393ddc9384c2484c327c8b752c6133bb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

Requirements-Based Testing Dr. Mats P. E. Heimdahl University of Minnesota Software Engineering Center Dr. Steven P. Miller Dr. Michael W. Whalen Advanced Computing Systems Rockwell Collins 400 Collins Road NE, MS 108 -206 Cedar Rapids, Iowa 52498 spmiller@rockwellcollins. com Advanced Technology Center Slide 1

Outline of Presentation Motivation Validation Testing Conformance Testing What’s Next Advanced Technology Center Slide 2
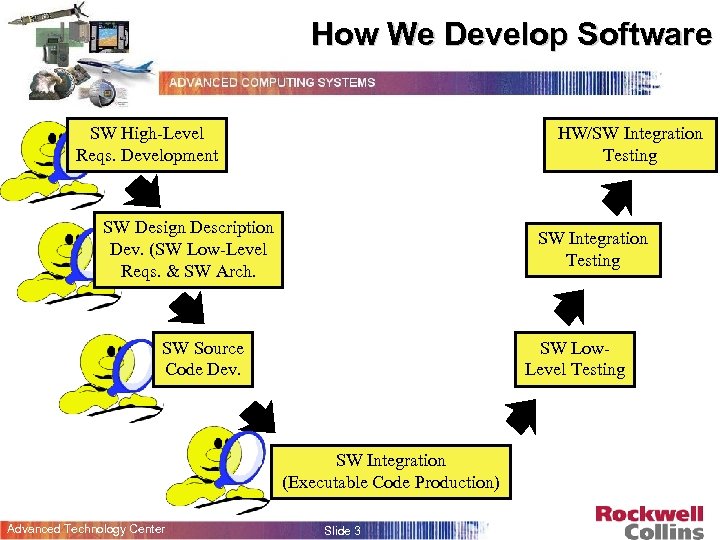
How We Develop Software SW High-Level Reqs. Development HW/SW Integration Testing SW Design Description Dev. (SW Low-Level Reqs. & SW Arch. SW Integration Testing SW Source Code Dev. SW Low. Level Testing SW Integration (Executable Code Production) Advanced Technology Center Slide 3
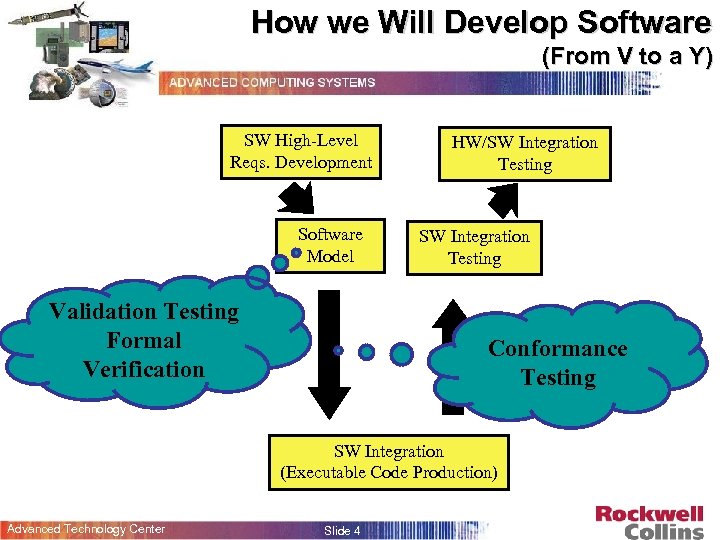
How we Will Develop Software (From V to a Y) SW High-Level Reqs. Development Software Model Validation Testing How do we know our model is Formal Verification correct? HW/SW Integration Testing Can we trust Conformance the code Testing generator? SW Integration (Executable Code Production) Advanced Technology Center Slide 4

Outline of Presentation Motivation Validation Testing Conformance Testing What’s Next Advanced Technology Center Slide 5
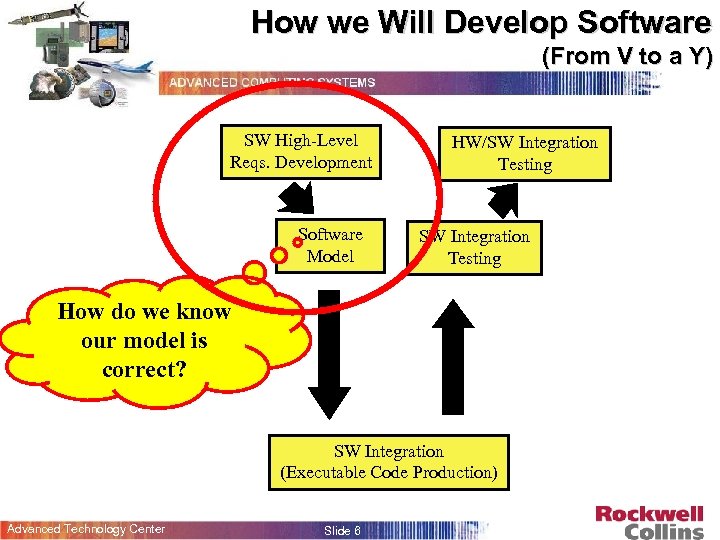
