06027e0dd2c8efdb44f026d858290d21.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 65

Renewable Energy An Overview of Brazil by Leandro Rocha

Table of Contents n n n n n 1. Definition of Renewable Energy A- Renewable Energy vs. Non-renewable Energy 2. Brazil Renewable Energy Structure A- Brazil General Index B- Domestic Energy Supply (1) General (2) Renewable C- Domestic Energy Capacity 3. Government Regulation A- Basic Legal Frame Work B- Organizational Frame Work 4. Brazilian Renewable Natural Resources A- Hydroelectric Power plants B- Biofuels 2008 1 - Ethanol 2 - Biodiesel C- Biomass Power 2008 D- Wind Power 2008 E- Solar Power 2008
Definition of Renewable Energy Renewable energy is energy generated from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable. In other words, it is the energy that can be replaced by natural processes at a rate comparable or faster than its rate of consumption by humans. in Brazil, divided in 5 renewable grups: ¨ ¨ ¨ A- Hydroelectric Power plants B- Biofuels C- Biomass Power D- Wind Power E- Solar Power

Non renewable vs. Renewable n n n Environmental Impacts of large scale Scarcity High Emissions (CO 2) Offer/Demand imbalance Cost/benefit uneven Higher prices eventually n n n Alternative Sources Environmental Impacts more manageable Can be replenished following market demand Less pollutant Accessible price

Non renewable vs. Renewable Key Drivers focusing on Renewable Energy: Global Climate Change & Sustainability: n Pressures for reduction of greenhouse gas emissions n More sustainable use of the natural resource base Limitations of conventional resources: n Oil and gas reserves are finite n Uneven distribution of reserves Energy security: n Nations want to produce their own energy n Nations want access to secure sources of energy

Renewable Energy Brazil’s Scenario n n n n n The largest economy in South America 5 th largest country in the World and 5 th most populated 45. 4% of Brazilian Energy Matrix is renewable Renewable resources supply on average 2/3 country's energy requirements 86% of Electrical Generation is renewable (hydro+biomass) 1 st largest ethanol exporter 2 nd largest ethanol producer Pioneer in sugar-cane ethanol technology (plantation/fuel) In 2008 Brazil produced 24. 5 billion litres of ethanol (record) 37. 3% of the world's total ethanol used as fuel (Brazil)

