1376f67c5027917231916e2970a1f072.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 89
 Research Activities at Computer Vision and Image Understanding Group Florida State University Xiuwen Liu Florida State Vision Group Department of Computer Science Florida State University http: //fsvision. cs. fsu. edu
Research Activities at Computer Vision and Image Understanding Group Florida State University Xiuwen Liu Florida State Vision Group Department of Computer Science Florida State University http: //fsvision. cs. fsu. edu
 Outline ? Motivations • Some applications of computer vision techniques ? Computer Vision and Image Understanding Group ? Some of the research projects ? Contact information
Outline ? Motivations • Some applications of computer vision techniques ? Computer Vision and Image Understanding Group ? Some of the research projects ? Contact information
 Introduction ? An image patch represented by hexadecimals
Introduction ? An image patch represented by hexadecimals
 Introduction - continued ? Fundamental problem in computer vision • Given a matrix of numbers representing an image, or a sequence of images, how to generate a perceptually meaningful description of the matrix? – An image can be a color image, gray level image, or other format such as remote sensing images – A two-dimensional matrix represents a signal image – A three-dimensional matrix represents a sequence of images § A video sequence is a 3 -D matrix § A movie is also a 3 -D matrix
Introduction - continued ? Fundamental problem in computer vision • Given a matrix of numbers representing an image, or a sequence of images, how to generate a perceptually meaningful description of the matrix? – An image can be a color image, gray level image, or other format such as remote sensing images – A two-dimensional matrix represents a signal image – A three-dimensional matrix represents a sequence of images § A video sequence is a 3 -D matrix § A movie is also a 3 -D matrix
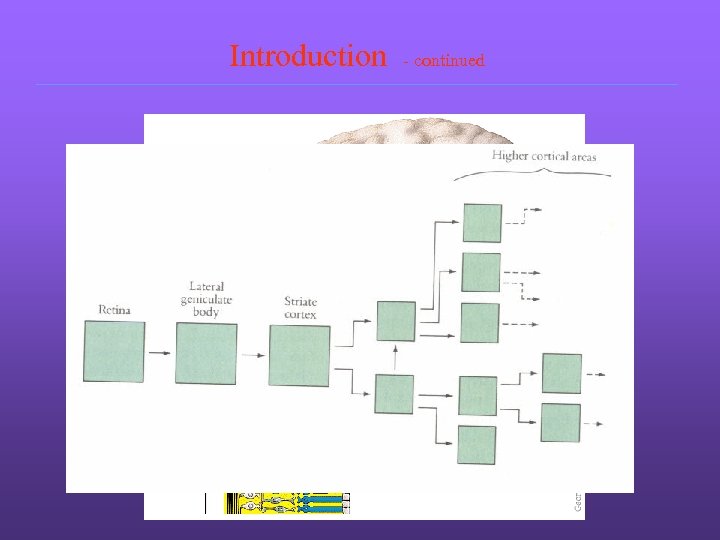 Introduction - continued
Introduction - continued
 Introduction - continued ? Why do we want to work on this problem? • It is very interesting theoretically – It involves many disciplines to develop a computational model for the problem • It is the key component to understand model intelligence – Note that 50% of the brain is devoted to vision • It has many practical applications – Internet applications – Movie-making applications – Military applications
Introduction - continued ? Why do we want to work on this problem? • It is very interesting theoretically – It involves many disciplines to develop a computational model for the problem • It is the key component to understand model intelligence – Note that 50% of the brain is devoted to vision • It has many practical applications – Internet applications – Movie-making applications – Military applications
 Computer Vision Applications ? No hands across America • sponsored by Delco Electronics, Assist. Ware Technology, and Carnegie Mellon University • Navlab 5 drove from Pittsburgh, PA to San Diego, CA, using the RALPH computer program. • The trip was 2849 miles of which 2797 miles were driven automatically with no hands – Which is 98. 2%
Computer Vision Applications ? No hands across America • sponsored by Delco Electronics, Assist. Ware Technology, and Carnegie Mellon University • Navlab 5 drove from Pittsburgh, PA to San Diego, CA, using the RALPH computer program. • The trip was 2849 miles of which 2797 miles were driven automatically with no hands – Which is 98. 2%
 Computer Vision Applications – continued
Computer Vision Applications – continued
 Computer Vision Applications – continued DARPA Grant Challenge: http: //www. darpa. mil/grandchallenge/index. htm
Computer Vision Applications – continued DARPA Grant Challenge: http: //www. darpa. mil/grandchallenge/index. htm
 Computer Vision Applications – continued ? Military applications • Automated target recognition
Computer Vision Applications – continued ? Military applications • Automated target recognition
 Computer Vision Applications – continued
Computer Vision Applications – continued
 Computer Vision Applications – continued ? Extracted hydrographic regions
Computer Vision Applications – continued ? Extracted hydrographic regions
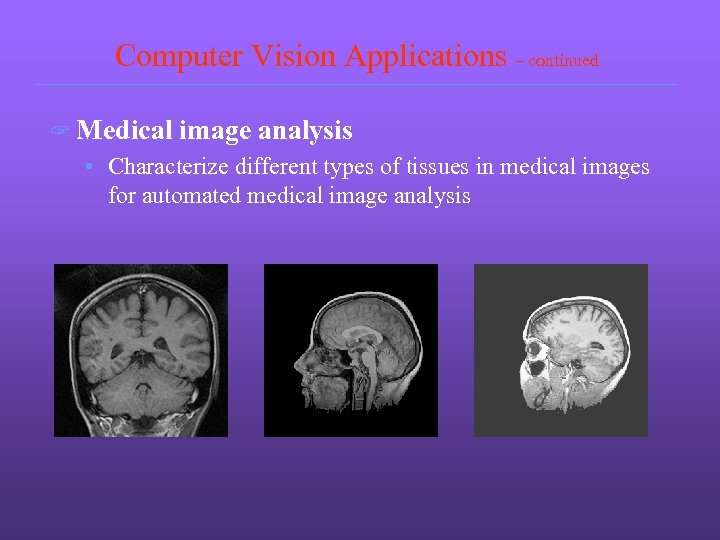 Computer Vision Applications – continued ? Medical image analysis • Characterize different types of tissues in medical images for automated medical image analysis
Computer Vision Applications – continued ? Medical image analysis • Characterize different types of tissues in medical images for automated medical image analysis
 Computer Vision Applications – continued
Computer Vision Applications – continued
 Computer Vision Applications – continued ? Biometrics • From faces, fingerprints, iris patterns. . . • It has many applications such as security, ATM withdrawal, credit card managements. . .
Computer Vision Applications – continued ? Biometrics • From faces, fingerprints, iris patterns. . . • It has many applications such as security, ATM withdrawal, credit card managements. . .
 Computer Vision Applications – cont.
Computer Vision Applications – cont.
 Computer Vision Applications – continued ? Content-based image retrieval has become an active research area to meet the needs of searching images on the web in a meaningful way • Color histogram has been widely used
Computer Vision Applications – continued ? Content-based image retrieval has become an active research area to meet the needs of searching images on the web in a meaningful way • Color histogram has been widely used
 Content-Based Image Retrieval – cont.
Content-Based Image Retrieval – cont.
 Vision-Based Image Morphing