How we Will Develop Software (From V to a Y) SW High-Level Reqs. Development Software Model HW/SW Integration Testing How do we know our model is correct? SW Integration (Executable Code Production) Advanced Technology Center Slide 6
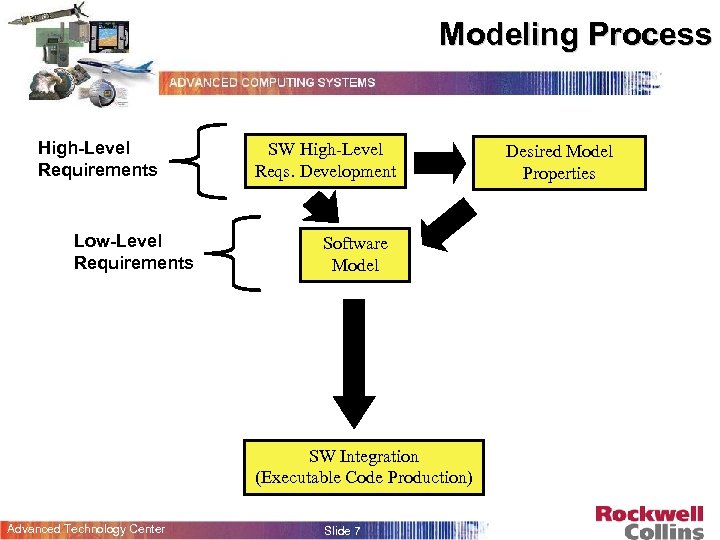
Modeling Process High-Level Requirements Low-Level Requirements SW High-Level Reqs. Development Software Model SW Integration (Executable Code Production) Advanced Technology Center Slide 7 Desired Model Properties
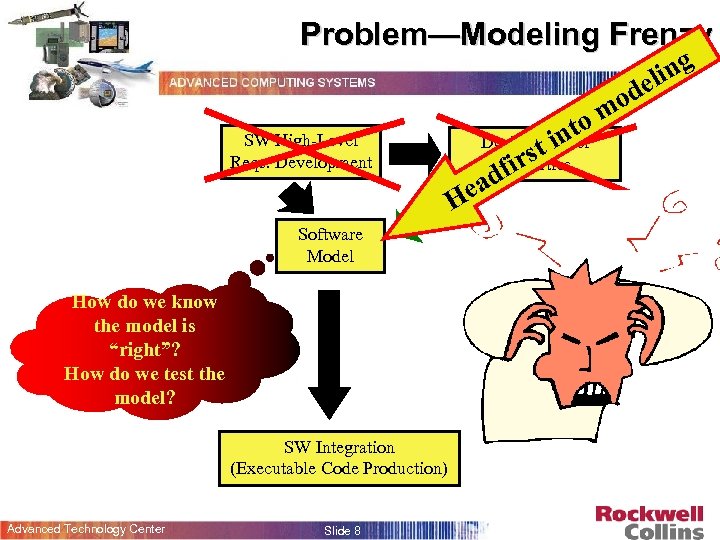
Problem—Modeling Frenzy ing el SW High-Level Reqs. Development Software Model How do we know the model is “right”? How do we test the model? SW Integration (Executable Code Production) Advanced Technology Center Slide 8 to Desired t in Model s Properties fir ead H od m
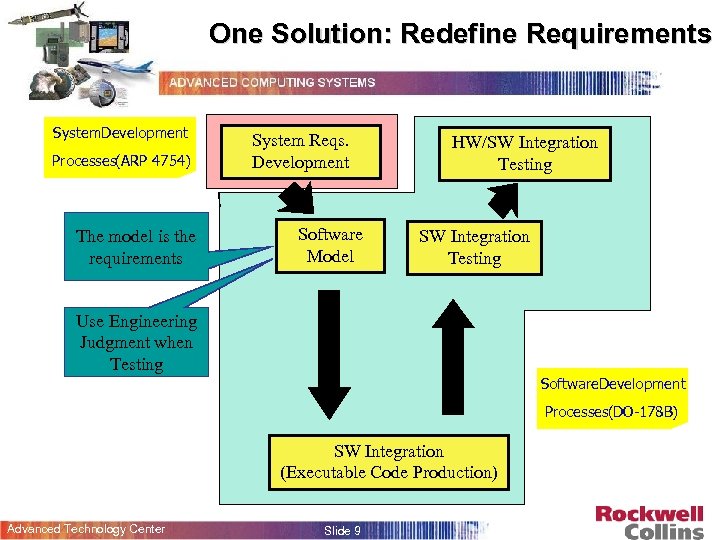
One Solution: Redefine Requirements System. Development Processes(ARP 4754) The model is the requirements System Reqs. Development Software Model HW/SW Integration Testing Use Engineering Judgment when Testing Software. Development Processes(DO-178 B) SW Integration (Executable Code Production) Advanced Technology Center Slide 9
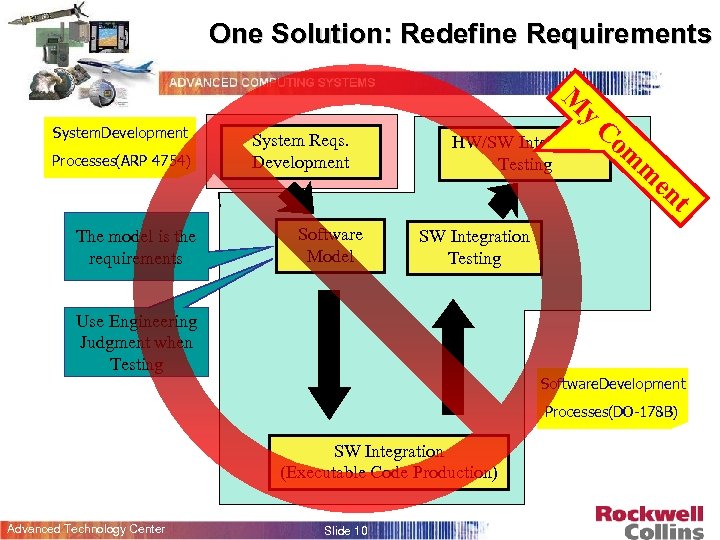
One Solution: Redefine Requirements M System. Development Processes(ARP 4754) The model is the requirements y System Reqs. Development Software Model C HW/SW Integration Testing om m en t SW Integration Testing Use Engineering Judgment when Testing Software. Development Processes(DO-178 B) SW Integration (Executable Code Production) Advanced Technology Center Slide 10
