bbe4b3672c06364965e639bc97f8eb40.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

renewable energy the real alternative?
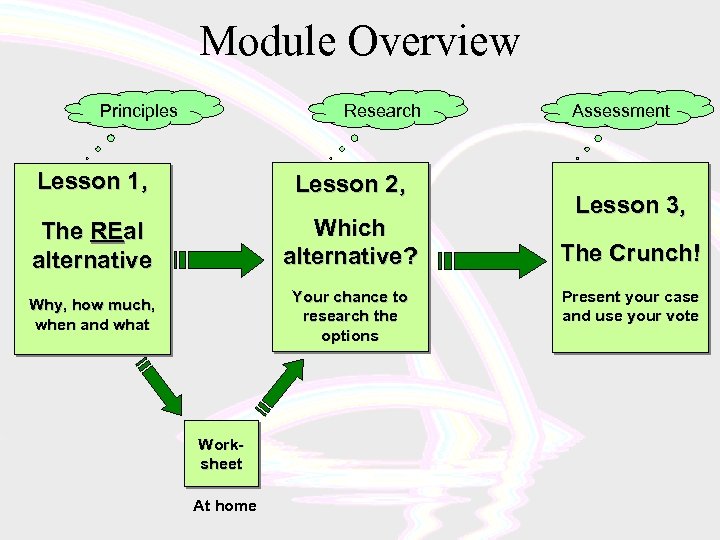
Module Overview Principles Research Lesson 1, Lesson 2, The REal alternative Which alternative? Why, how much, when and what Your chance to research the options Worksheet At home Assessment Lesson 3, The Crunch! Present your case and use your vote

Why Bother? • Because energy resources are limited – Oil and gas will run out, probably in your lifetime • Because burning fossil fuels release greenhouse gases and pollutants – Affecting your environment and health • Because you can do something about it – Using your energy and vote
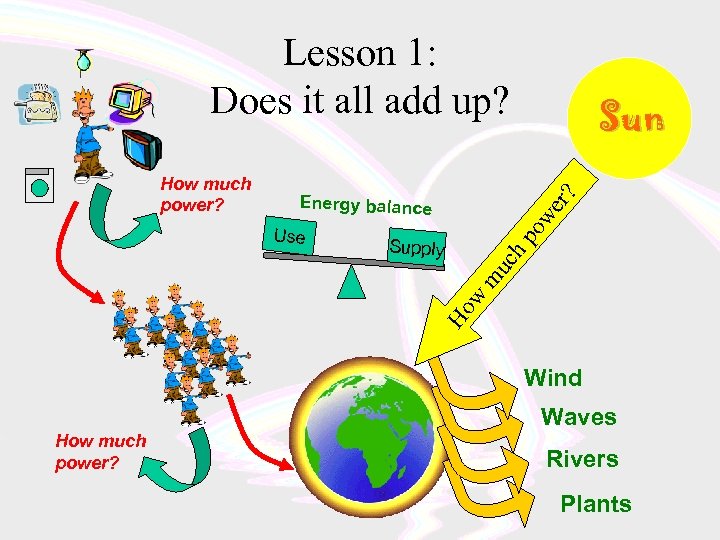
Lesson 1: Does it all add up? er ? hp Supply Ho w m Use ow Energy balance uc How much power? Sun Wind Waves How much power? Rivers Plants
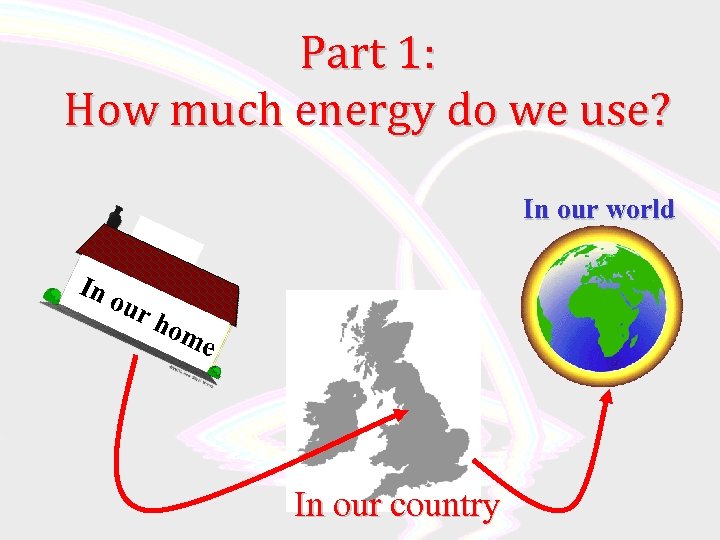
Part 1: How much energy do we use? In our world In our hom e In our country

Starting in YOUR Household • How much energy do you use?
