cf62ffd0ca565cf23bb997d9512fb29d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

Renewable Energy Yesterday’s alternative – tomorrow’s mainstream Philip Wolfe ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 1

There’s still time ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 2

The end ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 3

Taking a different path Achieving quantum change – the politics Vision to delivery – targets and directives Leadership or drift – UK energy policy Changing the paradigm – 2020 scenarios Brave new world – renewable hotspots ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 4

Achieving quantum change – the politics ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 5

Environment trends ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 6

Vision to delivery – targets and directives ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 7

The EU commitments for 2020 Emissions reductions Binding > 20% unilateral, or > 30% if multilateral Energy conservation ’Non-binding %s 0 > of 2 projections 20% below current A lot Renewables Binding > 20% of total energy > 10% of transport fuels ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 8
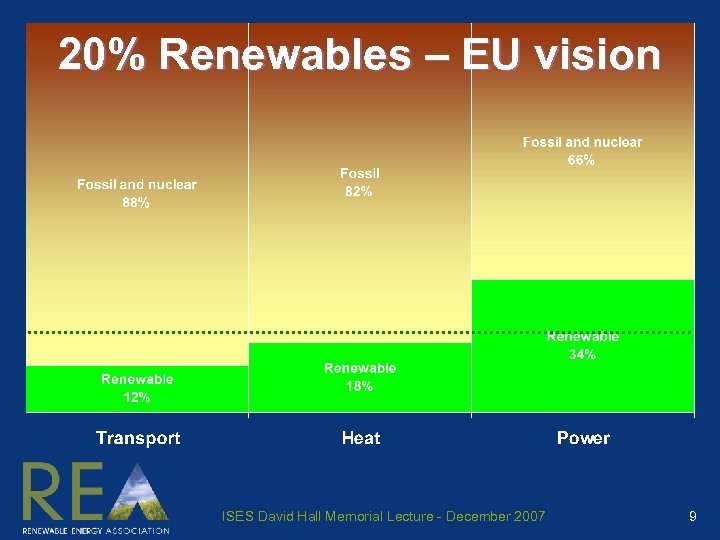
20% Renewables – EU vision ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 9

Leadership or drift – UK energy policy ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 10

Energy White Paper “The 20% renewables target is an ambitious goal … by 2020, on the basis of existing policies, renewables would contribute around 5% of the UK’s consumption … we will bring forward the appropriate measures, beyond those set out in this White Paper, to make our contribution to meeting these targets. ” ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 11

Changing the paradigm – 2020 scenarios ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 12

First: Cut energy consumption Energy conservation measures More efficient energy usage > Regulate against inefficient products > Regulate against parasitic loads More efficient energy generation > Limit generating stations’ waste energy UK consumption in 2020 same as now as a rough working assumption ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 13
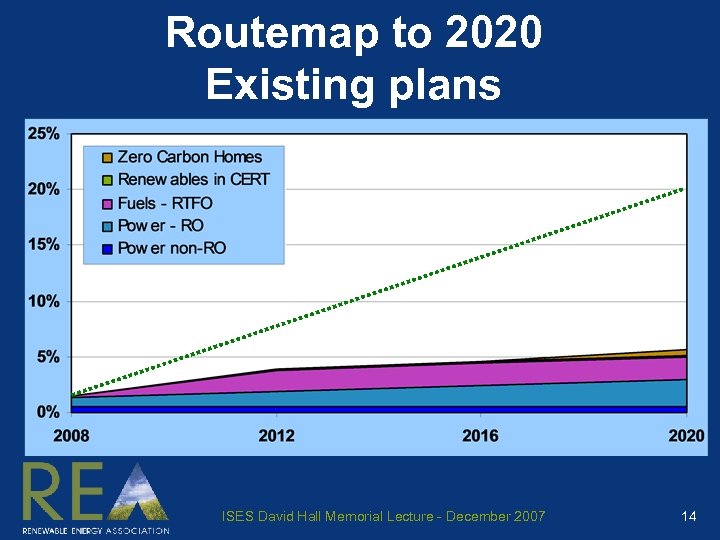
Routemap to 2020 Existing plans ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 14

