69f5fff07ac382072d99086da2eeb8b1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

Reliable Multicast In Mobile Ad Hoc Networks 【 FAT vs. RALM 】 v教授 :林振緯 v班級:碩士在職專班(一) v學號: 492515045 v姓名:呂國銓 v日期: 93. 04. 27 1

OUTLINE Introduction Family ACK Tree Protocol RALM Protocol FAT vs. RALM Simulation Reference 2
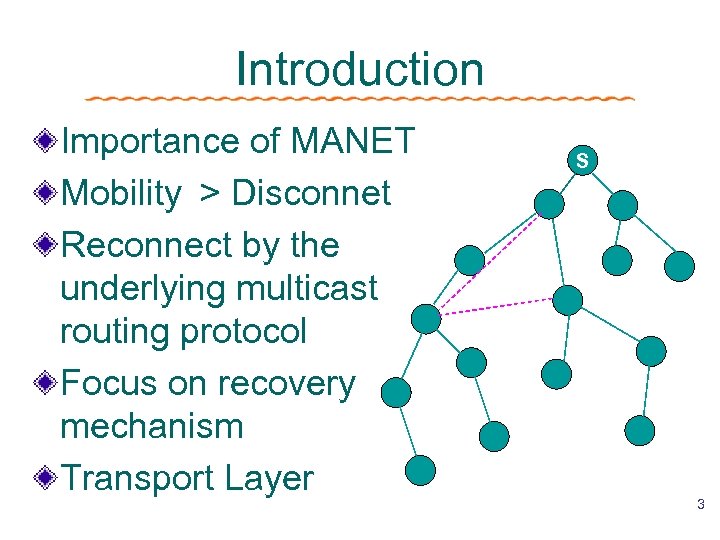
Introduction Importance of MANET Mobility > Disconnet Reconnect by the underlying multicast routing protocol Focus on recovery mechanism Transport Layer S 3
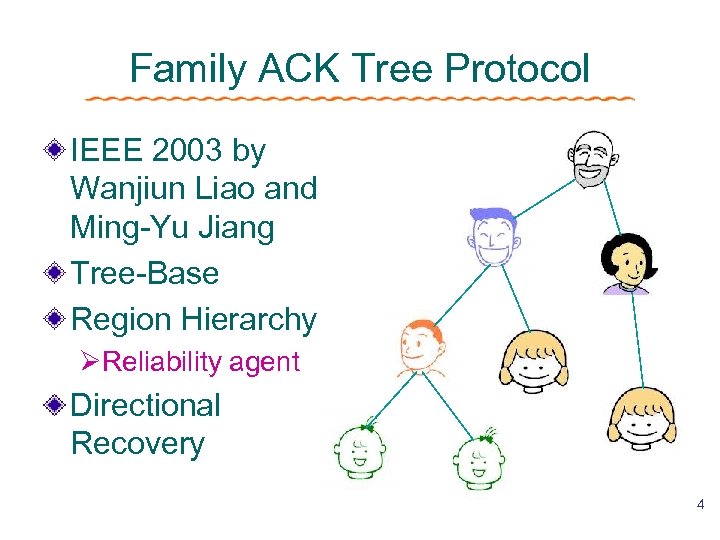
Family ACK Tree Protocol IEEE 2003 by Wanjiun Liao and Ming-Yu Jiang Tree-Base Region Hierarchy ØReliability agent Directional Recovery 4
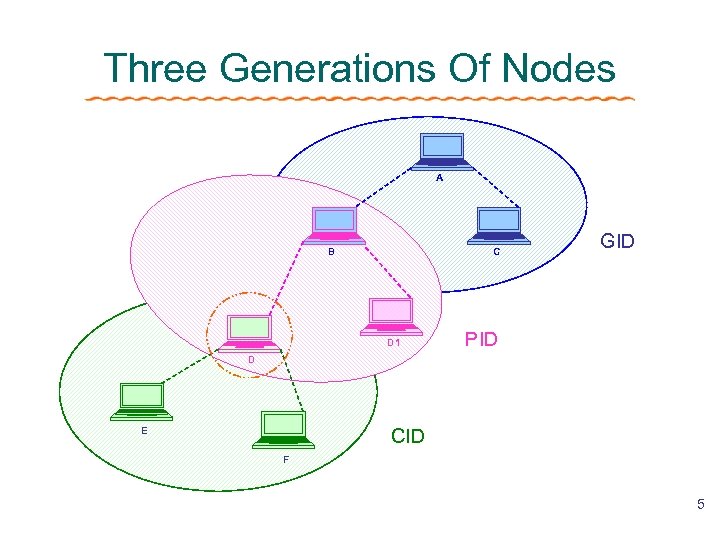
Three Generations Of Nodes A B C D 1 GID PID D CID E F 5

Two Control Message Types Subgroup ID Advertisement (Ad) ØBroadcast PID & CID to neighbors ØGenerate CID different from GID , PID and siblings’ CID (child node receive Ad) ØConfigure the ACK table Retransmission Request (RTQ) ØReport a loss gap to its reliability agent ØRequest a retransmission 6