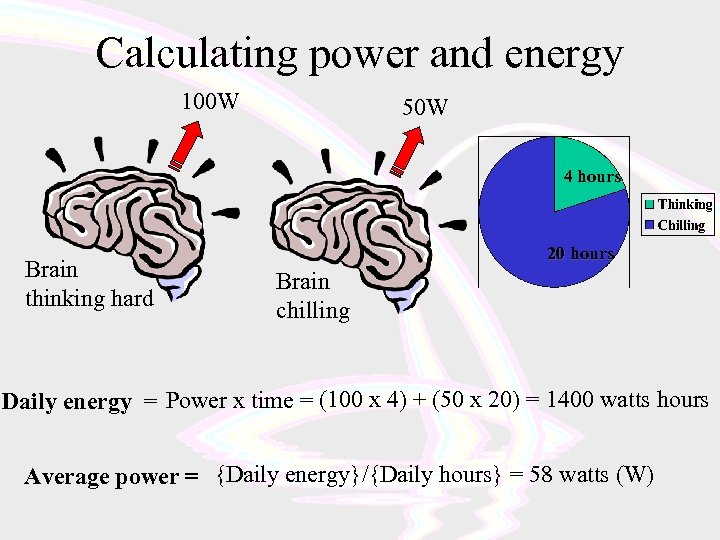
Calculating power and energy 100 W 50 W 4 hours Brain thinking hard 20 hours Brain chilling Daily energy = Power x time = (100 x 4) + (50 x 20) = 1400 watts hours Average power = {Daily energy}/{Daily hours} = 58 watts (W)
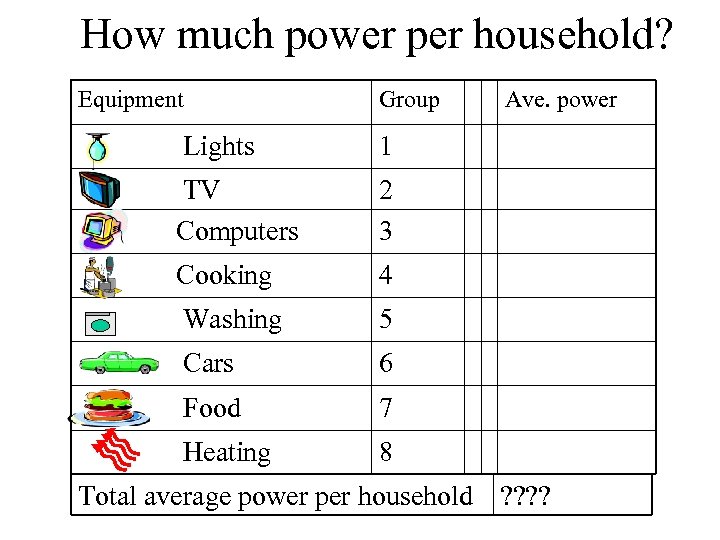
How much power per household? Equipment Group Lights 1 TV Computers 2 3 Cooking 4 Washing 5 Cars 6 Food 7 Heating Ave. power 8 Total average power per household ? ?

