7527fe4eac021e0253d79eced7417b5a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 Renaissance Changes Literature • Renaissance writers produced works that reflected the time period • However, their works also used techniques still used today • Some followed the example of medieval writer Dante • He wrote in the vernacular (Italian) rather than classical Latin • Vernacular = native language • In addition, writers wrote either for selfexpression • Or to portray (show) the individuality of their subjects • These trends are still used by modern writers today
Renaissance Changes Literature • Renaissance writers produced works that reflected the time period • However, their works also used techniques still used today • Some followed the example of medieval writer Dante • He wrote in the vernacular (Italian) rather than classical Latin • Vernacular = native language • In addition, writers wrote either for selfexpression • Or to portray (show) the individuality of their subjects • These trends are still used by modern writers today
 Petrarch & Boccaccio • Francesco Petrarch was one of the earliest and most influential humanists • He was also a great poet • Petrarch wrote both in Italian & Latin • In Italian he wrote sonnets (14 line poems) • They were about Laura, his ideal woman • Little is known about her except she died in the plague • The Italian writer Boccaccio is best known for the Decameron, • It is a series of realistic, sometimes offcolor stories • It is told by a group of worldly young people waiting in a villa to avoid the plague sweeping through Florence • The humor of the Decameron is cutting & presents the follies of humans with sarcasm
Petrarch & Boccaccio • Francesco Petrarch was one of the earliest and most influential humanists • He was also a great poet • Petrarch wrote both in Italian & Latin • In Italian he wrote sonnets (14 line poems) • They were about Laura, his ideal woman • Little is known about her except she died in the plague • The Italian writer Boccaccio is best known for the Decameron, • It is a series of realistic, sometimes offcolor stories • It is told by a group of worldly young people waiting in a villa to avoid the plague sweeping through Florence • The humor of the Decameron is cutting & presents the follies of humans with sarcasm
 Machiavelli • The Prince (1513), by Niccolo Machiavelli also examines the imperfect conduct of humans • He does it in the form of a political guidebook named The Prince • Machiavelli examines how a ruler can gain power • But more importantly keep it in spite of his enemies • He begins with the idea that most people are selfish, fickle, & corrupt • To succeed in such a wicked world he said a prince must be strong as a lion & shrewd as a fox • He might have to trick his enemies and even his own people for the good of the state
Machiavelli • The Prince (1513), by Niccolo Machiavelli also examines the imperfect conduct of humans • He does it in the form of a political guidebook named The Prince • Machiavelli examines how a ruler can gain power • But more importantly keep it in spite of his enemies • He begins with the idea that most people are selfish, fickle, & corrupt • To succeed in such a wicked world he said a prince must be strong as a lion & shrewd as a fox • He might have to trick his enemies and even his own people for the good of the state
 Northern Writers • Just as Italian art influenced Northern painters, so did Renaissance ideas influence the writers & philosophers of Northern Europe • Writers adopted the ideas of humanism but put more of a religious slant to it • Because of this, some northern humanists were also called Christian humanist • The best known of the Christian humanist were close friends, Desiderius Erasmus of Holland & Thomas More of England • Erasmus’ famous work is The Praise of Folly • The book poked fun at greedy merchants, heartsick lovers, quarrelsome scholars & pompous priests • Erasmus believed in a Christianity of the heart, not of ceremonies & rules • Bible study was more important to him