Vision-Based Image Morphing
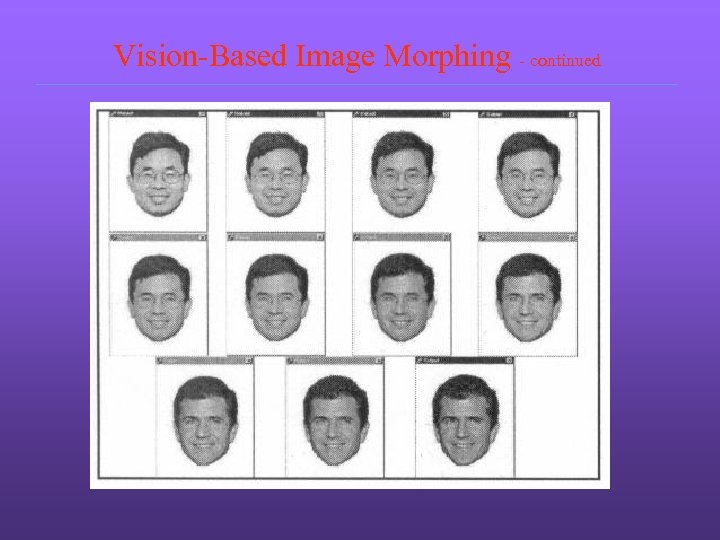 Vision-Based Image Morphing - continued
Vision-Based Image Morphing - continued
 Computer Vision and Image Understanding Group ? Faculty: Xiuwen Liu, Anuj Srivastava, Washington Mio, Eric Klassen ? Goals: Develop and implement effective image understanding algorithms and systems for images and videos from multi modalities including visible, infrared, and range sensors ? Approaches: Learning-based vision algorithms, statistical modeling of objects, computational modeling and analysis of textures, statistical modeling of shapes, stochastic optimization, inference algorithms on manifolds, and Bayesian inference
Computer Vision and Image Understanding Group ? Faculty: Xiuwen Liu, Anuj Srivastava, Washington Mio, Eric Klassen ? Goals: Develop and implement effective image understanding algorithms and systems for images and videos from multi modalities including visible, infrared, and range sensors ? Approaches: Learning-based vision algorithms, statistical modeling of objects, computational modeling and analysis of textures, statistical modeling of shapes, stochastic optimization, inference algorithms on manifolds, and Bayesian inference
 Research Projects ? The group offers a wide range of research possibilities • • Implementation projects Development of new applications Development of new algorithms Theoretical and mathematical analysis of algorithms
Research Projects ? The group offers a wide range of research possibilities • • Implementation projects Development of new applications Development of new algorithms Theoretical and mathematical analysis of algorithms
 Implementation Projects ? These projects involve implementing proven ideas and algorithms on specific datasets with specific interface and programming language constraints • For example, Haitao Wu implemented a graphical user interface for a face recognition algorithm we have as his Masters project • Yu Wang implemented a web-based interface for a content-based image retrieval algorithm
Implementation Projects ? These projects involve implementing proven ideas and algorithms on specific datasets with specific interface and programming language constraints • For example, Haitao Wu implemented a graphical user interface for a face recognition algorithm we have as his Masters project • Yu Wang implemented a web-based interface for a content-based image retrieval algorithm
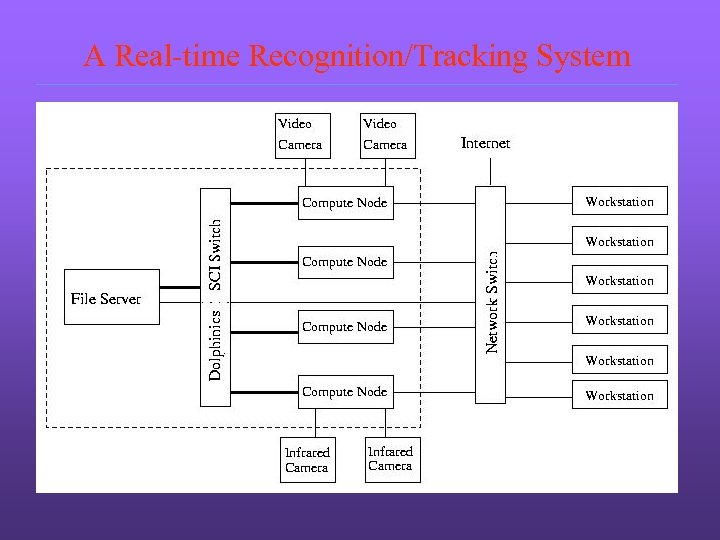 A Real-time Recognition/Tracking System
A Real-time Recognition/Tracking System
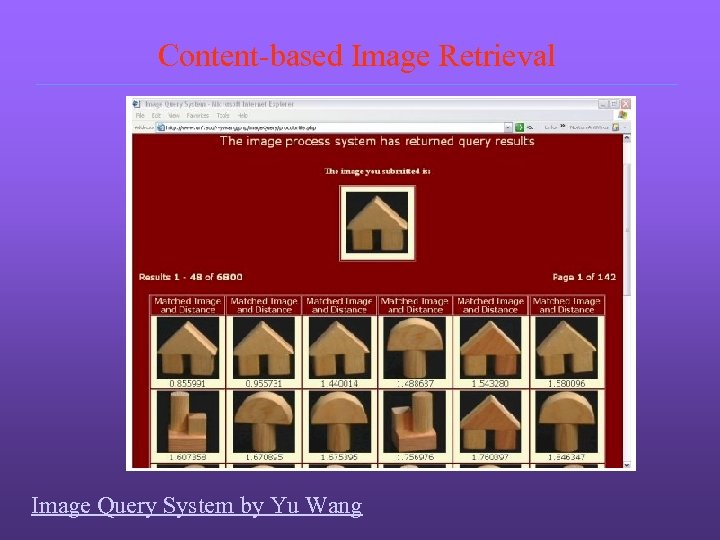 Content-based Image Retrieval Image Query System by Yu Wang
Content-based Image Retrieval Image Query System by Yu Wang
 Future Implementation Possibilities ? Implement a Java-based system for face detection ? Implement a Java-based system for learning ? Implement and improve web-based systems for content-based image and video retrieval
Future Implementation Possibilities ? Implement a Java-based system for face detection ? Implement a Java-based system for learning ? Implement and improve web-based systems for content-based image and video retrieval
 Generic Image Modeling ? How can we characterize all these images perceptually?
Generic Image Modeling ? How can we characterize all these images perceptually?
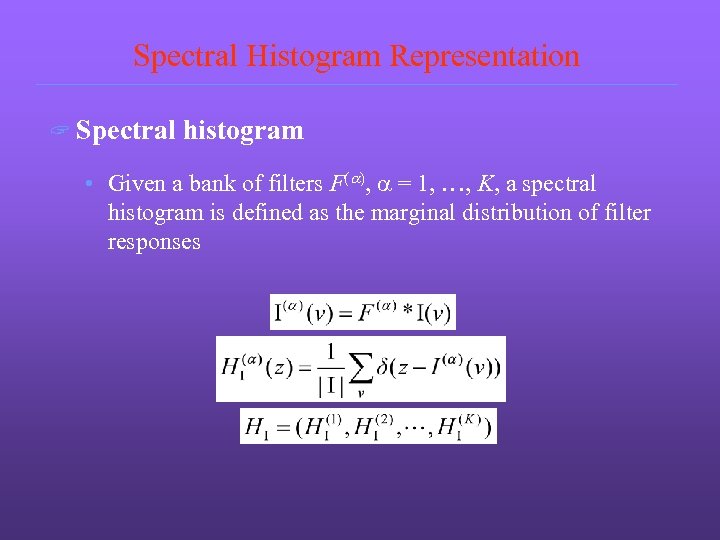 Spectral Histogram Representation ? Spectral histogram • Given a bank of filters F(a), a = 1, …, K, a spectral histogram is defined as the marginal distribution of filter responses
Spectral Histogram Representation ? Spectral histogram • Given a bank of filters F(a), a = 1, …, K, a spectral histogram is defined as the marginal distribution of filter responses
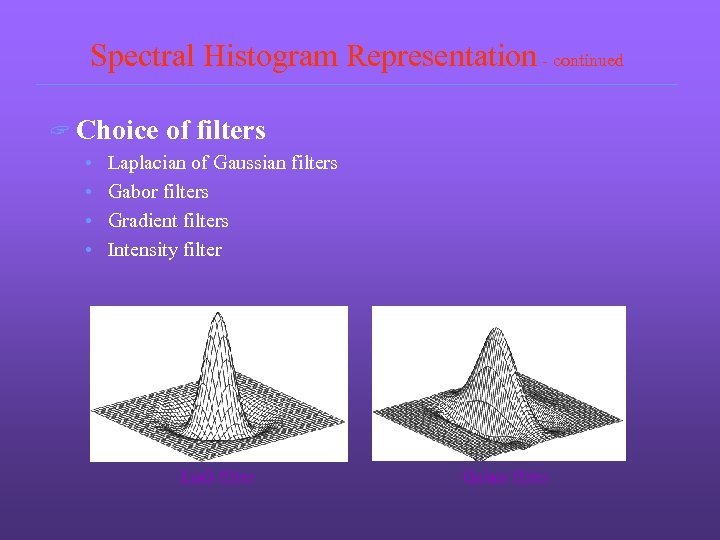 Spectral Histogram Representation - continued ? Choice • • of filters Laplacian of Gaussian filters Gabor filters Gradient filters Intensity filter Lo. G filter Gabor filter
Spectral Histogram Representation - continued ? Choice • • of filters Laplacian of Gaussian filters Gabor filters Gradient filters Intensity filter Lo. G filter Gabor filter
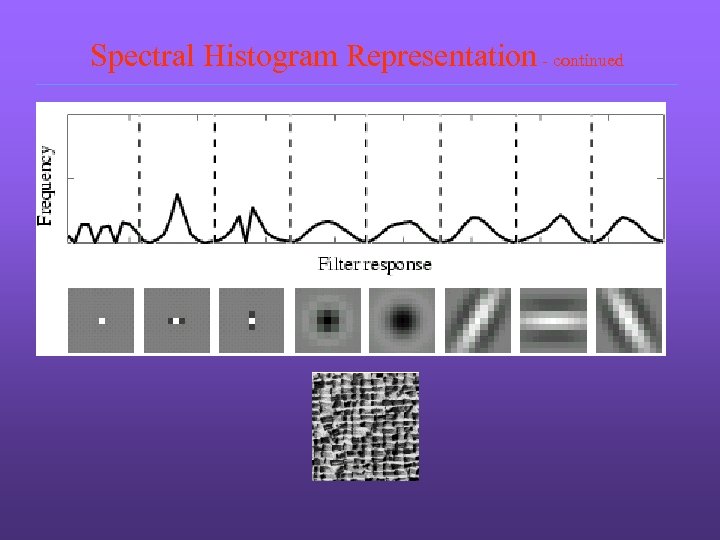 Spectral Histogram Representation - continued
Spectral Histogram Representation - continued
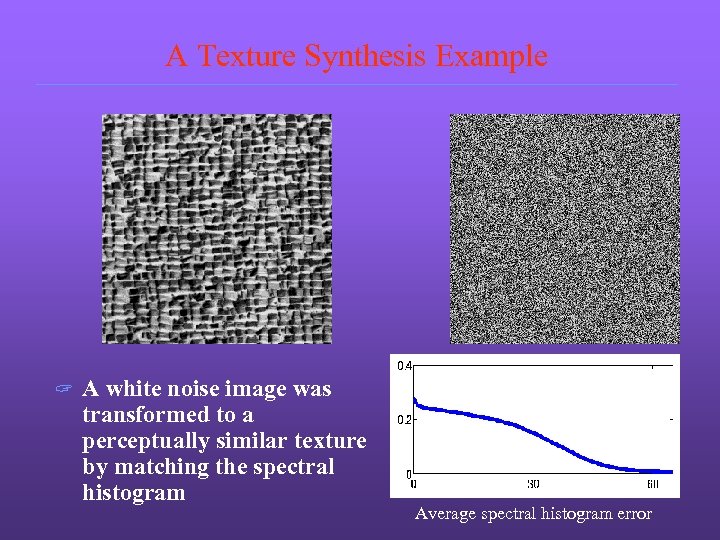 A Texture Synthesis Example ? A white noise image was transformed to a perceptually similar texture by matching the spectral histogram Average spectral histogram error
A Texture Synthesis Example ? A white noise image was transformed to a perceptually similar texture by matching the spectral histogram Average spectral histogram error
 Texture Synthesis Examples - continued Observed image ? A random texture image Synthesized image
Texture Synthesis Examples - continued Observed image ? A random texture image Synthesized image
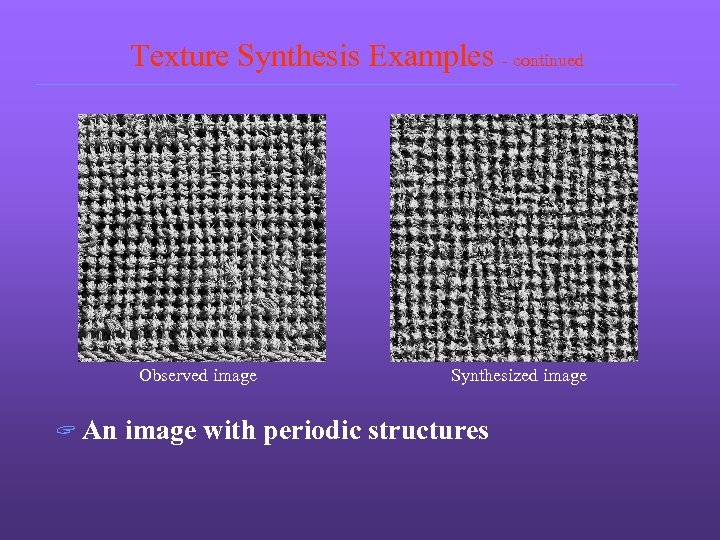 Texture Synthesis Examples - continued Observed image ? An Synthesized image with periodic structures
Texture Synthesis Examples - continued Observed image ? An Synthesized image with periodic structures
 Texture Synthesis Examples - continued Mud image Synthesized image ? A mud image with some animal foot prints
Texture Synthesis Examples - continued Mud image Synthesized image ? A mud image with some animal foot prints
 Texture Synthesis Examples - continued Observed image Synthesized image ? A random texture image with elements
Texture Synthesis Examples - continued Observed image Synthesized image ? A random texture image with elements
 Object Synthesis Examples As in texture synthesis, we start from a random image ? In addition, similar object images are used as boundary conditions in that the corresponding pixel values are not updated during sampling process ?
