6b94e4864c977308618671ab696c444b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Religion, Culture, and Trust FA 9550 -15 -1 -0008 PI: Adam B. Cohen (Arizona State University: Psychology) Co-PI: Gene A. Brewer (Arizona State University: Psychology) Senior Personnel: Chris Blais (Arizona State University: Psychology) Steven Corman (Arizona State University: Communication) Roger C. Mayer (North Carolina State University: Organizational Behavior) Matthew L. Newman (Research Now, Dallas TX) AFOSR Program Review: Trust & Influence June 13 -17 2016, Arlington VA
Religion, Culture, and Trust FA 9550 -15 -1 -0008 PI: Adam B. Cohen (Arizona State University: Psychology) Co-PI: Gene A. Brewer (Arizona State University: Psychology) Senior Personnel: Chris Blais (Arizona State University: Psychology) Steven Corman (Arizona State University: Communication) Roger C. Mayer (North Carolina State University: Organizational Behavior) Matthew L. Newman (Research Now, Dallas TX) AFOSR Program Review: Trust & Influence June 13 -17 2016, Arlington VA
 Trust is Critical in Military Contexts • US military needs to cultivate and accurately assess trust and credibility in diverse cultural and religious contexts • Trust in multicultural teams where people are truly vulnerable to actions of other team members • Religion and culture may affect trust • US, Singapore, and Israel • Individualism-Collectivism • Tightness-Looseness • Religious Ingroup-Outgroup Identities • Supernatural Monitoring • Religious Costly Signaling
Trust is Critical in Military Contexts • US military needs to cultivate and accurately assess trust and credibility in diverse cultural and religious contexts • Trust in multicultural teams where people are truly vulnerable to actions of other team members • Religion and culture may affect trust • US, Singapore, and Israel • Individualism-Collectivism • Tightness-Looseness • Religious Ingroup-Outgroup Identities • Supernatural Monitoring • Religious Costly Signaling
 Costly Signaling and Trust • Religion often involves costly signals of commitment to the ingroup which promote trust (Sosis & Alcorta, 2003) – elaborate rituals, charity, sacrifices, circumcision, dietary restrictions, etc. • Does the presence of ingroup religious signals increase trust? • Does the presence of outgroup costly signals decrease trust?
Costly Signaling and Trust • Religion often involves costly signals of commitment to the ingroup which promote trust (Sosis & Alcorta, 2003) – elaborate rituals, charity, sacrifices, circumcision, dietary restrictions, etc. • Does the presence of ingroup religious signals increase trust? • Does the presence of outgroup costly signals decrease trust?
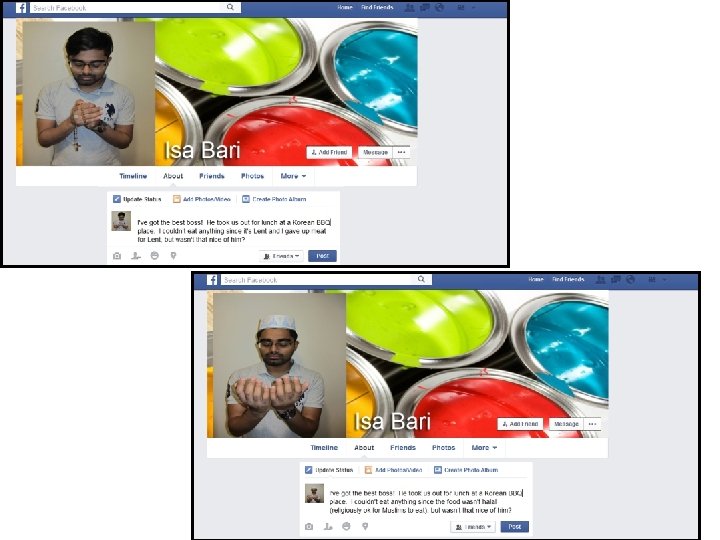
 Friending on Facebook • 393 Christian undergraduates (308 Protestant, 85 Catholic) • 153 male, 240 female • Manipulated – religious group – beliefs about God – costly signaling
Friending on Facebook • 393 Christian undergraduates (308 Protestant, 85 Catholic) • 153 male, 240 female • Manipulated – religious group – beliefs about God – costly signaling
 Trust Scale, α =. 82 • Do you think this person is trustworthy? • Would you trust this person with a sensitive secret? • Would you lend this person money and expect to get it back? • Do you think this person has the ability to be trustworthy? • Do you think this person is benevolent? • Do you think this person has integrity?
