Lecture 6 (Reprogramming).ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Reprogramming • WSNs usually are unattended for a long period of time. • However, programs on the nodes may need to be changed. – Changing parameters – Changing functions – Fixing bugs – Over-the-air reprogramming needed due to accessibility, network size etc.
Reprogramming • WSNs usually are unattended for a long period of time. • However, programs on the nodes may need to be changed. – Changing parameters – Changing functions – Fixing bugs – Over-the-air reprogramming needed due to accessibility, network size etc.
 Reprogramming protocols • There have been developed several protocols thus far – XNP, MOAP, MNP, Deluge, etc. • The protocols can be classified according to their encoding and code dissemination techniques
Reprogramming protocols • There have been developed several protocols thus far – XNP, MOAP, MNP, Deluge, etc. • The protocols can be classified according to their encoding and code dissemination techniques
 Encoding techniques • Instead of sending the entire code, it could be possible to send only the difference – Energy efficient – Faster
Encoding techniques • Instead of sending the entire code, it could be possible to send only the difference – Energy efficient – Faster
 XNP (Crossbow In-Network Programming) • Designed for complete networks, i. e. , nodes that are in the communication range of a sink – The sink broadcasts the new code – Nodes copies the code capsules in external memory – Then the sink broadcasts query if there are nodes who have not received the entire code. – If necessary, nodes can request unreceived capsules
XNP (Crossbow In-Network Programming) • Designed for complete networks, i. e. , nodes that are in the communication range of a sink – The sink broadcasts the new code – Nodes copies the code capsules in external memory – Then the sink broadcasts query if there are nodes who have not received the entire code. – If necessary, nodes can request unreceived capsules
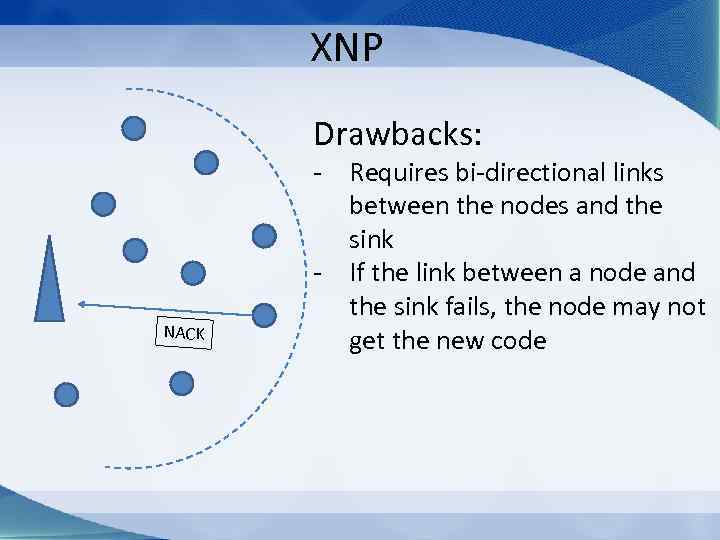 XNP Drawbacks: NACK - Requires bi-directional links between the nodes and the sink - If the link between a node and the sink fails, the node may not get the new code
XNP Drawbacks: NACK - Requires bi-directional links between the nodes and the sink - If the link between a node and the sink fails, the node may not get the new code
 Multihop Over-the-Air Programming (MOAP) • Addresses the drawbacks of XNP • Updates codes of nodes in a multihop fashion • Whenever a node gets a new code, it forwards the code • NACK is used to request missing packets
Multihop Over-the-Air Programming (MOAP) • Addresses the drawbacks of XNP • Updates codes of nodes in a multihop fashion • Whenever a node gets a new code, it forwards the code • NACK is used to request missing packets
 Deluge • Like MOAP it is multihop based • Uses NACK • Unlike MOAP, it divides the code into fixedsize pages, each page is divided into packets • Pages are delivered in a sequential order • Uses pipelining technique – Whenever a node gets a page, it can start to forward it
Deluge • Like MOAP it is multihop based • Uses NACK • Unlike MOAP, it divides the code into fixedsize pages, each page is divided into packets • Pages are delivered in a sequential order • Uses pipelining technique – Whenever a node gets a page, it can start to forward it
 Multihop Network Programming (MNP) • Like Deluge, divides the code into segments • Uses pipelining technique • Unlike Deluge, it selects one forwarded at a time in a given neighborhood
Multihop Network Programming (MNP) • Like Deluge, divides the code into segments • Uses pipelining technique • Unlike Deluge, it selects one forwarded at a time in a given neighborhood
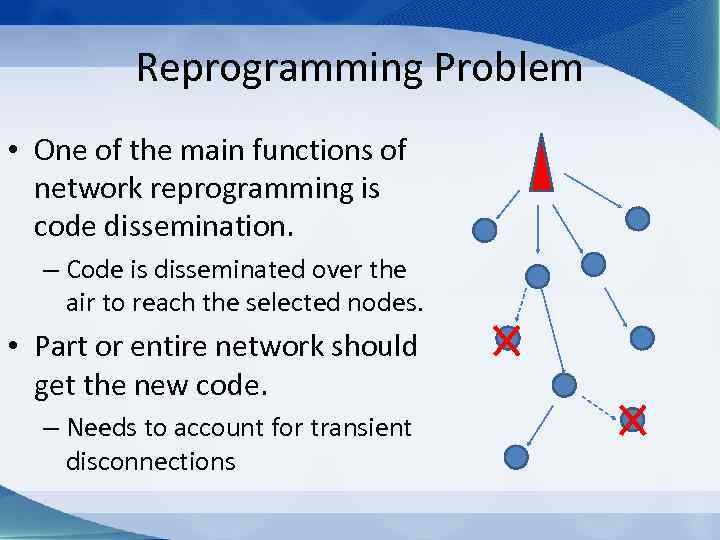 Reprogramming Problem • One of the main functions of network reprogramming is code dissemination. – Code is disseminated over the air to reach the selected nodes. • Part or entire network should get the new code. – Needs to account for transient disconnections
Reprogramming Problem • One of the main functions of network reprogramming is code dissemination. – Code is disseminated over the air to reach the selected nodes. • Part or entire network should get the new code. – Needs to account for transient disconnections
 Reprogramming Problem • Solution could be code advertisement. – Advertise metadata (version number) • Idea: we continuously broadcast the metadata. • Too expensive – In general, message transmission is the main energy consumption function. – Moreover sending metadata may cause unnecessary collisions.