Object Synthesis Examples As in texture synthesis, we start from a random image ? In addition, similar object images are used as boundary conditions in that the corresponding pixel values are not updated during sampling process ?
 Object Synthesis Examples - continued
Object Synthesis Examples - continued
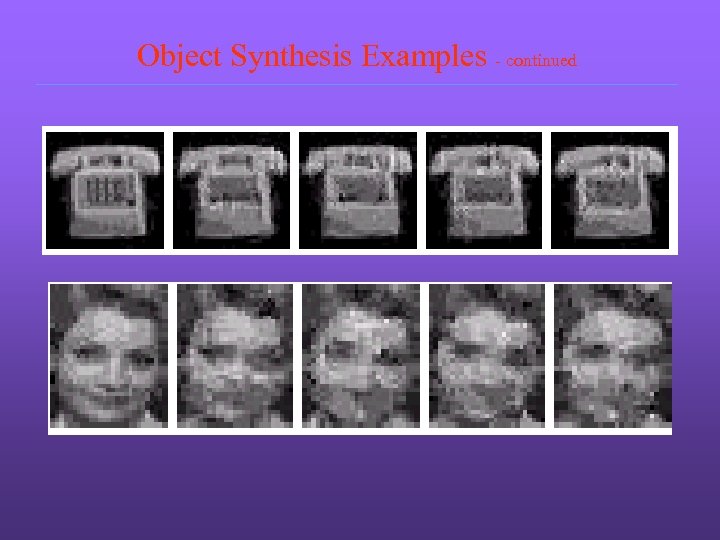 Object Synthesis Examples - continued
Object Synthesis Examples - continued
 Principal Component Analysis
Principal Component Analysis
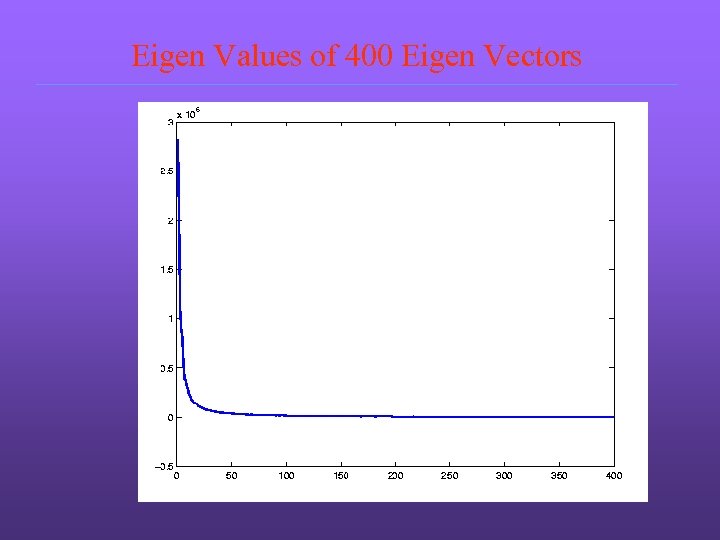 Eigen Values of 400 Eigen Vectors
Eigen Values of 400 Eigen Vectors
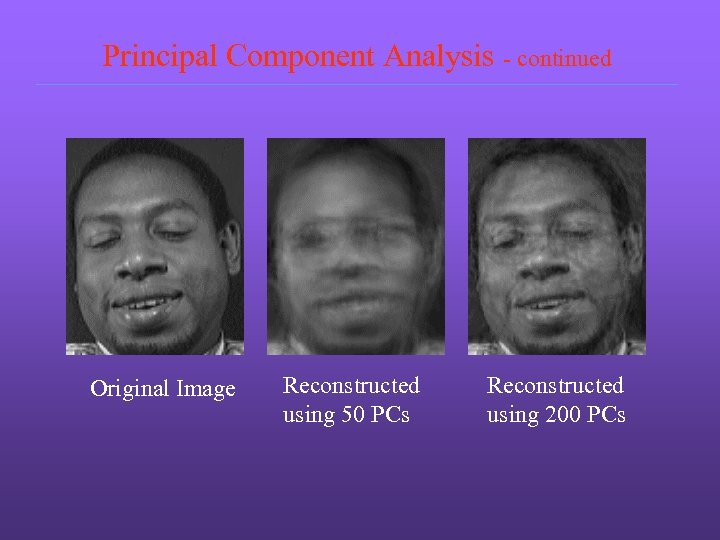 Principal Component Analysis - continued Original Image Reconstructed using 50 PCs Reconstructed using 200 PCs
Principal Component Analysis - continued Original Image Reconstructed using 50 PCs Reconstructed using 200 PCs
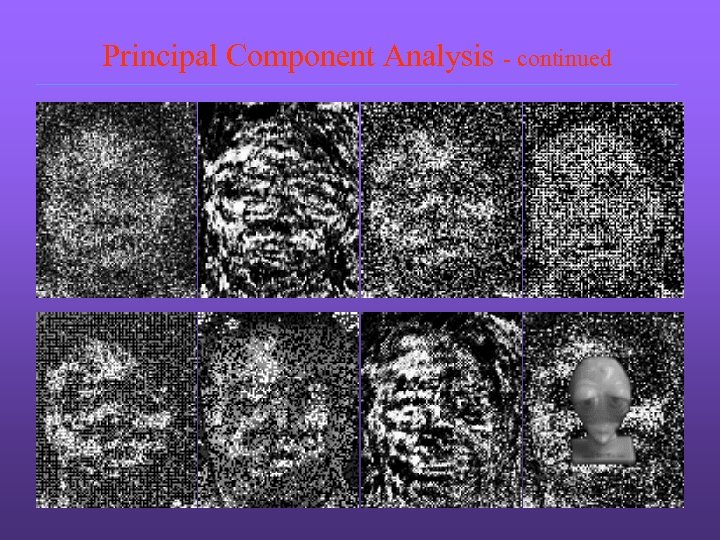 Principal Component Analysis - continued
Principal Component Analysis - continued
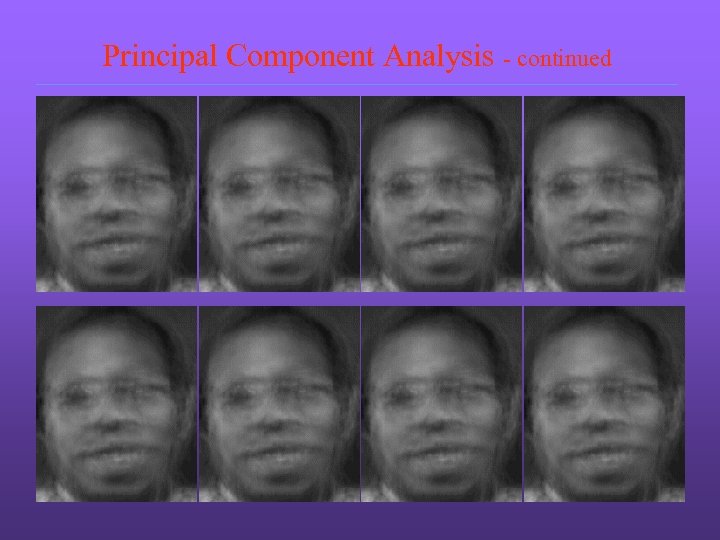 Principal Component Analysis - continued
Principal Component Analysis - continued
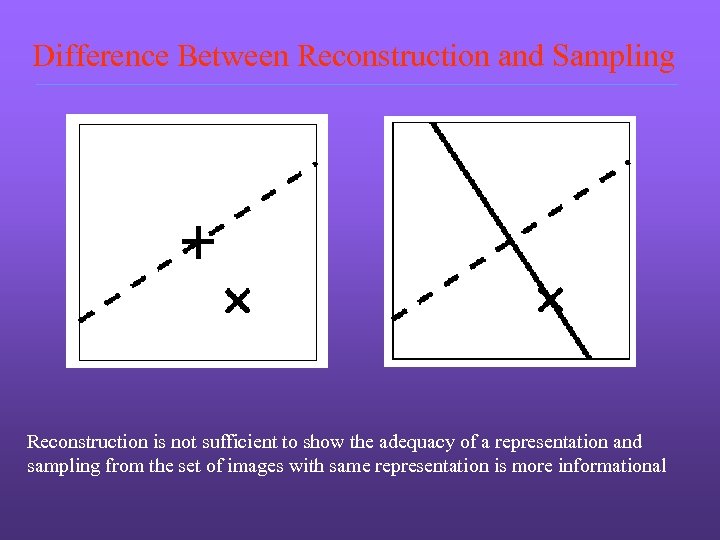 Difference Between Reconstruction and Sampling Reconstruction is not sufficient to show the adequacy of a representation and sampling from the set of images with same representation is more informational
Difference Between Reconstruction and Sampling Reconstruction is not sufficient to show the adequacy of a representation and sampling from the set of images with same representation is more informational
 Face detection based on spectral representations ? Face detection is to detect all instances of faces in a given image ? Each image window is represented by its spectral histogram • A support vector machine is trained on training faces • Then the trained support vector machine is used to classify each image window in an input image ? More results at http: //fsvision. fsu. edu/face-detection
Face detection based on spectral representations ? Face detection is to detect all instances of faces in a given image ? Each image window is represented by its spectral histogram • A support vector machine is trained on training faces • Then the trained support vector machine is used to classify each image window in an input image ? More results at http: //fsvision. fsu. edu/face-detection
