Электрические сети 3.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 20
 REQUIREMENTS FOR ELECTRICAL NETWORKS
REQUIREMENTS FOR ELECTRICAL NETWORKS
 The main requirements to the networks • Reliability • Power Quality • Economy • Safety and ease of use • The possibility of further development
The main requirements to the networks • Reliability • Power Quality • Economy • Safety and ease of use • The possibility of further development
 Reliability is the extent to which an experiment, test, or any measuring procedure yields the same result on repeated trials. The reliability of the electrical system (association) - the ability to perform its basic function - uninterrupted power supply of consumers with electricity required (normative) quality and the elimination of hazardous situations for people and the environment.
Reliability is the extent to which an experiment, test, or any measuring procedure yields the same result on repeated trials. The reliability of the electrical system (association) - the ability to perform its basic function - uninterrupted power supply of consumers with electricity required (normative) quality and the elimination of hazardous situations for people and the environment.
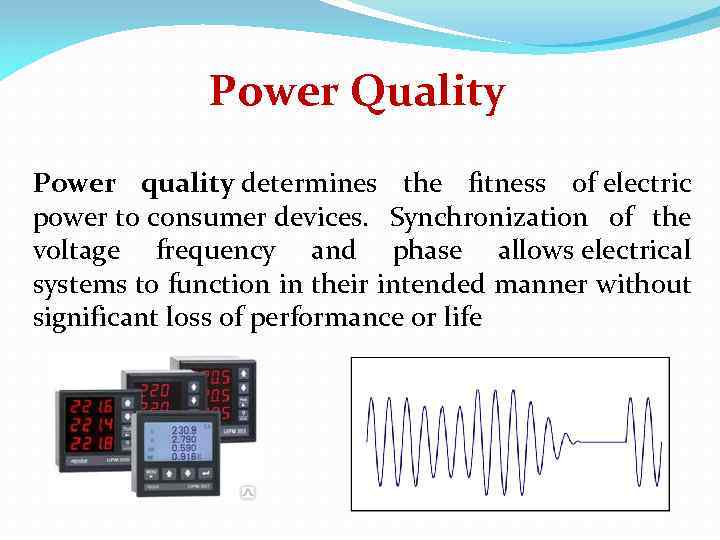 Power Quality Power quality determines the fitness of electric power to consumer devices. Synchronization of the voltage frequency and phase allows electrical systems to function in their intended manner without significant loss of performance or life
Power Quality Power quality determines the fitness of electric power to consumer devices. Synchronization of the voltage frequency and phase allows electrical systems to function in their intended manner without significant loss of performance or life
 Economy • reduction of losses • the commissioning of new high-efficient and technologically advanced power plants • reliability and continuity
Economy • reduction of losses • the commissioning of new high-efficient and technologically advanced power plants • reliability and continuity
 Safety and ease of use
Safety and ease of use
 The possibility of further development
The possibility of further development
 The construction of overhead power lines
The construction of overhead power lines
 An overhead power line is a structure used in electric power transmission and distribution to transmit electrical energy along large distances.
An overhead power line is a structure used in electric power transmission and distribution to transmit electrical energy along large distances.