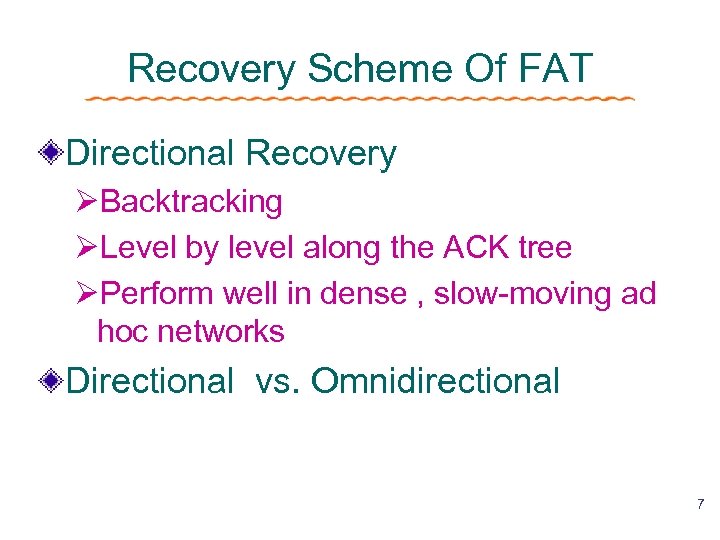
Recovery Scheme Of FAT Directional Recovery ØBacktracking ØLevel by level along the ACK tree ØPerform well in dense , slow-moving ad hoc networks Directional vs. Omnidirectional 7
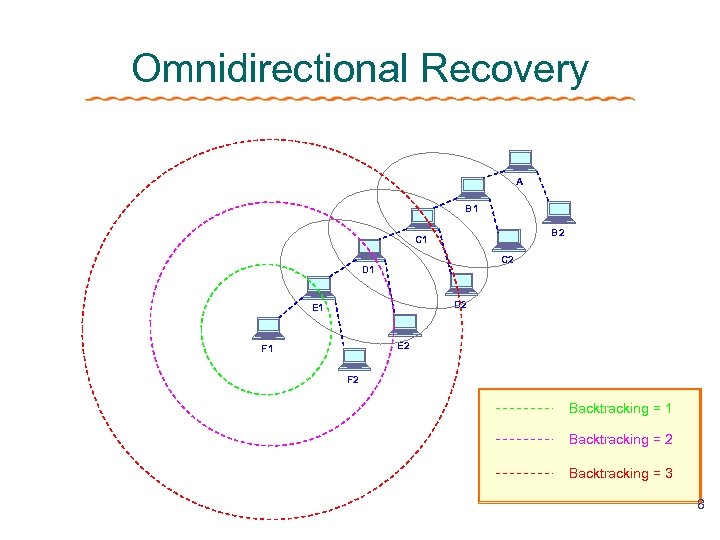
Omnidirectional Recovery A B 1 B 2 C 1 C 2 D 1 D 2 E 1 E 2 F 1 F 2 Backtracking = 1 Backtracking = 2 Backtracking = 3 8
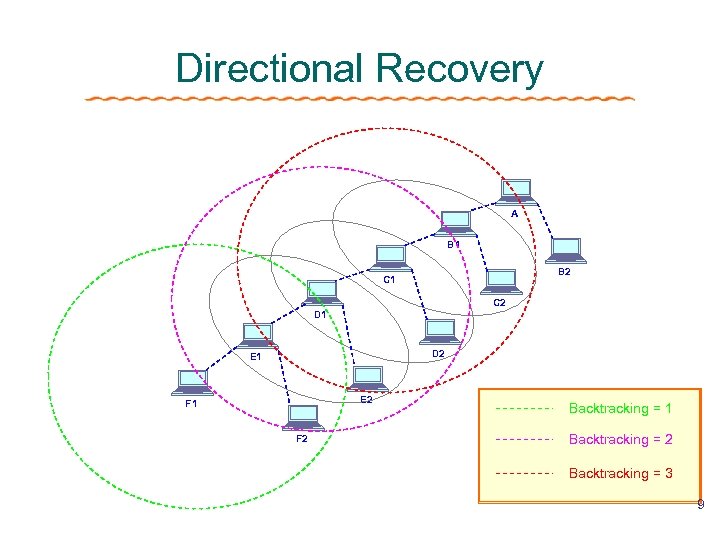
Directional Recovery A B 1 B 2 C 1 C 2 D 1 D 2 E 1 E 2 F 1 F 2 Backtracking = 1 Backtracking = 2 Backtracking = 3 9
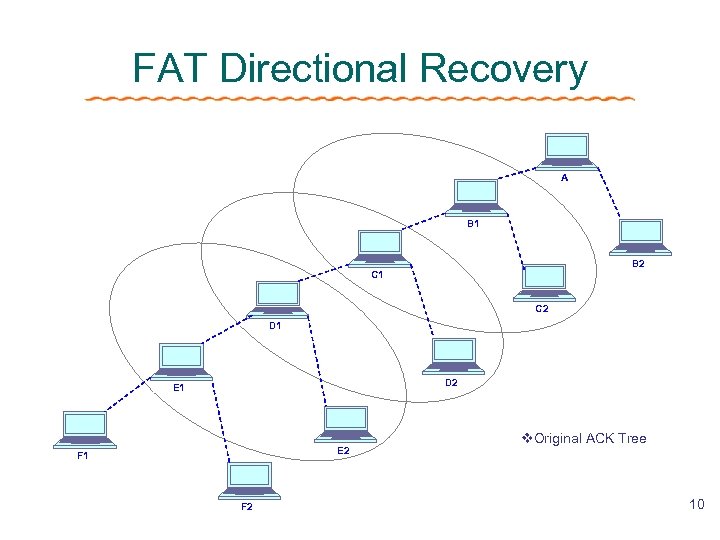
FAT Directional Recovery A B 1 B 2 C 1 C 2 D 1 D 2 E 1 E 2 F 1 F 2 v. Original ACK Tree 10
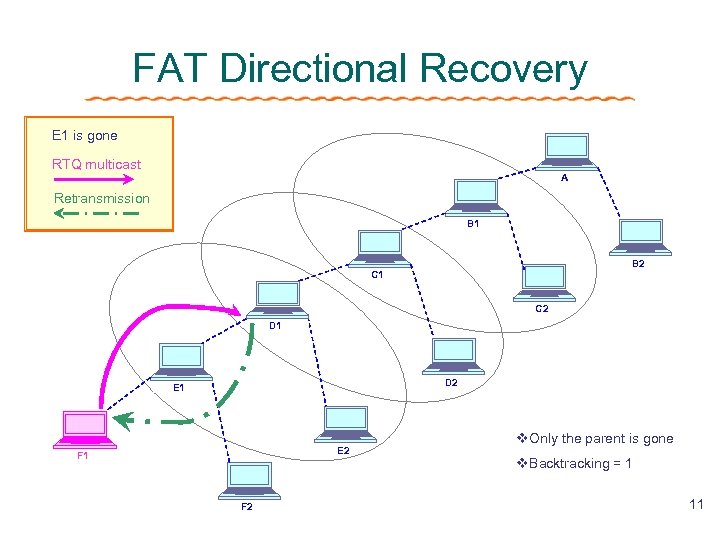
FAT Directional Recovery E 1 is gone RTQ multicast A Retransmission B 1 B 2 C 1 C 2 D 1 D 2 E 1 E 2 F 1 F 2 v. Only the parent is gone v. Backtracking = 1 11