 Face detection - continued
Face detection - continued
 Face detection - continued
Face detection - continued
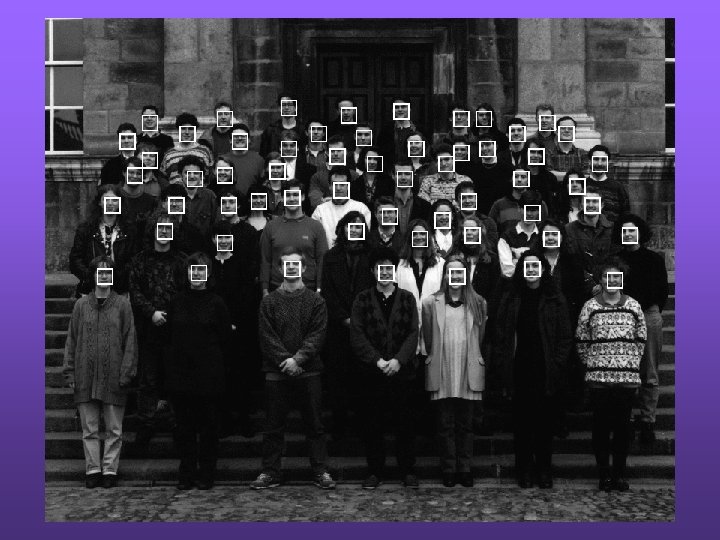

 Face detection - continued
Face detection - continued
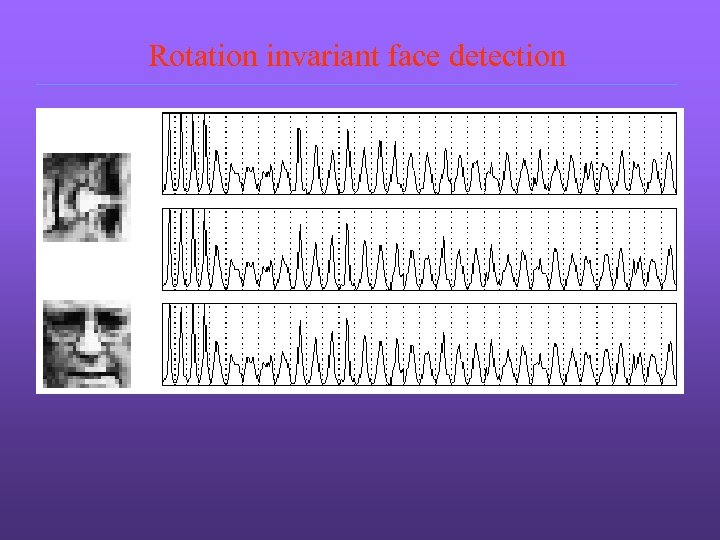 Rotation invariant face detection
Rotation invariant face detection
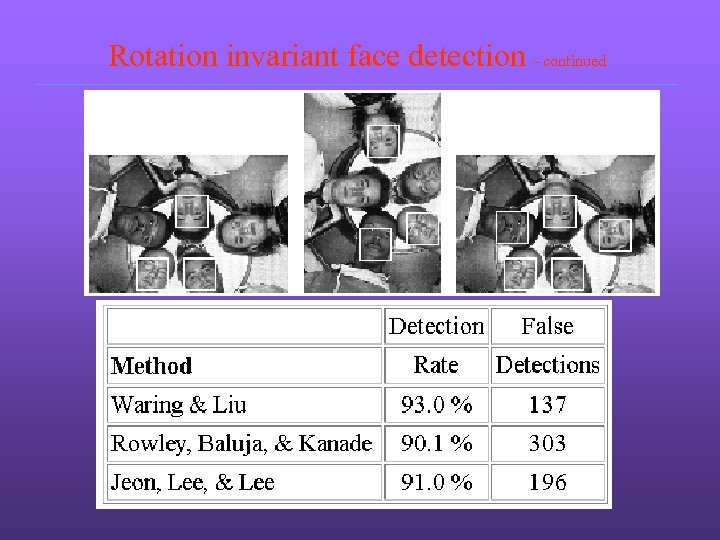 Rotation invariant face detection - continued
Rotation invariant face detection - continued
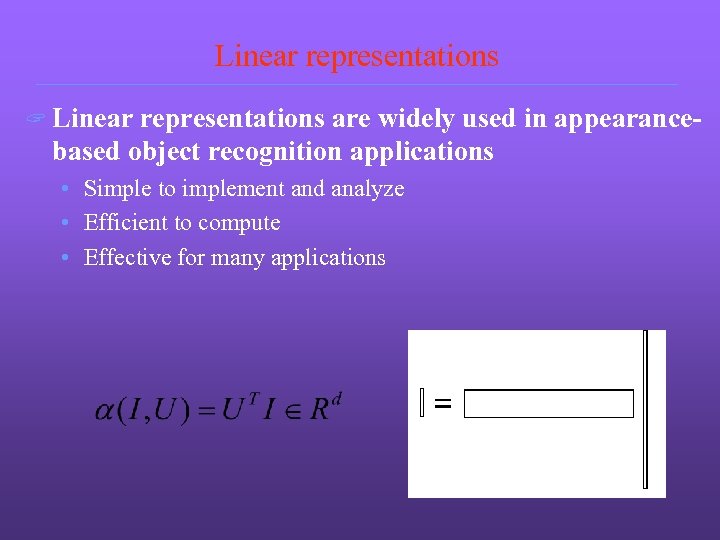 Linear representations ? Linear representations are widely used in appearancebased object recognition applications • Simple to implement and analyze • Efficient to compute • Effective for many applications
Linear representations ? Linear representations are widely used in appearancebased object recognition applications • Simple to implement and analyze • Efficient to compute • Effective for many applications
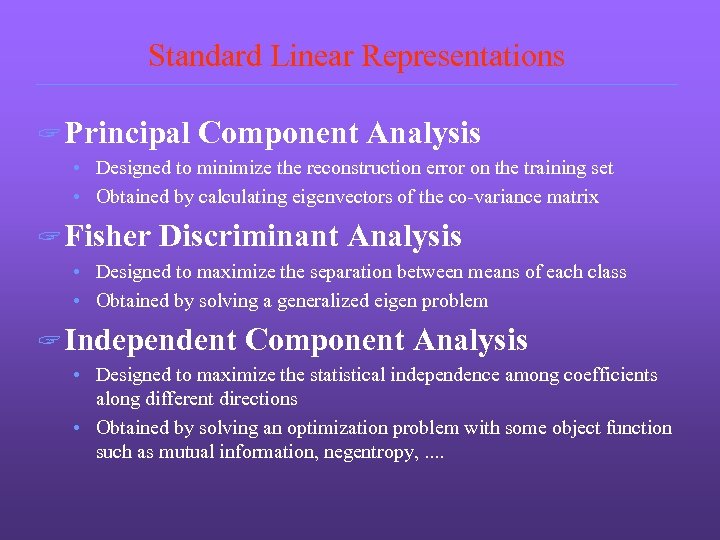 Standard Linear Representations ? Principal Component Analysis • Designed to minimize the reconstruction error on the training set • Obtained by calculating eigenvectors of the co-variance matrix ? Fisher Discriminant Analysis • Designed to maximize the separation between means of each class • Obtained by solving a generalized eigen problem ? Independent Component Analysis • Designed to maximize the statistical independence among coefficients along different directions • Obtained by solving an optimization problem with some object function such as mutual information, negentropy, . .
Standard Linear Representations ? Principal Component Analysis • Designed to minimize the reconstruction error on the training set • Obtained by calculating eigenvectors of the co-variance matrix ? Fisher Discriminant Analysis • Designed to maximize the separation between means of each class • Obtained by solving a generalized eigen problem ? Independent Component Analysis • Designed to maximize the statistical independence among coefficients along different directions • Obtained by solving an optimization problem with some object function such as mutual information, negentropy, . .
