5cea9f51d512aa1366933be56db4df2b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Renal Denervation for Resistant Hypertension & FIM Evaluation of a New, Multi-Electrode RF System for Renal Denervation (Medtronic) CRT February 26 th 2013, Washington DC Martin T Rothman MB, Ch. B, FACC FESC FRCP Vice President Medical Affairs Coronary & Renal Denervation Medtronic Inc. Professor of Interventional Cardiology Barts Health London, UK
Renal Denervation for Resistant Hypertension & FIM Evaluation of a New, Multi-Electrode RF System for Renal Denervation (Medtronic) CRT February 26 th 2013, Washington DC Martin T Rothman MB, Ch. B, FACC FESC FRCP Vice President Medical Affairs Coronary & Renal Denervation Medtronic Inc. Professor of Interventional Cardiology Barts Health London, UK
 Martin T. Rothman, MD, MB, Ch. B I/we have no real or apparent conflicts of interest to report.
Martin T. Rothman, MD, MB, Ch. B I/we have no real or apparent conflicts of interest to report.
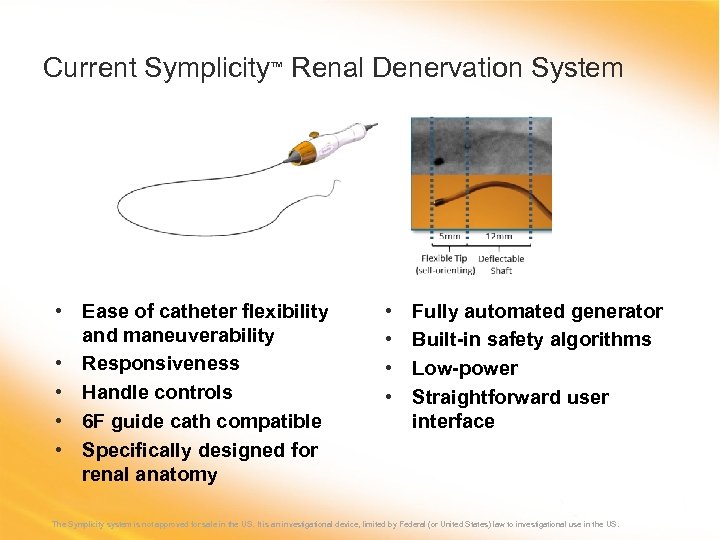 Current Symplicity™ Renal Denervation System • Ease of catheter flexibility and maneuverability • Responsiveness • Handle controls • 6 F guide cath compatible • Specifically designed for renal anatomy • • Fully automated generator Built-in safety algorithms Low-power Straightforward user interface The Symplicity system is not approved for sale in the US. It is an investigational device, limited by Federal (or United States) law to investigational use in the US.
Current Symplicity™ Renal Denervation System • Ease of catheter flexibility and maneuverability • Responsiveness • Handle controls • 6 F guide cath compatible • Specifically designed for renal anatomy • • Fully automated generator Built-in safety algorithms Low-power Straightforward user interface The Symplicity system is not approved for sale in the US. It is an investigational device, limited by Federal (or United States) law to investigational use in the US.
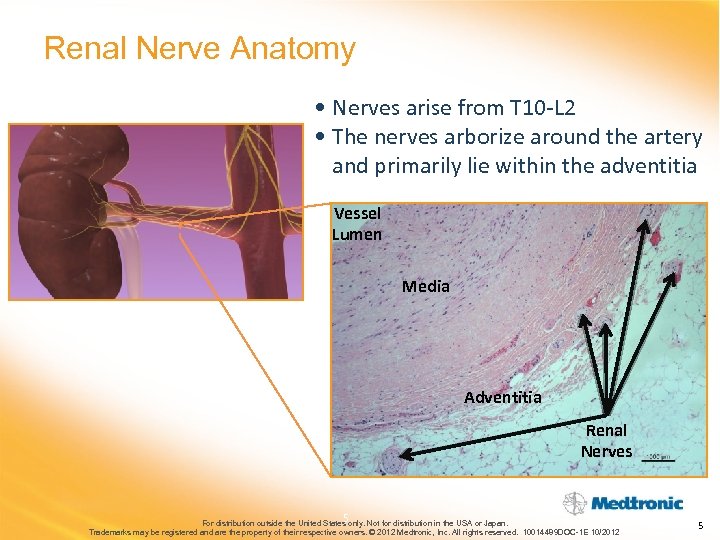 Renal Nerve Anatomy • Nerves arise from T 10 -L 2 • The nerves arborize around the artery and primarily lie within the adventitia Vessel Lumen Media Adventitia Renal Nerves 5 For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 5
Renal Nerve Anatomy • Nerves arise from T 10 -L 2 • The nerves arborize around the artery and primarily lie within the adventitia Vessel Lumen Media Adventitia Renal Nerves 5 For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 5
 Symplicity HTN-1 Lancet. 2009; 373: 1275 -1281 Hypertension. 2011; 57: 911 -917. Initial Cohort – Reported in the Lancet, 2009: -First-in-man, non-randomized -Cohort of 45 patients with resistant HTN (SBP ≥ 160 mm. Hg on ≥ 3 anti-HTN drugs, including a diuretic; e. GFR ≥ 45 m. L/min) - 12 -month data Expanded Cohort – This Report (Symplicity HTN-1): -Expanded cohort of patients (n=153) -24 and 36 -month follow-up Symplicity HTN-1 Investigators. Hypertension. 2011; 57: 911 -917. Schlaich M – TCT 2012 For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 7