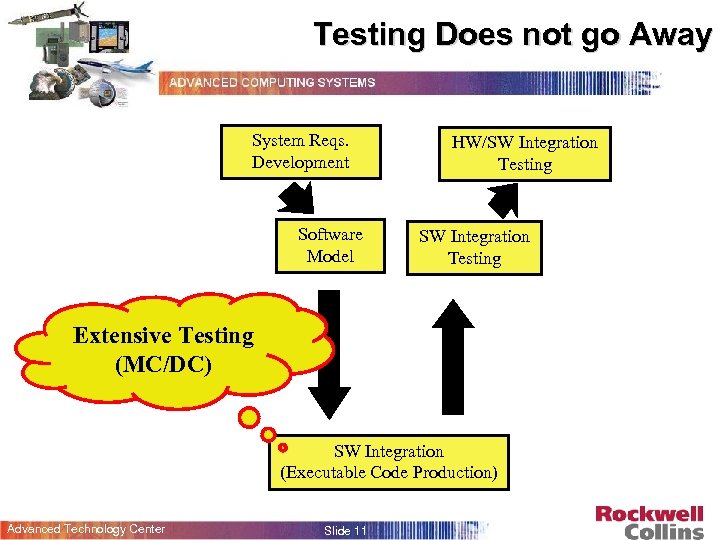
Testing Does not go Away System Reqs. Development Software Model HW/SW Integration Testing Extensive Testing (MC/DC) SW Integration (Executable Code Production) Advanced Technology Center Slide 11
It Simply Moves System Reqs. Development Software Model HW/SW Integration Testing Extensive Testing (MC/DC) SW Integration (Executable Code Production) Advanced Technology Center Slide 12
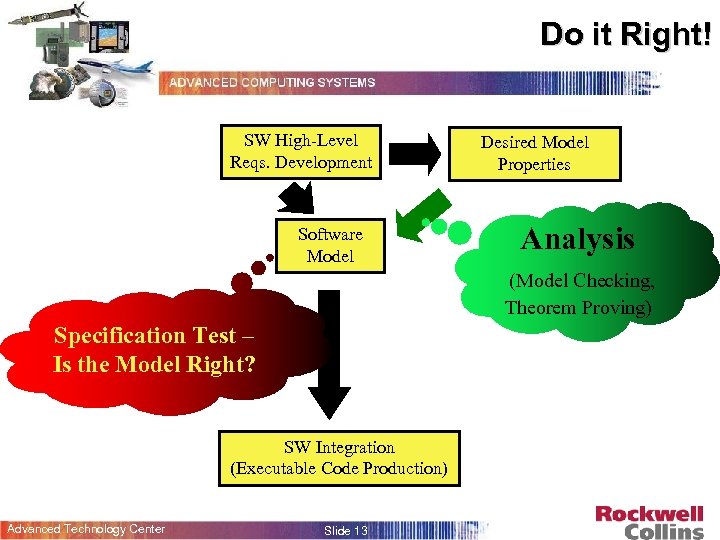
Do it Right! SW High-Level Reqs. Development Software Model Desired Model Properties Analysis (Model Checking, Theorem Proving) Specification Test – Is the Model Right? SW Integration (Executable Code Production) Advanced Technology Center Slide 13
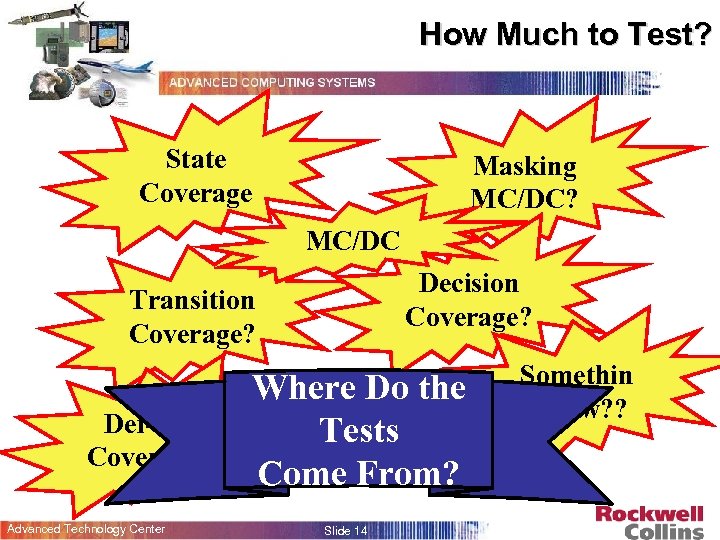
How Much to Test? State Coverage Masking MC/DC? MC/DC Decision Coverage? Transition Coverage? Def-Use Coverage? Advanced Technology Center Where Do the Tests Come From? Slide 14 Somethin g New? ?
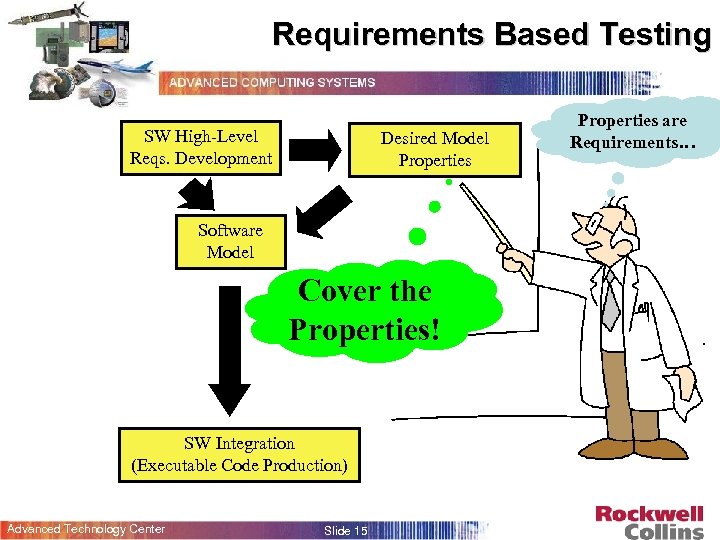
Requirements Based Testing SW High-Level Reqs. Development Desired Model Properties Software Model Cover the Properties! SW Integration (Executable Code Production) Advanced Technology Center Slide 15 Properties are Requirements…
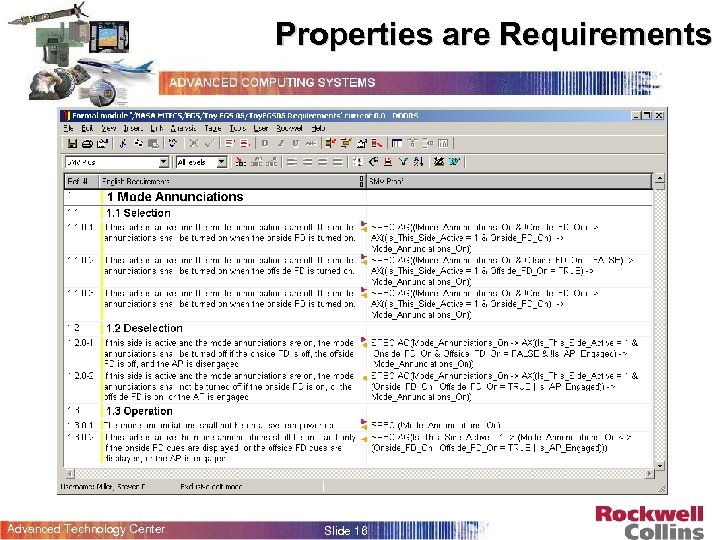
Properties are Requirements Advanced Technology Center Slide 16