Existing policies, measures and assumptions Merchant power RO 1 achieves ~15% of electricity > > Banding achieves diversity Doesn’t harm onshore wind (not ‘net neutral’) Planning & grid restrictions overcome > > > All energy planning to IPC 2 “Connect & manage” grid access Beauly-Denny transmission upgrade 1 2 Renewable (electricity) Obligation Infrastructure Planning Commission ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 15
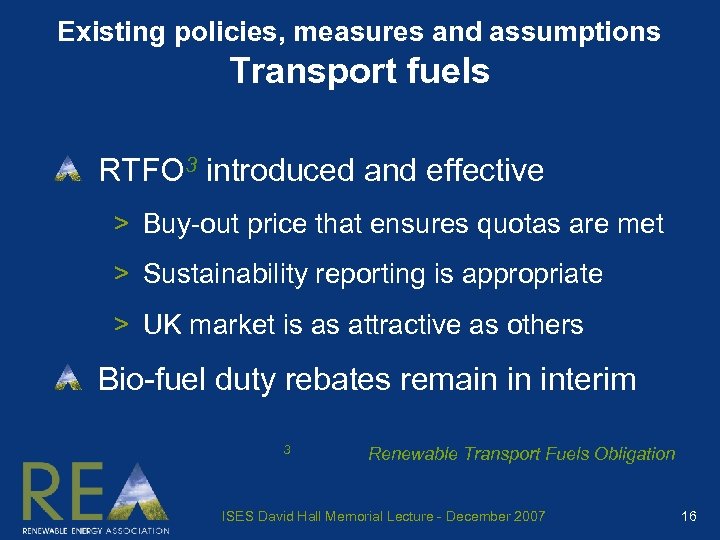
Existing policies, measures and assumptions Transport fuels RTFO 3 introduced and effective > Buy-out price that ensures quotas are met > Sustainability reporting is appropriate > UK market is as attractive as others Bio-fuel duty rebates remain in interim 3 Renewable Transport Fuels Obligation ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 16

Existing policies, measures and assumptions Onsite energy Zero carbon new homes from 2016 > Building regs: CSH 4 level 6 from 2016 CERT 5 effective for ‘micro-renewables’ > Appropriate multipliers for renewables Positive planning > Extend ‘Merton Rule’ 6 nationwide Encourage renewables in existing houses > Energy certificates in home info packs 4 Code for Sustainable Homes – Level 6 is ‘zero carbon’ 5 6 Carbon Emission Reduction Target (formerly EEC) Larger developments require [10%] renewable energy ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 17
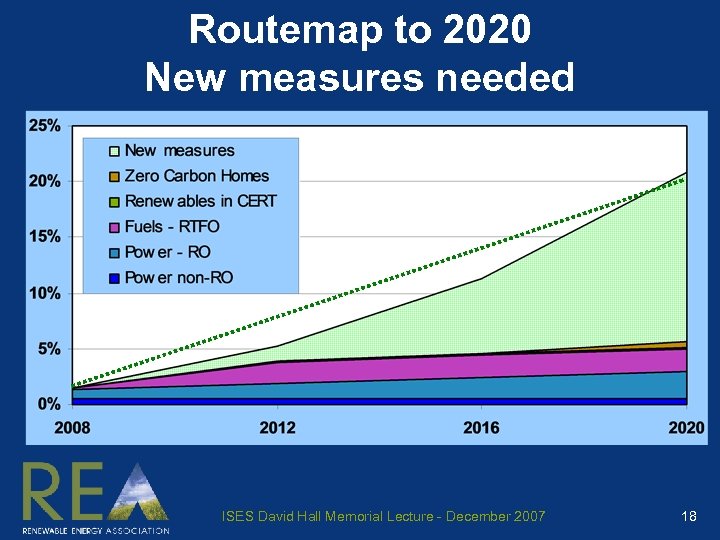
Routemap to 2020 New measures needed ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 18

Policies, measures and proposals Enhanced plans – merchant power Increased RO 1 objective ~22% in 2020 > > > Set 25% quota and increase headroom Retain buyout link to retail price index Offshore super-grid? Tidal lagoons, barrages and new large hydro? Incentives for large scale CHP 7 > > Large thermal generators must use heat Renewable Heat (or Gas? ) Obligation Measures to deliver biomass strategy 1. Renewable (electricity) Obligation 7 Combined heat and power ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 19

Policies, measures and proposals Enhanced plans – transport fuels Higher RTFO 3 quotas – 13% (by volume) in 2020 > RTFO linked to sustainability measures Availability of high blend fuels > Pumps on every large forecourt > Fuel duty rebate within Alternative Fuels Framework Second generation bio-fuels Incentives for high blend and flex-fuel vehicles > Lower vehicle excise duty > Tax breaks for company cars > Congestion charge exemptions 3 Renewable Transport Fuels Obligation ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 20

Policies, measures and proposals Enhanced plans – onsite domestic Building regulations for new homes > CSH 4 level 4 from 2010, level 5 from 2013 Smart metering roll-out programme Retrofit programme for existing houses > 100, 000 rising to 1, 000 per annum > Owner occupiers and private landlords: > Feed-in tariffs for electricity; similar for heat > Stamp duty breaks, council tax concessions > Financing measures, mortgages and loans > Social rented and fuel poor: > Through local authorities and housing associations 4 Code for Sustainable Homes – Level 5 is ‘low carbon’ ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 21