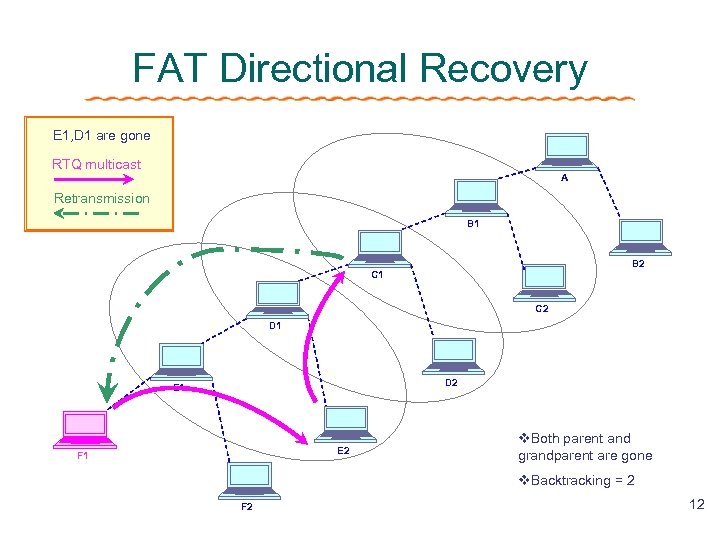
FAT Directional Recovery E 1, D 1 are gone RTQ multicast A Retransmission B 1 B 2 C 1 C 2 D 1 D 2 E 1 E 2 F 1 v. Both parent and grandparent are gone v. Backtracking = 2 F 2 12
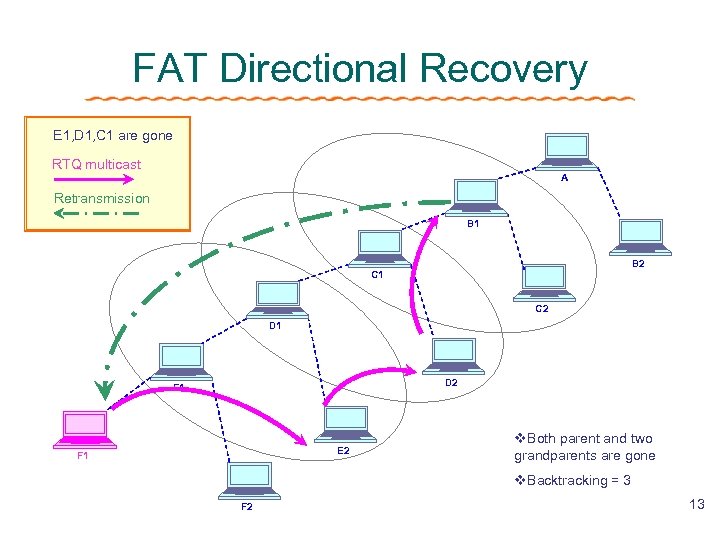
FAT Directional Recovery E 1, D 1, C 1 are gone RTQ multicast A Retransmission B 1 B 2 C 1 C 2 D 1 D 2 E 1 E 2 F 1 v. Both parent and two grandparents are gone v. Backtracking = 3 F 2 13

RALM Protocol Reliable Adaptive Lightweight Multicast IEEE 2003 by Ken Tang, Katia Obraczka , Sung-Ju Lee and Mario Gerla Two Important Components ØReliability ØCongestion Control Reliable Multicast Transport Protocol 14

RALM Operation Receiver List NACK= > add to the Receiver List Loss Recovery Feedback Receiver Unicast request to source Multicast to all of the Receiver List Once at one time: send-and-wait Round-Robin fashion 15
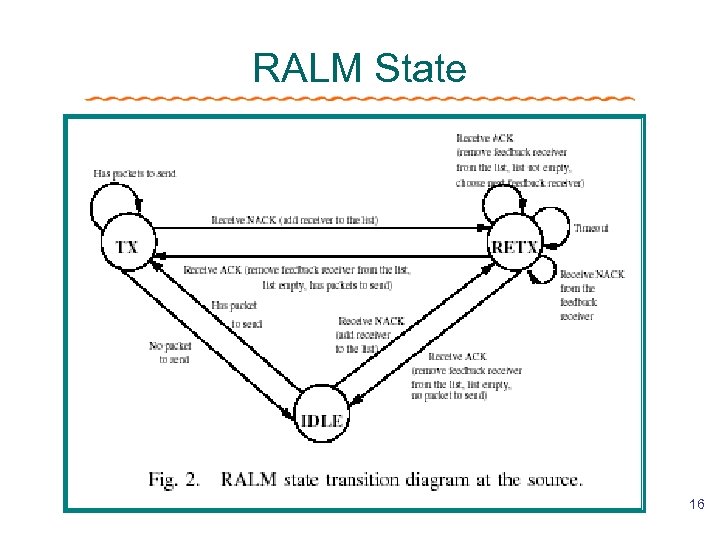
RALM State 16