Symplicity HTN-1 Lancet. 2009; 373: 1275 -1281 Hypertension. 2011; 57: 911 -917. Initial Cohort – Reported in the Lancet, 2009: -First-in-man, non-randomized -Cohort of 45 patients with resistant HTN (SBP ≥ 160 mm. Hg on ≥ 3 anti-HTN drugs, including a diuretic; e. GFR ≥ 45 m. L/min) - 12 -month data Expanded Cohort – This Report (Symplicity HTN-1): -Expanded cohort of patients (n=153) -24 and 36 -month follow-up Symplicity HTN-1 Investigators. Hypertension. 2011; 57: 911 -917. Schlaich M – TCT 2012 For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 7
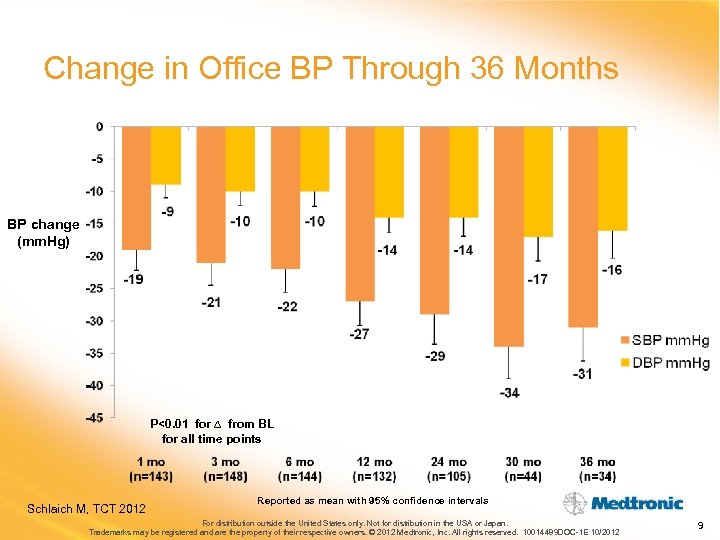 Change in Office BP Through 36 Months BP change (mm. Hg) P<0. 01 for ∆ from BL for all time points Schlaich M, TCT 2012 Reported as mean with 95% confidence intervals For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 9
Change in Office BP Through 36 Months BP change (mm. Hg) P<0. 01 for ∆ from BL for all time points Schlaich M, TCT 2012 Reported as mean with 95% confidence intervals For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 9
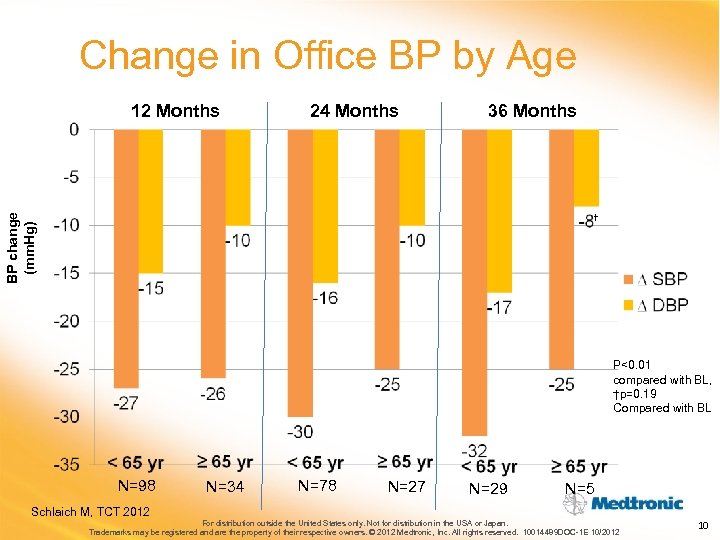 Change in Office BP by Age 12 Months 24 Months 36 Months BP change (mm. Hg) † P<0. 01 compared with BL, †p=0. 19 Compared with BL N=98 Schlaich M, TCT 2012 N=34 N=78 N=27 N=29 N=5 For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 10
Change in Office BP by Age 12 Months 24 Months 36 Months BP change (mm. Hg) † P<0. 01 compared with BL, †p=0. 19 Compared with BL N=98 Schlaich M, TCT 2012 N=34 N=78 N=27 N=29 N=5 For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 10
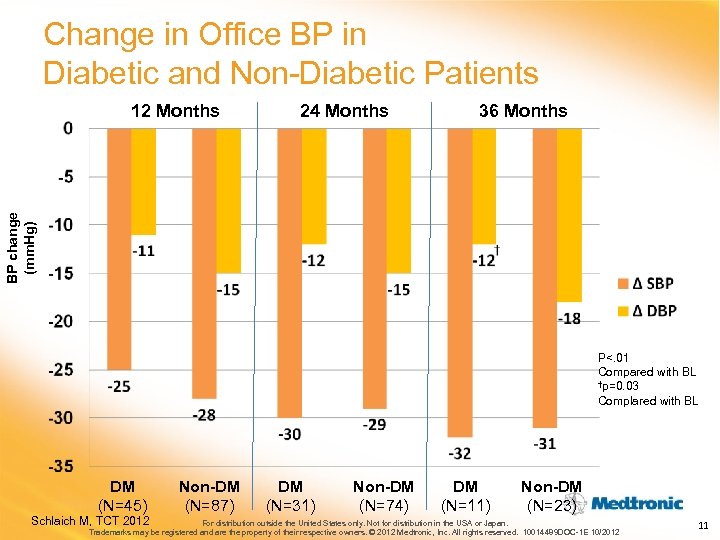 Change in Office BP in Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Patients 24 Months 36 Months BP change (mm. Hg) 12 Months P<. 01 Compared with BL †p=0. 03 Complared with BL DM (N=45) Schlaich M, TCT 2012 Non-DM (N=87) DM (N=31) Non-DM (N=74) DM (N=11) Non-DM (N=23) For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 11
Change in Office BP in Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Patients 24 Months 36 Months BP change (mm. Hg) 12 Months P<. 01 Compared with BL †p=0. 03 Complared with BL DM (N=45) Schlaich M, TCT 2012 Non-DM (N=87) DM (N=31) Non-DM (N=74) DM (N=11) Non-DM (N=23) For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 11
 Symplicity HTN-2 Lancet. 2010; 376: 1903 -1909. • • • Purpose: To demonstrate the effectiveness of catheter-based renal denervation for reducing blood pressure in patients with uncontrolled hypertension in a prospective, randomized, controlled, clinical trial Patients: 106 patients randomized 1: 1 to treatment with renal denervation vs. control Clinical Sites: 24 centers in Europe, Australia, & New Zealand (67% were designated hypertension centers of excellence) Symplicity HTN-2 Investigators. Lancet. 2010; 376: 1903 -1909. For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 12