Reprogramming Problem • Solution could be code advertisement. – Advertise metadata (version number) • Idea: we continuously broadcast the metadata. • Too expensive – In general, message transmission is the main energy consumption function. – Moreover sending metadata may cause unnecessary collisions.
 Trickle • Uses suppression mechanism. • A node periodically sends metadata message at time t selected randomly between [t/2, t], where tl t th – – – If a node hears the same metadata, increment counter. If the counter is less than K at t time, it broadcasts its metadata. Else if t expires, it doubles the value of t. If a node hears new metadata/code, it sets t to tl. If a node hears older metadata, send updates. counter < K 0 tl t/2 t t th time
Trickle • Uses suppression mechanism. • A node periodically sends metadata message at time t selected randomly between [t/2, t], where tl t th – – – If a node hears the same metadata, increment counter. If the counter is less than K at t time, it broadcasts its metadata. Else if t expires, it doubles the value of t. If a node hears new metadata/code, it sets t to tl. If a node hears older metadata, send updates. counter < K 0 tl t/2 t t th time
 Trickle • When there is no new code in the network, Trickle continuous sending metadata at [th/2, th] • Therefore, it consumes linear energy as a function of time.
Trickle • When there is no new code in the network, Trickle continuous sending metadata at [th/2, th] • Therefore, it consumes linear energy as a function of time.
 Varuna • Main idea: send metadata only when necessary. – Tries to improve on Trickle that requires periodic advertisement. – May lead to energy reduction. • Uses a table to store consistent nodes. – If updated node receives data from outdated node, then send metadata, send update, store ID of the node in the table.
Varuna • Main idea: send metadata only when necessary. – Tries to improve on Trickle that requires periodic advertisement. – May lead to energy reduction. • Uses a table to store consistent nodes. – If updated node receives data from outdated node, then send metadata, send update, store ID of the node in the table.
 Varuna • In Trickle, inconsistency is detected either by an updated node or by an outdated node. • In Varuna, inconsistency is detected by an updated node. • Varuna has been shown to have almost constant energy usage.
Varuna • In Trickle, inconsistency is detected either by an updated node or by an outdated node. • In Varuna, inconsistency is detected by an updated node. • Varuna has been shown to have almost constant energy usage.
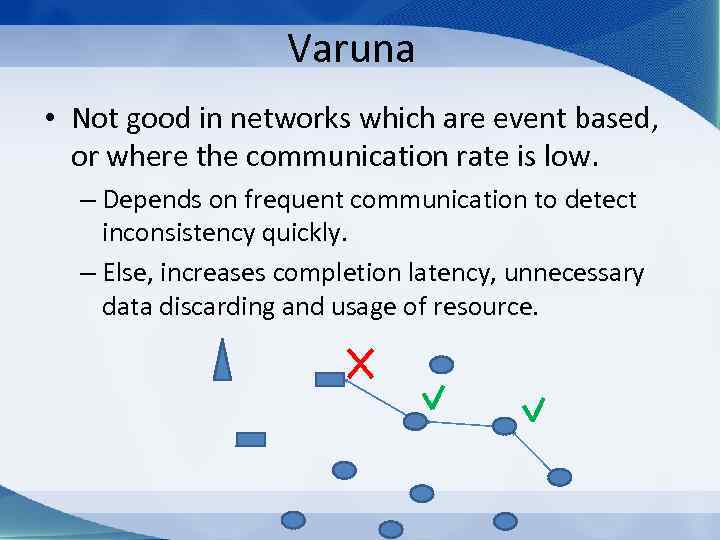 Varuna • Not good in networks which are event based, or where the communication rate is low. – Depends on frequent communication to detect inconsistency quickly. – Else, increases completion latency, unnecessary data discarding and usage of resource.
Varuna • Not good in networks which are event based, or where the communication rate is low. – Depends on frequent communication to detect inconsistency quickly. – Else, increases completion latency, unnecessary data discarding and usage of resource.


