7fb59e3c959e1b7780b315e26a516d3e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

Renewable Energy Agricultural Multipurpose System for Farmers RAMse. S (EU-FP 6 Contract No 032447) Fadi Karam Lebanese Agricultural Research Institute Department of Irrigation and Agro-Meteorology (http: //www. lari. gov. lb) Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Forum, 7 June 2010, Amman, Jordan

A proposed methodology to determine the minimum horsepower requirements needed for the RAMse. S-MPV (At Lebanon Test Site)
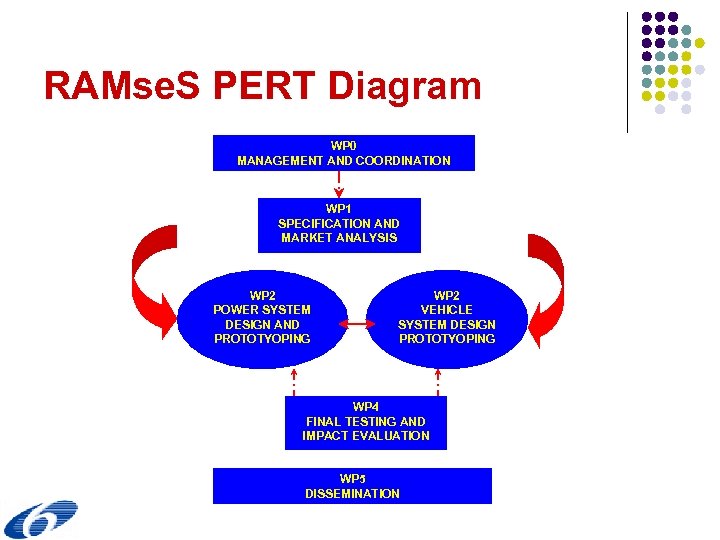
RAMse. S PERT Diagram WP 0 MANAGEMENT AND COORDINATION WP 1 SPECIFICATION AND MARKET ANALYSIS WP 2 POWER SYSTEM DESIGN AND PROTOTYOPING WP 2 VEHICLE SYSTEM DESIGN PROTOTYOPING WP 4 FINAL TESTING AND IMPACT EVALUATION WP 5 DISSEMINATION

WP 4 FINAL TESTING AND IMPACT EVALUATION Objectives l l l Installation and testing of the developed solar-power generation system integrated to the multi-purposes vehicle at the EU test site; Transfer of the solar-power generation system integrated to the multi -purposes vehicle and testing at the MPC test site; Analyze the mechanical and energetic efficiency of the installed integrated systems at the MPC test site; Determine the economic impact of the project at the MPC test site; Determine the social impact of the project at the MPC test site; Determine the agricultural and environmental impact of the project in MPC sites.

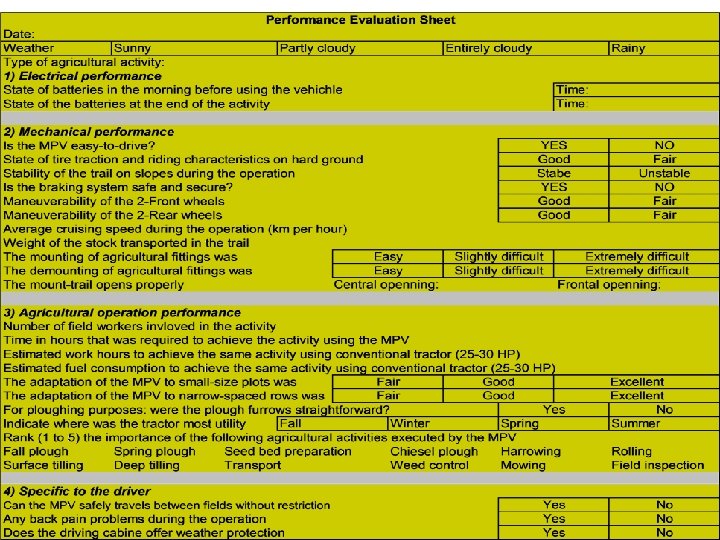
The assessment procedure l Test of the system performance; l Analyze socio-economic, agricultural and environmental effects of the project on the local rural community; l Realization of cost-effectiveness of the project results (including the reduction in the electricity and energy bills).

