1387da587bcad27fd6f9d955064695e2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Report On The Ten Years’ EIM Meeting Munich, 11 th September 2010 Jacques de Mouzon, EIM chairman
Report On The Ten Years’ EIM Meeting Munich, 11 th September 2010 Jacques de Mouzon, EIM chairman
 EIM – The beginning • First discussion in Goteborg in 1998 by Karl Nygren Luca Gianaroli and Bruno Van Den Eede • First meeting: Tours June 1999, 19 European countries, • At first data collection on paper. Now by a software. • First results presented at the 16 th Annual Meeting (Bologna), June 2000. • 10 reports published so far, 11 presentations
EIM – The beginning • First discussion in Goteborg in 1998 by Karl Nygren Luca Gianaroli and Bruno Van Den Eede • First meeting: Tours June 1999, 19 European countries, • At first data collection on paper. Now by a software. • First results presented at the 16 th Annual Meeting (Bologna), June 2000. • 10 reports published so far, 11 presentations
 EIM – Present Steering Committee (2009 – 2011) Chairman J. de Mouzon, France Past Chairman A. N. Andersen, Denmark Chairman-elect A. P. Ferraretti, Italy Coordinator data collection V. Goosens, Belgium Members K. Nygren, Sweden (advisor) S. Bhattacharya, UK M. S. Kupka, Germany J. A. Castilla Alcala, Spain V. Korsak, Russia
EIM – Present Steering Committee (2009 – 2011) Chairman J. de Mouzon, France Past Chairman A. N. Andersen, Denmark Chairman-elect A. P. Ferraretti, Italy Coordinator data collection V. Goosens, Belgium Members K. Nygren, Sweden (advisor) S. Bhattacharya, UK M. S. Kupka, Germany J. A. Castilla Alcala, Spain V. Korsak, Russia
 Meeting objectives (1) To show the importance of building national and European registers in getting data on the practice and results in a major field for human being, reproduction and its treatments - (2) To detail the main aspects to consider when building a register on ART - (3) To progress in the EIM register functioning - (4) To celebrate a 10 years of experience and success at the level of Europe through ESHRE • - • • •
Meeting objectives (1) To show the importance of building national and European registers in getting data on the practice and results in a major field for human being, reproduction and its treatments - (2) To detail the main aspects to consider when building a register on ART - (3) To progress in the EIM register functioning - (4) To celebrate a 10 years of experience and success at the level of Europe through ESHRE • - • • •