Requirements Based Testing Advantages § Objective Measurement of Model Validation Efforts – Requirements Coverage in Model-based Development – Help Identify Missing Requirements • Measure converge of model § Basis for Automated Generation of Requirements-based Tests – Even If Properties Are Not Used for Verification, They Can Be Used for Test Automation How Are Properties “Covered” with Requirements-based Tests? Advanced Technology Center Slide 17

Property Coverage “If the onside FD cues are off, the onside FD cues shall be displayed when the AP is engaged” – G(((!Onside_FD_On & !Is_AP_Engaged) -> X(Is_AP_Engaged -> Onside_FD_On)) § Property Automata Coverage – Cover a Synchronous Observer Representing the Requirement (Property) § Structural Property Coverage – Demonstrate Structurally “Interesting” Ways in Which the Requirement (Property) Is Met Advanced Technology Center Slide 18
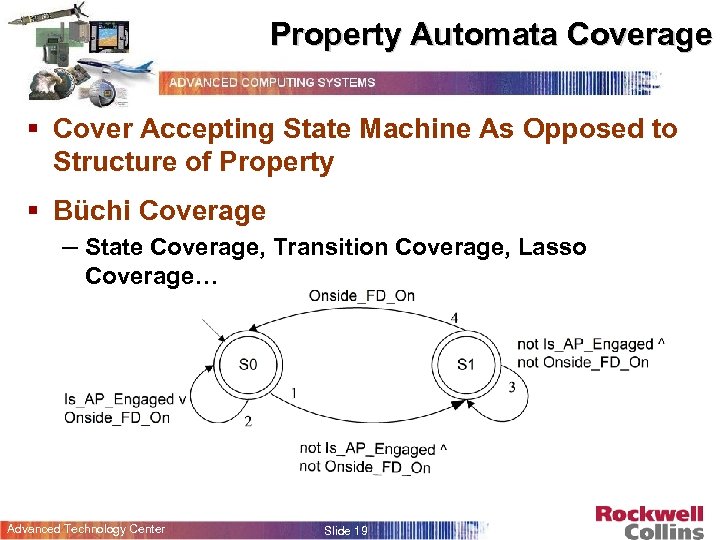
Property Automata Coverage § Cover Accepting State Machine As Opposed to Structure of Property § Büchi Coverage – State Coverage, Transition Coverage, Lasso Coverage… Advanced Technology Center Slide 19
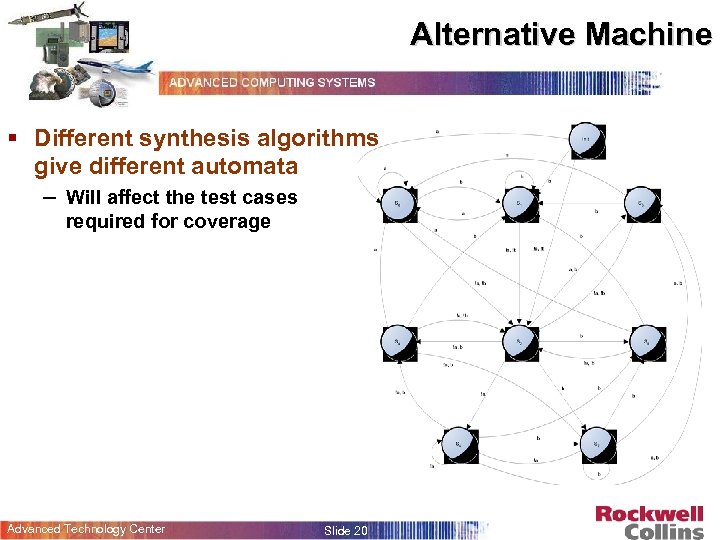
Alternative Machine § Different synthesis algorithms give different automata – Will affect the test cases required for coverage Advanced Technology Center Slide 20