Policies, measures and proposals Enhanced plans – non-residential A new Code for Sustainable Buildings > Equivalent to CSH 4 – and in Building Regs Heat networks in new developments > Regulatory system for heat networks Positive planning > Progressively rising ‘Merton Rule’ 6 %s Renewables in agriculture > Anaerobic digestion on 000’s of farms 6 4 Code for Sustainable Homes Larger developments require [10%] renewable energy ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 22
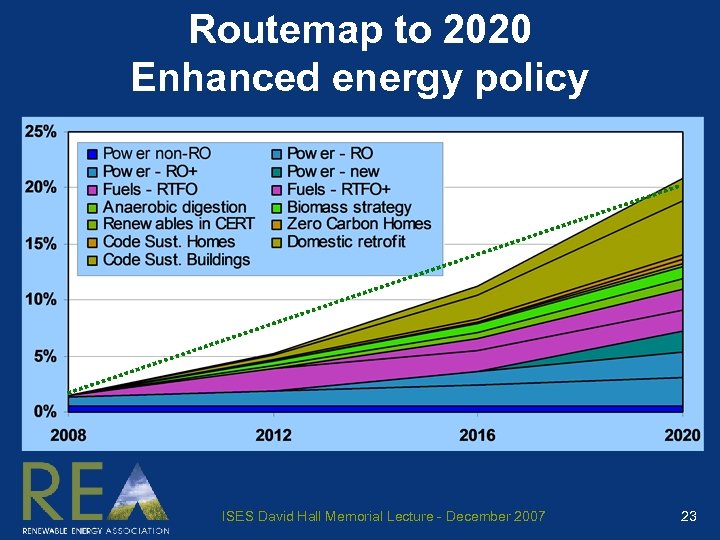
Routemap to 2020 Enhanced energy policy ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 23

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 Combined heat-and-power generation Expansion of renewable energies in the power sector CCS technologies Smart metering Clean power-station technologies Introduction of modern energy management systems Support programmes for climate protection and energy efficiency Energy-efficient products Provisions on the feed-in of biogas to natural gas grids Energy Saving Ordinance Operating costs of rental accommodation Modernisation programme to reduce CO 2 emissions from buildings Energy-efficient modernisation of social infrastructure Renewable Energies Heat Act Programme for the energy-efficient modernisation of federal buildings CO 2 strategy for passenger cars Expansion of the biofuels market Reform of vehicle tax on CO 2 basis Energy labelling of passenger cars Reinforcing the influence of the HGV toll Aviation Shipping Reduction of emissions of fluorinated greenhouse gases Procurement of energy-efficient products and services Energy research and innovation Electric mobility International projects on climate protection and energy efficiency Reporting on energy ISES David Hallpolicy by German embassies and consulates 24 and climate Memorial Lecture - December 2007 Transatlantic climate and technology initiative A coherent policy package?
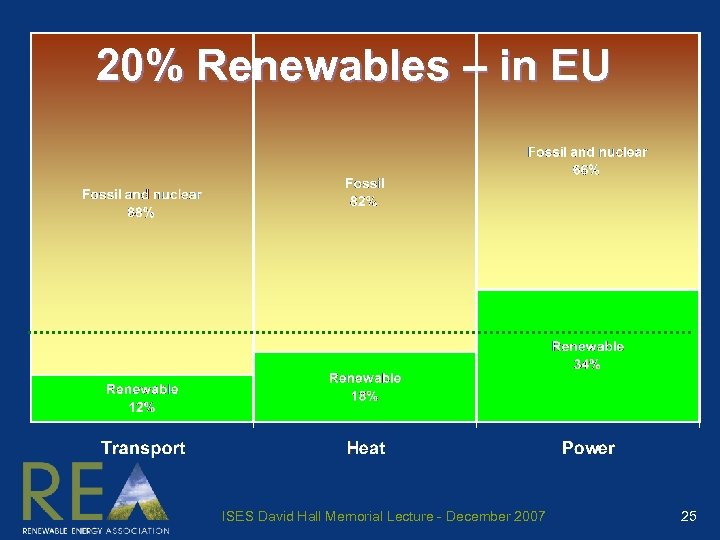
20% Renewables – in EU ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 25
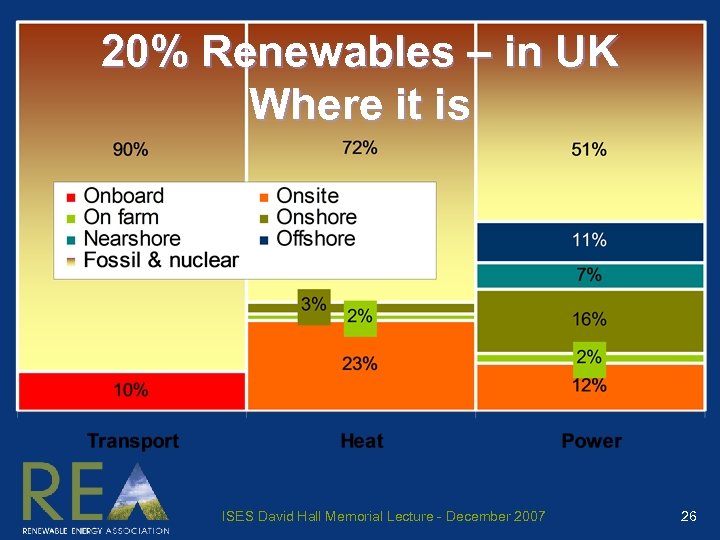
20% Renewables – in UK Where it is ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 26
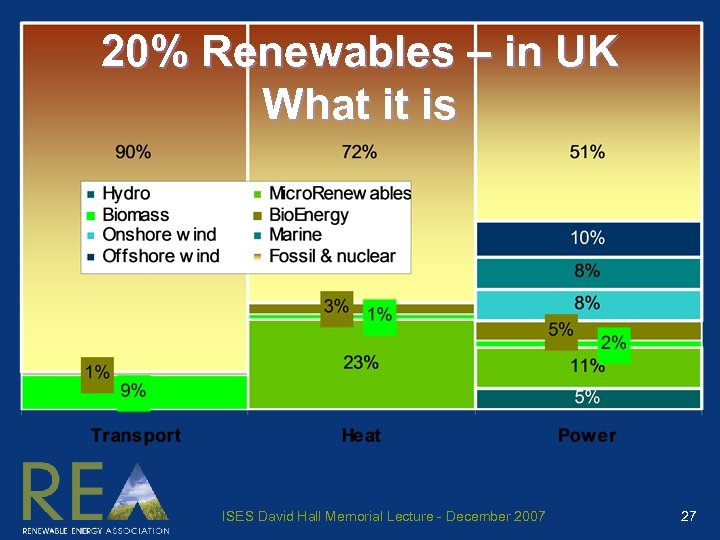
20% Renewables – in UK What it is ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 27
Renewables in total energy ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 28