Experiments • Split into seven groups • Use equipment supplied to estimate the average power consumed in a typical household • Report back to the class when complete • Use the information to estimate the total average power used by a typical family • Consider the error involved in this estimation
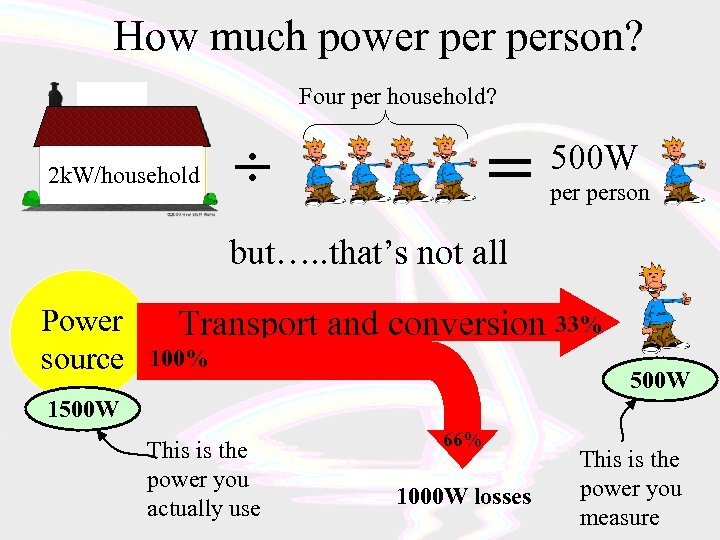
How much power person? Four per household? 2 k. W/household = ÷ 500 W person but…. . that’s not all Power source Transport and conversion 33% 100% 500 W 1500 W This is the power you actually use 66% 1000 W losses This is the power you measure

How much power person? but…. . that’s still not all Industrial/commercial Power consumed Domestic Power consumed 1500 W ¼ ¾ 4500 W You!! You are responsible for about 6000 W of power consumption!!!!
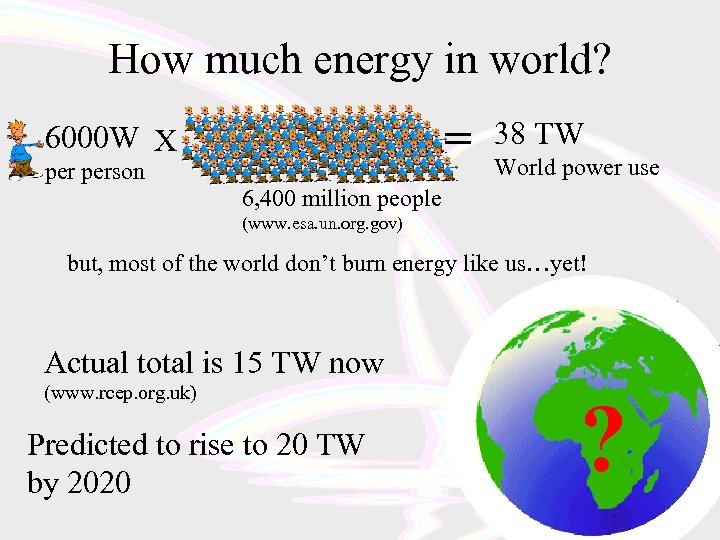
How much energy in world? = 6000 W X person 38 TW World power use 6, 400 million people (www. esa. un. org. gov) but, most of the world don’t burn energy like us…yet! Actual total is 15 TW now (www. rcep. org. uk) Predicted to rise to 20 TW by 2020 ?
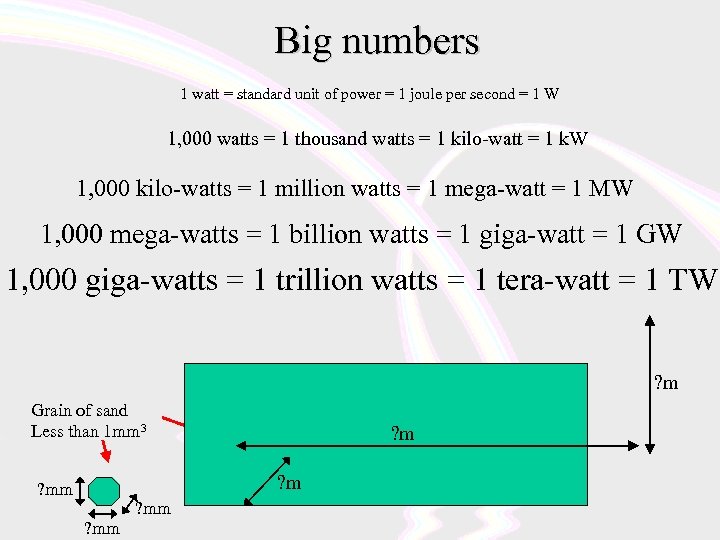
Big numbers 1 watt = standard unit of power = 1 joule per second = 1 W 1, 000 watts = 1 thousand watts = 1 kilo-watt = 1 k. W 1, 000 kilo-watts = 1 million watts = 1 mega-watt = 1 MW 1, 000 mega-watts = 1 billion watts = 1 giga-watt = 1 GW 1, 000 giga-watts = 1 trillion watts = 1 tera-watt = 1 TW ? m Grain of sand Less than 1 mm 3 ? m ? mm

Part 2: Where does the energy come from?