Structural Property Coverage § Define Structural Coverage Criteria for the Property Specification – Traditional Condition-based Criteria such as MC/DC Prime Candidates § Property Coverage Different than Code Coverage – Coverage of Code and Models • Evaluate a decision with a specific combination of truth values in the decision – Coverage of Properties • Run an execution scenario that illustrates a specific way a requirement (temporal property) is satisfied Advanced Technology Center Slide 21
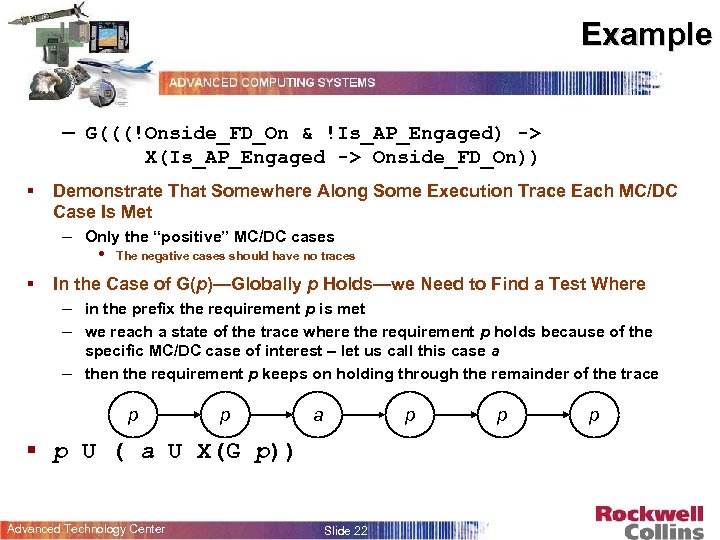
Example – G(((!Onside_FD_On & !Is_AP_Engaged) -> X(Is_AP_Engaged -> Onside_FD_On)) § Demonstrate That Somewhere Along Some Execution Trace Each MC/DC Case Is Met – Only the “positive” MC/DC cases • The negative cases should have no traces § In the Case of G(p)—Globally p Holds—we Need to Find a Test Where – in the prefix the requirement p is met – we reach a state of the trace where the requirement p holds because of the specific MC/DC case of interest – let us call this case a – then the requirement p keeps on holding through the remainder of the trace p p a p § p U ( a U X(G p)) Advanced Technology Center Slide 22 p p

Summary § Objective Measurement of Model Validation Efforts – Requirements Coverage in Model-based Development – Help Identify Missing Requirements § Basis for Automated Generation of Requirements-based Tests – Even If Properties Are Not Used for Verification, They Can Be Used for Test Automation and Test Measurement § Challenges – How Are Properties