Trust Scale, α =. 82 • Do you think this person is trustworthy? • Would you trust this person with a sensitive secret? • Would you lend this person money and expect to get it back? • Do you think this person has the ability to be trustworthy? • Do you think this person is benevolent? • Do you think this person has integrity?
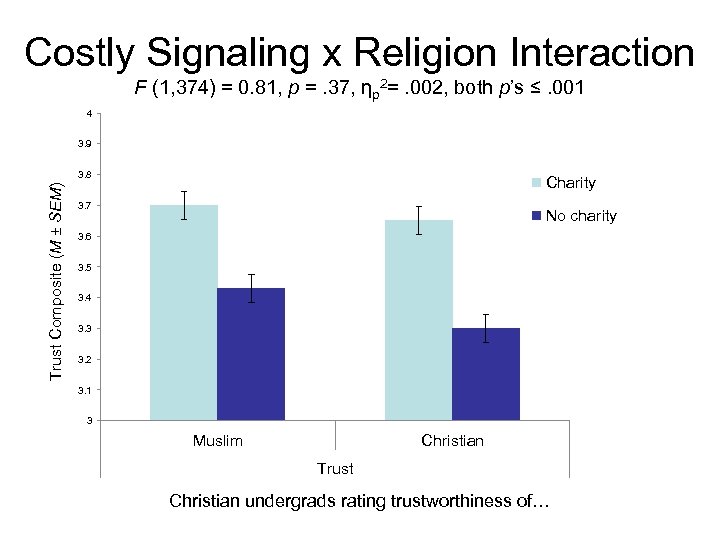 Costly Signaling x Religion Interaction F (1, 374) = 0. 81, p =. 37, ηp 2=. 002, both p’s ≤. 001 4 3. 9 Trust Composite (M ± SEM) 3. 8 Charity 3. 7 No charity 3. 6 3. 5 3. 4 3. 3 3. 2 3. 1 3 Muslim Christian Trust Christian undergrads rating trustworthiness of…
Costly Signaling x Religion Interaction F (1, 374) = 0. 81, p =. 37, ηp 2=. 002, both p’s ≤. 001 4 3. 9 Trust Composite (M ± SEM) 3. 8 Charity 3. 7 No charity 3. 6 3. 5 3. 4 3. 3 3. 2 3. 1 3 Muslim Christian Trust Christian undergrads rating trustworthiness of…
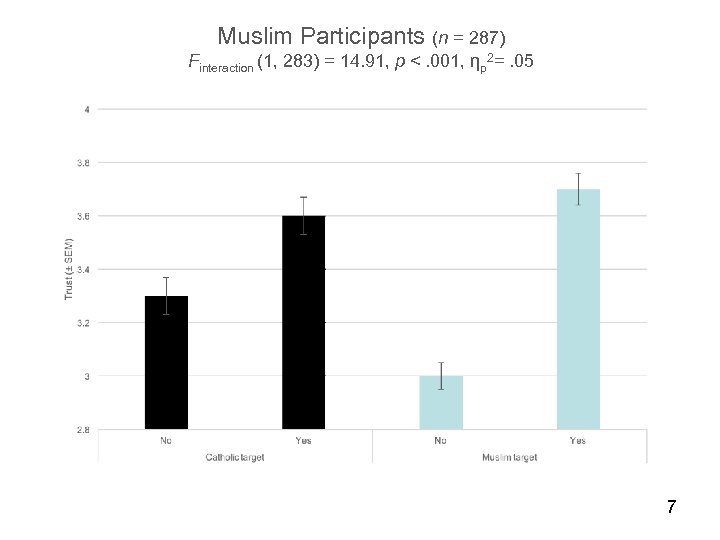 Muslim Participants (n = 287) Finteraction (1, 283) = 14. 91, p <. 001, ηp 2=. 05 7
Muslim Participants (n = 287) Finteraction (1, 283) = 14. 91, p <. 001, ηp 2=. 05 7
 8
8
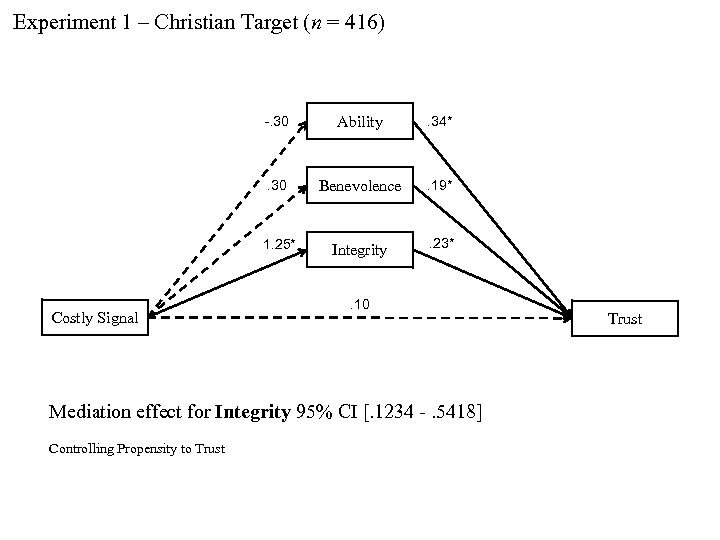 Experiment 1 – Christian Target (n = 416) -. 30 . 34* . 30 Benevolence . 19* 1. 25* Costly Signal Ability Integrity . 23* . 10 Mediation effect for Integrity 95% CI [. 1234 -. 5418] Controlling Propensity to Trust
Experiment 1 – Christian Target (n = 416) -. 30 . 34* . 30 Benevolence . 19* 1. 25* Costly Signal Ability Integrity . 23* . 10 Mediation effect for Integrity 95% CI [. 1234 -. 5418] Controlling Propensity to Trust
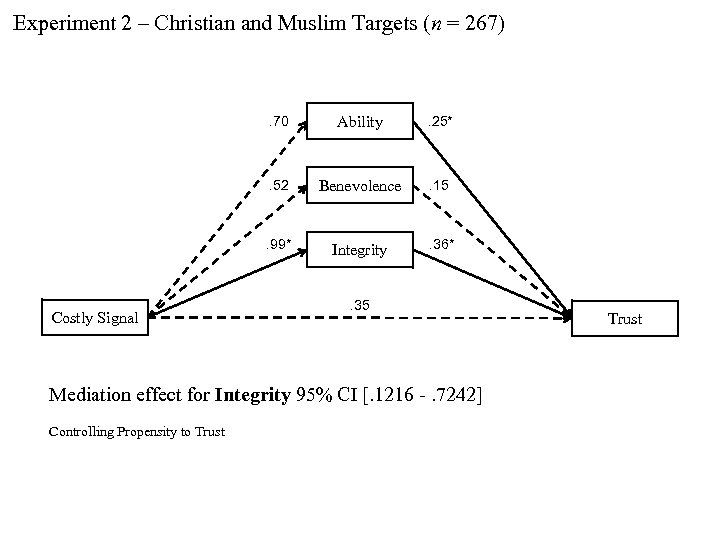 Experiment 2 – Christian and Muslim Targets (n = 267) . 70 . 25* . 52 Benevolence . 15* . 99* Costly Signal Ability Integrity . 36* . 35 Mediation effect for Integrity 95% CI [. 1216 -. 7242] Controlling Propensity to Trust
Experiment 2 – Christian and Muslim Targets (n = 267) . 70 . 25* . 52 Benevolence . 15* . 99* Costly Signal Ability Integrity . 36* . 35 Mediation effect for Integrity 95% CI [. 1216 -. 7242] Controlling Propensity to Trust