2. Brazil Renewable Energy Structure
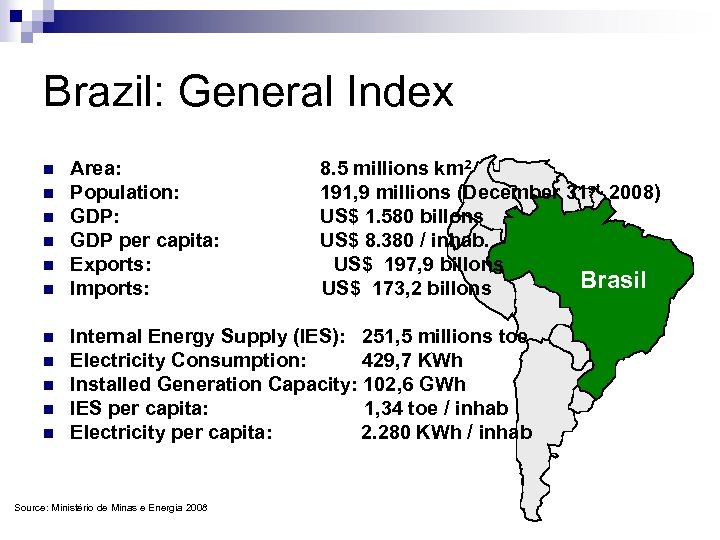
Brazil: General Index n n n Area: Population: GDP per capita: Exports: Imports: 8. 5 millions km 2 191, 9 millions (December 31 st, 2008) US$ 1. 580 billons US$ 8. 380 / inhab. US$ 197, 9 billons Brasil US$ 173, 2 billons Internal Energy Supply (IES): 251, 5 millions toe Electricity Consumption: 429, 7 KWh Installed Generation Capacity: 102, 6 GWh IES per capita: 1, 34 toe / inhab Electricity per capita: 2. 280 KWh / inhab Source: Ministério de Minas e Energia 2008
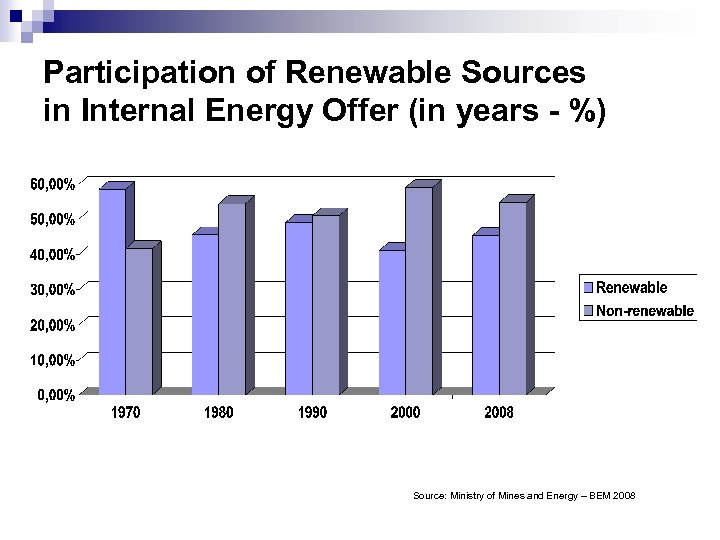
Participation of Renewable Sources in Internal Energy Offer (in years - %) Source: Ministry of Mines and Energy – BEM 2008
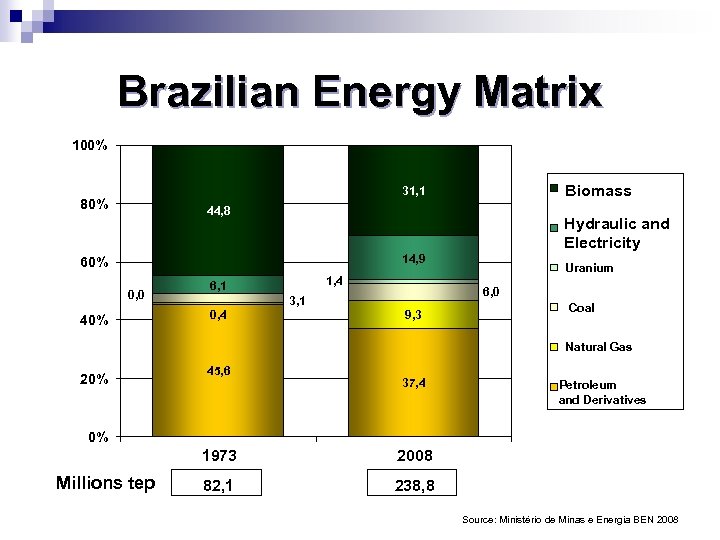
Brazilian Energy Matrix 100% Biomass 31, 1 80% 44, 8 Hydraulic and Electricity 14, 9 60% 0, 0 40% 1, 4 6, 1 6, 0 3, 1 0, 4 Uranium 9, 3 Coal Natural Gas 20% 45, 6 37, 4 Petroleum and Derivatives 0% 1973 Millions tep 2008 82, 1 238, 8 Source: Ministério de Minas e Energia BEN 2008
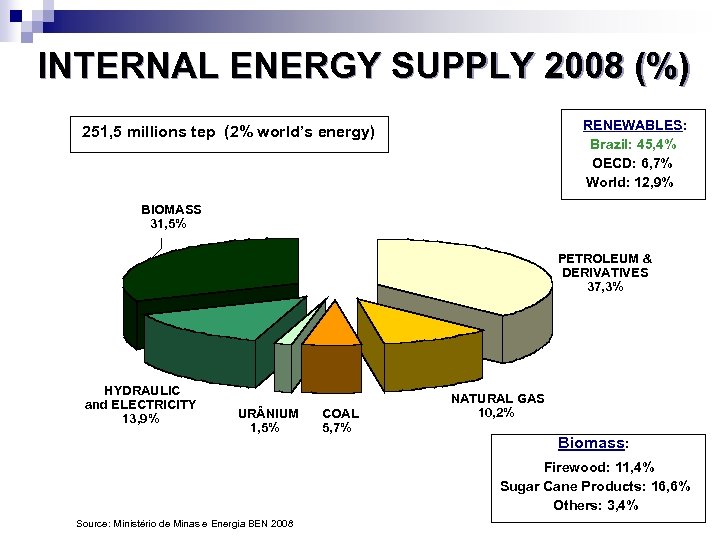
INTERNAL ENERGY SUPPLY 2008 (%) RENEWABLES: Brazil: 45, 4% OECD: 6, 7% World: 12, 9% 251, 5 millions tep (2% world’s energy) BIOMASS 31, 5% PETROLEUM & DERIVATIVES 37, 3% HYDRAULIC and ELECTRICITY 13, 9% UR NIUM 1, 5% COAL 5, 7% NATURAL GAS 10, 2% Biomass: Firewood: 11, 4% Sugar Cane Products: 16, 6% Others: 3, 4% Source: Ministério de Minas e Energia BEN 2008
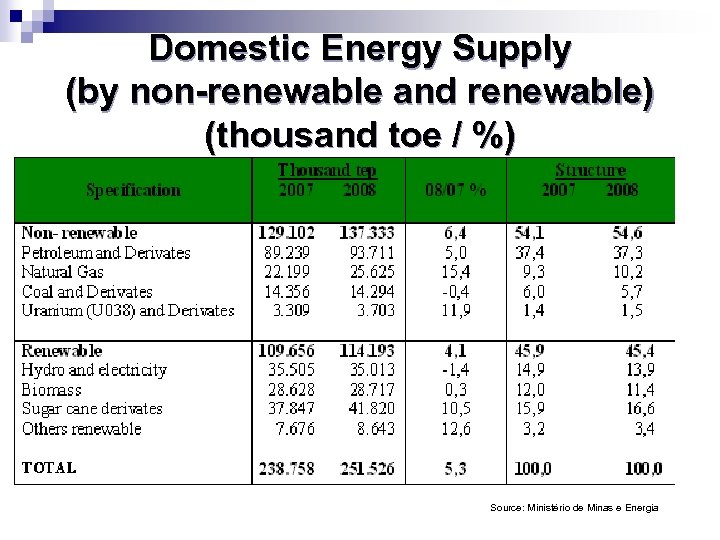
Domestic Energy Supply (by non-renewable and renewable) (thousand toe / %) Source: Ministério de Minas e Energia
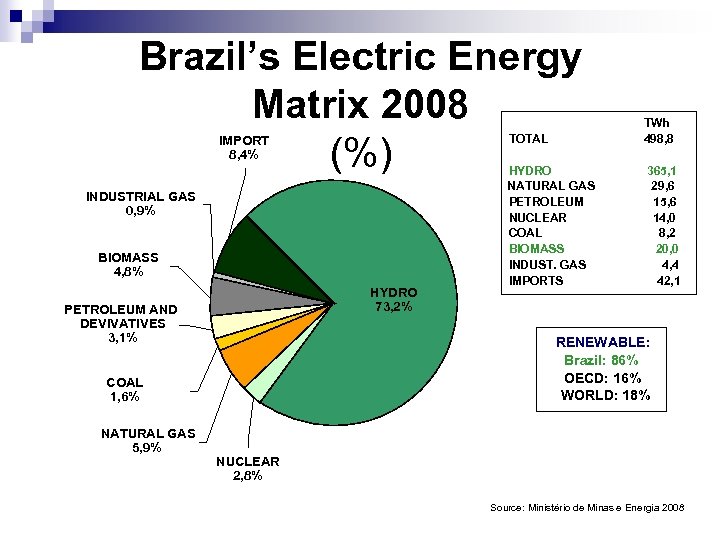
Brazil’s Electric Energy Matrix 2008 (%) TOTAL IMPORT 8, 4% INDUSTRIAL GAS 0, 9% BIOMASS 4, 8% HYDRO 73, 2% PETROLEUM AND DEVIVATIVES 3, 1% HYDRO NATURAL GAS PETROLEUM NUCLEAR COAL BIOMASS INDUST. GAS IMPORTS 365, 1 29, 6 15, 6 14, 0 8, 2 20, 0 4, 4 42, 1 RENEWABLE: Brazil: 86% OECD: 16% WORLD: 18% COAL 1, 6% NATURAL GAS 5, 9% TWh 498, 8 NUCLEAR 2, 8% Source: Ministério de Minas e Energia 2008
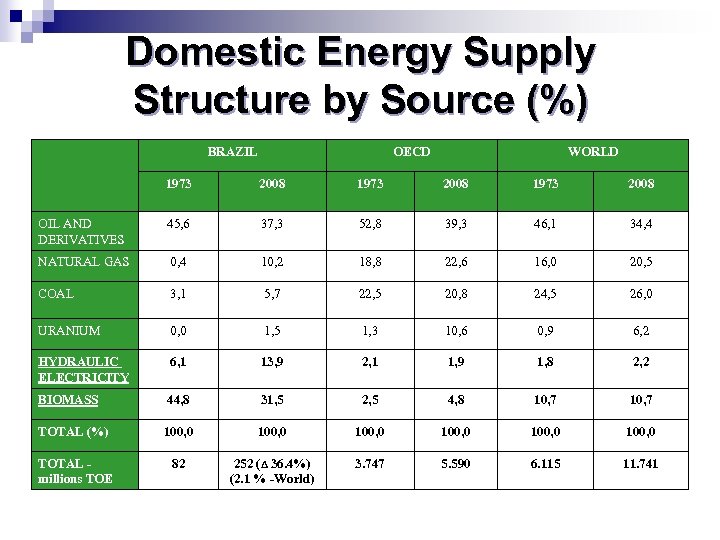
Domestic Energy Supply Structure by Source (%) BRAZIL OECD WORLD 1973 2008 OIL AND DERIVATIVES 45, 6 37, 3 52, 8 39, 3 46, 1 34, 4 NATURAL GAS 0, 4 10, 2 18, 8 22, 6 16, 0 20, 5 COAL 3, 1 5, 7 22, 5 20, 8 24, 5 26, 0 URANIUM 0, 0 1, 5 1, 3 10, 6 0, 9 6, 2 HYDRAULIC ELECTRICITY 6, 1 13, 9 2, 1 1, 9 1, 8 2, 2 BIOMASS 44, 8 31, 5 2, 5 4, 8 10, 7 TOTAL (%) 100, 0 100, 0 TOTAL millions TOE 82 252 (Δ 36. 4%) (2. 1 % -World) 3. 747 5. 590 6. 115 11. 741

3. Government Regulation

Basic Legal Framework Constitution 1988 Article 174 – Renewable Energy n n Exploitation of a renewable energy potential of small capacity does not require an authorization or concession. Larger projects (>30 MW) require government participation, analysis and concession through auction or bidding proccess

Basic Legal Framework n Decree Law No. 230 of 2003, which deals with incentives to develop renewable energy sources. (Feed-in Policy) n (Ethanol Addition) Decree-Law No. 737: Minimum mixture of 20% ethanol with gasoline n National Biodiesel Program, which began in 2005, along with the law n º 11. 097