The sun provides more than 99. 9% of our primary energy It is a nuclear reactor 200, 000 trillion times more powerful than nuclear power stations
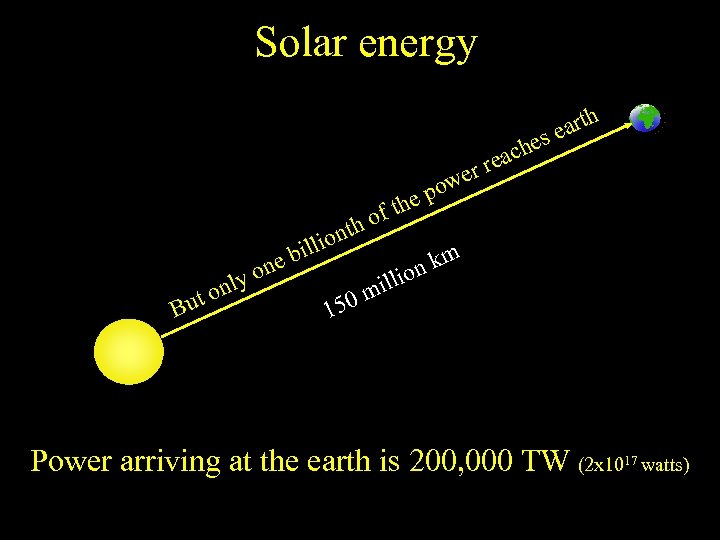
Solar energy th ear es y onl ut B one h ont i bill the of m k on li mil 0 15 wer po ach re Power arriving at the earth is 200, 000 TW (2 x 1017 watts)
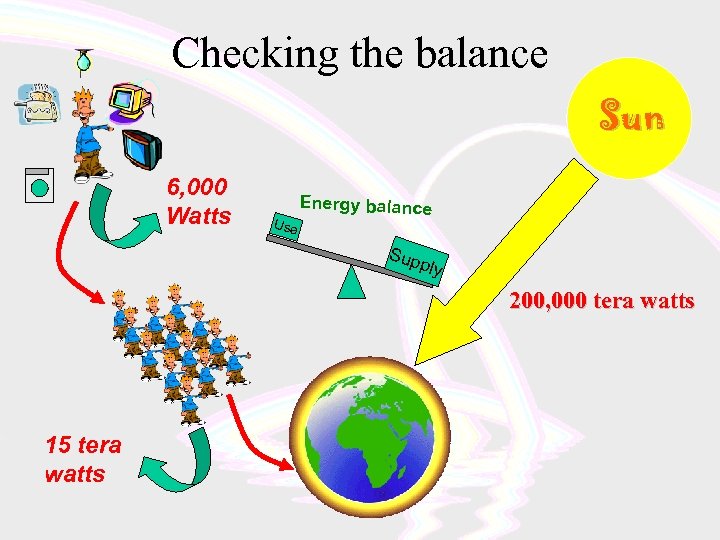
Checking the balance Sun 6, 000 Watts Use Energy balance Sup p ly 200, 000 tera watts 15 tera watts