 Course organization • 4 sessions • • Main achievements General aspects of national registers Registries experiences EIM register discussion • Course principles • To share experiences • To let as many countries as possible participating • To improve EIM functioning
Course organization • 4 sessions • • Main achievements General aspects of national registers Registries experiences EIM register discussion • Course principles • To share experiences • To let as many countries as possible participating • To improve EIM functioning
 Session 1. Main achievements 1. ART data in Europe. An overview. Anders Nyboe Andersen 2. Use of ART data from Europe and World – what have we learned? Karl G. Nygren
Session 1. Main achievements 1. ART data in Europe. An overview. Anders Nyboe Andersen 2. Use of ART data from Europe and World – what have we learned? Karl G. Nygren
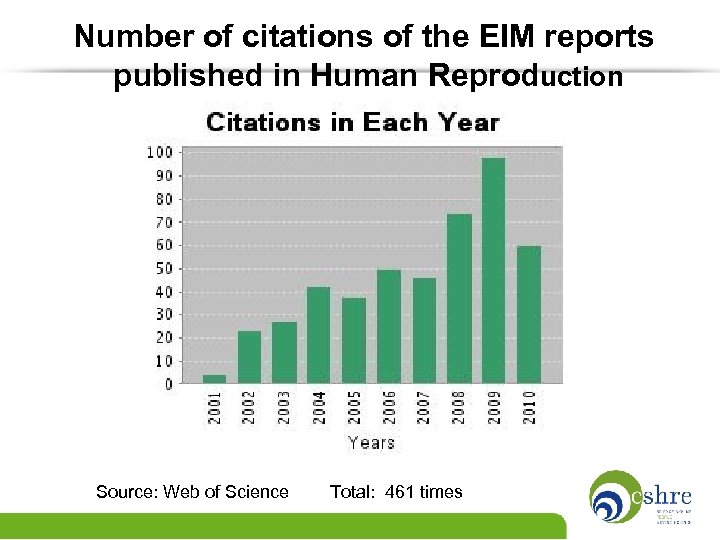 Number of citations of the EIM reports published in Human Reproduction Source: Web of Science Total: 461 times
Number of citations of the EIM reports published in Human Reproduction Source: Web of Science Total: 461 times
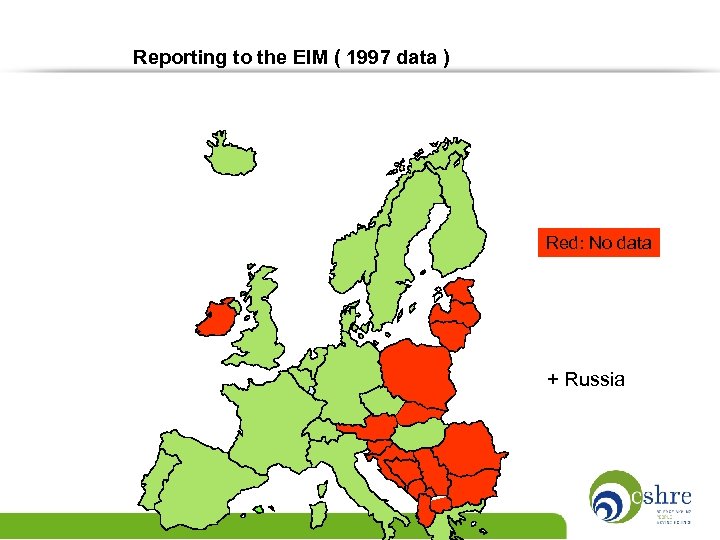 Reporting to the EIM ( 1997 data ) Red: No data + Russia
Reporting to the EIM ( 1997 data ) Red: No data + Russia
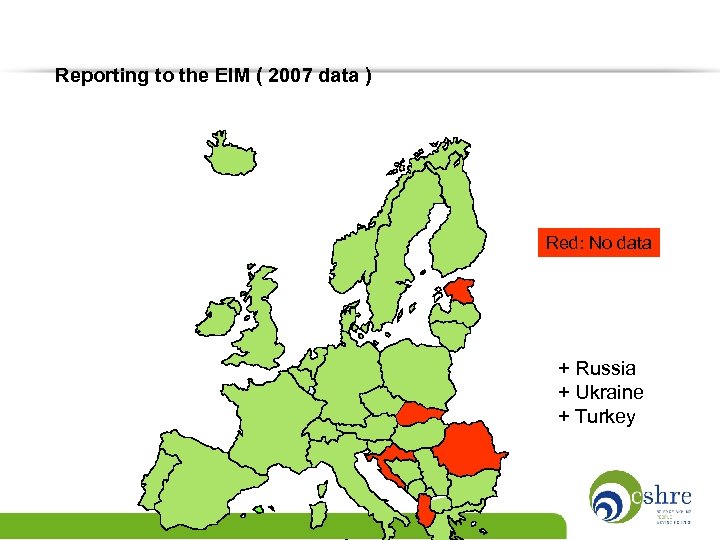 Reporting to the EIM ( 2007 data ) Red: No data + Russia + Ukraine + Turkey
Reporting to the EIM ( 2007 data ) Red: No data + Russia + Ukraine + Turkey
 Development in the EIM reporting system from 1997 – 2007. 1997 2007 Countries 18 32 Clinics reporting 482 1016 Proportion of clinics Unknown 88% Countries with 10 203 893 No 203 893 complete reporting ART cycles IUI reporting All cycles 19 479 288 168. 178 647 466
Development in the EIM reporting system from 1997 – 2007. 1997 2007 Countries 18 32 Clinics reporting 482 1016 Proportion of clinics Unknown 88% Countries with 10 203 893 No 203 893 complete reporting ART cycles IUI reporting All cycles 19 479 288 168. 178 647 466
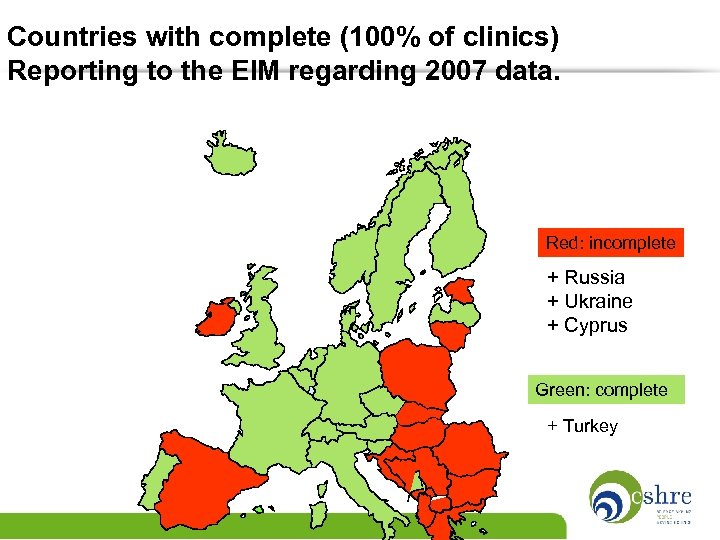 Countries with complete (100% of clinics) Reporting to the EIM regarding 2007 data. Red: incomplete + Russia + Ukraine + Cyprus Green: complete + Turkey
Countries with complete (100% of clinics) Reporting to the EIM regarding 2007 data. Red: incomplete + Russia + Ukraine + Cyprus Green: complete + Turkey
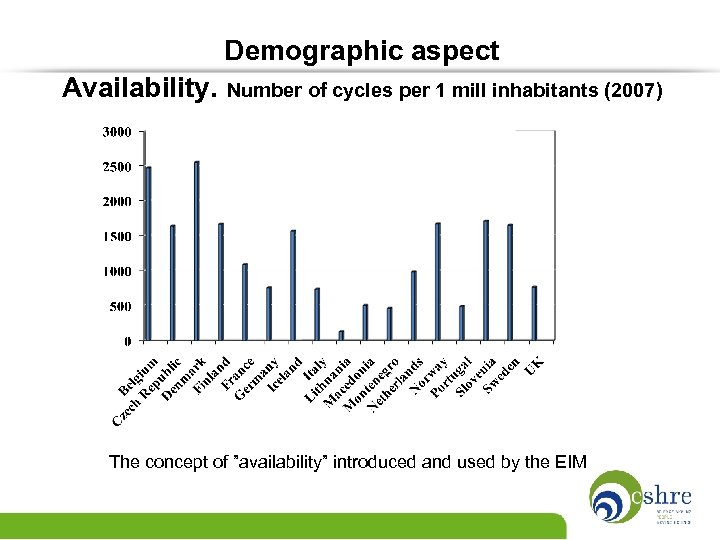 Demographic aspect Availability. Number of cycles per 1 mill inhabitants (2007) The concept of ”availability” introduced and used by the EIM