Specified? • Combination of Observers and Temporal Properties – What Coverage Criteria Are Suitable? – How Is Automation Achieved? – How Do We Eliminate “Obviously” Bad Tests? Should We? – How Do We Generate “Realistic” Test-cases? – Rigorous Empirical Studies Badly Needed Advanced Technology Center Slide 23

Outline of Presentation Motivation Validation Testing Conformance Testing What’s Next Advanced Technology Center Slide 24
How we Will Develop Software (From V to a Y) SW High-Level Reqs. Development Software Model HW/SW Integration Testing Can we trust the code generator? SW Integration (Executable Code Production) Advanced Technology Center Slide 25
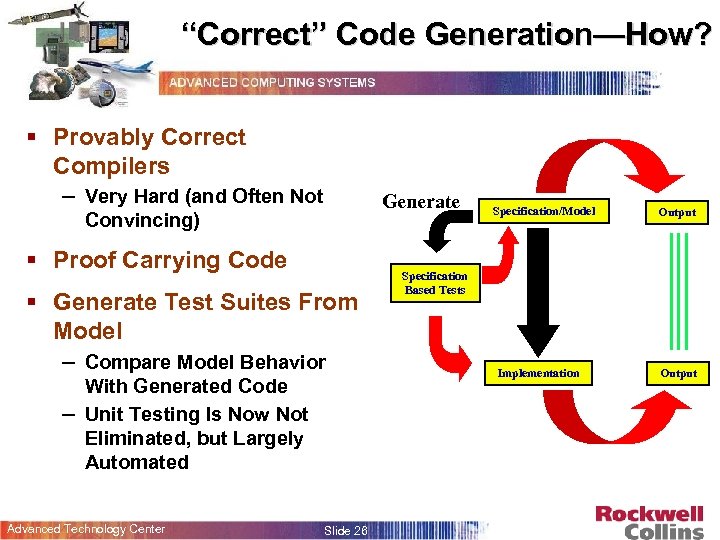
“Correct” Code Generation—How? § Provably Correct Compilers – Very Hard (and Often Not Generate Convincing) § Proof Carrying Code § Generate Test Suites From Model – Compare Model Behavior With Generated Code – Unit Testing Is Now Not Eliminated, but Largely Automated Advanced Technology Center Slide 26 Specification/Model Output Specification Based Tests Implementation Output

Existing Capabilities § Several Commercial and Research Tools for Test. Case Generation – TVEC • Theorem Proving and Constraint Solving techniques – Reactis from Reactive Systems Inc. • Random, Heuristic, and Guided Search – University of Minnesota • Bounded Model Checking – NASA Langley • Bounded Model Checking/Decision Procedures/Constraint Solving § Tools Applicable to Relevant Notations – In Our Case Simulink Advanced Technology Center Slide 27