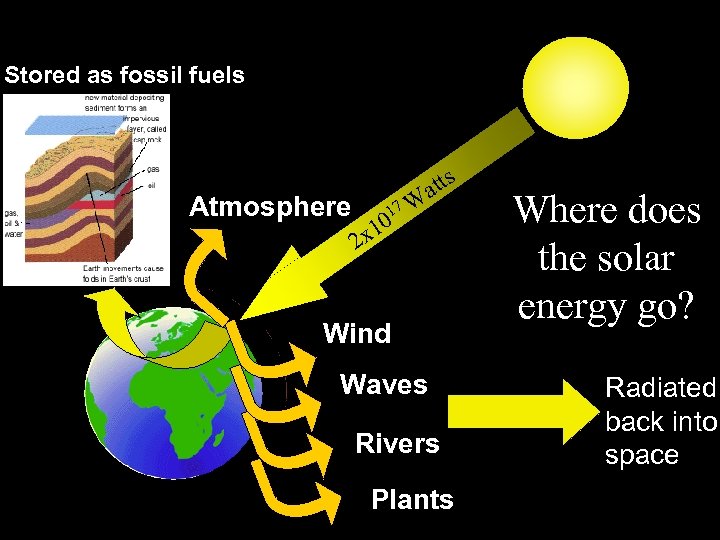
Stored as fossil fuels Atmosphere 17 2 x 10 s att W Wind Waves Rivers Plants Where does the solar energy go? Radiated back into space
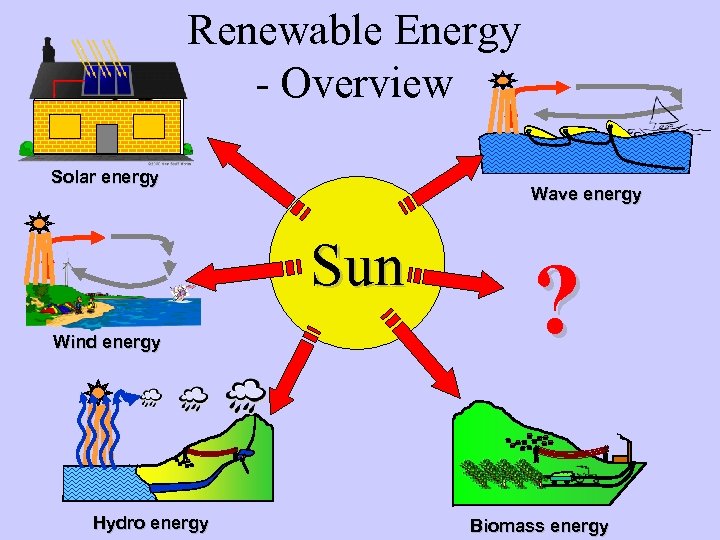
Renewable Energy - Overview Solar energy Wave energy Sun Wind energy Hydro energy ? Biomass energy
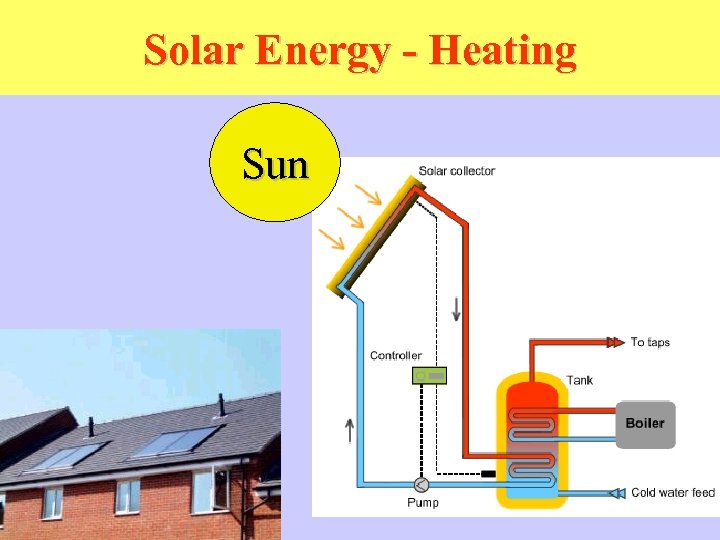
Solar Energy - Heating Sun
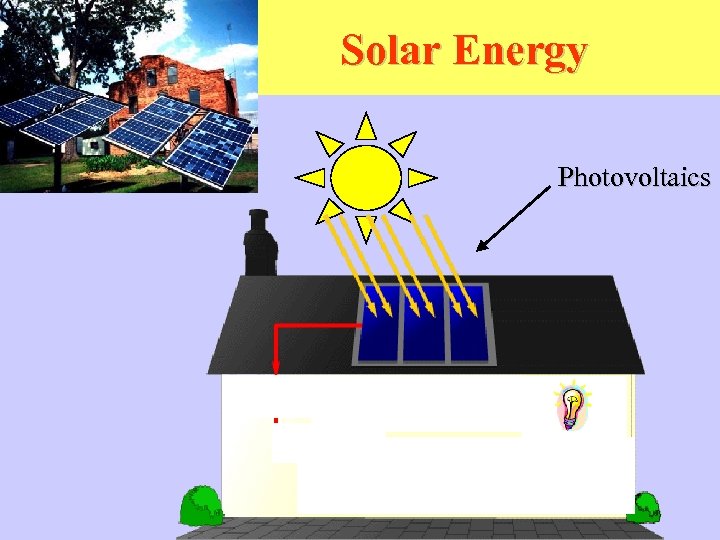