Can solar tractors replace the traditional diesel tractors? l l Working in agriculture may bothered by the noise and smelly exhaust tractors produce; Dealing with toxic, explosive fuel, grease, oil and the constant maintenance may also be a hassle; Degraded air quality, climate change, and global conflict over remaining oil supplies are the results of petroleum dependence; In addition, bigger machines and centralized corporate monoculture are causing a loss of biodiversity and traditional farming skills which threaten future food supplies and our very existence.
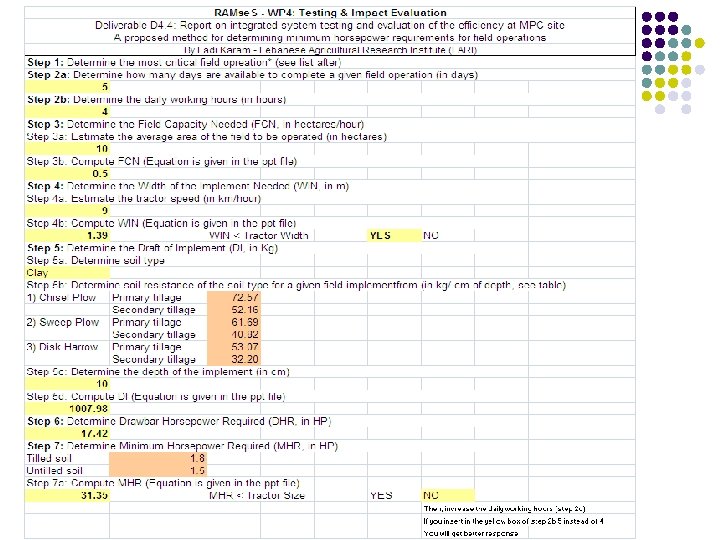
RAMse. S - WP 4: Testing & Impact Evaluation Deliverable D 4. 4: Report on integrated system testing and evaluation of the efficiency at MPC site A suggested procedure for determining the minimum horsepower requirements needed for the MPV to implement field operation at Lebanon Test Site
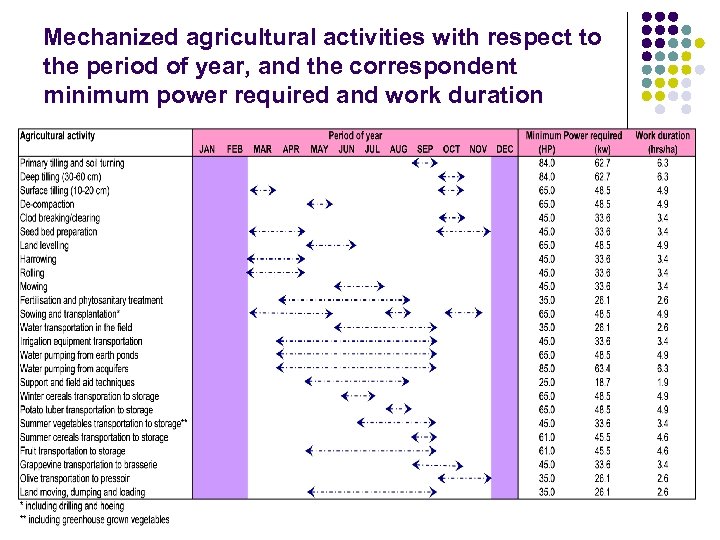
Mechanized agricultural activities with respect to the period of year, and the correspondent minimum power required and work duration

The Procedure

Step 1. Determine the most critical field operation requiring implements with a high draft: l By determining the critical high draft tillage operation, it would become practical to the tractor users to decide if the tractor can achieve or not the required field operation. For example, if soil surface is hard for plowing, it would become easier in this case to disk prior to planting than to plow (surface or deep plow).

Step 2. From past agricultural experiences, determine the available time for a given field operation. l For example, if there are 20 days of calendar time per year for primary tillage, during a season span, 5 days are estimated to be available for field work, with 4 working hours per day (a sub-total of 20 working hours per season, or 80 working hours per year). This would help in accounting for the diesel consumption that a traditional PTO tractor with the same HP size of the MPV would have per year. It also helps in accounting for the savings from the non-diesel consumption of the MPV.