 EEG and Autonomic Psychophysiology Model of Trust Decisions 11
EEG and Autonomic Psychophysiology Model of Trust Decisions 11
 12
12
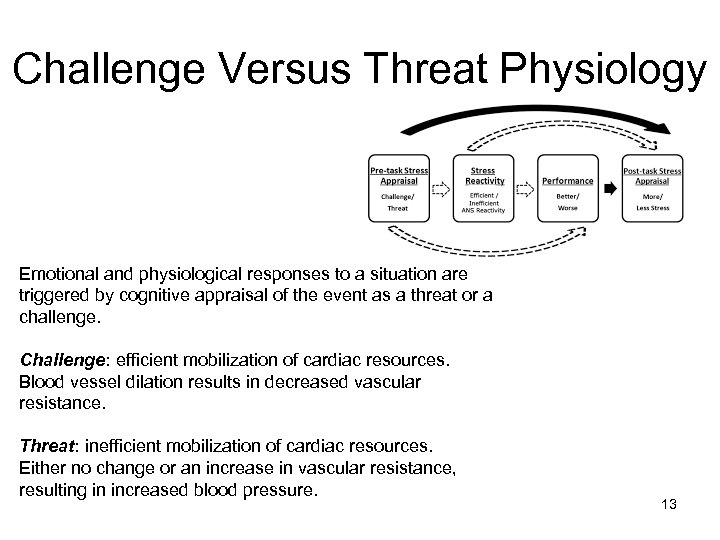 Challenge Versus Threat Physiology Emotional and physiological responses to a situation are triggered by cognitive appraisal of the event as a threat or a challenge. Challenge: efficient mobilization of cardiac resources. Blood vessel dilation results in decreased vascular resistance. Threat: inefficient mobilization of cardiac resources. Either no change or an increase in vascular resistance, resulting in increased blood pressure. 13
Challenge Versus Threat Physiology Emotional and physiological responses to a situation are triggered by cognitive appraisal of the event as a threat or a challenge. Challenge: efficient mobilization of cardiac resources. Blood vessel dilation results in decreased vascular resistance. Threat: inefficient mobilization of cardiac resources. Either no change or an increase in vascular resistance, resulting in increased blood pressure. 13
 EEG study Which EEG signals mediate trust/distrust decisions? All “profiles” correctly report the result of the coin flip on 66% of trials 14
EEG study Which EEG signals mediate trust/distrust decisions? All “profiles” correctly report the result of the coin flip on 66% of trials 14
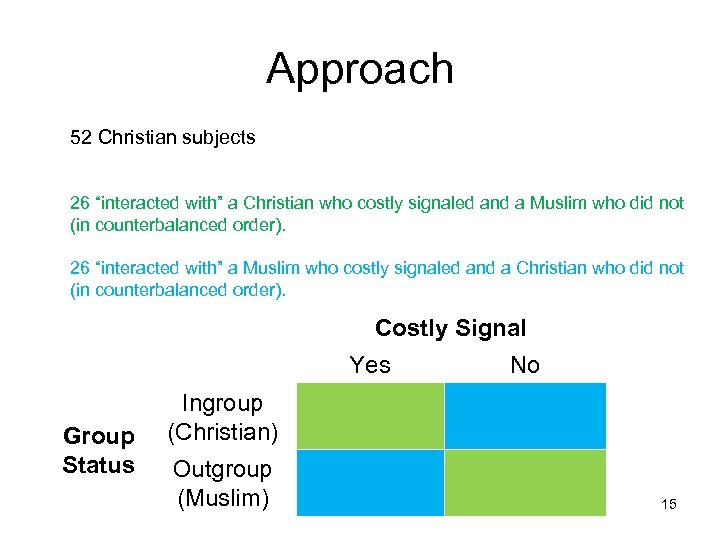 Approach 52 Christian subjects 26 “interacted with” a Christian who costly signaled and a Muslim who did not (in counterbalanced order). 26 “interacted with” a Muslim who costly signaled and a Christian who did not (in counterbalanced order). Costly Signal Yes Group Status No Ingroup (Christian) Outgroup (Muslim) 15
Approach 52 Christian subjects 26 “interacted with” a Christian who costly signaled and a Muslim who did not (in counterbalanced order). 26 “interacted with” a Muslim who costly signaled and a Christian who did not (in counterbalanced order). Costly Signal Yes Group Status No Ingroup (Christian) Outgroup (Muslim) 15
