 Requirements Analysis Document Augmented Reality Team Christopher Lee, Jeremy Jones, Michael Fortson Yik Lin Khoo, Leong Teo, Li Qiu Augmented Reality RAD 1
Requirements Analysis Document Augmented Reality Team Christopher Lee, Jeremy Jones, Michael Fortson Yik Lin Khoo, Leong Teo, Li Qiu Augmented Reality RAD 1
 Current System • No Augmented Reality – Miniature Blueprints – Grease Pencil • Drawbacks – Limited accuracy – Limited amount of detail Augmented Reality RAD 2
Current System • No Augmented Reality – Miniature Blueprints – Grease Pencil • Drawbacks – Limited accuracy – Limited amount of detail Augmented Reality RAD 2
 Scenario • An inspector puts on a Stars PEDD • He turns on the PEDD and walks over to a damaged F-18 • He stands at the nose cone of the plane • He calibrates the wire-frame • He begins his inspection of the plane Augmented Reality RAD 3
Scenario • An inspector puts on a Stars PEDD • He turns on the PEDD and walks over to a damaged F-18 • He stands at the nose cone of the plane • He calibrates the wire-frame • He begins his inspection of the plane Augmented Reality RAD 3
 Proposed System • User Interface Manager – To manage and display the user interfaces of other subsystems • Calibration User Interface – An interface for calibrating the wire-frame overlay • Device Drivers to Support I/O Devices – Joystick, HMD, Positioning and Orientation Devices • Event System – To interpret low level events and dispatch them to the appropriate subsystems Augmented Reality RAD 4
Proposed System • User Interface Manager – To manage and display the user interfaces of other subsystems • Calibration User Interface – An interface for calibrating the wire-frame overlay • Device Drivers to Support I/O Devices – Joystick, HMD, Positioning and Orientation Devices • Event System – To interpret low level events and dispatch them to the appropriate subsystems Augmented Reality RAD 4
 Functional Requirements • • Manage the HMD Calibration of the wire-frame display Interpret low-level data from input devices Dispatch events to other subsystems Augmented Reality RAD 5
Functional Requirements • • Manage the HMD Calibration of the wire-frame display Interpret low-level data from input devices Dispatch events to other subsystems Augmented Reality RAD 5
 Hardware Considerations • PEDD must be capable of running a JVM • Java 3 D – Open. GL or Direct. X required for Java 3 D on the Windows 98 platform • Positioning Device – Data must be accurate within three inches for extensibility • Orientation Device – Sensitive enough to track head movement Augmented Reality RAD 6
Hardware Considerations • PEDD must be capable of running a JVM • Java 3 D – Open. GL or Direct. X required for Java 3 D on the Windows 98 platform • Positioning Device – Data must be accurate within three inches for extensibility • Orientation Device – Sensitive enough to track head movement Augmented Reality RAD 6