Who pays? … How much? The consumer pays (indirectly) for: > Obligations > Feed-in tariffs > Building Regulations (land-owner pays? ) > Energy prices will rise The taxpayer (via the Treasury) pays for: polluter > Retrofit programme through local authorities > Fiscal incentives > Cost (a fraction of Stern’s 1% of GDP) from: > NFFO 7 surplus (and obligations buy-out funds? ) > Auction of EU-ETS 8 carbon allowances 7 8 The RO gets a surplus from Non-Fossil Fuel Order projects Emission allocations in the EU Emissions Trading Scheme ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 29

Brave new world – renewable hotspots ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 30

Engineering impacts and opportunities Elemental conversion technologies New approaches in established technologies > Offshore wind > Tidal barrages and lagoons > Building-integrated PV and solar thermal Higher volumes and efficiencies > Heat pumps > Micro-hydro Emerging renewable technologies > Tidal stream energy > Wave energy conversion ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 31

Engineering impacts and opportunities Bio-energy conversion technologies New approaches in established technologies > Sustainable biofuels > Bio-methane for the gas grid Higher volumes and efficiencies > Biomass boilers and CHP > Anaerobic digestion Emerging renewable technologies > Second generation biofuels > Microbial energy ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 32

Engineering impacts and opportunities More decentralised energy system Heat networks Intelligent distribution systems Smart metering > Improved user interfaces > Real-time pricing Active load management > Non-traditional storage options ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 33

Engineering impacts and opportunities New energy integration options ‘On-site’ energy systems > Intelligent user interfaces > Small-scale CHP / fuel cells ‘In-store’ energy systems > Renewable cooling ‘On-farm’ energy systems Everyone is in the energy business ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 34

Some conclusions On renewables: Never call it ‘alternative energy’ On fossil fuels: The Stone Age didn’t end because they ran out of stones “There’s still time” ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 35

Renewable Energy Yesterday’s alternative – tomorrow’s mainstream Philip Wolfe Renewable Energy Association www. r-e-a. net ISES David Hall Memorial Lecture - December 2007 36
cf62ffd0ca565cf23bb997d9512fb29d.ppt