Demographic aspect Availability. Number of cycles per 1 mill inhabitants (2007) The concept of ”availability” introduced and used by the EIM
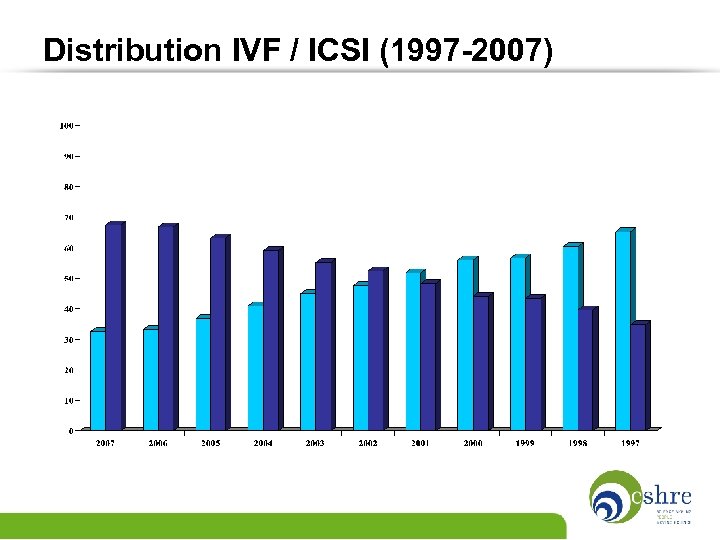 Distribution IVF / ICSI (1997 -2007)
Distribution IVF / ICSI (1997 -2007)
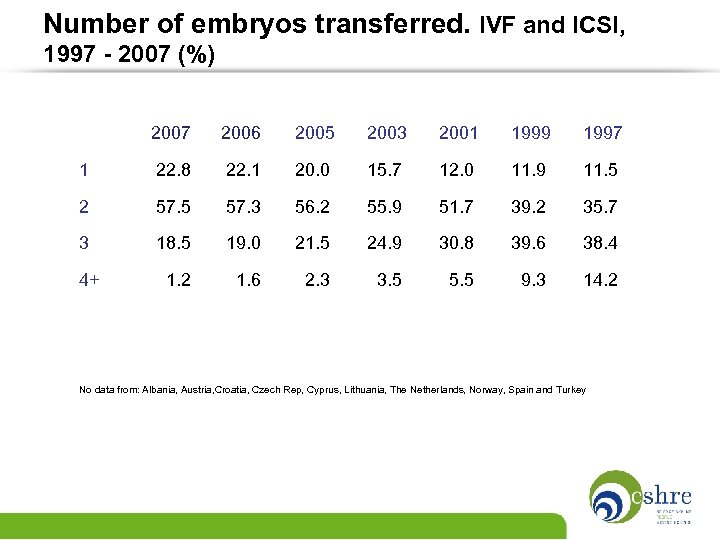 Number of embryos transferred. IVF and ICSI, 1997 - 2007 (%) 2007 2006 2005 2003 2001 1999 1997 1 22. 8 22. 1 20. 0 15. 7 12. 0 11. 9 11. 5 2 57. 5 57. 3 56. 2 55. 9 51. 7 39. 2 35. 7 3 18. 5 19. 0 21. 5 24. 9 30. 8 39. 6 38. 4 4+ 1. 2 1. 6 2. 3 3. 5 5. 5 9. 3 14. 2 No data from: Albania, Austria, Croatia, Czech Rep, Cyprus, Lithuania, The Netherlands, Norway, Spain and Turkey
Number of embryos transferred. IVF and ICSI, 1997 - 2007 (%) 2007 2006 2005 2003 2001 1999 1997 1 22. 8 22. 1 20. 0 15. 7 12. 0 11. 9 11. 5 2 57. 5 57. 3 56. 2 55. 9 51. 7 39. 2 35. 7 3 18. 5 19. 0 21. 5 24. 9 30. 8 39. 6 38. 4 4+ 1. 2 1. 6 2. 3 3. 5 5. 5 9. 3 14. 2 No data from: Albania, Austria, Croatia, Czech Rep, Cyprus, Lithuania, The Netherlands, Norway, Spain and Turkey
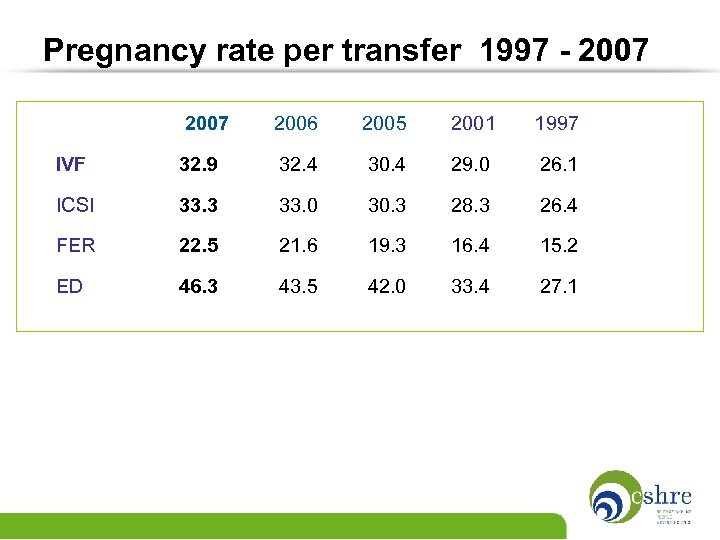 Pregnancy rate per transfer 1997 - 2007 2006 2005 2001 1997 IVF 32. 9 32. 4 30. 4 29. 0 26. 1 ICSI 33. 3 33. 0 30. 3 28. 3 26. 4 FER 22. 5 21. 6 19. 3 16. 4 15. 2 ED 46. 3 43. 5 42. 0 33. 4 27. 1
Pregnancy rate per transfer 1997 - 2007 2006 2005 2001 1997 IVF 32. 9 32. 4 30. 4 29. 0 26. 1 ICSI 33. 3 33. 0 30. 3 28. 3 26. 4 FER 22. 5 21. 6 19. 3 16. 4 15. 2 ED 46. 3 43. 5 42. 0 33. 4 27. 1
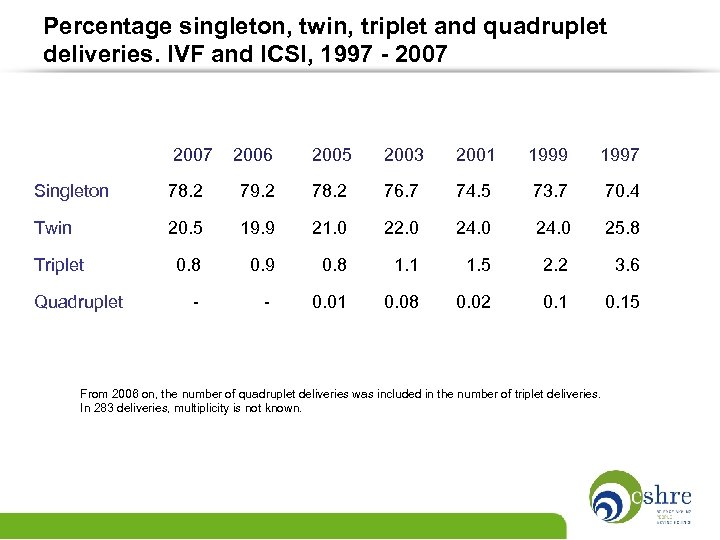 Percentage singleton, twin, triplet and quadruplet deliveries. IVF and ICSI, 1997 - 2007 2006 2005 2003 2001 1999 1997 73. 7 70. 4 Singleton 78. 2 79. 2 78. 2 76. 7 74. 5 Twin 20. 5 19. 9 21. 0 22. 0 24. 0 25. 8 Triplet 0. 8 0. 9 0. 8 1. 1 1. 5 2. 2 3. 6 Quadruplet - 0. 01 0. 08 0. 02 0. 15 From 2006 on, the number of quadruplet deliveries was included in the number of triplet deliveries. In 283 deliveries, multiplicity is not known.
Percentage singleton, twin, triplet and quadruplet deliveries. IVF and ICSI, 1997 - 2007 2006 2005 2003 2001 1999 1997 73. 7 70. 4 Singleton 78. 2 79. 2 78. 2 76. 7 74. 5 Twin 20. 5 19. 9 21. 0 22. 0 24. 0 25. 8 Triplet 0. 8 0. 9 0. 8 1. 1 1. 5 2. 2 3. 6 Quadruplet - 0. 01 0. 08 0. 02 0. 15 From 2006 on, the number of quadruplet deliveries was included in the number of triplet deliveries. In 283 deliveries, multiplicity is not known.