Solar Energy Photovoltaics Direct current devices Charger Batteries Inverter Alternating current devices

Energy from Rivers (Hydro) Large schemes with reservoirs and dams Supply town and cities Small schemes without reservoirs or dams Supply villages

Demonstration • Several demonstrations of energy processes around classroom – Evaporation-condensation cycle – Solar-powered “wind turbines” – Wind-up radios – Tap water powered hydro-turbines • Make a note of the energy conversions and estimate the power involved
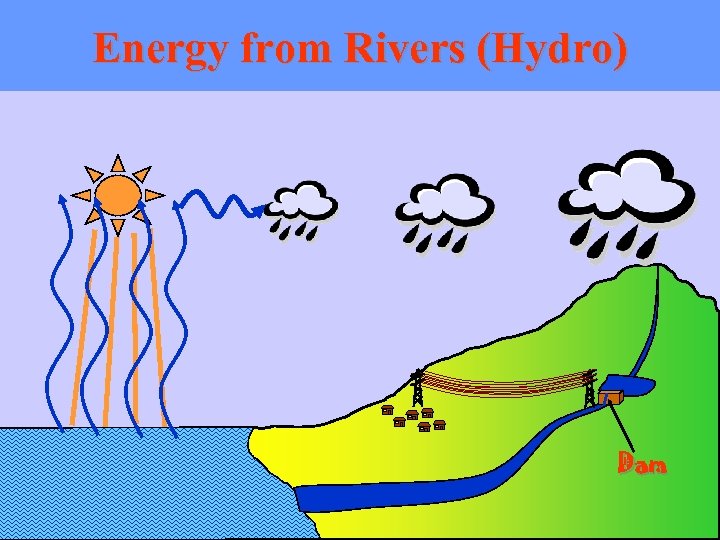
Energy from Rivers (Hydro) Dam
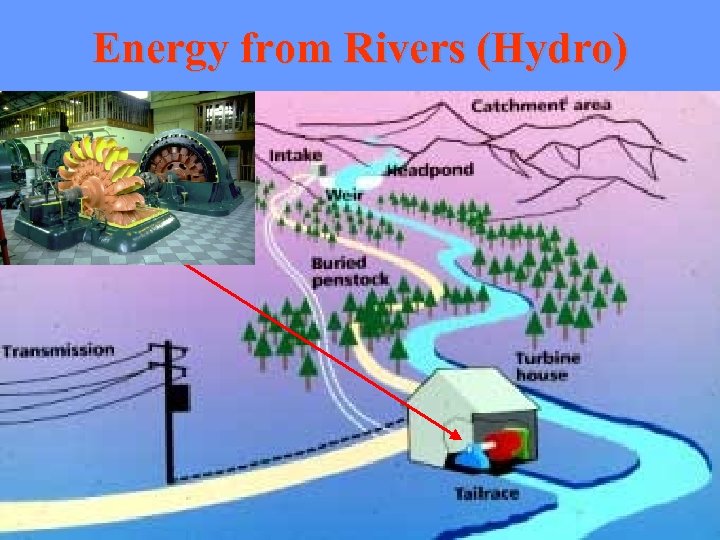
Energy from Rivers (Hydro)

Energy from Wind
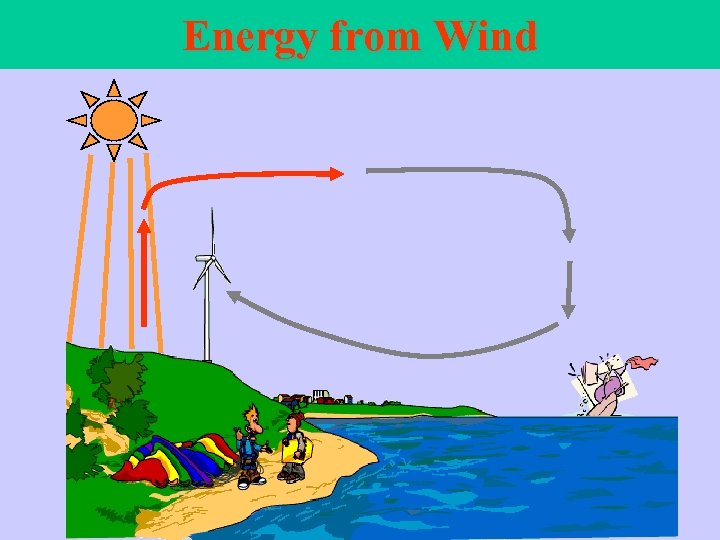
Energy from Wind
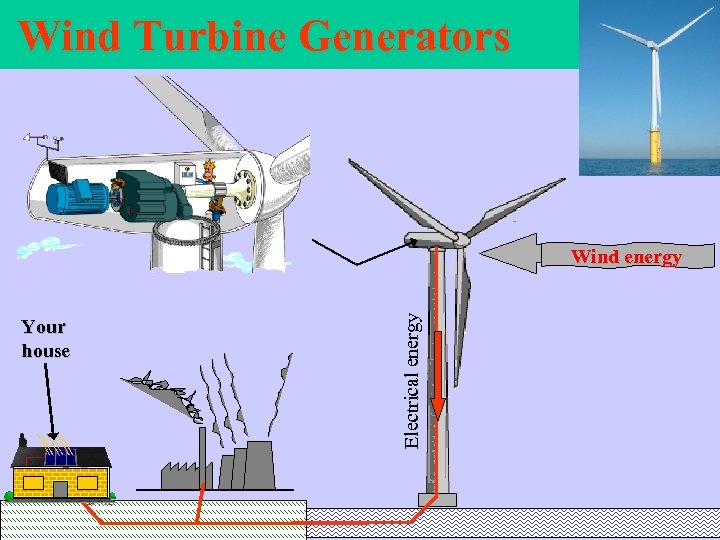
Wind Turbine Generators Your house Electrical energy Wind energy

Energy from Waves
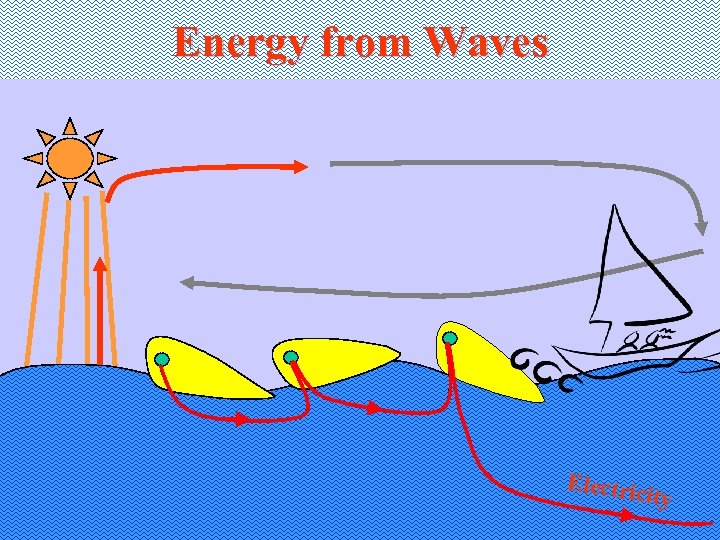
Energy from Waves Electric ity

Other Wave Devices

Energy from Biomass