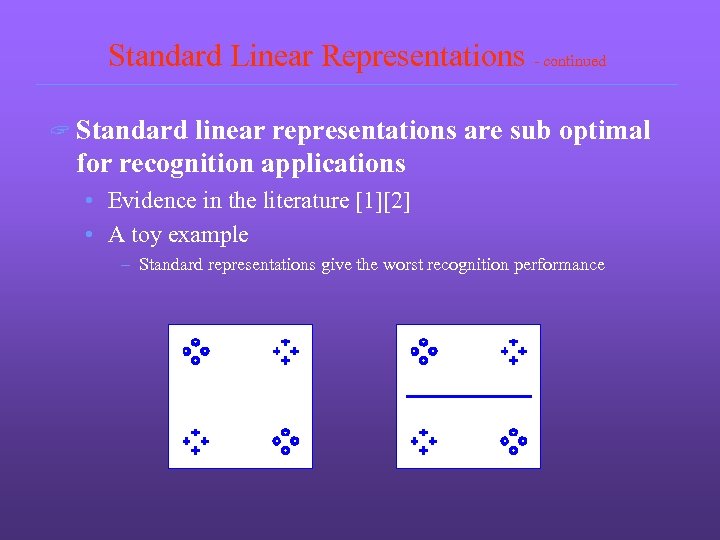 Standard Linear Representations - continued ? Standard linear representations are sub optimal for recognition applications • Evidence in the literature [1][2] • A toy example – Standard representations give the worst recognition performance
Standard Linear Representations - continued ? Standard linear representations are sub optimal for recognition applications • Evidence in the literature [1][2] • A toy example – Standard representations give the worst recognition performance
 Proposed Approach ? Optimal Component Analysis (OCA) • Derive a performance function that is related to the recognition performance • Formulate the problem of finding optimal representations as an optimization one on the Grassmann manifold • Use MCMC stochastic gradient algorithm for optimization
Proposed Approach ? Optimal Component Analysis (OCA) • Derive a performance function that is related to the recognition performance • Formulate the problem of finding optimal representations as an optimization one on the Grassmann manifold • Use MCMC stochastic gradient algorithm for optimization
 Performance Measure It must have continuous directional derivatives ? It must be related to the recognition performance ? It can be computed efficiently ? Based on the nearest neighbor classifier ? • However, it can be applied to other classifiers as it forms clusters of images from the same class that far from clusters from other classes • See an example for support vector machines
Performance Measure It must have continuous directional derivatives ? It must be related to the recognition performance ? It can be computed efficiently ? Based on the nearest neighbor classifier ? • However, it can be applied to other classifiers as it forms clusters of images from the same class that far from clusters from other classes • See an example for support vector machines
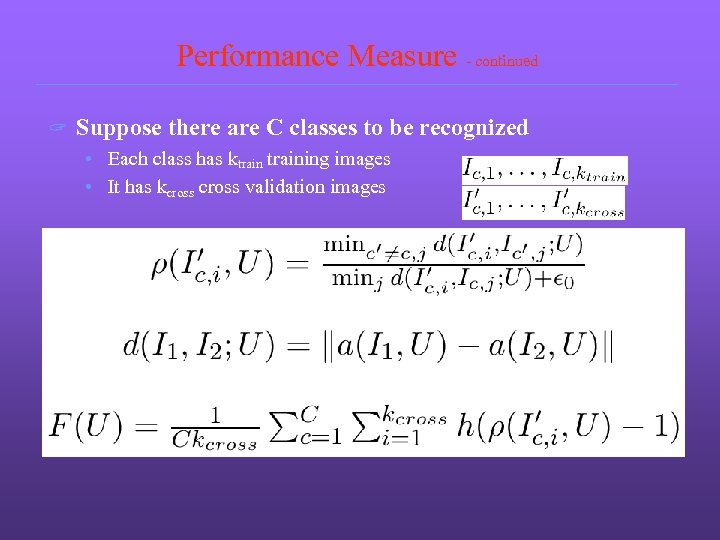 Performance Measure - continued ? Suppose there are C classes to be recognized • Each class has ktraining images • It has kcross validation images
Performance Measure - continued ? Suppose there are C classes to be recognized • Each class has ktraining images • It has kcross validation images
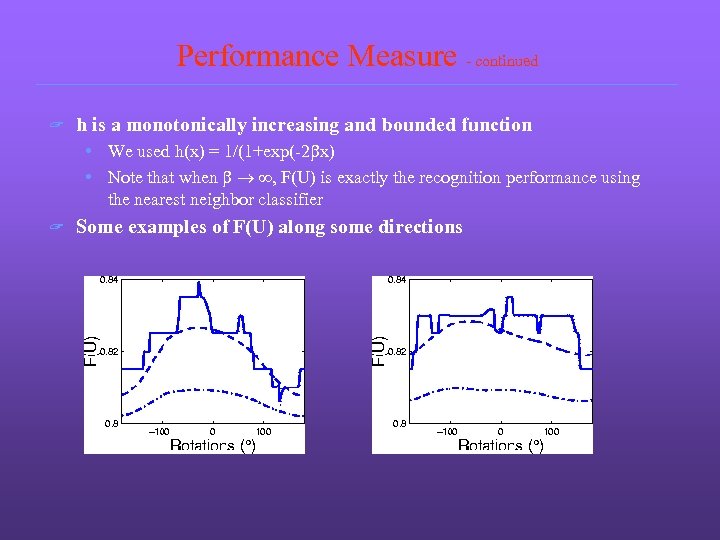 Performance Measure - continued ? h is a monotonically increasing and bounded function • We used h(x) = 1/(1+exp(-2 bx) • Note that when b , F(U) is exactly the recognition performance using the nearest neighbor classifier ? Some examples of F(U) along some directions
Performance Measure - continued ? h is a monotonically increasing and bounded function • We used h(x) = 1/(1+exp(-2 bx) • Note that when b , F(U) is exactly the recognition performance using the nearest neighbor classifier ? Some examples of F(U) along some directions
 Performance Measure - continued ? F(U) depends on the span of U but is invariant to change of basis • In other words, F(U)=F(UO) for any orthonormal matrix O • The search space of F(U) is the set of all the subspaces, which is known as the Grassmann manifold – It is not a flat vector space and gradient flow must take the underlying geometry of the manifold into account; see [3] [4] [5] for related work
Performance Measure - continued ? F(U) depends on the span of U but is invariant to change of basis • In other words, F(U)=F(UO) for any orthonormal matrix O • The search space of F(U) is the set of all the subspaces, which is known as the Grassmann manifold – It is not a flat vector space and gradient flow must take the underlying geometry of the manifold into account; see [3] [4] [5] for related work
![Deterministic Gradient Flow - continued ? Gradient at [J] (first d columns of n Deterministic Gradient Flow - continued ? Gradient at [J] (first d columns of n](https://present5.com/presentation/1376f67c5027917231916e2970a1f072/image-60.jpg) Deterministic Gradient Flow - continued ? Gradient at [J] (first d columns of n x n identity matrix)
Deterministic Gradient Flow - continued ? Gradient at [J] (first d columns of n x n identity matrix)
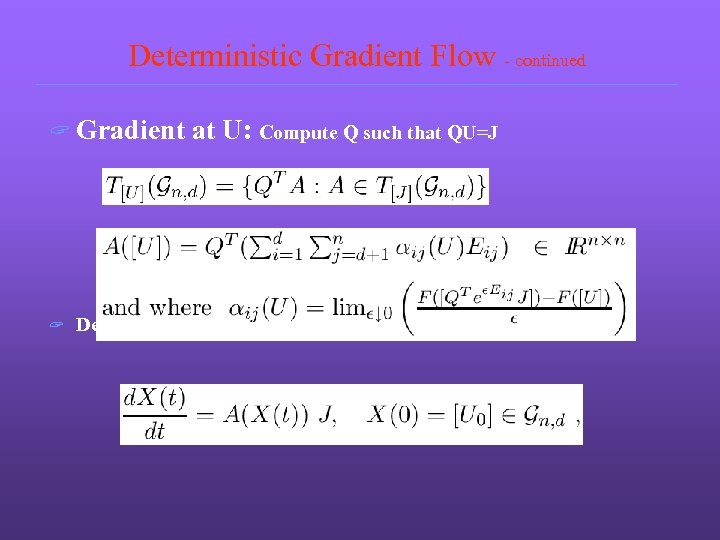 Deterministic Gradient Flow - continued ? Gradient ? at U: Compute Q such that QU=J Deterministic gradient flow on Grassmann manifold
Deterministic Gradient Flow - continued ? Gradient ? at U: Compute Q such that QU=J Deterministic gradient flow on Grassmann manifold
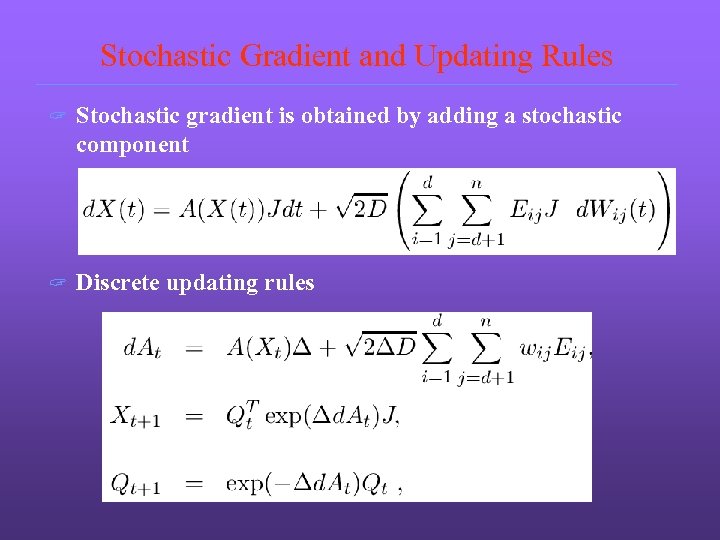 Stochastic Gradient and Updating Rules ? Stochastic gradient is obtained by adding a stochastic component ? Discrete updating rules
Stochastic Gradient and Updating Rules ? Stochastic gradient is obtained by adding a stochastic component ? Discrete updating rules
