5ccc672fb8128fd17a3eb0edd715edd1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10
 Reported Speech I. Introduction 1. 1. Direct Speech vs Reported Speech. 1. 2. Structure. II. General Changes 2. 1. Tenses backshift. 2. 2. Pronouns (subject/object/possessive) 2. 3. Adverbs (time/place) III. Reported Statements IV. Reported Questions V. Reported Commands and requests VI. Reporting Verbs
Reported Speech I. Introduction 1. 1. Direct Speech vs Reported Speech. 1. 2. Structure. II. General Changes 2. 1. Tenses backshift. 2. 2. Pronouns (subject/object/possessive) 2. 3. Adverbs (time/place) III. Reported Statements IV. Reported Questions V. Reported Commands and requests VI. Reporting Verbs
 I. INTRODUCTION 1. 1. DIRECT SPEECH versus REPORTED SPEECH • Whenever we want to repeat other people’s words we have two options: a. Repeating exactly word by word (Direct speech) b. Reporting approximately their speech (Reported speech) Example: a. Joy said: ‘She made me laugh yesterday’ • b. Joy said that she had made him laugh the day before. No matter which option we choose, but we have to use the correct pattern: a. DIRECT SPEECH: Reporting clause : ‘quote’. b. REPORTED SPEECH: Reporting clause (LINK) reported quote. • Moreover, we have to keep the differences between oral language and written language : a. DIRECT SPEECH: punctuation marks ( , . ‘’, ! ? ) contractions (can’t, I’m, he’s, …), interjections (listen!, look!, Great!, I see, …). • b. REPORTED SPEECH: NO punctuation marks, NO contractions, NO oral interjections.
I. INTRODUCTION 1. 1. DIRECT SPEECH versus REPORTED SPEECH • Whenever we want to repeat other people’s words we have two options: a. Repeating exactly word by word (Direct speech) b. Reporting approximately their speech (Reported speech) Example: a. Joy said: ‘She made me laugh yesterday’ • b. Joy said that she had made him laugh the day before. No matter which option we choose, but we have to use the correct pattern: a. DIRECT SPEECH: Reporting clause : ‘quote’. b. REPORTED SPEECH: Reporting clause (LINK) reported quote. • Moreover, we have to keep the differences between oral language and written language : a. DIRECT SPEECH: punctuation marks ( , . ‘’, ! ? ) contractions (can’t, I’m, he’s, …), interjections (listen!, look!, Great!, I see, …). • b. REPORTED SPEECH: NO punctuation marks, NO contractions, NO oral interjections.
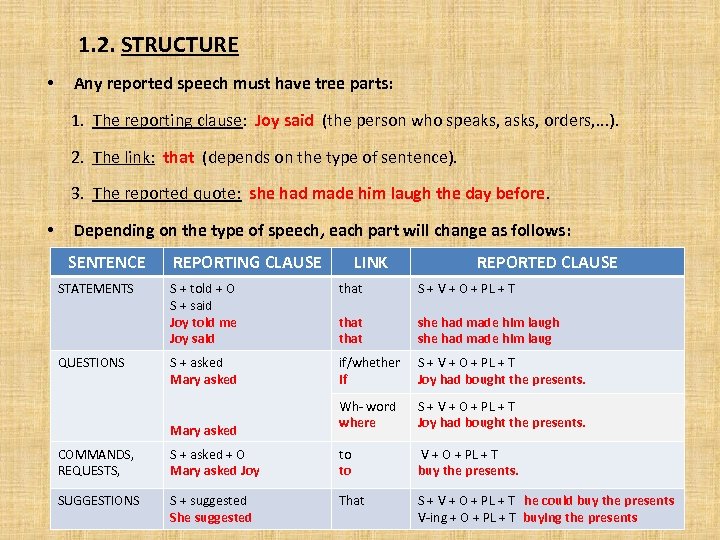 1. 2. STRUCTURE • Any reported speech must have tree parts: 1. The reporting clause: Joy said (the person who speaks, asks, orders, . . . ). 2. The link: that (depends on the type of sentence). 3. The reported quote: she had made him laugh the day before. • Depending on the type of speech, each part will change as follows: SENTENCE STATEMENTS QUESTIONS REPORTING CLAUSE LINK REPORTED CLAUSE S + told + O S + said Joy told me Joy said that S + V + O + PL + T that she had made him laugh she had made him laug S + asked Mary asked if/whether if S + V + O + PL + T Joy had bought the presents. Wh- word where S + V + O + PL + T Joy had bought the presents. Mary asked COMMANDS, REQUESTS, S + asked + O Mary asked Joy to to V + O + PL + T buy the presents. SUGGESTIONS S + suggested She suggested That S + V + O + PL + T he could buy the presents V-ing + O + PL + T buying the presents