 Performance Characteristics • Frame Rate – Wire-frame updates must be smooth • Input Devices – Update in real-time to ensure accurate feedback Augmented Reality RAD 7
Performance Characteristics • Frame Rate – Wire-frame updates must be smooth • Input Devices – Update in real-time to ensure accurate feedback Augmented Reality RAD 7
 Error Handling and Extreme Conditions • Bounds Checking – Make sure information from input devices is valid • Positioning or Orientation Device Failure – Invokes a manual calibration mode • PEDD Failure – No persistent data, requires only a recalibration Augmented Reality RAD 8
Error Handling and Extreme Conditions • Bounds Checking – Make sure information from input devices is valid • Positioning or Orientation Device Failure – Invokes a manual calibration mode • PEDD Failure – No persistent data, requires only a recalibration Augmented Reality RAD 8
 System Interfacing • Maintenance – Request services of the UI Manager – Receive input from our input device handlers • Modeling – Request services of the UI Manager – Receive input from the input device handlers Augmented Reality RAD 9
System Interfacing • Maintenance – Request services of the UI Manager – Receive input from our input device handlers • Modeling – Request services of the UI Manager – Receive input from the input device handlers Augmented Reality RAD 9
 System Modification • New Input Devices Require New Events • New Hardware Requires New Device Drivers – Examples: Transparent HMD, more accurate positioning device • User Interfaces – May change with new technology requiring and update in the UI Manager • Calibration – May become fully automated with newer technology Augmented Reality RAD 10
System Modification • New Input Devices Require New Events • New Hardware Requires New Device Drivers – Examples: Transparent HMD, more accurate positioning device • User Interfaces – May change with new technology requiring and update in the UI Manager • Calibration – May become fully automated with newer technology Augmented Reality RAD 10
 Security Issues • Augmented Reality has no risk of attack – No persistent data – No transmission to external systems • Other Subsystems – Authentication systems – Implemented on systems containing protected data Augmented Reality RAD 11
Security Issues • Augmented Reality has no risk of attack – No persistent data – No transmission to external systems • Other Subsystems – Authentication systems – Implemented on systems containing protected data Augmented Reality RAD 11
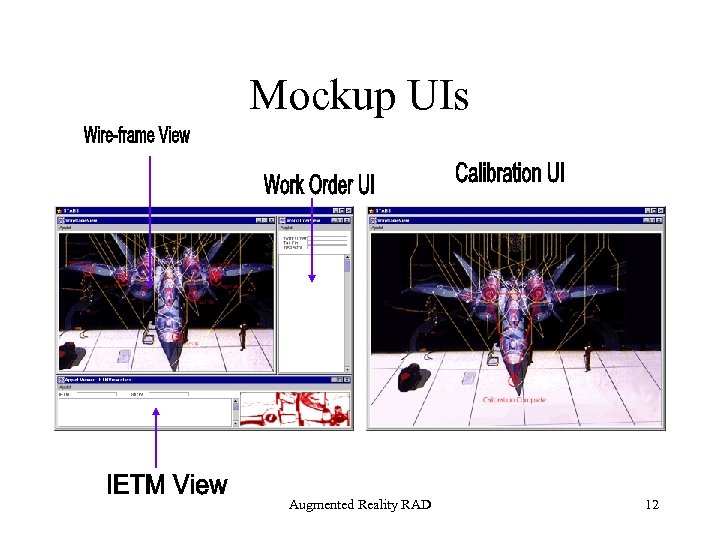 Mockup UIs Augmented Reality RAD 12
Mockup UIs Augmented Reality RAD 12
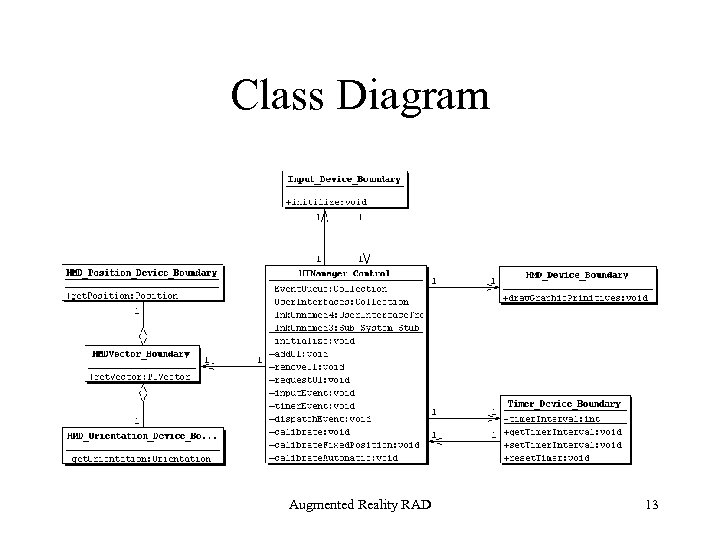 Class Diagram Augmented Reality RAD 13
Class Diagram Augmented Reality RAD 13