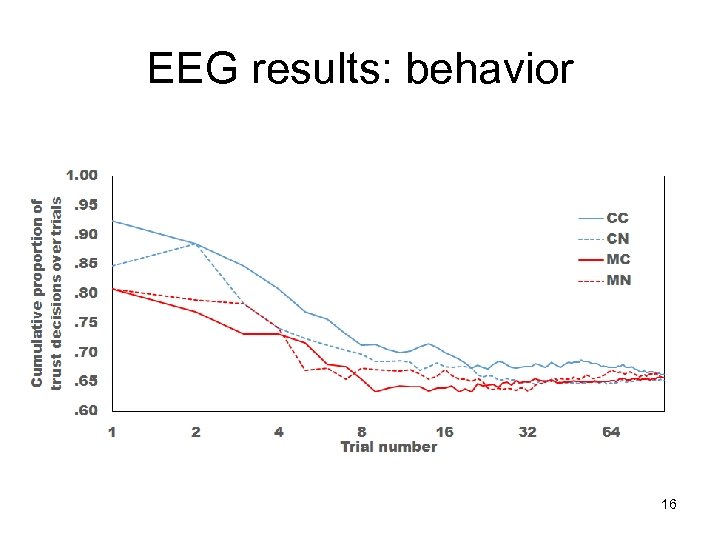 EEG results: behavior 16
EEG results: behavior 16
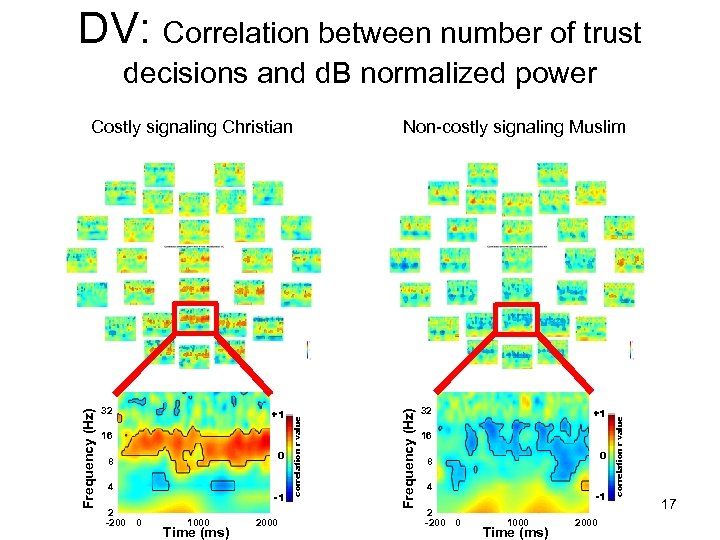 DV: Correlation between number of trust decisions and d. B normalized power 16 0 8 4 2 -200 0 -1 1000 Time (ms) 2000 32 +1 16 0 8 4 2 -200 0 -1 1000 Time (ms) 2000 correlation r value +1 Non-costly signaling Muslim Frequency (Hz) 32 correlation r value Frequency (Hz) Costly signaling Christian 17
DV: Correlation between number of trust decisions and d. B normalized power 16 0 8 4 2 -200 0 -1 1000 Time (ms) 2000 32 +1 16 0 8 4 2 -200 0 -1 1000 Time (ms) 2000 correlation r value +1 Non-costly signaling Muslim Frequency (Hz) 32 correlation r value Frequency (Hz) Costly signaling Christian 17
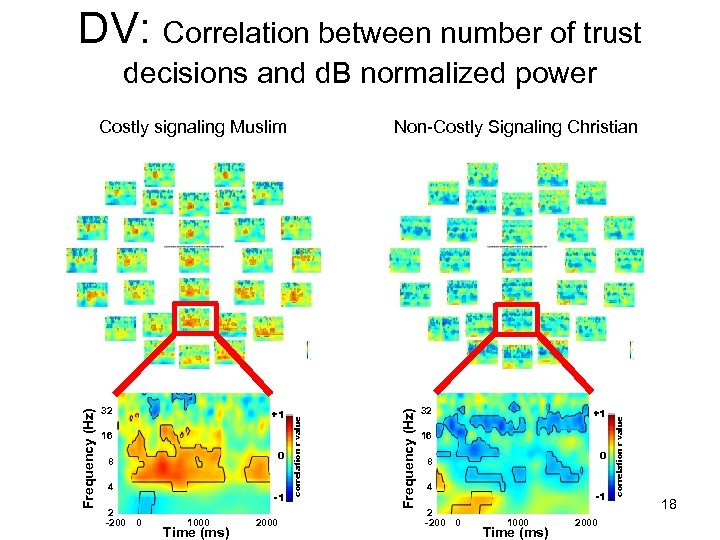 DV: Correlation between number of trust decisions and d. B normalized power 16 0 8 4 2 -200 0 -1 1000 Time (ms) 2000 32 +1 16 0 8 4 2 -200 0 -1 1000 Time (ms) 2000 correlation r value +1 Frequency (Hz) 32 Non-Costly Signaling Christian correlation r value Frequency (Hz) Costly signaling Muslim 18
DV: Correlation between number of trust decisions and d. B normalized power 16 0 8 4 2 -200 0 -1 1000 Time (ms) 2000 32 +1 16 0 8 4 2 -200 0 -1 1000 Time (ms) 2000 correlation r value +1 Frequency (Hz) 32 Non-Costly Signaling Christian correlation r value Frequency (Hz) Costly signaling Muslim 18
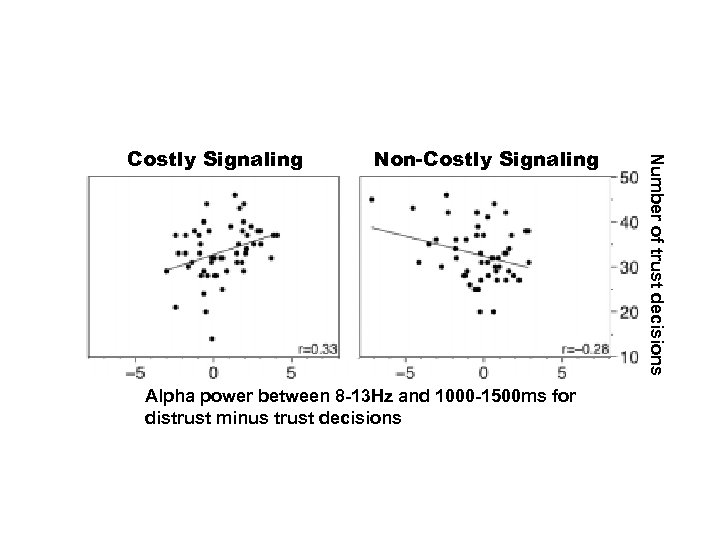 Non-Costly Signaling Alpha power between 8 -13 Hz and 1000 -1500 ms for distrust minus trust decisions Number of trust decisions Costly Signaling
Non-Costly Signaling Alpha power between 8 -13 Hz and 1000 -1500 ms for distrust minus trust decisions Number of trust decisions Costly Signaling
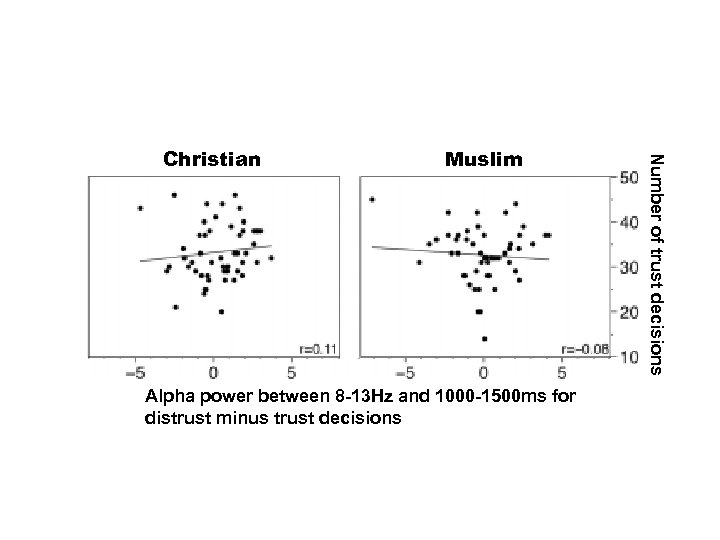 Muslim Alpha power between 8 -13 Hz and 1000 -1500 ms for distrust minus trust decisions Number of trust decisions Christian
Muslim Alpha power between 8 -13 Hz and 1000 -1500 ms for distrust minus trust decisions Number of trust decisions Christian