1. 2. STRUCTURE • Any reported speech must have tree parts: 1. The reporting clause: Joy said (the person who speaks, asks, orders, . . . ). 2. The link: that (depends on the type of sentence). 3. The reported quote: she had made him laugh the day before. • Depending on the type of speech, each part will change as follows: SENTENCE STATEMENTS QUESTIONS REPORTING CLAUSE LINK REPORTED CLAUSE S + told + O S + said Joy told me Joy said that S + V + O + PL + T that she had made him laugh she had made him laug S + asked Mary asked if/whether if S + V + O + PL + T Joy had bought the presents. Wh- word where S + V + O + PL + T Joy had bought the presents. Mary asked COMMANDS, REQUESTS, S + asked + O Mary asked Joy to to V + O + PL + T buy the presents. SUGGESTIONS S + suggested She suggested That S + V + O + PL + T he could buy the presents V-ing + O + PL + T buying the presents
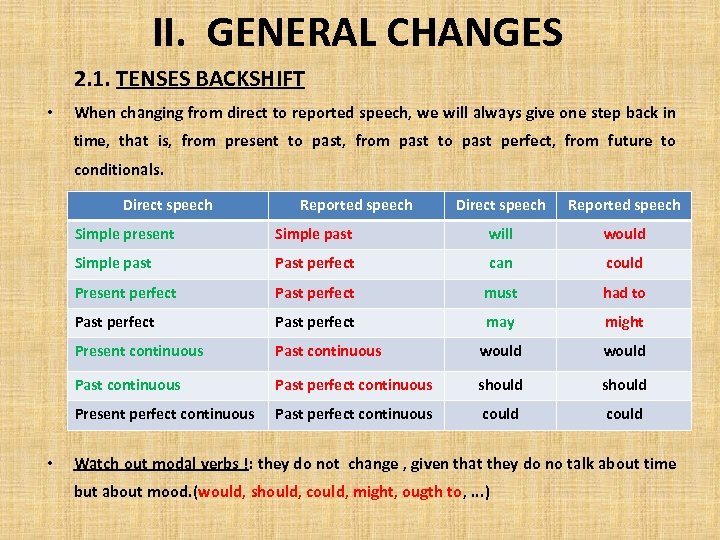 II. GENERAL CHANGES 2. 1. TENSES BACKSHIFT • When changing from direct to reported speech, we will always give one step back in time, that is, from present to past, from past to past perfect, from future to conditionals. Direct speech Reported speech Simple present will would Simple past Past perfect can could Present perfect Past perfect must had to Past perfect may might Present continuous Past continuous would Past continuous Past perfect continuous should Present perfect continuous • Simple past Past perfect continuous could Watch out modal verbs !: they do not change , given that they do no talk about time but about mood. (would, should, could, might, ougth to, . . . )
II. GENERAL CHANGES 2. 1. TENSES BACKSHIFT • When changing from direct to reported speech, we will always give one step back in time, that is, from present to past, from past to past perfect, from future to conditionals. Direct speech Reported speech Simple present will would Simple past Past perfect can could Present perfect Past perfect must had to Past perfect may might Present continuous Past continuous would Past continuous Past perfect continuous should Present perfect continuous • Simple past Past perfect continuous could Watch out modal verbs !: they do not change , given that they do no talk about time but about mood. (would, should, could, might, ougth to, . . . )
 2. 2. PRONOUNS • Furthermore, it is necessary to make changes in personal references –that is, pronouns. There is not a fixed rule, but we can do the following: a. If there is any reference in the reporting clause, we will do the changes according to it. Example: Mary told John: ´I don’t know your sister’ Mary told John that she did not know his sister b. If there is not any reference, we can follow these changes: I/ we you me/ us you my/our your You I/ we you me, /us your my our He, she, it, they him, her, it, them his, her, its, their Example: ´I don’t know your sister` She said that the she did not know my sister