The Same Of FAT And RALM Focus on Reliable Solution for Recovery Reduce the control message Transport Layer Protocol 17
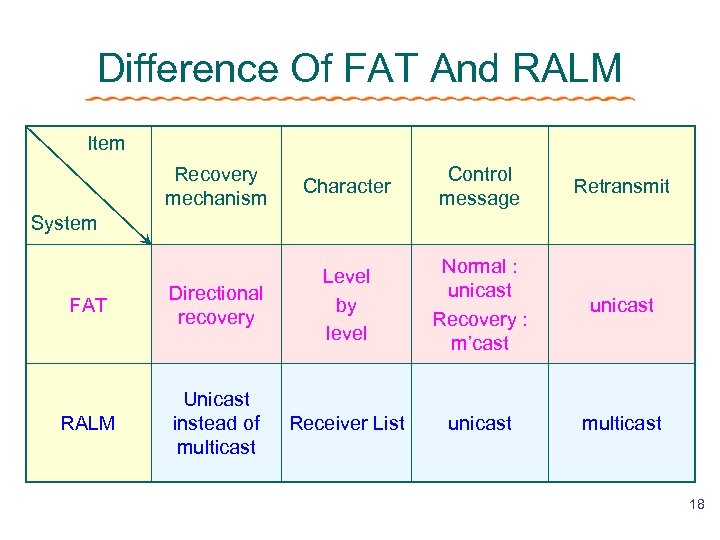
Difference Of FAT And RALM Item Recovery mechanism Character Control message Retransmit FAT Directional recovery Level by level Normal : unicast Recovery : m’cast unicast RALM Unicast instead of multicast Receiver List unicast multicast System 18
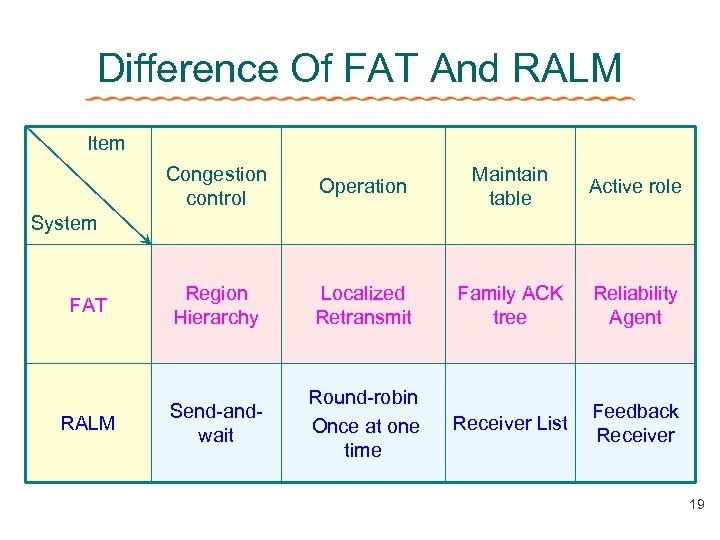
Difference Of FAT And RALM Item Congestion control Operation Maintain table Active role FAT Region Hierarchy Localized Retransmit Family ACK tree Reliability Agent RALM Send-andwait Round-robin Once at one time Receiver List Feedback Receiver System 19
![Metrics Of FAT Simulation Reliability Index = Normalized RI = [ buffer ] granted Metrics Of FAT Simulation Reliability Index = Normalized RI = [ buffer ] granted](https://present5.com/presentation/69f5fff07ac382072d99086da2eeb8b1/image-20.jpg)