 MCMC Simulated Annealing Optimization Algorithm ? Let X(0) be any initial condition and t=0 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Calculate the gradient matrix A(Xt) Generate d(n-d) independent realizations of wij’s Compute Y (Xt+1) according to the updating rules Compute F(Y) and F(Xt) and set d. F=F(Y)- F(Xt) Set Xt+1 = Y with probability min{exp(d. F/Dt), 1} Set Dt+1 = Dt / g and set t=t+1 Go to step 1
MCMC Simulated Annealing Optimization Algorithm ? Let X(0) be any initial condition and t=0 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Calculate the gradient matrix A(Xt) Generate d(n-d) independent realizations of wij’s Compute Y (Xt+1) according to the updating rules Compute F(Y) and F(Xt) and set d. F=F(Y)- F(Xt) Set Xt+1 = Y with probability min{exp(d. F/Dt), 1} Set Dt+1 = Dt / g and set t=t+1 Go to step 1
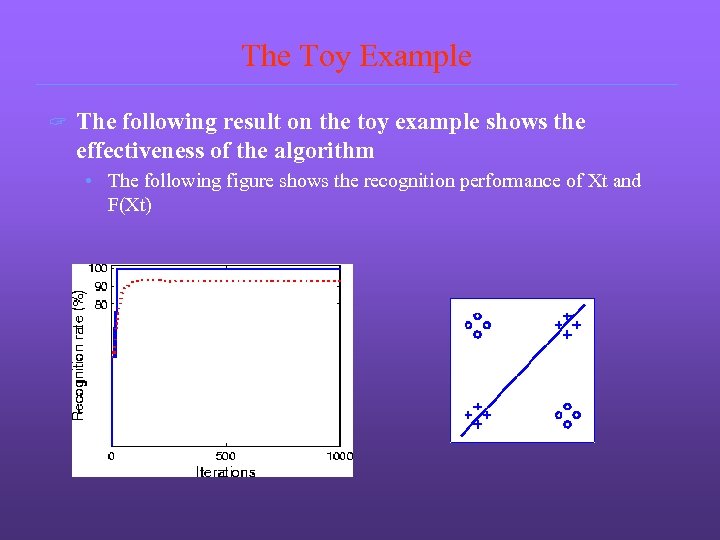 The Toy Example ? The following result on the toy example shows the effectiveness of the algorithm • The following figure shows the recognition performance of Xt and F(Xt)
The Toy Example ? The following result on the toy example shows the effectiveness of the algorithm • The following figure shows the recognition performance of Xt and F(Xt)
 ORL Face Dataset
ORL Face Dataset
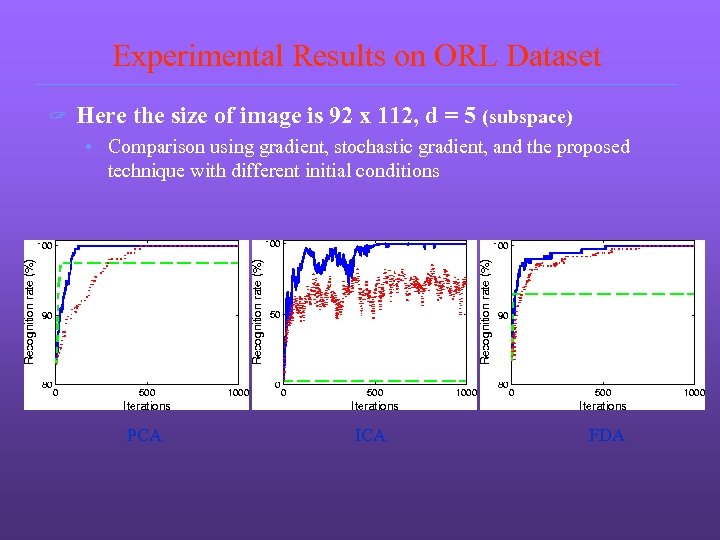 Experimental Results on ORL Dataset ? Here the size of image is 92 x 112, d = 5 (subspace) • Comparison using gradient, stochastic gradient, and the proposed technique with different initial conditions PCA ICA FDA
Experimental Results on ORL Dataset ? Here the size of image is 92 x 112, d = 5 (subspace) • Comparison using gradient, stochastic gradient, and the proposed technique with different initial conditions PCA ICA FDA
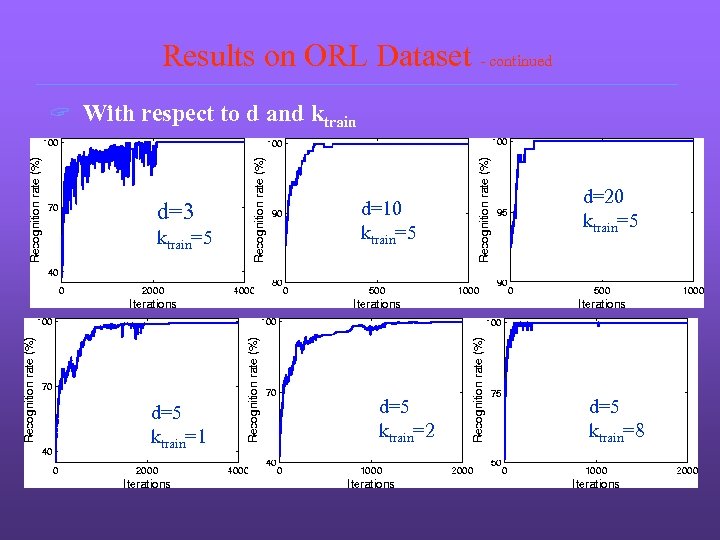 Results on ORL Dataset - continued ? With respect to d and ktrain d=3 ktrain=5 d=5 ktrain=1 d=10 ktrain=5 d=5 ktrain=2 d=20 ktrain=5 d=5 ktrain=8
Results on ORL Dataset - continued ? With respect to d and ktrain d=3 ktrain=5 d=5 ktrain=1 d=10 ktrain=5 d=5 ktrain=2 d=20 ktrain=5 d=5 ktrain=8
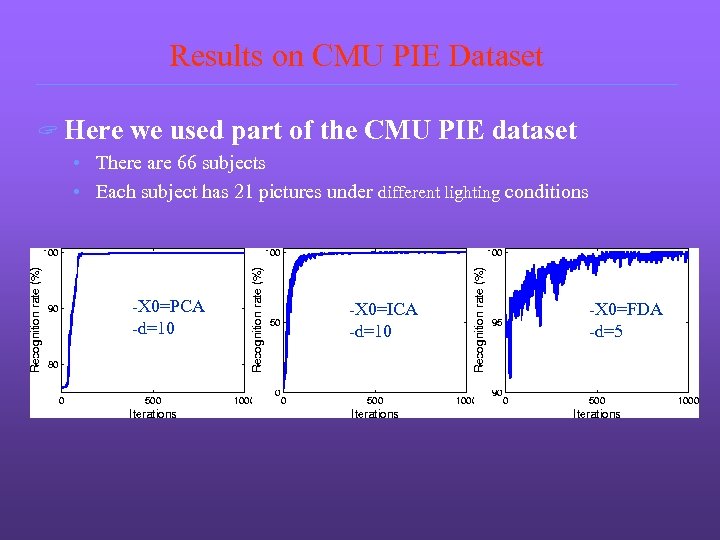 Results on CMU PIE Dataset ? Here we used part of the CMU PIE dataset • There are 66 subjects • Each subject has 21 pictures under different lighting conditions -X 0=PCA -d=10 -X 0=ICA -d=10 -X 0=FDA -d=5
Results on CMU PIE Dataset ? Here we used part of the CMU PIE dataset • There are 66 subjects • Each subject has 21 pictures under different lighting conditions -X 0=PCA -d=10 -X 0=ICA -d=10 -X 0=FDA -d=5
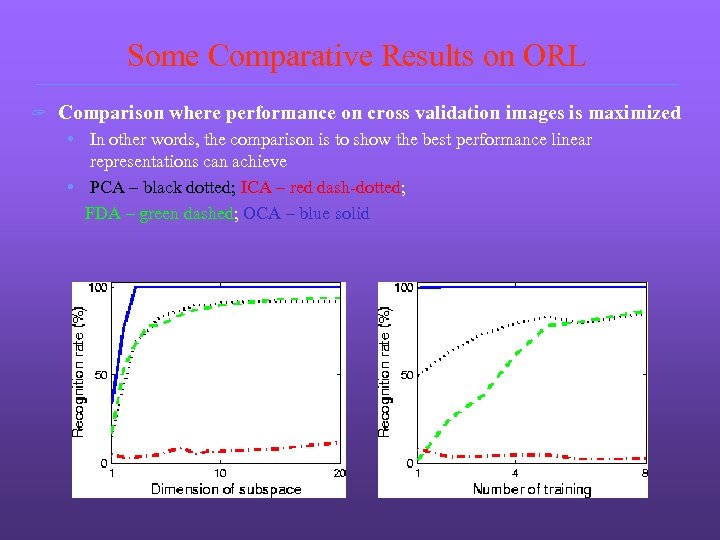 Some Comparative Results on ORL ? Comparison where performance on cross validation images is maximized • In other words, the comparison is to show the best performance linear representations can achieve • PCA – black dotted; ICA – red dash-dotted; FDA – green dashed; OCA – blue solid
Some Comparative Results on ORL ? Comparison where performance on cross validation images is maximized • In other words, the comparison is to show the best performance linear representations can achieve • PCA – black dotted; ICA – red dash-dotted; FDA – green dashed; OCA – blue solid
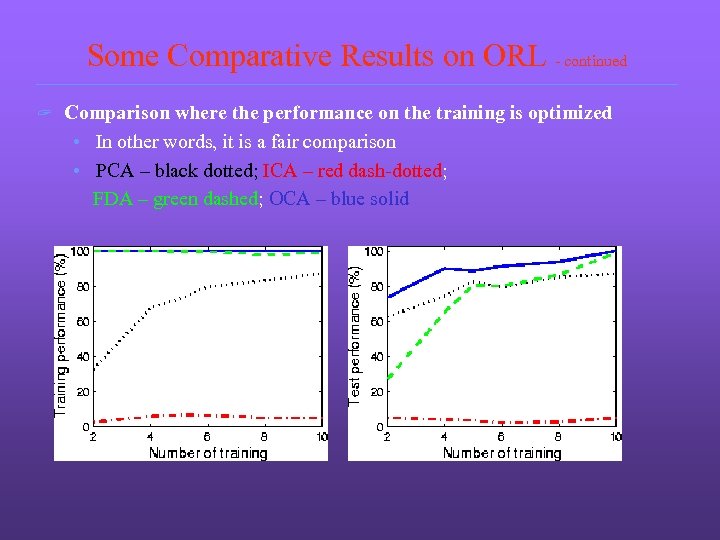 Some Comparative Results on ORL - continued ? Comparison where the performance on the training is optimized • In other words, it is a fair comparison • PCA – black dotted; ICA – red dash-dotted; FDA – green dashed; OCA – blue solid
Some Comparative Results on ORL - continued ? Comparison where the performance on the training is optimized • In other words, it is a fair comparison • PCA – black dotted; ICA – red dash-dotted; FDA – green dashed; OCA – blue solid
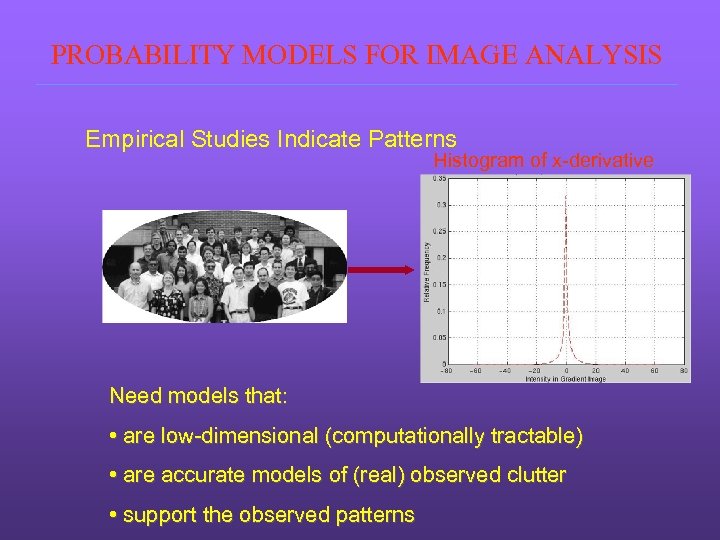 PROBABILITY MODELS FOR IMAGE ANALYSIS Empirical Studies Indicate Patterns Histogram of x-derivative Need models that: • are low-dimensional (computationally tractable) • are accurate models of (real) observed clutter • support the observed patterns
PROBABILITY MODELS FOR IMAGE ANALYSIS Empirical Studies Indicate Patterns Histogram of x-derivative Need models that: • are low-dimensional (computationally tractable) • are accurate models of (real) observed clutter • support the observed patterns
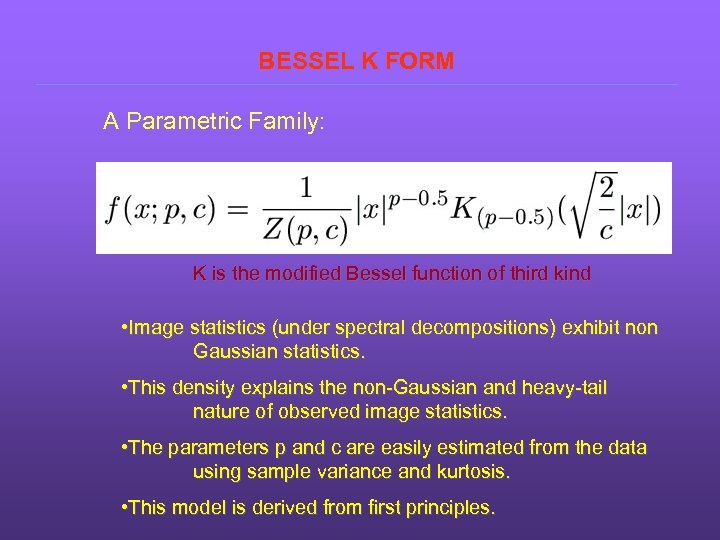 BESSEL K FORM A Parametric Family: K is the modified Bessel function of third kind • Image statistics (under spectral decompositions) exhibit non Gaussian statistics. • This density explains the non-Gaussian and heavy-tail nature of observed image statistics. • The parameters p and c are easily estimated from the data using sample variance and kurtosis. • This model is derived from first principles.