Symplicity HTN-2 Lancet. 2010; 376: 1903 -1909. • • • Purpose: To demonstrate the effectiveness of catheter-based renal denervation for reducing blood pressure in patients with uncontrolled hypertension in a prospective, randomized, controlled, clinical trial Patients: 106 patients randomized 1: 1 to treatment with renal denervation vs. control Clinical Sites: 24 centers in Europe, Australia, & New Zealand (67% were designated hypertension centers of excellence) Symplicity HTN-2 Investigators. Lancet. 2010; 376: 1903 -1909. For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 12
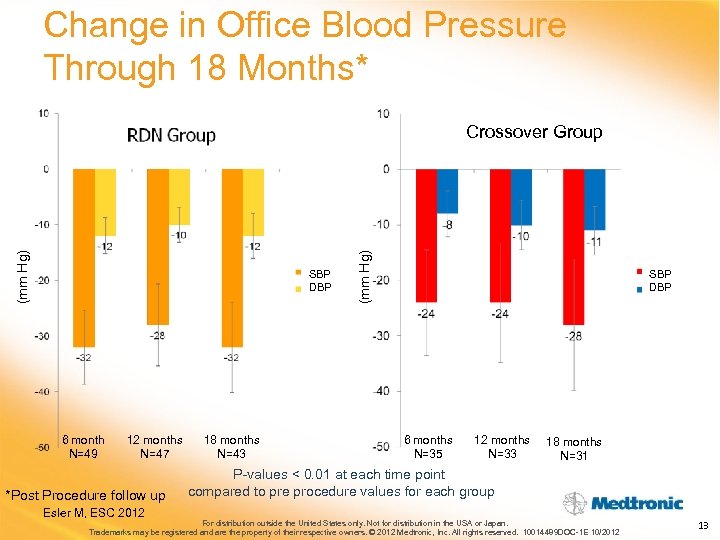 Change in Office Blood Pressure Through 18 Months* SBP DBP 6 month N=49 12 months N=47 *Post Procedure follow up Esler M, ESC 2012 18 months N=43 (mm Hg) Crossover Group SBP DBP 6 months N=35 12 months N=33 18 months N=31 P-values < 0. 01 at each time point compared to pre procedure values for each group For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 13
Change in Office Blood Pressure Through 18 Months* SBP DBP 6 month N=49 12 months N=47 *Post Procedure follow up Esler M, ESC 2012 18 months N=43 (mm Hg) Crossover Group SBP DBP 6 months N=35 12 months N=33 18 months N=31 P-values < 0. 01 at each time point compared to pre procedure values for each group For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 13
 Objectives: § Assess procedural and long term safety of renal denervation § Evaluate effectiveness of renal denervation on clinical outcomes § § Establish procedural benchmarking & physician practice patterns Evaluate the effect of geographical variations in patients and procedural characteristics on clinical outcomes § Perform Quality of Life analysis Scope: First enrollment February 2 nd, 2012 • Over 200 sites world wide; at least 5000 patients • Prospective, single-arm, open-label, non-interventional registry • In accordance with Instructions For Use • Geographies with commercial availability of Medtronic Symplicity Renal Denervation System For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 14
Objectives: § Assess procedural and long term safety of renal denervation § Evaluate effectiveness of renal denervation on clinical outcomes § § Establish procedural benchmarking & physician practice patterns Evaluate the effect of geographical variations in patients and procedural characteristics on clinical outcomes § Perform Quality of Life analysis Scope: First enrollment February 2 nd, 2012 • Over 200 sites world wide; at least 5000 patients • Prospective, single-arm, open-label, non-interventional registry • In accordance with Instructions For Use • Geographies with commercial availability of Medtronic Symplicity Renal Denervation System For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 14