 The composition of the overhead line • Wires • Traverses • Insulators • Fittings • Supports • Ground wire • Arresters • Grounding • Partitioned device • Fiber-optic communication lines • Auxiliary equipment • Label elements of high-voltage wires
The composition of the overhead line • Wires • Traverses • Insulators • Fittings • Supports • Ground wire • Arresters • Grounding • Partitioned device • Fiber-optic communication lines • Auxiliary equipment • Label elements of high-voltage wires
 Wires Wire overhead transmission line for the transmission of electrical energy from the source to the consumer electrical receivers. By construction: • multiwire • single-wired • multiwire conductors of the two metals • сopper wire • aluminum wire • steel-aluminum wires
Wires Wire overhead transmission line for the transmission of electrical energy from the source to the consumer electrical receivers. By construction: • multiwire • single-wired • multiwire conductors of the two metals • сopper wire • aluminum wire • steel-aluminum wires
 Location wire on an overhead line
Location wire on an overhead line
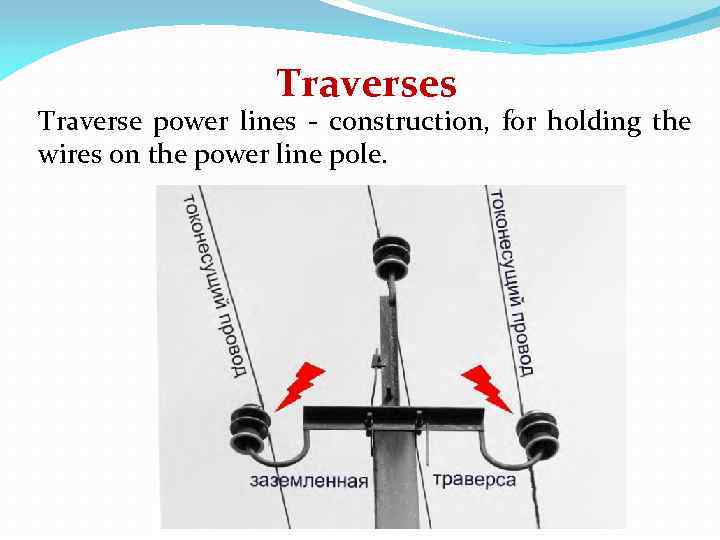 Traverses Traverse power lines - construction, for holding the wires on the power line pole.
Traverses Traverse power lines - construction, for holding the wires on the power line pole.
 Insulators An electrical insulator is a material whose internal electric charges do not flow freely, and therefore make it nearly impossible to conduct an electric current under the influence of an electric field. • porcelain insulators • glass insulators • polymeric insulators
Insulators An electrical insulator is a material whose internal electric charges do not flow freely, and therefore make it nearly impossible to conduct an electric current under the influence of an electric field. • porcelain insulators • glass insulators • polymeric insulators
 Fittings - special types of parts for connecting wires, insulators in connection garlands, fixing wires to them, the suspension strings on poles of power lines and other functions.
Fittings - special types of parts for connecting wires, insulators in connection garlands, fixing wires to them, the suspension strings on poles of power lines and other functions.
 Supports Support overhead power line (transmission towers) - construction to hold the wires in the presence of - ground wire overhead power line and fiber-optic communication lines at a predetermined distance from the ground and from each other.
Supports Support overhead power line (transmission towers) - construction to hold the wires in the presence of - ground wire overhead power line and fiber-optic communication lines at a predetermined distance from the ground and from each other.
 Ground wire - galvanized steel rope, designed for protection of overhead transmission lines from atmospheric overvoltage and direct lightning strikes
Ground wire - galvanized steel rope, designed for protection of overhead transmission lines from atmospheric overvoltage and direct lightning strikes
 Arresters Arrester - electrical device designed to limit overvoltage in electrical installations and electrical networks.
Arresters Arrester - electrical device designed to limit overvoltage in electrical installations and electrical networks.
 Grounding - intentional electrical connection to any point of the network, or electrical equipment grounding device.
Grounding - intentional electrical connection to any point of the network, or electrical equipment grounding device.
 Classification of the overhead line • By current • AC • DC • By appointment • Ultra-long overhead lines of 500 k. V and above • Trunk overhead lines with voltage of 220 k. V and 330 k. V • Distribution voltage overhead lines 35, 110 and 150 k. V • Overhead lines 20 k. V and below • By voltage • Overhead lines up to 1000 V • Overhead lines above 1000 V • 1 -35 k. V overhead lines • 35 -330 k. V overhead lines • 500 -750 k. V overhead lines • 750 k. V overhead line above
Classification of the overhead line • By current • AC • DC • By appointment • Ultra-long overhead lines of 500 k. V and above • Trunk overhead lines with voltage of 220 k. V and 330 k. V • Distribution voltage overhead lines 35, 110 and 150 k. V • Overhead lines 20 k. V and below • By voltage • Overhead lines up to 1000 V • Overhead lines above 1000 V • 1 -35 k. V overhead lines • 35 -330 k. V overhead lines • 500 -750 k. V overhead lines • 750 k. V overhead line above