 Other achievements • Analysis of national differences: • transfer policies / multiple pregnancies, cumulative PR, Benchmarking • Transparency • Collaboration to World register (ICMART) • Trends, citations, promotion of ICMART glossary • Still to be improved • Consensus on minimal data set for ART • Explanation for large countries differences
Other achievements • Analysis of national differences: • transfer policies / multiple pregnancies, cumulative PR, Benchmarking • Transparency • Collaboration to World register (ICMART) • Trends, citations, promotion of ICMART glossary • Still to be improved • Consensus on minimal data set for ART • Explanation for large countries differences
 Session 2. General aspects of national registers
Session 2. General aspects of national registers
 Six main aspects of a national register • From a professional to a public health authorities register. French experience. T Shojaei • Prospective digital recording: the German organization. Marcus Kupka • Use of the Italian register data following the change of the Italian law on ART. Anna Pia Ferraretti and Giulia Scaravelli • The Nordic MART project. Possibilities and limitations with pooling of ART outcome data from different countries. AK Henningsen (Denmark) • Is a voluntary register valid for collect data of cross-border patients. Jose Antonio Castilla (Spain) • Pros and Cons of the UK data disclosure system. Siladitya Bhattachayra (United Kingdom)
Six main aspects of a national register • From a professional to a public health authorities register. French experience. T Shojaei • Prospective digital recording: the German organization. Marcus Kupka • Use of the Italian register data following the change of the Italian law on ART. Anna Pia Ferraretti and Giulia Scaravelli • The Nordic MART project. Possibilities and limitations with pooling of ART outcome data from different countries. AK Henningsen (Denmark) • Is a voluntary register valid for collect data of cross-border patients. Jose Antonio Castilla (Spain) • Pros and Cons of the UK data disclosure system. Siladitya Bhattachayra (United Kingdom)
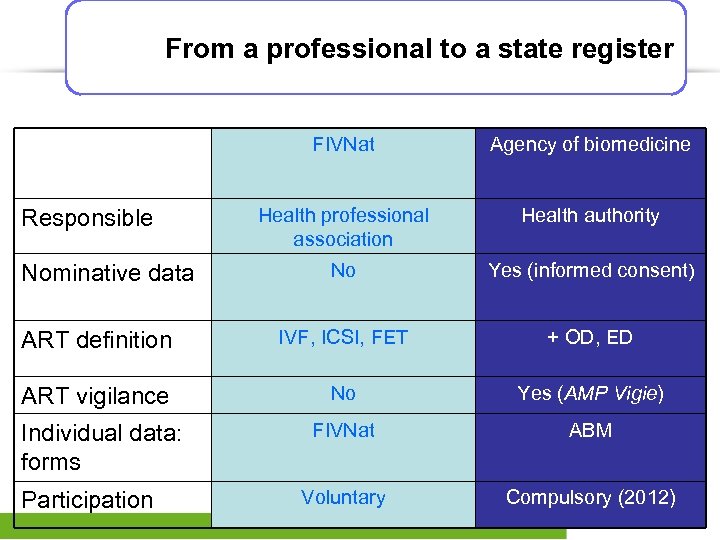 From a professional to a state register FIVNat Agency of biomedicine Health professional association Health authority No Yes (informed consent) ART definition IVF, ICSI, FET + OD, ED ART vigilance No Yes (AMP Vigie) FIVNat ABM Voluntary Compulsory (2012) Responsible Nominative data Individual data: forms Participation
From a professional to a state register FIVNat Agency of biomedicine Health professional association Health authority No Yes (informed consent) ART definition IVF, ICSI, FET + OD, ED ART vigilance No Yes (AMP Vigie) FIVNat ABM Voluntary Compulsory (2012) Responsible Nominative data Individual data: forms Participation
 From a professional to a state register • Improvement • • • Professional register Comprehensive aspects of register Data transmission from the centres through software Higher financial potential Nominative data Increase in transparency Risk • Professional less involved • Decrease in research
From a professional to a state register • Improvement • • • Professional register Comprehensive aspects of register Data transmission from the centres through software Higher financial potential Nominative data Increase in transparency Risk • Professional less involved • Decrease in research