An Initial Experiment § Used a Model of the Mode Logic of a Flight Guidance System As a Case Example § Fault Seeding – Representative Faults – Generated 100 Faulty Specifications § Generate Test Suites – Selection of Common (and Not So Common) Criteria § Fault Detection – Ran the Test Suites Against the Faulty Specifications – Recorded the Total Number of Faults Detected Advanced Technology Center Slide 28
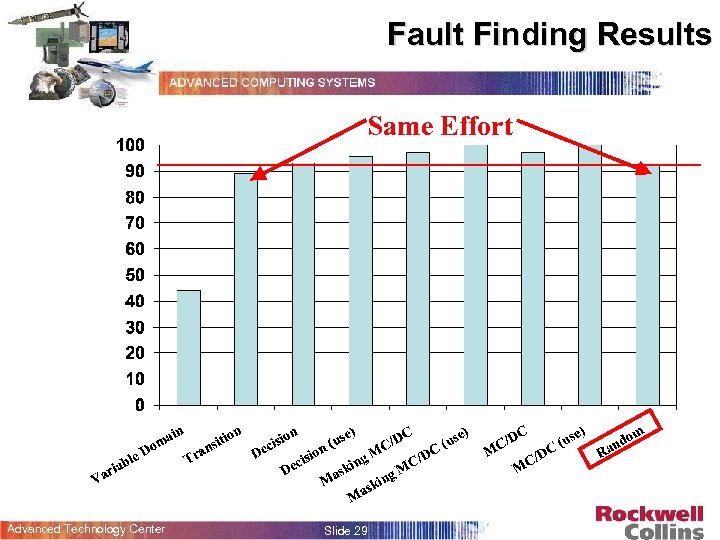
Fault Finding Results Same Effort Advanced Technology Center Slide 29
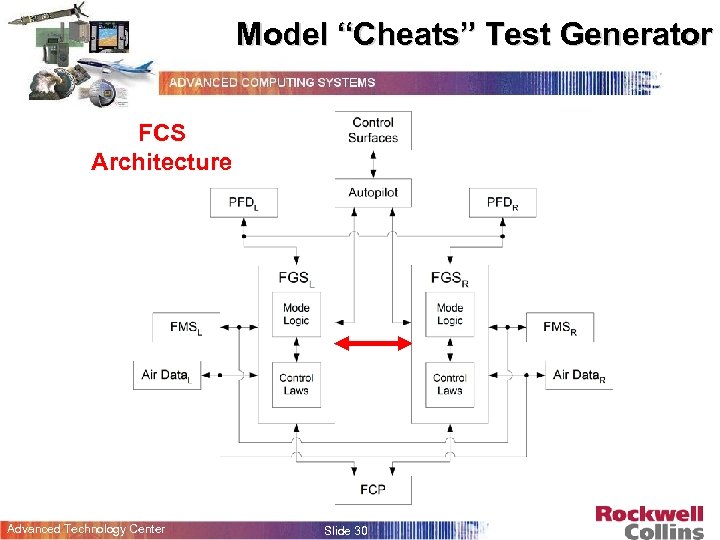
Model “Cheats” Test Generator FCS Architecture Advanced Technology Center Slide 30
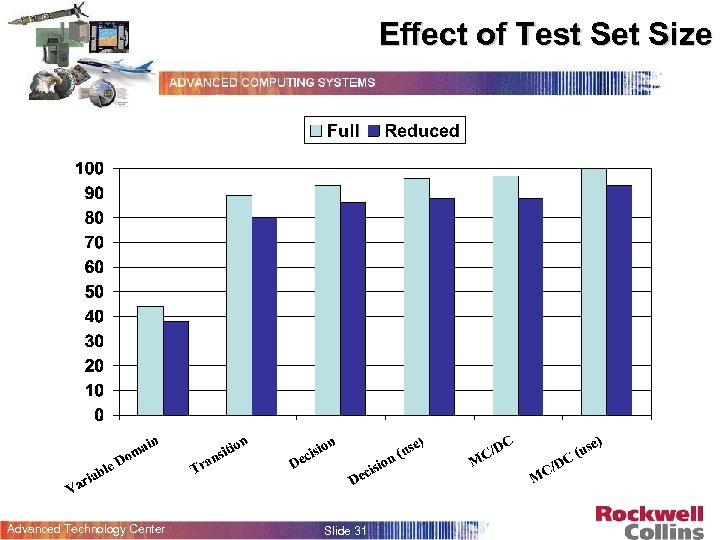
Effect of Test Set Size Advanced Technology Center Slide 31

Summary § Automated Generation of Conformance Tests – Current Technology Largely Allows This Automation § Challenges – Development of Suitable Coverage Criteria – Effect of Test Set Size on Test Set Effectiveness – Effect of Model Structure on Coverage Criteria Effectiveness – Traceability of Tests to Constructs Tested – Empirical Studies of Great Importance Advanced Technology Center Slide 32

Outline of Presentation Motivation Conformance Testing Validation Testing What’s Next Advanced Technology Center Slide 33

