4c14cf8fcf54a59521da87deb3cfe1e0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56
 RELIGION
RELIGION
 Definition • An institution consisting of beliefs, pratices, and values pertaining to the distinction between the empirical and the super-empirical.
Definition • An institution consisting of beliefs, pratices, and values pertaining to the distinction between the empirical and the super-empirical.
 MAJOR FUNCTIONS • World Construction and Maintenance • Theodicy—dealing with suffering and evil • Instrumental—health, wealth, happiness, etc.
MAJOR FUNCTIONS • World Construction and Maintenance • Theodicy—dealing with suffering and evil • Instrumental—health, wealth, happiness, etc.
 THEORIES OF RELIGION • Functional Analysis – Durkheim: The Sacred and the Profane – People celebrate the power of their society – Religion performs three major functions • Social Cohesion • Social Control • Meaning and Purpose – Criticism
THEORIES OF RELIGION • Functional Analysis – Durkheim: The Sacred and the Profane – People celebrate the power of their society – Religion performs three major functions • Social Cohesion • Social Control • Meaning and Purpose – Criticism
 • Symbolic Interaction (Peter Berger) – Religion provides a cosmic frame of reference, a “Sacred Canopy. ” – Criticism • Conflict Theory (Marx) – Alliance between religion and politicaleconomic power – “The opium of the people” – Religion and Patriarchy – Colonialism, Slavery, Segregation – Criticism
• Symbolic Interaction (Peter Berger) – Religion provides a cosmic frame of reference, a “Sacred Canopy. ” – Criticism • Conflict Theory (Marx) – Alliance between religion and politicaleconomic power – “The opium of the people” – Religion and Patriarchy – Colonialism, Slavery, Segregation – Criticism
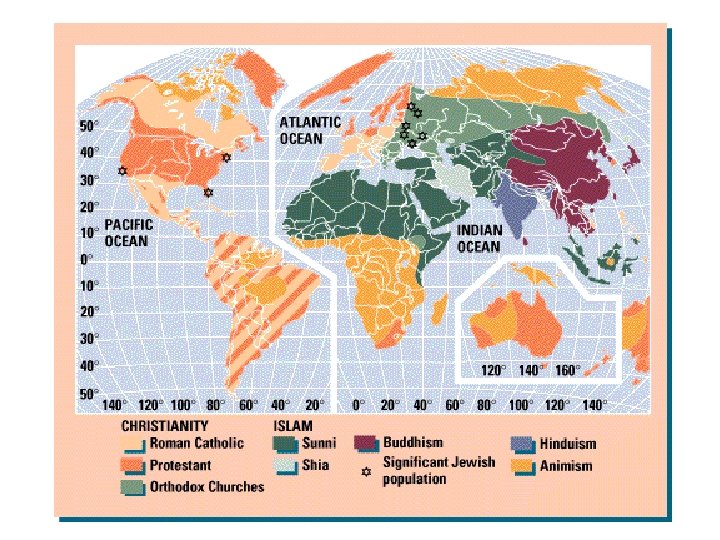

 CHRISTIANITY • 1. 9 billion followers. c. 1/3 of humanity. • Most in Europe or Americas. • Began as cult, incorporating much from Judaism. • Trinity, Jesus as Son of God, Resurrection • 312, became official religion of Holy Roman Empire
CHRISTIANITY • 1. 9 billion followers. c. 1/3 of humanity. • Most in Europe or Americas. • Began as cult, incorporating much from Judaism. • Trinity, Jesus as Son of God, Resurrection • 312, became official religion of Holy Roman Empire


