b8ce0795c596aa4086e85f1342086f50.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Report for the Inquiry into the Role of Libraries in the On-line Environment Matthew Tutaki Sydney, NSW May 2003
Report for the Inquiry into the Role of Libraries in the On-line Environment Matthew Tutaki Sydney, NSW May 2003
 (A) The current community patterns of demand for public information services through libraries, including the provision of such information on-line: • Increase in the number of terminals located at libraries across the nation • The development of virtual communities of learning • The recognition of libraries as a physical storehouse of knowledge and information • The development of on-line initiatives such as www. goask. gov. au • Cross Collaboration of ideas and the sharing of processes • The move of members of the public to an on-line environment
(A) The current community patterns of demand for public information services through libraries, including the provision of such information on-line: • Increase in the number of terminals located at libraries across the nation • The development of virtual communities of learning • The recognition of libraries as a physical storehouse of knowledge and information • The development of on-line initiatives such as www. goask. gov. au • Cross Collaboration of ideas and the sharing of processes • The move of members of the public to an on-line environment
 (C) Possible strategies which would enhance the wider use and distribution of information resources held by libraries, including the establishment of library networks, improved online access in libraries, online libraries, and greater public knowledge and skill in using library resources • The development of a National Strategy that seeks to develop an information nation
(C) Possible strategies which would enhance the wider use and distribution of information resources held by libraries, including the establishment of library networks, improved online access in libraries, online libraries, and greater public knowledge and skill in using library resources • The development of a National Strategy that seeks to develop an information nation
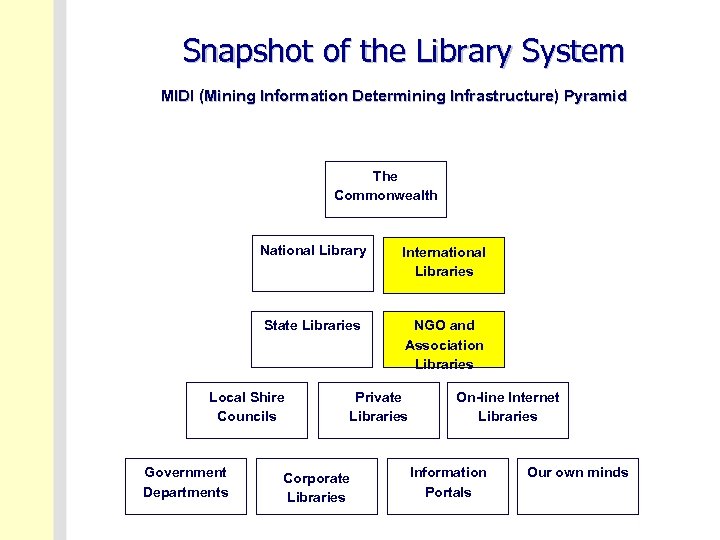 Snapshot of the Library System MIDI (Mining Information Determining Infrastructure) Pyramid The Commonwealth National Library International Libraries State Libraries NGO and Association Libraries Local Shire Councils Government Departments Private Libraries Corporate Libraries On-line Internet Libraries Information Portals Our own minds
Snapshot of the Library System MIDI (Mining Information Determining Infrastructure) Pyramid The Commonwealth National Library International Libraries State Libraries NGO and Association Libraries Local Shire Councils Government Departments Private Libraries Corporate Libraries On-line Internet Libraries Information Portals Our own minds
 The role of our national, state and local library system should be to collaborate in order to ensure information and knowledge is provided 24 hours a day seven days a week, anywhere, anytime. The role of the library system should be to act as the central, pivotal standard bearer of the information nation.
The role of our national, state and local library system should be to collaborate in order to ensure information and knowledge is provided 24 hours a day seven days a week, anywhere, anytime. The role of the library system should be to act as the central, pivotal standard bearer of the information nation.