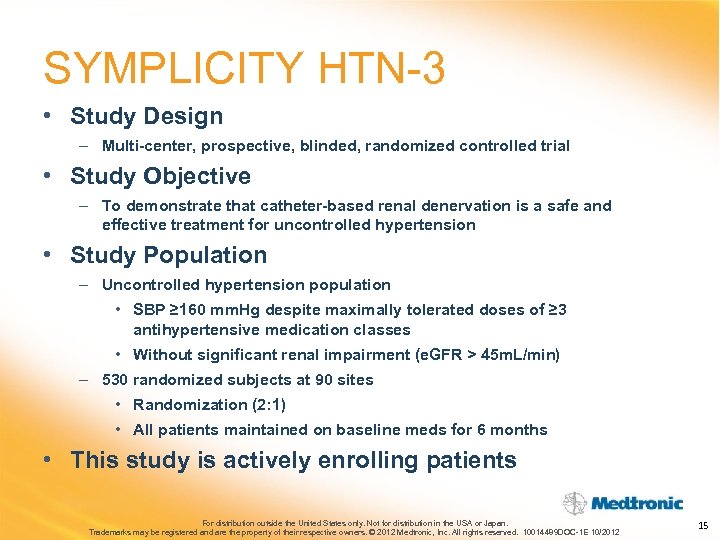 SYMPLICITY HTN-3 • Study Design – Multi-center, prospective, blinded, randomized controlled trial • Study Objective – To demonstrate that catheter-based renal denervation is a safe and effective treatment for uncontrolled hypertension • Study Population – Uncontrolled hypertension population • SBP ≥ 160 mm. Hg despite maximally tolerated doses of ≥ 3 antihypertensive medication classes • Without significant renal impairment (e. GFR > 45 m. L/min) – 530 randomized subjects at 90 sites • Randomization (2: 1) • All patients maintained on baseline meds for 6 months • This study is actively enrolling patients For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 15
SYMPLICITY HTN-3 • Study Design – Multi-center, prospective, blinded, randomized controlled trial • Study Objective – To demonstrate that catheter-based renal denervation is a safe and effective treatment for uncontrolled hypertension • Study Population – Uncontrolled hypertension population • SBP ≥ 160 mm. Hg despite maximally tolerated doses of ≥ 3 antihypertensive medication classes • Without significant renal impairment (e. GFR > 45 m. L/min) – 530 randomized subjects at 90 sites • Randomization (2: 1) • All patients maintained on baseline meds for 6 months • This study is actively enrolling patients For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 15
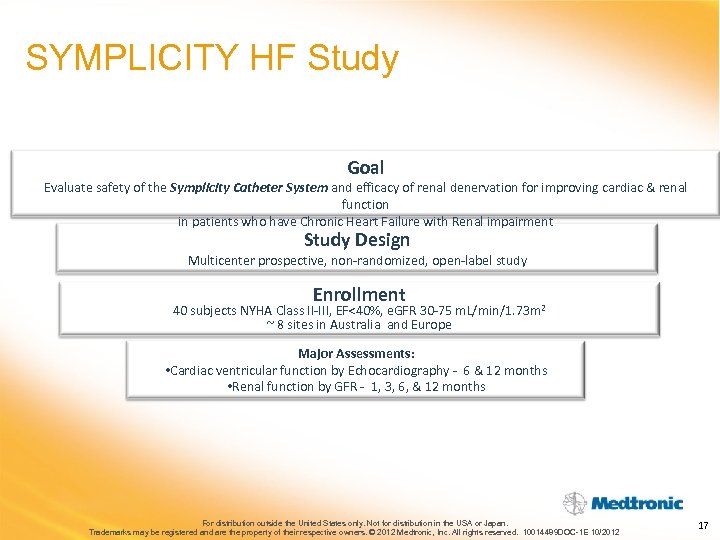 SYMPLICITY HF Study Goal Evaluate safety of the Symplicity Catheter System and efficacy of renal denervation for improving cardiac & renal function in patients who have Chronic Heart Failure with Renal impairment Study Design Multicenter prospective, non-randomized, open-label study Enrollment 40 subjects NYHA Class II-III, EF<40%, e. GFR 30 -75 m. L/min/1. 73 m 2 ~ 8 sites in Australia and Europe Major Assessments: • Cardiac ventricular function by Echocardiography - 6 & 12 months • Renal function by GFR - 1, 3, 6, & 12 months For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 17
SYMPLICITY HF Study Goal Evaluate safety of the Symplicity Catheter System and efficacy of renal denervation for improving cardiac & renal function in patients who have Chronic Heart Failure with Renal impairment Study Design Multicenter prospective, non-randomized, open-label study Enrollment 40 subjects NYHA Class II-III, EF<40%, e. GFR 30 -75 m. L/min/1. 73 m 2 ~ 8 sites in Australia and Europe Major Assessments: • Cardiac ventricular function by Echocardiography - 6 & 12 months • Renal function by GFR - 1, 3, 6, & 12 months For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 17
 New Multi-Electrode System Design Goals One size fits all Reduced Ablation Time Multi. Electrode 6 F Guide Compatible Monorail Delivery Non-Occlusive Vessel Conformability Electrodes
New Multi-Electrode System Design Goals One size fits all Reduced Ablation Time Multi. Electrode 6 F Guide Compatible Monorail Delivery Non-Occlusive Vessel Conformability Electrodes
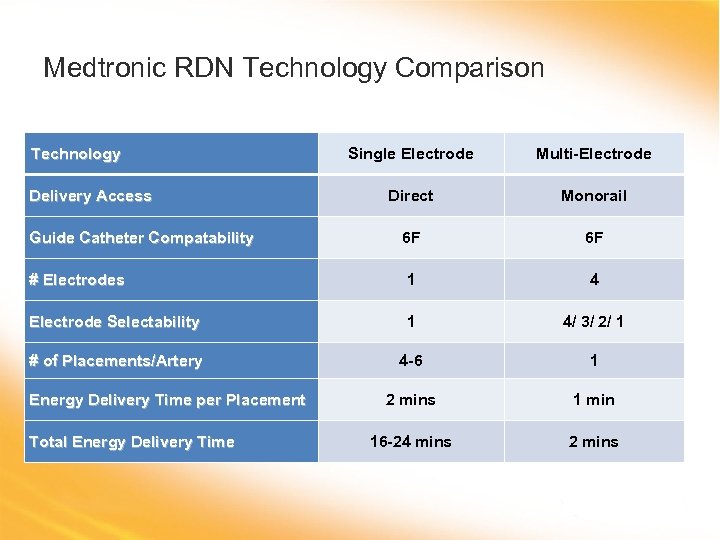 Medtronic RDN Technology Comparison Technology Single Electrode Multi-Electrode Direct Monorail 6 F 6 F # Electrodes 1 4 Electrode Selectability 1 4/ 3/ 2/ 1 # of Placements/Artery 4 -6 1 2 mins 1 min 16 -24 mins 2 mins Delivery Access Guide Catheter Compatability Energy Delivery Time per Placement Total Energy Delivery Time