Step 3. Determine the Field Capacity Needed (FCN, in ha/hour). For example: The Monastery of Saints Sarkis & Achkout has a total cultivated land of 10. 0 ha (100 mostly cropped with vineyard. If there are 20 days of calendar time per year for during which the average working hours per day FCN is equal to: Bakhos in dounoms), fall tillage, is 4, then,
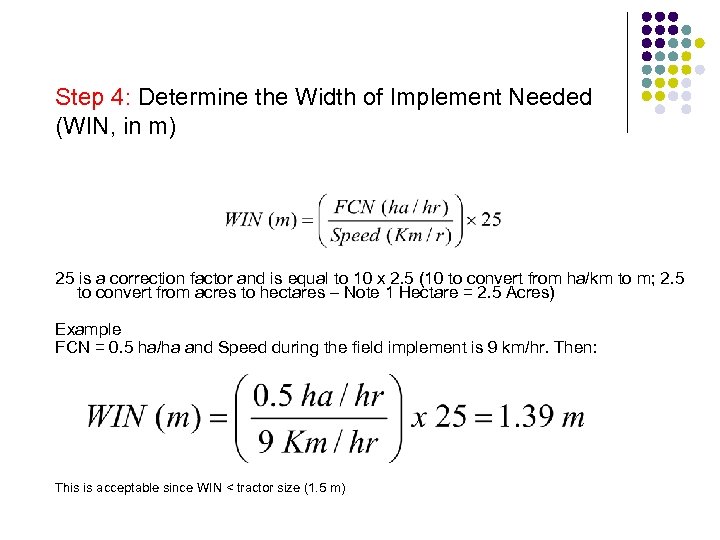
Step 4: Determine the Width of Implement Needed (WIN, in m) 25 is a correction factor and is equal to 10 x 2. 5 (10 to convert from ha/km to m; 2. 5 to convert from acres to hectares – Note 1 Hectare = 2. 5 Acres) Example FCN = 0. 5 ha/ha and Speed during the field implement is 9 km/hr. Then: This is acceptable since WIN < tractor size (1. 5 m)
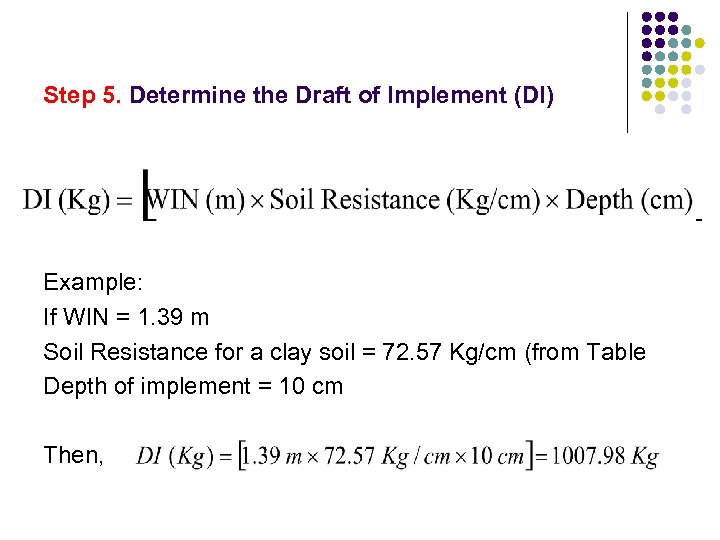
Step 5. Determine the Draft of Implement (DI) Example: If WIN = 1. 39 m Soil Resistance for a clay soil = 72. 57 Kg/cm (from Table Depth of implement = 10 cm Then,

Step 6: Determine Drawbar Horsepower Required (DHR, in HP) 375/0. 72 is a conversion factor from American Unit System (Pounds for DI and MPH for Speed) into SI Units. Example If DI = 1007. 98 Kg Speed = 9 Km/hr Then,
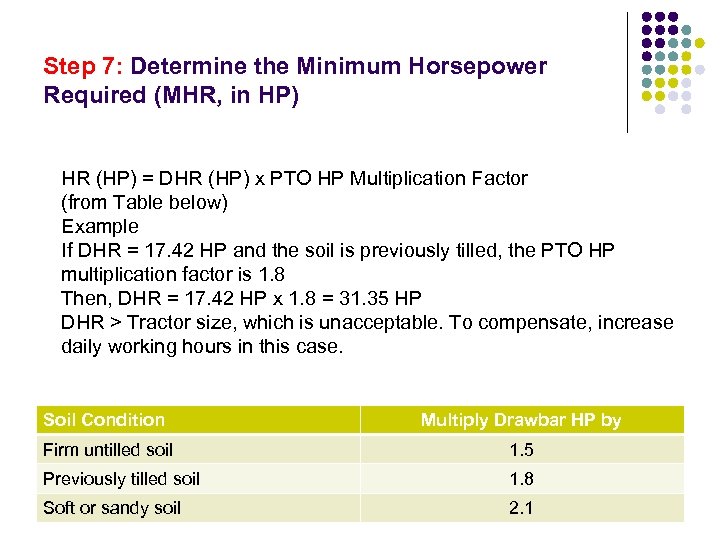
Step 7: Determine the Minimum Horsepower Required (MHR, in HP) HR (HP) = DHR (HP) x PTO HP Multiplication Factor (from Table below) Example If DHR = 17. 42 HP and the soil is previously tilled, the PTO HP multiplication factor is 1. 8 Then, DHR = 17. 42 HP x 1. 8 = 31. 35 HP DHR > Tractor size, which is unacceptable. To compensate, increase daily working hours in this case. Soil Condition Multiply Drawbar HP by Firm untilled soil 1. 5 Previously tilled soil 1. 8 Soft or sandy soil 2. 1

Field implementation Hoeing Preparing holes for new plantations Courtesy, ALMEE, 2010

Field implementation Hoeing Increasing the number of workers in field activities (Lebanon Test Site, Feb-Mar 2010) Courtesy, ALMEE, 2010

Field implementation Phyto-sanitary treatments (late spring summer, Lebanon Test Site) Courtesy, ALMEE, 2010

As a consequence There was an expansion of vineyard cultivated plots in the test site Courtesy, ALMEE, 2010

Field implementation Mowing EU Test Site (Italy) Courtesy, DEART, 2008

Field implementation Mowing herbs and weeds in applegrown orchards (EU Test Site, Italy) Courtesy, DEART, 2008

Field implements Potato sowing (EU Test Site, Poland) Courtesy, IBMER, 2008

Promoting solar powered vehicle The system will make agriculture farm independent from conventional sources of energy. The system is reliable and easy in use. Thank you
7fb59e3c959e1b7780b315e26a516d3e.ppt