Northern Writers • Just as Italian art influenced Northern painters, so did Renaissance ideas influence the writers & philosophers of Northern Europe • Writers adopted the ideas of humanism but put more of a religious slant to it • Because of this, some northern humanists were also called Christian humanist • The best known of the Christian humanist were close friends, Desiderius Erasmus of Holland & Thomas More of England • Erasmus’ famous work is The Praise of Folly • The book poked fun at greedy merchants, heartsick lovers, quarrelsome scholars & pompous priests • Erasmus believed in a Christianity of the heart, not of ceremonies & rules • Bible study was more important to him
 Thomas More’s Utopia • Also concerned with society’s flaws, Thomas More tried to show a better model • In 1516, he wrote the book Utopia about an imaginary land inhabited by peace-loving people • In Greek, Utopia means “no place” • However, in English it has come to mean an “ideal place” because of More’s book • In Utopia, greed, corruption, war & crime had been weeded out • Because the Utopians weren’t greedy, they had little use for money
Thomas More’s Utopia • Also concerned with society’s flaws, Thomas More tried to show a better model • In 1516, he wrote the book Utopia about an imaginary land inhabited by peace-loving people • In Greek, Utopia means “no place” • However, in English it has come to mean an “ideal place” because of More’s book • In Utopia, greed, corruption, war & crime had been weeded out • Because the Utopians weren’t greedy, they had little use for money
 Rabelais • The French humanist Francois Rabelais provided a contrast to Erasmus & More in several ways • They wrote in Latin, while Rabelais wrote in vernacular (French) • Rabelais’ comic adventure Gargantua & Pantagruel was more secular than Erasmus & More’s work • Rabelais believed that human beings were basically good • They should lived by instincts rather than religious rules • It is the story of two giants, a father (Gargantua) and his son (Pantagruel) and their adventures, written in an amusing, extravagant, satirical vein
Rabelais • The French humanist Francois Rabelais provided a contrast to Erasmus & More in several ways • They wrote in Latin, while Rabelais wrote in vernacular (French) • Rabelais’ comic adventure Gargantua & Pantagruel was more secular than Erasmus & More’s work • Rabelais believed that human beings were basically good • They should lived by instincts rather than religious rules • It is the story of two giants, a father (Gargantua) and his son (Pantagruel) and their adventures, written in an amusing, extravagant, satirical vein
 Shakespeare • William Shakespeare wrote in Renaissance England • Regarded as the greatest playwright of all time • His works display a deep understanding of human beings • He reveals the souls of men & women through dramatic conflict • His most famous plays include the tragedies Macbeth, King Lear, Hamlet, & Romeo & Juliet • However he was also skillful at writing comedies like A Midsummer Night’s Dream • Many of these plays examine human flaws • However, he also expresses the Renaissance high view of human nature • He also studied classical culture, as shown in his Julius Caesar, the story of the Roman leader’s assassination
Shakespeare • William Shakespeare wrote in Renaissance England • Regarded as the greatest playwright of all time • His works display a deep understanding of human beings • He reveals the souls of men & women through dramatic conflict • His most famous plays include the tragedies Macbeth, King Lear, Hamlet, & Romeo & Juliet • However he was also skillful at writing comedies like A Midsummer Night’s Dream • Many of these plays examine human flaws • However, he also expresses the Renaissance high view of human nature • He also studied classical culture, as shown in his Julius Caesar, the story of the Roman leader’s assassination
 Elizabethan Age • The Renaissance in England is also called the Elizabethan Age for Queen Elizabeth I • She reigned from 1508 -1603 • She was well educated, speaking French, Italian, Latin, & Greek • In addition to running the kingdom, she also wrote poetry • She was a patron for artists & writers
Elizabethan Age • The Renaissance in England is also called the Elizabethan Age for Queen Elizabeth I • She reigned from 1508 -1603 • She was well educated, speaking French, Italian, Latin, & Greek • In addition to running the kingdom, she also wrote poetry • She was a patron for artists & writers