Metrics Of FAT Simulation Reliability Index = Normalized RI = [ buffer ] granted request total received requests Reliability Index with certain buffer Reliability Index with infinite buffer Retransmission numbers Overhead ※Mobility = 1 pause time of node 20
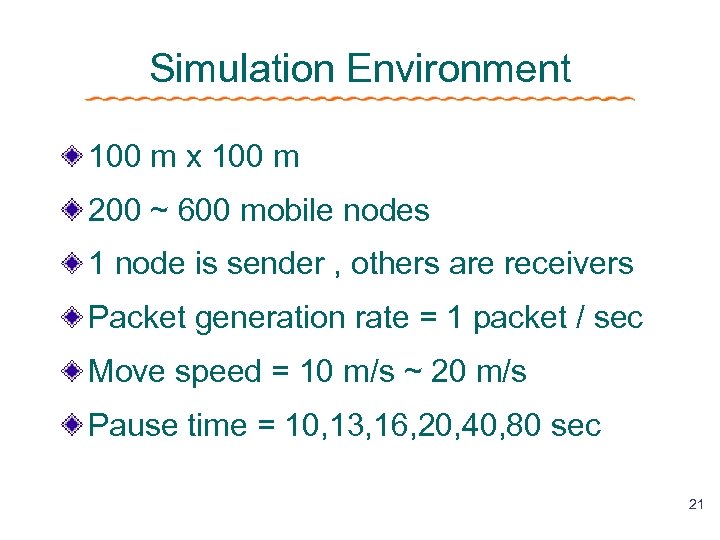
Simulation Environment 100 m x 100 m 200 ~ 600 mobile nodes 1 node is sender , others are receivers Packet generation rate = 1 packet / sec Move speed = 10 m/s ~ 20 m/s Pause time = 10, 13, 16, 20, 40, 80 sec 21
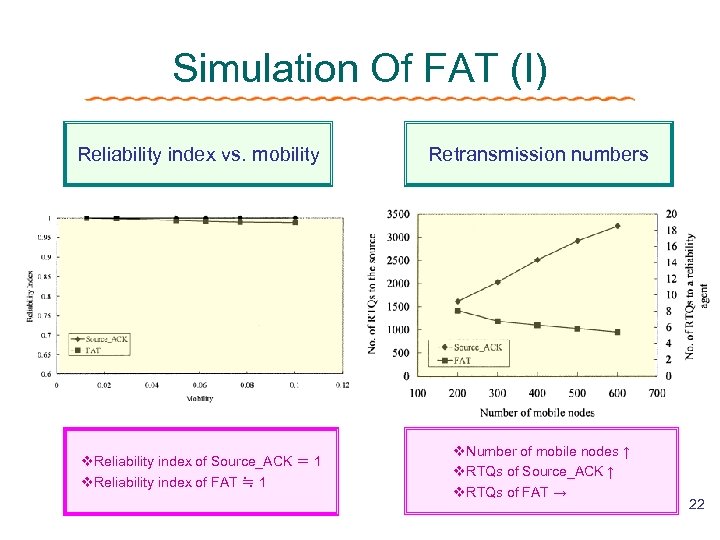
Simulation Of FAT (I) Reliability index vs. mobility Retransmission numbers v. Reliability index of Source_ACK = 1 v. Reliability index of FAT ≒ 1 v. Number of mobile nodes ↑ v. RTQs of Source_ACK ↑ v. RTQs of FAT → 22
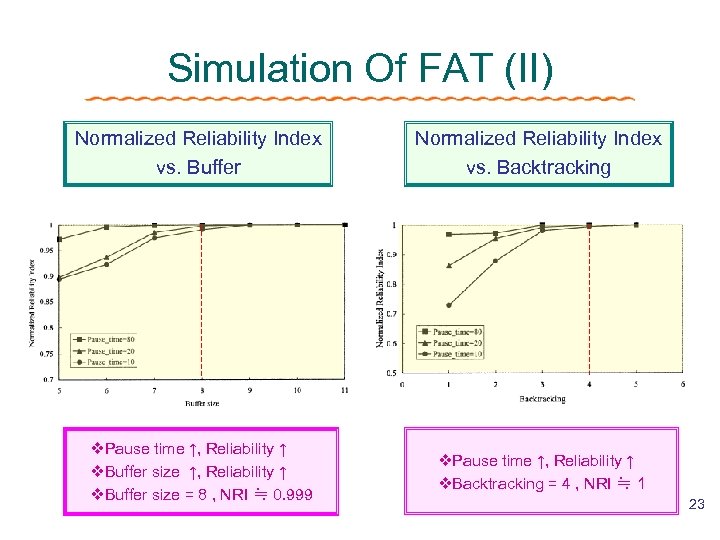
Simulation Of FAT (II) Normalized Reliability Index vs. Buffer Normalized Reliability Index vs. Backtracking v. Pause time ↑, Reliability ↑ v. Buffer size = 8 , NRI ≒ 0. 999 v. Pause time ↑, Reliability ↑ v. Backtracking = 4 , NRI ≒ 1 23