Medtronic RDN Technology Comparison Technology Single Electrode Multi-Electrode Direct Monorail 6 F 6 F # Electrodes 1 4 Electrode Selectability 1 4/ 3/ 2/ 1 # of Placements/Artery 4 -6 1 2 mins 1 min 16 -24 mins 2 mins Delivery Access Guide Catheter Compatability Energy Delivery Time per Placement Total Energy Delivery Time
 Martin T Rothman FACC FESC FRCP Vice President Medical Affairs Coronary & Renal Denervation Medtronic Inc. Conflict of Interest: Full time employee of Medtronic, Inc. Medtronic Equity Holder Professor of Interventional Cardiology Barts Health London, UK Presentation on behalf of: Prof. Robert Whitbourn MBBS, BMed. Sc, BSc(Hons), MD • Director, Cardiac Cath Lab & Coronary Intervention • Director, The Cardiovascular Research Centre St. Vincent’s Hospital, Melbourne, Australia • Assoc, Prof, University of Melbourne • Professor, Australian Catholic University © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners
Martin T Rothman FACC FESC FRCP Vice President Medical Affairs Coronary & Renal Denervation Medtronic Inc. Conflict of Interest: Full time employee of Medtronic, Inc. Medtronic Equity Holder Professor of Interventional Cardiology Barts Health London, UK Presentation on behalf of: Prof. Robert Whitbourn MBBS, BMed. Sc, BSc(Hons), MD • Director, Cardiac Cath Lab & Coronary Intervention • Director, The Cardiovascular Research Centre St. Vincent’s Hospital, Melbourne, Australia • Assoc, Prof, University of Melbourne • Professor, Australian Catholic University © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners
 Multi-Electrode System FIM: First 9 patients September 24 th & 26 th 2012, St Vincent’s Hospital, Melbourne, Australia PI: Robert Whitbourn • No pre-selection on basis of anatomy • No on-table exclusion on basis of anatomy after first angiography • Stable catheter positions • Measurable parameters pre- and peri-treatment in line with goals • All treatment times = 1 min (8 ablations completed in 2 min/patient) • No observed spasm • No renal blood flow disturbance • Procedures completed successfully
Multi-Electrode System FIM: First 9 patients September 24 th & 26 th 2012, St Vincent’s Hospital, Melbourne, Australia PI: Robert Whitbourn • No pre-selection on basis of anatomy • No on-table exclusion on basis of anatomy after first angiography • Stable catheter positions • Measurable parameters pre- and peri-treatment in line with goals • All treatment times = 1 min (8 ablations completed in 2 min/patient) • No observed spasm • No renal blood flow disturbance • Procedures completed successfully
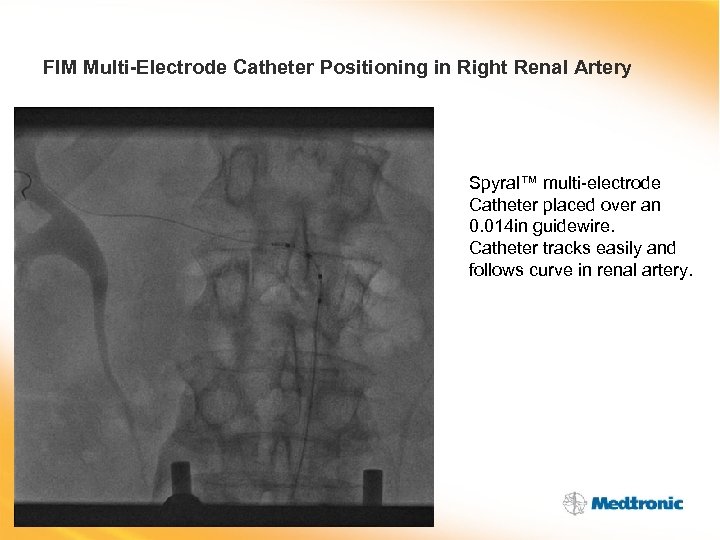 FIM Multi-Electrode Catheter Positioning in Right Renal Artery Spyral™ multi-electrode Catheter placed over an 0. 014 in guidewire. Catheter tracks easily and follows curve in renal artery.