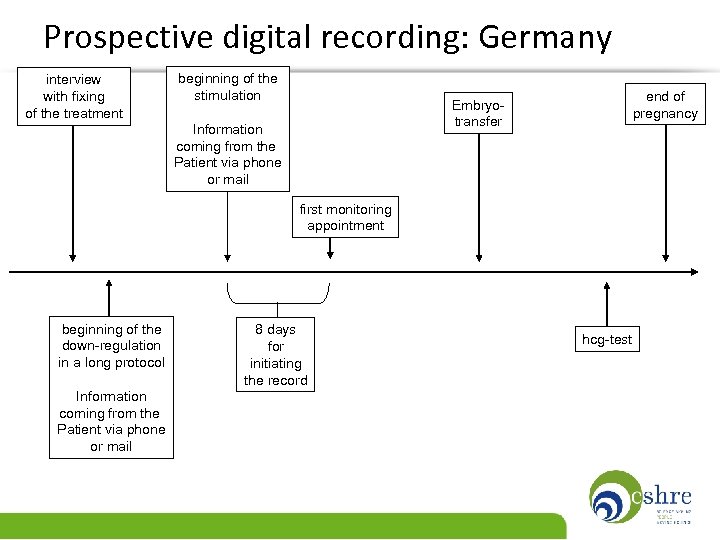 Prospective digital recording: Germany interview with fixing of the treatment beginning of the stimulation end of pregnancy Embryotransfer Information coming from the Patient via phone or mail first monitoring appointment beginning of the down-regulation in a long protocol Information coming from the Patient via phone or mail 8 days for initiating the record hcg-test
Prospective digital recording: Germany interview with fixing of the treatment beginning of the stimulation end of pregnancy Embryotransfer Information coming from the Patient via phone or mail first monitoring appointment beginning of the down-regulation in a long protocol Information coming from the Patient via phone or mail 8 days for initiating the record hcg-test
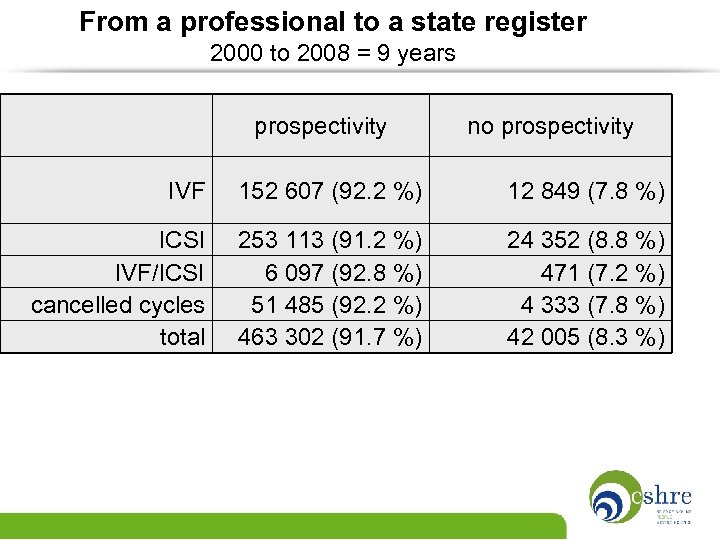 From a professional to a state register 2000 to 2008 = 9 years prospectivity no prospectivity IVF 152 607 (92. 2 %) 12 849 (7. 8 %) ICSI IVF/ICSI cancelled cycles total 253 113 (91. 2 %) 6 097 (92. 8 %) 51 485 (92. 2 %) 463 302 (91. 7 %) 24 352 (8. 8 %) 471 (7. 2 %) 4 333 (7. 8 %) 42 005 (8. 3 %)
From a professional to a state register 2000 to 2008 = 9 years prospectivity no prospectivity IVF 152 607 (92. 2 %) 12 849 (7. 8 %) ICSI IVF/ICSI cancelled cycles total 253 113 (91. 2 %) 6 097 (92. 8 %) 51 485 (92. 2 %) 463 302 (91. 7 %) 24 352 (8. 8 %) 471 (7. 2 %) 4 333 (7. 8 %) 42 005 (8. 3 %)
 Impact of law on ART: Italy • LAW 40/2004 • mandatory national data collection • accreditation and licensing • heterosexual infertility couples only • Gamete and embryo donation forbidden • No more than three embryos, cryopreservation forbidden • 2009, less restriction on freezing, embryo number, PGD
Impact of law on ART: Italy • LAW 40/2004 • mandatory national data collection • accreditation and licensing • heterosexual infertility couples only • Gamete and embryo donation forbidden • No more than three embryos, cryopreservation forbidden • 2009, less restriction on freezing, embryo number, PGD
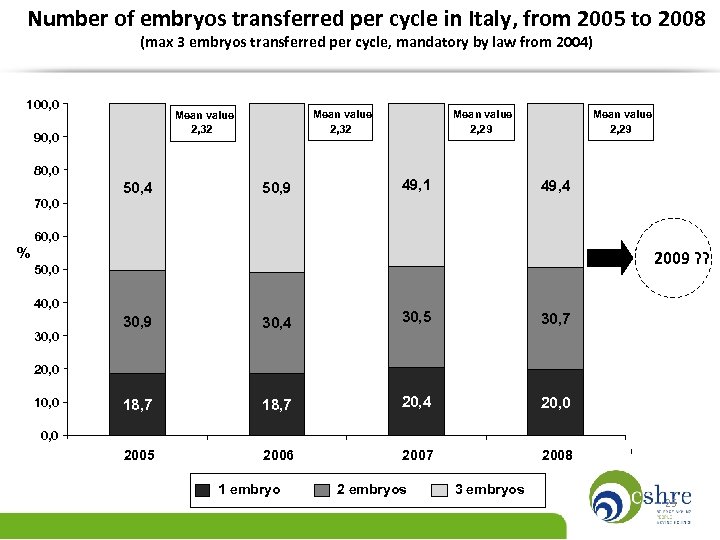 Number of embryos transferred per cycle in Italy, from 2005 to 2008 (max 3 embryos transferred per cycle, mandatory by law from 2004) 100, 0 Mean value 2, 32 90, 0 80, 0 50, 4 70, 0 50, 9 Mean value 2, 29 49, 1 Mean value 2, 29 49, 4 60, 0 % 2009 ? ? 50, 0 40, 0 30, 9 30, 4 30, 5 30, 7 18, 7 20, 4 20, 0 2005 2006 2007 2008 20, 0 10, 0 1 embryo 2 embryos 3 embryos 25
Number of embryos transferred per cycle in Italy, from 2005 to 2008 (max 3 embryos transferred per cycle, mandatory by law from 2004) 100, 0 Mean value 2, 32 90, 0 80, 0 50, 4 70, 0 50, 9 Mean value 2, 29 49, 1 Mean value 2, 29 49, 4 60, 0 % 2009 ? ? 50, 0 40, 0 30, 9 30, 4 30, 5 30, 7 18, 7 20, 4 20, 0 2005 2006 2007 2008 20, 0 10, 0 1 embryo 2 embryos 3 embryos 25
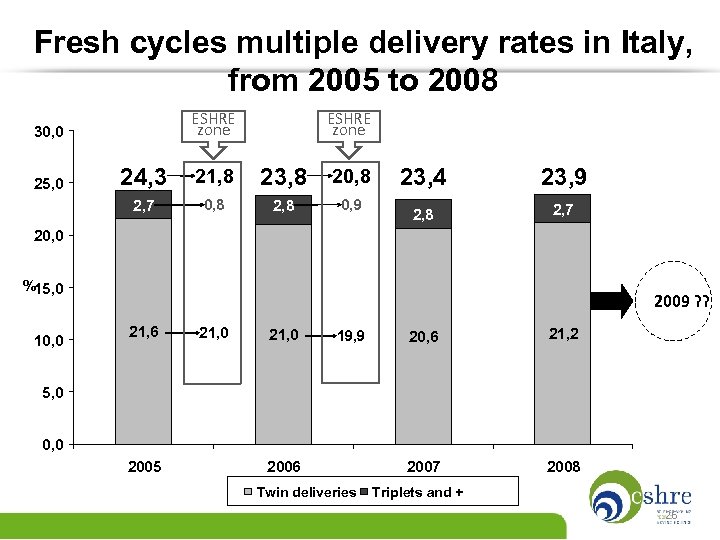 Fresh cycles multiple delivery rates in Italy, from 2005 to 2008 ESHRE zone 30, 0 ESHRE zone 24, 3 21, 8 23, 8 20, 8 2, 7 25, 0 0, 8 2, 8 0, 9 23, 4 23, 9 2, 8 2, 7 20, 0 %15, 0 10, 0 2009 ? ? 21, 6 21, 0 19, 9 20, 6 21, 2 2007 2008 5, 0 0, 0 2005 2006 Twin deliveries Triplets and + 26