Renewable Energy Policy n National Fund for R & D of Alternative Renewable Sources (2% net operanting income - Thermoelectrics) n Programs for the generation of decentralized renewable energy or isolated systems n Tax waiver for the import of equipment for generation from renewable sources n Feed-in Tariff : reduces the risk for entrepreneurs, to connect the generators and power distribution n Reduction of 20% in value of the electric bill - solar water heating systems

Draft law 230/2003 (Proj. Lei No 230/2003) n Auction processes and tax incentives: Energy Auctions- Annual Recruitment - 200 megawatts average for each source (wind, biomass and small hydroelectric power plants). ¨ National industry- Local Content Policy (60%) ¨ Thermal power plants- Reduced use of fossil fuels in thermal power and switch to alternative sources in isolated systems. ¨ Hiring - auctions process to hire alternative sources for the areas of isolated systems ¨ Taxation- Exemption from Tax on Industrialized Product (IPI) for vehicles, equipment for deployment of facilities generating alternative renewable energy ¨ Imports: Imports of goods and services for the assembly of power plants will be exempted from contribution ¨ R&D Fund: The National Fund for Research and Development of Alternative Sources of Renewable Energy ¨

Concerned Govermental Organisms n MME - Ministry of Minas and Energy MMA – Ministry of Environment n Eletrobras – Brazilian Power Company n Special Committee on Renewable Energy (House of Representatives) n CNPE - National Energy Policy Council n ANP – National Agency of Petroleum, Natural Gas and Biofuel n IBAMA (MMA) - Brazilian Institute for the Environment and Renewable Natural Resources n n PROINFA - Alternative Energy Sources Incentive Program EPE (MME)– Brazilian Enterprise of Energy Research (BEN Report) n Embrapa (M. Agric) – Brazilian Corporation of Agriculture Research n
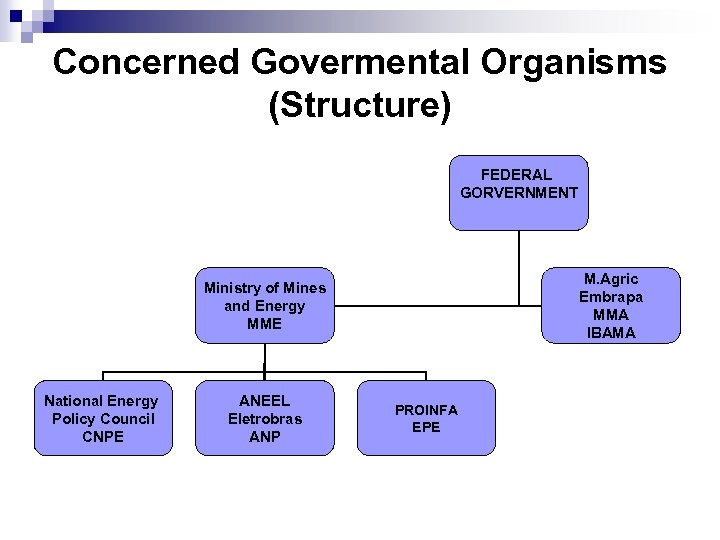
Concerned Govermental Organisms (Structure) FEDERAL GORVERNMENT M. Agric Embrapa MMA IBAMA Ministry of Mines and Energy MME National Energy Policy Council CNPE ANEEL Eletrobras ANP PROINFA EPE

4. Renewable Energy Resources A) Hydroelectric Power plants

Brazilian Hydroelectric System n n n n The hydro generation - 40% of Brazil’s internal Energy Supply 77. 4% of Internal Electricity Offer Potential of the Amazon (2005 – 2020) Total of HEP in Operation: 171 units (all together) Total Installed Capacity: 100, 4 GW Generation of Electricity: 444. 6 TWh (2008) Net imports: 41. 4 TWh (8. 5% eletricity used) Final Consumption: 412. 1 TWh