FIM Multi-Electrode Catheter Positioning in Right Renal Artery Spyral™ multi-electrode Catheter placed over an 0. 014 in guidewire. Catheter tracks easily and follows curve in renal artery.
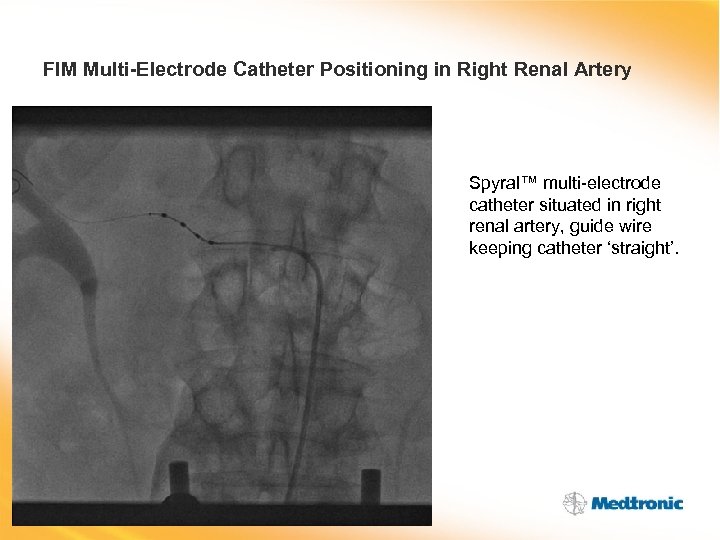 FIM Multi-Electrode Catheter Positioning in Right Renal Artery Spyral™ multi-electrode catheter situated in right renal artery, guide wire keeping catheter ‘straight’.
FIM Multi-Electrode Catheter Positioning in Right Renal Artery Spyral™ multi-electrode catheter situated in right renal artery, guide wire keeping catheter ‘straight’.
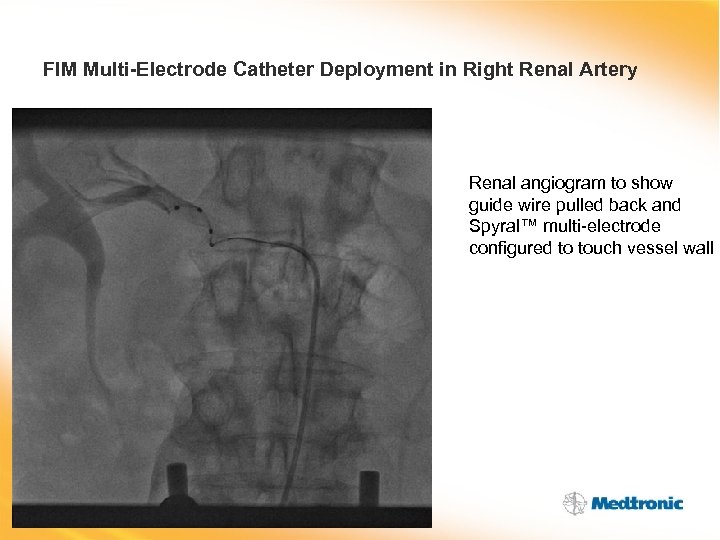 FIM Multi-Electrode Catheter Deployment in Right Renal Artery Renal angiogram to show guide wire pulled back and Spyral™ multi-electrode configured to touch vessel wall
FIM Multi-Electrode Catheter Deployment in Right Renal Artery Renal angiogram to show guide wire pulled back and Spyral™ multi-electrode configured to touch vessel wall
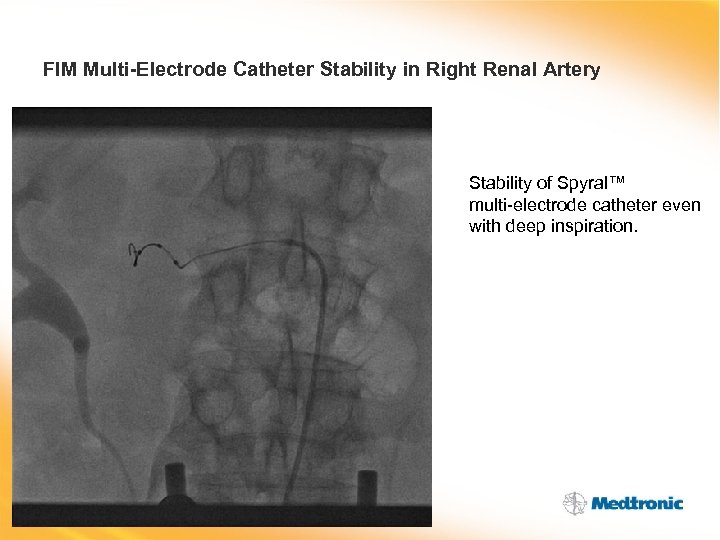 FIM Multi-Electrode Catheter Stability in Right Renal Artery Stability of Spyral™ multi-electrode catheter even with deep inspiration.
FIM Multi-Electrode Catheter Stability in Right Renal Artery Stability of Spyral™ multi-electrode catheter even with deep inspiration.