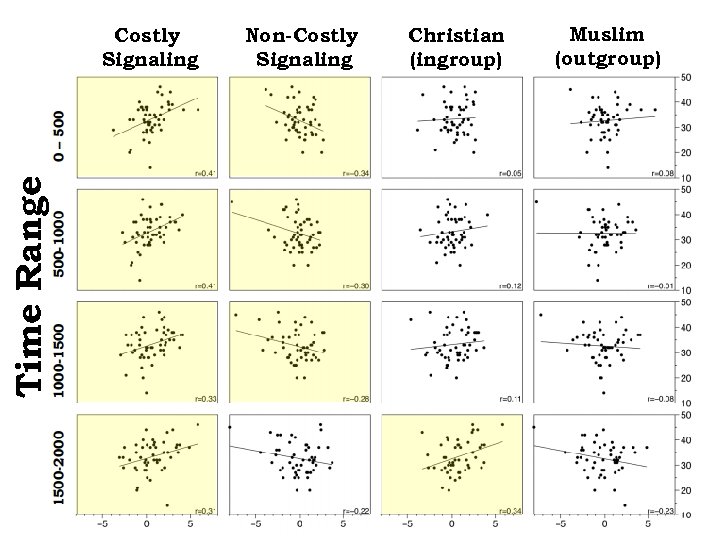 Time Range Costly Signaling Non-Costly Signaling Christian (ingroup) Muslim (outgroup)
Time Range Costly Signaling Non-Costly Signaling Christian (ingroup) Muslim (outgroup)
 Summary • Religion, often an assumed stumbling block to building trust, can build trust in volatile world environments – People can find outgroup members trustworthy – Costly signaling promotes trust within and across groups, seemingly related to integrity – Counter-intuitive effects of cross-group signaling? • Similarity but some nuance across religious groups (Christians, Muslims) • EEG predictor of trust decisions 22
Summary • Religion, often an assumed stumbling block to building trust, can build trust in volatile world environments – People can find outgroup members trustworthy – Costly signaling promotes trust within and across groups, seemingly related to integrity – Counter-intuitive effects of cross-group signaling? • Similarity but some nuance across religious groups (Christians, Muslims) • EEG predictor of trust decisions 22
 Publications, Awards, Patents, or Transitions Attributed to the Grant Papers Blais, C. , Ellis, D. M. , Wingert, K. , Cohen, A. B. , Brewer, G. A. (in preparation). Trust decisions are mediated by alpha suppression over parietal electrode sites. Ellis, D. M. , Mayer, R. C. , Cohen, A. B. , Brewer, G. A. (in preparation). Costly signaling influence perceptions of trustworthiness: Integrity as a mediator. Corman, S. , Wingert, K. , Cohen, A. B. , & Brewer, G. A. (in preparation). Aristotle was wrong: Dimensions of trust and credibility. Hall, D. , Cohen, A. B. , Meyer, K. K. , Varley, A. , & Brewer, G. A. . (2015). Costly signaling increases trust, even across religious affiliations. Psychological Science, 26, 1368 -1376. Presentations Cohen, A. B. , Hall, D. , & Brewer, G. A. . (2015, May). Religious costly signaling increases trust. Invited address delivered in J. L. Preston (chair), Fresh New Findings on the Ancient Topic of Religion, Association for Psychological Science, New