Top 5 hydroelectric power plants Plants in order of installed power n Hydroelectric Plant of Itaipu ¨ Paraná River, 14. 000 MW - Paraná n Hydroelectric Plant of Belo Monte ¨ Xingu River, 11. 233 MW - Pará (approved) n Hydroelectric Plant of São Luiz do Tapajós ¨ Tapajós River, 8. 381 MW - Pará (projected) n Hydroelectric Plant of Tucuruí ¨ Tocantins River, 8. 370 MW - Pará n Hydroelectric Plant of Jirau – ¨ Madeira River, 3. 450 MW - Rondônia (bidding process)
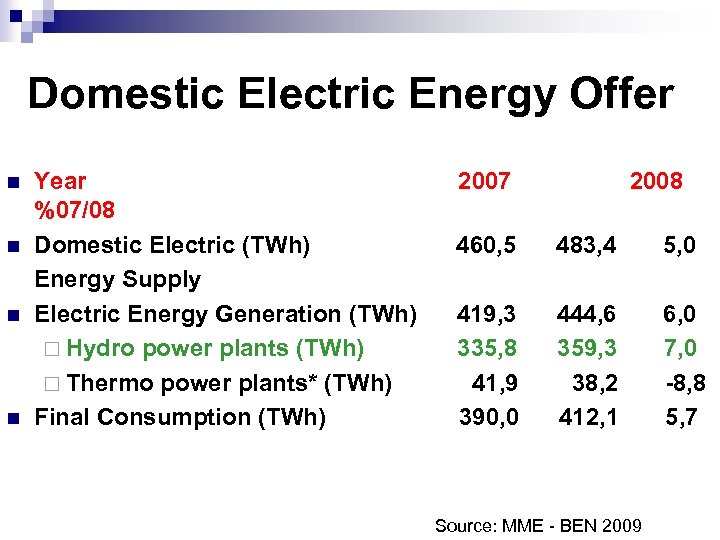
Domestic Electric Energy Offer n n Year %07/08 Domestic Electric (TWh) Energy Supply Electric Energy Generation (TWh) ¨ Hydro power plants (TWh) ¨ Thermo power plants* (TWh) Final Consumption (TWh) 2007 2008 460, 5 483, 4 5, 0 419, 3 335, 8 41, 9 390, 0 444, 6 359, 3 38, 2 412, 1 6, 0 7, 0 -8, 8 5, 7 Source: MME - BEN 2009
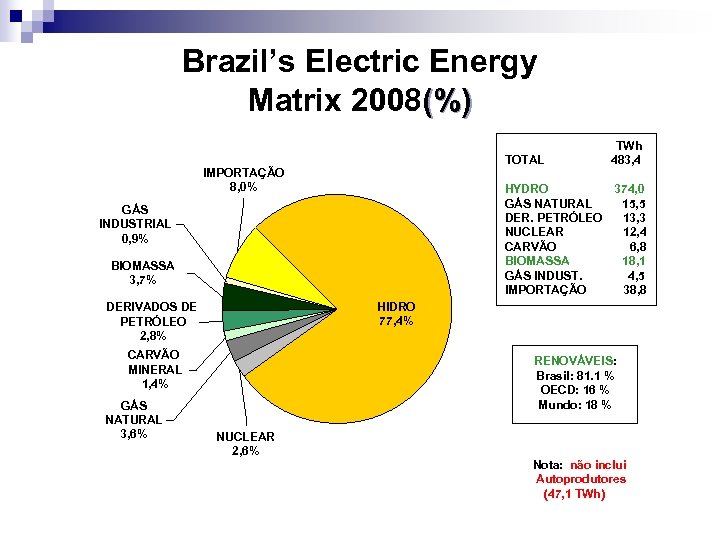
Brazil’s Electric Energy Matrix 2008(%) TOTAL IMPORTAÇÃO 8, 0% HYDRO 374, 0 GÁS NATURAL 15, 5 DER. PETRÓLEO 13, 3 NUCLEAR 12, 4 CARVÃO 6, 8 BIOMASSA 18, 1 GÁS INDUST. 4, 5 IMPORTAÇÃO 38, 8 GÁS INDUSTRIAL 0, 9% BIOMASSA 3, 7% HIDRO 77, 4% DERIVADOS DE PETRÓLEO 2, 8% CARVÃO MINERAL 1, 4% GÁS NATURAL 3, 6% TWh 483, 4 RENOVÁVEIS: Brasil: 81. 1 % OECD: 16 % Mundo: 18 % NUCLEAR 2, 6% Nota: não inclui Autoprodutores (47, 1 TWh)
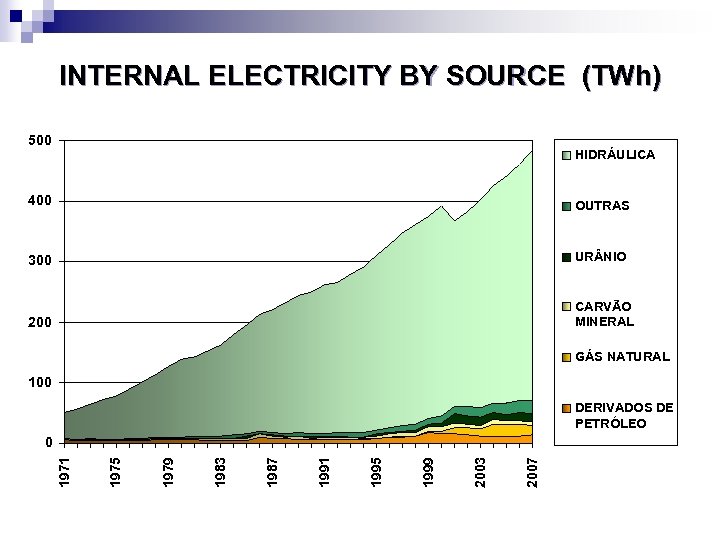
INTERNAL ELECTRICITY BY SOURCE (TWh) 500 HIDRÁULICA 400 OUTRAS 300 UR NIO 200 CARVÃO MINERAL GÁS NATURAL 100 DERIVADOS DE PETRÓLEO 2007 2003 1999 1995 1991 1987 1983 1979 1975 1971 0
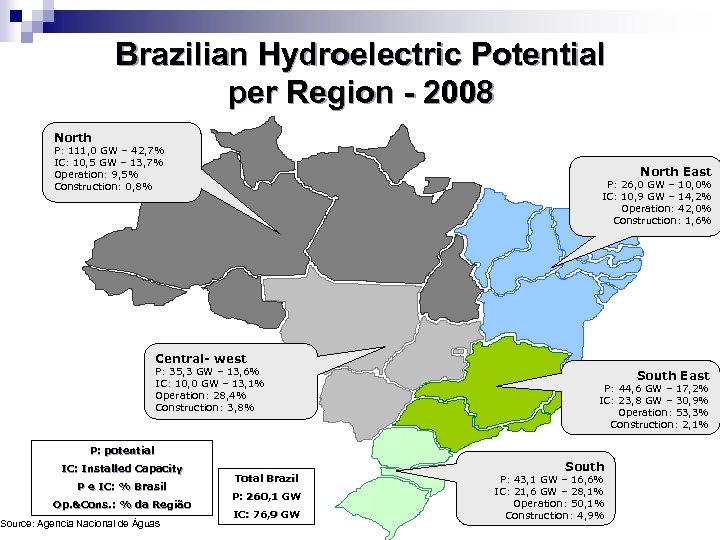
Brazilian Hydroelectric Potential per Region - 2008 North P: 111, 0 GW – 42, 7% IC: 10, 5 GW – 13, 7% Operation: 9, 5% Construction: 0, 8% North East P: 26, 0 GW – 10, 0% IC: 10, 9 GW – 14, 2% Operation: 42, 0% Construction: 1, 6% Central- west P: 35, 3 GW – 13, 6% IC: 10, 0 GW – 13, 1% Operation: 28, 4% Construction: 3, 8% South East P: 44, 6 GW – 17, 2% IC: 23, 8 GW – 30, 9% Operation: 53, 3% Construction: 2, 1% P: potential IC: Installed Capacity P e IC: % Brasil Op. &Cons. : % da Região Source: Agencia Nacional de Águas Total Brazil P: 260, 1 GW IC: 76, 9 GW South P: 43, 1 GW – 16, 6% IC: 21, 6 GW – 28, 1% Operation: 50, 1% Construction: 4, 9%
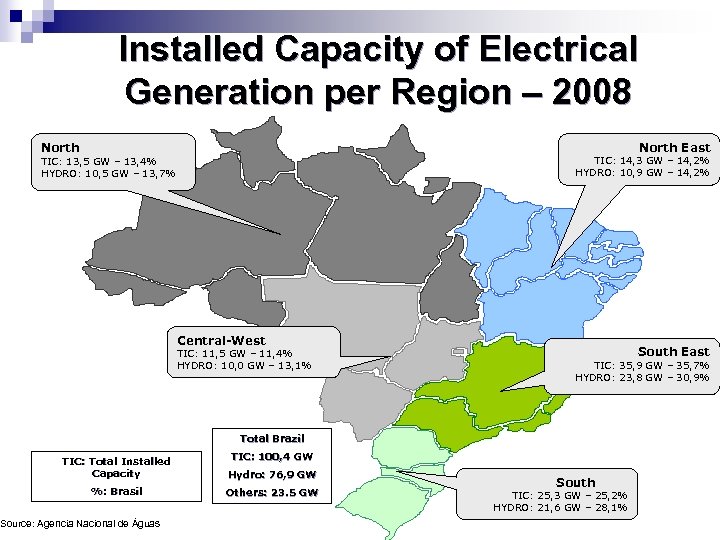
Installed Capacity of Electrical Generation per Region – 2008 North East North TIC: 14, 3 GW – 14, 2% HYDRO: 10, 9 GW – 14, 2% TIC: 13, 5 GW – 13, 4% HYDRO: 10, 5 GW – 13, 7% Central-West TIC: 11, 5 GW – 11, 4% HYDRO: 10, 0 GW – 13, 1% South East TIC: 35, 9 GW – 35, 7% HYDRO: 23, 8 GW – 30, 9% Total Brazil TIC: 100, 4 GW TIC: Total Installed Capacity Hydro: 76, 9 GW Hydro: %: Brasil Others: 23. 5 GW Others: Source: Agencia Nacional de Águas South TIC: 25, 3 GW – 25, 2% HYDRO: 21, 6 GW – 28, 1%
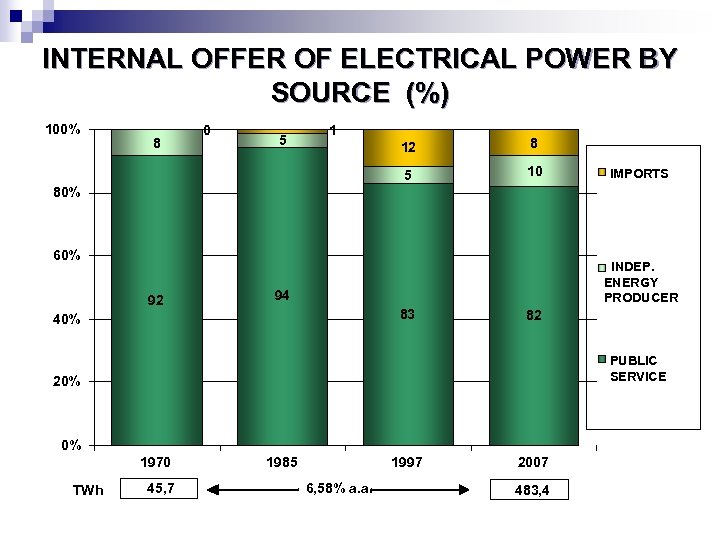
INTERNAL OFFER OF ELECTRICAL POWER BY SOURCE (%) 100% 8 0 5 1 12 8 5 10 IMPORTS 80% 60% 92 INDEP. ENERGY PRODUCER 94 83 40% 82 PUBLIC SERVICE 20% 0% 1970 TWh 45, 7 1985 1997 6, 58% a. a. 2007 483, 4