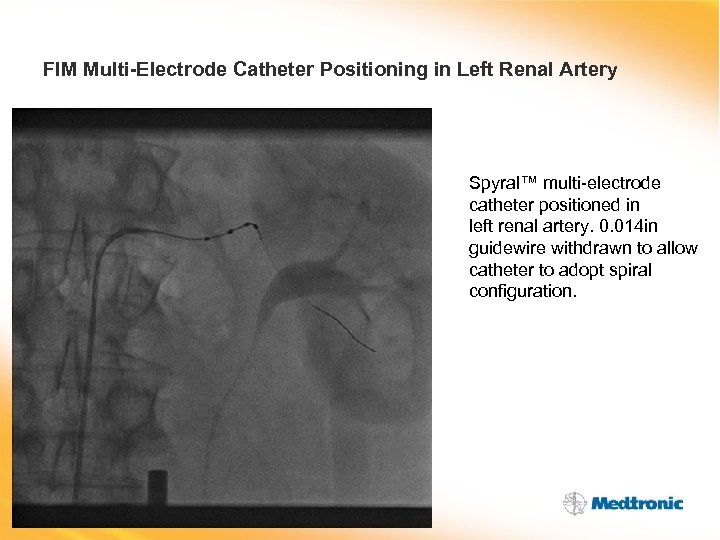 FIM Multi-Electrode Catheter Positioning in Left Renal Artery Spyral™ multi-electrode catheter positioned in left renal artery. 0. 014 in guidewire withdrawn to allow catheter to adopt spiral configuration.
FIM Multi-Electrode Catheter Positioning in Left Renal Artery Spyral™ multi-electrode catheter positioned in left renal artery. 0. 014 in guidewire withdrawn to allow catheter to adopt spiral configuration.
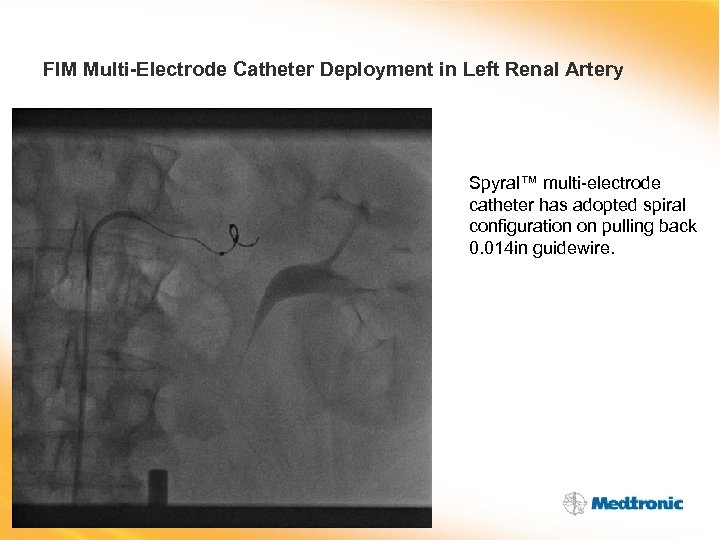 FIM Multi-Electrode Catheter Deployment in Left Renal Artery Spyral™ multi-electrode catheter has adopted spiral configuration on pulling back 0. 014 in guidewire.
FIM Multi-Electrode Catheter Deployment in Left Renal Artery Spyral™ multi-electrode catheter has adopted spiral configuration on pulling back 0. 014 in guidewire.
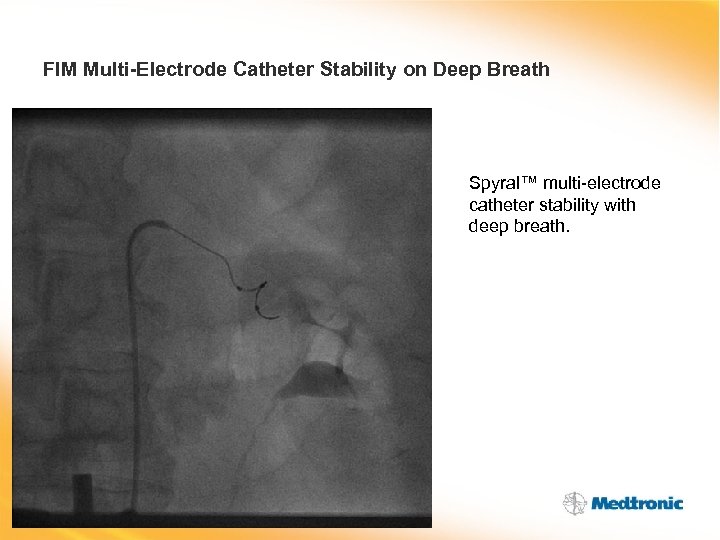 FIM Multi-Electrode Catheter Stability on Deep Breath Spyral™ multi-electrode catheter stability with deep breath.
FIM Multi-Electrode Catheter Stability on Deep Breath Spyral™ multi-electrode catheter stability with deep breath.