2. 2. PRONOUNS • Furthermore, it is necessary to make changes in personal references –that is, pronouns. There is not a fixed rule, but we can do the following: a. If there is any reference in the reporting clause, we will do the changes according to it. Example: Mary told John: ´I don’t know your sister’ Mary told John that she did not know his sister b. If there is not any reference, we can follow these changes: I/ we you me/ us you my/our your You I/ we you me, /us your my our He, she, it, they him, her, it, them his, her, its, their Example: ´I don’t know your sister` She said that the she did not know my sister
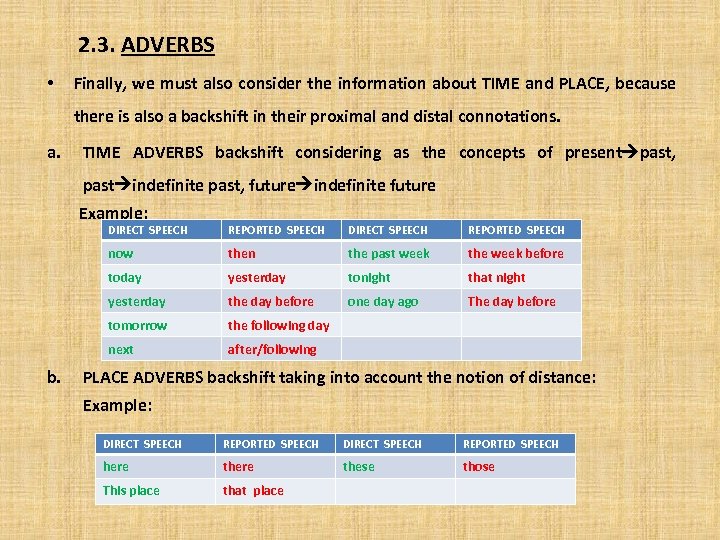 2. 3. ADVERBS • Finally, we must also consider the information about TIME and PLACE, because there is also a backshift in their proximal and distal connotations. a. TIME ADVERBS backshift considering as the concepts of present past, past indefinite past, future indefinite future Example: DIRECT SPEECH REPORTED SPEECH now then the past week the week before today yesterday tonight that night yesterday the day before one day ago The day before tomorrow the following day next b. REPORTED SPEECH after/following PLACE ADVERBS backshift taking into account the notion of distance: Example: DIRECT SPEECH REPORTED SPEECH here these those This place that place
2. 3. ADVERBS • Finally, we must also consider the information about TIME and PLACE, because there is also a backshift in their proximal and distal connotations. a. TIME ADVERBS backshift considering as the concepts of present past, past indefinite past, future indefinite future Example: DIRECT SPEECH REPORTED SPEECH now then the past week the week before today yesterday tonight that night yesterday the day before one day ago The day before tomorrow the following day next b. REPORTED SPEECH after/following PLACE ADVERBS backshift taking into account the notion of distance: Example: DIRECT SPEECH REPORTED SPEECH here these those This place that place
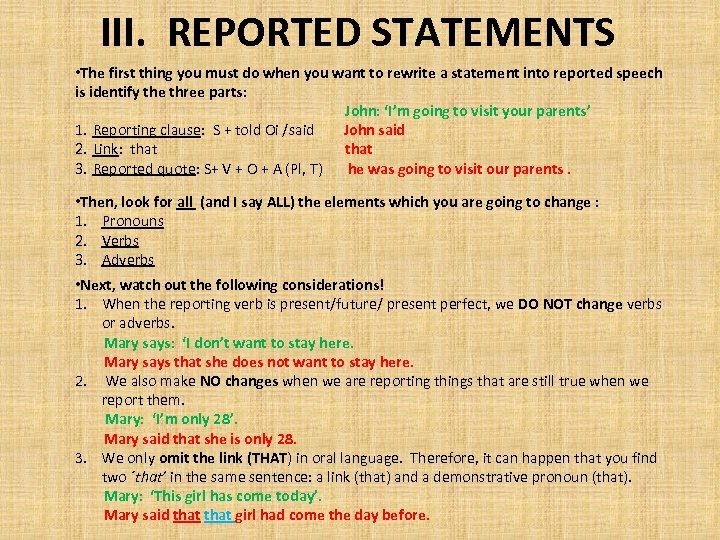 III. REPORTED STATEMENTS • The first thing you must do when you want to rewrite a statement into reported speech is identify the three parts: John: ‘I’m going to visit your parents’ 1. Reporting clause: S + told Oi /said John said 2. Link: that 3. Reported quote: S+ V + O + A (Pl, T) he was going to visit our parents. • Then, look for all (and I say ALL) the elements which you are going to change : 1. Pronouns 2. Verbs 3. Adverbs • Next, watch out the following considerations! 1. When the reporting verb is present/future/ present perfect, we DO NOT change verbs or adverbs. Mary says: ‘I don’t want to stay here. Mary says that she does not want to stay here. 2. We also make NO changes when we are reporting things that are still true when we report them. Mary: ‘I’m only 28’. Mary said that she is only 28. 3. We only omit the link (THAT) in oral language. Therefore, it can happen that you find two ´that’ in the same sentence: a link (that) and a demonstrative pronoun (that). Mary: ‘This girl has come today’. Mary said that girl had come the day before.