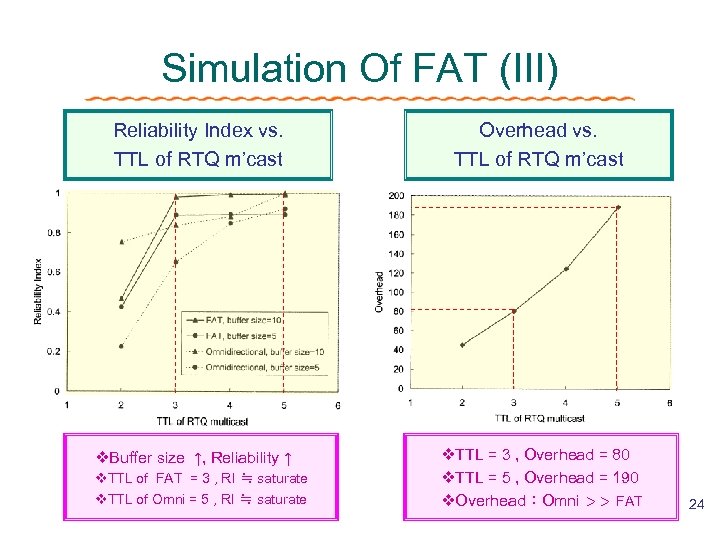
Simulation Of FAT (III) Reliability Index vs. TTL of RTQ m’cast v. Buffer size ↑, Reliability ↑ v. TTL of FAT = 3 , RI ≒ saturate v. TTL of Omni = 5 , RI ≒ saturate Overhead vs. TTL of RTQ m’cast v. TTL = 3 , Overhead = 80 v. TTL = 5 , Overhead = 190 v. Overhead:Omni >> FAT 24
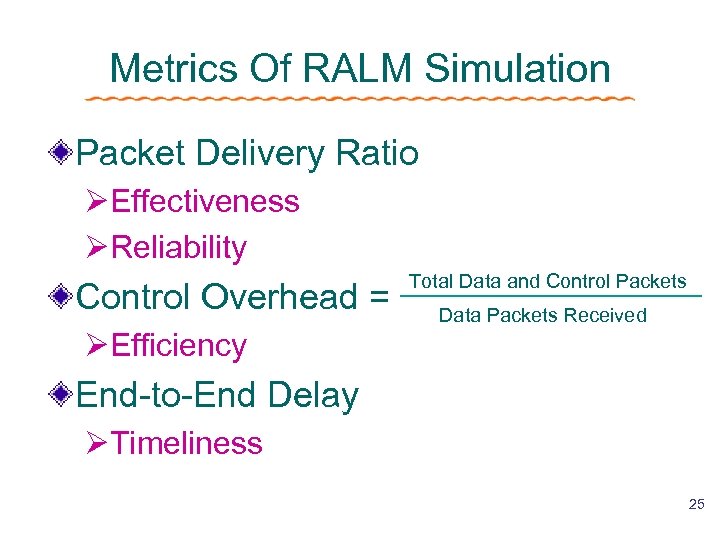
Metrics Of RALM Simulation Packet Delivery Ratio ØEffectiveness ØReliability Control Overhead = ØEfficiency Total Data and Control Packets Data Packets Received End-to-End Delay ØTimeliness 25
Simulation Environment 1500 m x 1500 m 50 nodes 5 senders , 10 ~ 40 receivers Buffer size is 30 packets Channel capacity is 2 Mb/s Propagation range is 375 m 26
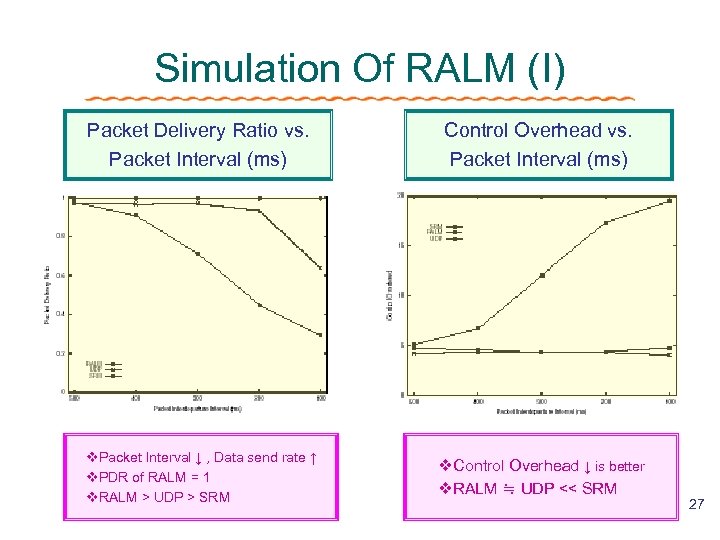
Simulation Of RALM (I) Packet Delivery Ratio vs. Packet Interval (ms) Control Overhead vs. Packet Interval (ms) v. Packet Interval ↓ , Data send rate ↑ v. PDR of RALM = 1 v. RALM > UDP > SRM v. Control Overhead ↓ is better v. RALM ≒ UDP << SRM 27