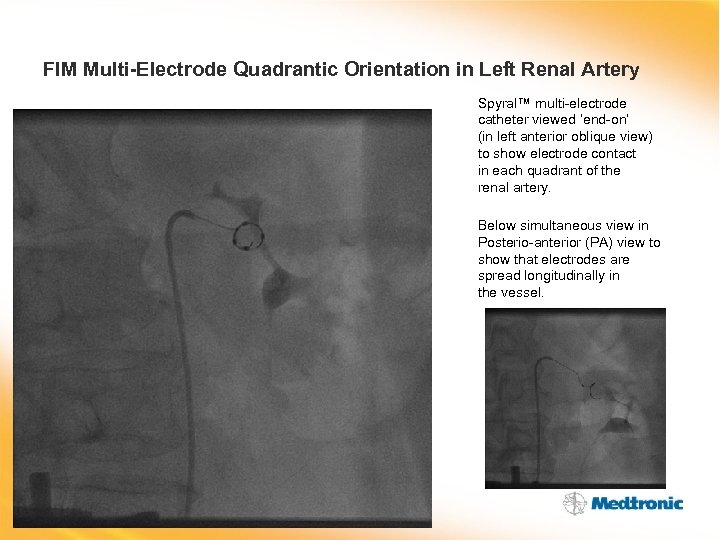 FIM Multi-Electrode Quadrantic Orientation in Left Renal Artery Spyral™ multi-electrode catheter viewed ‘end-on’ (in left anterior oblique view) to show electrode contact in each quadrant of the renal artery. Below simultaneous view in Posterio-anterior (PA) view to show that electrodes are spread longitudinally in the vessel.
FIM Multi-Electrode Quadrantic Orientation in Left Renal Artery Spyral™ multi-electrode catheter viewed ‘end-on’ (in left anterior oblique view) to show electrode contact in each quadrant of the renal artery. Below simultaneous view in Posterio-anterior (PA) view to show that electrodes are spread longitudinally in the vessel.
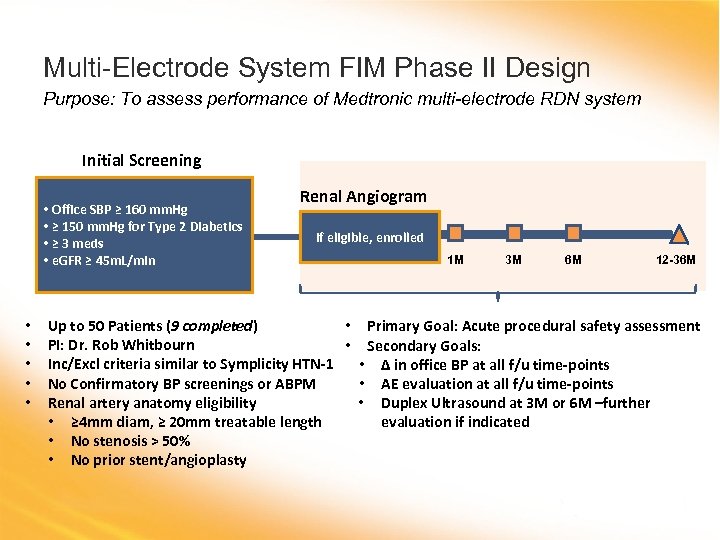 Multi-Electrode System FIM Phase II Design Purpose: To assess performance of Medtronic multi-electrode RDN system Initial Screening • Office SBP ≥ 160 mm. Hg • ≥ 150 mm. Hg for Type 2 Diabetics • ≥ 3 meds • e. GFR ≥ 45 m. L/min • • • Renal Angiogram If eligible, enrolled 1 M 3 M 6 M 12 -36 M Up to 50 Patients (9 completed) • Primary Goal: Acute procedural safety assessment PI: Dr. Rob Whitbourn • Secondary Goals: Inc/Excl criteria similar to Symplicity HTN-1 • Δ in office BP at all f/u time-points No Confirmatory BP screenings or ABPM • AE evaluation at all f/u time-points Renal artery anatomy eligibility • Duplex Ultrasound at 3 M or 6 M –further • ≥ 4 mm diam, ≥ 20 mm treatable length evaluation if indicated • No stenosis > 50% • No prior stent/angioplasty
Multi-Electrode System FIM Phase II Design Purpose: To assess performance of Medtronic multi-electrode RDN system Initial Screening • Office SBP ≥ 160 mm. Hg • ≥ 150 mm. Hg for Type 2 Diabetics • ≥ 3 meds • e. GFR ≥ 45 m. L/min • • • Renal Angiogram If eligible, enrolled 1 M 3 M 6 M 12 -36 M Up to 50 Patients (9 completed) • Primary Goal: Acute procedural safety assessment PI: Dr. Rob Whitbourn • Secondary Goals: Inc/Excl criteria similar to Symplicity HTN-1 • Δ in office BP at all f/u time-points No Confirmatory BP screenings or ABPM • AE evaluation at all f/u time-points Renal artery anatomy eligibility • Duplex Ultrasound at 3 M or 6 M –further • ≥ 4 mm diam, ≥ 20 mm treatable length evaluation if indicated • No stenosis > 50% • No prior stent/angioplasty
 Conclusions Symplicity • Largest research experience – HTN 1 153 pts >4 yrs FU – HTN 2 106 pts >3 yrs FU – HTN 3 348 randomised of 530 • Largest evidence of clinical efficacy and safety • GSR 1000 of 5000 • Clinical use >6, 000 pts treated Spyral • Multi-element catheter, monorail – 14 FIM • 1 min per renal artery For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 31
Conclusions Symplicity • Largest research experience – HTN 1 153 pts >4 yrs FU – HTN 2 106 pts >3 yrs FU – HTN 3 348 randomised of 530 • Largest evidence of clinical efficacy and safety • GSR 1000 of 5000 • Clinical use >6, 000 pts treated Spyral • Multi-element catheter, monorail – 14 FIM • 1 min per renal artery For distribution outside the United States only. Not for distribution in the USA or Japan. Trademarks may be registered and are the property of their respective owners. © 2012 Medtronic, Inc. All rights reserved. 10014489 DOC-1 E 10/2012 31