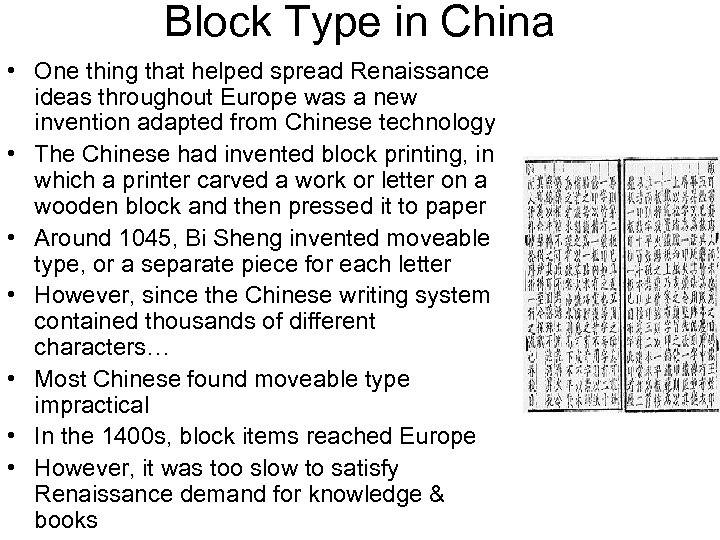 Block Type in China • One thing that helped spread Renaissance ideas throughout Europe was a new invention adapted from Chinese technology • The Chinese had invented block printing, in which a printer carved a work or letter on a wooden block and then pressed it to paper • Around 1045, Bi Sheng invented moveable type, or a separate piece for each letter • However, since the Chinese writing system contained thousands of different characters… • Most Chinese found moveable type impractical • In the 1400 s, block items reached Europe • However, it was too slow to satisfy Renaissance demand for knowledge & books
Block Type in China • One thing that helped spread Renaissance ideas throughout Europe was a new invention adapted from Chinese technology • The Chinese had invented block printing, in which a printer carved a work or letter on a wooden block and then pressed it to paper • Around 1045, Bi Sheng invented moveable type, or a separate piece for each letter • However, since the Chinese writing system contained thousands of different characters… • Most Chinese found moveable type impractical • In the 1400 s, block items reached Europe • However, it was too slow to satisfy Renaissance demand for knowledge & books
 Gutenberg Printing Press • Johann Gutenberg, a craftsman from Mainz, Germany reinvented moveable type around 1440 • The method was more practical for Europeans because their languages have a very small number of letters • Gutenberg then invented the printing press • The printing press is a machine that presses paper against a tray full of inked moveable type • Using this invention, Gutenberg printed a complete Bible, the “Gutenberg Bible” in 1455 • It was the first full sized book printed with moveable type
Gutenberg Printing Press • Johann Gutenberg, a craftsman from Mainz, Germany reinvented moveable type around 1440 • The method was more practical for Europeans because their languages have a very small number of letters • Gutenberg then invented the printing press • The printing press is a machine that presses paper against a tray full of inked moveable type • Using this invention, Gutenberg printed a complete Bible, the “Gutenberg Bible” in 1455 • It was the first full sized book printed with moveable type
 Printing Press Creates Change • The printing press has a revolutionary impact on European society • It enabled a printer to produce hundreds of copies, all exactly alike, of a single work • Books became cheap enough that many people could buy them • Printing spread quickly, so that by 1500, presses in about 250 cities were producing 10 million books • Thus, new ideas spread quicker • Many people were illiterate, so it encouraged people to learn to read • At first books were mostly religious, but it soon spread to other subjects
Printing Press Creates Change • The printing press has a revolutionary impact on European society • It enabled a printer to produce hundreds of copies, all exactly alike, of a single work • Books became cheap enough that many people could buy them • Printing spread quickly, so that by 1500, presses in about 250 cities were producing 10 million books • Thus, new ideas spread quicker • Many people were illiterate, so it encouraged people to learn to read • At first books were mostly religious, but it soon spread to other subjects
 Legacy of the Renaissance • In both Italy & northern Europe, the Renaissance had stirred a burst of creative activity • Artists in both regions studied classical culture & praised individual achievement • They also produced works using new techniques • During the 1600 s, new ideas & artistic styles appeared • Nonetheless, Renaissance ideals continued to influence European thought • For example, the Renaissance belief in the dignity of the individual played a key role in the rise of democratic ideas
Legacy of the Renaissance • In both Italy & northern Europe, the Renaissance had stirred a burst of creative activity • Artists in both regions studied classical culture & praised individual achievement • They also produced works using new techniques • During the 1600 s, new ideas & artistic styles appeared • Nonetheless, Renaissance ideals continued to influence European thought • For example, the Renaissance belief in the dignity of the individual played a key role in the rise of democratic ideas