New Challenges for Testing § Model Validation – Requirements-based Testing – How Do We Best Formalize the Requirements? – What Coverage Criteria Are Feasible? – Which Coverage Criteria Are Effective (If Any)? – How Do We Generate “Realistic” Tests? – Will This Be a Practical (Tractable) Solution? § Conformance Testing – What Coverage Criteria Are Effective? • Detecting Faults From Manual Coding • Detecting Faults From Code Generation – Relationship Between Model Structure and Criteria Effectiveness – Traceability From Tests to Model – Relationship Between Model Coverage and Code Coverage • Optimizations in Code Generator Will Compromise Coverage Advanced Technology Center Slide 34

Discussion Advanced Technology Center Slide 35

Perfection is Not Necessary ≥ Missed Faults § Tools and Models Only Need To Be Better Than Manual Processes… I Think Many – How Do We Demonstrate This? Already Are • Empirical Studies Are of Great Importance Advanced Technology Center Slide 36
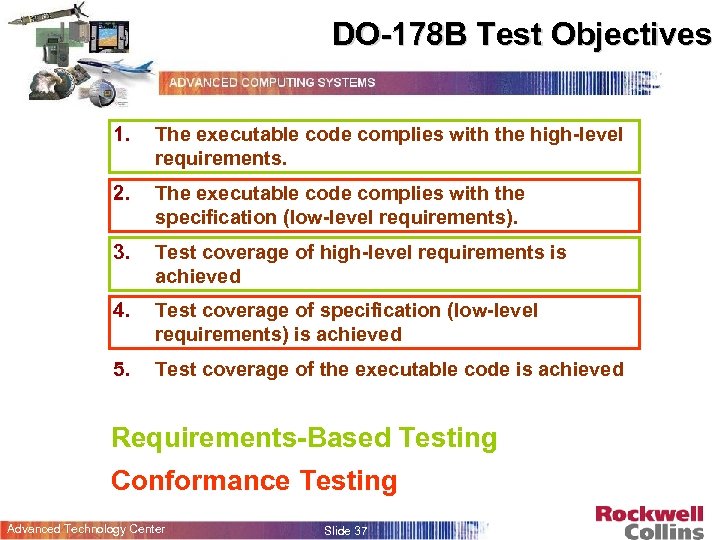
DO-178 B Test Objectives 1. The executable code complies with the high-level requirements. 2. The executable code complies with the specification (low-level requirements). 3. Test coverage of high-level requirements is achieved 4. Test coverage of specification (low-level requirements) is achieved 5. Test coverage of the executable code is achieved Requirements-Based Testing Conformance Testing Advanced Technology Center Slide 37
393ddc9384c2484c327c8b752c6133bb.ppt