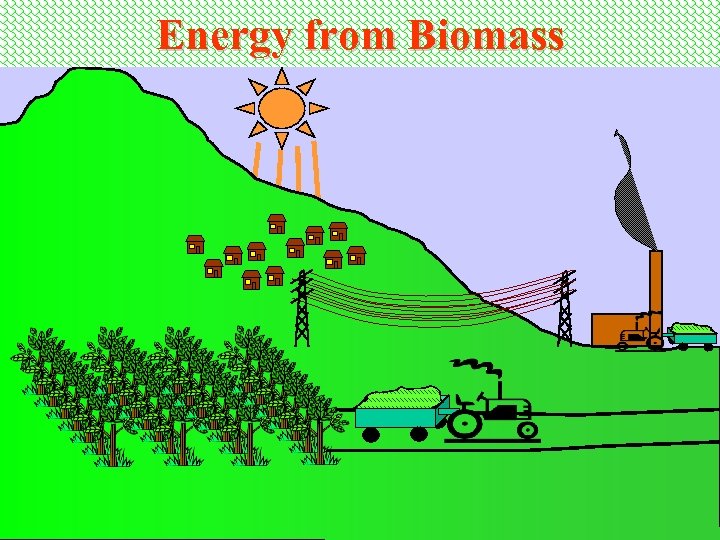
Energy from Biomass
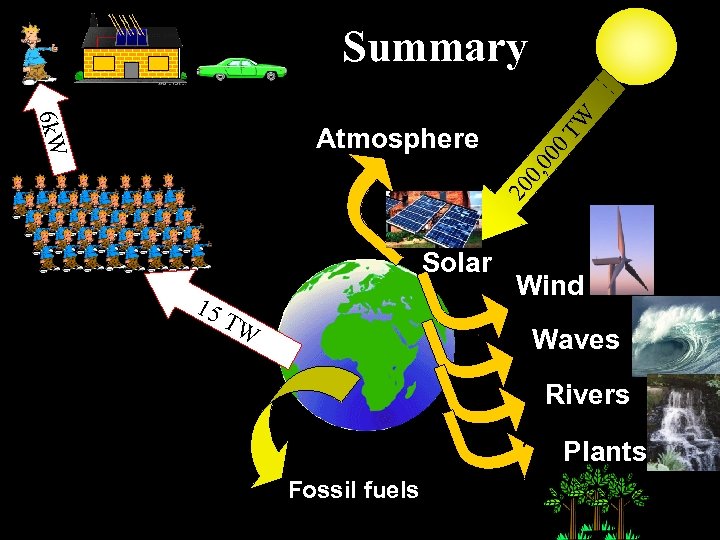
6 k. W TW Summary 20 0, 0 00 Atmosphere Solar 15 TW Wind Waves Rivers Plants Fossil fuels
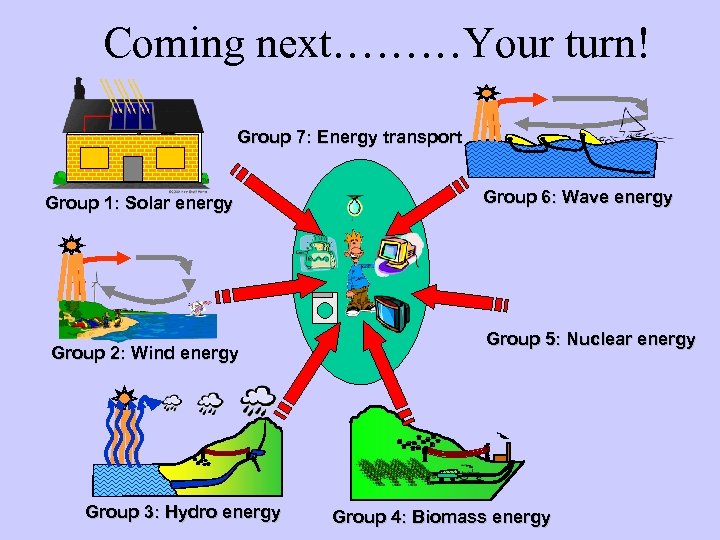
Coming next………Your turn! Group 7: Energy transport Group 1: Solar energy Group 2: Wind energy Group 3: Hydro energy Group 6: Wave energy Group 5: Nuclear energy Group 4: Biomass energy

The End
bbe4b3672c06364965e639bc97f8eb40.ppt