BESSEL K FORM A Parametric Family: K is the modified Bessel function of third kind • Image statistics (under spectral decompositions) exhibit non Gaussian statistics. • This density explains the non-Gaussian and heavy-tail nature of observed image statistics. • The parameters p and c are easily estimated from the data using sample variance and kurtosis. • This model is derived from first principles.
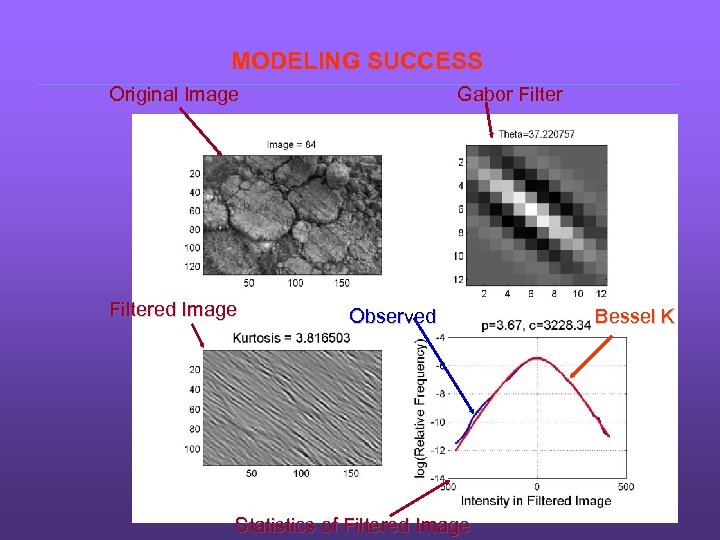 MODELING SUCCESS Original Image Filtered Image Gabor Filter Observed Statistics of Filtered Image Bessel K
MODELING SUCCESS Original Image Filtered Image Gabor Filter Observed Statistics of Filtered Image Bessel K
 SHAPE ANALYSIS • Represent shapes as elements of infinite-dimensional manifolds • Analyze shapes using geometry of that manifold -- connect shapes using geodesic paths on the manifold -- quantify shape differences using geodesic lengths -- compute shape statistics (mean, variance) • Applications: -- clustering of objects according to shapes (learning) -- shape based recognition of objects (recognition) -- predicting shapes of partially-obscured objects (completion)
SHAPE ANALYSIS • Represent shapes as elements of infinite-dimensional manifolds • Analyze shapes using geometry of that manifold -- connect shapes using geodesic paths on the manifold -- quantify shape differences using geodesic lengths -- compute shape statistics (mean, variance) • Applications: -- clustering of objects according to shapes (learning) -- shape based recognition of objects (recognition) -- predicting shapes of partially-obscured objects (completion)
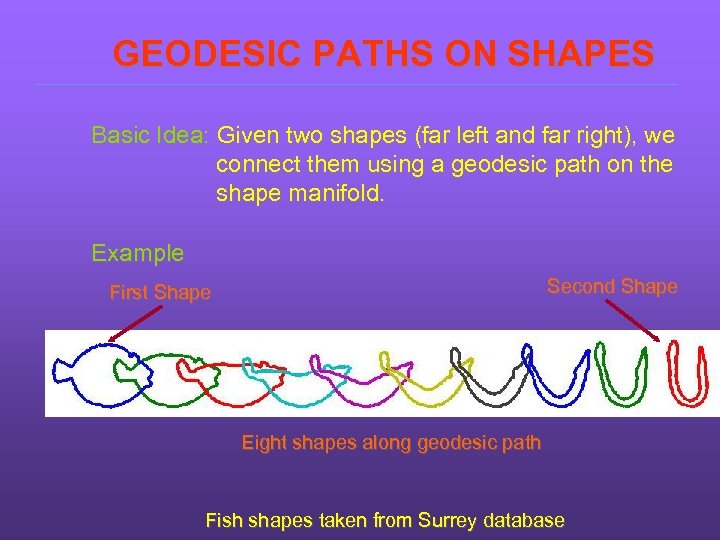 GEODESIC PATHS ON SHAPES Basic Idea: Given two shapes (far left and far right), we connect them using a geodesic path on the shape manifold. Example Second Shape First Shape Eight shapes along geodesic path Fish shapes taken from Surrey database
GEODESIC PATHS ON SHAPES Basic Idea: Given two shapes (far left and far right), we connect them using a geodesic path on the shape manifold. Example Second Shape First Shape Eight shapes along geodesic path Fish shapes taken from Surrey database
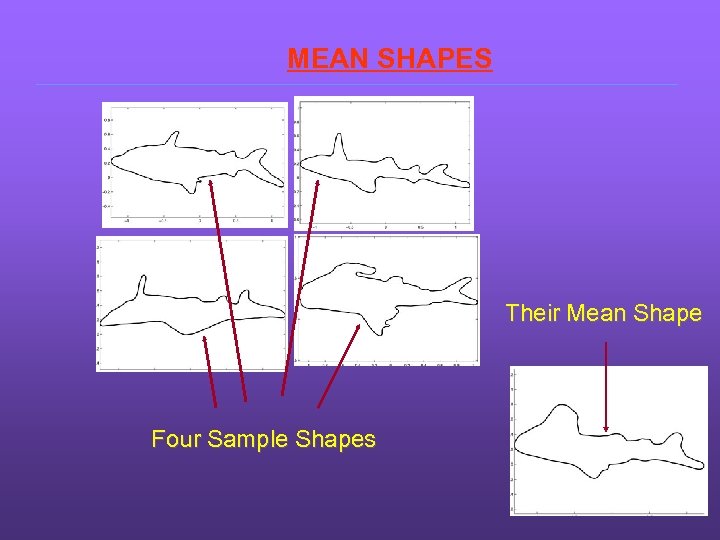 MEAN SHAPES Their Mean Shape Four Sample Shapes
MEAN SHAPES Their Mean Shape Four Sample Shapes
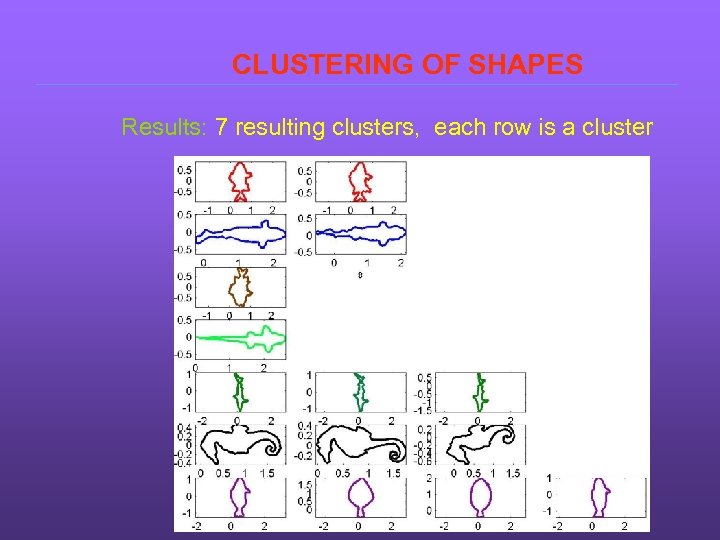 CLUSTERING OF SHAPES Results: 7 resulting clusters, each row is a cluster
CLUSTERING OF SHAPES Results: 7 resulting clusters, each row is a cluster
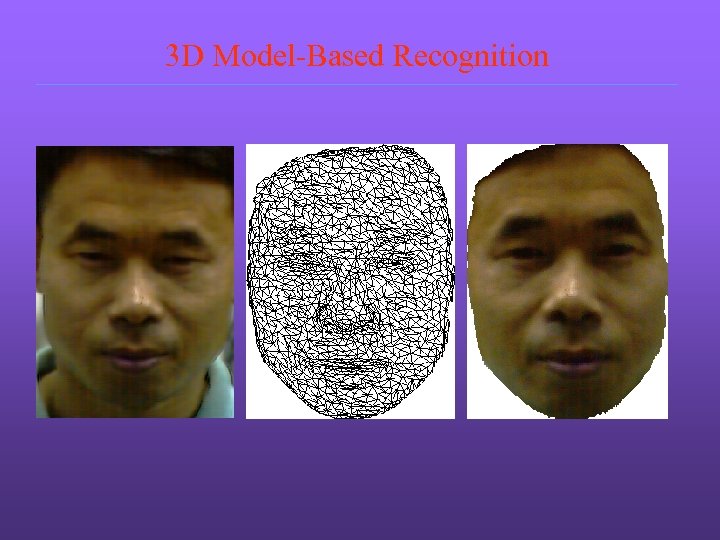 3 D Model-Based Recognition
3 D Model-Based Recognition
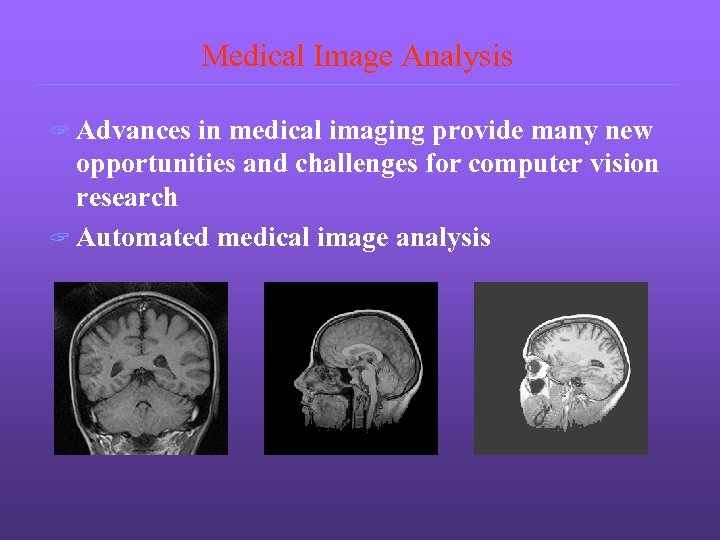 Medical Image Analysis ? Advances in medical imaging provide many new opportunities and challenges for computer vision research ? Automated medical image analysis
Medical Image Analysis ? Advances in medical imaging provide many new opportunities and challenges for computer vision research ? Automated medical image analysis
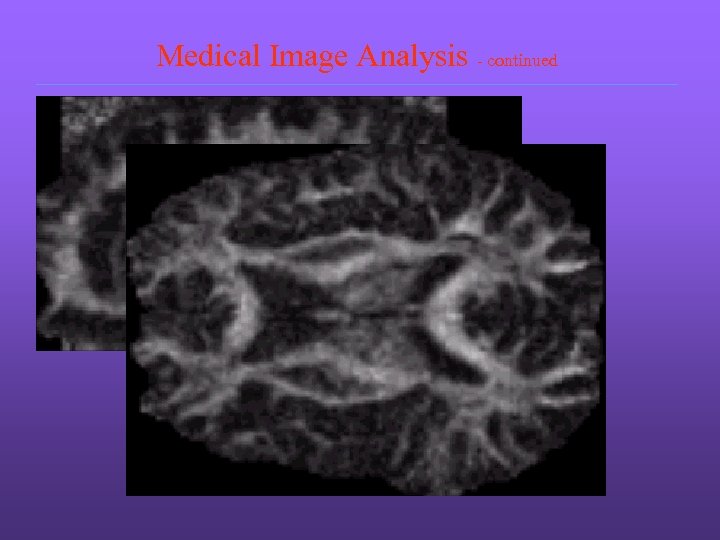 Medical Image Analysis - continued
Medical Image Analysis - continued
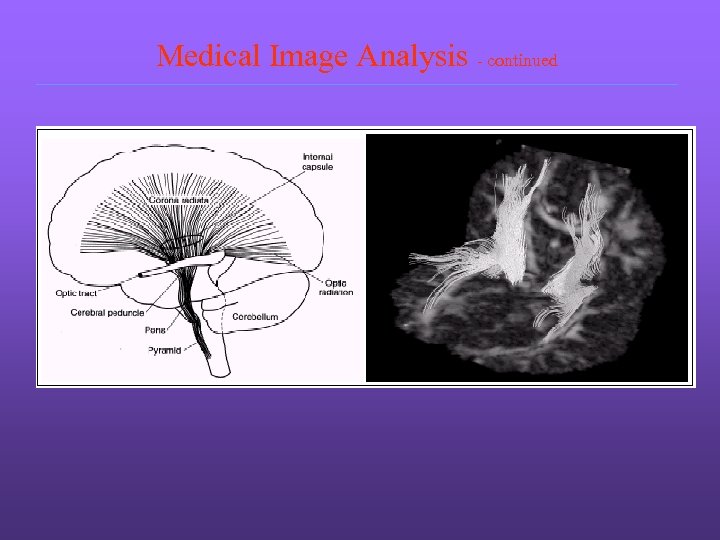 Medical Image Analysis - continued
Medical Image Analysis - continued
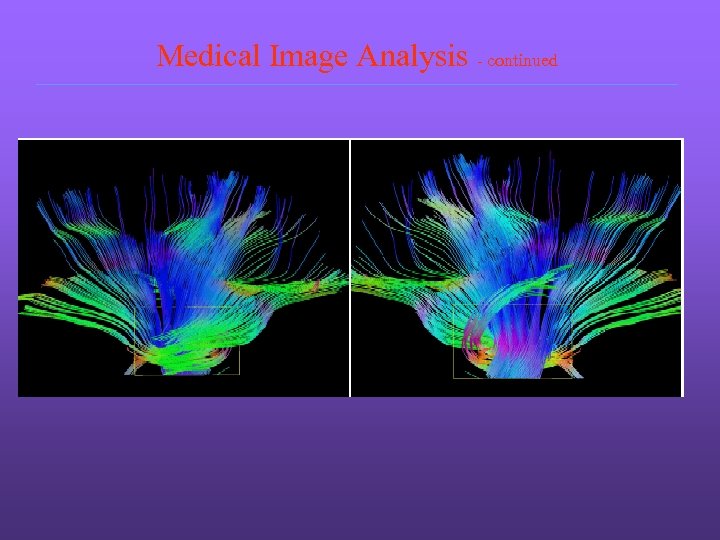 Medical Image Analysis - continued
Medical Image Analysis - continued
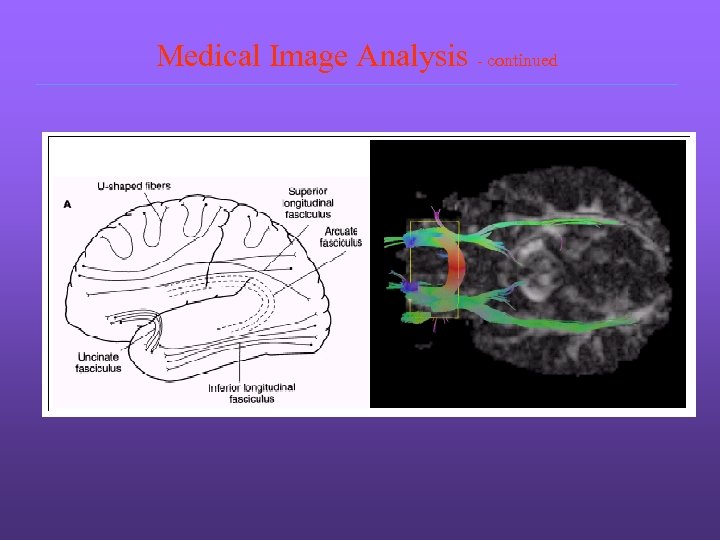 Medical Image Analysis - continued
Medical Image Analysis - continued