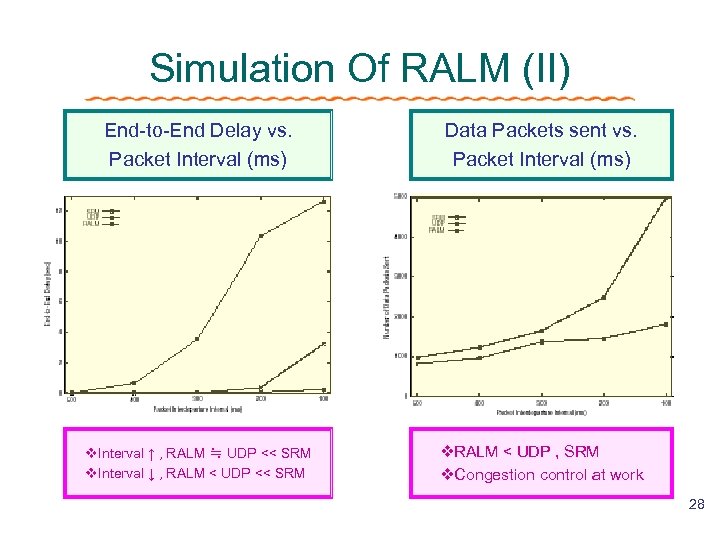
Simulation Of RALM (II) End-to-End Delay vs. Packet Interval (ms) Data Packets sent vs. Packet Interval (ms) v. Interval ↑ , RALM ≒ UDP << SRM v. Interval ↓ , RALM < UDP << SRM v. RALM < UDP , SRM v. Congestion control at work 28
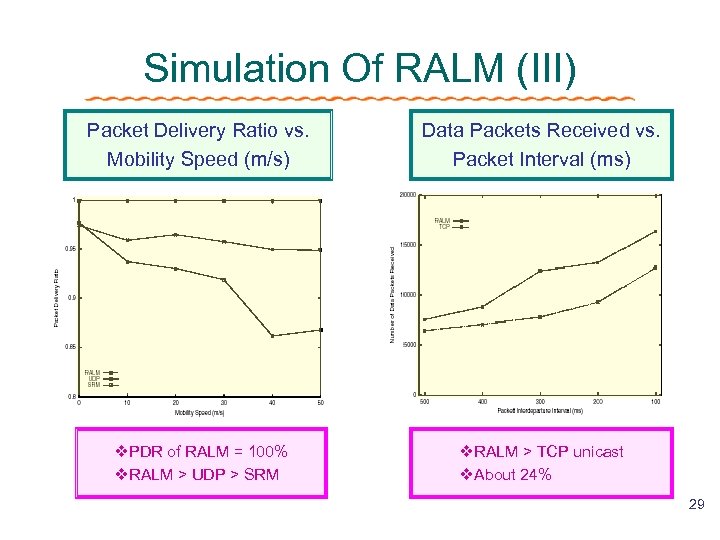
Simulation Of RALM (III) Packet Delivery Ratio vs. Mobility Speed (m/s) Data Packets Received vs. Packet Interval (ms) v. PDR of RALM = 100% v. RALM > UDP > SRM v. RALM > TCP unicast v. About 24% 29
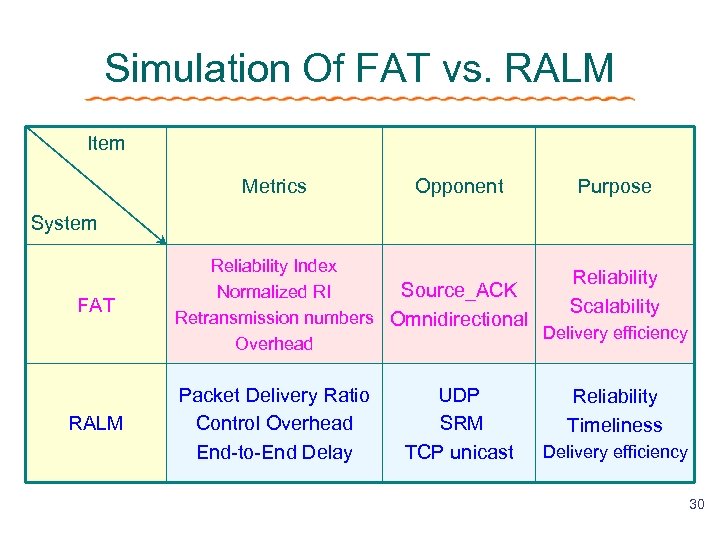
Simulation Of FAT vs. RALM Item Metrics Opponent Purpose System FAT RALM Reliability Index Reliability Source_ACK Normalized RI Scalability Retransmission numbers Omnidirectional Delivery efficiency Overhead Packet Delivery Ratio Control Overhead End-to-End Delay UDP SRM TCP unicast Reliability Timeliness Delivery efficiency 30