III. REPORTED STATEMENTS • The first thing you must do when you want to rewrite a statement into reported speech is identify the three parts: John: ‘I’m going to visit your parents’ 1. Reporting clause: S + told Oi /said John said 2. Link: that 3. Reported quote: S+ V + O + A (Pl, T) he was going to visit our parents. • Then, look for all (and I say ALL) the elements which you are going to change : 1. Pronouns 2. Verbs 3. Adverbs • Next, watch out the following considerations! 1. When the reporting verb is present/future/ present perfect, we DO NOT change verbs or adverbs. Mary says: ‘I don’t want to stay here. Mary says that she does not want to stay here. 2. We also make NO changes when we are reporting things that are still true when we report them. Mary: ‘I’m only 28’. Mary said that she is only 28. 3. We only omit the link (THAT) in oral language. Therefore, it can happen that you find two ´that’ in the same sentence: a link (that) and a demonstrative pronoun (that). Mary: ‘This girl has come today’. Mary said that girl had come the day before.
 IV. REPORTED QUESTIONS • Again, the first thing you must do when you want to rewrite a question into reported speech is identify the three parts: John: ‘Have you seen Mary lately? ’ 1. Reporting clause: S + asked John asked 2. Link: if/ wh-word if 3. Reported quote: S+ V + O + A (Pl, T) I had seen Mary recently. • Then, look for all (and I say ALL) the elements which you are going to change : 1. Pronouns 2. Verbs 3. Adverbs • Next, watch out the following considerations. 1. If we have to report a closed question (aux + S + V + O + C ? ), the link will be IF or WHETHER (when there is a choice between two or more things). Mary asked: ‘Are you happy now? ” Mary asked if I was happy then. 2. Mary asked: ‘Are you happy now or are you not? Mary asked whether I was happy or not. If we have to report an open question (wh-word + aux + S + V + O + C? ), the link will be the WH-word. Mary: ‘Where are you going next weekend? Mary asked where I was going the weekend after. 3. Be careful with WHICH + Noun phrase because the link includes the noun phrase. Mary: ‘Which coulour do you prefer? Mary asked which coulour I preferred.
IV. REPORTED QUESTIONS • Again, the first thing you must do when you want to rewrite a question into reported speech is identify the three parts: John: ‘Have you seen Mary lately? ’ 1. Reporting clause: S + asked John asked 2. Link: if/ wh-word if 3. Reported quote: S+ V + O + A (Pl, T) I had seen Mary recently. • Then, look for all (and I say ALL) the elements which you are going to change : 1. Pronouns 2. Verbs 3. Adverbs • Next, watch out the following considerations. 1. If we have to report a closed question (aux + S + V + O + C ? ), the link will be IF or WHETHER (when there is a choice between two or more things). Mary asked: ‘Are you happy now? ” Mary asked if I was happy then. 2. Mary asked: ‘Are you happy now or are you not? Mary asked whether I was happy or not. If we have to report an open question (wh-word + aux + S + V + O + C? ), the link will be the WH-word. Mary: ‘Where are you going next weekend? Mary asked where I was going the weekend after. 3. Be careful with WHICH + Noun phrase because the link includes the noun phrase. Mary: ‘Which coulour do you prefer? Mary asked which coulour I preferred.
 V. REPORTED COMMANDS AND REQUESTS • Remember that , in English, imperatives are done by dropping the subject: 1. Affirmative imperative: ‘Wait a minute!’, ‘Be honest!’, ‘Come here!’ 2. Negative imperative: ‘Don’t wait for me!’, ‘Don’t be rude!’, ‘Don’t go alone!’ • Whenever we want to report any kind of imperative (orders, commands, requests), we must also identify the three parts: Mary told me: ‘ close your mouth right now’ 1. Reporting clause: S + told Oi /said to Oi Mary told me 2. Link: to / not to to 3. Reported quote: V + O + A (Pl, T) close my mouth at that very moment. • Then, look for all (and I say ALL) the elements which you are going to change : 1. Pronouns All tenses are replaced by the infinitive with to 2. Adverbs • Next, watch out the following considerations! 1. The negative imperative is reported by adding NOT before TO Mary said to John: ‘Don’t wait for me!’ Mary said to John not to wait for her. 2. Suggestions are reported in two ways: a. If the subject of the reporting subject is included in the reported quote, the link is -ING Mary said: ‘Let’s cook dinner ‘ Mary suggested cooking dinner. b. If there are two different subjects the link is THAT + S + V(infinitive) + O + C Mary said: ‘Why don’t you cook dinner? ’ Mary suggested that I cook dinner. 3. SHALL can be reported in two ways: a. Would for information questions: ‘Shall I see you again? ’ She asked if she would see me again b. Should for offers and requests: ‘Shall I carry your bag? ’ She asked if she should carry my bag.