 ISLAM • 1. 1 billion (c. 19% of humanity) Muslims • 6 million in U. S. (disputed) • Muhammad (born c. 570), Mecca, Medina. Qur’an, • Hijra—Flight to Medina. 622 B. C. E. A. H. 1 • Sunni, Shi’a (c. 10%)
ISLAM • 1. 1 billion (c. 19% of humanity) Muslims • 6 million in U. S. (disputed) • Muhammad (born c. 570), Mecca, Medina. Qur’an, • Hijra—Flight to Medina. 622 B. C. E. A. H. 1 • Sunni, Shi’a (c. 10%)
 • Five Pillars of Faith – The Profession: One God, Allah, Muhammad his Prophet – Prayer – Alms – Fasting during Ramadan – Hajj—pilgrimage to Mecca at least once • Dualism: Heaven and Hell
• Five Pillars of Faith – The Profession: One God, Allah, Muhammad his Prophet – Prayer – Alms – Fasting during Ramadan – Hajj—pilgrimage to Mecca at least once • Dualism: Heaven and Hell
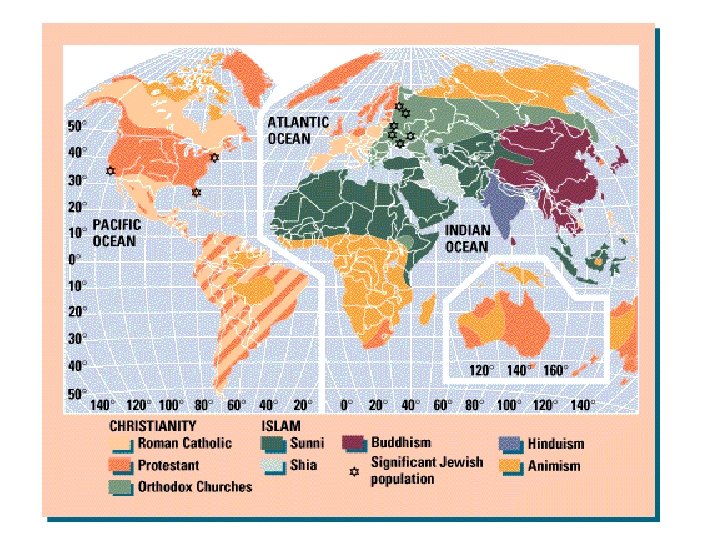
 JUDAISM • • 14 million world wide, most in U. S. and Israel Moses, Exodus, 13 th cty. B. C. E. (Passover) Monotheism Denominations: – Orthodox – Reform – Conservative • Sects: e. g. Chabad/Lubavitcher
JUDAISM • • 14 million world wide, most in U. S. and Israel Moses, Exodus, 13 th cty. B. C. E. (Passover) Monotheism Denominations: – Orthodox – Reform – Conservative • Sects: e. g. Chabad/Lubavitcher

 HINDUSIM • Oldest (At least 4, 500 years ago) • 775 million— 14% of humanity. 1. 3 million in U. S. • India (also Pakistan, Southern Africa, Indonesia) • No single person is key. Sacred writings, but not seen in same light as Bible and Qur’an • Deities: Brahma, Shiva, Vishnu— Brahman-Atman. (Others)
HINDUSIM • Oldest (At least 4, 500 years ago) • 775 million— 14% of humanity. 1. 3 million in U. S. • India (also Pakistan, Southern Africa, Indonesia) • No single person is key. Sacred writings, but not seen in same light as Bible and Qur’an • Deities: Brahma, Shiva, Vishnu— Brahman-Atman. (Others)
 • Karma/Samsara (Reincarnation) • Moral order in every element of nature • Rituals
• Karma/Samsara (Reincarnation) • Moral order in every element of nature • Rituals

 BUDDHISM • 330 million (6%). Mostly Asia. Myanmar (Burma) Thailand, Cambodia, Japan, India, PRC, Vietnam • Origin in India. Siddartha Gautama. • Asoka (3 rd cty B. C. E. ). • Life involves suffering, pleasures transitory. Goal of spiritual transformation. • Acts have consequences. Reincarnation.
BUDDHISM • 330 million (6%). Mostly Asia. Myanmar (Burma) Thailand, Cambodia, Japan, India, PRC, Vietnam • Origin in India. Siddartha Gautama. • Asoka (3 rd cty B. C. E. ). • Life involves suffering, pleasures transitory. Goal of spiritual transformation. • Acts have consequences. Reincarnation.
 CONFUCIANISM • From c. 200 B. C. E. till 1900, the official religion of China. • Suppressed after 1949 revolution. Still influential. Mostly in China, but also in North America. • Confucius c. 551 -479 B. C. E. • Strict code of moral conduct. • No clear sense of sacred, supernatural.
CONFUCIANISM • From c. 200 B. C. E. till 1900, the official religion of China. • Suppressed after 1949 revolution. Still influential. Mostly in China, but also in North America. • Confucius c. 551 -479 B. C. E. • Strict code of moral conduct. • No clear sense of sacred, supernatural.
 SECULARIZATION • KEY TERMS – Secularism – Secularization • The Secularization Hypothesis • Evidence?
SECULARIZATION • KEY TERMS – Secularism – Secularization • The Secularization Hypothesis • Evidence?
 Survey Data on Religion www. thearda. com
Survey Data on Religion www. thearda. com
 Believe in God?
Believe in God?