Investments Opportunities n Acquisition of concession of electricity production through bidding process or auctions (royalties) Source: Agencia Nacional de Petróleo ANP

Risks Investor’s Reality ¨ High investment costs to build a hydroeletric power plant (long-term project) ¨ Fear that the conditions imposed by the government for participation of foreign groups are restrictive to the point of reducing interest of international investments. Source: Valor Econômico, 06/08/09

4. Renewable Natural Resources (B). Biofuels 1 - Brazilian Ethanol

Brazilian Ethanol n PRÓALCOOL: created in 1976 Reasons: Oil Crisis 1972 and 1979 ¨ E 100: Alternative to high oil prices ¨ n Brazil – the world's first sustainable biofuels economy n Brazil - the largest and most successful bio-fuel programs in the world (sugar-cane ethanol) n 1977 - mandatory to blend 20% (E 20) with gasoline (gasohol) – nowadays, blend is 25%(E 25) n Brazil’s vehicle fleet: Dual or flexible-fuel vehicles

Production, Net Export, Consumption, Reserves and Install Capacity n Total ethanol fuel production (2008) : 24, 497 Million liters n Flexible-fuel vehicle fleet: 7. 5 + Million Autos and light trucks only. Brazil as of April 2009 n about 90% of new cars in Brazil run on either ethanol or gasoline (mixed with 25% ethanol). n In 2008, ethanol accounted for more than 52% of fuel consumed by light vehicles in Brazil. Source: MME - BEN 2009
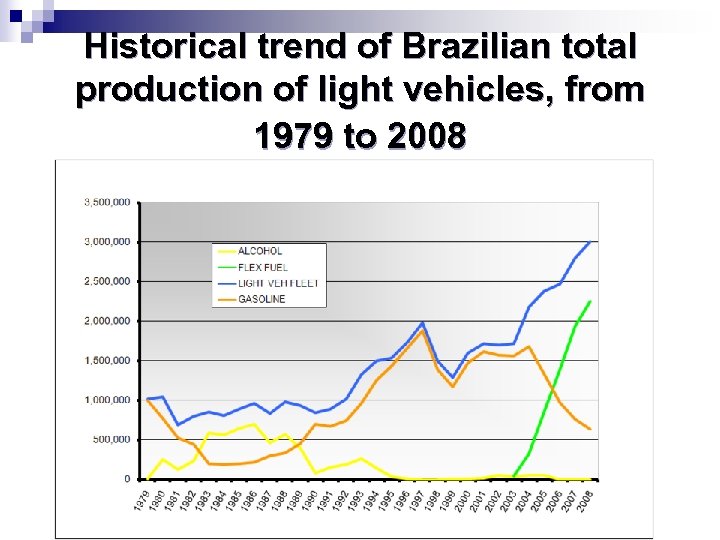
Historical trend of Brazilian total production of light vehicles, from 1979 to 2008
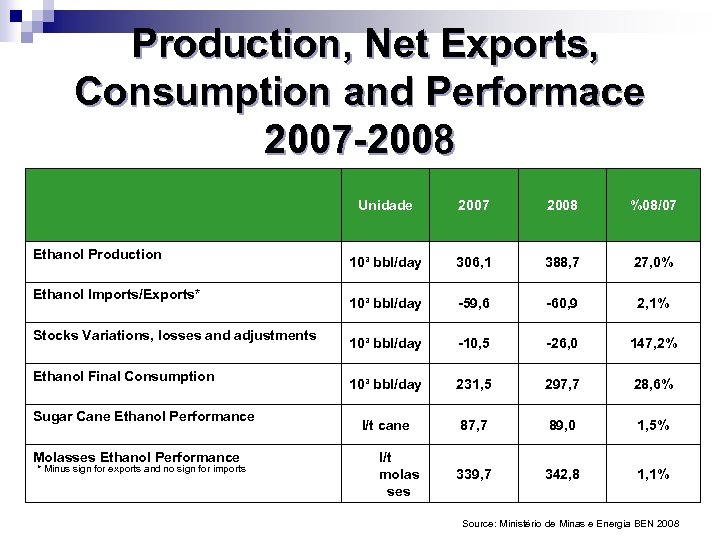
Production, Net Exports, Consumption and Performace 2007 -2008 Unidade Ethanol Production Ethanol Imports/Exports* Stocks Variations, losses and adjustments Ethanol Final Consumption Sugar Cane Ethanol Performance Molasses Ethanol Performance * Minus sign for exports and no sign for imports 2007 2008 %08/07 10³ bbl/day 306, 1 388, 7 27, 0% 10³ bbl/day -59, 6 -60, 9 2, 1% 10³ bbl/day -10, 5 -26, 0 147, 2% 10³ bbl/day 231, 5 297, 7 28, 6% l/t cane 87, 7 89, 0 1, 5% 339, 7 342, 8 1, 1% l/t molas ses Source: Ministério de Minas e Energia BEN 2008
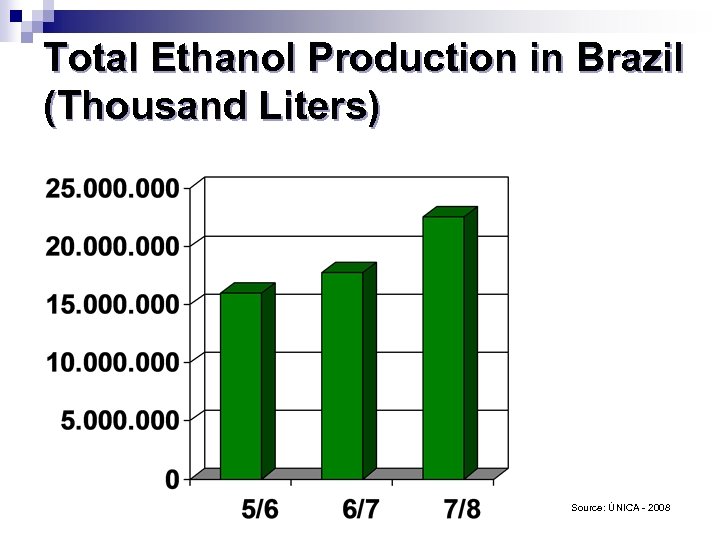
Total Ethanol Production in Brazil (Thousand Liters) Source: ÚNICA - 2008
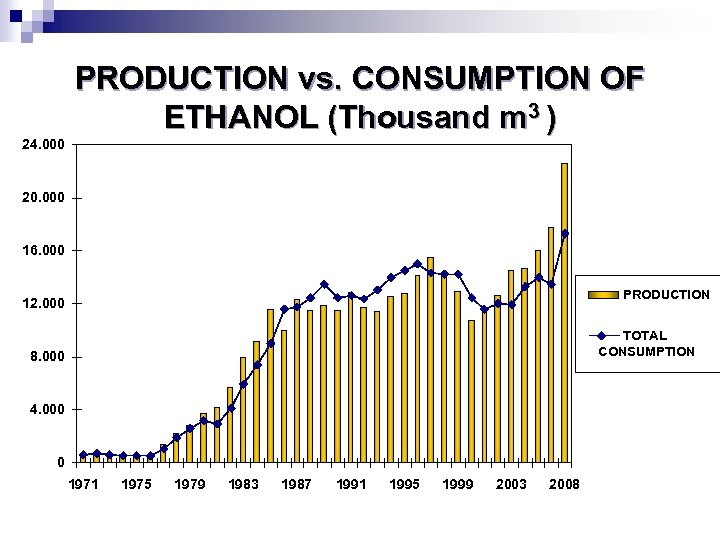
PRODUCTION vs. CONSUMPTION OF ETHANOL (Thousand m 3 ) 24. 000 20. 000 16. 000 PRODUCTION 12. 000 TOTAL CONSUMPTION 8. 000 4. 000 0 1971 1975 1979 1983 1987 1991 1995 1999 2003 2008
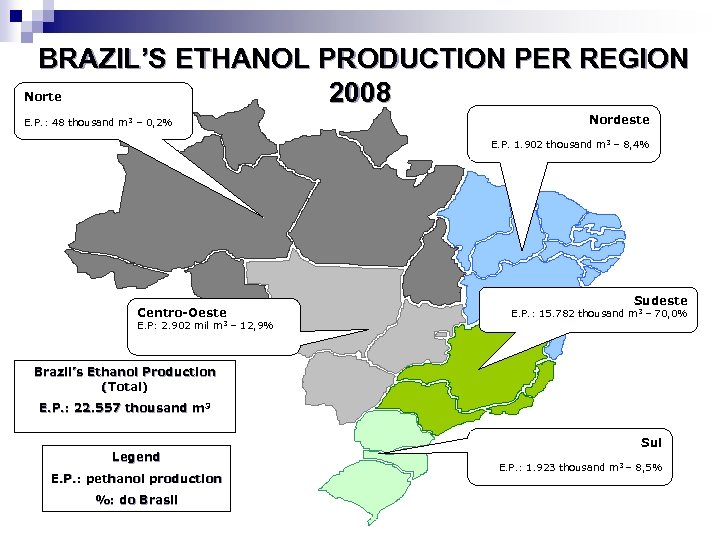
BRAZIL’S ETHANOL PRODUCTION PER REGION Norte 2008 E. P. : 48 thousand m 3 – 0, 2% Nordeste E. P. 1. 902 thousand m 3 – 8, 4% Centro-Oeste E. P: 2. 902 mil m 3 – 12, 9% Sudeste E. P. : 15. 782 thousand m 3 – 70, 0% Brazil’s Ethanol Production (Total) E. P. : 22. 557 thousand m 3 Legend E. P. : pethanol production %: do Brasil Sul E. P. : 1. 923 thousand m 3 – 8, 5%
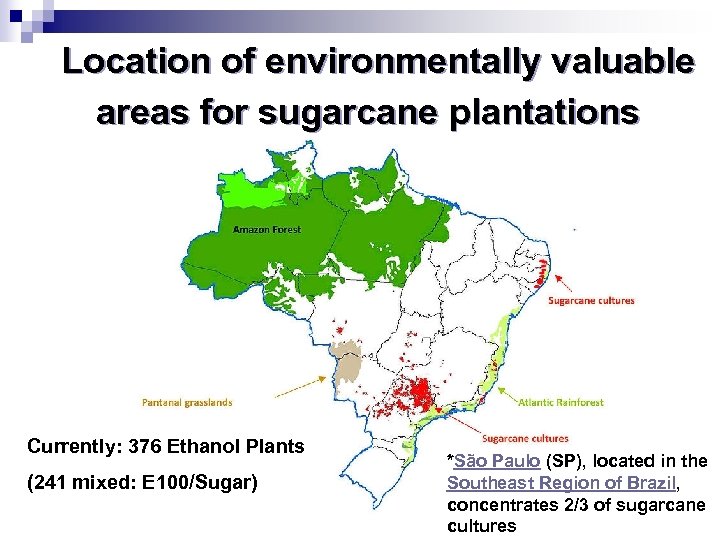
Location of environmentally valuable areas for sugarcane plantations Currently: 376 Ethanol Plants (241 mixed: E 100/Sugar) *São Paulo (SP), located in the Southeast Region of Brazil, concentrates 2/3 of sugarcane cultures