References v. Wanjiun Liao and Ming-Yu Jiang , “ Family ACK Tree (FAT): Supporting Reliable Multicast in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks “ , Vehicular Technology, IEEE Transactions on , Volume: 52 , Issue: 6 , Nov. 2003. Pages: 1675 - 1685 v. Tang, K. ; Obraczka, K. ; Lee, S. -J. ; Gerla, M. , ” Reliable Adaptive Lightweight Multicast Protocol “ Communications, 2003. ICC '03. IEEE International Conference on , Volume: 2 , 11 -15 May 2003 pages: 1054 - 1058 vol. 2 v. S. Floyd, V. Jacobson, S. Mc. Canne, C. Liu, and L. Zhang, “A reliable multicast framework for lightweight sessions and application-level framing, ” IEEE/ACM Trans. Networking, vol. 5, no. 6, pp. 784– 803, Dec. 1997. v. Tang, K. ; Obraczka, K. ; Sung-Ju Lee; Geria, M. , “A reliable, congestion-control led multicast transport protocol in multimedia multi-hop networks” Wireless Personal Multimedia Communications, 2002. The 5 th International Symposium on , Volume: 1 , 2730 Oct. 2002 Pages: 252 - 256 vol. 1 31
69f5fff07ac382072d99086da2eeb8b1.ppt