 Vision for the Future § An integrated, results-oriented library system characterized by strategic leadership, ubiquitous communication, and invisible technology. § An effective, flexible and sustainable Library Service enterprise-wide information and technology environment that enables people to make and implement efficient and agile decisions. § A knowledge-centric culture where trust and respect facilitate information sharing and organizational learning.
Vision for the Future § An integrated, results-oriented library system characterized by strategic leadership, ubiquitous communication, and invisible technology. § An effective, flexible and sustainable Library Service enterprise-wide information and technology environment that enables people to make and implement efficient and agile decisions. § A knowledge-centric culture where trust and respect facilitate information sharing and organizational learning.
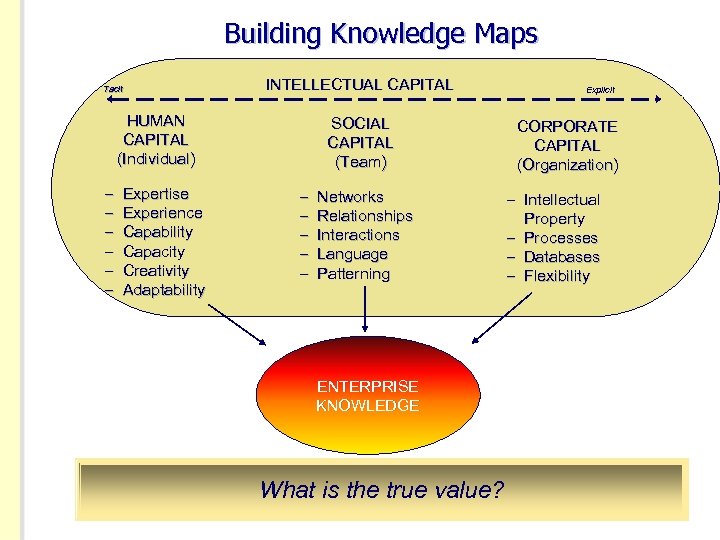 Building Knowledge Maps Tacit INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL HUMAN CAPITAL (Individual) – – – Expertise Experience Capability Capacity Creativity Adaptability SOCIAL CAPITAL (Team) – – – Networks Relationships Interactions Language Patterning ENTERPRISE KNOWLEDGE What is the true value? Explicit CORPORATE CAPITAL (Organization) – Intellectual Property – Processes – Databases – Flexibility
Building Knowledge Maps Tacit INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL HUMAN CAPITAL (Individual) – – – Expertise Experience Capability Capacity Creativity Adaptability SOCIAL CAPITAL (Team) – – – Networks Relationships Interactions Language Patterning ENTERPRISE KNOWLEDGE What is the true value? Explicit CORPORATE CAPITAL (Organization) – Intellectual Property – Processes – Databases – Flexibility
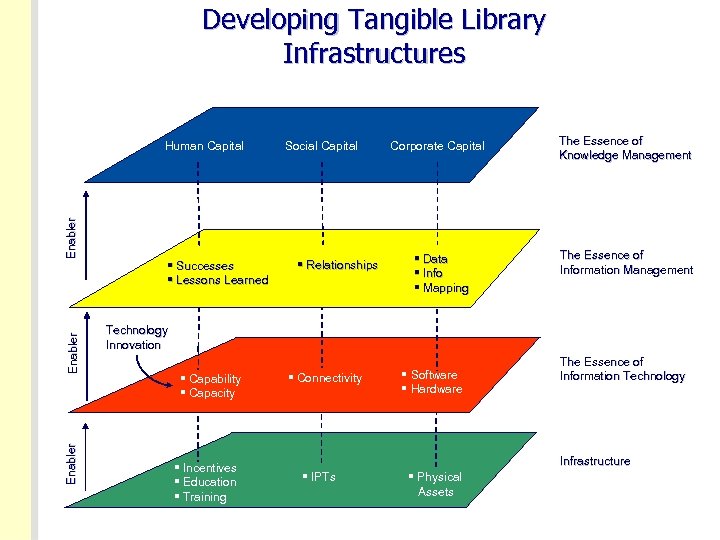 Developing Tangible Library Infrastructures Enabler Human Capital § Successes § Lessons Learned Social Capital § Relationships Corporate Capital § Data § Info § Mapping The Essence of Knowledge Management The Essence of Information Management Technology Innovation § Capability § Capacity § Incentives § Education § Training § Connectivity § Software § Hardware The Essence of Information Technology Infrastructure § IPTs § Physical Assets
Developing Tangible Library Infrastructures Enabler Human Capital § Successes § Lessons Learned Social Capital § Relationships Corporate Capital § Data § Info § Mapping The Essence of Knowledge Management The Essence of Information Management Technology Innovation § Capability § Capacity § Incentives § Education § Training § Connectivity § Software § Hardware The Essence of Information Technology Infrastructure § IPTs § Physical Assets