4. Renewable Natural Resources (B)- Biofuels 2 - Biodiesel

Brazil´s Biodiesel Production 2008 Production: 840 million liters ¨ Biodiesel B 2 type (1 Billion liters project until 2012) n 212 Biodiesel Plants (128 in construction) ¨ n 93% - Petrobras Biodiesel Plants ANP – Biodiesel Auction: Nov. 2009 ¨ (B 5 type for 2013, now mandatory in 2010)

Biodiesel Law No 11097/2005
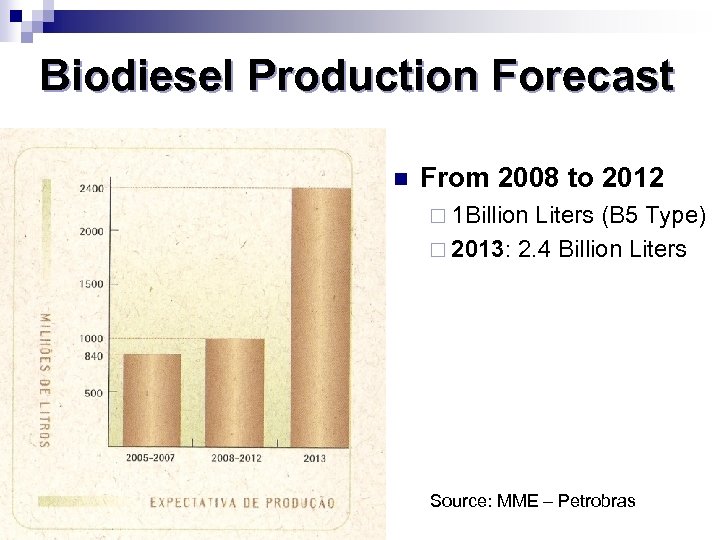
Biodiesel Production Forecast n From 2008 to 2012 ¨ 1 Billion Liters (B 5 Type) ¨ 2013: 2. 4 Billion Liters Source: MME – Petrobras
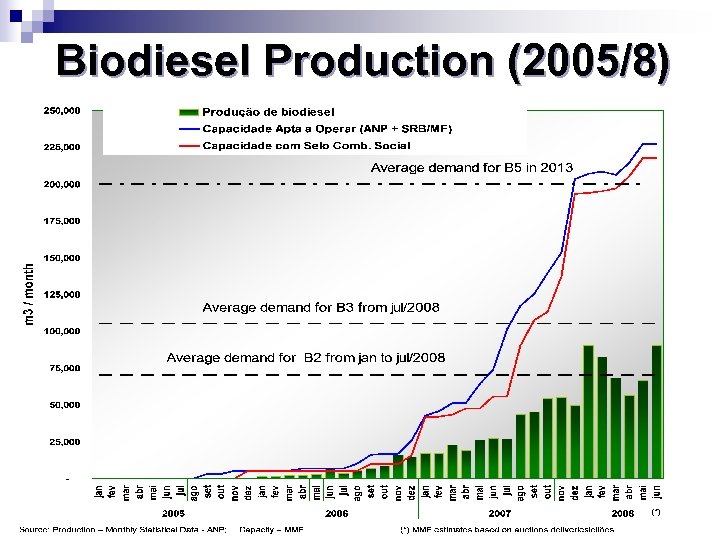
Biodiesel Production (2005/8)
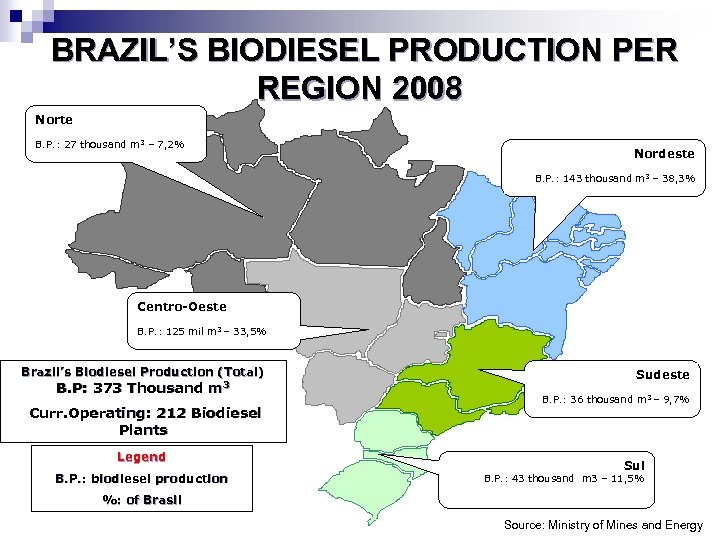
BRAZIL’S BIODIESEL PRODUCTION PER REGION 2008 Norte B. P. : 27 thousand m 3 – 7, 2% Nordeste B. P. : 143 thousand m 3 – 38, 3% Centro-Oeste B. P. : 125 mil m 3 – 33, 5% Brazil’s Biodiesel Production (Total) B. P: 373 Thousand m 3 Curr. Operating: 212 Biodiesel Plants Legend B. P. : biodiesel production Sudeste B. P. : 36 thousand m 3 – 9, 7% Sul B. P. : 43 thousand m 3 – 11, 5% %: of Brasil Source: Ministry of Mines and Energy