V. REPORTED COMMANDS AND REQUESTS • Remember that , in English, imperatives are done by dropping the subject: 1. Affirmative imperative: ‘Wait a minute!’, ‘Be honest!’, ‘Come here!’ 2. Negative imperative: ‘Don’t wait for me!’, ‘Don’t be rude!’, ‘Don’t go alone!’ • Whenever we want to report any kind of imperative (orders, commands, requests), we must also identify the three parts: Mary told me: ‘ close your mouth right now’ 1. Reporting clause: S + told Oi /said to Oi Mary told me 2. Link: to / not to to 3. Reported quote: V + O + A (Pl, T) close my mouth at that very moment. • Then, look for all (and I say ALL) the elements which you are going to change : 1. Pronouns All tenses are replaced by the infinitive with to 2. Adverbs • Next, watch out the following considerations! 1. The negative imperative is reported by adding NOT before TO Mary said to John: ‘Don’t wait for me!’ Mary said to John not to wait for her. 2. Suggestions are reported in two ways: a. If the subject of the reporting subject is included in the reported quote, the link is -ING Mary said: ‘Let’s cook dinner ‘ Mary suggested cooking dinner. b. If there are two different subjects the link is THAT + S + V(infinitive) + O + C Mary said: ‘Why don’t you cook dinner? ’ Mary suggested that I cook dinner. 3. SHALL can be reported in two ways: a. Would for information questions: ‘Shall I see you again? ’ She asked if she would see me again b. Should for offers and requests: ‘Shall I carry your bag? ’ She asked if she should carry my bag.
 VI. REPORTING VERBS • Finally, just to clear up some tips about the reporting verbs (that is, the verbs which introduce the reported speech). The general rule is that reported quotes are introduced by: 1. told+Oi/said (statements) He told me that it was too late to change. 2. asked (questions) She asked if he had changed his mind. 3. said to+Oi/told+Oi/asked to+Oi (imperatives) He asked to me not to be late. • However, there are other reporting verbs which transmit the speaker’s intention o mood 1. Statements: agree, answer, apologize complain, deny, explain, inform, insist, mention, … He complained that he had been in troubles with a flatmate. 2. Questions: enquire, request, want to know, wonder She wondered if he would come to the party that night. 3. Imperatives: advise, invite, suggest, recommend, beb, demand, order, shout, warn He advised me not to cross the road alone. • Watch out the following reporting verbs as they must be followed by TO or ING a. He advised her to go back to dance school. a. He offered to see her again in six months a. The boys agreed to take the money b. He suggested finding an agent. b. He thanked her for coming to the audition. b. We apologized for not being able to publish her book. c. He insisted that they did not have a role for her in the show. c. They explained that we were unfashionable.
VI. REPORTING VERBS • Finally, just to clear up some tips about the reporting verbs (that is, the verbs which introduce the reported speech). The general rule is that reported quotes are introduced by: 1. told+Oi/said (statements) He told me that it was too late to change. 2. asked (questions) She asked if he had changed his mind. 3. said to+Oi/told+Oi/asked to+Oi (imperatives) He asked to me not to be late. • However, there are other reporting verbs which transmit the speaker’s intention o mood 1. Statements: agree, answer, apologize complain, deny, explain, inform, insist, mention, … He complained that he had been in troubles with a flatmate. 2. Questions: enquire, request, want to know, wonder She wondered if he would come to the party that night. 3. Imperatives: advise, invite, suggest, recommend, beb, demand, order, shout, warn He advised me not to cross the road alone. • Watch out the following reporting verbs as they must be followed by TO or ING a. He advised her to go back to dance school. a. He offered to see her again in six months a. The boys agreed to take the money b. He suggested finding an agent. b. He thanked her for coming to the audition. b. We apologized for not being able to publish her book. c. He insisted that they did not have a role for her in the show. c. They explained that we were unfashionable.