York, NY. Blais, C. , Ellis, D. M. , Wingert, K. , Cohen, A. B. , & Brewer, G. A. (2016, April). Trust decisions are mediated by alpha suppression over parietal electrode sites. Poster submitted for presentation at Cognitive Neuroscience Society Annual Meeting, New York, NY Northover, S. , Bigman, Y. , & Cohen, A. B. (2016, January). Both religious believers and nonbelievers report greater trust in an outgroup religious costly signaler. Poster presented at the meeting of the Society for Personality and Social Psychology, San Diego, CA. Rayes, D. , Cohen, A. B. , Brewer, G. A. . (2015, March). Paradox of Healing & Stigmatization: Mental Health Stigma in Arab Culture. Poster presented at the 7 th annual Muslim Mental Health Conference, Dearborn, MI. Cohen, A. B. (2015, March). Religion and trust: Aim high! Address delivered to psychology alumni group, ASU. Cohen, A. B. , Hall, D. , & Brewer, G. A. . (2015, March). Religious costly signaling increases trust. In K. Laurin, chair, Religious dimensions and morality: Perspectives on a multifaceted relationship. Symposium conducted at International Congress on Psych Science conference, Amsterdam. Cohen, A. B. , Hall, D. , & Brewer, G. A. . (2015, February). Religious costly signaling increases trust. Invited address delivered at Justice preconference of the Society of Personality and Social Psychology conference, Long Beach, CA. Media coverage Neil Farber’s blog in Psychology Today: “Do Christians trust Muslims? A surprising study of good faith. ” [Essential Read by the 23 Psychology Today editors, 13 May 2015]
Publications, Awards, Patents, or Transitions Attributed to the Grant Papers Blais, C. , Ellis, D. M. , Wingert, K. , Cohen, A. B. , Brewer, G. A. (in preparation). Trust decisions are mediated by alpha suppression over parietal electrode sites. Ellis, D. M. , Mayer, R. C. , Cohen, A. B. , Brewer, G. A. (in preparation). Costly signaling influence perceptions of trustworthiness: Integrity as a mediator. Corman, S. , Wingert, K. , Cohen, A. B. , & Brewer, G. A. (in preparation). Aristotle was wrong: Dimensions