 Video Sequence Analysis and Summary ? Motion analysis based on correspondence ? Video stream-based surveillance ? Video summary
Video Sequence Analysis and Summary ? Motion analysis based on correspondence ? Video stream-based surveillance ? Video summary
 Courses ? Most Relevant Courses • CAP 5638 Pattern Recognition (Spring 2004) • CAP 5415 Principles and Algorithms of Computer Vision – Fall 2004 • CAP 6417 Theoretical Foundations of Computer Vision – STA 5106 Computational Methods in Statistics I – STA 5107 Computational Methods in Statistics I I – Seminars and advanced studies ? Related Courses • CAP 5615 Artificial Neural Networks • CAP 5600 Artificial Intelligence • CAP 5 xxx Machine Learning
Courses ? Most Relevant Courses • CAP 5638 Pattern Recognition (Spring 2004) • CAP 5415 Principles and Algorithms of Computer Vision – Fall 2004 • CAP 6417 Theoretical Foundations of Computer Vision – STA 5106 Computational Methods in Statistics I – STA 5107 Computational Methods in Statistics I I – Seminars and advanced studies ? Related Courses • CAP 5615 Artificial Neural Networks • CAP 5600 Artificial Intelligence • CAP 5 xxx Machine Learning
 CAP 5638 Pattern Recognition ? It will be offered Spring 2004 • • ? Tuesday and Thursday 6: 45 -8: 00 PM At Love 103 The course ref #: 07842 http: //www. cs. fsu. edu/~liux/courses/cap 5638/ It will cover • The basics for pattern recognition – Neural networks • Machine learning algorithms • Applications in data mining, pattern discovery, artificial intelligence, and security, ? It should be interesting to anyone interested in more intelligent computer learning algorithms
CAP 5638 Pattern Recognition ? It will be offered Spring 2004 • • ? Tuesday and Thursday 6: 45 -8: 00 PM At Love 103 The course ref #: 07842 http: //www. cs. fsu. edu/~liux/courses/cap 5638/ It will cover • The basics for pattern recognition – Neural networks • Machine learning algorithms • Applications in data mining, pattern discovery, artificial intelligence, and security, ? It should be interesting to anyone interested in more intelligent computer learning algorithms
 Funding of the Group ? National • • Science Foundation DMS CISE IIS FRG ACT ? National Imagery and Mapping Agency • NGA – National Geo-spatial Intelligence Agency ? Army Research Office
Funding of the Group ? National • • Science Foundation DMS CISE IIS FRG ACT ? National Imagery and Mapping Agency • NGA – National Geo-spatial Intelligence Agency ? Army Research Office
 Summary ? Florida State Vision group offers many interesting research topics/projects • Efficient represent for generic images • Computational models for object recognition and image classification • Medical image analysis • Motion/video sequence analysis and modeling • They are challenging • They are interesting
Summary ? Florida State Vision group offers many interesting research topics/projects • Efficient represent for generic images • Computational models for object recognition and image classification • Medical image analysis • Motion/video sequence analysis and modeling • They are challenging • They are interesting
 Contact Information Name • Web site at • Email at • Office at • Phone • Xiuwen Liu http: //fsvision. fsu. edu http: //www. cs. fsu. edu/~liux@cs. fsu. edu LOV 166 644 -0050
Contact Information Name • Web site at • Email at • Office at • Phone • Xiuwen Liu http: //fsvision. fsu. edu http: //www. cs. fsu. edu/~liux@cs. fsu. edu LOV 166 644 -0050