4. Renewable Natural Resources (C) Biomass Power
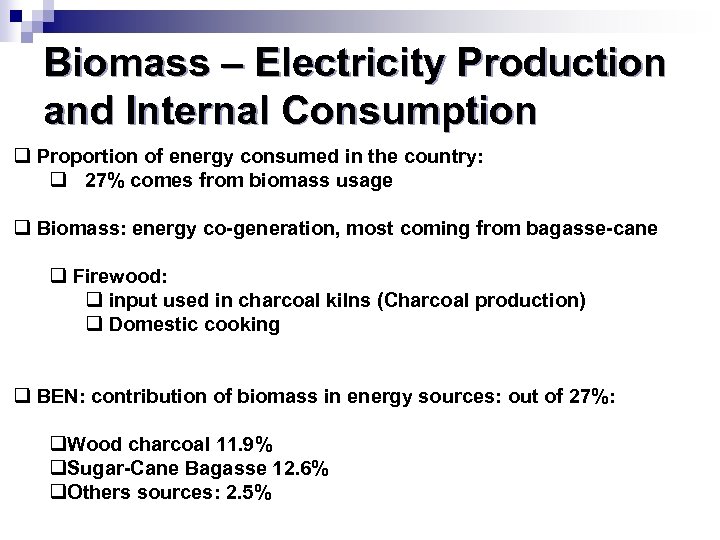
Biomass – Electricity Production and Internal Consumption q Proportion of energy consumed in the country: q 27% comes from biomass usage q Biomass: energy co-generation, most coming from bagasse-cane q Firewood: q input used in charcoal kilns (Charcoal production) q Domestic cooking q BEN: contribution of biomass in energy sources: out of 27%: q. Wood charcoal 11. 9% q. Sugar-Cane Bagasse 12. 6% q. Others sources: 2. 5%
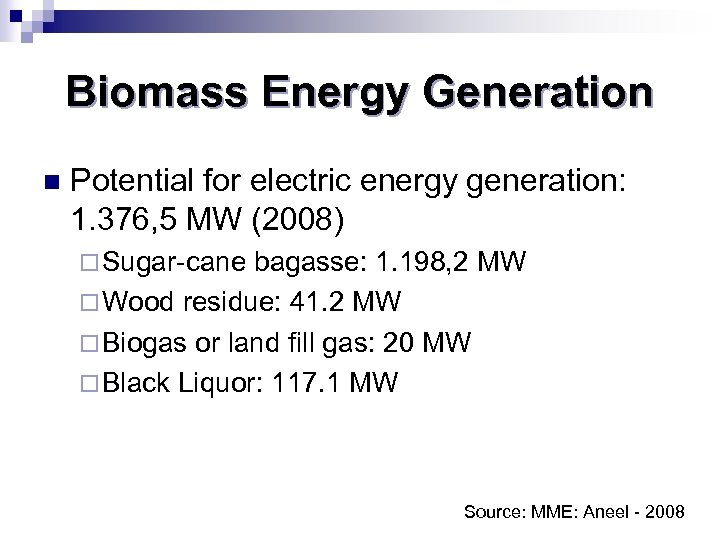
Biomass Energy Generation n Potential for electric energy generation: 1. 376, 5 MW (2008) ¨ Sugar-cane bagasse: 1. 198, 2 MW ¨ Wood residue: 41. 2 MW ¨ Biogas or land fill gas: 20 MW ¨ Black Liquor: 117. 1 MW Source: MME: Aneel - 2008

Brazil’s Biomass Production 2008 n Total of Residues: 245. 300. 000 tons ¨ Cane Bagasse: 84. 300. 000 tons ¨ Rice Husk: 10. 000 tons ¨ Agricultural residue: 90. 000 tons ¨ Wood Industry: 60. 000 tons ¨ Coconut Shell: 1. 000 tons ¨ Cashew Nut: 900. 000 tons n Biomass Origen: Certified Commercial Forests

Investments Opportunities n Industrial process with production units with forest biomass waste for power cogeneration of energy n (thermo power plants)

4. Renewable Natural Resources D) Wind Power

Brazil’s Wind Power n Brazil (throughout AL & Caribbean) ¨ Greatest potential for wind power generation Potencial production capacity: 247 MW, (208 MW installed in 2006) n Wind power: 0, 2% Electric Energy Matrix n