 Developing Communities of Practice § § § § Shared Domain of Practice/Interest Alignment with strategic direction Critical Factors Crosses operational, functional and • Personal organizational boundaries passion • Trust • Sense of Urgency Defined by knowledge, not tasks Managed by making connections • Key thought leaders Focus on value, added mutual exchange and Respect • • Open Communication continuous learning Evolving agenda Communities emerging across the organisation “…you cannot force a plant to grow by pulling its leaves… what you can do is create the infrastructure in which it can prosper. ”
Developing Communities of Practice § § § § Shared Domain of Practice/Interest Alignment with strategic direction Critical Factors Crosses operational, functional and • Personal organizational boundaries passion • Trust • Sense of Urgency Defined by knowledge, not tasks Managed by making connections • Key thought leaders Focus on value, added mutual exchange and Respect • • Open Communication continuous learning Evolving agenda Communities emerging across the organisation “…you cannot force a plant to grow by pulling its leaves… what you can do is create the infrastructure in which it can prosper. ”
 Community of Practice Goals § Performance Support § Knowledge Retrieval § Knowledge Capture § Collaboration and Solutions Environment § Generation of New Knowledge
Community of Practice Goals § Performance Support § Knowledge Retrieval § Knowledge Capture § Collaboration and Solutions Environment § Generation of New Knowledge
 How to manage organisational knowledge - People § Real-time shared understanding of the objective § Rapid synchronization of actions § Mitigates the fog of organisational change § Change never ends § Implications § Cultural Adaption § Strategy and Clear and Defined § Everyone understands the “endgame”
How to manage organisational knowledge - People § Real-time shared understanding of the objective § Rapid synchronization of actions § Mitigates the fog of organisational change § Change never ends § Implications § Cultural Adaption § Strategy and Clear and Defined § Everyone understands the “endgame”
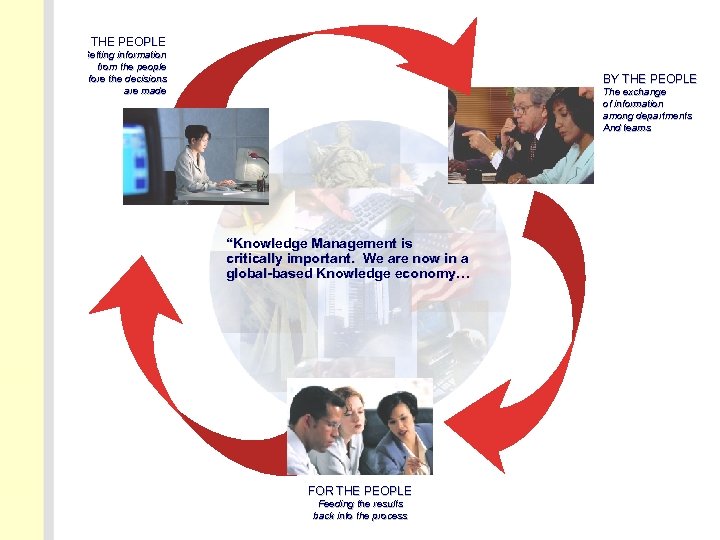 OF THE PEOPLE Getting information from the people before the decisions are made BY THE PEOPLE The exchange of information among departments And teams “Knowledge Management is critically important. We are now in a global-based Knowledge economy… FOR THE PEOPLE Feeding the results back into the process
OF THE PEOPLE Getting information from the people before the decisions are made BY THE PEOPLE The exchange of information among departments And teams “Knowledge Management is critically important. We are now in a global-based Knowledge economy… FOR THE PEOPLE Feeding the results back into the process
 Reasons why we do and do not share knowledge Tick for yes Increased efficiencies Organisational learning Communities of practice Rapid deployment Increased customer service Meeting stakeholder objectives Flexible Virtual Technology supporting people Integrative competency Communication empowerment Tick for no Fear No knowledge Confidence Obscurity Insecure Loathing Tradition Culture Ineffectiveness Inability