Fresh cycles multiple delivery rates in Italy, from 2005 to 2008 ESHRE zone 30, 0 ESHRE zone 24, 3 21, 8 23, 8 20, 8 2, 7 25, 0 0, 8 2, 8 0, 9 23, 4 23, 9 2, 8 2, 7 20, 0 %15, 0 10, 0 2009 ? ? 21, 6 21, 0 19, 9 20, 6 21, 2 2007 2008 5, 0 0, 0 2005 2006 Twin deliveries Triplets and + 26
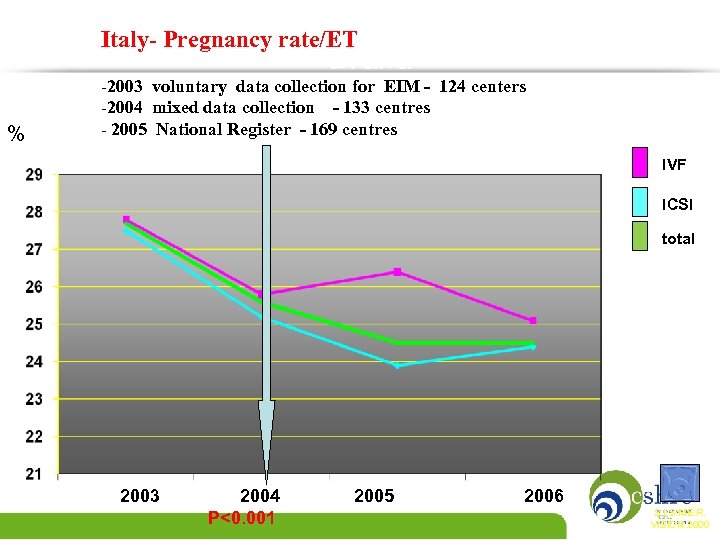 Italy- Pregnancy rate/ET Italia % -2003 voluntary data collection for EIM - 124 centers -2004 mixed data collection - 133 centres - 2005 National Register - 169 centres IVF ICSI total 2003 2004 P<0. 001 2005 2006 S. I. S. ME. R. VISION 2000
Italy- Pregnancy rate/ET Italia % -2003 voluntary data collection for EIM - 124 centers -2004 mixed data collection - 133 centres - 2005 National Register - 169 centres IVF ICSI total 2003 2004 P<0. 001 2005 2006 S. I. S. ME. R. VISION 2000
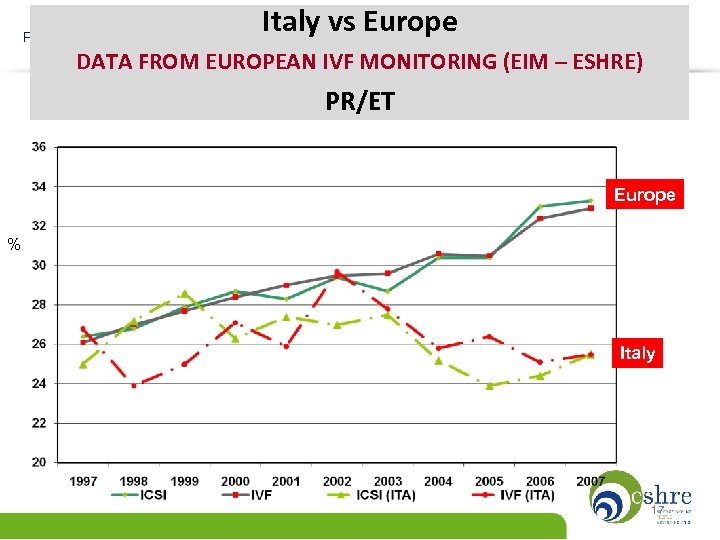 Italy vs Europe PREGNANCY RATE PER TRANSFER 1997 -2006 DATA FROM EUROPEAN IVF MONITORING (EIM – ESHRE) PR/ET Europe % Italy 17
Italy vs Europe PREGNANCY RATE PER TRANSFER 1997 -2006 DATA FROM EUROPEAN IVF MONITORING (EIM – ESHRE) PR/ET Europe % Italy 17
 Possibilities and limitations with pooling of data from different countries The Nordic MART project • Documentation of the safety of ART: children’s health/morbidity • Funding • ESHRE, University of Copenhagen • Danish Agency of Science, Technology and Innovation • National health registers in the Nordic countries • Unique personal identification numbers • Cross-linking of registers
Possibilities and limitations with pooling of data from different countries The Nordic MART project • Documentation of the safety of ART: children’s health/morbidity • Funding • ESHRE, University of Copenhagen • Danish Agency of Science, Technology and Innovation • National health registers in the Nordic countries • Unique personal identification numbers • Cross-linking of registers
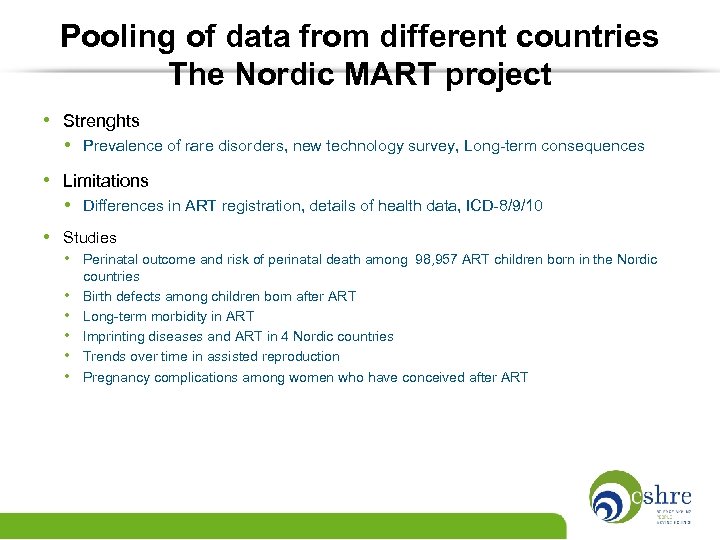 Pooling of data from different countries The Nordic MART project • Strenghts • Prevalence of rare disorders, new technology survey, Long-term consequences • Limitations • Differences in ART registration, details of health data, ICD-8/9/10 • Studies • Perinatal outcome and risk of perinatal death among 98, 957 ART children born in the Nordic • • • countries Birth defects among children born after ART Long-term morbidity in ART Imprinting diseases and ART in 4 Nordic countries Trends over time in assisted reproduction Pregnancy complications among women who have conceived after ART
Pooling of data from different countries The Nordic MART project • Strenghts • Prevalence of rare disorders, new technology survey, Long-term consequences • Limitations • Differences in ART registration, details of health data, ICD-8/9/10 • Studies • Perinatal outcome and risk of perinatal death among 98, 957 ART children born in the Nordic • • • countries Birth defects among children born after ART Long-term morbidity in ART Imprinting diseases and ART in 4 Nordic countries Trends over time in assisted reproduction Pregnancy complications among women who have conceived after ART