 Church Membership • Record-keeping varies among denominations • Long Range: 6% in 1800; 35% in 1900; 77% in 1936. • Decline started in 1960 s. Mostly among liberal churches. Slide stabilized in 1978. • About 60% claim membership (86% claim a preference (NORC 1999)
Church Membership • Record-keeping varies among denominations • Long Range: 6% in 1800; 35% in 1900; 77% in 1936. • Decline started in 1960 s. Mostly among liberal churches. Slide stabilized in 1978. • About 60% claim membership (86% claim a preference (NORC 1999)
 Personal Salience • Religiosity: “very important” or “important” • Bible study, book sales, • New Age Spirituality. 35 million at laest somewhat interested
Personal Salience • Religiosity: “very important” or “important” • Bible study, book sales, • New Age Spirituality. 35 million at laest somewhat interested


 SECULARIZATION (? ) • Perceived Influence of Religion • Evidence for Secularity – Moral relativism – Bias against religion in media, education – Lack of regard for religious factors in diplomatic circles.
SECULARIZATION (? ) • Perceived Influence of Religion • Evidence for Secularity – Moral relativism – Bias against religion in media, education – Lack of regard for religious factors in diplomatic circles.
 Conclusions • Data do not support general secularization • Problems of measuring religiosity • Problems of time frame • Evidence tricky • Secularization is segmental. Occurs simultaneously with revival.
Conclusions • Data do not support general secularization • Problems of measuring religiosity • Problems of time frame • Evidence tricky • Secularization is segmental. Occurs simultaneously with revival.
 Religion and the Election 2004
Religion and the Election 2004
 Catholics Mainline Protestant 23% eligible voters (27% actual voters) c. 22% White Evangelicals Remainder c. 30% 25% eligible (22% actual) Black = 8% Jews = 2% Non-Jud-Xn = 4% Secular = 10
Catholics Mainline Protestant 23% eligible voters (27% actual voters) c. 22% White Evangelicals Remainder c. 30% 25% eligible (22% actual) Black = 8% Jews = 2% Non-Jud-Xn = 4% Secular = 10






 Why Evangelicals Love Bush • They feel persecuted, marginalized. He makes them feel better. • Bush was transformed, born again. • He was “called” to his role. • Moral Clarity
Why Evangelicals Love Bush • They feel persecuted, marginalized. He makes them feel better. • Bush was transformed, born again. • He was “called” to his role. • Moral Clarity
 CAUSES OF SECULARIZATION • RATIONALIZATION (Weber) • STRUCTURAL DIFFERENTIATION – – Division of Labor Education Secular State Religious foundations of morality give way to legal technicalities – Critics of differentiation, specialization
CAUSES OF SECULARIZATION • RATIONALIZATION (Weber) • STRUCTURAL DIFFERENTIATION – – Division of Labor Education Secular State Religious foundations of morality give way to legal technicalities – Critics of differentiation, specialization
 Causes (cont. ) • • Spread of Capitalism—the great solvent Growth of Science Disenchantment, demystification Pluralism—no world view holds a monopoly. Post-modernism • Privatization, Individualism
Causes (cont. ) • • Spread of Capitalism—the great solvent Growth of Science Disenchantment, demystification Pluralism—no world view holds a monopoly. Post-modernism • Privatization, Individualism
 Stark and Bainbridge Theory • Secularization is Self-Limiting – Stimulates revival and innovation – Sources of religion vary; amount remains about the same. – Sects arise where religion strong; cults where it is weak.
Stark and Bainbridge Theory • Secularization is Self-Limiting – Stimulates revival and innovation – Sources of religion vary; amount remains about the same. – Sects arise where religion strong; cults where it is weak.
 • Critique – Losses not obviously offset by gains. E. g. , Great Britain. – Secularization continues as a major trend, following rationalization. Affects segments of society differentially. – Groups differ in openness to religious appeals. • CONCLUSIONS
• Critique – Losses not obviously offset by gains. E. g. , Great Britain. – Secularization continues as a major trend, following rationalization. Affects segments of society differentially. – Groups differ in openness to religious appeals. • CONCLUSIONS