Reasons why we do and do not share knowledge Tick for yes Increased efficiencies Organisational learning Communities of practice Rapid deployment Increased customer service Meeting stakeholder objectives Flexible Virtual Technology supporting people Integrative competency Communication empowerment Tick for no Fear No knowledge Confidence Obscurity Insecure Loathing Tradition Culture Ineffectiveness Inability
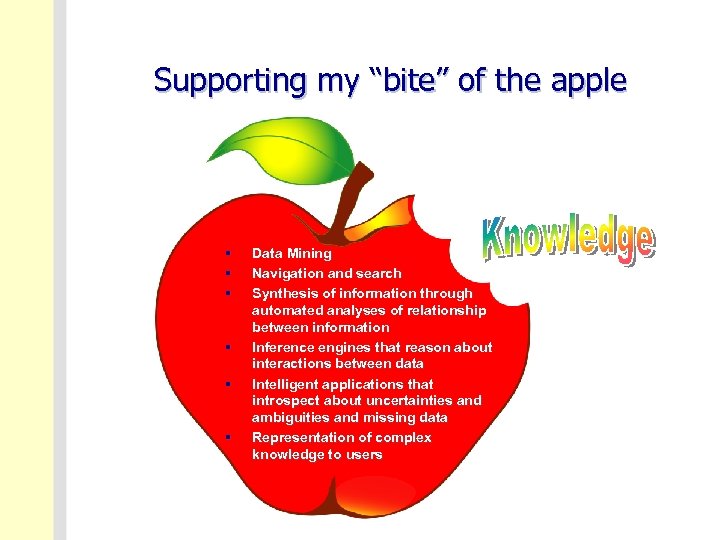 Supporting my “bite” of the apple § § § Data Mining Navigation and search Synthesis of information through automated analyses of relationship between information Inference engines that reason about interactions between data Intelligent applications that introspect about uncertainties and ambiguities and missing data Representation of complex knowledge to users
Supporting my “bite” of the apple § § § Data Mining Navigation and search Synthesis of information through automated analyses of relationship between information Inference engines that reason about interactions between data Intelligent applications that introspect about uncertainties and ambiguities and missing data Representation of complex knowledge to users
 The truth § Perfect information does not equal perfect decisions § Behaviors are not changed by technology alone § Connecting is not sufficient to create value
The truth § Perfect information does not equal perfect decisions § Behaviors are not changed by technology alone § Connecting is not sufficient to create value
 Implementation § § § § Phased approach focused on a critical need Meets people and teams where they are Embeds core organisational collaboration practices and tools and introduces simple learning tools Makes collaboration part of the job with real bottom line impact, not something extra Leverages investment in existing technology base Creates business ownership for the outcomes Creates agile organizations better able to solve the problems facing the Government Delivers tangible business results Small steps, not big leaps
Implementation § § § § Phased approach focused on a critical need Meets people and teams where they are Embeds core organisational collaboration practices and tools and introduces simple learning tools Makes collaboration part of the job with real bottom line impact, not something extra Leverages investment in existing technology base Creates business ownership for the outcomes Creates agile organizations better able to solve the problems facing the Government Delivers tangible business results Small steps, not big leaps