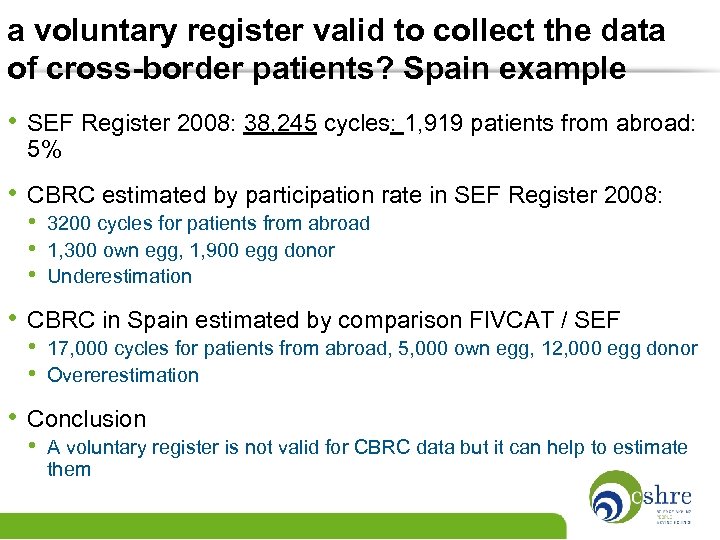 a voluntary register valid to collect the data of cross-border patients? Spain example • SEF Register 2008: 38, 245 cycles: 1, 919 patients from abroad: 5% • CBRC estimated by participation rate in SEF Register 2008: • 3200 cycles for patients from abroad • 1, 300 own egg, 1, 900 egg donor • Underestimation • CBRC in Spain estimated by comparison FIVCAT / SEF • 17, 000 cycles for patients from abroad, 5, 000 own egg, 12, 000 egg donor • Overerestimation • Conclusion • A voluntary register is not valid for CBRC data but it can help to estimate them
a voluntary register valid to collect the data of cross-border patients? Spain example • SEF Register 2008: 38, 245 cycles: 1, 919 patients from abroad: 5% • CBRC estimated by participation rate in SEF Register 2008: • 3200 cycles for patients from abroad • 1, 300 own egg, 1, 900 egg donor • Underestimation • CBRC in Spain estimated by comparison FIVCAT / SEF • 17, 000 cycles for patients from abroad, 5, 000 own egg, 12, 000 egg donor • Overerestimation • Conclusion • A voluntary register is not valid for CBRC data but it can help to estimate them
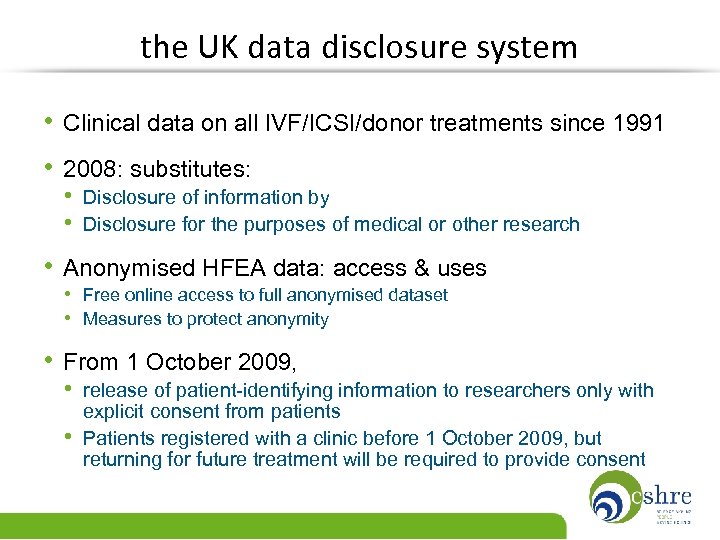 the UK data disclosure system • Clinical data on all IVF/ICSI/donor treatments since 1991 • 2008: substitutes: • Disclosure of information by • Disclosure for the purposes of medical or other research • Anonymised HFEA data: access & uses • Free online access to full anonymised dataset • Measures to protect anonymity • From 1 October 2009, • release of patient-identifying information to researchers only with • explicit consent from patients Patients registered with a clinic before 1 October 2009, but returning for future treatment will be required to provide consent
the UK data disclosure system • Clinical data on all IVF/ICSI/donor treatments since 1991 • 2008: substitutes: • Disclosure of information by • Disclosure for the purposes of medical or other research • Anonymised HFEA data: access & uses • Free online access to full anonymised dataset • Measures to protect anonymity • From 1 October 2009, • release of patient-identifying information to researchers only with • explicit consent from patients Patients registered with a clinic before 1 October 2009, but returning for future treatment will be required to provide consent
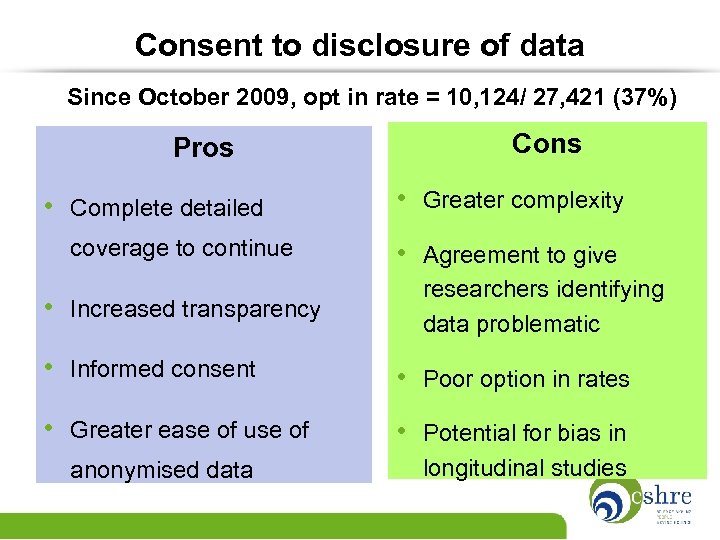 Consent to disclosure of data Since October 2009, opt in rate = 10, 124/ 27, 421 (37%) Pros • Complete detailed coverage to continue • Increased transparency Cons • Greater complexity • Agreement to give researchers identifying data problematic • Informed consent • Poor option in rates • Greater ease of use of • Potential for bias in anonymised data longitudinal studies
Consent to disclosure of data Since October 2009, opt in rate = 10, 124/ 27, 421 (37%) Pros • Complete detailed coverage to continue • Increased transparency Cons • Greater complexity • Agreement to give researchers identifying data problematic • Informed consent • Poor option in rates • Greater ease of use of • Potential for bias in anonymised data longitudinal studies
 Session 3. Registries experiences
Session 3. Registries experiences
 Session Plan • 6 presentations on national experiences • Turkey: 122 centres, 44 000 cycles 2008 • State data collection, compulsory but imperfect, Summaries • Needs for involving professional • Russia: 78% participation, 35 000 cycles, low ICSI • Increase in SET, DET, surrogacy allowed • Austria: analysis of differences public/private (Better results) • Belgium: compulsory register held by"College of Physicians Reproductive Medicine. • Law : decrease in multiple, from 30 -35% to 12 -14%, reimburs. • Slovenia: 3 centres, high activity, SET encouraged • Switzerland: experience of data auditing: improvement in data collection; hopes in a new software