of trust and credibility. Hall, D. , Cohen, A. B. , Meyer, K. K. , Varley, A. , & Brewer, G. A. . (2015). Costly signaling increases trust, even across religious affiliations. Psychological Science, 26, 1368 -1376. Presentations Cohen, A. B. , Hall, D. , & Brewer, G. A. . (2015, May). Religious costly signaling increases trust. Invited address delivered in J. L. Preston (chair), Fresh New Findings on the Ancient Topic of Religion, Association for Psychological Science, New York, NY. Blais, C. , Ellis, D. M. , Wingert, K. , Cohen, A. B. , & Brewer, G. A. (2016, April). Trust decisions are mediated by alpha suppression over parietal electrode sites. Poster submitted for presentation at Cognitive Neuroscience Society Annual Meeting, New York, NY Northover, S. , Bigman, Y. , & Cohen, A. B. (2016, January). Both religious believers and nonbelievers report greater trust in an outgroup religious costly signaler. Poster presented at the meeting of the Society for Personality and Social Psychology, San Diego, CA. Rayes, D. , Cohen, A. B. , Brewer, G. A. . (2015, March). Paradox of Healing & Stigmatization: Mental Health Stigma in Arab Culture. Poster presented at the 7 th annual Muslim Mental Health Conference, Dearborn, MI. Cohen, A. B. (2015, March). Religion and trust: Aim high! Address delivered to psychology alumni group, ASU. Cohen, A. B. , Hall, D. , & Brewer, G. A. . (2015, March). Religious costly signaling increases trust. In K. Laurin, chair, Religious dimensions and morality: Perspectives on a multifaceted relationship. Symposium conducted at International Congress on Psych Science conference, Amsterdam. Cohen, A. B. , Hall, D. , & Brewer, G. A. . (2015, February). Religious costly signaling increases trust. Invited address delivered at Justice preconference of the Society of Personality and Social Psychology conference, Long Beach, CA. Media coverage Neil Farber’s blog in Psychology Today: “Do Christians trust Muslims? A surprising study of good faith. ” [Essential Read by the 23 Psychology Today editors, 13 May 2015]