Electricity Production and Internal Consumption n Installed Capacity: 247 MW (208 units in 2006) n Main Wind Power Plants: ¨ parque eólico de Osório (Osório - RS) 75 Towers n Installed Capacity: 150 MW ( enough energy to supply a town of 700 thousand people (Biggest Wind Farm in South America ¨ Parque eólico de Rio do Fogo (Rio do Fogo – RN) n Installed Capacity: 49, 3 Mega Watts (MW), n Brazil´s 2 nd biggest – 62 Towers (Stablish. : June, 2006)
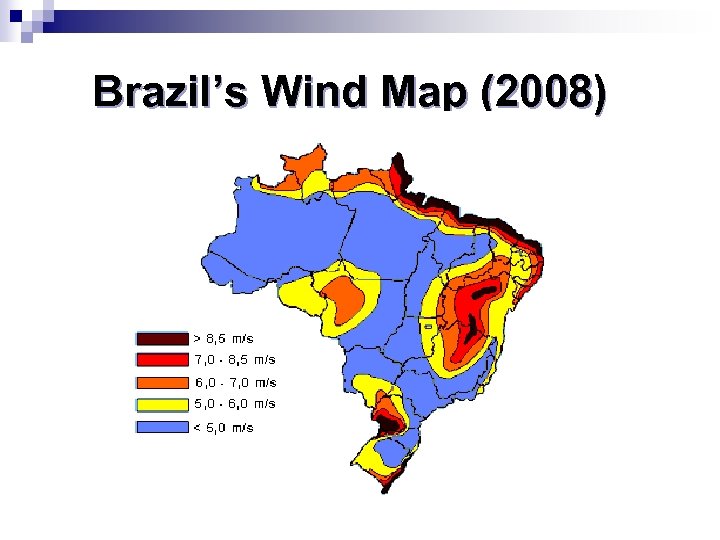
Brazil’s Wind Map (2008)
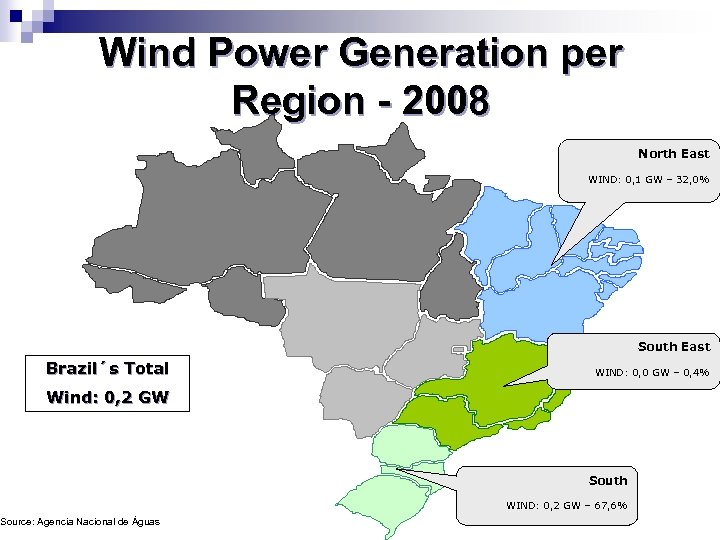
Wind Power Generation per Region - 2008 North East WIND: 0, 1 GW – 32, 0% South East Brazil´s Total WIND: 0, 0 GW – 0, 4% Wind: 0, 2 GW Source: Agencia Nacional de Águas South WIND: 0, 2 GW – 67, 6%
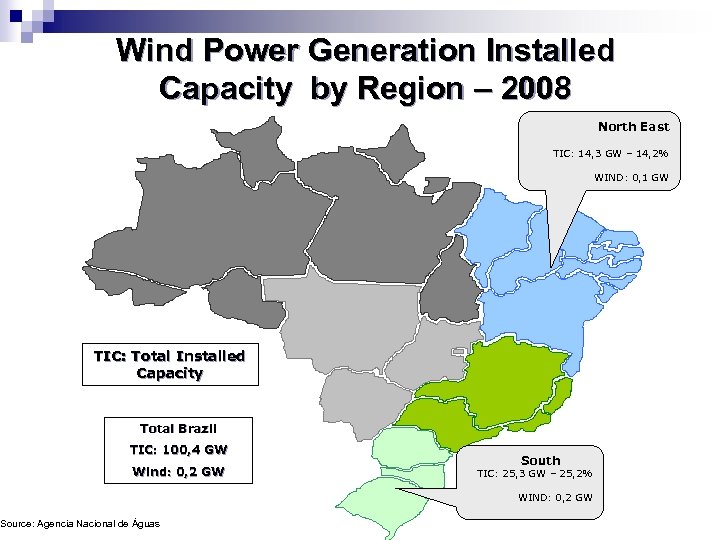
Wind Power Generation Installed Capacity by Region – 2008 North East TIC: 14, 3 GW – 14, 2% WIND: 0, 1 GW TIC: Total Installed Capacity Total Brazil TIC: 100, 4 GW Wind: 0, 2 GW Source: Agencia Nacional de Águas South TIC: 25, 3 GW – 25, 2% WIND: 0, 2 GW

4. Renewable Natural Resources E) Solar Power

Brazil’s Solar Power Usage n n n Industrial production is mostly oriented in the segment of solar heating systems for domestic use. Optimization of Electric Energy Usage O draft-law 230/2003: reduction of 20% in value of the electric bill of residential and commercial customers who install solar water heating system. n Moreover, from 2014 consumers who do not have the equipment, will have an increase of 20% on their bills.

Basic Legal Framework n Law 14. 459, of July 3, 2007 regulated by Dec. N º 49, 148 of 21 January 2008 ¨ Provides for the installation of water heating system by solar energy in new buildings n It is planned to install system for heating water by solar energy in residential, government and industrial facilities, when it is needed (state of SP)
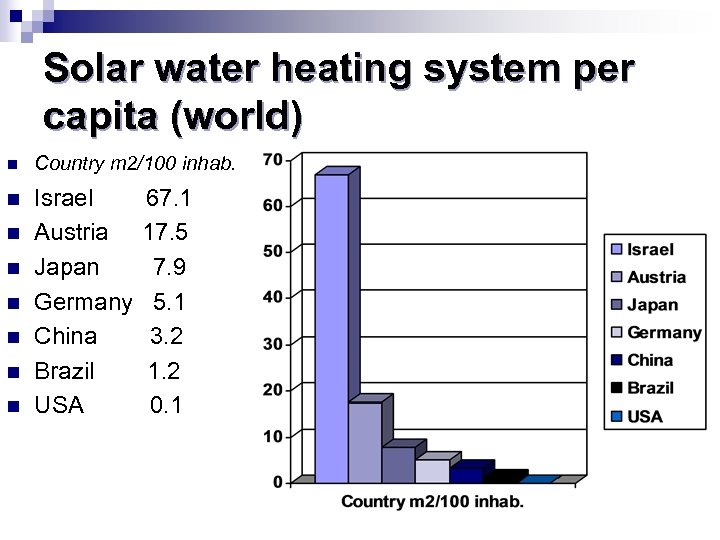
Solar water heating system per capita (world) n Country m 2/100 inhab. n Israel Austria Japan Germany China Brazil USA n n n 67. 1 17. 5 7. 9 5. 1 3. 2 1. 2 0. 1

Investment Opportunities in Brazil
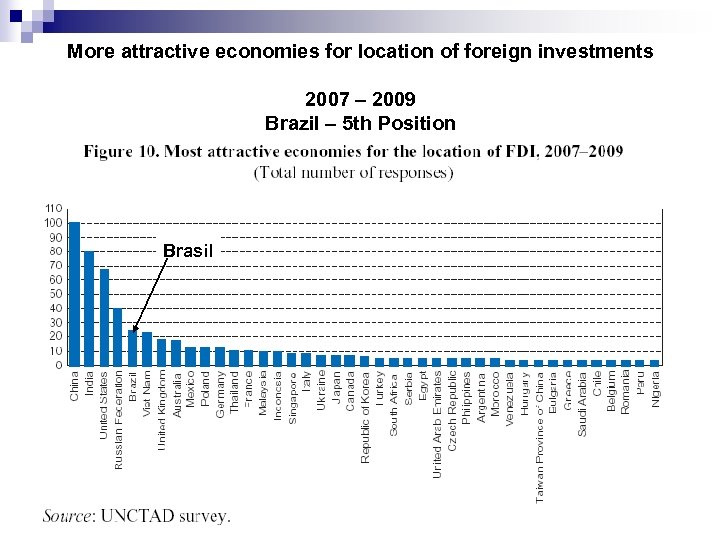
More attractive economies for location of foreign investments 2007 – 2009 Brazil – 5 th Position Brasil

감사합니다
06027e0dd2c8efdb44f026d858290d21.ppt