planning, equipment installation and configuration, network optimisation, outside plant inventory, and design and diagnostic tools. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
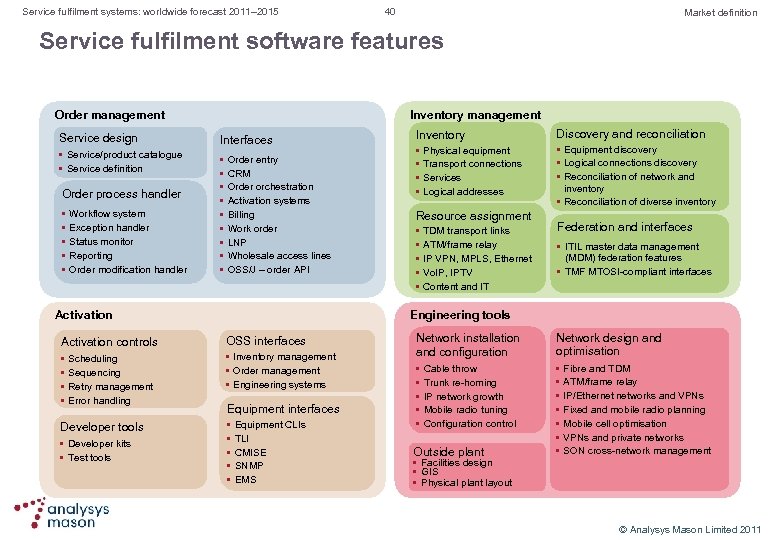 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 40 Market definition Service fulfilment software features Order management Inventory management Service design Interfaces Inventory Discovery and reconciliation • Service/product catalogue • Service definition • • • • Equipment discovery • Logical connections discovery • Reconciliation of network and inventory • Reconciliation of diverse inventory Resource assignment Order process handler • • • Workflow system Exception handler Status monitor Reporting Order modification handler Order entry CRM Order orchestration Activation systems Billing Work order LNP Wholesale access lines OSS/J – order API Activation OSS interfaces • • • Inventory management • Order management • Engineering systems Developer tools • Developer kits • Test tools TDM transport links ATM/frame relay IP VPN, MPLS, Ethernet Vo. IP, IPTV Content and IT Federation and interfaces • ITIL master data management (MDM) federation features • TMF MTOSI compliant interfaces Engineering tools Activation controls Scheduling Sequencing Retry management Error handling • • • Physical equipment Transport connections Services Logical addresses Equipment interfaces • • • Equipment CLIs TLI CMISE SNMP EMS Network installation and configuration Network design and optimisation • • • Cable throw Trunk re homing IP network growth Mobile radio tuning Configuration control Outside plant Fibre and TDM ATM/frame relay IP/Ethernet networks and VPNs Fixed and mobile radio planning Mobile cell optimisation VPNs and private networks SON cross network management • Facilities design • GIS • Physical plant layout © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 40 Market definition Service fulfilment software features Order management Inventory management Service design Interfaces Inventory Discovery and reconciliation • Service/product catalogue • Service definition • • • • Equipment discovery • Logical connections discovery • Reconciliation of network and inventory • Reconciliation of diverse inventory Resource assignment Order process handler • • • Workflow system Exception handler Status monitor Reporting Order modification handler Order entry CRM Order orchestration Activation systems Billing Work order LNP Wholesale access lines OSS/J – order API Activation OSS interfaces • • • Inventory management • Order management • Engineering systems Developer tools • Developer kits • Test tools TDM transport links ATM/frame relay IP VPN, MPLS, Ethernet Vo. IP, IPTV Content and IT Federation and interfaces • ITIL master data management (MDM) federation features • TMF MTOSI compliant interfaces Engineering tools Activation controls Scheduling Sequencing Retry management Error handling • • • Physical equipment Transport connections Services Logical addresses Equipment interfaces • • • Equipment CLIs TLI CMISE SNMP EMS Network installation and configuration Network design and optimisation • • • Cable throw Trunk re homing IP network growth Mobile radio tuning Configuration control Outside plant Fibre and TDM ATM/frame relay IP/Ethernet networks and VPNs Fixed and mobile radio planning Mobile cell optimisation VPNs and private networks SON cross network management • Facilities design • GIS • Physical plant layout © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
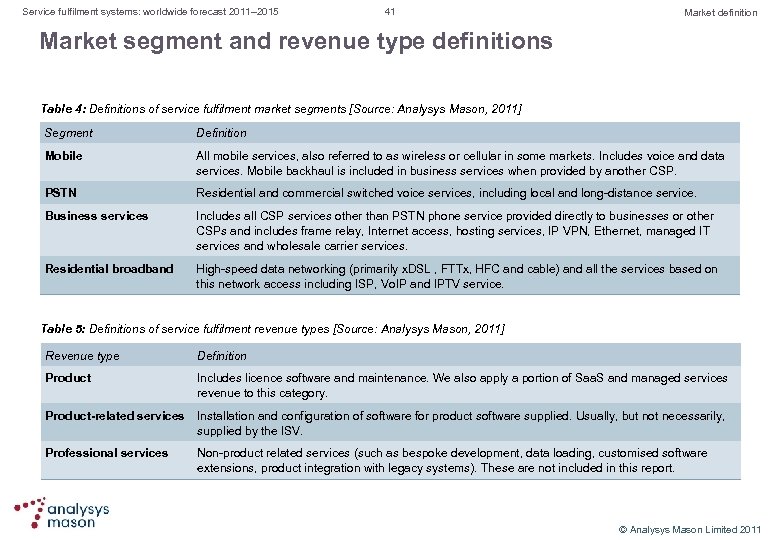 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 41 Market definition Market segment and revenue type definitions Table 4: Definitions of service fulfilment market segments [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Segment Definition Mobile All mobile services, also referred to as wireless or cellular in some markets. Includes voice and data services. Mobile backhaul is included in business services when provided by another CSP. PSTN Residential and commercial switched voice services, including local and long distance service. Business services Includes all CSP services other than PSTN phone service provided directly to businesses or other CSPs and includes frame relay, Internet access, hosting services, IP VPN, Ethernet, managed IT services and wholesale carrier services. Residential broadband High speed data networking (primarily x. DSL , FTTx, HFC and cable) and all the services based on this network access including ISP, Vo. IP and IPTV service. Table 5: Definitions of service fulfilment revenue types [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Revenue type Definition Product Includes licence software and maintenance. We also apply a portion of Saa. S and managed services revenue to this category. Product-related services Installation and configuration of software for product software supplied. Usually, but not necessarily, supplied by the ISV. Professional services Non product related services (such as bespoke development, data loading, customised software extensions, product integration with legacy systems). These are not included in this report. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 41 Market definition Market segment and revenue type definitions Table 4: Definitions of service fulfilment market segments [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Segment Definition Mobile All mobile services, also referred to as wireless or cellular in some markets. Includes voice and data services. Mobile backhaul is included in business services when provided by another CSP. PSTN Residential and commercial switched voice services, including local and long distance service. Business services Includes all CSP services other than PSTN phone service provided directly to businesses or other CSPs and includes frame relay, Internet access, hosting services, IP VPN, Ethernet, managed IT services and wholesale carrier services. Residential broadband High speed data networking (primarily x. DSL , FTTx, HFC and cable) and all the services based on this network access including ISP, Vo. IP and IPTV service. Table 5: Definitions of service fulfilment revenue types [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Revenue type Definition Product Includes licence software and maintenance. We also apply a portion of Saa. S and managed services revenue to this category. Product-related services Installation and configuration of software for product software supplied. Usually, but not necessarily, supplied by the ISV. Professional services Non product related services (such as bespoke development, data loading, customised software extensions, product integration with legacy systems). These are not included in this report. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
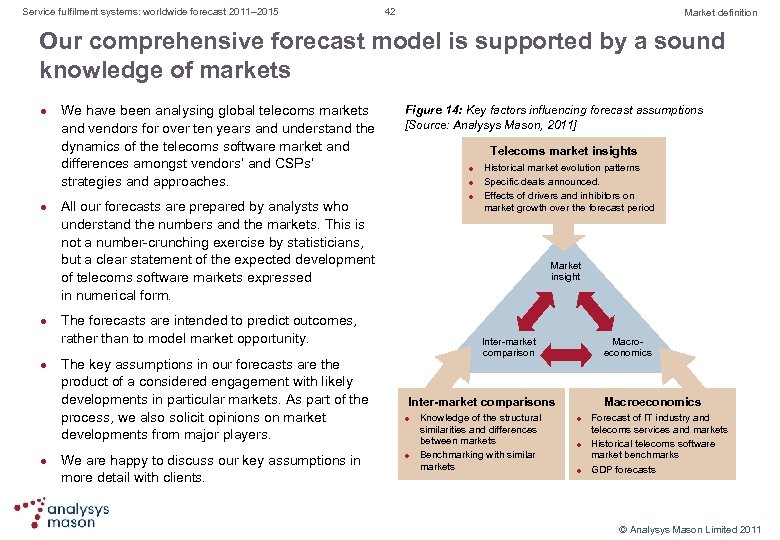 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 42 Market definition Our comprehensive forecast model is supported by a sound knowledge of markets l l l We have been analysing global telecoms markets and vendors for over ten years and understand the dynamics of the telecoms software market and differences amongst vendors’ and CSPs’ strategies and approaches. Figure 14: Key factors influencing forecast assumptions [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Telecoms market insights l l l All our forecasts are prepared by analysts who understand the numbers and the markets. This is not a number crunching exercise by statisticians, but a clear statement of the expected development of telecoms software markets expressed in numerical form. Market insight The forecasts are intended to predict outcomes, rather than to model market opportunity. The key assumptions in our forecasts are the product of a considered engagement with likely developments in particular markets. As part of the process, we also solicit opinions on market developments from major players. We are happy to discuss our key assumptions in more detail with clients. Historical market evolution patterns Specific deals announced. Effects of drivers and inhibitors on market growth over the forecast period Inter market comparison Macro economics Inter-market comparisons l l Knowledge of the structural similarities and differences between markets Benchmarking with similar markets Macroeconomics l l l Forecast of IT industry and telecoms services and markets Historical telecoms software market benchmarks GDP forecasts © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 42 Market definition Our comprehensive forecast model is supported by a sound knowledge of markets l l l We have been analysing global telecoms markets and vendors for over ten years and understand the dynamics of the telecoms software market and differences amongst vendors’ and CSPs’ strategies and approaches. Figure 14: Key factors influencing forecast assumptions [Source: Analysys Mason, 2011] Telecoms market insights l l l All our forecasts are prepared by analysts who understand the numbers and the markets. This is not a number crunching exercise by statisticians, but a clear statement of the expected development of telecoms software markets expressed in numerical form. Market insight The forecasts are intended to predict outcomes, rather than to model market opportunity. The key assumptions in our forecasts are the product of a considered engagement with likely developments in particular markets. As part of the process, we also solicit opinions on market developments from major players. We are happy to discuss our key assumptions in more detail with clients. Historical market evolution patterns Specific deals announced. Effects of drivers and inhibitors on market growth over the forecast period Inter market comparison Macro economics Inter-market comparisons l l Knowledge of the structural similarities and differences between markets Benchmarking with similar markets Macroeconomics l l l Forecast of IT industry and telecoms services and markets