 Project Summary Research Objectives: Technical Approach: • Elucidate the cultural and religious factors that promote or hinder trustworthiness • Experimental social psychology • Examine the neural (EEG) and physiological correlates of trust • Cross-cultural and –religion research • EEG techniques • Autonomic physiology assessment • Refine theory, measurement on factors of trustworthiness Key Findings: • People can find outgroup members trustworthy • Costly signaling promotes trust within and across groups, surprisingly – related to integrity Benefits to the wider academic or Do. D community: Strategies to assess, predict, and cultivate trust in teams in various cultural-religious contexts Begins to suggest religion, often an assumed stumbling block to building trust, can build trust in volatile world environments • Similarity but some nuance across religious groups (Christians, Muslims, atheists) Project Start Date: 01 Feb 2015 • EEG predictor of trust decisions Project End Date: 31 Jan 2018 24
Project Summary Research Objectives: Technical Approach: • Elucidate the cultural and religious factors that promote or hinder trustworthiness • Experimental social psychology • Examine the neural (EEG) and physiological correlates of trust • Cross-cultural and –religion research • EEG techniques • Autonomic physiology assessment • Refine theory, measurement on factors of trustworthiness Key Findings: • People can find outgroup members trustworthy • Costly signaling promotes trust within and across groups, surprisingly – related to integrity Benefits to the wider academic or Do. D community: Strategies to assess, predict, and cultivate trust in teams in various cultural-religious contexts Begins to suggest religion, often an assumed stumbling block to building trust, can build trust in volatile world environments • Similarity but some nuance across religious groups (Christians, Muslims, atheists) Project Start Date: 01 Feb 2015 • EEG predictor of trust decisions Project End Date: 31 Jan 2018 24