 Implementation Process § Build awareness and spread Library expertise § Identify key knowledge assets § Design projects: determine project focus, feasibility, resources, costs, ROI; and prioritize knowledge assets – Create maps of owners and users of knowledge assets – Define metrics for evaluation of project, e. g. , reliability of knowledge assets; usability of knowledge system; reduction in process cycle time – Design, develop and deploy systems to collect, organize, distill, disseminate – Build Communities of Practice around "hot" topics
Implementation Process § Build awareness and spread Library expertise § Identify key knowledge assets § Design projects: determine project focus, feasibility, resources, costs, ROI; and prioritize knowledge assets – Create maps of owners and users of knowledge assets – Define metrics for evaluation of project, e. g. , reliability of knowledge assets; usability of knowledge system; reduction in process cycle time – Design, develop and deploy systems to collect, organize, distill, disseminate – Build Communities of Practice around "hot" topics
 Key Strategy Concepts § Pull, not push § Leadership Alignment, not control § Embed into our business, not the business § Little, not a big program § Where appropriate, not everywhere § Find a bridge and link it with organisational structure
Key Strategy Concepts § Pull, not push § Leadership Alignment, not control § Embed into our business, not the business § Little, not a big program § Where appropriate, not everywhere § Find a bridge and link it with organisational structure
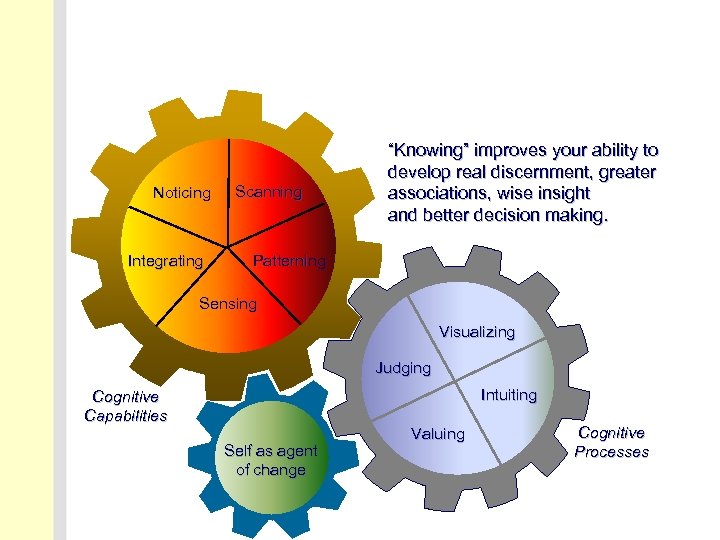 Noticing Integrating Scanning “Knowing” improves your ability to develop real discernment, greater associations, wise insight and better decision making. Patterning Sensing Visualizing Judging Intuiting Cognitive Capabilities Self as agent of change Valuing Cognitive Processes
Noticing Integrating Scanning “Knowing” improves your ability to develop real discernment, greater associations, wise insight and better decision making. Patterning Sensing Visualizing Judging Intuiting Cognitive Capabilities Self as agent of change Valuing Cognitive Processes
 Information literacy is a survival skill in the Information Age. Instead of drowning in the abundance of information that floods their lives, information literate people know how to find, evaluate, and use information effectively to solve a particular problem or make a decision…
Information literacy is a survival skill in the Information Age. Instead of drowning in the abundance of information that floods their lives, information literate people know how to find, evaluate, and use information effectively to solve a particular problem or make a decision…
 On the Horizon Some contact details: Matthew Tutaki: matthew. tutaki@syntropy. com. au Neville Buch: neville. buch@syntropy. com. au Phone: Fax: 02 9262 1155 02 9262 5599 www. syntropy. com. au
On the Horizon Some contact details: Matthew Tutaki: matthew. tutaki@syntropy. com. au Neville Buch: neville. buch@syntropy. com. au Phone: Fax: 02 9262 1155 02 9262 5599 www. syntropy. com. au