Historical telecoms software market benchmarks GDP forecasts © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 43 Document map: About the author and Analysys Mason Document map Executive summary Recommendations Forecast Market drivers and inhibitors Business environment Market definition About the author and Analysys Mason © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 43 Document map: About the author and Analysys Mason Document map Executive summary Recommendations Forecast Market drivers and inhibitors Business environment Market definition About the author and Analysys Mason © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 44 About the author and Analysys Mason Author Customer Care research CRM Mark H. Mortensen (Principal Analyst) is the lead analyst for Analysys Mason’s and Service Fulfilment research programmes, which are part of the Telecoms Software stream. His primary areas of specialisation include customer self care, M 2 M and cloud operations, master catalogue and data management architectures and multi channel marketing architectures. The first 20 years of Mark’s career were spent at Bell Laboratories, where he specialised in starting software products for new markets and network technologies and in the interaction of software with the underlying network hardware. Mark was Chief Scientist of Management Systems at Bell Labs, and has also been president of his own OSS strategy consulting company, CMO at the inventory specialist Granite Systems, VP of Product Strategy at Telcordia Technologies, and SVP of Marketing with a network planning software vendor. Mark holds an MPhil and a Ph. D in physics from Yale University and has received two AT&T Architecture awards for innovative software solutions. He is also an adjunct faculty member of UMass Lowell in the College of Management. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 44 About the author and Analysys Mason Author Customer Care research CRM Mark H. Mortensen (Principal Analyst) is the lead analyst for Analysys Mason’s and Service Fulfilment research programmes, which are part of the Telecoms Software stream. His primary areas of specialisation include customer self care, M 2 M and cloud operations, master catalogue and data management architectures and multi channel marketing architectures. The first 20 years of Mark’s career were spent at Bell Laboratories, where he specialised in starting software products for new markets and network technologies and in the interaction of software with the underlying network hardware. Mark was Chief Scientist of Management Systems at Bell Labs, and has also been president of his own OSS strategy consulting company, CMO at the inventory specialist Granite Systems, VP of Product Strategy at Telcordia Technologies, and SVP of Marketing with a network planning software vendor. Mark holds an MPhil and a Ph. D in physics from Yale University and has received two AT&T Architecture awards for innovative software solutions. He is also an adjunct faculty member of UMass Lowell in the College of Management. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 45 About the author and Analysys Mason Copyright Published by Analysys Mason Limited, Bush House, North West Wing, Aldwych, London WC 2 B 4 PJ, UK Tel: +44 (0)845 600 5244; Fax: +44 (0)20 7395 9001; Email: research@analysysmason. com; Web: www. analysysmason. com/research Registered in England No. 5177472 © Analysys Mason Limited 2011 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means – electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise – without the prior written permission of the publisher. ISBN 978 1 906881 97 9 Disclaimer Analysys Mason Limited maintains that all reasonable care and skill have been used in the compilation of this publication. However, Analysys Mason Limited shall not be under any liability for loss or damage (including consequential loss) whatsoever or howsoever arising as a result of the use of this publication by the customer, his servants, agents or any third party. Analysys Mason Limited recognises that many terms appearing in this report are proprietary; all such trademarks are acknowledged and every effort has been made to indicate them by the normal UK publishing practice of capitalisation. However, the presence of a term, in whatever form, does not affect its legal status as a trademark. The opinions expressed are those of the stated author only. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 45 About the author and Analysys Mason Copyright Published by Analysys Mason Limited, Bush House, North West Wing, Aldwych, London WC 2 B 4 PJ, UK Tel: +44 (0)845 600 5244; Fax: +44 (0)20 7395 9001; Email: research@analysysmason. com; Web: www. analysysmason. com/research Registered in England No. 5177472 © Analysys Mason Limited 2011 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means – electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise – without the prior written permission of the publisher. ISBN 978 1 906881 97 9 Disclaimer Analysys Mason Limited maintains that all reasonable care and skill have been used in the compilation of this publication. However, Analysys Mason Limited shall not be under any liability for loss or damage (including consequential loss) whatsoever or howsoever arising as a result of the use of this publication by the customer, his servants, agents or any third party. Analysys Mason Limited recognises that many terms appearing in this report are proprietary; all such trademarks are acknowledged and every effort has been made to indicate them by the normal UK publishing practice of capitalisation. However, the presence of a term, in whatever form, does not affect its legal status as a trademark. The opinions expressed are those of the stated author only. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 46 About the author and Analysys Mason About Analysys Mason We’re experts in telecoms, media and technology (TMT). This know how underpins everything we do and helps our clients change their businesses for the better. Regulation Systems and infrastructure Strategy and planning Transaction support Telecoms, media and technology (TMT) Marketing and products Technical audit and assurance Procurement At the heart of our approach is a simple, but enormously powerful idea: applied intelligence. By harnessing our collective brainpower we can solve real world problems and deliver tangible benefits for our customers. As a Japanese proverb says, ‘all of us are smarter than any of us’. We’re passionate about what we do, with the focus and determination to take on and solve the toughest problems to help our clients. We’ll rise to the challenge and enjoy it. In fact when it comes to problem solving, there’s a real sense of ‘the tougher the better’. It’s this unique combination of our applied intelligence, effective problem solving and the ability to look closer and see further that makes Analysys Mason special. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 46 About the author and Analysys Mason About Analysys Mason We’re experts in telecoms, media and technology (TMT). This know how underpins everything we do and helps our clients change their businesses for the better. Regulation Systems and infrastructure Strategy and planning Transaction support Telecoms, media and technology (TMT) Marketing and products Technical audit and assurance Procurement At the heart of our approach is a simple, but enormously powerful idea: applied intelligence. By harnessing our collective brainpower we can solve real world problems and deliver tangible benefits for our customers. As a Japanese proverb says, ‘all of us are smarter than any of us’. We’re passionate about what we do, with the focus and determination to take on and solve the toughest problems to help our clients. We’ll rise to the challenge and enjoy it. In fact when it comes to problem solving, there’s a real sense of ‘the tougher the better’. It’s this unique combination of our applied intelligence, effective problem solving and the ability to look closer and see further that makes Analysys Mason special. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 47 About the author and Analysys Mason Research from Analysys Mason Our subscription research programmes address key industry dynamics in order to help clients interpret the changing market The programmes focus on five key areas: Consumer services Enterprise services Network technologies Telecoms software Regional markets We analyse, track and forecast the different services accessed by consumers and enterprises, as well as the software, infrastructure and technology that underpins the delivery of those services. Subscribing to our research programmes gives you regular and timely intelligence. It also provides direct access to our team of analysts – that is, the opportunity to engage one to one with our subject experts for insight, opinion and practical advice relating to your most critical business decisions. Our custom research service offers in-depth, tailored analysis that addresses specific issues to meet your exact requirements Our experienced custom research team can undertake market sizing and analysis, and competitor and partner profiling, supported by all the analysis and insight you require. In addition, we can carry out expert interviews and quantitative surveys to obtain fresh and genuine insights, and we can deliver reliable benchmark data together with first class interpretation and advice on getting the best from such information. For more information about our research programmes and custom research services, please visit www. analysysmason. com/research. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 47 About the author and Analysys Mason Research from Analysys Mason Our subscription research programmes address key industry dynamics in order to help clients interpret the changing market The programmes focus on five key areas: Consumer services Enterprise services Network technologies Telecoms software Regional markets We analyse, track and forecast the different services accessed by consumers and enterprises, as well as the software, infrastructure and technology that underpins the delivery of those services. Subscribing to our research programmes gives you regular and timely intelligence. It also provides direct access to our team of analysts – that is, the opportunity to engage one to one with our subject experts for insight, opinion and practical advice relating to your most critical business decisions. Our custom research service offers in-depth, tailored analysis that addresses specific issues to meet your exact requirements Our experienced custom research team can undertake market sizing and analysis, and competitor and partner profiling, supported by all the analysis and insight you require. In addition, we can carry out expert interviews and quantitative surveys to obtain fresh and genuine insights, and we can deliver reliable benchmark data together with first class interpretation and advice on getting the best from such information. For more information about our research programmes and custom research services, please visit www. analysysmason. com/research. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
 Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 48 About the author and Analysys Mason Consulting from Analysys Mason For more than 25 years, our consultants have been bringing the benefits of applied intelligence to enable clients around the world to make the most of their opportunities Unlike some consultancies, our focus is exclusively on TMT. We advise clients on regulatory matters, support multi billion dollar investments, advise on network performance and recommend commercial partnering options and new business strategies. Such projects result in a depth of knowledge and a range of expertise that sets us apart. We look beyond the obvious to understand a situation from a client’s perspective. We blend our range of skills each day, every day, to solve our clients’ most complex challenges. Regulation Transaction support Technical and audit assurance We offer regulatory advice to operators, vendors, media rights owners, regulators and policy makers We provide due diligence and business planning expertise to help vendors, purchasers and lenders We help major organisations to maximise returns from investment in networks and technology Marketing and products We help operators, broadcasters and content providers to create profitable service opportunities in the consumer, enterprise and public sector markets Procurement Our procurement experience translates into highly effective vendor management for clients in both the public and private sector Strategy and planning Systems and infrastructure We’re experts in the development and critical appraisal of operational plans and strategy We advise operators, vendors, and public and private sector clients on business systems and infrastructure For more information about our consulting services, please visit www. analysysmason. com/consulting. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011
Service fulfilment systems: worldwide forecast 2011– 2015 48 About the author and Analysys Mason Consulting from Analysys Mason For more than 25 years, our consultants have been bringing the benefits of applied intelligence to enable clients around the world to make the most of their opportunities Unlike some consultancies, our focus is exclusively on TMT. We advise clients on regulatory matters, support multi billion dollar investments, advise on network performance and recommend commercial partnering options and new business strategies. Such projects result in a depth of knowledge and a range of expertise that sets us apart. We look beyond the obvious to understand a situation from a client’s perspective. We blend our range of skills each day, every day, to solve our clients’ most complex challenges. Regulation Transaction support Technical and audit assurance We offer regulatory advice to operators, vendors, media rights owners, regulators and policy makers We provide due diligence and business planning expertise to help vendors, purchasers and lenders We help major organisations to maximise returns from investment in networks and technology Marketing and products We help operators, broadcasters and content providers to create profitable service opportunities in the consumer, enterprise and public sector markets Procurement Our procurement experience translates into highly effective vendor management for clients in both the public and private sector Strategy and planning Systems and infrastructure We’re experts in the development and critical appraisal of operational plans and strategy We advise operators, vendors, and public and private sector clients on business systems and infrastructure For more information about our consulting services, please visit www. analysysmason. com/consulting. © Analysys Mason Limited 2011