Session Plan • 6 presentations on national experiences • Turkey: 122 centres, 44 000 cycles 2008 • State data collection, compulsory but imperfect, Summaries • Needs for involving professional • Russia: 78% participation, 35 000 cycles, low ICSI • Increase in SET, DET, surrogacy allowed • Austria: analysis of differences public/private (Better results) • Belgium: compulsory register held by"College of Physicians Reproductive Medicine. • Law : decrease in multiple, from 30 -35% to 12 -14%, reimburs. • Slovenia: 3 centres, high activity, SET encouraged • Switzerland: experience of data auditing: improvement in data collection; hopes in a new software
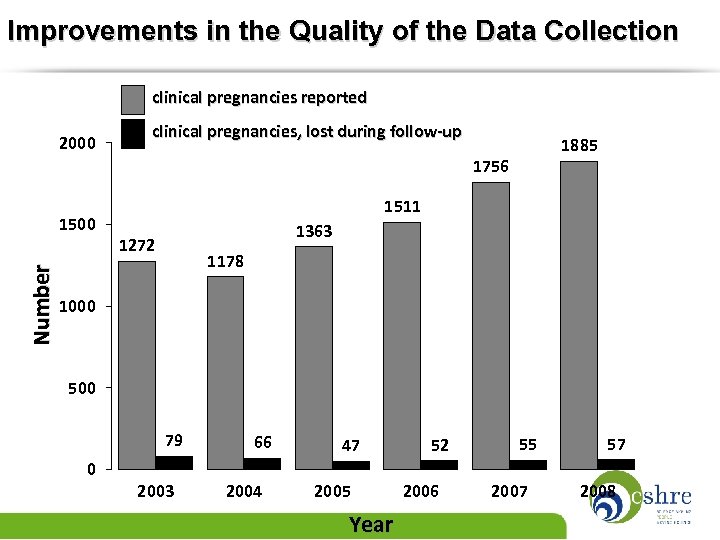 Improvements in the Quality of the Data Collection clinical pregnancies reported 2000 clinical pregnancies, lost during follow-up 1885 1756 Number 1500 1511 1363 1272 1178 1000 500 79 0 2003 66 2004 47 2005 Year 52 2006 55 2007 57 2008
Improvements in the Quality of the Data Collection clinical pregnancies reported 2000 clinical pregnancies, lost during follow-up 1885 1756 Number 1500 1511 1363 1272 1178 1000 500 79 0 2003 66 2004 47 2005 Year 52 2006 55 2007 57 2008
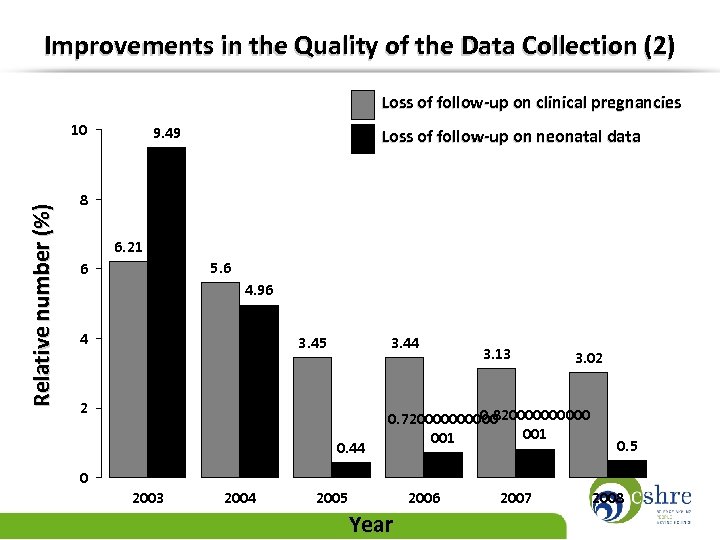 Improvements in the Quality of the Data Collection (2) Loss of follow-up on clinical pregnancies Relative number (%) 10 9. 49 Loss of follow-up on neonatal data 8 6. 21 5. 6 6 4. 96 4 3. 45 3. 44 2 0. 44 3. 13 3. 02 0. 8200000 0. 7200000 001 0. 5 0 2003 2004 2005 Year 2006 2007 2008
Improvements in the Quality of the Data Collection (2) Loss of follow-up on clinical pregnancies Relative number (%) 10 9. 49 Loss of follow-up on neonatal data 8 6. 21 5. 6 6 4. 96 4 3. 45 3. 44 2 0. 44 3. 13 3. 02 0. 8200000 0. 7200000 001 0. 5 0 2003 2004 2005 Year 2006 2007 2008
 Session 4. Round tables
Session 4. Round tables
 Three round tables • EIM Forms : • small changes (semen donation, more info on IUI) • clarification • EIM organization: Proposition for • modifying country representation, • steering committee election process (ESHRE / registries) • Organizing meetings like this one • Assistance for countries • Additional studies • Increase them • Board meeting will prepare propositions for next ESHRE congress in Stockholm
Three round tables • EIM Forms : • small changes (semen donation, more info on IUI) • clarification • EIM organization: Proposition for • modifying country representation, • steering committee election process (ESHRE / registries) • Organizing meetings like this one • Assistance for countries • Additional studies • Increase them • Board meeting will prepare propositions for next ESHRE congress in Stockholm
 Conclusion • Very fruitful meeting • 12 experiences shared • Covering most of the fields • Active participation • Participants satisfied • To be renewed
Conclusion • Very fruitful meeting • 12 experiences shared • Covering most of the fields • Active participation • Participants satisfied • To be renewed


